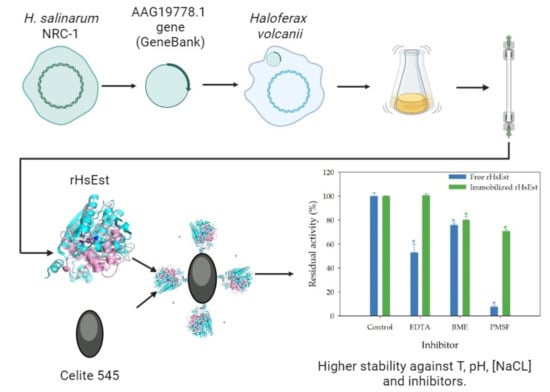
Cloning, Expression, Characterization and Immobilization of a Recombinant Carboxylesterase from the Halophilic Archaeon, Halobacterium salinarum NCR-1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganism
2.2. Culture Media for H. volcanii
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.4. Cloning, Overexpression and Purification of Recombinant Carboxylesterase
2.5. Standard Assay of Esterase Activity
2.6. Kinetic Parameters of rHsEst
2.7. Effect of Metal Ions, Organic Solvents and Detergents, on the Esterase Activity of rHsEst
2.8. Immobilization of rHsEst
2.9. Substrate Specificity of Free and Immobilized rHsEst

