Methods for Detection and Mapping of Methylated and Hydroxymethylated Cytosine in DNA
Abstract
1. Introduction
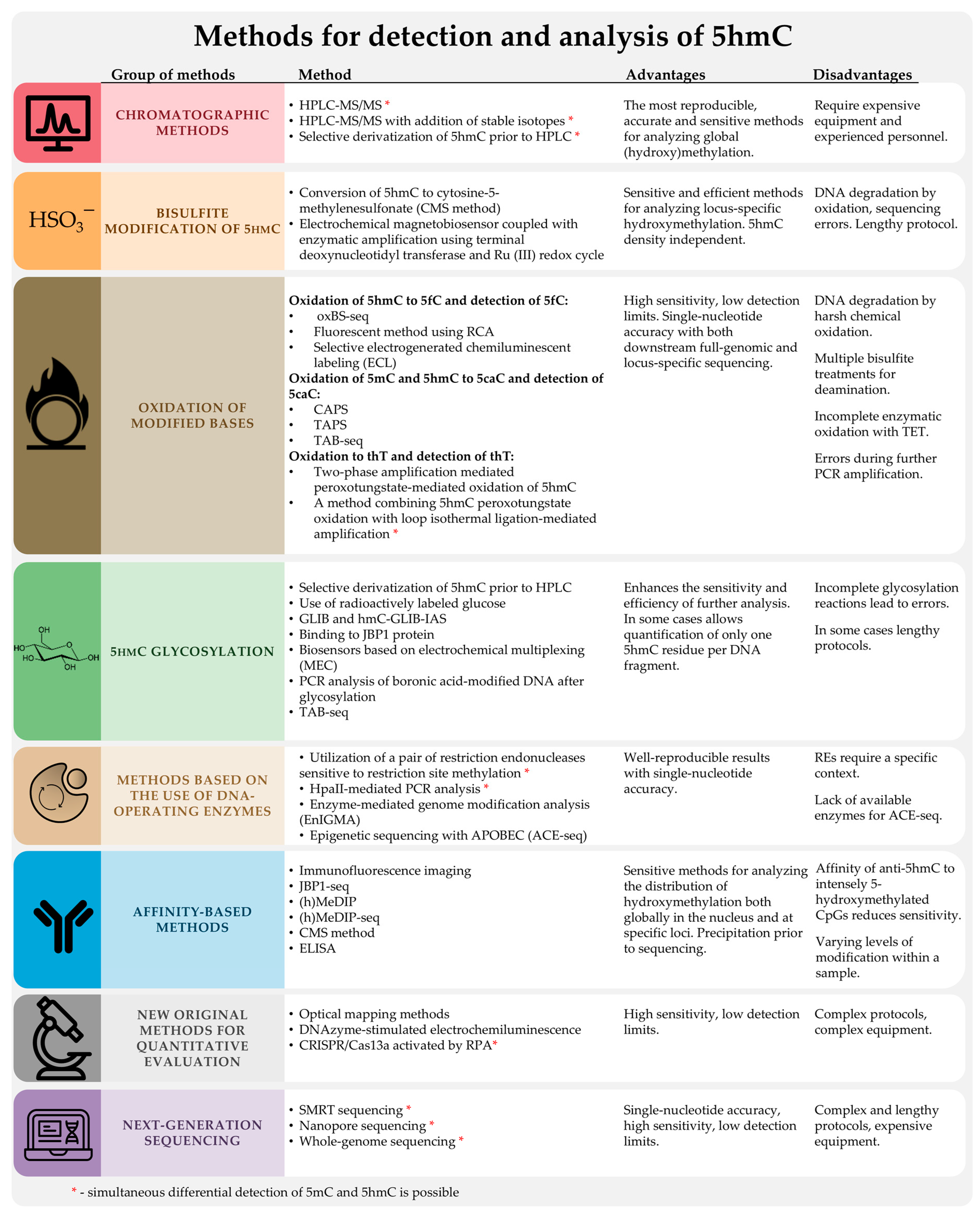
2. Standard Methods for DNA Methylation Analysis
2.1. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Mass Spectrometric Detection (HPLC-MS) and Other Chromatographic Methods
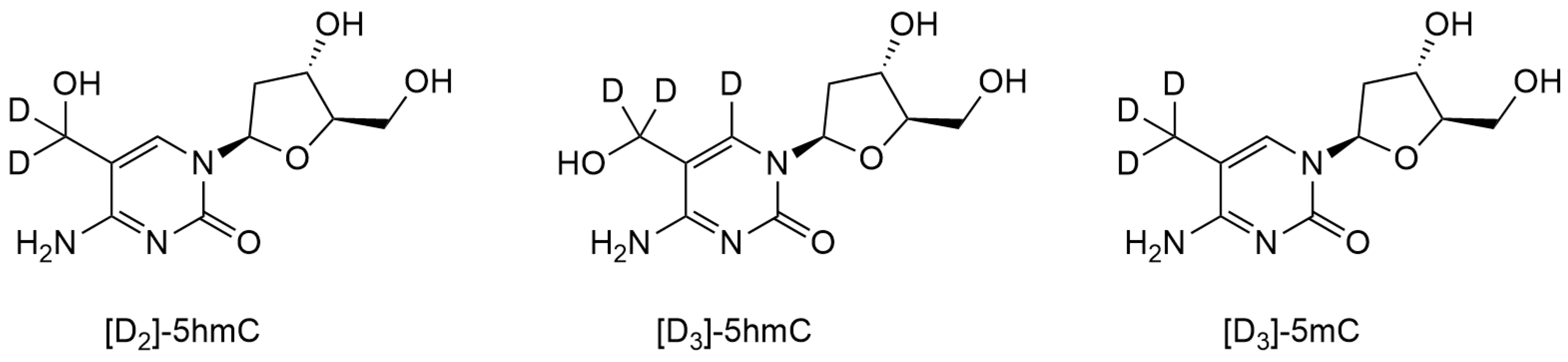
2.1.1. HPLC-MS/MS with Stable Isotope Labeling
2.1.2. Selective Derivatization of 5hmC Prior to HPLC
2.1.3. 5hmC Quantitation Using Guanine as an Internal Standard
3. Chemical or Enzymatic Modification of DNA Containing 5hmC to Increase Detection Sensitivity Based on Various Detection Principles
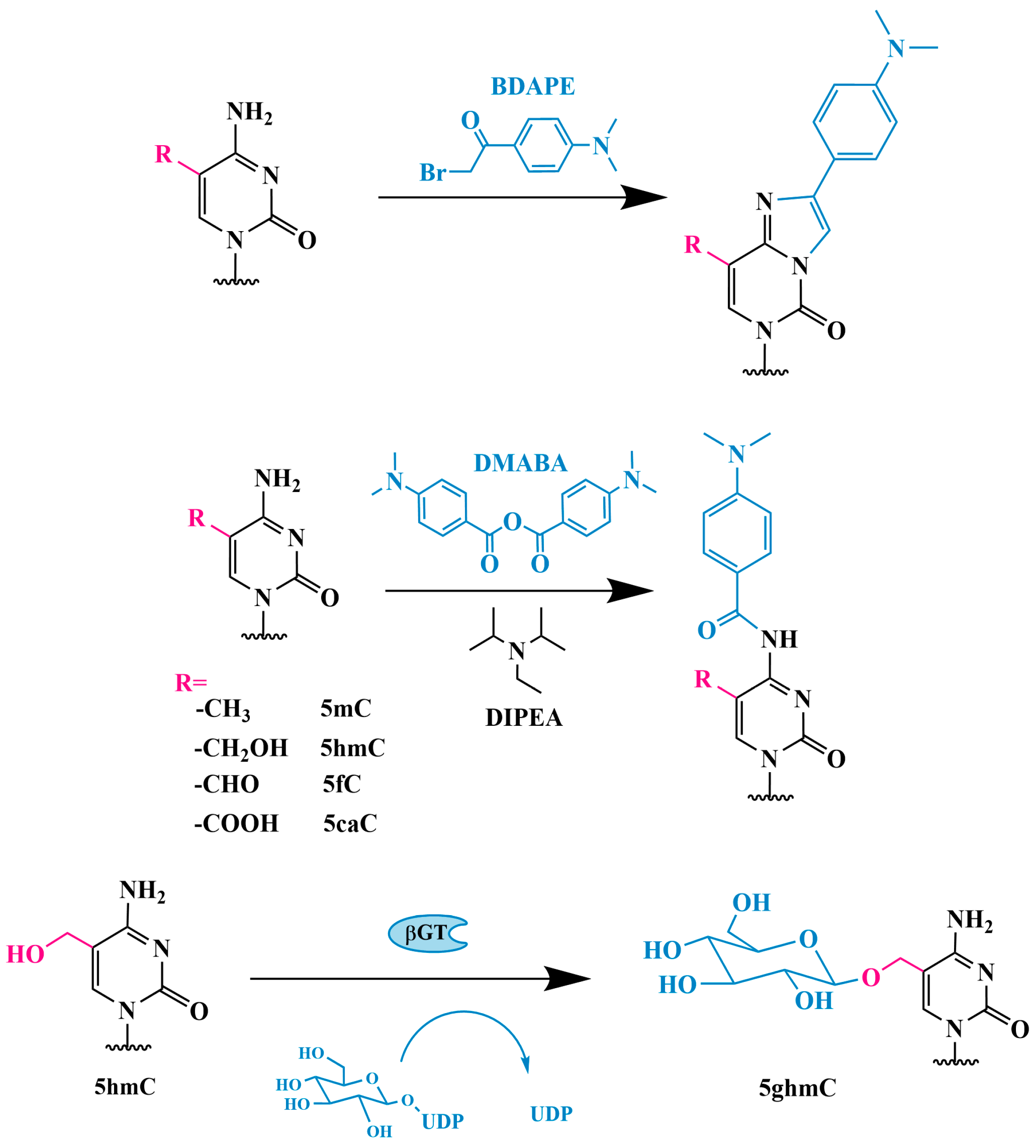
3.1. Glycosylation
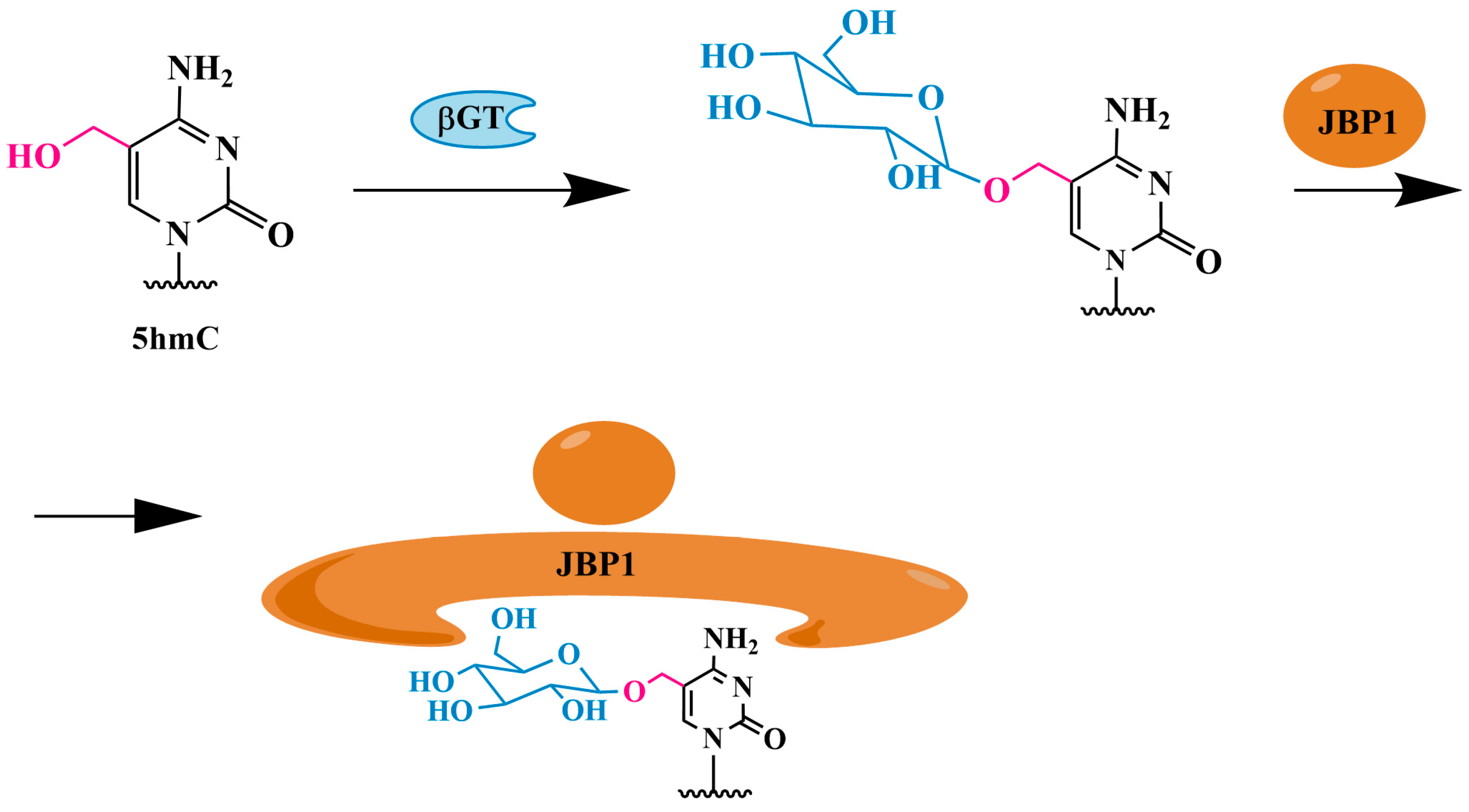
3.1.1. Glycosylation and Detection Using [3H]-Glucose
3.1.2. 5hmC Identification Using J-Binding Protein 1
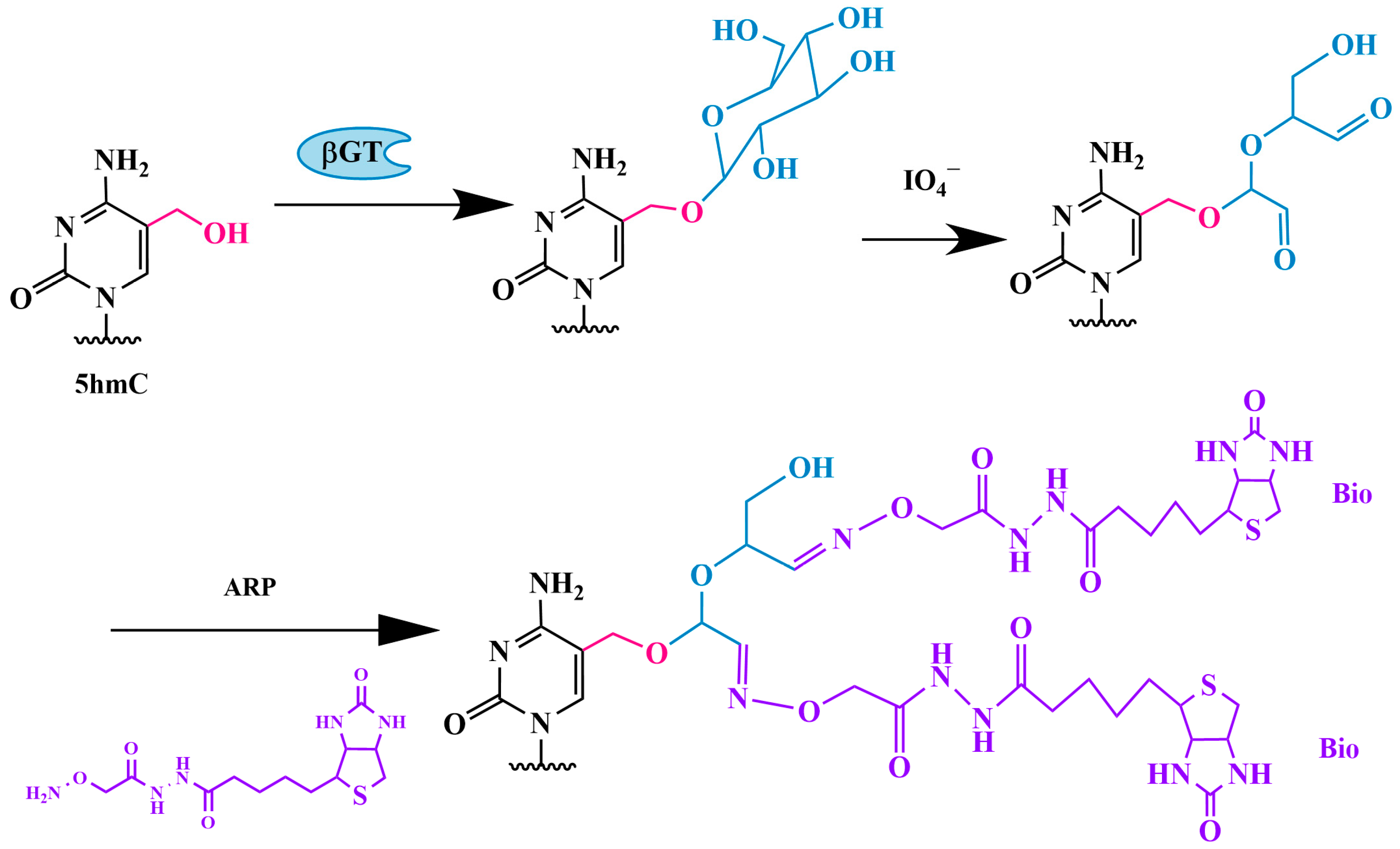
3.1.3. Method of Sequential Glycosylation, Oxidation and Biotinylation (GLIB)
Modified GLIB Method—hmC-GLIB-IAS Strategy
Multiplex Electrochemical (MEC) Biosensor for 5hmC Detection
3.1.4. Glycosylation and Boronic Acid Derivative Modification Followed by PCR Analysis
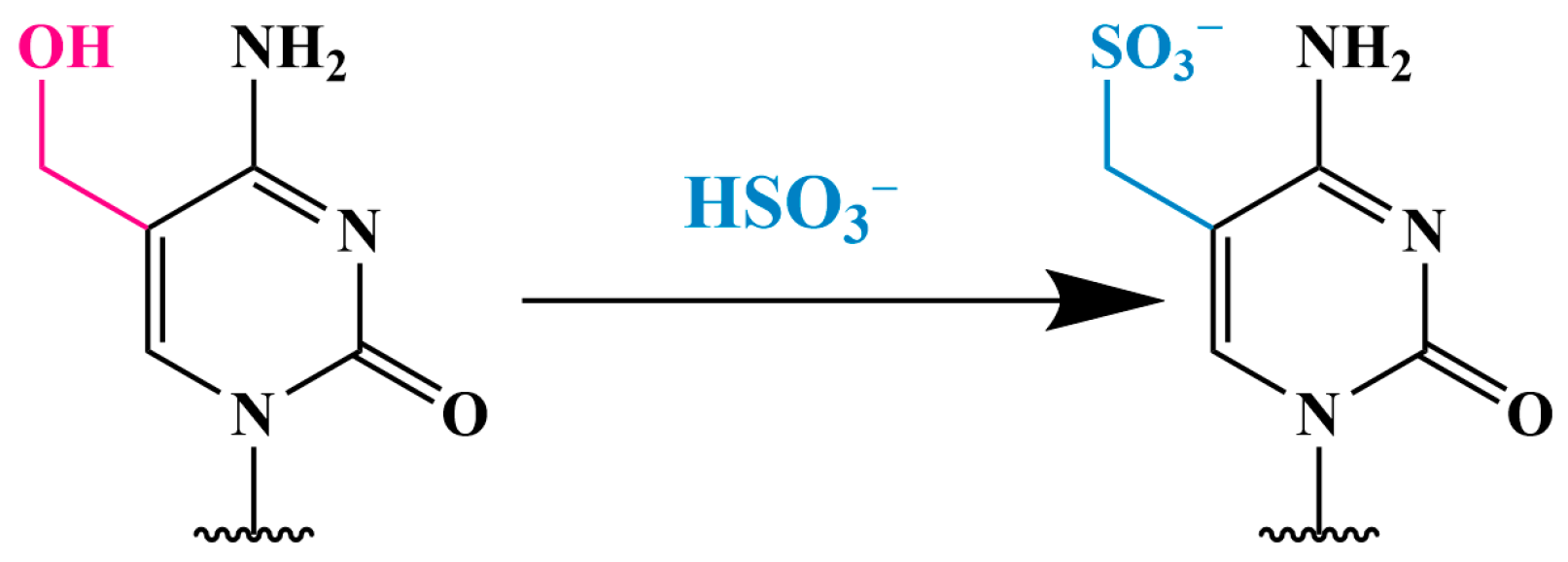
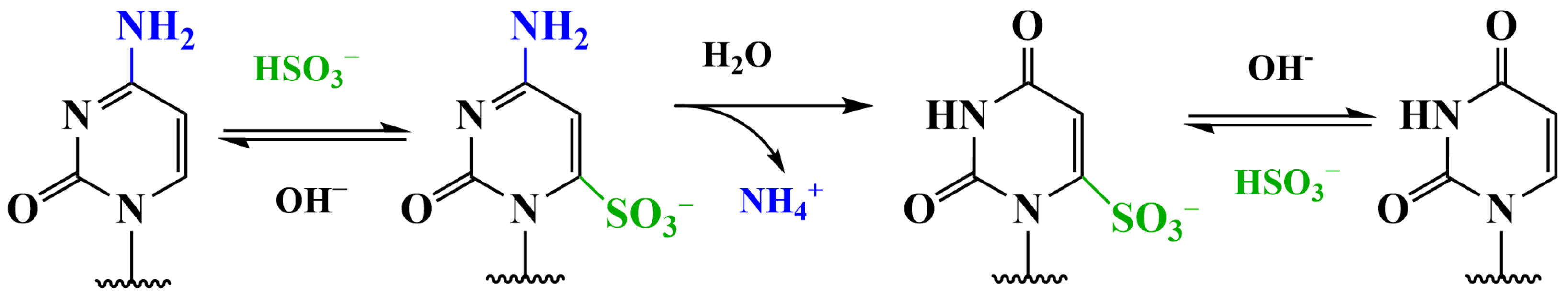
3.2. Methods Using Sodium Bisulfite
3.2.1. Conversion of 5hmC into Cytosine-5-Methylene Sulfonate (CMS) (CMS Method)
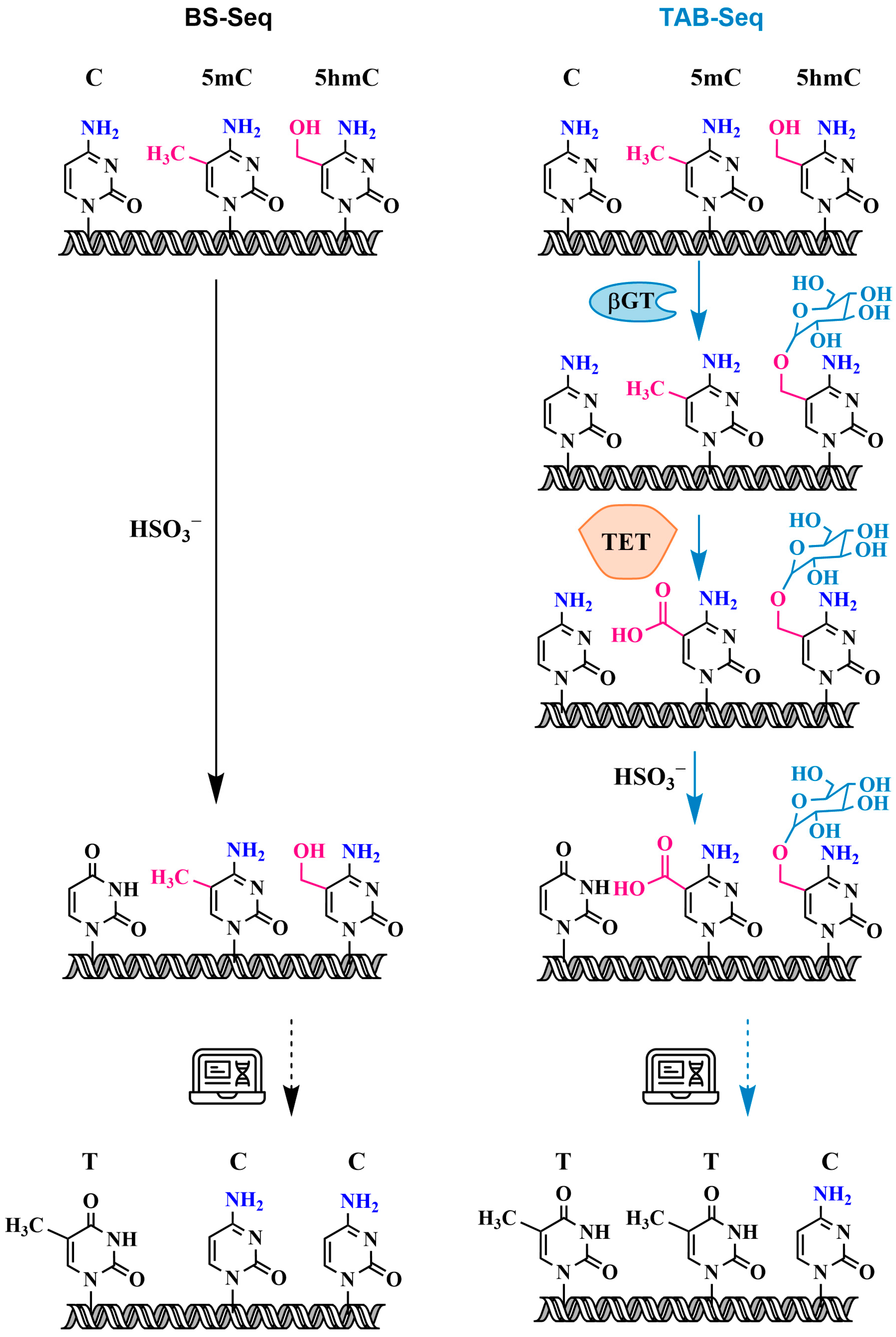
3.2.2. Oxidative Bisulfite Sequencing Using TET (TAB-Seq) with 5hmC Protection Through Glycosylation
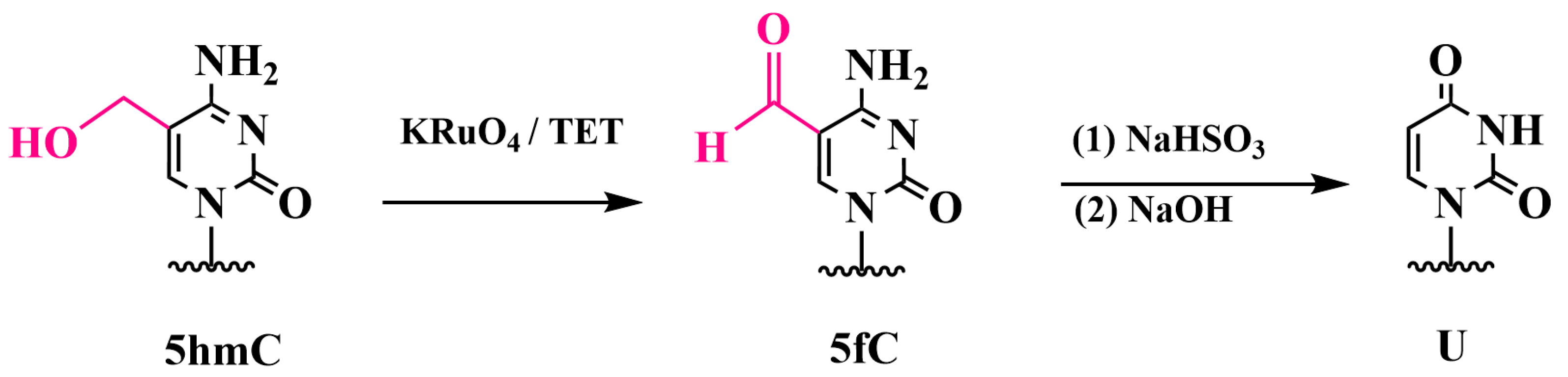
3.3. Specific Oxidation of 5hmC to 5-Formylcytosine and Detection of 5fC: Oxidative Bisulfite Sequencing (oxBS-Seq)
Chemiluminescent Method for Detecting 5fC in DNA
3.4. Electrochemical Magnetobiosensor for Analyzing the Presence of 5hmC by Using Amplification
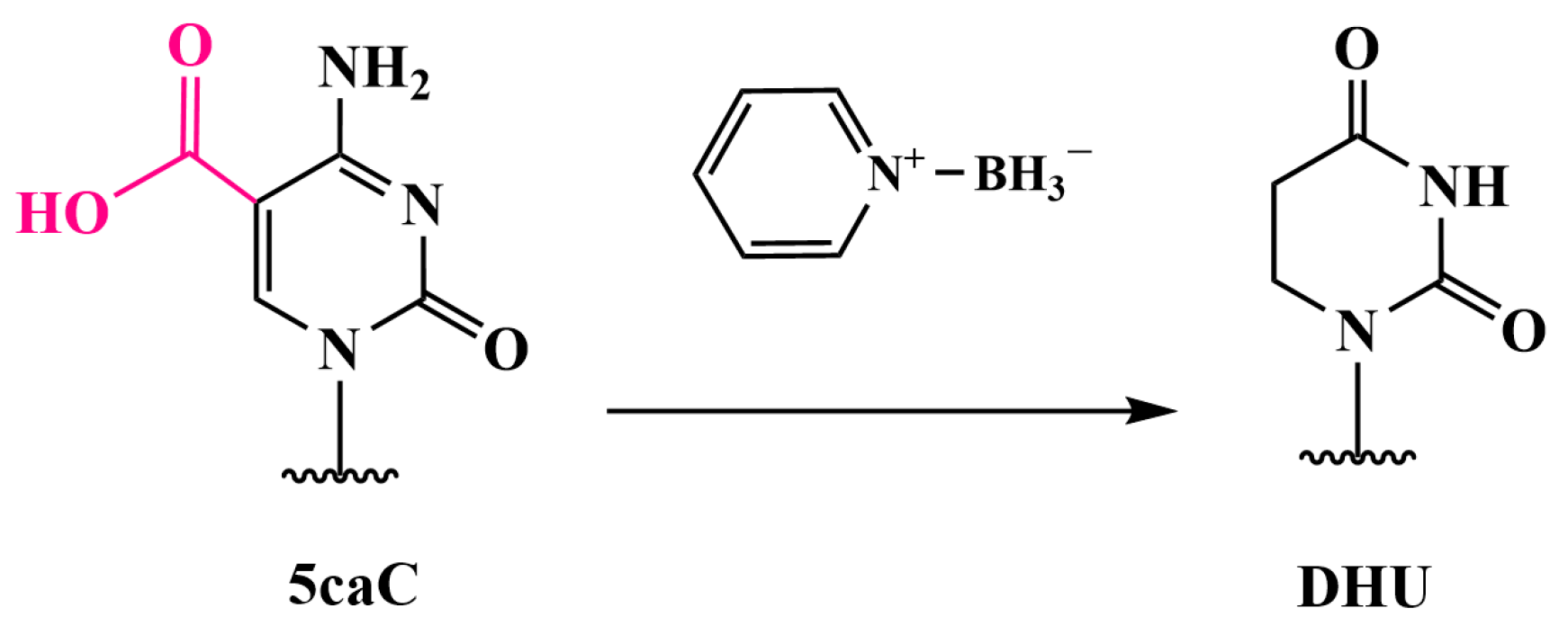
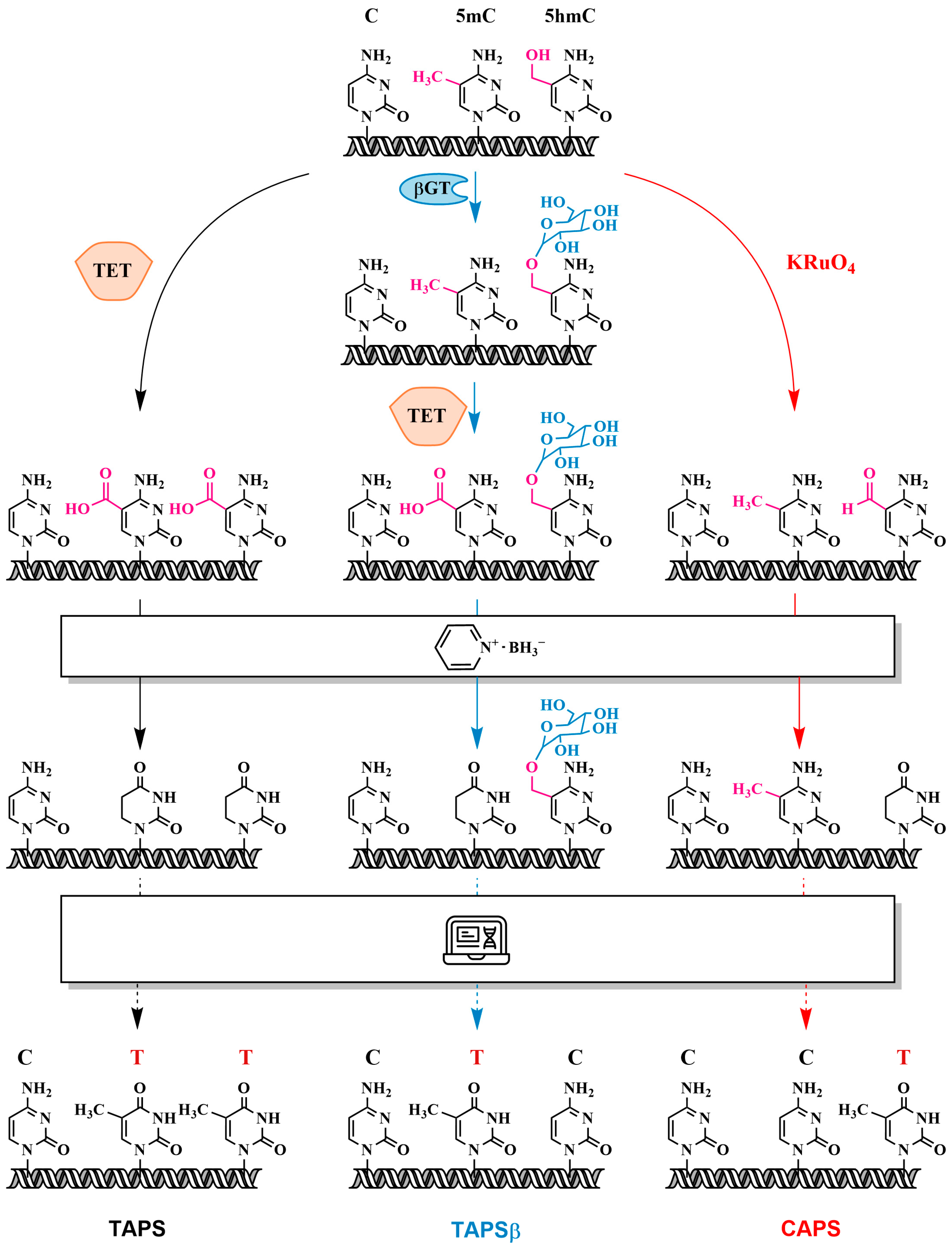
3.5. Oxidation of 5mC and 5hmC to 5-Carboxycytosine (5caC)—Pyridine Borane Sequencing with TET (TAPS) and KRuO₄ (CAPS)
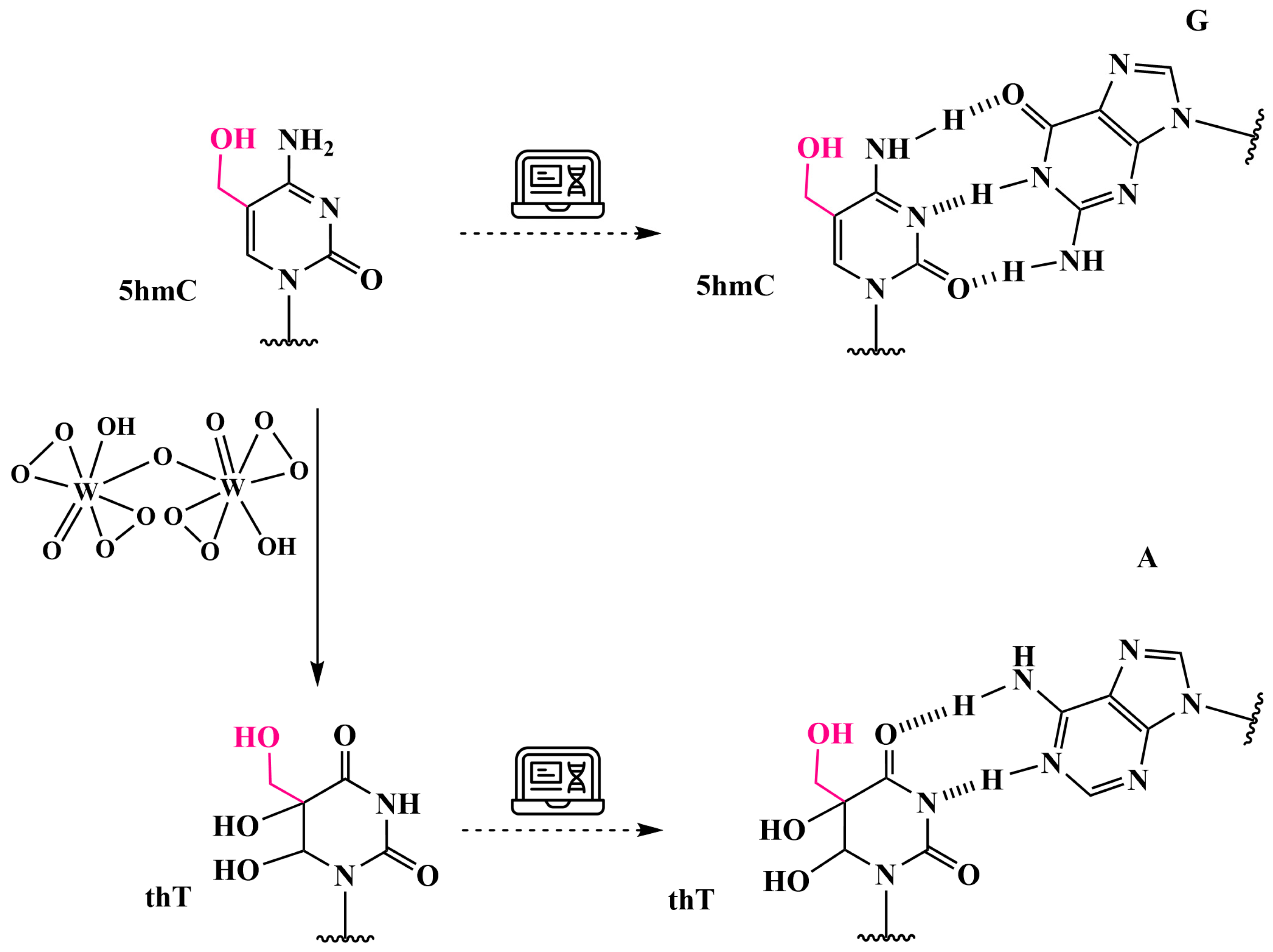
3.6. Analysis of 5hmC Presence by Chemical Oxidation with Peroxotungstate to Trihydroxythymine (thT)
4. Methods Based on the Use of DNA-Modifying Enzymes
4.1. Use of Restriction Endonucleases
4.2. Use of DNMT1 Methyltransferase: EnIGMA Method
4.3. Use of DNA Deaminases: AMD-Seq and ACE-Seq Methods
5. Affinity-Based Methods: Immunostaining and Immunoprecipitation
6. Next-Generation Sequencing
6.1. Single-Molecule Real-Time (SMRT) DNA Sequencing
6.2. Nanopore Sequencing (ONT)
6.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing
7. New, Original Methods for Quantitative Assessment of 5hmC
8. 5hmC as a Biomarker for Diagnosing Cancer and Neurodegenerative Diseases
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, Z.D.; Meissner, A. DNA Methylation: Roles in Mammalian Development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulis, M.; Esteller, M. DNA Methylation and Cancer. Adv. Genet. 2010, 70, 27–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabel, H.W.; Kinde, B.; Stroud, H.; Gilbert, C.S.; Harmin, D.A.; Kastan, N.R.; Hemberg, M.; Ebert, D.H.; Greenberg, M.E. Disruption of DNA-Methylation-Dependent Long Gene Repression in Rett Syndrome. Nature 2015, 522, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, G.; Li, X.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, Z. Insights into the Role of DNA Methylation in Immune Cell Development and Autoimmune Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 757318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaton, A.M.; Bird, A. CpG Islands and the Regulation of Transcription. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Kondo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Ahmed, S.; Shu, J.; Chen, X.; Waterland, R.A.; Issa, J.-P.J. Genome-Wide Profiling of DNA Methylation Reveals a Class of Normally Methylated CpG Island Promoters. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, e181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukatz, M.; Dittrich, M.; Stahl, E.; Adam, S.; de Mendoza, A.; Bashtrykov, P.; Jeltsch, A. DNA Methyltransferase DNMT3A Forms Interaction Networks with the CpG Site and Flanking Sequence Elements for Efficient Methylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Karnik, R.; Gu, H.; Ziller, M.J.; Clement, K.; Tsankov, A.M.; Akopian, V.; Gifford, C.A.; Donaghey, J.; Galonska, C.; et al. Targeted Disruption of DNMT1, DNMT3A and DNMT3B in Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahiliani, M.; Koh, K.P.; Shen, Y.; Pastor, W.A.; Bandukwala, H.; Brudno, Y.; Agarwal, S.; Iyer, L.M.; Liu, D.R.; Aravind, L.; et al. Conversion of 5-Methylcytosine to 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Mammalian DNA by MLL Partner TET1. Science 2009, 324, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Shen, L.; Dai, Q.; Wu, S.C.; Collins, L.B.; Swenberg, J.A.; He, C.; Zhang, Y. Tet Proteins Can Convert 5-Methylcytosine to 5-Formylcytosine and 5-Carboxylcytosine. Science 2011, 333, 1300–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Su, Y.; Guerrero, C.; Zeng, Y.; Mitra, D.; Brooks, P.J.; Fisher, D.E.; Song, H.; Wang, Y. Quantitative Assessment of Tet-Induced Oxidation Products of 5-Methylcytosine in Cellular and Tissue DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 6421–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, R.M.; Zhang, Y. TET Enzymes, TDG and the Dynamics of DNA Demethylation. Nature 2013, 502, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.-F.; Feng, Y.