Effect of Essential Oil Components on the Activity of Steroidogenic Cytochrome P450
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Terpenes
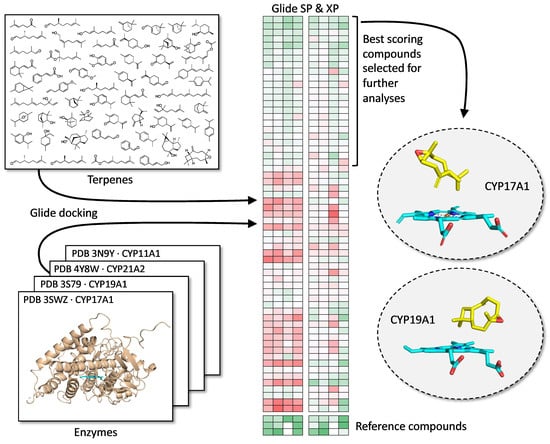
2.2. Molecular Docking Analysis
2.3. Chemicals
2.4. Cell Line and Culture
2.5. Cell Viability Assays
2.6. CYP17A1 Enzyme Assays
2.7. Steroid Profiling
2.8. CYP19A1 Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Docking with CYP17A1 and CYP19A1
3.2. Effect on CYP17A1 Activity
3.3. Effect on CYP19A1 Activity
3.4. Effect on PCa Cell Viability
3.5. Steroid Analysis by LC-MS/MS
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mendonca, A.; Jackson-Davis, A.; Moutiq, R.; Thomas-Popo, E. Chapter 14—Use of Natural Antimicrobials of Plant Origin to Improve the Microbiological Safety of Foods. In Food and Feed Safety Systems and Analysis; Ricke, S.C., Atungulu, G.G., Rainwater, C.E., Park, S.H., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 249–272. [Google Scholar]
- Cimino, C.; Maurel, O.M.; Musumeci, T.; Bonaccorso, A.; Drago, F.; Souto, E.M.B.; Pignatello, R.; Carbone, C. Essential Oils: Pharmaceutical Applications and Encapsulation Strategies into Lipid-Based Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, A.C.; Schmidt, E. Essential Oils, Part I: Introduction. Dermatitis 2016, 27, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakkali, F.; Averbeck, S.; Averbeck, D.; Idaomar, M. Biological effects of essential oils—A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 446–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paco, N. Terpenes in Essential Oils: Bioactivity and Applications. In Terpenes and Terpenoids; Shagufta, P., Areej Mohammad, A.-T., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2020; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Sharmeen, J.B.; Mahomoodally, F.M.; Zengin, G.; Maggi, F. Essential Oils as Natural Sources of Fragrance Compounds for Cosmetics and Cosmeceuticals. Molecules 2021, 26, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, A.C.; Schmidt, E. Essential Oils, Part III: Chemical Composition. Dermatitis 2016, 27, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, J.T.; Shropshire, B.C.; Nagy, T.R.; Chambers, K.D.; Li, Y.; Korach, K.S. Essential Oils and Health. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2020, 93, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ali, B.; Al-Wabel, N.A.; Shams, S.; Ahamad, A.; Khan, S.A.; Anwar, F. Essential oils used in aromatherapy: A systemic review. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2015, 5, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, S. Essential oils: Their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, P.R.; Rana, A.; Jaitak, V. Essential Oils: An Impending Substitute of Synthetic Antimicrobial Agents to Overcome Antimicrobial Resistance. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 605–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, B.; Terekeci, H.; Sandal, S.; Kelestimur, F. Endocrine disrupting chemicals: Exposure, effects on human health, mechanism of action, models for testing and strategies for prevention. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 21, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henley, D.V.; Lipson, N.; Korach, K.S.; Bloch, C.A. Prepubertal gynecomastia linked to lavender and tea tree oils. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.L.; Auchus, R.J. The molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology of human steroidogenesis and its disorders. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 81–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matteson, K.J.; Picado-Leonard, J.; Chung, B.C.; Mohandas, T.K.; Miller, W.L. Assignment of the gene for adrenal P450c17 (steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase) to human chromosome 10. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1986, 63, 789–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, B.C.; Picado-Leonard, J.; Haniu, M.; Bienkowski, M.; Hall, P.F.; Shively, J.E.; Miller, W.L. Cytochrome P450c17 (steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase): Cloning of human adrenal and testis cDNAs indicates the same gene is expressed in both tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallan, P.S.; Nagy, L.D.; Lei, L.; Gonzalez, E.; Kramlinger, V.M.; Azumaya, C.M.; Wawrzak, Z.; Waterman, M.R.; Guengerich, F.P.; Egli, M. Structural and kinetic basis of steroid 17alpha,20-lyase activity in teleost fish cytochrome P450 17A1 and its absence in cytochrome P450 17A2. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 3248–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuber, M.X.; Simpson, E.R.; Waterman, M.R. Expression of bovine 17 alpha-hydroxylase cytochrome P-450 cDNA in nonsteroidogenic (COS 1) cells. Science 1986, 234, 1258–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagibashi, K.; Hall, P.F. Role of electron transport in the regulation of the lyase activity of C21 side-chain cleavage P-450 from porcine adrenal and testicular microsomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 8429–8433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.V.; Flück, C.E. NADPH P450 oxidoreductase: Structure, function, and pathology of diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 138, 229–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auchus, R.J.; Lee, T.C.; Miller, W.L. Cytochrome b5 augments the 17,20-lyase activity of human P450c17 without direct electron transfer. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 3158–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.V.; Miller, W.L. Regulation of 17,20 lyase activity by cytochrome b5 and by serine phosphorylation of P450c17. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 13265–13271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Rodriguez, H.; Ohno, S.; Miller, W.L. Serine phosphorylation of human P450c17 increases 17,20-lyase activity: Implications for adrenarche and the polycystic ovary syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 10619–10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.V.; Mellon, S.H.; Miller, W.L. Protein phosphatase 2A and phosphoprotein SET regulate androgen production by P450c17. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 2837–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempna, P.; Hirsch, A.; Hofer, G.; Mullis, P.E.; Fluck, C.E. Impact of differential P450c17 phosphorylation by cAMP stimulation and by starvation conditions on enzyme activities and androgen production in NCI-H295R cells. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3686–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Tee, M.K.; Miller, W.L. Human cytochrome p450c17: Single step purification and phosphorylation of serine 258 by protein kinase a. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.L.; Tee, M.K. The post-translational regulation of 17,20 lyase activity. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2015, 408, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tee, M.K.; Miller, W.L. Phosphorylation of human cytochrome P450c17 by p38alpha selectively increases 17,20 lyase activity and androgen biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 23903–23913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prins, G.S. Endocrine disruptors and prostate cancer risk. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2008, 15, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.H.E.; Li, J.; Xu, H.E.; Melcher, K.; Yong, E.-L. Androgen receptor: Structure, role in prostate cancer and drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-J.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Yang, C.-Q.; Zeng, X.-B.; Li, J.; Zhu, K.; Zhao, S.-Q.; Lu, H.-M.; Yin, D.-C.; et al. Comparison of the roles of estrogens and androgens in breast cancer and prostate cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 2756–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrunak, E.M.; DeVore, N.M.; Porubsky, P.R.; Scott, E.E. Structures of human steroidogenic cytochrome P450 17A1 with substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 32952–32964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; Griswold, J.; Erman, M.; Pangborn, W. X-ray structure of human aromatase reveals an androgen-specific active site. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 118, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, J.; Di Nardo, G.; Griswold, J.; Egbuta, C.; Jiang, W.; Gilardi, G.; Ghosh, D. Structural basis for the functional roles of critical residues in human cytochrome p450 aromatase. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 5821–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Griswold, J.; Erman, M.; Pangborn, W. Structural basis for androgen specificity and oestrogen synthesis in human aromatase. Nature 2009, 457, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastry, G.M.