2.10. Effect of Temperature, pH, NaCl Concentration and Inhibitors on the Esterase Activity of Free and Immobilized rHsEst
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of HsEst gene
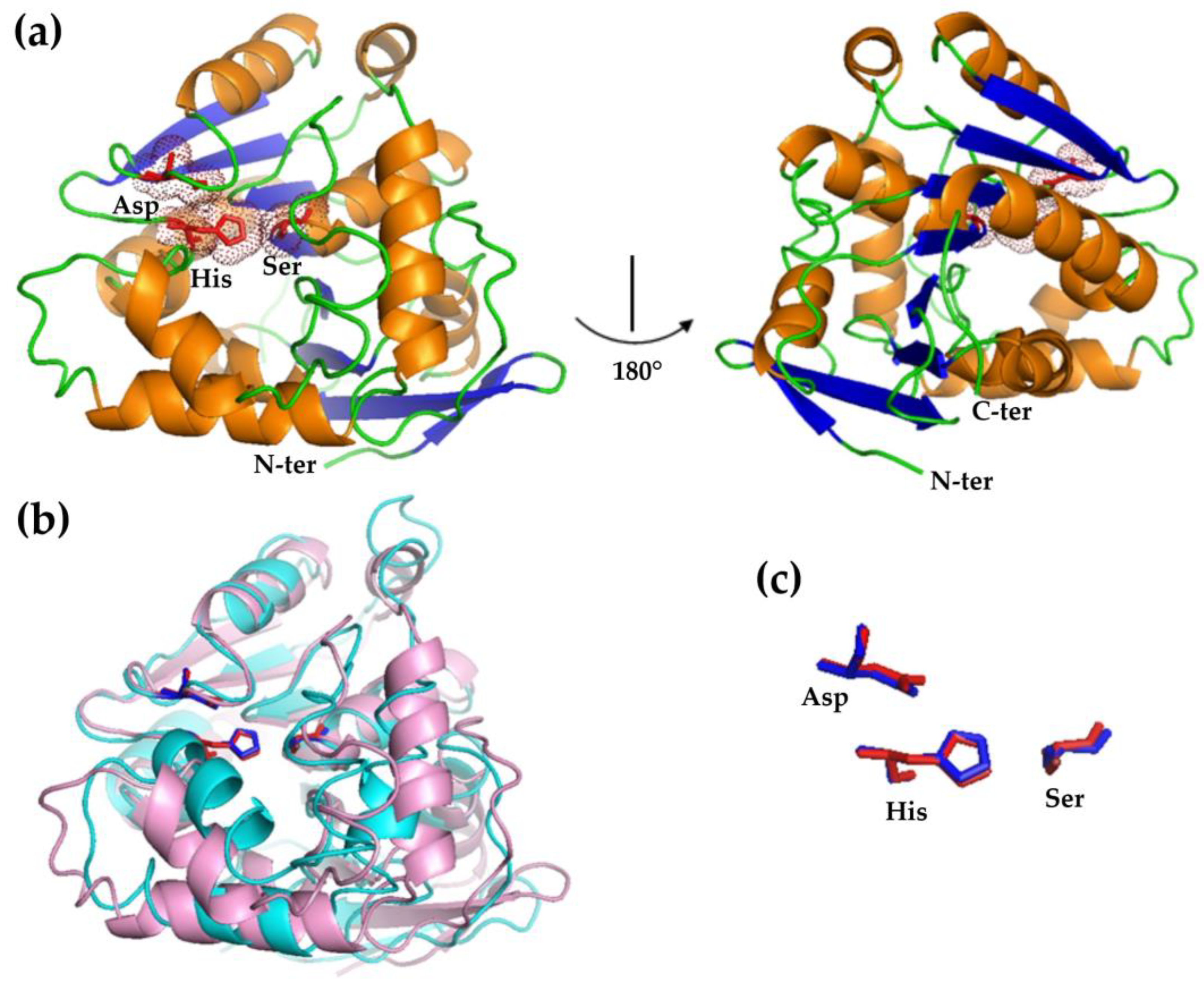
3.2. Structural Modeling of HsEst
3.3. Cloning, Overexpression and Purification of Recombinant Carboxylesterase