-Q. Recent Advances in the Analysis of 5-Methylcytosine and Its Oxidation Products. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 54, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.-F.; Li, B.-Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Ding, J.; Jia, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; et al. Tet-Mediated Formation of 5-Carboxylcytosine and Its Excision by TDG in Mammalian DNA. Science 2011, 333, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spruijt, C.G.; Gnerlich, F.; Smits, A.H.; Pfaffeneder, T.; Jansen, P.W.T.C.; Bauer, C.; Münzel, M.; Wagner, M.; Müller, M.; Khan, F.; et al. Dynamic Readers for 5-(Hydroxy)Methylcytosine and Its Oxidized Derivatives. Cell 2013, 152, 1146–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellinger, M.W.; Song, C.-X.; Chong, J.; Lu, X.-Y.; He, C.; Wang, D. 5-Formylcytosine and 5-Carboxylcytosine Reduce the Rate and Substrate Specificity of RNA Polymerase II Transcription. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 831–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.-W.; Liu, Y.-L.; Vargas, M.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.-Q.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, B.-F. Mutagenic and Cytotoxic Properties of Oxidation Products of 5-Methylcytosine Revealed by Next-Generation Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münzel, M.; Globisch, D.; Brückl, T.; Wagner, M.; Welzmiller, V.; Michalakis, S.; Müller, M.; Biel, M.; Carell, T. Quantification of the Sixth DNA Base Hydroxymethylcytosine in the Brain. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 5375–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, G.R.; Cohen, S.S. The Bases of the Nucleic Acids of Some Bacterial and Animal Viruses: The Occurrence of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Biochem. J. 1953, 55, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, N.W.; Suwalski, R.; O’Riley, C.; Bojanowski, K.; Yura, R. The Presence of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Animal Deoxyribonucleic Acid. Biochem. J. 1972, 126, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valinluck, V. Oxidative Damage to Methyl-CpG Sequences Inhibits the Binding of the Methyl-CpG Binding Domain (MBD) of Methyl-CpG Binding Protein 2 (MeCP2). Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 4100–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriaucionis, S.; Heintz, N. The Nuclear DNA Base 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is Present in Purkinje Neurons and the Brain. Science 2009, 324, 929–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Globisch, D.; Münzel, M.; Müller, M.; Michalakis, S.; Wagner, M.; Koch, S.; Brückl, T.; Biel, M.; Carell, T. Tissue Distribution of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine and Search for Active Demethylation Intermediates. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; D’Alessio, A.C.; Ito, S.; Wang, Z.; Cui, K.; Zhao, K.; Sun, Y.E.; Zhang, Y. Genome-Wide Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Distribution Reveals Its Dual Function in Transcriptional Regulation in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimova, O.A.; Koltsova, A.S.; Krapivin, M.I.; Tikhonov, A.V.; Pendina, A.A. Environmental Epigenetics and Genome Flexibility: Focus on 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.A.; Pacis, A.; Chen, G.G.; Barreiro, L.B.; Ernst, C.; Turecki, G. Characterizing 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Human Prefrontal Cortex at Single Base Resolution. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppieters, N.; Dieriks, B.V.; Lill, C.; Faull, R.L.M.; Curtis, M.A.; Dragunow, M. Global Changes in DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation in Alzheimer’s Disease Human Brain. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroud, H.; Feng, S.; Morey Kinney, S.; Pradhan, S.; Jacobsen, S.E. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is Associated with Enhancers and Gene Bodies in Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, M.R.; Ficz, G.; Reik, W. Uncovering the Role of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in the Epigenome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valinluck, V.; Sowers, L.C. Endogenous Cytosine Damage Products Alter the Site Selectivity of Human DNA Maintenance Methyltransferase DNMT1. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.; Tian, Z.; Bi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Long, J.; Song, C.; Diao, J. Quantitation and Mapping of the Epigenetic Marker 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. BioEssays 2017, 39, 1700010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X.; You, L.; Song, Y.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Nie, J.; Zheng, W.; Xu, D.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures in Circulating Cell-Free DNA as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Human Cancers. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1243–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shen, Q.; Xu, S.; Yu, H.; Pei, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, D. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures in Circulating Cell-Free DNA as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 85, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Chen, J.; Zheng, J.; Liang, Y.; Yu, T.; Liu, Y.; Gao, F.; Long, J.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Q.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures in Circulating Cell-Free DNA as Diagnostic and Predictive Biomarkers for Coronary Artery Disease. Clin. Epigenet. 