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and ligand preparation: Parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelley, J.C.; Cholleti, A.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Timlin, M.R.; Uchimaya, M. Epik: A software program for pK(a) prediction and protonation state generation for drug-like molecules. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2007, 21, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVore, N.M.; Scott, E.E. Structures of cytochrome P450 17A1 with prostate cancer drugs abiraterone and TOK-001. Nature 2012, 482, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Petrunak, E.M.; Estrada, D.F.; Scott, E.E. Structural insights into the function of steroidogenic cytochrome P450 17A1. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2017, 441, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Egbuta, C.; Lo, J. Testosterone complex and non-steroidal ligands of human aromatase. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 181, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra Precision Glide: Docking and Scoring Incorporating a Model of Hydrophobic Enclosure for Protein−Ligand Complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 2. Enrichment Factors in Database Screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainey, W.E.; Saner, K.; Schimmer, B.P. Adrenocortical cell lines. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2004, 228, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazdar, A.F.; Oie, H.K.; Shackleton, C.H.; Chen, T.R.; Triche, T.J.; Myers, C.E.; Chrousos, G.P.; Brennan, M.F.; Stein, C.A.; La Rocca, R.V. Establishment and characterization of a human adrenocortical carcinoma cell line that expresses multiple pathways of steroid biosynthesis. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 5488–5496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Gong, S.; Roy-Burman, P.; Lee, P.; Culig, Z. Current mouse and cell models in prostate cancer research. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2013, 20, R155–R170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riss, T.L.; Moravec, R.A.; Niles, A.L.; Duellman, S.; Benink, H.A.; Worzella, T.J.; Minor, L. Cell Viability Assays. In Assay Guidance Manual; Markossian, S., Grossman, A., Brimacombe, K., Arkin, M., Auld, D., Austin, C., Baell, J., Chung, T.D.Y., Coussens, N.P., Dahlin, J.L., et al., Eds.; Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiloglu, S.; Sari, G.; Ozdal, T.; Capanoglu, E. Guidelines for cell viability assays. Food Front. 2020, 1, 332–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, G.A.; Barrie, S.E.; Jarman, M.; Rowlands, M.G. Novel Steroidal Inhibitors of Human Cytochrome P45017.alpha.-Hydroxylase-C17,20-lyase): Potential Agents for the Treatment of Prostatic Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 2463–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udhane, S.S.; Dick, B.; Hu, Q.; Hartmann, R.W.; Pandey, A.V. Specificity of anti-prostate cancer CYP17A1 inhibitors on androgen biosynthesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaño, P.R.; Parween, S.; Pandey, A.V. Bioactivity of Curcumin on the Cytochrome P450 Enzymes of the Steroidogenic Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staels, B.; Hum, D.W.; Miller, W.L. Regulation of steroidogenesis in NCI-H295 cells: A cellular model of the human fetal adrenal. Mol. Endocrinol. 1993, 7, 423–433. [Google Scholar]
- Potts, G.O.; Creange, J.E.; Harding, H.R.; Schane, H.P. Trilostane, an orally active inhibitor of steroid biosynthesis. Steroids 1978, 32, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.W.; Fishman, L.M. Biosynthesis and metabolism of steroid hormones by human adrenal carcinomas. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2000, 33, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Morán, F.M.; VandeVoort, C.A.; Overstreet, J.W.; Lasley, B.L.; Conley, A.J. Molecular Target of Endocrine Disruption in Human Luteinizing Granulosa Cells by 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin: Inhibition of Estradiol Secretion Due to Decreased 17α-Hydroxylase/17,20-Lyase Cytochrome P450 Expression. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McManus, J.M.; Bohn, K.; Alyamani, M.; Chung, Y.M.; Klein, E.A.; Sharifi, N. Rapid and structure-specific cellular uptake of selected steroids. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrieu, T.; du Toit, T.; Vogt, B.; Mueller, M.D.; Groessl, M. Parallel targeted and non-targeted quantitative analysis of steroids in human serum and peritoneal fluid by liquid chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 7461–7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siiteri, P.K.; Thompson, E.A. Studies of human placental aromatase. J. Steroid Biochem. 1975, 6, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lephart, E.D.; Simpson, E.R. Assay of aromatase activity. Methods Enzymol. 1991, 206, 477–483. [Google Scholar]
