The Role of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Chronic Pain: Links to Central Sensitization and Neuroinflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Physiological Role of BDNF
3. The Role of BDNF in Patients with Chronic Pain
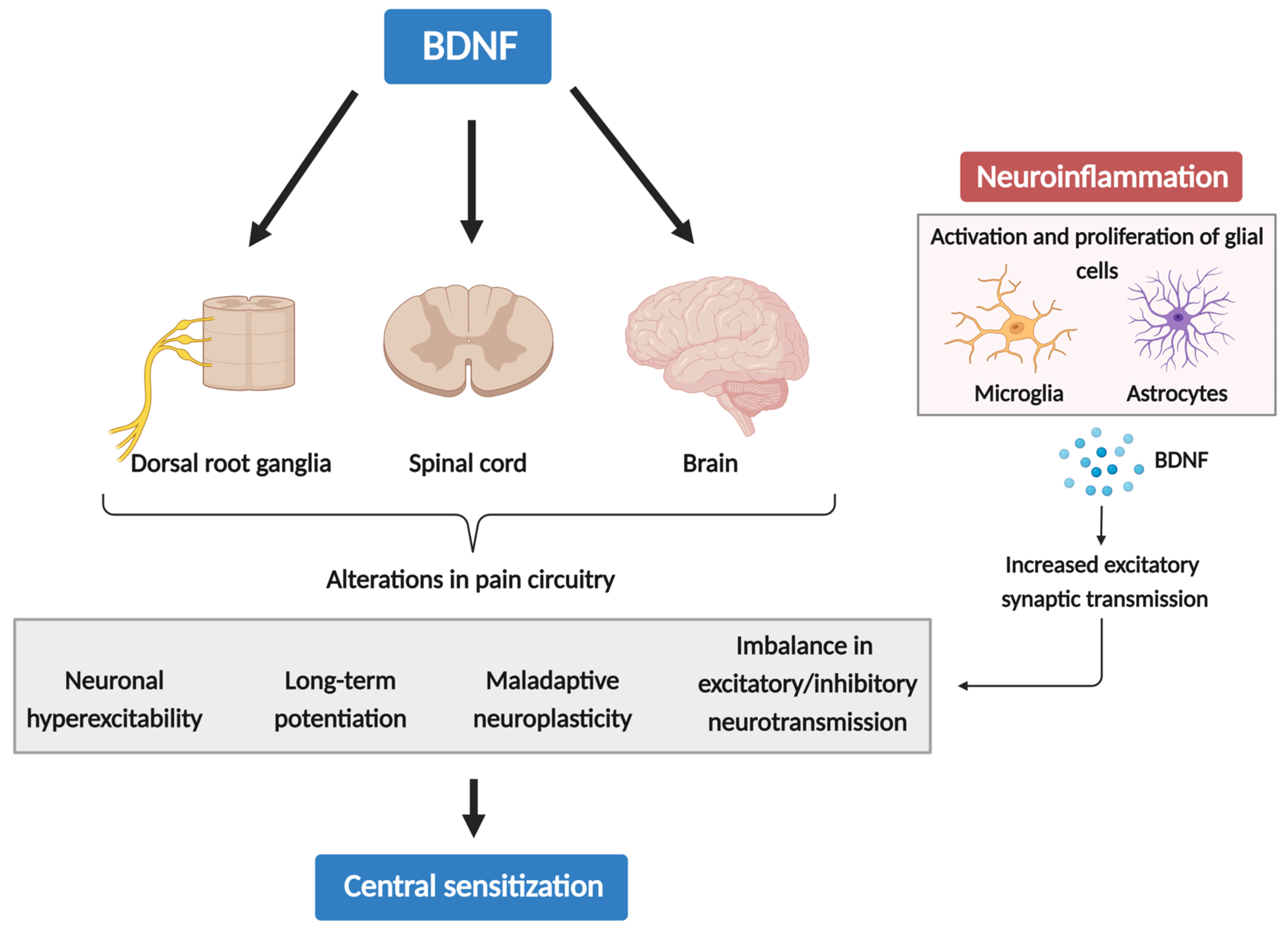
3.1. The Role of BDNF in Central Sensitization
3.2. Neuroinflammation Drives Chronic Pain via Glial-Derived BDNF and CS
3.3. Pro-Nociceptive and Anti-Nociceptive Role of BDNF
| Reference | Study Population | Source of BDNF Measurement | Mean ± SD BDNF Values | p-Values | Correlation with Pain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polli et al., 2020 [127] | Chronic fatigue syndrome and comorbid fibromyalgia (n = 28) Healthy controls (n = 26) | Serum | Chronic fatigue syndrome and comorbid fibromyalgia: 17.75 ± 4.48, Healthy controls: 14.89 ± 3.55 (values in ng/mL) | Sig | Higher BDNF levels predicted participants’ symptoms and widespread hyperalgesia |
| Jasim et al., 2020 [128] | Chronic temporomandibular disorder myalgia (n = 39) Healthy controls (n = 39) | Plasma | Chronic temporomandibular disorder myalgia: 263.33 ± 245.13, Healthy controls: 151.81 ± 125.90 (values in pg/mL) | Sig | Not evaluated |
| Stefani et al., 2019 [111] | Fibromyalgia (n = 117) Osteoarthritis (n = 88) Chronic tensional-type headache (n = 33) Healthy controls (n = 41) | Serum | Osteoarthritis: 24.85, Fibromyalgia: 38.60, Chronic tensional type headache: 37.22, Healthy controls: 22.85 (values in pg/mL) | Sig | Not evaluated |
| Jablochkova et al., 2019 [107] | Fibromyalgia (n = 75) Healthy controls (n = 25) | Plasma | Fibromyalgia: 1553.30, Healthy controls: 671.6 (values in pg/mL) | Sig | No correlation |
| Caumo et al., 2016 [78] | Fibromyalgia (n = 19), osteoarthritis (n = 27), myofascial pain syndrome (n = 54), healthy controls (n = 14) | Serum | Fibromyalgia: 50.78 ± 16.06, Osteoarthritis: 17.91 ± 7.27, Myofascial pain syndrome: 29.28 ± 20.01, Healthy controls: 19.00 ± 8.79 (values in ng/mL) | Sig | Higher BDNF levels were significantly correlated with decreased inhibitory system as assessed through conditioned pain modulation |
| Deitos et al., 2015 [129] | Central sensitivity syndrome absent of structural pathology (n = 81) Central sensitivity syndrome with persistent nociception (n = 59) Healthy controls (n = 37) | Serum | Central sensitivity syndrome absent of structural pathology: 49.87 ± 31.86, Central sensitivity syndrome with persistent nociception: 20.44 ± 8.30, Healthy controls: 14.09 ± 11.80 (values in ng/mL) | Sig | Not evaluated |
| Bidari et al., 2022 [114] | Fibromyalgia (n = 53) Non-fibromyalgia chronic nociceptive pain (n = 60) | Serum | No differences between the two groups | Not Sig | Decreasing serum BDNF after treatment with duloxetine was associated with the improvement in the disease severity, depression, and pain level |
| Ranzolin et al., 2016 [130] | Fibromyalgia (n = 69) Healthy controls (n = 61) | Serum | No differences between the two groups | Not Sig | Not evaluated |
| Iannuccelli et al., 2022 [131] | Fibromyalgia (n = 40) Healthy controls (n = 40) | Serum | Fibromyalgia: 3.38 ± 2.49, Healthy controls: 8.57 ± 3.65 (values in ng/mL) | Sig | No correlation |
3.4. Genetics and BDNF in Chronic Pain
| Reference | Study Population | Tissue | Genotyping Method | Genotype Model (BDNF rs6265) | Main Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goto et al., 2023 [140] | Female cancer survivors (n = 393) | Buccal swab | Isolated genomic DNA from buccal cells. The analysis of the BDNF genotype involved using the PCR SNP Genotyping assays | Val/Val (n = 258) Val/Met (n = 123) Met/Met (n = 12) | Participants with the Met/Met BDNF genotype reported significantly worse cancer-related fatigue and neuropathic pain. |
| Álvaro et al., 2022 [136] | Fibromyalgia (n = 42) | Blood | RT-PCR | Val/Val (n = 30) Val/Met (n = 12) | Val/Met genotypes showed higher efficiency of the descending pain modulatory system and lower disability due to pain. FM patients carrying the Val/Met BDNF genotype presented an increased functional connectivity across the motor and prefrontal cortex in response to acute pain associated with differences in acute pain perception and FM. |
| Yamada et al., 2021 [150] | Chronic low back pain (n = 107) | Blood | RT-PCR | Val/Val (n = 81) Val/Met (n = 26) | No significant associations between the Val66Met genotypes and pain outcomes. |
| Camila et al., 2020 [137] | Fibromyalgia (n = 108) Healthy controls (n = 108) | Blood | RT-PCR | Val/Val (n = 87) Val/Met (n = 21) | Val allele was significantly more frequent in patients with FM compared to the healthy controls. The BDNF Val/Val homozygotes are a potential genetic risk factor associated with higher scores in the Pain Catastrophizing Scale domains: magnification and rumination in patients with FM. |
| Reddy et al., 2014 [151] | Chronic abdominal pain (n = 18) Healthy controls (n = 31) | Blood | RT-PCR | Val/Val (n = 13) Met allele (n = 5) | No significant associations observed with regard to BDNF genotypes with sleep quality or pain grouping. |
3.5. The Epigenetic Regulation of BDNF Expression in Chronic Pain
4. Clinical and Methodological Implications
4.1. BDNF Treatment for Chronic Pain in a Broader Picture
4.2. Using BDNF as an Objective Biomarker
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2021 Low Back Pain Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of low back pain, 1990–2020, its attributable risk factors, and projections to 2050: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e316–e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.P.; Vase, L.; Hooten, W.M. Chronic pain: An update on burden, best practices, and new advances. Lancet 2021, 397, 2082–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, S.E.E.; Nicolson, K.P.; Smith, B.H. Chronic pain: A review of its epidemiology and associated factors in population-based studies. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 123, e273–e283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannister, K.; Sachau, J.; Baron, R.; Dickenson, A.H. Neuropathic Pain: Mechanism-Based Therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 60, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneja, A.; Della Pasqua, O.; Danhof, M. Challenges in translational drug research in neuropathic and inflammatory pain: The prerequisites for a new paradigm. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 73, 1219–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, D.P.; Wong, C.H.; Siah, K.W.; Lo, A.W. Estimates of Probabilities of Successful Development of Pain Medications: An Analysis of Pharmaceutical Clinical Development Programs from 2000 to 2020. Anesthesiology 2022, 137, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basbaum, A.I.; Braz, J.M. Cell transplants to treat the “disease” of neuropathic pain and itch. Pain 2016, 157 (Suppl. 1), S42–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moayedi, M.; Weissman-Fogel, I.; Salomons, T.V.; Crawley, A.P.; Goldberg, M.B.; Freeman, B.V.; Tenenbaum, H.C.; Davis, K.D. Abnormal gray matter aging in chronic pain patients. Brain Res. 2012, 1456, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijs, J.; George, S.Z.; Clauw, D.J.; Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Kosek, E.; Ickmans, K.; Fernández-Carnero, J.; Polli, A.; Kapreli, E.; Huysmans, E.; et al. Central sensitisation in chronic pain conditions: Latest discoveries and their potential for precision medicine. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e383–e392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kregel, J.; Meeus, M.; Malfliet, A.; Dolphens, M.; Danneels, L.; Nijs, J.; Cagnie, B. Structural and functional brain abnormalities in chronic low back pain: A systematic review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 45, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, D.S.; Forsberg, A.; Sandstrom, A.; Bergan, C.; Kadetoff, D.; Protsenko, E.; Lampa, J.; Lee, Y.C.; Hoglund, C.O.; Catana, C.; et al. Brain glial activation in fibromyalgia—A multi-site positron emission tomography investigation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 75, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Morlion, B.; Perrot, S.; Dahan, A.; Dickenson, A.; Kress, H.G.; Wells, C.; Bouhassira, D.; Mohr Drewes, A. Assessment and manifestation of central sensitisation across different chronic pain conditions. Eur. J. Pain 2018, 22, 216–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuner, R.; Flor, H. Structural plasticity and reorganisation in chronic pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 18, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.A. BDNF: No gain without pain? Neuroscience 2014, 283, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowianski, P.; Lietzau, G.; Czuba, E.; Waskow, M.; Steliga, A.; Morys, J. BDNF: A Key Factor with Multipotent Impact on Brain Signaling and Synaptic Plasticity. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dussan-Sarria, J.A.; da Silva, N.R.J.; Deitos, A.; Stefani, L.C.; Laste, G.; Souza, A.; Torres, I.L.S.; Fregni, F.; Caumo, W. Higher Cortical Facilitation and Serum BDNF Are Associated with Increased Sensitivity to Heat Pain and Reduced Endogenous Pain Inhibition in Healthy Males. Pain Med. 2018, 19, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Wang, L.; Hua, J.; Jin, X.H.; Ji, F.; Peng, K.; Zhou, B.; Yang, J.; Meng, X.W. Inhibiting BDNF/TrkB.T1 receptor improves resiniferatoxin-induced postherpetic neuralgia through decreasing ASIC3 signaling in dorsal root ganglia. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima Giacobbo, B.; Doorduin, J.; Klein, H.C.; Dierckx, R.; Bromberg, E.; de Vries, E.F.J. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Brain Disorders: Focus on Neuroinflammation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 3295–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notaras, M.; van den Buuse, M. Neurobiology of BDNF in fear memory, sensitivity to stress, and stress-related disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 2251–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.L.; Barbosa, I.G.; Diniz, B.S.; Kummer, A. Circulating levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor: Correlation with mood, cognition and motor function. Biomark. Med. 2010, 4, 871–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Poo, M.M. Neurotrophin regulation of neural circuit development and function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, M.P.; Maudsley, S.; Martin, B. BDNF and 5-HT: A dynamic duo in age-related neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci. 2004, 27, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernfors, P.; Lee, K.F.; Jaenisch, R. Mice lacking brain-derived neurotrophic factor develop with sensory deficits. Nature 1994, 368, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.R.; Farinas, I.; Backus, C.; Reichardt, L.F. Targeted disruption of the BDNF gene perturbs brain and sensory neuron development but not motor neuron development. Cell 1994, 76, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hempstead, B.L. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: Three Ligands, Many Actions. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2015, 126, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.C.; Yao, W.; Hashimoto, K. Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF)-TrkB Signaling in Inflammation-related Depression and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andero, R.; Choi, D.C.; Ressler, K.J. BDNF-TrkB receptor regulation of distributed adult neural plasticity, memory formation, and psychiatric disorders. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2014, 122, 169–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.H.; Zhou, S.F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, F.; Dai, R.P.; Hu, Z.L.; Li, C.Q. Injection of Anti-proBDNF Attenuates Hippocampal-Dependent Learning and Memory Dysfunction in Mice With Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 665757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, N.H.; Teng, H.K.; Siao, C.J.; Chiaruttini, C.; Pang, P.T.; Milner, T.A.; Hempstead, B.L.; Lu, B. Activation of p75NTR by proBDNF facilitates hippocampal long-term depression. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Pang, P.T.; Woo, N.H. The yin and yang of neurotrophin action. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sochal, M.; Ditmer, M.; Gabryelska, A.; Bialasiewicz, P. The Role of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Immune-Related Diseases: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofer, M.; Pagliusi, S.R.; Hohn, A.; Leibrock, J.; Barde, Y.A. Regional distribution of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA in the adult mouse brain. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 2459–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, R.; Zaidi, S.I.; Mayer, C.; Katz, D.M. BDNF is a target-derived survival factor for arterial baroreceptor and chemoafferent primary sensory neurons. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 2131–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biane, J.; Conner, J.M.; Tuszynski, M.H. Nerve growth factor is primarily produced by GABAergic neurons of the adult rat cortex. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2014, 8, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejot, Y.; Prigent-Tessier, A.; Cachia, C.; Giroud, M.; Mossiat, C.; Bertrand, N.; Garnier, P.; Marie, C. Time-dependent contribution of non neuronal cells to BDNF production after ischemic stroke in rats. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 58, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taves, S.; Berta, T.; Chen, G.; Ji, R.R. Microglia and spinal cord synaptic plasticity in persistent pain. Neural Plast. 2013, 2013, 753656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Rosenfeld, R.D.; Matheson, C.R.; Hawkins, N.; Lopez, O.T.; Bennett, L.; Welcher, A.A. Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein in the adult rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 1997, 78, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahashi, T.; Fujimura, H.; Altar, C.A.; Li, J.; Kambayashi, J.; Tandon, N.N.; Sun, B. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize and secrete brain-derived neurotrophic factor. FEBS Lett. 2000, 470, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, S.; Suzuki, H.; Hirowatari, Y.; Hatase, M.; Nagasawa, A.; Matsuno, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Moriyama, T. Release reaction of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) through PAR1 activation and its two distinct pools in human platelets. Thromb. Res. 2011, 128, e55–e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Blanc, J.; Fleury, S.; Boukhatem, I.; Belanger, J.C.; Welman, M.; Lordkipanidze, M. Platelets Selectively Regulate the Release of BDNF, But Not That of Its Precursor Protein, proBDNF. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 575607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, P.; Brassard, P.; Adser, H.; Pedersen, M.V.; Leick, L.; Hart, E.; Secher, N.H.; Pedersen, B.K.; Pilegaard, H. Evidence for a release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor from the brain during exercise. Exp. Physiol. 