2020, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Wang, S.; West-Szymanski, D.; Karpus, J.; Shah, S.; Ganguly, S.; Smith, J.; Zu, Y.; He, C.; Li, Z. Cell-Free DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is an Emerging Marker of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, J.; Lai, M.; Zhang, H. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine and Disease. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2014, 762, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanthakumar, A.; Godley, L.A. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Cancer: Significance in Diagnosis and Therapy. Cancer Genet. 2015, 208, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wu, Y.; Cao, D.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, X. Genome-Wide 5-Hydroxymethylcytosines in Circulating Cell-Free DNA as Noninvasive Diagnostic Markers for Gastric Cancer. Gastric Cancer 2024, 27, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazimoradi, M.H.; Pakravan, K.; Khalafizadeh, A.; Babashah, S. TET1 Regulates Stem Cell Properties and Cell Cycle of Cancer Stem Cells in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer via DNA Demethylation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 219, 115913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Hon, G.C.; Szulwach, K.E.; Song, C.-X.; Zhang, L.; Kim, A.; Li, X.; Dai, Q.; Shen, Y.; Park, B.; et al. Base-Resolution Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in the Mammalian Genome. Cell 2012, 149, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Kim, K.-P.; Fan, G.; Faull, K.F. A Sensitive Mass Spectrometry Method for Simultaneous Quantification of DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation Levels in Biological Samples. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 412, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenthal, M.S.; Quittman, E.; Phinney, K.W. Absolute Quantification of RNA or DNA Using Acid Hydrolysis and Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 14569–14576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Mo, J.; Yin, J.; Lyu, C.; Wang, H. Profiling of Epigenetic DNA Modifications by Advanced Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Technologies. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, N.; Wang, H. Multienzyme Cascade Bioreactor for a 10 Min Digestion of Genomic DNA into Single Nucleosides and Quantitative Detection of Structural DNA Modifications in Cellular Genomic DNA. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 21883–21890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chong, Z.; Yin, R.; Song, S.-H.; Zhao, C.; Li, C.; Huang, H.; Sun, B.-F.; et al. Redox-Active Quinones Induces Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Changes by an Iron-Mediated and Tet-Dependent Mechanism. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vető, B.; Szabó, P.; Bacquet, C.; Apró, A.; Hathy, E.; Kiss, J.; Réthelyi, J.M.; Szeri, F.; Szüts, D.; Arányi, T. Inhibition of DNA Methyltransferase Leads to Increased Genomic 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Levels in Hematopoietic Cells. FEBS Open Bio 2018, 8, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdyukov, S.; Bullock, M. DNA Methylation Analysis: Choosing the Right Method. Biology 2016, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.F.; Valledor, L.; Vallejo, F.; Cañal, M.J.; Fraga, M.F. Quantification of Global DNA Methylation Levels by Mass Spectrometry. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Clifton, N.J., Ed.; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 1708, pp. 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Du, C.; Kurabe, N.; Matsushima, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Kahyo, T.; Ohnishi, I.; Tanioka, F.; Tajima, S.; Goto, M.; Yamada, H.; et al. Robust Quantitative Assessments of Cytosine Modifications and Changes in the Expressions of Related Enzymes in Gastric Cancer. Gastric Cancer 2015, 18, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Mo, J.; Lu, M.; Wang, H. Detection of Human Urinary 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine by Stable Isotope Dilution HPLC-MS/MS Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1846–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-T.; Zhang, L.-J.; Zhang, J.-J.; Ye, X.-X.; Xie, A.-M.; Chen, L.-Y.; Kang, J.X.; Cai, C. Quantification of The Sixth DNA Base 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Colorectal Cancer Tissue and C-26 Cell Line. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.-X.; Guo, N.; Ru, S.-W.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Sui, H.-J.; Xu, Y.-S.; Yao, Z.-D. The Deficiency of 5-Methylcytosine (5mC) and Its Ramification in the Occurrence and Prognosis of Colon Cancer. Medicine 2023, 102, e34860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.-F. 5-Methylcytosine and Its Derivatives. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2014, 67, 151–187. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Zheng, S.-J.; Qi, C.-B.; Feng, Y.-Q.; Yuan, B.-F. Sensitive and Simultaneous Determination of 5-Methylcytosine and Its Oxidation Products in Genomic DNA by Chemical Derivatization Coupled with Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 3445–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D.; Du, W.; Yin, D.; Lyu, N.; Zhao, G.; Guo, C.; Tang, D. Accurate Quantification of 5-Methylcytosine, 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine, 5-Formylcytosine, and 5-Carboxylcytosine in Genomic DNA from Breast Cancer by Chemical Derivatization Coupled with Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography- Electrospray Quadrupole Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry Analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91248–91257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chu, J.