- Zehetner, P.; Höferl, M.; Buchbauer, G. Essential oil components and cytochrome P450 enzymes: A review. Flavour Fragr. J. 2019, 34, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Myslivečková, Z.; Szotáková, B.; Špičáková, A.; Lněničková, K.; Ambrož, M.; Kubíček, V.; Krasulová, K.; Anzenbacher, P.; Skálová, L. The inhibitory effects of β-caryophyllene, β-caryophyllene oxide and α-humulene on the activities of the main drug-metabolizing enzymes in rat and human liver in vitro. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2017, 278, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špičáková, A.; Bazgier, V.; Skálová, L.; Otyepka, M.; Anzenbacher, P. beta-caryophyllene oxide and trans-nerolidol affect enzyme activity of CYP3A4—In vitro and in silico studies. Physiol. Res. 2019, 68 (Suppl. S1), S51–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.-U.; Kwon, S.-S.; Kong, T.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.S. Inhibitory Effects of Cedrol, β-Cedrene, and Thujopsene on Cytochrome P450 Enzyme Activities in Human Liver Microsomes. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2014, 77, 1522–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, M.N.; Patel, N.; Bershadskiy, A.; Sokoloff, A.; Singer, E.A. Androgen synthesis inhibitors in the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Asian J. Androl. 2014, 16, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, J.D.; Ellison, S.J.; Baker, J.G.; Stagg, D.B.; Wardell, S.E.; Park, S.; Alley, H.M.; Baldi, R.M.; Yllanes, A.; Andreano, K.J.; et al. Androgen receptor antagonism drives cytochrome P450 17A1 inhibitor efficacy in prostate cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 2326–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, I.M.; Abbott, D.H. The hunt for a selective 17,20 lyase inhibitor; learning lessons from nature. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 163, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wróbel, T.M.; Jørgensen, F.S.; Pandey, A.V.; Grudzińska, A.; Sharma, K.; Yakubu, J.; Björkling, F. Non-steroidal CYP17A1 Inhibitors: Discovery and Assessment. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 6542–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Pas, R.; Hofland, L.J.; Hofland, J.; Taylor, A.E.; Arlt, W.; Steenbergen, J.; van Koetsveld, P.M.; de Herder, W.W.; de Jong, F.H.; Feelders, R.A. Fluconazole inhibits human adrenocortical steroidogenesis in vitro. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 215, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attard, G.; Reid, A.H.M.; Yap, T.A.; Raynaud, F.; Dowsett, M.; Settatree, S.; Barrett, M.; Parker, C.; Martins, V.; Folkerd, E.; et al. Phase I Clinical Trial of a Selective Inhibitor of CYP17, Abiraterone Acetate, Confirms That Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Commonly Remains Hormone Driven. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 4563–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, M.; Hara, T.; Hitaka, T.; Kaku, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Takahashi, J.; Asahi, S.; Miki, H.; Tasaka, A.; Kusaka, M. Orteronel (TAK-700), a novel non-steroidal 17,20-lyase inhibitor: Effects on steroid synthesis in human and monkey adrenal cells and serum steroid levels in cynomolgus monkeys. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 129, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njar, V.C.O.; Brodie, A.M.H. Discovery and Development of Galeterone (TOK-001 or VN/124-1) for the Treatment of All Stages of Prostate Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 2077–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Hu, Q. CYP17 inhibitors—Abiraterone, C17,20-lyase inhibitors and multi-targeting agents. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2014, 11, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, S.; Hansen, C.H.; Petrunak, E.M.; Scott, E.E.; Styrishave, B.; Jorgensen, F.S.; Olsen, L. Promising Tools in Prostate Cancer Research: Selective Non-Steroidal Cytochrome P450 17A1 Inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, M.; Hansen, C.H.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Islin, J.; Styrishave, B.; Olsen, L.; Jorgensen, F.S. Structure-based optimisation of non-steroidal cytochrome P450 17A1 inhibitors. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 3118–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrobel, T.M.; Rogova, O.; Andersen, K.L.; Yadav, R.; Brixius-Anderko, S.; Scott, E.E.; Olsen, L.; Jorgensen, F.S.; Bjorkling, F. Discovery of Novel Non-Steroidal Cytochrome P450 17A1 Inhibitors as Potential Prostate Cancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrobel, T.M.; Rogova, O.; Sharma, K.; Rojas Velazquez, M.N.; Pandey, A.V.; Jorgensen, F.S.; Arendrup, F.S.; Andersen, K.L.; Bjorkling, F. Synthesis and Structure-Activity Relationships of Novel Non-Steroidal CYP17A1 Inhibitors as Potential Prostate Cancer Agents. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malikova, J.; Brixius-Anderko, S.; Udhane, S.S.; Parween, S.; Dick, B.; Bernhardt, R.; Pandey, A.V. CYP17A1 inhibitor abiraterone, an anti-prostate cancer drug, also inhibits the 21-hydroxylase activity of CYP21A2. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 174, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, C.D.; Bart, A.G.; Yadav, R.; Scott, E.E.; Aubé, J. Effects of fluorine substitution on substrate conversion by cytochromes P450 17A1 and 21A2. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 7664–7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, J.; Lim, A.C.; Hay, C.W.; Taylor, A.E.; Wingate, A.; Nowakowska, K.; Pezaro, C.; Carreira, S.; Goodall, J.; Arlt, W.; et al. Interactions of Abiraterone, Eplerenone, and Prednisolone with Wild-type and Mutant Androgen Receptor: A Rationale for Increasing Abiraterone Exposure or Combining with MDV3100. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2176–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, R.B.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Vessella, R.; Hess, D.L.; Kalhorn, T.F.; Higano, C.S.; True, L.D.; Nelson, P.S. Maintenance of Intratumoral Androgens in Metastatic Prostate Cancer: A Mechanism for Castration-Resistant Tumor Growth. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4447–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, M.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Auchus, R.J.; Storbeck, K.-H. The role of adrenal derived androgens in castration resistant prostate cancer. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 197, 105506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambury, R.M.; Rathkopf, D.E. Novel and next-generation androgen receptor–directed therapies for prostate cancer: Beyond abiraterone and enzalutamide. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2016, 34, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Hu, Q.; Hartmann, R.W. Recent Progress in Pharmaceutical Therapies for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 13958–13978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, K.; Lanzilotto, A.; Yakubu, J.; Therkelsen, S.; Vöegel, C.D.; Du Toit, T.; Jørgensen, F.S.; Pandey, A.V. Effect of Essential Oil Components on the Activity of Steroidogenic Cytochrome P450. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14020203
Sharma K, Lanzilotto A, Yakubu J, Therkelsen S, Vöegel CD, Du Toit T, Jørgensen FS, Pandey AV. Effect of Essential Oil Components on the Activity of Steroidogenic Cytochrome P450. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(2):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14020203
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Katyayani, Angelo Lanzilotto, Jibira Yakubu, Søren Therkelsen, Clarissa Daniela Vöegel, Therina Du Toit, Flemming Steen Jørgensen, and Amit V. Pandey. 2024. "Effect of Essential Oil Components on the Activity of Steroidogenic Cytochrome P450" Biomolecules 14, no. 2: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14020203
APA StyleSharma, K., Lanzilotto, A., Yakubu, J., Therkelsen, S., Vöegel, C. D., Du Toit, T., Jørgensen, F. S., & Pandey, A. V. (2024). Effect of Essential Oil Components on the Activity of Steroidogenic Cytochrome P450. Biomolecules, 14(2), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14020203