Peptidomics as a Tool to Assess the Cleavage of Wine Haze Proteins by Peptidases from Drosophila suzukii Larvae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wine Proteins
2.2. Rearing of Drosophila suzukii
2.3. Extraction of Peptidases from D. suzukii Larvae
2.4. Proteolytic Activity
2.5. Purification and Characterization of Peptidases from D. suzukii Larvae
2.5.1. Chromatography
2.5.2. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.5.3. Gene Expression Analysis by Quantitative RT-PCR
2.6. Analysis of Cleavage Sites in rTLP and rCHI
3. Results
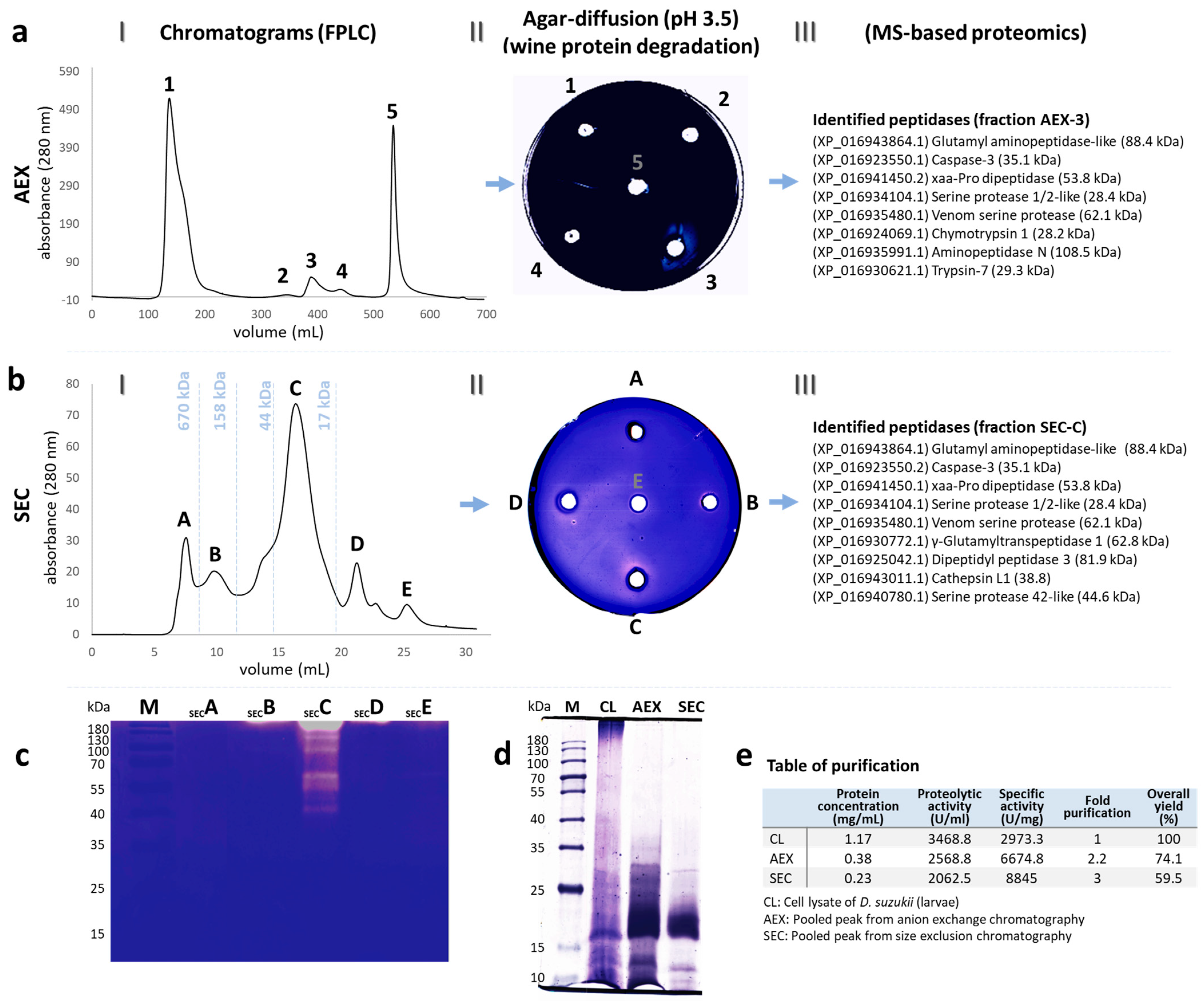
3.1. Purified Peptidases
3.2. Characterization of Peptidases by MS-Based Proteomics
3.3. Gene Expression Analysis
3.4. Identification of Intact Peptides (LC-MS/MS Top–Down Proteomics)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Batista, L.; Monteiro, S.; Loureiro, V.B.; Teixeira, A.R.; Ferreira, R.B. The complexity of protein haze formation in wines. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, W.; Seidel, L.; Zorn, H.; Will, F.; Gand, M. Haze formation and the challenges for peptidases in wine protein fining. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 14402–14414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangon, M.; van Sluyter, S.C.; Waters, E.J.; Menz, R.I. Structure of haze forming proteins in white wines: Vitis vinifera thaumatin-like proteins. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waters, E.J.; Shirley, N.J.; Williams, P.J. Nuisance proteins of wine are grape pathogenesis-related proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangon, M.; Sauvage, F.X.; Waters, E.J.; Vernhet, A. Effects of ionic strength and sulfate upon thermal aggregation of grape chitinases and thaumatin-like proteins in a model system. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2652–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, F.N.; Marangon, M.; Labbé, M.; Lira, E.; Rodríguez-Bencomo, J.J.; López, F. Comparative study of sodium bentonite and sodium-activated bentonite fining during white wine fermentation: Its effect on protein content, protein stability, lees volume, and volatile compounds. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 2043–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvage, F.-X.; Bach, B.; Moutounet, M.; Vernhet, A. Proteins in white wines: Thermo-sensitivity and differential adsorbtion by bentonite. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñas, E.; di Lorenzo, C.; Uberti, F.; Restani, P. Allergenic proteins in enology: A review on technological applications and safety aspects. Molecules 2015, 20, 13144–13164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waters, E.J.; Hayasaka, Y.; Tattersall, D.B.; Adams, K.S.; Williams, P.J. Sequence analysis of grape (Vitis vinifera) berry chitinases that cause haze formation in wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4950–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, W.; Ghezellou, P.; Li, B.; Spengler, B.; Will, F.; Zorn, H.; Gand, M. Identification of intact peptides by top-down peptidomics reveals cleavage spots in thermolabile wine proteins. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Nguyen, H.H.; Ogorzalek Loo, R.R.; Campuzano, I.D.G.; Loo, J.A. An integrated native mass spectrometry and top-down proteomics method that connects sequence to structure and function of macromolecular complexes. Nat. Chem 2018, 10, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Rohrs, H.W.; Gross, M.L. Top-down mass spectrometry: Recent developments, applications and perspectives. Analyst 2011, 136, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Standing, K.G. Peptide and protein de novo sequencing by mass spectrometry. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2003, 13, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canas, B. Mass spectrometry technologies for proteomics. Brief. Funct. Genom. Proteom. 2006, 4, 295–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seidler, J.; Zinn, N.; Boehm, M.E.; Lehmann, W.D. De novo sequencing of peptides by MS/MS. Proteomics 2010, 10, 634–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywood, A.; Lamont, I.L. Cell envelope proteases and peptidases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Multiple roles, multiple mechanisms. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 857–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppen, M.; Langer, T. Protein degradation within mitochondria: Versatile activities of AAA proteases and other peptidases. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 42, 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mika, N.; Gorshkov, V.; Spengler, B.; Zorn, H.; Rühl, M. Characterization of novel insect associated peptidases for hydrolysis of food proteins. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagdale, S.; Bansode, S.; Joshi, R. Insect proteases: Structural-functional outlook. In Proteases in Physiology and Pathology; Chakraborti, S., Dhalla, N.S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 451–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.R.; Dias, R.O.; Fuzita, F.J.; Ferreira, C.; Terra, W.R.; Silva-Filho, M.C. The evolution, gene expression profile, and secretion of digestive peptidases in Lepidoptera species. Catalysts 2020, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terra, W.R.; Ferreira, C. Insect digestive enzymes: Properties, compartmentalization and function. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1994, 109, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elpidina, E.N.; Goptar, I.A. Digestive peptidases in Tenebrio molitor and possibility of use to treat celiac disease. Entomol. Res. 2007, 37, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.V.; Pereira, D.A.; Souza, D.P.; Silva, M.-L.S.; Alencar, L.M.R.; Sousa, J.S.; Queiroz, J.-F.N.; Freitas, C.D.T. Peptidases and peptidase inhibitors in gut of caterpillars and in the latex of their host plants. Planta 2015, 241, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, J.C.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, L.; Hamm, C.A.; Cridland, J.M.; Saelao, P.; Hamby, K.A.; Lee, E.K.; Kwok, R.S.; Zhang, G.; et al. Genome of Drosophila suzukii, the Spotted Wing Drosophila. Genes Genomes Genet. 2013, 3, 2257–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Disi, J.O.; van Timmeren, S.; Gress, B.; Zalom, F.; Isaacs, R.; Sial, A. Insecticide residue longevity for on-site screening of Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura) resistance. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2918–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioriatti, C.; Walton, V.; Dalton, D.; Anfora, G.; Grassi, A.; Maistri, S.; Mazzoni, V. Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae) and its potential impact to wine grapes during harvest in two cool climate wine grape production regions. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albuquerque, W.; Sturm, P.; Schneider, Q.; Ghezellou, P.; Seidel, L.; Bakonyi, D.; Will, F.; Spengler, B.; Zorn, H.; Gand, M. Recombinant thaumatin-like protein (rTLP) and chitinase (rCHI) from Vitis vinifera as models for wine haze formation. Molecules 2022, 27, 6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leighton, T.J.; Doi, R.H.; Warren, R.A.J.; Kelln, R.A. The relationship of serine protease activity to RNA polymerase modification and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Mol. Biol. 1973, 76, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikström, M.; Elwing, H.; Linde, A. Determination of proteolytic activity: A sensitive and simple assay utilizing substrate adsorbed to a plastic surface and radial diffusion in gel. Anal. Biochem. 1981, 118, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.H.; Qiao, R.; Xin, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Shan, B.; Ghodsi, A.; Li, M. Deep learning enables de novo peptide sequencing from data-independent-acquisition mass spectrometry. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesari, P.; Patil, D.N.; Kumar, P.; Tomar, S.; Sharma, A.K.; Kumar, P. Structural and functional evolution of chitinase-like proteins from plants. Proteomics 2015, 15, 1693–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falconer, R.J.; Marangon, M.; van Sluyter, S.C.; Neilson, K.A.; Chan, C.; Waters, E.J. Thermal stability of thaumatin-like protein, chitinase, and invertase isolated from Sauvignon blanc and Semillon juice and their role in haze formation in wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christeller, J.T.; Laing, W.A.; Markwick, N.P.; Burgess, E.P.J. Midgut protease activities in 12 phytophagous lepidopteran larvae: Dietary and protease inhibitor interactions. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1992, 22, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, K.; Cardullo, R.A.; Thaler, C.D. Culex pipiens sperm motility is initiated by a trypsin-like protease from male accessory glands. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2018, 85, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizioli, J.; Catteruccia, F.; della Torre, A.; Reckmann, I.; Müller, H.M. Blood digestion in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae: Molecular cloning and biochemical characterization of two inducible chymotrypsins. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 4027–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tereshchenkova, V.F.; Goptar, I.A.; Zhuzhikov, D.P.; Belozersky, M.A.; Dunaevsky, Y.E.; Oppert, B.; Filippova, I.Y.; Elpidina, E.N. Prolidase is a critical enzyme for complete gliadin digestion in Tenebrio molitor larvae. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 95, e21395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.R.; Stack, C.M.; O’Neill, S.M.; Doyle, S.; Ryan, T.; Brennan, G.P.; Mousley, A.; Stewart, M.; Maule, A.G.; Dalton, J.P.; et al. Cathepsin L1, the major protease involved in liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica) virulence. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 17038–17046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.; Jiang, H. Building a platform for predicting functions of serine protease-related proteins in Drosophila melanogaster and other insects. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 103, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Mhetre, A.; Ratnaparkhi, G.S.; Kamat, S.S. A superfamily-wide activity atlas of serine hydrolases in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochemistry 2021, 60, 1312–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, W.R.; Dias, R.O.; Ferreira, C. Recruited lysosomal enzymes as major digestive enzymes in insects. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, M.Y.; Hahn, B.-S.; Ryu, K.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, I.; Kim, Y.S. Purification and characterization of a serine protease with fibrinolytic activity from the dung beetles, Catharsius molossus. Thromb. Res. 2003, 112, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, K.A.; Lee, M.J.; Gatehouse, J.A.; Anstee, J.H. The partial purification and characterisation of serine protease activity in midgut of larval Helicoverpa armigera. Insect Biochem. 1991, 21, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfson, J.L.; Murdock, L.L. Diversity in digestive proteinase activity among insects. J. Chem. Ecol. 1990, 16, 1089–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, Y.; Xu, W. The structure and main functions of aminopeptidase N. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Fowler, J.H.; Walling, L.L. Leucine aminopeptidases: Diversity in structure and function. Biol. Chem. 2006, 387, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomate, P.R.; Hivrale, V.K. Partial purification and characterization of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) active aminopeptidase secreted in midgut. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 155, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.A.; Oliveira, M.G.A.; Guedes, R.N.C.; Soares, M.J. Morphology and preliminary enzyme characterization of the salivary glands from the predatory bug Podisus nigrispinus (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2006, 96, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorkhabi-Abdolmaleki, S.; Zibaee, A.; Hoda, H.; Hosseini, R.; Fazeli-Dinan, M. Proteolytic compartmentalization and activity in the midgut of Andrallus spinidens Fabricius (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J. Entomol. Acarol. Res. 2013, 45, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goptar, I.A.; Semashko, T.A.; Danilenko, S.A.; Lysogorskaya, E.N.; Oksenoit, E.S.; Zhuzhikov, D.P.; Belozersky, M.A.; Dunaevsky, Y.E.; Oppert, B.; Filippova, I.Y.; et al. Cysteine digestive peptidases function as post-glutamine cleaving enzymes in tenebrionid stored-product pests. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 161, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabossi, A.; Stoka, V.; Puizdar, V.; Turk, V.; Quesada-Allué, L.A. Purification and characterization of two cysteine peptidases of the Mediterranean fruit fly Ceratitis capitata during metamorphosis. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2008, 68, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrone, L.; di Giovanni, M.; di Fiore, M.M.; Chieffi Baccari, G.; Santillo, A. Effects of D-aspartate treatment on D-aspartate oxidase, superoxide dismutase, and caspase 3 activities in frog (Rana esculenta) tissues. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, L.; Casani, S.; Ceccarelli, N.; Galleschi, L.; Picciarelli, P.; Lorenzi, R. Programmed cell death of the nucellus during Sechium edule Sw. seed development is associated with activation of caspase-like proteases. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2949–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, D.N.; Baehrecke, E.H. Caspases function in autophagic programmed cell death in Drosophila. Development 2004, 131, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ki, M.R. Glutamine-induced production and secretion of Helicobacter pylori γ-Glutamyltranspeptidase at low pH and its putative role in glutathione transport. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 23, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Taniguchi, N. Gene expression of γ-Glutamyltranspeptidase. Meth. Enzymol. 2005, 401, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Kumagai, H.; Tochikura, T. γ-Glutamyltranspeptidase from Escherichia coli K-12: Purification and properties. J. Bacteriol. Res. 1986, 168, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roozendaal, R.; Vellenga, E.; de Jong, M.A.; Traanberg, K.F.; Postma, D.S.; de Monchy, J.G.R.; Kauffman, H.F. Resistance of activated human Th2 cells to NO-induced apoptosis is mediated by γ-glutamyltranspeptidase. Int. Immunol. 2001, 13, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofoletti, P.T.; Ribeiro, A.F.; Terra, W.R. The cathepsin L-like proteinases from the midgut of Tenebrio molitor larvae: Sequence, properties, immunocytochemical localization and function. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 35, 883–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowther, J.; Robinson, M.W.; Donnelly, S.M.; Xu, W.; Stack, C.M.; Matthews, J.M.; Dalton, J.P. The importance of pH in regulating the function of the Fasciola hepatica cathepsin L1 cysteine protease. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J.; Bateman, A. MEROPS: The database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D343–D350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, J.; Cui, S.; Pu, H.; Jiang, S. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of cathepsin L1 cysteine protease from pearl oyster Pinctada fucata. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.; Bellinello, G.L.; Ribeiro, A.F.; Terra, W.R. Digestive enzymes associated with the glycocalyx, microvillar membranes and secretory vesicles from midgut cells of Tenebrio molitor larvae. Insect Biochem. 1990, 20, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Mahmoud, S.; Ramos, J.E.; Shatters, R.G.; Rougé, P.; Powell, C.A.; Smagghe, G.; Borovsky, D. Cloning and characterization of a basic cysteine-like protease (cathepsin L1) expressed in the gut of larval Diaprepes abbreviatus L. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J. Insect Physiol. 2015, 72, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turk, V.; Stoka, V.; Vasiljeva, O.; Renko, M.; Sun, T.; Turk, B.; Turk, D. Cysteine cathepsins: From structure, function and regulation to new frontiers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2012, 1824, 68–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sui, Y.; Wollan, D.; McRae, J.M.; Muhlack, R.; Capone, D.L.; Godden, P.; Wilkinson, K.L. Chemical and sensory profiles of Sauvignon blanc wine following protein stabilization using a combined ultrafiltration/heat/protease treatment. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Peptidase | ID (NCBI) | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glutamyl aminopeptidase-like | XP_016943864.1 | 5′-TGTGCATCATTGTGTCCGAC-3′ | 5′-TCGATCTGATGGGAAGTGGC-3′ |
| Caspase-3 | XP_016923550.1 | 5′-GACTGCCAGGACGCCAAC-3′ | 5′-CGCTCGCAATTCTCGTATGT-3′ |
| Serine protease 1/2-like | XP_016934104.1 | 5′-GCGACAACACTATCTGCACC-3′ | 5′-CTGACTCCCACCAGCTTGTT-3′ |