-M.; Huang, W.; Xiong, J.; Xing, X.-W.; Zhou, X.; Feng, Y.-Q.; Yuan, B.-F. Hydrophilic Material for the Selective Enrichment of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine and Its Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Detection. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6129–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Németh, K.; Mészáros, K.; Szabó, B.; Butz, H.; Arányi, T.; Szabó, P.T. A Relative Quantitation Method for Measuring DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation Using Guanine as an Internal Standard. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 4614–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xiong, J.; Jiang, H.-P.; Zheng, S.-J.; Feng, Y.-Q.; Yuan, B.-F. Determination of Oxidation Products of 5-Methylcytosine in Plants by Chemical Derivatization Coupled with Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7764–7772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwagierczak, A.; Bultmann, S.; Schmidt, C.S.; Spada, F.; Leonhardt, H. Sensitive Enzymatic Quantification of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Genomic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Pastor, W.A.; Zepeda-Martínez, J.A.; Rao, A. The Anti-CMS Technique for Genome-Wide Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1897–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.-G.; Kadam, S.; Pfeifer, G.P. Examination of the Specificity of DNA Methylation Profiling Techniques towards 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, T.; Li, H.; Wu, X.; Pfeifer, G.P. MIRA-Assisted Microarray Analysis, a New Technology for the Determination of DNA Methylation Patterns, Identifies Frequent Methylation of Homeodomain-Containing Genes in Lung Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7939–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.B.; Dahl, J.A.; Vågbø, C.B.; Tripathi, P.; Krokan, H.E.; Klungland, A. A Novel Method for the Efficient and Selective Identification of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Genomic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.B.; Dahl, J.A.; Ougland, R.; Klungland, A. Pull-down of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine DNA Using JBP1-Coated Magnetic Beads. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Chung, T.H.; Tan, D.; Sun, X.; Jia, X.-Y. JBP1-Seq: A Fast and Efficient Method for Genome-Wide Profiling of 5hmC. Genomics 2014, 104, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, W.A.; Huang, Y.; Henderson, H.R.; Agarwal, S.; Rao, A. The GLIB Technique for Genome-Wide Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.-X.; Szulwach, K.E.; Fu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Yi, C.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Zhang, W.; Jian, X.; et al. Selective Chemical Labeling Reveals the Genome-Wide Distribution of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahal, T.; Green, O.; Hananel, U.; Michaeli, Y.; Shabat, D.; Ebenstein, Y. Simple and Cost-Effective Fluorescent Labeling of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2016, 4, 044003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dong, Y.; Zou, X.; Luo, X.; Shen, D.; Hu, J.; Zhang, C. Label-Free and Template-Free Chemiluminescent Biosensor for Sensitive Detection of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Genomic DNA. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 1939–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Dou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, F.; Su, J.; Fan, C.; Song, S. High-Sensitivity and High-Efficiency Detection of DNA Hydroxymethylation in Genomic DNA by Multiplexing Electrochemical Biosensing. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 3476–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, B.; Li, C.; Yin, R.; Song, M.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, G. Boronic Acid-Mediated Polymerase Chain Reaction for Gene- and Fragment-Specific Detection of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, M.; Huang, Y.; Jankowska, A.M.; Pape, U.J.; Tahiliani, M.; Bandukwala, H.S.; An, J.; Lamperti, E.D.; Koh, K.P.; Ganetzky, R.; et al. Impaired Hydroxylation of 5-Methylcytosine in Myeloid Cancers with Mutant TET2. Nature 2010, 468, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, W.A.; Pape, U.J.; Huang, Y.; Henderson, H.R.; Lister, R.; Ko, M.; McLoughlin, E.M.; Brudno, Y.; Mahapatra, S.; Kapranov, P.; et al. Genome-Wide Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Embryonic Stem Cells. Nature 2011, 473, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frommer, M.; McDonald, L.E.; Millar, D.S.; Collis, C.M.; Watt, F.; Grigg, G.W.; Molloy, P.L.; Paul, C.L. A Genomic Sequencing Protocol That Yields a Positive Display of 5-Methylcytosine Residues in Individual DNA Strands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 1827–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Pastor, W.A.; Shen, Y.; Tahiliani, M.; Liu, D.R.; Rao, A. The Behaviour of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Bisulfite Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, M.J.; Ost, T.W.B.; Beraldi, D.; Bell, N.M.; Branco, M.R.; Reik, W.; Balasubramanian, S. Oxidative Bisulfite Sequencing of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayatsu, H.; Shiragami, M. Reaction of Bisulfite with the 5-Hydroxymethyl Group in Pyrimidines and in Phage DNAs. Biochemistry 1979, 18, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant, K.E.; Nahar, M.S.; Dolinoy, D.C. DNA Methylation Screening and Analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 889, 385–406. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Hon, G.C.; Szulwach, K.E.; Song, C.-X.; Jin, P.; Ren, B.; He, C. Tet-Assisted Bisulfite Sequencing of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 2159–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, M.J.; Branco, M.R.; Ficz, G.; Oxley, D.; Krueger, F.; Reik, W.; Balasubramanian, S. Quantitative Sequencing of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine at Single-Base Resolution. Science 2012, 336, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C. Sensitive and Label-Free Discrimination of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine and 5-Methylcytosine in DNA by Ligation-Mediated Rolling Circle Amplification. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 8602–8605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Qi, H.; Zheng, J. Discrimination between 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine and 5-Methylcytosine in DNA via Selective Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence (ECL) Labeling. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 9934–9940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Hu, J.; Wang, M.; Li, C.; Zhang, C. Label-Free and Immobilization-Free Electrochemical Magneto-biosensor for Sensitive Detection of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Genomic DNA. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Siejka-Zielińska, P.; Velikova, G.; Bi, Y.; Yuan, F.; Tomkova, M.; Bai, C.; Chen, L.; Schuster-Böckler, B.; Song, C.-X. Bisulfite-Free Direct Detection of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine at Base Resolution. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Siejka-Zielińska, P.; Weldon, C.; Roberts, H.; Lopopolo, M.; Magri, A.; D’Arienzo, V.; Harris, J.M.; McKeating, J.A.; et al. Accurate Targeted Long-Read DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation Sequencing with TAPS. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Siejka-Zielińska, P.; Liu, Y.; Chandran, A.; Kriaucionis, S.; Song, C.-X. Endonuclease Enrichment TAPS for Cost-Effective Genome-Wide Base-Resolution DNA Methylation Detection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cheng, J.; Chen, X.; Inoue, M.; Liu, Y.; Song, C.-X. Whole-Genome Long-Read TAPS Deciphers DNA Methylation Patterns at Base Resolution Using PacBio SMRT Sequencing Technology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siejka-Zielińska, P.; Cheng, J.; Jackson, F.; Liu, Y.; Soonawalla, Z.; Reddy, S.; Silva, M.; Puta, L.; McCain, M.V.; Culver, E.L.; et al. Cell-Free DNA TAPS Provides Multimodal Information for Early Cancer Detection. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabh0534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, A.; Sugizaki, K.; Nakamura, A.; Yanagisawa, H.; Ikeda, S. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine-Selective Oxidation with Peroxotungstate. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 11231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, G.; Koyama, K.; Shiota, H.; Kamio, A.; Umeda, T.; Nagae, G.; Aburatani, H.; Okamoto, A. Base-Resolution Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine by One-Pot Bisulfite-Free Chemical Conversion with Peroxotungstate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 14178–14181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, J.; Li, Z. Peroxotungstate Oxidation-Mediated Two-Phase Amplification System (POM-TPAS) for Bisulfite-Free Quantification of Locus-Specific 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 3111–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, N.; Mori, Y.; Kanda, H.; Notomi, T. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) of Gene Sequences and Simple Visual Detection of Products. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, T.; Qi, Y.; Dai, Y.; Lao, K.; Gou, X. Rapid and Highly Specific Detection of Site-Specific 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Based on Peroxotungstate Oxidation and Mismatch Ligation-Based LAMP. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 19885–19889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedar, H.; Solage, A.; Glaser, G.; Razin, A. Direct Detection of Methylated Cytosine in DNA by Use of the Restriction Enzyme Mspl. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979, 6, 2125–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, S.M.; Chin, H.G.; Vaisvila, R.; Bitinaite, J.; Zheng, Y.; Estève, P.O.; Feng, S.; Stroud, H.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Pradhan, S. Tissue-Specific Distribution and Dynamic Changes of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Mammalian Genomes. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 24685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, R.; Cheruba, E.; Wong, P.M.; Yi, Y.; Ngang, S.; Chong, D.Q.; Loh, Y.H.; Tan, I.B.; Cheow, L.F. DARESOME Enables Concurrent Profiling of Multiple DNA Modifications with Restriction Enzymes in Single Cells and Cell-Free DNA. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadi0197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Kokubun, S.; Itoi, E.; Roach, H.I. Improved Quantification of DNA Methylation Using Methylation-Sensitive Restriction Enzymes and Real-Time PCR. Epigenetics 2007, 2, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Terragni, J.; Borgaro, J.G.; Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; Guan, S.; Wang, H.; Sun, D.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, Z.; et al. High-Resolution Enzymatic Mapping of Genomic 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Karni, D.; Xu, D.; Apone, L.; Fomenkov, A.; Sun, Z.; Davis, P.J.; Morey Kinney, S.R.; Yamada-Mabuchi, M.; Xu, S.; Davis, T.; et al. The MspJI Family of Modification-Dependent Restriction Endonucleases for Epigenetic Studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11040–11045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shan, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, W.; Yan, J.; Li, Z. Highly Sensitive Quantification of Site-Specific 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine at Single-Base Resolution by HpaII-Mediated Ligation PCR. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 9849–9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Kuroda, Y.; Suetake, I.; Tajima, S.; Ishino, F.; Kohda, T. A Novel Method for the Simultaneous Identification of Methylcytosine and Hydroxymethylcytosine at a Single Base Resolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, gkw994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutsky, E.K.; DeNizio, J.E.; Hu, P.; Liu, M.Y.; Nabel, C.S.; Fabyanic, E.B.; Hwang, Y.; Bushman, F.D.; Wu, H.; Kohli, R.M. Nondestructive, Base-Resolution Sequencing of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Using a DNA Deaminase. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.-B.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Ji, T.-T.; Guo, X.; Gang, F.-Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; Feng, Y.-Q.; Liang, Y.; Ci, W.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine at Base Resolution by Bisulfite-Free Single-Step Deamination with Engineered Cytosine Deaminase. ACS Cent. Sci. 2023, 9, 2315–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaujean, N.; Salvaing, J.; Hadi, N.A.A.; Pennings, S. Antibody-Based Detection of Global Nuclear DNA Methylation in Cells, Tissue Sections, and Mammalian Embryos. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1708, 59–80. [Google Scholar]
- Olova, N.N. ELISA-Based Quantitation of Global 5hmC Levels. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2272, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Li, Z.; Jiang, T.; Li, X.; Wang, H. Immunofluorescence Imaging Strategy for Evaluation of the Accessibility of DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Chromatins. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5702–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Lai, Y.; Liu, J.; Diao, J. Epigenetic Quantification of DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Using DNA Hybridization-Based Single-Molecule Immunofluorescent Imaging. Small Methods 2021, 5, 2100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.-G.; Wu, X.; Li, A.X.; Pfeifer, G.P. Genomic Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in the Human Brain. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 5015–5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficz, G.; Branco, M.R.; Seisenberger, S.; Santos, F.; Krueger, F.; Hore, T.A.; Marques, C.J.; Andrews, S.; Reik, W. Dynamic Regulation of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Mouse ES Cells and during Differentiation. Nature 2011, 473, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellén, M.; Ayata, P.; Dewell, S.; Kriaucionis, S.; Heintz, N. MeCP2 Binds to 5hmC Enriched within Active Genes and Accessible Chromatin in the Nervous System. Cell 2012, 151, 1417–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, J.; Fehr, A.; Gray, J.; Luong, K.; Lyle, J.; Otto, G.; Peluso, P.; Rank, D.; Baybayan, P.; Bettman, B.; et al. Real-Time DNA Sequencing from Single Polymerase Molecules. Science 2009, 323, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flusberg, B.A.; Webster, D.R.; Lee, J.H.; Travers, K.J.; Olivares, E.C.; Clark, T.A.; Korlach, J.; Turner, S.W. Direct Detection of DNA Methylation during Single-Molecule, Real-Time Sequencing. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schadt, E.E.; Banerjee, O.; Fang, G.; Feng, Z.; Wong, W.H.; Zhang, X.; Kislyuk, A.; Clark, T.A.; Luong, K.; Keren-Paz, A.; et al. Modeling Kinetic Rate Variation in Third Generation DNA Sequencing Data to Detect Putative Modifications to DNA Bases. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulaurier, J.; Zhang, X.-S.; Zhu, S.; Sebra, R.; Rosenbluh, C.; Deikus, G.; Shen, N.; Munera, D.; Waldor, M.K.; Chess, A.; et al. Single Molecule-Level Detection and Long Read-Based Phasing of Epigenetic Variations in Bacterial Methylomes. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, N.; Arakawa, K. Nanopore Sequencing: Review of Potential Applications in Functional Genomics. Dev. Growth Differ. 