2009, 94, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, T.; Anderson, J.; Barton, D.; Lambert, E.; Esler, M.; Hotchkin, E.; Haikerwal, D.; Kaye, D.; Lambert, G. Reduced overflow of BDNF from the brain is linked with suicide risk in depressive illness. Mol. Psychiatry 2007, 12, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Banks, W.A.; Fasold, M.B.; Bluth, J.; Kastin, A.J. Transport of brain-derived neurotrophic factor across the blood-brain barrier. Neuropharmacology 1998, 37, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, A.; Kale, A.; Joshi, S.; Naphade, N.; Raju, M.S.; Nasrallah, H.; Mahadik, S.P. Decreased BDNF levels in CSF of drug-naive first-episode psychotic subjects: Correlation with plasma BDNF and psychopathology. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 13, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.B.; Williamson, R.; Santini, M.A.; Clemmensen, C.; Ettrup, A.; Rios, M.; Knudsen, G.M.; Aznar, S. Blood BDNF concentrations reflect brain-tissue BDNF levels across species. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 14, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gejl, A.K.; Enevold, C.; Bugge, A.; Andersen, M.S.; Nielsen, C.H.; Andersen, L.B. Associations between serum and plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor and influence of storage time and centrifugation strategy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karege, F.; Schwald, M.; Cisse, M. Postnatal developmental profile of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rat brain and platelets. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 328, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poduslo, J.F.; Curran, G.L. Permeability at the blood-brain and blood-nerve barriers of the neurotrophic factors: NGF, CNTF, NT-3, BDNF. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1996, 36, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, F.; Gelfo, F.; De Bartolo, P.; Caltagirone, C.; Petrosini, L. BDNF concentrations are decreased in serum and parietal cortex in immunotoxin 192 IgG-Saporin rat model of cholinergic degeneration. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 59, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Tsuji, M.; Oguchi, T.; Kasuga, K.; Kimura, A.; Futamura, A.; Sugimoto, A.; Kasai, H.; Kuroda, T.; Yano, S.; et al. Serum BDNF as a Potential Biomarker of Alzheimer’s Disease: Verification Through Assessment of Serum, Cerebrospinal Fluid, and Medial Temporal Lobe Atrophy. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 653267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, M.C.; Goncalves, G.S.; Rocha, N.P.; Moraes, E.N.; Bicalho, M.A.; Gualberto Cintra, M.T.; Jardim de Paula, J.; Jose Ravic de Miranda, L.F.; Clayton de Souza Ferreira, A.; Teixeira, A.L.; et al. Increased plasma levels of BDNF and inflammatory markers in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 53, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meacham, K.; Shepherd, A.; Mohapatra, D.P.; Haroutounian, S. Neuropathic Pain: Central vs. Peripheral Mechanisms. Curr. Pain. Headache Rep. 2017, 21, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latremoliere, A.; Woolf, C.J. Central sensitization: A generator of pain hypersensitivity by central neural plasticity. J. Pain 2009, 10, 895–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retamal, J.; Reyes, A.; Ramirez, P.; Bravo, D.; Hernandez, A.; Pelissier, T.; Villanueva, L.; Constandil, L. Burst-Like Subcutaneous Electrical Stimulation Induces BDNF-Mediated, Cyclotraxin B-Sensitive Central Sensitization in Rat Spinal Cord. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolf, C.J.; Salter, M.W. Neuronal plasticity: Increasing the gain in pain. Science 2000, 288, 1765–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wei, Y.; Pu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulation of T-type Ca(2+) channels in sensory neurons contributes to increased peripheral pain sensitivity. Sci. Signal 2019, 12, eaaw2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverry, S.; Shi, X.Q.; Yang, M.; Huang, H.; Wu, Y.; Lorenzo, L.E.; Perez-Sanchez, J.; Bonin, R.P.; De Koninck, Y.; Zhang, J. Spinal microglia are required for long-term maintenance of neuropathic pain. Pain 2017, 158, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramer, L.M.; McPhail, L.T.; Borisoff, J.F.; Soril, L.J.; Kaan, T.K.; Lee, J.H.; Saunders, J.W.; Hwi, L.P.; Ramer, M.S. Endogenous TrkB ligands suppress functional mechanosensory plasticity in the deafferented spinal cord. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 5812–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikandar, S.; Minett, M.S.; Millet, Q.; Santana-Varela, S.; Lau, J.; Wood, J.N.; Zhao, J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor derived from sensory neurons plays a critical role in chronic pain. Brain 2018, 141, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Lu, Y.G.; Pan, Z.Z. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated downregulation of brainstem K+-Cl- cotransporter and cell-type-specific GABA impairment for activation of descending pain facilitation. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 84, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, V.B.; Ballanyi, K.; Colmers, W.F.; Smith, P.A. Neuron type-specific effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rat superficial dorsal horn and their relevance to ‘central sensitization’. J. Physiol. 2007, 584, 543–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Cai, J.; Li, S.; Liu, X.D.; Wan, Y.; Xing, G.G. BDNF contributes to the development of neuropathic pain by induction of spinal long-term potentiation via SHP2 associated GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors activation in rats with spinal nerve ligation. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 73, 428–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Xie, Z.; Li, C.; Xing, Z.; Xie, S.; Li, M.; Yao, J. Driving effect of BDNF in the spinal dorsal horn on neuropathic pain. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 756, 135965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolf, C.J. Central sensitization: Implications for the diagnosis and treatment of pain. Pain 2011, 152, S2–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijs, J.; Meeus, M.; Versijpt, J.; Moens, M.; Bos, I.; Knaepen, K.; Meeusen, R. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor as a driving force behind neuroplasticity in neuropathic and central sensitization pain: A new therapeutic target? Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.S.; Kavalali, E.T.; Monteggia, L.M. BDNF signaling in context: From synaptic regulation to psychiatric disorders. Cell 2022, 185, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappoli, N.; Tabolacci, E.; Aceto, P.; Dello Russo, C. The emerging role of the BDNF-TrkB signaling pathway in the modulation of pain perception. J. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 349, 577406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, M. A synaptic model for pain: Long-term potentiation in the anterior cingulate cortex. Mol. Cells 2007, 23, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Song, S.H.; Augustine, G.J. Calcium-Dependent and Synapsin-Dependent Pathways for the Presynaptic Actions of BDNF. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2017, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsis, M.; Timmusk, T.; Arenas, E.; Persson, H. Differential usage of multiple brain-derived neurotrophic factor promoters in the rat brain following neuronal activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8802–8806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, Q.; Yue, J.; Ying, X.; Li, S.; Lou, X.; Yang, G.; Tu, W.; Zhou, K.; et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P2 x 4, GABAA gamma 2 and long-term potentiation in spinal cord of rats with neuropathic pain. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 162, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obata, K.; Noguchi, K. MAPK activation in nociceptive neurons and pain hypersensitivity. Life Sci. 2004, 74, 2643–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saw, G.; Krishna, K.; Gupta, N.; Soong, T.W.; Mallilankaraman, K.; Sajikumar, S.; Dheen, S.T. Epigenetic regulation of microglial phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway involved in long-term potentiation and synaptic plasticity in rats. Glia 2020, 68, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; de Carvalho-Barbosa, M.; Kavelaars, A.; Heijnen, C.J.; Albrecht, P.J.; Dougherty, P.M. Dorsal Root Ganglion Infiltration by Macrophages Contributes to Paclitaxel Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. J. Pain 2016, 17, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.L.; Noh, C.; Neupane, C.; Sharma, R.; Shin, H.J.; Park, K.D.; Lee, C.J.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, J.B. MAO-B Inhibitor, KDS2010, Alleviates Spinal Nerve Ligation-induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats Through Competitively Blocking the BDNF/TrkB/NR2B Signaling. J. Pain 2022, 23, 2092–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollins, M.; Bryen, C.P.; Taylor, D. Effects of chronic pain history on perceptual and cognitive inhibition. Exp. Brain Res. 2020, 238, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caumo, W.; Deitos, A.; Carvalho, S.; Leite, J.; Carvalho, F.; Dussan-Sarria, J.A.; Lopes Tarrago Mda, G.; Souza, A.; Torres, I.L.; Fregni, F. Motor Cortex Excitability and BDNF Levels in Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain According to Structural Pathology. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simis, M.; Imamura, M.; de Melo, P.S.; Marduy, A.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Teixeira, P.E.P.; Battistella, L.; Fregni, F. Increased motor cortex inhibition as a marker of compensation to chronic pain in knee osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatelli, M.D.; Siepmann, T.; Illigens, B.M.; Souza Dos Santos, V.; Lucena da, S.T.I.; Fregni, F.; Caumo, W. Mapping of predictors of the disengagement of the descending inhibitory pain modulation system in fibromyalgia: An exploratory study. Br. J. Pain 2021, 15, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Lv, L.; Duan, W.; Bai, R.; Meng, Z.; Shao, X. Involvement of the BDNF-TrkB-KCC2 pathway in neuropathic pain after brachial plexus avulsion. Brain Behav. 2022, 12, e2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitayama, T. The Role of K(+)-Cl(-)-Cotransporter-2 in Neuropathic Pain. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.N.; Rice, D.A.; McNair, P.J. Conditioned pain modulation in populations with chronic pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Pain 2012, 13, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.R.; Nackley, A.; Huh, Y.; Terrando, N.; Maixner, W. Neuroinflammation and Central Sensitization in Chronic and Widespread Pain. Anesthesiology 2018, 129, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Wang, X.Q. Bibliometric Analysis of Research on the Comorbidity of Pain and Inflammation. Pain Res. Manag. 2021, 2021, 6655211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.R.; Chamessian, A.; Zhang, Y.Q. Pain regulation by non-neuronal cells and inflammation. Science 2016, 354, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.R.; Xu, Z.Z.; Gao, Y.J. Emerging targets in neuroinflammation-driven chronic pain. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bathina, S.; Das, U.N. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its clinical implications. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015, 11, 1164–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.T.; Wu, J.R.; Chen, Z.Y.; Liu, Z.X.; Miao, B. Effects of dexmedetomidine on P2X4Rs, p38-MAPK and BDNF in spinal microglia in rats with spared nerve injury. Brain Res. 2014, 1568, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coull, J.A.; Beggs, S.; Boudreau, D.; Boivin, D.; Tsuda, M.; Inoue, K.; Gravel, C.; Salter, M.W.; De Koninck, Y. BDNF from microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying neuropathic pain. Nature 2005, 438, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrini, F.; Trang, T.; Mattioli, T.A.; Laffray, S.; Del’Guidice, T.; Lorenzo, L.E.; Castonguay, A.; Doyon, N.; Zhang, W.; Godin, A.G.; et al. Morphine hyperalgesia gated through microglia-mediated disruption of neuronal Cl(-) homeostasis. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kras, J.V.; Weisshaar, C.L.; Quindlen, J.; Winkelstein, B.A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is upregulated in the cervical dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord and contributes to the maintenance of pain from facet joint injury in the rat. J. Neurosci. Res. 2013, 91, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibault, K.; Lin, W.K.; Rancillac, A.; Fan, M.; Snollaerts, T.; Sordoillet, V.; Hamon, M.; Smith, G.M.; Lenkei, Z.; Pezet, S. BDNF-dependent plasticity induced by peripheral inflammation in the primary sensory and the cingulate cortex triggers cold allodynia and reveals a major role for endogenous BDNF as a tuner of the affective aspect of pain. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 14739–14751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomotsuka, N.; Kaku, R.; Obata, N.; Matsuoka, Y.; Kanzaki, H.; Taniguchi, A.; Muto, N.; Omiya, H.; Itano, Y.; Sato, T.; et al. Up-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the dorsal root ganglion of the rat bone cancer pain model. J. Pain Res. 2014, 7, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanelderen, P.; Rouwette, T.; Kozicz, T.; Roubos, E.; Van Zundert, J.; Heylen, R.; Vissers, K. The role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in different animal models of neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pain 2010, 14, 473.e1–473.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.R.; Berta, T.; Nedergaard, M. Glia and pain: Is chronic pain a gliopathy? Pain 2013, 154 (Suppl. 1), S10–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, T.; Beggs, S.; Salter, M.W. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor from microglia: A molecular substrate for neuropathic pain. Neuron Glia Biol. 2011, 7, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merighi, A.; Salio, C.; Ghirri, A.; Lossi, L.; Ferrini, F.; Betelli, C.; Bardoni, R. BDNF as a pain modulator. Prog. Neurobiol. 2008, 85, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, A.M.; Jiang, X.; Wu, X.; Tian, F.; Zhu, D.; Okagaki, P.; Lipsky, R.H. Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and NF-kappaB in neuronal plasticity and survival: From genes to phenotype. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2004, 22, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Mannion, R.J.; Costigan, M.; Decosterd, I.; Amaya, F.; Ma, Q.P.; Holstege, J.C.; Ji, R.R.; Acheson, A.; Lindsay, R.M.; Wilkinson, G.A.; et al. Neurotrophins: Peripherally and centrally acting modulators of tactile stimulus-induced inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9385–9390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, T.; Sun, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Luo, W.; Luo, R.; Shen, W.; Luo, C.; Fu, D. Up-Regulation of ProBDNF/p75(NTR) Signaling in Spinal Cord Drives Inflammatory Pain in Male Rats. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, B.C.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, L.Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, T.Y.; Yang, L.H.; Liao, D.Q.; Zhang, W.S.; Wang, T.H. OECs transplantation results in neuropathic pain associated with BDNF regulating ERK activity in rats following cord hemisection. BMC Neurosci. 