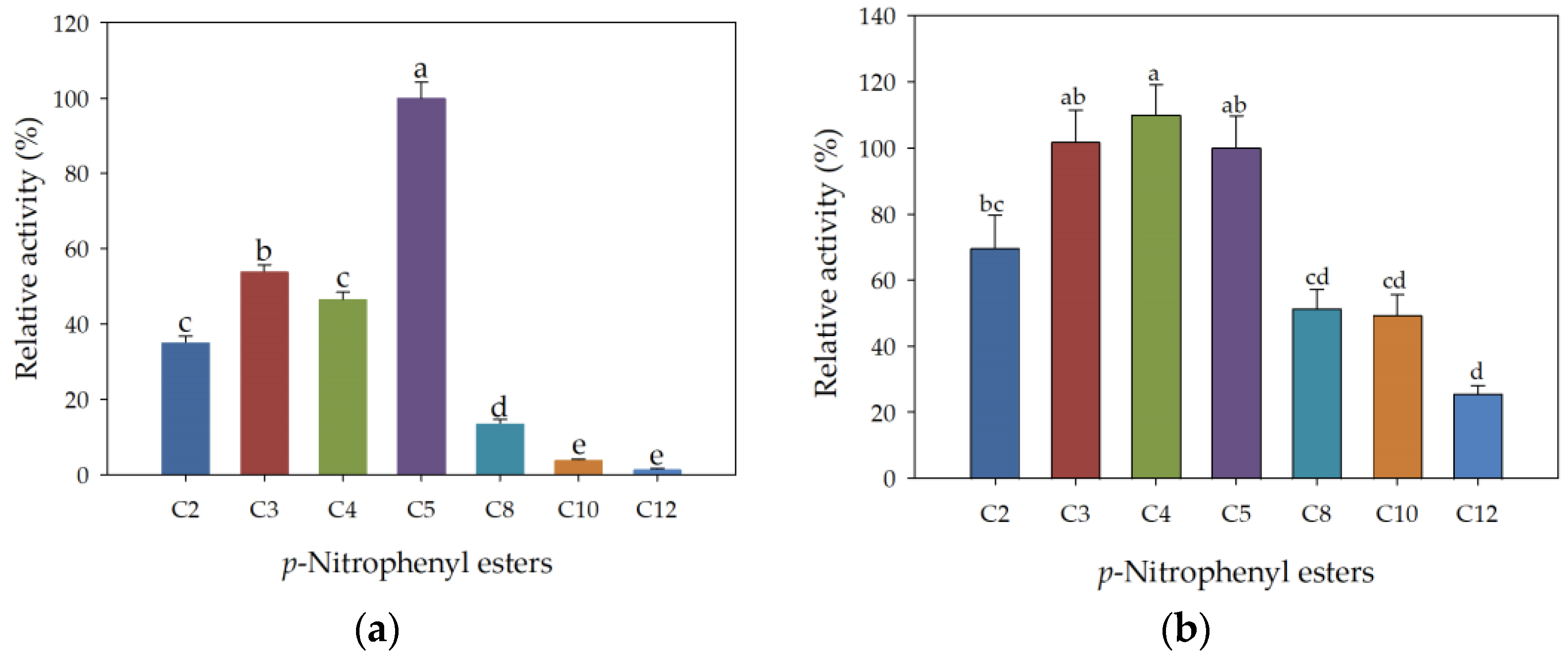
3.4. Kinetic Parameters of rHsEst Calculated from the Hydrolysis of Three Substrates
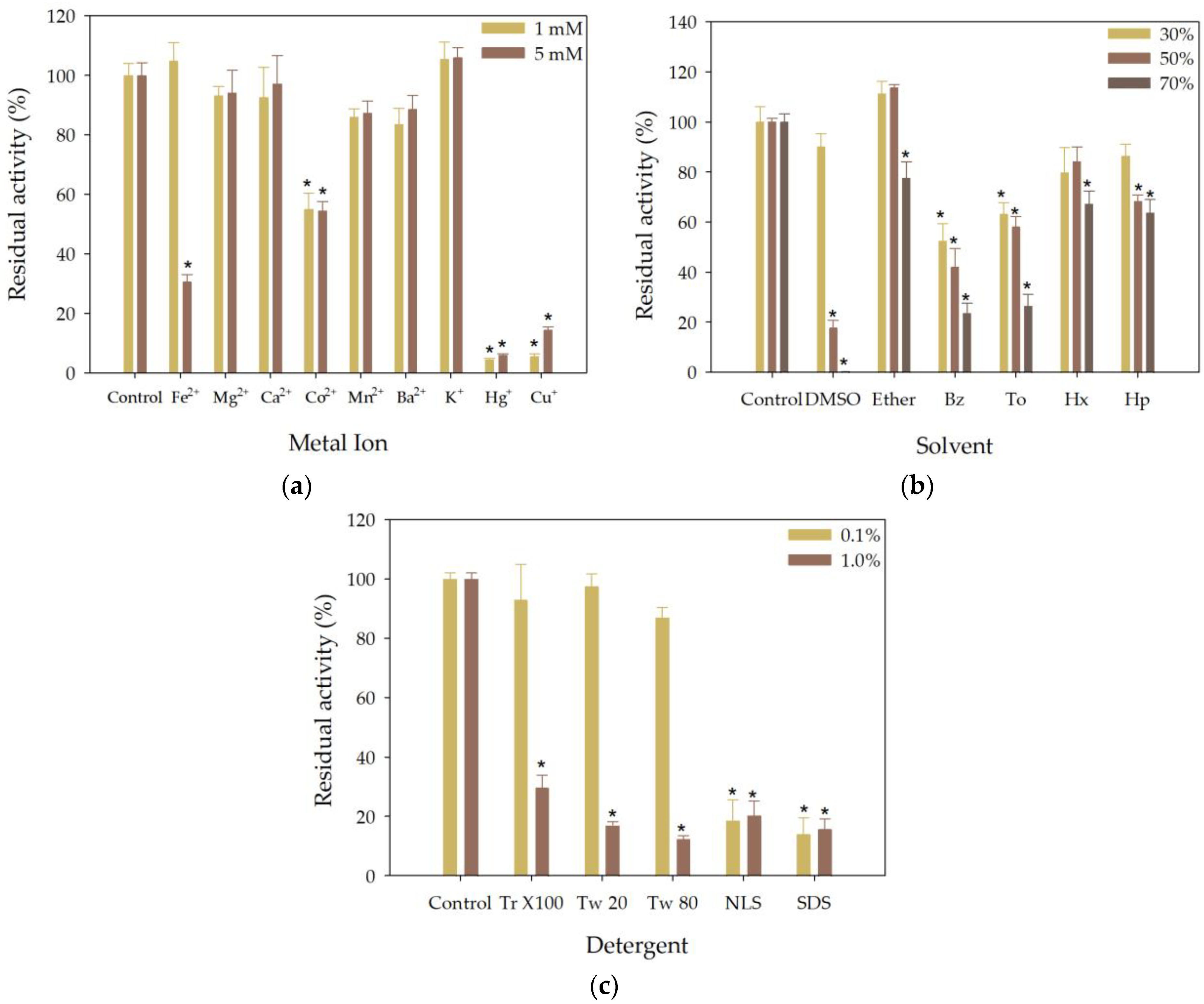
3.5. Effect of Metal Ions, Organic Solvents and Detergents on the Esterase Activity of rHsEst
3.5.1. Effect of Metal Ions on the Esterase Activity of rHsEst