| Dipeptidyl peptidase III | XP_016925042.1 | 5′-CGAGCACTACATCCGATCCT-3′ | 5′-TCCCTTGTCCTTGATCCACC-3′ |
| Cathepsin L1 | XP_016943011.1 | 5′-CAACTGCAATCGTTCCCCAA-3′ | 5′-TCGTCCGAGTATACCTTGCC-3′ |
| n | Accession No. (NCBI) | Description | Peptides | Type | Coverage [%] | Unique Peptides | MW (kDa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AEX step | |||||||
| 1 | XP_016943864.1 | Glutamyl aminopeptidase-like | R.QAFPCFDEPALK.A K.YNIEWLAR.N K.WWNDLWLNEGFAR.F | Metallo | 4 | 3 | 88.4 |
| 2 | XP_016923550.1 | Caspase-3 | R.TYDDLTFSDINDK.L | Cysteine | 4 | 1 | 35.1 |
| 3 | XP_016941450.2 | Xaa-Pro dipeptidase | K.SLYNTDVDYVFR.Q | Metallo | 2 | 1 | 53.8 |
| 4 | XP_016934104.1 | Serine protease 1/2-like | K.VELPSYNDR.Y | Serine | 5 | 1 | 28.4 |
| 5 | XP_016935480.1 | Venom serine protease | K.FLQQDFVGMNPFVAGWGAVK.H | Serine | 4.1 | 1 | 62.1 |
| 6 | XP_016924069.1 | Chymotrypsin 1 | R.ILGGEDVEQGEYPWSASVR.Y | Serine | 8.6 | 1 | 28.2 |
| 7 | XP_016935991.1 | Aminopeptidase N | K.QLIDPIFNK.I | Metallo | 1 | 1 | 108.5 |
| 8 | XP_016930621.1 | Trypsin 7 | R.EWLEETIEANK.D | Serine | 4 | 1 | 29.3 |
| SEC step | |||||||
| 1 | XP_016943864.1 | Glutamyl aminopeptidase-like | R.QAFPCFDEPALK.A K.YNIEWLAR.N K.WWNDLWLNEGFAR.F | Metallo | 4 | 3 | 88.4 |
| 2 | XP_016923550.1 | Caspase-3 | R.TYDDLTFSDINDK.L | Cysteine | 4 | 1 | 35.1 |
| 3 | XP_016941450.2 | Xaa-Pro dipeptidase | K.SLYNTDVDYVFR.Q | Metallo | 2 | 1 | 53.8 |
| 4 | XP_016934104.1 | Serine protease 1/2-like | K.VELPSYNDR.Y | Serine | 5 | 1 | 28.4 |
| 5 | XP_016935480.1 | Venom serine protease | K.FLQQDFVGMNPFVAGWGAVK.H | Serine | 4.1 | 1 | 62.1 |
| 6 | XP_016930772.1 | γ-Glutamyltranspeptidase 1 | R.YGILPWK.R R.LFEPSIK.L K.EIYDGGETGR.K | Cysteine | 4.1 | 3 | 62.8 |
| 7 | XP_016925042.1 | Dipeptidyl peptidase 3 | K.IFDK.V | Metallo | 2 | 2 | 81.9 |
| 8 | XP_016943011.1 | Cathepsin L1 | R.LGVNPLADMTR.K | Cysteine | 3.1 | 1 | 38.8 |
| 9 | XP_016940780.1 | Serine protease 42-like | K.DGEYQVILK.K K.LWNIDPK.Y | Serine | 3.9 | 2 | 44.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albuquerque, W.; Ghezellou, P.; Lee, K.-Z.; Schneider, Q.; Gross, P.; Kessel, T.; Omokungbe, B.; Spengler, B.; Vilcinskas, A.; Zorn, H.; et al. Peptidomics as a Tool to Assess the Cleavage of Wine Haze Proteins by Peptidases from Drosophila suzukii Larvae. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030451
Albuquerque W, Ghezellou P, Lee K-Z, Schneider Q, Gross P, Kessel T, Omokungbe B, Spengler B, Vilcinskas A, Zorn H, et al. Peptidomics as a Tool to Assess the Cleavage of Wine Haze Proteins by Peptidases from Drosophila suzukii Larvae. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(3):451. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030451
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbuquerque, Wendell, Parviz Ghezellou, Kwang-Zin Lee, Quintus Schneider, Phillip Gross, Tobias Kessel, Bodunrin Omokungbe, Bernhard Spengler, Andreas Vilcinskas, Holger Zorn, and et al. 2023. "Peptidomics as a Tool to Assess the Cleavage of Wine Haze Proteins by Peptidases from Drosophila suzukii Larvae" Biomolecules 13, no. 3: 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030451
APA StyleAlbuquerque, W., Ghezellou, P., Lee, K.-Z., Schneider, Q., Gross, P., Kessel, T., Omokungbe, B., Spengler, B., Vilcinskas, A., Zorn, H., & Gand, M. (2023). Peptidomics as a Tool to Assess the Cleavage of Wine Haze Proteins by Peptidases from Drosophila suzukii Larvae. Biomolecules, 13(3), 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030451