2013, 14, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hempstead, B.L. The many faces of p75NTR. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2002, 12, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, M.V. Neurotrophins and their receptors: A convergence point for many signalling pathways. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slack, S.E.; Pezet, S.; McMahon, S.B.; Thompson, S.W.; Malcangio, M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces NMDA receptor subunit one phosphorylation via ERK and PKC in the rat spinal cord. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 1769–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarchielli, P.; Mancini, M.L.; Floridi, A.; Coppola, F.; Rossi, C.; Nardi, K.; Acciarresi, M.; Pini, L.A.; Calabresi, P. Increased levels of neurotrophins are not specific for chronic migraine: Evidence from primary fibromyalgia syndrome. J. Pain 2007, 8, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablochkova, A.; Backryd, E.; Kosek, E.; Mannerkorpi, K.; Ernberg, M.; Gerdle, B.; Ghafouri, B. Unaltered low nerve growth factor and high brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in plasma from patients with fibromyalgia after a 15-week progressive resistance exercise. J. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 51, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, L.; Portela, L.V.; Bohmer, A.E.; Oses, J.P.; Lara, D.R. Increased plasma levels of brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in patients with fibromyalgia. Neurochem. Res. 2010, 35, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simao, A.P.; Mendonca, V.A.; de Oliveira Almeida, T.M.; Santos, S.A.; Gomes, W.F.; Coimbra, C.C.; Lacerda, A.C. Involvement of BDNF in knee osteoarthritis: The relationship with inflammation and clinical parameters. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 34, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laske, C.; Stransky, E.; Eschweiler, G.W.; Klein, R.; Wittorf, A.; Leyhe, T.; Richartz, E.; Kohler, N.; Bartels, M.; Buchkremer, G.; et al. Increased BDNF serum concentration in fibromyalgia with or without depression or antidepressants. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2007, 41, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, L.C.; Leite, F.M.; da Graca, L.T.M.; Zanette, S.A.; de Souza, A.; Castro, S.M.; Caumo, W. BDNF and serum S100B levels according the spectrum of structural pathology in chronic pain patients. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 706, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugraha, B.; Korallus, C.; Gutenbrunner, C. Serum level of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in fibromyalgia syndrome correlates with depression but not anxiety. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanette, S.A.; Dussan-Sarria, J.A.; Souza, A.; Deitos, A.; Torres, I.L.; Caumo, W. Higher serum S100B and BDNF levels are correlated with a lower pressure-pain threshold in fibromyalgia. Mol. Pain. 2014, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidari, A.; Ghavidel-Parsa, B.; Gharibpoor, F. Comparison of the serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) between fibromyalgia and nociceptive pain groups; and effect of duloxetine on the BDNF level. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, K.; Aeschlimann, A.; Jordan, S.; Gay, R.; Gay, S.; Sprott, H. ATP induced brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression and release from osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts is mediated by purinergic receptor P2X4. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimsholm, O.; Guo, Y.; Ny, T.; Forsgren, S. Expression patterns of neurotrophins and neurotrophin receptors in articular chondrocytes and inflammatory infiltrates in knee joint arthritis. Cells Tissues Organs 2008, 188, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowler, P.R.W.; Li, L.; Woodhams, S.G.; Bennett, A.J.; Suzuki, R.; Walsh, D.A.; Chapman, V. Peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor contributes to chronic osteoarthritis joint pain. Pain 2020, 161, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrini, F.; Salio, C.; Boggio, E.M.; Merighi, A. Interplay of BDNF and GDNF in the Mature Spinal Somatosensory System and Its Potential Therapeutic Relevance. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 1225–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, T.; Prowse, N.; McFee, A.; Heiratifar, N.; Fortin, T.; Paquette, C.; Hayley, S. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) has direct anti-inflammatory effects on microglia. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1188672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.M.; Cao, S.B.; Zhang, H.L.; Lyu, D.M.; Chen, L.P.; Xu, H.; Pan, Z.Q.; Shen, W. Downregulation of miR-219 enhances brain-derived neurotrophic factor production in mouse dorsal root ganglia to mediate morphine analgesic tolerance by upregulating CaMKIIgamma. Mol. Pain 2016, 12, 1744806916666283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejas, P.J.; Martinez, M.; Karmally, S.; McKillop, M.; McKillop, J.; Plunkett, J.A.; Oudega, M.; Eaton, M.J. Lumbar transplant of neurons genetically modified to secrete brain-derived neurotrophic factor attenuates allodynia and hyperalgesia after sciatic nerve constriction. Pain 2000, 86, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wei, N.; Zhu, J.; Lu, T.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; Liu, X. Effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on local inflammation in experimental stroke of rat. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 372423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrientos, R.M.; Sprunger, D.B.; Campeau, S.; Watkins, L.R.; Rudy, J.W.; Maier, S.F. BDNF mRNA expression in rat hippocampus following contextual learning is blocked by intrahippocampal IL-1beta administration. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004, 155, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Pan, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wan, J.; Jiang, H. Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation: A Potential Target for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 3083–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finamor, F.; Scarabelot, V.L.; Medeiros, L.F.; Stein, D.J.; da Silva, M.D.; Callai, E.; Caumo, W.; de Souza, A.; Torres, I.L.S. Involvement of GABAergic, glutamatergic, opioidergic, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor systems in the trigeminal neuropathic pain process. Neurosci. Lett. 2023, 793, 136970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z. Persistent inflammation-induced up-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) promotes synaptic delivery of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor GluA1 subunits in descending pain modulatory circuits. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 22196–22204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polli, A.; Ghosh, M.; Bakusic, J.; Ickmans, K.; Monteyne, D.; Velkeniers, B.; Bekaert, B.; Godderis, L.; Nijs, J. DNA Methylation and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Expression Account for Symptoms and Widespread Hyperalgesia in Patients With Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Comorbid Fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1936–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, H.; Ghafouri, B.; Gerdle, B.; Hedenberg-Magnusson, B.; Ernberg, M. Altered levels of salivary and plasma pain related markers in temporomandibular disorders. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitos, A.; Dussan-Sarria, J.A.; Souza, A.; Medeiros, L.; Tarrago Mda, G.; Sehn, F.; Chassot, M.; Zanette, S.; Schwertner, A.; Fregni, F.; et al. Clinical Value of Serum Neuroplasticity Mediators in Identifying the Central Sensitivity Syndrome in Patients With Chronic Pain With and Without Structural Pathology. Clin. J. Pain 2015, 31, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranzolin, A.; Duarte, A.L.; Bredemeier, M.; da Costa Neto, C.A.; Ascoli, B.M.; Wollenhaupt-Aguiar, B.; Kapczinski, F.; Xavier, R.M. Evaluation of cytokines, oxidative stress markers and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in patients with fibromyalgia—A controlled cross-sectional study. Cytokine 2016, 84, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannuccelli, C.; Lucchino, B.; Gioia, C.; Dolcini, G.; Rabasco, J.; Venditto, T.; Ioppolo, F.; Santilli, V.; Conti, F.; Di Franco, M. Gender influence on clinical manifestations, depressive symptoms and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) serum levels in patients affected by fibromyalgia. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 41, 2171–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, M.F.; Kojima, M.; Callicott, J.H.; Goldberg, T.E.; Kolachana, B.S.; Bertolino, A.; Zaitsev, E.; Gold, B.; Goldman, D.; Dean, M.; et al. The BDNF val66met polymorphism affects activity-dependent secretion of BDNF and human memory and hippocampal function. Cell 2003, 112, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.B.; Zuo, X.L.; Zhao, Q.J.; Chen, F.X.; Yang, J.; Dong, Y.Y.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.Q. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor contributes to abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 2012, 61, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vossen, H.; Kenis, G.; Rutten, B.; van Os, J.; Hermens, H.; Lousberg, R. The genetic influence on the cortical processing of experimental pain and the moderating effect of pain status. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Han, D.; Fang, D.; Qiu, X.; Yang, X.; Qiao, Z.; Ma, J.; Wang, L.; et al. BDNF Val66Met polymorphism, life stress and depression: A meta-analysis of gene-environment interaction. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 227, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Franco, A.; de Oliveira Venturini, G.; da Silveira Alves, C.F.; Alves, R.L.; Vicuna, P.; Ramalho, L.; Tomedi, R.; Bruck, S.M.; Torres, I.L.S.; Fregni, F.; et al. Functional connectivity response to acute pain assessed by fNIRS is associated with BDNF genotype in fibromyalgia: An exploratory study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silveira Alves, C.F.; Caumo, W.; Silvestri, J.M.; Zortea, M.; Dos Santos, V.S.; Cardoso, D.F.; Regner, A.; de Souza, A.H.; Simon, D. Pain catastrophizing is associated with the Val66Met polymorphism of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor in fibromyalgia. Adv. Rheumatol. 2020, 60, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, X.; Jia, M.; Yu, H.; Lichtner, P.; Shi, Y.; Meng, Z.; Kou, S.; Ho, I.H.T.; Jia, B.; et al. Targeted Genotyping Identifies Susceptibility Locus in Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor Gene for Chronic Postsurgical Pain. Anesthesiology 2018, 128, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, M.; van der Meij, A.; van Deurzen, P.A.; Janzing, J.G.; Arias-Vasquez, A.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Franke, B. Meta-analysis of the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism in major depressive disorder: Effects of gender and ethnicity. Mol. Psychiatry 2010, 15, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Von Ah, D.; Li, X.; Xiang, L.; Kwiat, C.; Nguyen, C.; Hsiao, C.P.; Saligan, L.N. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor rs6265 polymorphism is associated with severe cancer-related fatigue and neuropathic pain in female cancer survivors. J. Cancer Surviv. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, J.C.; Boakye, M. BDNF Val66Met polymorphism alters spinal DC stimulation-induced plasticity in humans. J. Neurophysiol. 2013, 110, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheeran, B.; Talelli, P.; Mori, F.; Koch, G.; Suppa, A.; Edwards, M.; Houlden, H.; Bhatia, K.; Greenwood, R.; Rothwell, J.C. A common polymorphism in the brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene (BDNF) modulates human cortical plasticity and the response to rTMS. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 5717–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dincheva, I.; Glatt, C.E.; Lee, F.S. Impact of the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism on cognition: Implications for behavioral genetics. Neuroscientist 2012, 18, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volz, M.S.; Suarez-Contreras, V.; Portilla, A.L.; Fregni, F. Mental imagery-induced attention modulates pain perception and cortical excitability. BMC Neurosci. 2015, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.J.; Kim, S.H.; Nah, S.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, Y.A.; Hong, S.J.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, H.A.; et al. Association between brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene polymorphisms and fibromyalgia in a Korean population: A multicenter study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.A.; Rao, V.; Kesler, S.R. The association of genetic polymorphisms with neuroconnectivity in breast cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.J.; Jenkins, L.C.; Humburg, P.; Schabrun, S.M. Human assumed central sensitization in people with acute non-specific low back pain: A cross-sectional study of the association with brain-derived neurotrophic factor, clinical, psychological and demographic factors. Eur. J. Pain 2023, 27, 530–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, L.C.; Chang, W.J.; Buscemi, V.; Liston, M.; Humburg, P.; Nicholas, M.; Graven-Nielsen, T.; Hodges, P.W.; McAuley, J.H.; Schabrun, S.M. Cortical function and sensorimotor plasticity are prognostic factors associated with future low back pain after an acute episode: The Understanding persistent Pain Where it ResiDes prospective cohort study. Pain 2023, 164, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, L.C.; Chang, W.J.; Buscemi, V.; Liston, M.; Skippen, P.; Cashin, A.G.; McAuley, J.H.; Schabrun, S.M. Low Somatosensory Cortex Excitability in the Acute Stage of Low Back Pain Causes Chronic Pain. J. Pain 2022, 23, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, A.S.; Antunes, F.T.T.; Ferraz, C.; de Souza, A.H.; Simon, D. The genetic influence of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism in chronic low back pain. Adv. Rheumatol. 2021, 61, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.Y.; Rasmussen, N.A.; Fourie, N.H.; Berger, R.S.; Martino, A.C.; Gill, J.; Longchamps, R.; Wang, X.M.; Heitkemper, M.M.; Henderson, W.A. Sleep quality, BDNF genotype and gene expression in individuals with chronic abdominal pain. BMC Med. Genom. 2014, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, J.I.; Burri, A. Genetic and epigenetic epidemiology of chronic widespread pain. J. Pain Res. 2017, 10, 2021–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agnelli, S.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Gerra, M.C.; Zatorri, K.; Boggiani, L.; Baciarello, M.; Bignami, E. Fibromyalgia: Genetics and epigenetics insights may provide the basis for the development of diagnostic biomarkers. Mol. Pain 2019, 15, 1744806918819944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crow, M.; Denk, F.; McMahon, S.B. Genes and epigenetic processes as prospective pain targets. Genome Med. 2013, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauceri, D. Role of Epigenetic Mechanisms in Chronic Pain. Cells 2022, 11, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Shen, L.; Hou, Y. Epigenetic modification of BDNF mediates neuropathic pain via miR-30a-3p/EP300 axis in CCI rats. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20194442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Feng, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Han, Q.; Zhao, X.; Li, P. Long Non-coding RNA LINC01119 Promotes Neuropathic Pain by Stabilizing BDNF Transcript. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 673669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoloni-Giacobino, A.; Luthi, F.; Stenz, L.; Le Carre, J.; Vuistiner, P.; Leger, B. Altered BDNF Methylation in Patients with Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain and High Biopsychosocial Complexity. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, V.; Lyon, D.E.; Archer, K.J.; Zhou, Q.; Brumelle, J.; Jones, K.H.; Gao, G.; York, T.P.; Jackson-Cook, C. Epigenetic alterations and an increased frequency of micronuclei in women with fibromyalgia. Nurs. Res. Pract. 2013, 2013, 795784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, R. Overexpression of miR-206 ameliorates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in rats via the MEK/ERK pathway by targeting brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 646, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Yue, J.; Li, X.; Wu, Q.; Yang, G.; Li, S.; Sun, Q.; Jiang, S. Electroacupuncture Alleviates Neuropathic Pain through Regulating miR-206-3p Targeting BDNF after CCI. Neural Plast. 2022, 2022, 1489841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, K.I.; Voss, M.W.; Prakash, R.S.; Basak, C.; Szabo, A.; Chaddock, L.; Kim, J.S.; Heo, S.; Alves, H.; White, S.M.; et al. Exercise training increases size of hippocampus and improves memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3017–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.A.; Makino, S.; Kvetnansky, R.; Post, R.M. Stress and glucocorticoids affect the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 mRNAs in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 1768–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havekes, R.; Vecsey, C.G.; Abel, T. The impact of sleep deprivation on neuronal and glial signaling pathways important for memory and synaptic plasticity. Cell Signal 2012, 24, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.L. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature 2007, 447, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descalzi, G.; Ikegami, D.; Ushijima, T.; Nestler, E.J.; Zachariou, V.; Narita, M. Epigenetic mechanisms of chronic pain. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.Y.; Zheng, J.J.; Wang, X.Q. Non-invasive Brain Stimulation for Chronic Pain: State of the Art and Future Directions. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 888716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knotkova, H.; Hamani, C.; Sivanesan, E.; Le Beuffe, M.F.E.; Moon, J.Y.; Cohen, S.P.; Huntoon, M.A. Neuromodulation for chronic pain. Lancet 2021, 397, 2111–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.Y.; Cao, Y.Q.; Du, S.H.; Yang, Q.H.; He, S.Y.; Wang, X.Q. Effects of High-Definition Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Targeting the Anterior Cingulate Cortex on the Pain Thresholds: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Pain Med. 2023, 24, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamar, M.F.; Wivatvongvana, P.; Patumanond, J.; Bikson, M.; Truong, D.Q.; Datta, A.; Fregni, F. Focal modulation of the primary motor cortex in fibromyalgia using 4x1-ring high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation (HD-tDCS): Immediate and delayed analgesic effects of cathodal and anodal stimulation. J. Pain 2013, 14, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, E.M.; Omran, E.A.H.; Ismail, N.M.; El-Hammady, D.H.; Goma, S.H.; Kotb, H.; Galal, H.; Osman, A.M.; Farghaly, H.S.M.; Karim, A.A.; et al. Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on pain, mood and serum endorphin level in the treatment of fibromyalgia: A double blinded, randomized clinical trial. Brain Stimul. 2017, 10, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.I.; Bikson, M.; Datta, A.; Minhas, P.; Paulus, W.; Kuo, M.F.; Nitsche, M.A. Comparing cortical plasticity induced by conventional and high-definition 4 x 1 ring tDCS: A neurophysiological study. Brain Stimul. 2013, 6, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monte-Silva, K.; Kuo, M.F.; Hessenthaler, S.; Fresnoza, S.; Liebetanz, D.; Paulus, W.; Nitsche, M.A. Induction of late LTP-like plasticity in the human motor cortex by repeated non-invasive brain stimulation. Brain Stimul. 2013, 6, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarabelot, V.L.; de Oliveira, C.; Medeiros, L.F.; de Macedo, I.C.; Cioato, S.G.; Adachi, L.N.S.; Paz, A.H.; de Souza, A.; Caumo, W.; Torres, I.L.S. Transcranial direct-current stimulation reduces nociceptive behaviour in an orofacial pain model. J. Oral Rehabil. 2019, 46, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsch, B.; Reis, J.; Martinowich, K.; Schambra, H.M.; Ji, Y.; Cohen, L.G.; Lu, B. Direct current stimulation promotes BDNF-dependent synaptic plasticity: Potential implications for motor learning. Neuron 2010, 66, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, B.C.; Medeiros, L.F.; Silva de Souza, V.; Cioato, S.G.; Medeiros, H.R.; Regner, G.G.; Lino de Oliveira, C.; Fregni, F.; Caumo, W.; Torres, I.L.S. Transcranial direct current stimulation combined with exercise modulates the inflammatory profile and hyperalgesic response in rats subjected to a neuropathic pain model: Long-term effects. Brain Stimul. 2020, 13, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filho, P.R.; Vercelino, R.; Cioato, S.G.; Medeiros, L.F.; de Oliveira, C.; Scarabelot, V.L.; Souza, A.; Rozisky, J.R.; Quevedo Ada, S.; Adachi, L.N.; et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) reverts behavioral alterations and brainstem BDNF level increase induced by neuropathic pain model: Long-lasting effect. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 64, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchting, R.; Teixeira, A.L.; Ahn, B.; Colpo, G.D.; Park, J.; Ahn, H. Changes in Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor From Active and Sham Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Older Adults With Knee Osteoarthritis. Clin. J. Pain 2021, 37, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Moreira, S.F.; Medeiros, L.F.; de Souza, A.; de Oliveira, C.; Scarabelot, V.L.; Fregni, F.; Caumo, W.; Torres, I.L. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) neuromodulatory effects on mechanical hyperalgesia and cortical BDNF levels in ovariectomized rats. Life Sci. 2016, 145, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlatt, M.W.; Potter, M.C.; Lucassen, P.J.; van Praag, H. Running throughout middle-age improves memory function, hippocampal neurogenesis, and BDNF levels in female C57BL/6J mice. Dev. Neurobiol. 2012, 72, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.V.; Abner, T.S.S.; Sluka, K.A. Does exercise increase or decrease pain? Central mechanisms underlying these two phenomena. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 4141–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Moon, W.; Kim, J. Effect of yoga on pain, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and serotonin in premenopausal women with chronic low back pain. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 203173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Zhou, H.H.; Luo, Q.; Cui, S. The effect of physical exercise on circulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor in healthy subjects: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Brain Behav. 