2019, 61, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.M.; Martin, I.W.; Moschetti, W.E.; Kershaw, C.M.; Tsongalis, G.J. Third-Generation Sequencing in the Clinical Laboratory: Exploring the Advantages and Challenges of Nanopore Sequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 58, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszlo, A.H.; Derrington, I.M.; Brinkerhoff, H.; Langford, K.W.; Nova, I.C.; Samson, J.M.; Bartlett, J.J.; Pavlenok, M.; Gundlach, J.H. Detection and Mapping of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine with Nanopore MspA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18904–18909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkovich, A.K.; Pyshkina, O.A.; Zorina, A.A.; Rodin, V.A.; Panova, T.V.; Sergeev, V.G.; Zvereva, M.E. Direct Determination of the Structure of Single Biopolymer Molecules Using Nanopore Sequencing. Biochemistry 2024, 89, S234–S248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojević, D.; Li, Z.; Bakić, S.; Foo, R.; Šikić, M. Rockfish: A Transformer-Based Model for Accurate 5-Methylcytosine Prediction from Nanopore Sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Lu, X.; Shih, A.H.; Nie, J.; You, Q.; Xu, M.M.; Melnick, A.M.; Levine, R.L.; He, C. A Highly Sensitive and Robust Method for Genome-Wide 5hmC Profiling of Rare Cell Populations. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adey, A.; Morrison, H.G.; Asan; Xun, X.; Kitzman, J.O.; Turner, E.H.; Stackhouse, B.; MacKenzie, A.P.; Caruccio, N.C.; Zhang, X.; et al. Rapid, Low-Input, Low-Bias Construction of Shotgun Fragment Libraries by High-Density in Vitro Transposition. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Wen, L.; Liao, S.; Lin, X.; Ma, T.; Liu, J.; Song, C.; Wang, M.; He, C.; Han, C.; et al. Dynamics of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine during Mouse Spermatogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, H.; Guo, Z.; Zhu, C.; Yi, C. Simultaneous Single-Cell Analysis of 5mC and 5hmC with SIMPLE-Seq. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrieli, T.; Sharim, H.; Nifker, G.; Jeffet, J.; Shahal, T.; Arielly, R.; Levi-Sakin, M.; Hoch, L.; Arbib, N.; Michaeli, Y.; et al. Epigenetic Optical Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Nanochannel Arrays. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 7148–7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-R.; Wang, L.; Liang, W.-B.; Yuan, R.; Zhuo, Y. Epigenetic Quantification of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures via Regulatable DNAzyme Motor Triggered by Strand Displacement Amplification. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 3313–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.-H.; Pan, M.-C.; Zhang, P.; Liang, W.-B.; Zhong, X.; Zhuo, Y. Identification and Quantification of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine on Random DNA Sequences by a Nanoconfined Electrochemiluminescence Platform. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 9598–9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, K.P.; Yabuuchi, A.; Rao, S.; Huang, Y.; Cunniff, K.; Nardone, J.; Laiho, A.; Tahiliani, M.; Sommer, C.A.; Mostoslavsky, G.; et al. Tet1 and Tet2 Regulate 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Production and Cell Lineage Specification in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 8, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Luo, K.; Shi, H.; Yan, X.; Huang, R.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J.; Xie, D.; Zhang, W. Integrated 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine and Fragmentation Signatures as Enhanced Biomarkers in Lung Cancer. Clin. Epigenetics 2022, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; Ma, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ye, X.; et al. Loss of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is Linked to Gene Body Hypermethylation in Kidney Cancer. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Lin, S.; Cai, M.; Zhu, Y.; Song, Y.; Sui, Y.; Lin, J.; Liu, J.; Lu, X.; Zhong, Y.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Profiling from Genomic and Cell-free DNA for Colorectal Cancers Patients. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3530–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Xu, C.; Zhou, P.; Long, J.; Hu, G.; Jiang, M. The Role of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2017, 27, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.C.; Houseman, E.A.; King, J.E.; von Herrmann, K.M.; Fadul, C.E.; Christensen, B.C. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Localizes to Enhancer Elements and Is Associated with Survival in Glioblastoma Patients. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Dresser, K.; Chen, B.J. Loss of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine Immunohistochemical Expression Is a Useful Diagnostic Aid for Distinguishing Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cytology Fine Needle Aspiration Specimens. Cytopathology 2019, 30, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.-G.; Jiang, Y.; Qiu, R.; Rauch, T.A.; Wang, Y.; Schackert, G.; Krex, D.; Lu, Q.; Pfeifer, G.P. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is Strongly Depleted in Human Cancers but Its Levels Do Not Correlate with IDH1 Mutations. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7360–7365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.-X.; Yin, S.; Ma, L.; Wheeler, A.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, W.; Hu, J.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures in Cell-Free DNA Provide Information about Tumor Types and Stages. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, O.K.; Rivas, F.; Wang, F.; Sethi, K.; Reiss, K.; Bearden, S.; Hall, A.R. Solid-State Nanopore Analysis of Human Genomic DNA Shows Unaltered Global 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Content Associated with Early-Stage Breast Cancer. Nanomedicine 2021, 35, 102407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, L.; Ou, J.; Wang, B.; Cen, X. Loss of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine as a Poor Prognostic Factor for Primary Testicular Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 19, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson, R.V.; Shteinman, E.R.; Ansar, S.; Vergara, I.A.; Thompson, J.F.; Long, G.V.; Scolyer, R.A.; Wilmott, J.S. Diagnostic Utility of PRAME, P53 and 5-HmC Immunostaining for Distinguishing Melanomas from Naevi, Neurofibromas, Scars and Other Histological Mimics. Pathology 2022, 54, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grelus, A.; Nica, D.; Miklos, I.; Belengeanu, V.; Ioiart, I.; Popescu, C. Clinical Significance of Measuring Global Hydroxymethylation of White Blood Cell DNA in Prostate Cancer: Comparison to PSA in a Pilot Exploratory Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöström, M.; Zhao, S.G.; Levy, S.; Zhang, M.; Ning, Y.; Shrestha, R.; Lundberg, A.; Herberts, C.; Foye, A.; Aggarwal, R.; et al. The 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Landscape of Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 3888–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Stroup, E.K.; Zhang, Z.; Chiu, B.C.-H.; Zhang, W. Towards Precision Medicine: Advances in 5-hydroxymethylcytosine Cancer Biomarker Discovery in Liquid Biopsy. Cancer Commun. 2019, 39, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Nagaoka, K.; Zou, J.; Casulli, S.; Lu, S.; Cao, K.Y.; Zhang, H.; Iwagami, Y.; Carlson, R.I.; Brooks, K.; et al. Chronic Ethanol-mediated Hepatocyte Apoptosis Links to Decreased TET1 and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine Formation. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 1824–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, G.D.; Ning, Y.; Ku, C.-J.; Phillips, T.; McCarthy, E.; Ellison, C.K.; Bergamaschi, A.; Collin, F.; Lloyd, P.; Scott, A.; et al. Detection of Early Stage Pancreatic Cancer Using 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures in Circulating Cell Free DNA. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Sun, B.; Chen, C.; Gao, C.; Zhang, J.; Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Xing, Y.; Liu, R.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine as a Novel Diagnostic Biomarker for Esophageal Cancer. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, Y.; Lin, X.; Wang, J.-Q.; Wu, Y.-S.; Xie, W.; Wang, D.; Zhu, S.; Liao, Y.-Q.; Sun, Q.; et al. Genome-Wide Loss of 5-HmC Is a Novel Epigenetic Feature of Huntington’s Disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 3641–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Li, X.; Yan, L.; Tan, Y.; Li, R.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhang, Y.; Song, C.; et al. Whole-Genome Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine and 5-Methylcytosine at Base Resolution in the Human Brain. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, A.; Papale, L.A.; Alisch, R.S. New Hope: The Emerging Role of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Mental Health and Disease. Epigenomics 2016, 8, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley-Whitman, M.A.; Lovell, M.A. Epigenetic Changes in the Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2013, 134, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, E.; Gavin, D.P.; Chen, Y.; Davis, J. Upregulation of TET1 and Downregulation of APOBEC3A and APOBEC3C in the Parietal Cortex of Psychotic Patients. Transl. Psychiatry 2012, 2, e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.-Y.; Tseng, P.-T.; Lee, Y.; Hung, C.-F.; Lung, F.-W.; Chen, C.-S.; Chong, M.-Y. Age-Associated Decrease in Global DNA Methylation in Patients with Major Depression. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat 2014, 10, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Xu, Q.; Qin, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Wu, H.; Han, J.; Zhu, X.; Jin, P.; et al. Altered Hydroxymethylome in the Substantia Nigra of Parkinson’s Disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2022, 31, 3494–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, V.; Fernández, A.F.; Fraga, M.F. The Role of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Development, Aging and Age-Related Diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 37, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Yu, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Campbell, N.; Mazdo, J.; Vasanthakumar, A.; Bhagat, T.D.; Nischal, S.; Christopeit, M.; Parekh, S.; et al. Genome-Wide Hydroxymethylation Tested Using the HELP-GT Assay Shows Redistribution in Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kisil, O.; Sergeev, A.; Bacheva, A.; Zvereva, M. Methods for Detection and Mapping of Methylated and Hydroxymethylated Cytosine in DNA. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14111346
Kisil O, Sergeev A, Bacheva A, Zvereva M. Methods for Detection and Mapping of Methylated and Hydroxymethylated Cytosine in DNA. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(11):1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14111346
Chicago/Turabian StyleKisil, Olga, Alexander Sergeev, Anna Bacheva, and Maria Zvereva. 2024. "Methods for Detection and Mapping of Methylated and Hydroxymethylated Cytosine in DNA" Biomolecules 14, no. 11: 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14111346
APA StyleKisil, O., Sergeev, A., Bacheva, A., & Zvereva, M. (2024). Methods for Detection and Mapping of Methylated and Hydroxymethylated Cytosine in DNA. Biomolecules, 14(11), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14111346







