Cj0683 Is a Competence Protein Essential for Efficient Initialization of DNA Uptake in Campylobacter jejuni
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Growth Conditions
2.2. DNA Uptake Assay, Quantification and Transformation
2.3. Construction of Deletion Mutants and Respective Complemented Strains
2.4. Biofilm Formation Assay
2.5. Statistical and Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results
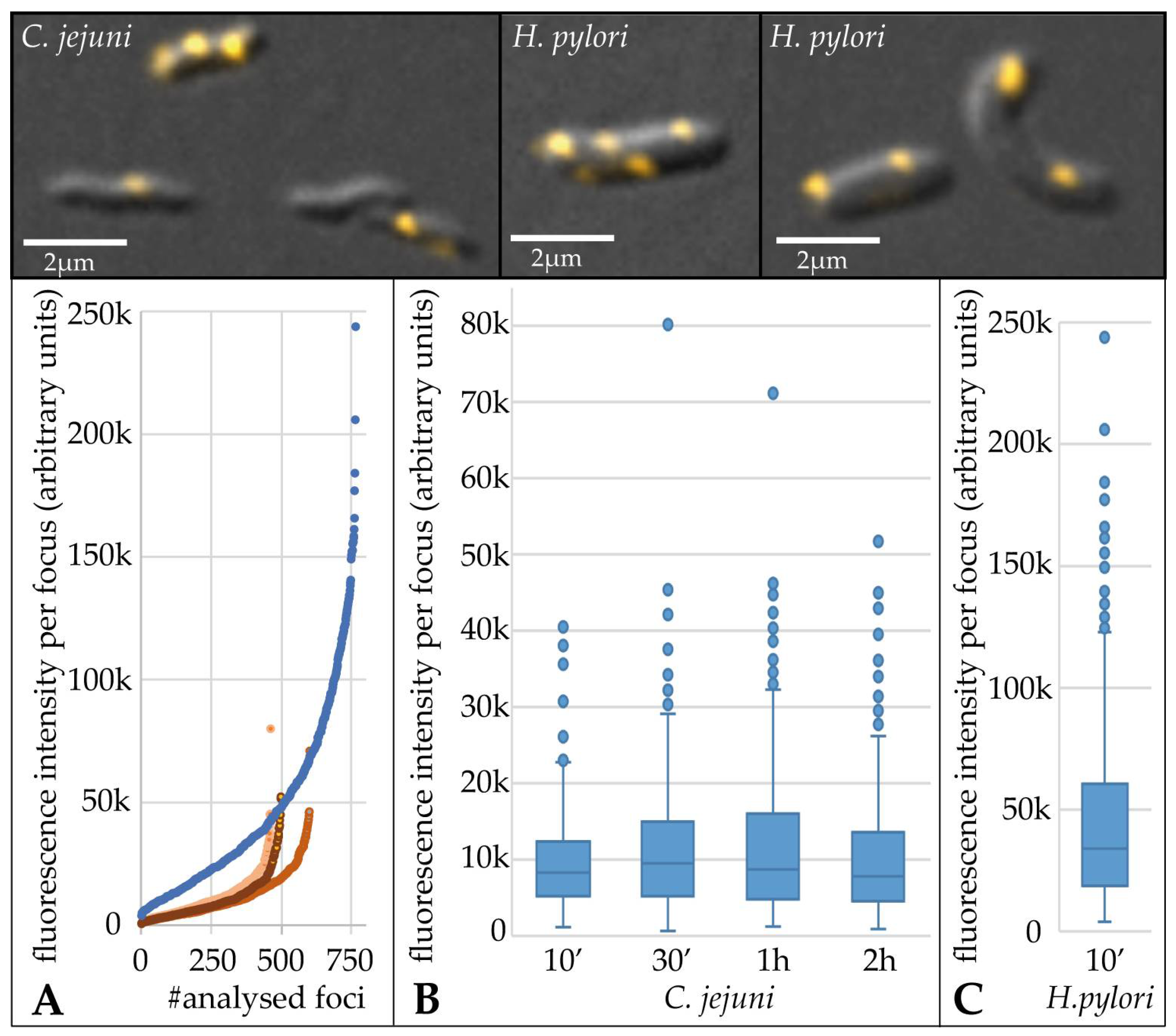
3.1. Multiple Fluorescent DNA Molecules Are Located within Distinct Periplasmic Foci during C. jejuni DNA Uptake
3.2. Estimation of DNA Uptake Capacity of C. jejuni Reveals Imported DNA Amounts in Median of around 30 kb
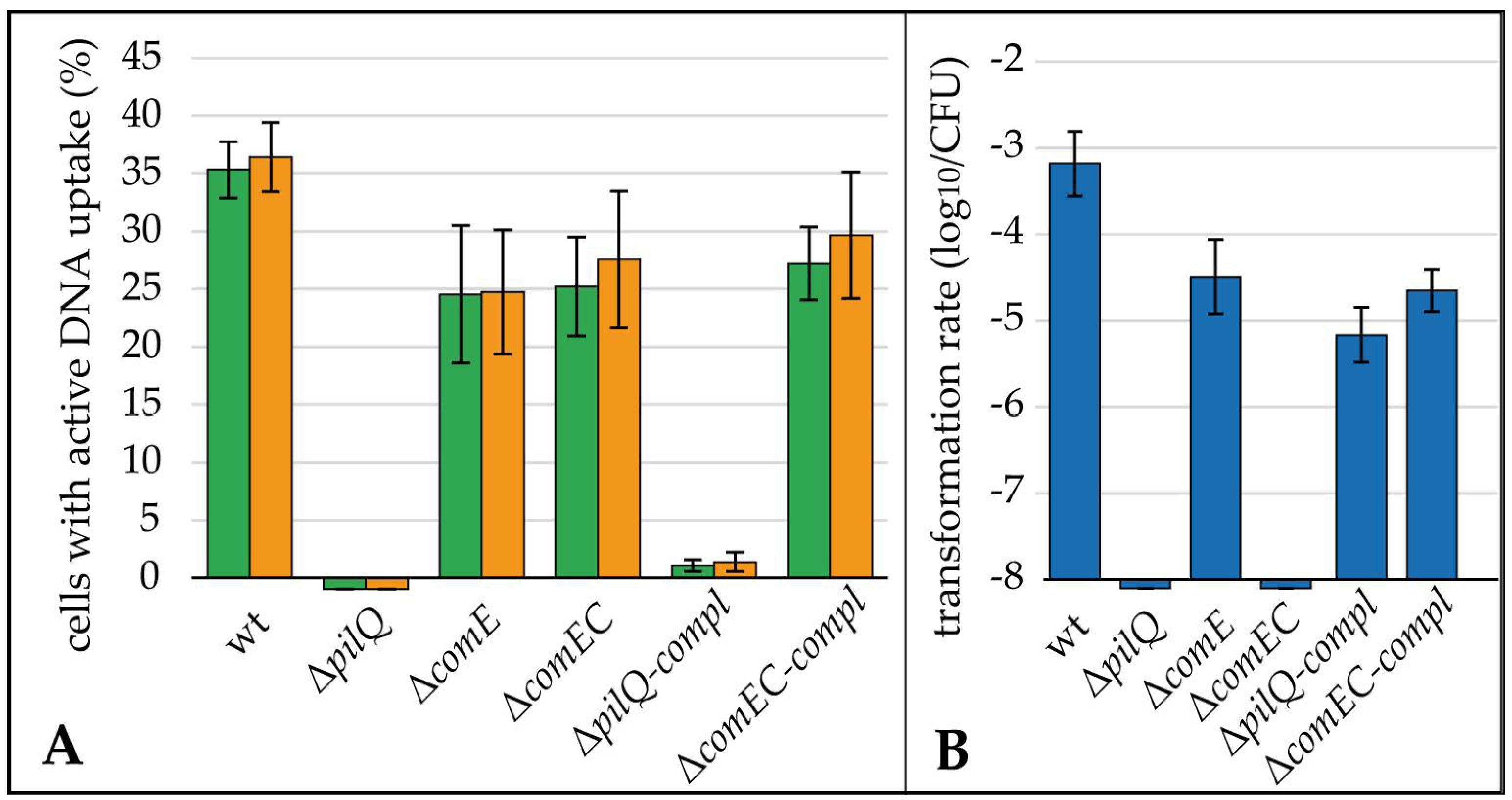
3.3. Essential Roles of pilQ (cj1474c) and comEC (cj1211) but Negligible Contribution of comE (cj0011c) to DNA Uptake in C. jejuni
3.4. Active DNA Transport Capacity Has No Impact in Biofilm Formation of C. jejuni
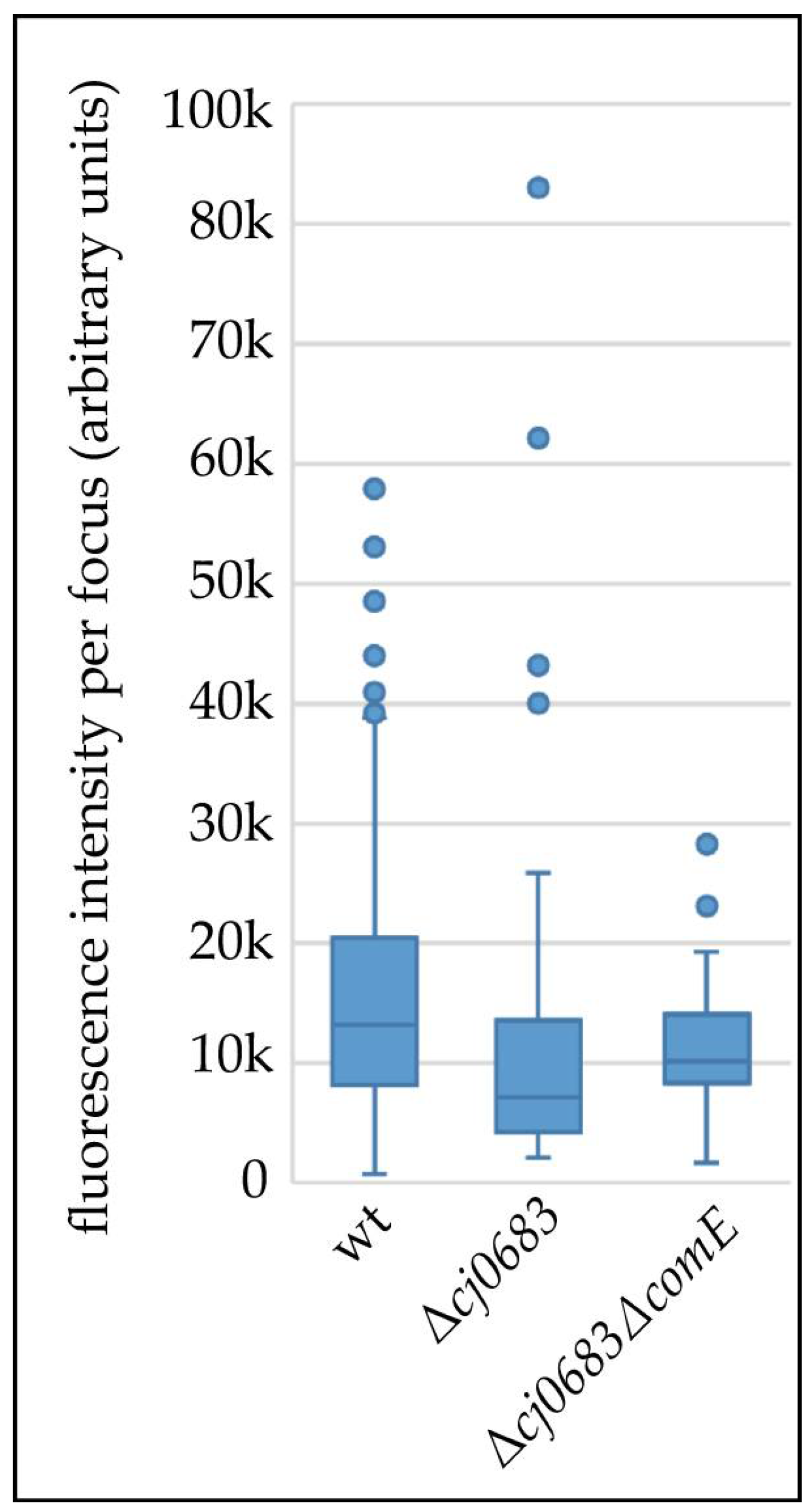
3.5. Cj0683 Is a Novel Periplasmic Protein Essential for Efficient Initialization of DNA Uptake in C. jejuni
4. Discussion
4.1. DNA Uptake Capacity in C. jejuni Is around Four-Fold Lower than in H. pylori
4.2. The Periplasmic Protein ComE Is Negligible for DNA Uptake in C. jejuni While ComEC and PilQ Play Essential Roles in Natural Tansformation
4.3. DNA Uptake Does Not Influence Biofilm Formation in C. jejuni
4.4. The Unique Periplasmic Protein Cj0683 Is Essential for Efficient Initialization of DNA Import into the Periplasm
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EFSA. The European Union One Health 2020 zoonoses report. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Backert, S.; Alter, T.; Bereswill, S. Human campylobacteriosis-A serious infectious threat in a One Health perspective. In Fighting Campylobacter Infections: Towards a One Health Approach; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2021; Volume 431, pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterer, J. Triggers of Guillain-Barré syndrome: Campylobacter jejuni predominates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.J.; Gabriel, E.; Leatherbarrow, A.J.; Cheesbrough, J.; Gee, S.; Bolton, E.; Fox, A.; Hart, C.A.; Diggle, P.J.; Fearnhead, P. Rapid evolution and the importance of recombination to the gastroenteric pathogen Campylobacter jejuni. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, S.K.; McCarthy, N.D.; Falush, D.; Maiden, M.C. Convergence of Campylobacter species: Implications for bacterial evolution. Science 2008, 320, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golz, J.C.; Epping, L.; Knüver, M.T.; Borowiak, M.; Hartkopf, F.; Deneke, C.; Malorny, B.; Semmler, T.; Stingl, K. Whole genome sequencing reveals extended natural transformation in Campylobacter impacting diagnostics and the pathogens adaptive potential. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafy, Z.; Osborne, J.A.; Miller, W.G.; Parker, C.T.; Olson, J.W.; Jackson, J.H., 3rd; Kathariou, S. Differences in the propensity of different antimicrobial resistance determinants to be disseminated via transformation in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golz, J.C.; Stingl, K. “Take it or leave it”-Factors regulating competence development and DNA uptake in Campylobacter jejuni. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golz, J.C.; Stingl, K. Natural competence and horizontal gene transfer in Campylobacter. In Fighting Campylobacter Infections; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2021; Volume 431, pp. 265–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubnau, D.; Blokesch, M. Mechanisms of DNA uptake by naturally competent bacteria. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2019, 53, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesner, R.S.; Hendrixson, D.R.; DiRita, V.J. Natural transformation of Campylobacter jejuni requires components of a type II secretion system. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 5408–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, J.M.; Erfurt, R.S.; DiRita, V.J. Characterization and localization of the Campylobacter jejuni transformation system proteins CtsE, CtsP, and CtsX. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, S.L.; Koomey, M. The product of the pilQ gene is essential for the biogenesis of type IV pili in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mol. Microbiol. 1995, 18, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assalkhou, R.; Balasingham, S.; Collins, R.F.; Frye, S.A.; Davidsen, T.; Benam, A.V.; Bjoras, M.; Derrick, J.P.; Tonjum, T. The outer membrane secretin PilQ from Neisseria meningitidis binds DNA. Microbiology 2007, 153, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, S.J.; Ortega, D.R.; Sazinsky, M.H.; Dalia, T.N.; Dalia, A.B.; Jensen, G.J. CryoEM structure of the type IVa pilus secretin required for natural competence in Vibrio cholerae. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison, C.K.; Dalia, T.N.; Vidal Ceballos, A.; Wang, J.C.; Biais, N.; Brun, Y.V.; Dalia, A.B. Retraction of DNA-bound type IV competence pili initiates DNA uptake during natural transformation in Vibrio cholerae. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obergfell, K.P.; Seifert, H.S. The pilin N-terminal domain maintains Neisseria gonorrhoeae transformation competence during pilus phase variation. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hepp, C.; Maier, B. Kinetics of DNA uptake during transformation provide evidence for a translocation ratchet mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12467–12472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, P.; Pezeshgi Modarres, H.; Borgeaud, S.; Bulushev, R.D.; Steinbock, L.J.; Radenovic, A.; Dal Peraro, M.; Blokesch, M. ComEA is essential for the transfer of external DNA into the periplasm in naturally transformable Vibrio cholerae cells. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stingl, K.; Müller, S.; Scheidgen-Kleyboldt, G.; Clausen, M.; Maier, B. Composite system mediates two-step DNA uptake into Helicobacter pylori. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1184–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damke, P.P.; Di Guilmi, A.M.; Varela, P.F.; Velours, C.; Marsin, S.; Veaute, X.; Machouri, M.; Gunjal, G.V.; Rao, D.N.; Charbonnier, J.B.; et al. Identification of the periplasmic DNA receptor for natural transformation of Helicobacter pylori. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangel, H.; Hepp, C.; Muller, S.; Oldewurtel, E.R.; Aas, F.E.; Koomey, M.; Maier, B. Concerted spatio-temporal dynamics of imported DNA and ComE DNA uptake protein during gonococcal transformation. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, B.; Zhang, Q. Cj0011c, a periplasmic single- and double-stranded DNA-binding protein, contributes to natural transformation in Campylobacter jejuni. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 7399–7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchamp, J.M.; Leveque, R.M.; Dawid, S.; DiRita, V.J. Methylation-dependent DNA discrimination in natural transformation of Campylobacter jejuni. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8053–E8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, Z.T.; Zhang, Y. Evolution of the natural transformation protein, ComEC, in bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, B.; Muraoka, W.; Sahin, O.; Zhang, Q. Role of Cj1211 in natural transformation and transfer of antibiotic resistance determinants in Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 2699–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, J.S.; Burmolle, M.; Hansen, L.H.; Sorensen, S.J. The interconnection between biofilm formation and horizontal gene transfer. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, F.C.; Tao, L.; Scheie, A.A. DNA binding-uptake system: A link between cell-to-cell communication and biofilm formation. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 4392–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronish, L.A.; Sidner, B.; Yu, Y.; Piepenbrink, K.H. Recognition of extracellular DNA by type IV pili promotes biofilm formation by Clostridioides difficile. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, N.J.; Knüver, M.T.; Zawilak-Pawlik, A.; Appel, B.; Stingl, K. Genetic diversity as consequence of a microaerobic and neutrophilic lifestyle. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korlath, J.A.; Osterholm, M.T.; Judy, L.A.; Forfang, J.C.; Robinson, R.A. A point-source outbreak of campylobacteriosis associated with consumption of raw milk. J. Infect. Dis. 1985, 152, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alm, R.A.; Ling, L.S.; Moir, D.T.; King, B.L.; Brown, E.D.; Doig, P.C.; Smith, D.R.; Noonan, B.; Guild, B.C.; deJonge, B.L.; et al. Genomic-sequence comparison of two unrelated isolates of the human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 1999, 397, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skouloubris, S.; Thiberge, J.M.; Labigne, A.; De Reuse, H. The Helicobacter pylori UreI protein is not involved in urease activity but is essential for bacterial survival in vivo. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 4517–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bury-Moné, S.; Skouloubris, S.; Dauga, C.; Thiberge, J.M.; Dailidiene, D.; Berg, D.E.; Labigne, A.; De Reuse, H. Presence of active aliphatic amidases in Helicobacter species able to colonize the stomach. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 5613–5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkhill, J.; Wren, B.W.; Mungall, K.; Ketley, J.M.; Churcher, C.; Basham, D.; Chillingworth, T.; Davies, R.M.; Feltwell, T.; Holroyd, S.; et al. The genome sequence of the food-borne pathogen Campylobacter jejuni reveals hypervariable sequences. Nature 2000, 403, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, A.H.; Wood, A.C.; Wooldridge, K.; Ketley, J.M.; Henderson, J. Genetic manipulation of enteric Campylobacter species. In Methods in Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 27, pp. 407–419. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, R.O.; Novik, V.; Hofreuter, D.; Lara-Tejero, M.; Galan, J.E. A MyD88-deficient mouse model reveals a role for Nramp1 in Campylobacter jejuni infection. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 1994–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Reeser, R.J.; Medler, R.T.; Billington, S.J.; Jost, B.H.; Joens, L.A. Characterization of Campylobacter jejuni biofilms under defined growth conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1908–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, K.A.; Seifert, H.S. Mutation of the priA gene of Neisseria gonorrhoeae affects DNA transformation and DNA repair. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 5347–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrish, J.R.; Yu, J.; Liu, G.; Hines, J.A.; Chan, J.E.; Mangiola, B.A.; Zhang, H.; Pacifico, S.; Fotouhi, F.; DiRita, V.J.; et al. A proteome-wide protein interaction map for Campylobacter jejuni. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teh, A.H.T.; Lee, S.M.; Dykes, G.A. Association of some Campylobacter jejuni with Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms increases attachment under conditions mimicking those in the environment. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Golz, J.C.; Preuß, S.; Püning, C.; Gölz, G.; Stingl, K. Cj0683 Is a Competence Protein Essential for Efficient Initialization of DNA Uptake in Campylobacter jejuni. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030514
Golz JC, Preuß S, Püning C, Gölz G, Stingl K. Cj0683 Is a Competence Protein Essential for Efficient Initialization of DNA Uptake in Campylobacter jejuni. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(3):514. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030514
Chicago/Turabian StyleGolz, Julia C., Sandra Preuß, Christoph Püning, Greta Gölz, and Kerstin Stingl. 2023. "Cj0683 Is a Competence Protein Essential for Efficient Initialization of DNA Uptake in Campylobacter jejuni" Biomolecules 13, no. 3: 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030514
APA StyleGolz, J. C., Preuß, S., Püning, C., Gölz, G., & Stingl, K. (2023). Cj0683 Is a Competence Protein Essential for Efficient Initialization of DNA Uptake in Campylobacter jejuni. Biomolecules, 13(3), 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030514