2022, 12, e2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, B.K. Physical activity and muscle-brain crosstalk. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di-Bonaventura, S.; Fernandez-Carnero, J.; Matesanz-Garcia, L.; Arribas-Romano, A.; Polli, A.; Ferrer-Pena, R. Effect of Different Physical Therapy Interventions on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels in Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain Patients: A Systematic Review. Life 2023, 13, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, V.G.C.; Mendonca, V.A.; Souza, A.L.C.; Fonseca, S.F.; Camargos, A.C.R.; Lage, V.K.S.; Neves, C.D.C.; Santos, J.M.; Teixeira, L.A.C.; Vieira, E.L.M.; et al. Inflammatory biomarkers responses after acute whole body vibration in fibromyalgia. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, e6775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knaepen, K.; Goekint, M.; Heyman, E.M.; Meeusen, R. Neuroplasticity-exercise-induced response of peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor: A systematic review of experimental studies in human subjects. Sports Med. 2010, 40, 765–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senba, E.; Kami, K. A new aspect of chronic pain as a lifestyle-related disease. Neurobiol. Pain 2017, 1, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polli, A.; Ickmans, K.; Godderis, L.; Nijs, J. When Environment Meets Genetics: A Clinical Review of the Epigenetics of Pain, Psychological Factors, and Physical Activity. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulle, F.; Kenis, G.; Cazorla, M.; Hamon, M.; Steinbusch, H.W.; Lanfumey, L.; van den Hove, D.L. TrkB inhibition as a therapeutic target for CNS-related disorders. Prog. Neurobiol. 2012, 98, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Y.; Bambah-Mukku, D.; Pollonini, G.; Alberini, C.M. Glucocorticoid receptors recruit the CaMKIIalpha-BDNF-CREB pathways to mediate memory consolidation. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yajima, Y.; Narita, M.; Usui, A.; Kaneko, C.; Miyatake, M.; Narita, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Tamaki, H.; Wachi, H.; Seyama, Y.; et al. Direct evidence for the involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the development of a neuropathic pain-like state in mice. J. Neurochem. 2005, 93, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte-Herbruggen, O.; Nassenstein, C.; Lommatzsch, M.; Quarcoo, D.; Renz, H.; Braun, A. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 regulate secretion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in human monocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2005, 160, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poutoglidou, F.; Pourzitaki, C.; Manthou, M.E.; Malliou, F.; Saitis, A.; Tsimoulas, I.; Panagiotopoulos, S.; Kouvelas, D. Effects of long-term infliximab and tocilizumab treatment on anxiety-like behavior and cognitive function in naive rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 2022, 74, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojtabavi, H.; Shaka, Z.; Momtazmanesh, S.; Ajdari, A.; Rezaei, N. Circulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor as a potential biomarker in stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, A.; Corey-Bloom, J.; Thomas, E.A.; Desplats, P. Evaluation of Biochemical and Epigenetic Measures of Peripheral Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) as a Biomarker in Huntington’s Disease Patients. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azoulay, D.; Horowitz, N.A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor as a potential biomarker of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and prognosis in haematological malignancies; what we have learned, the challenges and a need for global standardization. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 191, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacchini, A.; Metelli, G.; Francavilla, R.; Baj, G.; Florean, M.; Mascaretti, L.G.; Tongiorgi, E. A method for reproducible measurements of serum BDNF: Comparison of the performance of six commercial assays. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, B.; Acevedo, E.O. BDNF as a biomarker for neuropathic pain: Consideration of mechanisms of action and associated measurement challenges. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorina-Lichtenwalter, K.; Meloto, C.B.; Khoury, S.; Diatchenko, L. Genetic predictors of human chronic pain conditions. Neuroscience 2016, 338, 36–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reference | Study Population | Study Design | Epigenetic Assessment | Tissue | Assay | Main Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polli et al., 2020 [127] | Chronic fatigue syndrome and comorbid fibromyalgia (n = 28) Healthy controls (n = 26) | Cross-sectional | DNA methylation (BDNF gene-specific) | Blood | PCR amplification, pyrosequencing | Compared to controls, serum BNDF was higher in patients with CFS/FM (mean difference of 3.31 ng/mL; p = 0.001), whereas BDNF DNA methylation in exon 9 was lower (mean difference of −2.16%; p = 0.007). Lower methylation in the same region predicted higher BDNF levels (p = 0.009), which in turn predicted participants’ symptoms (p = 0.001) and widespread hyperalgesia (p = 0.044). |
| Paoloni-Giacobino et al., 2020 [158] | Chronic musculoskeletal pain (n = 58) Healthy controls (n = 18) | Cross-sectional | DNA methylation (BDNF gene-specific) | Blood | PCR amplification, pyrosequencing | The methylation values of BDNF were significantly (p< 0.005) increased 1.9-fold in patients with CMS as compared with the healthy controls. A high level of biopsychosocial complexity was associated with lower average CpG methylation values of BDNF (p = 0.02) in patients with CMS, and may therefore increase the level of BDNF. The upregulation of BDNF is associated with higher levels of biopsychosocial complexity. |
| Menzies et al., 2013 [159] | Fibromyalgia (n = 10) Healthy controls (n = 8) | Cross-sectional | DNA methylation (genome-wide) | Blood | 450 K human methylation assay | Authors found 69 differently methylated positions, in 47 different genes, i.e., AXL, HDAC4, BDNF, PRKCA, RTN1, PRKG1, SOD3. There is a significant difference in the methylation pattern of the BDNF gene between patients with FM and controls. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, H.-Y.; Hendrix, J.; Schabrun, S.; Wyns, A.; Campenhout, J.V.; Nijs, J.; Polli, A. The Role of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Chronic Pain: Links to Central Sensitization and Neuroinflammation. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010071
Xiong H-Y, Hendrix J, Schabrun S, Wyns A, Campenhout JV, Nijs J, Polli A. The Role of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Chronic Pain: Links to Central Sensitization and Neuroinflammation. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(1):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010071
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Huan-Yu, Jolien Hendrix, Siobhan Schabrun, Arne Wyns, Jente Van Campenhout, Jo Nijs, and Andrea Polli. 2024. "The Role of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Chronic Pain: Links to Central Sensitization and Neuroinflammation" Biomolecules 14, no. 1: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010071
APA StyleXiong, H.-Y., Hendrix, J., Schabrun, S., Wyns, A., Campenhout, J. V., Nijs, J., & Polli, A. (2024). The Role of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Chronic Pain: Links to Central Sensitization and Neuroinflammation. Biomolecules, 14(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010071








