Insight into Pathogenic Mechanism Underlying the Hereditary Cataract Caused by βB2-G149V Mutation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Plasmid Constructs and Site-Directed Mutagenesis
2.3. Protein Expression and Purification
2.4. Spectral Experiments
2.5. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.6. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.7. Western Blot and SDS-PAGE
2.8. Molecular Dynamic (MD) Simulations
3. Results
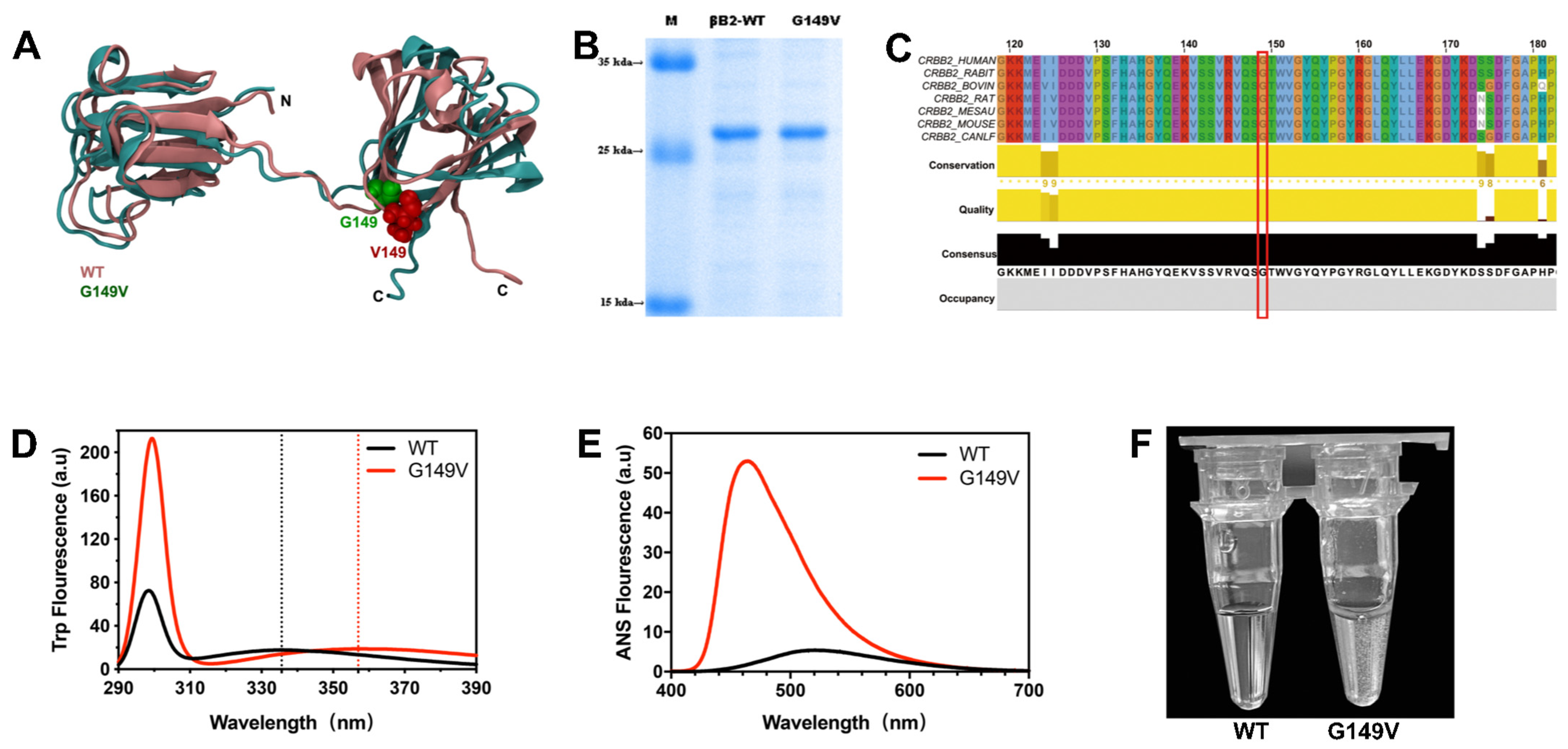
3.1. The G149V Mutation Impairs the Structure and Lowers the Solubility of βB2-Crystallin
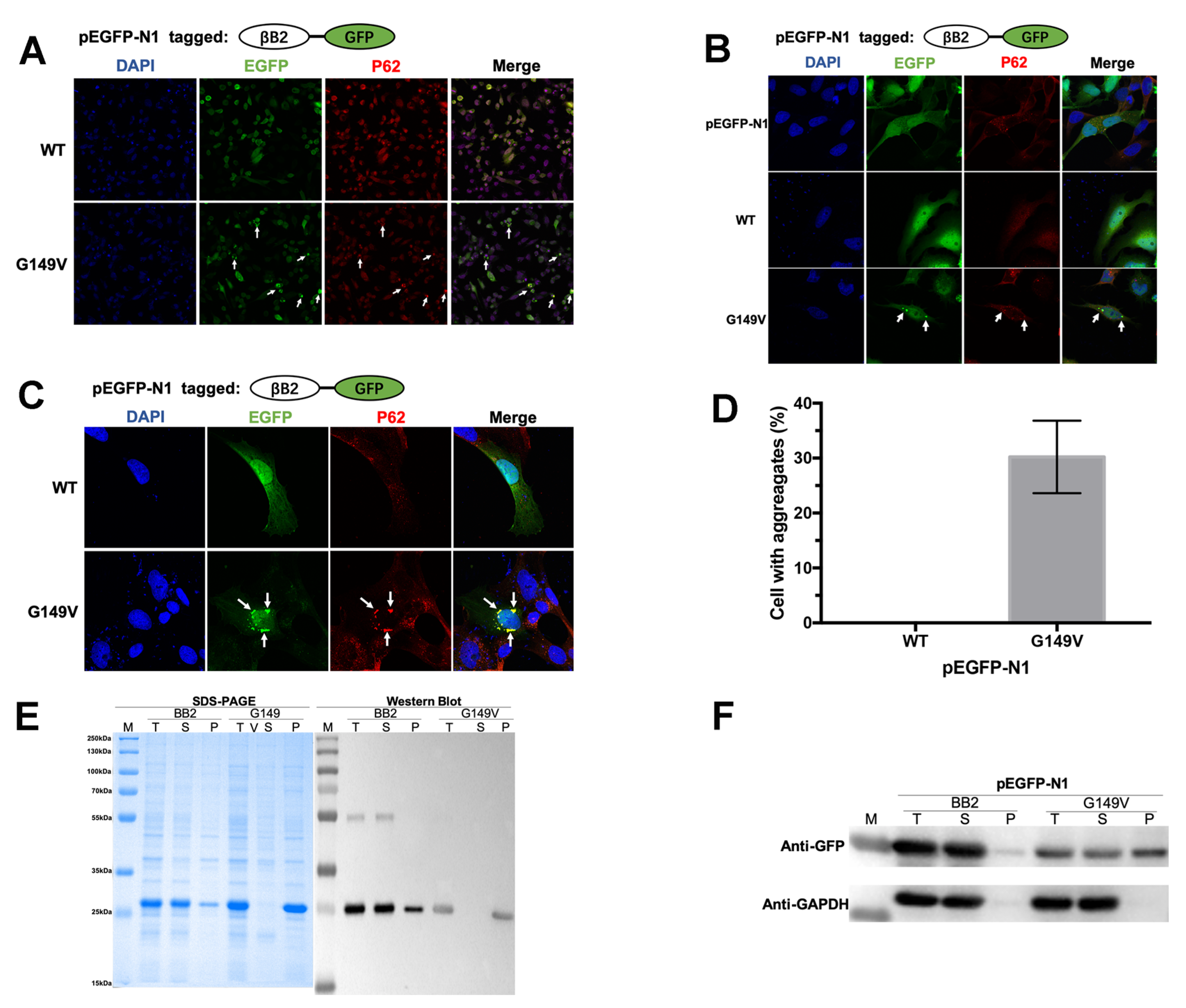
3.2. The G149V Mutation Promotes βB2 Aggregation in Both Human and E. coli Cells
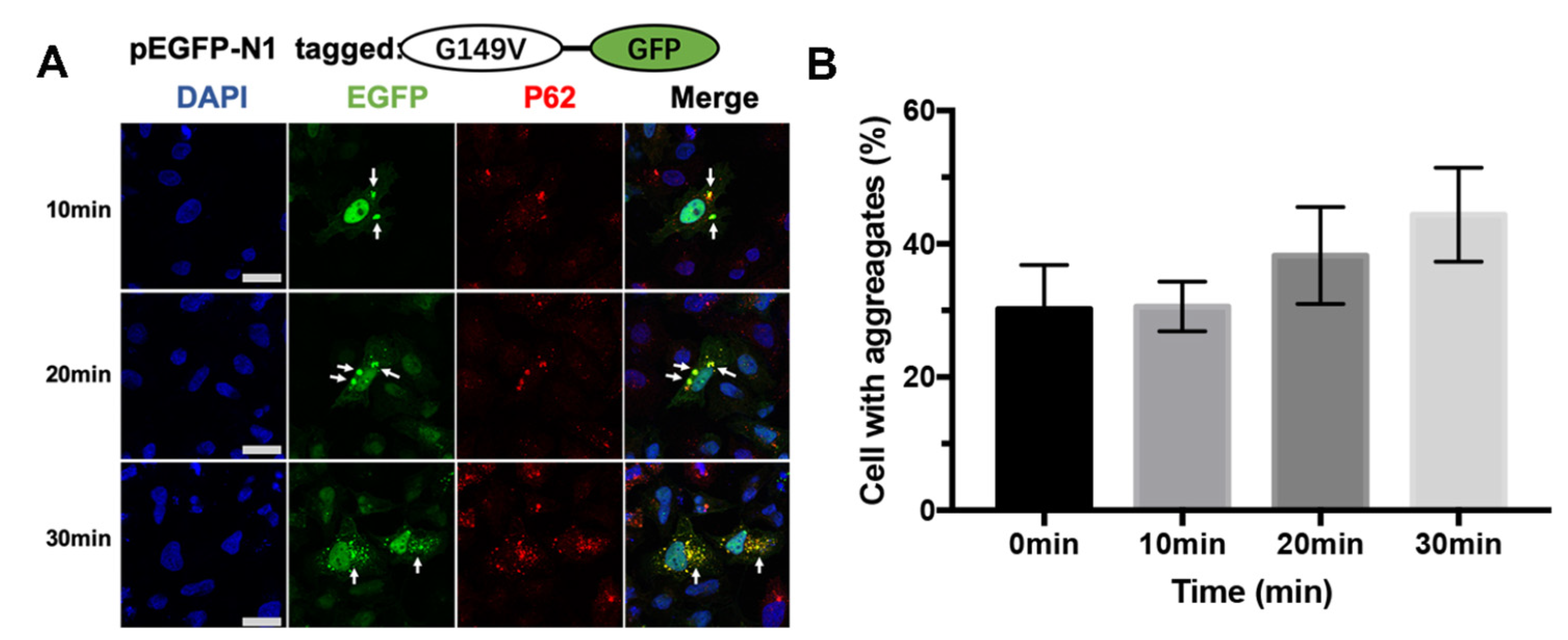
3.3. The G149V Mutation Intracellular Aggregates Were Promoted by H2O2
3.4. The G149V Mutation Intracellular Aggregates Were Promoted by UV Irradiation
3.5. The G149V Mutation Intracellular Aggregates Were Promoted by Heat Shock
3.6. G149V Mutation Significantly Altered the Stability of βB2-Crystallin
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tătaru, C.I.; Tătaru, C.P.; Costache, A.; Boruga, O.; Zemba, M.; Ciuluvică, R.C.; Sima, G. Congenital cataract—Clinical and morphological aspects. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2020, 61, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaxman, S.R.; Bourne, R.R.A.; Resnikoff, S.; Ackland, P.; Braithwaite, T.; Cicinelli, M.V.; Das, A.; Jonas, J.B.; Keeffe, J.; Kempen, J.H.; et al. Global causes of blindness and distance vision impairment 1990–2020: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e1221–e1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.C.; Wilkins, M.; Kim, T.; Malyugin, B.; Mehta, J.S. Cataracts. Lancet 2017, 390, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, V.; Georgiou, M.; Fujinami, K.; Quinlan, R.; Moore, A.; Michaelides, M. Inherited cataracts: Molecular genetics, clinical features, disease mechanisms and novel therapeutic approaches. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 104, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichi, F.; Lembo, A.; Serafino, M.; Nucci, P. Genetics of Congenital Cataract. In Developments in Ophthalmology; Chapter 1–14; Karger International: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, P.J.; Moore, A.T. Genetics of childhood cataract. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2004, 15, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, D.; Agrawal, S.A.; Slavotinek, A.; Lachke, S.A. Mutation update of transcription factor genes FOXE3, HSF4, MAF, and PITX3 causing cataracts and other developmental ocular defects. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 471–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiels, A.; Hejtmancik, J.F. Mutations and mechanisms in congenital and age-related cataracts. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 156, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, V.; Pontikos, N.; Dudakova, L.; Moore, A.T.; Quinlan, R.; Liskova, P.; Michaelides, M. A novel missense mutation in LIM2 causing isolated autosomal dominant congenital cataract. Ophthalmic Genet. 2020, 41, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhli-Hattenbach, C.; Lüchtenberg, M.; Kohnen, T.; Hattenbach, L.-O. Risk Factors for Complications after Congenital Cataract Surgery without Intraocular Lens Implantation in the First 18 Months of Life. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 146, 1–7.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, B.; Stacy, R.C.; Kruger, J.; Cestari, D.M. Deprivation Amblyopia and Congenital Hereditary Cataract. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2013, 28, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andley, U.P. Crystallins in the eye: Function and pathology. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2007, 26, 78–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, A.; Waiswo, M. The genetic and molecular basis of congenital cataract. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. 2011, 74, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, K.L.; King, J.A. Protein misfolding and aggregation in cataract disease and prospects for prevention. Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloemendal, H.; de Jong, W.; Jaenicke, R.; Lubsen, N.H.; Slingsby, C.; Tardieu, A. Ageing and vision: Structure, stability and function of lens crystallins. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2004, 86, 407–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, O.; Sarra, R.; van Genesen, S.; Kappé, G.; Lubsen, N.; Slingsby, C. The stability of human acidic β-crystallin oligomers and hetero-oligomers. Exp. Eye Res. 2003, 77, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Smith, D.L.; Smith, J.B. Human β-crystallins modified by backbone cleavage, deamidation and oxidation are prone to associate. Exp. Eye Res. 2003, 77, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, Y.; Duncan, M.K.; David, L.L. Lens Proteomics: The Accumulation of Crystallin Modifications in the Mouse Lens with Age. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 205–215. [Google Scholar]
- Lampi, K.J.; Shih, M.; Ueda, Y.; Shearer, T.R.; David, L.L. Lens Proteomics: Analysis of Rat Crystallin Sequences and Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis Map. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 216–224. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Wu, S.; Sui, R. Mutations in crystallin genes result in congenital cataract associated with other ocular abnormalities. Mol. Vis. 2017, 23, 977–986. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, W.-J.; Xi, Y.-B.; Yan, Y.-B.; Yao, K. The congenital cataract-linked A2V mutation impairs tetramer formation and promotes aggregation of βB2-crystallin. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Luo, W.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Lu, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, B.; Zhu, S.; Feng, S.; Yan, Y.-B.; et al. A novel mutation in Alpha A-crystallin (CRYAA) caused autosomal dominant congenital cataract in a large Chinese family. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, E.M.; Copp, J.N.; Ackerley, D.F. Site-saturation mutagenesis by overlap extension PCR. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1179, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, S.N.; Hunt, H.D.; Horton, R.M.; Pullen, J.K.; Pease, L.R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 1989, 77, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiyar, A.; Xiang, Y.; Leis, J. Site-directed mutagenesis using overlap extension PCR. Methods Mol. Biol. 1996, 57, 177–191. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Xu, J.; Fu, C.; Jia, Z.; Yao, K.; Chen, X. The cataract-related S39C variant increases gamma S-crystallin sensitivity to environmental stress by destroying the intermolecular disulfide cross-links. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 526, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Xu, J.; Jia, Z.; Yao, K.; Chen, X. Cataract-causing mutations L45P and Y46D promote γ C-crystallin aggregation by disturbing hydrogen bonds network in the second Greek key motif. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, A.; Xu, J.; Fu, C.; Jia, Z.; Yao, K.; Chen, X. βB2 W151R mutant is prone to degradation, aggregation and exposes the hydrophobic side chains in the fourth Greek Key motif. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, J.; Udupa, E.G.P.; Wang, J.; Sharma, K.K. Mini-αB-crystallin: A functional element of αB-crystallin with chaperone-like activity. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 3069–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, A.; Ghosh, K.S.; Banerjee, P.R.; Pande, J. Increase in surface hydrophobicity of the cataract-associated P23T mutant of human γD-crystallin is responsible for its dramatically lower, retrograde solubility. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 6122–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, R.; Santhoshkumar, P.; Mooney, B.P.; Sharma, K.K. The αA66–80 peptide interacts with soluble α-crystallin and induces its aggregation and precipitation: A contribution to age-related cataract Formation. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 3638–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, X.-J.; Zhu, J.; Xi, Y.-B.; Yang, X.; Hu, L.-D.; Ouyang, H.; Patel, S.H.; Jin, X.; Lin, D.; et al. Lanosterol reverses protein aggregation in cataracts. Nature 2015, 523, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, X.-J.; Xia, M.; He, H.-W.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Gong, H.; Yan, Y.-B. Chaperone-like effect of the linker on the isolated c-terminal domain of rabbit muscle creatine kinase. Biophys. J. 2012, 103, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.C.; Braun, R.; Wang, W.; Gumbart, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Villa, E.; Chipot, C.; Skeel, R.D.; Kalé, L.; Schulten, K. Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1781–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; King, J.A.; Zhou, R. Beta-Strand interactions at the domain interface critical for the stability of human lens gammaD-crystallin. Protein Sci. 2010, 19, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, O.; Slingsby, C. Structural studies on βH-crystallin from bovine eye lens. Exp. Eye Res. 1992, 55, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slingsby, C.; Bateman, O.A. Quaternary interactions in eye lens beta-crystallins: Basic and acidic subunits of beta-crystallins favor heterologous association. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 6592–6599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaye, M.; Tardieu, A. Short-range order of crystallin proteins accounts for eye lens transparency. Nature 1983, 302, 415–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhao, W.-J.; Leng, X.-Y.; Wang, S.; Yao, K.; Yan, Y.-B. The importance of the last strand at the C-terminus in βB2-crystallin stability and assembly. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, K.; Chakrabarti, B. Structure and stability of gamma-crystallins: Tryptophan, tyrosine, and cysteine accessibility. Biochemistry 1988, 27, 4564–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendra, V.P.R.; Khan, I.; Chandani, S.; Muniyandi, A.; Balasubramanian, D. Gamma crystallins of the human eye lens. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860 Pt B, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Chen, S.; Xu, J.; Xu, W.; Zheng, S.; Tian, Q.; Luo, C.; Chen, X.; Shentu, X. Insight into Pathogenic Mechanism Underlying the Hereditary Cataract Caused by βB2-G149V Mutation. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13050864
Wu J, Chen S, Xu J, Xu W, Zheng S, Tian Q, Luo C, Chen X, Shentu X. Insight into Pathogenic Mechanism Underlying the Hereditary Cataract Caused by βB2-G149V Mutation. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(5):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13050864
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jing, Silong Chen, Jingjie Xu, Wanyue Xu, Sifan Zheng, Qing Tian, Chenqi Luo, Xiangjun Chen, and Xingchao Shentu. 2023. "Insight into Pathogenic Mechanism Underlying the Hereditary Cataract Caused by βB2-G149V Mutation" Biomolecules 13, no. 5: 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13050864
APA StyleWu, J., Chen, S., Xu, J., Xu, W., Zheng, S., Tian, Q., Luo, C., Chen, X., & Shentu, X. (2023). Insight into Pathogenic Mechanism Underlying the Hereditary Cataract Caused by βB2-G149V Mutation. Biomolecules, 13(5), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13050864