3.5.2. Effect of Solvents on the Esterase Activity of rHsEst
3.5.3. Effect of Detergents on the Esterase Activity of rHsEst
3.6. Immobilization of rHsEst
3.7. Substrate Specificity of Free and Immobilized rHsEst
3.8. Effect of Temperature, pH, NaCl Concentration and Inhibitors on the Esterase Activity of Free and Immobilized rHsEst
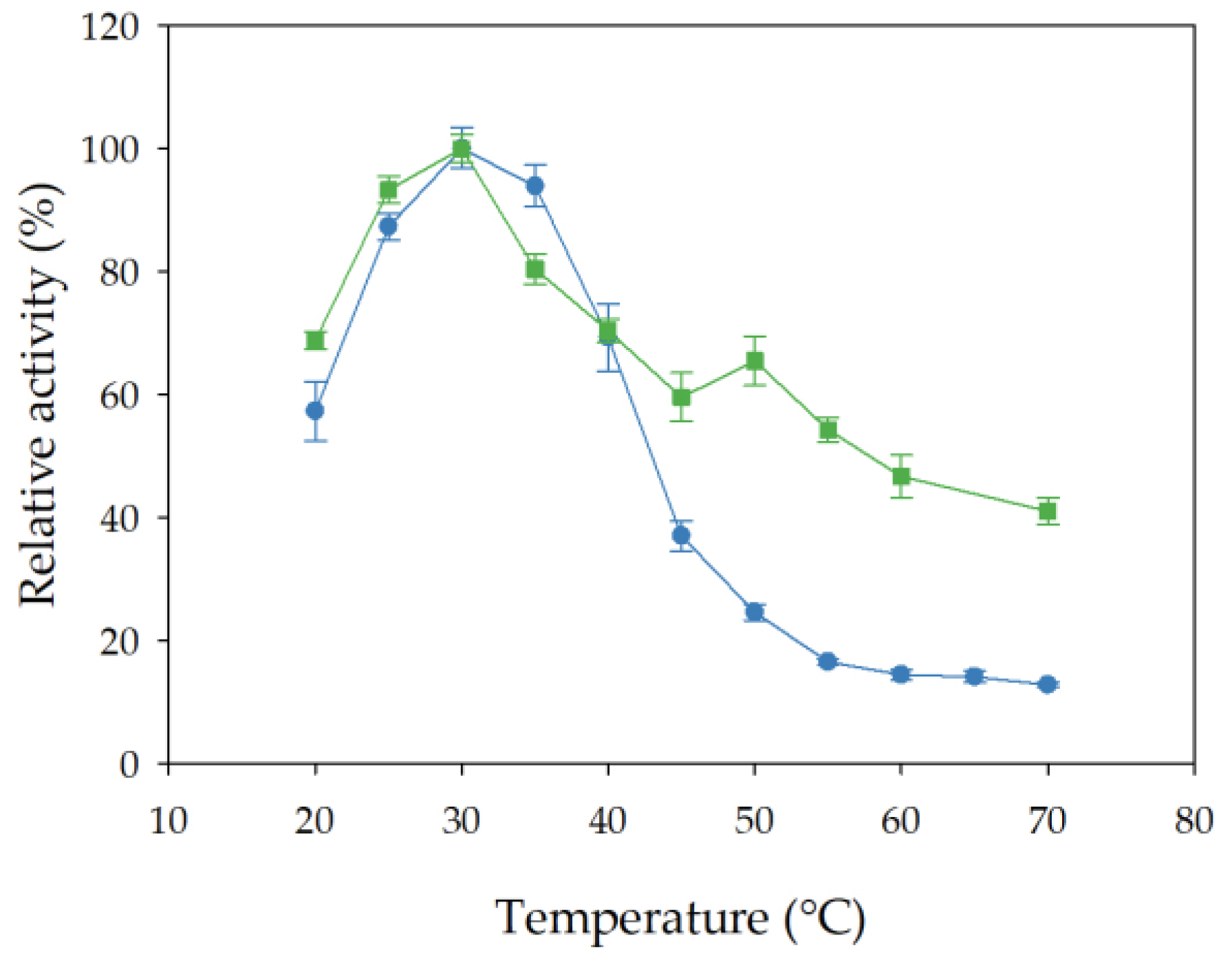
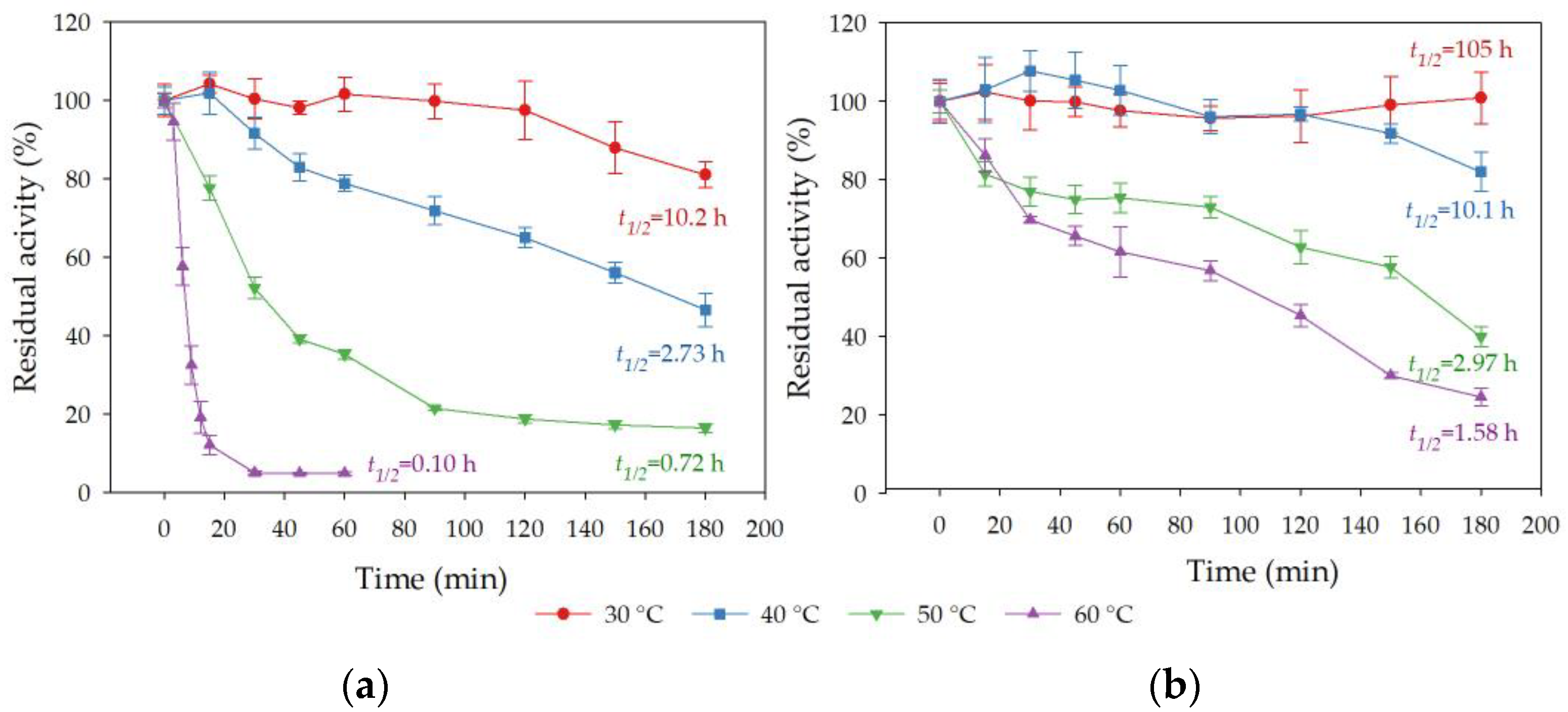
3.8.1. Effect of Incubation Temperature on Esterase Activity and Stability of Free and Immobilized rHsEst
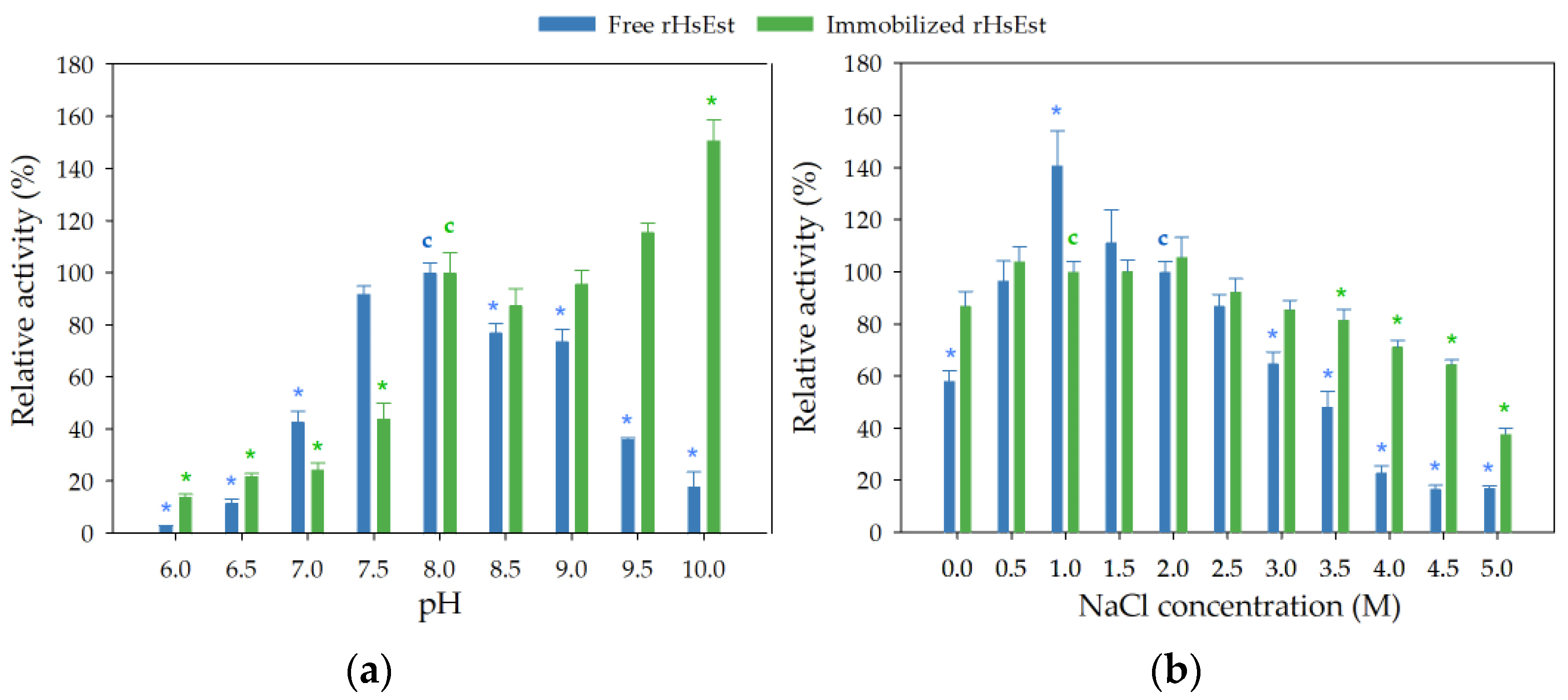
3.8.2. Effect of pH and NaCl Concentration on Esterase Activity of Free and Immobilized rHsEst
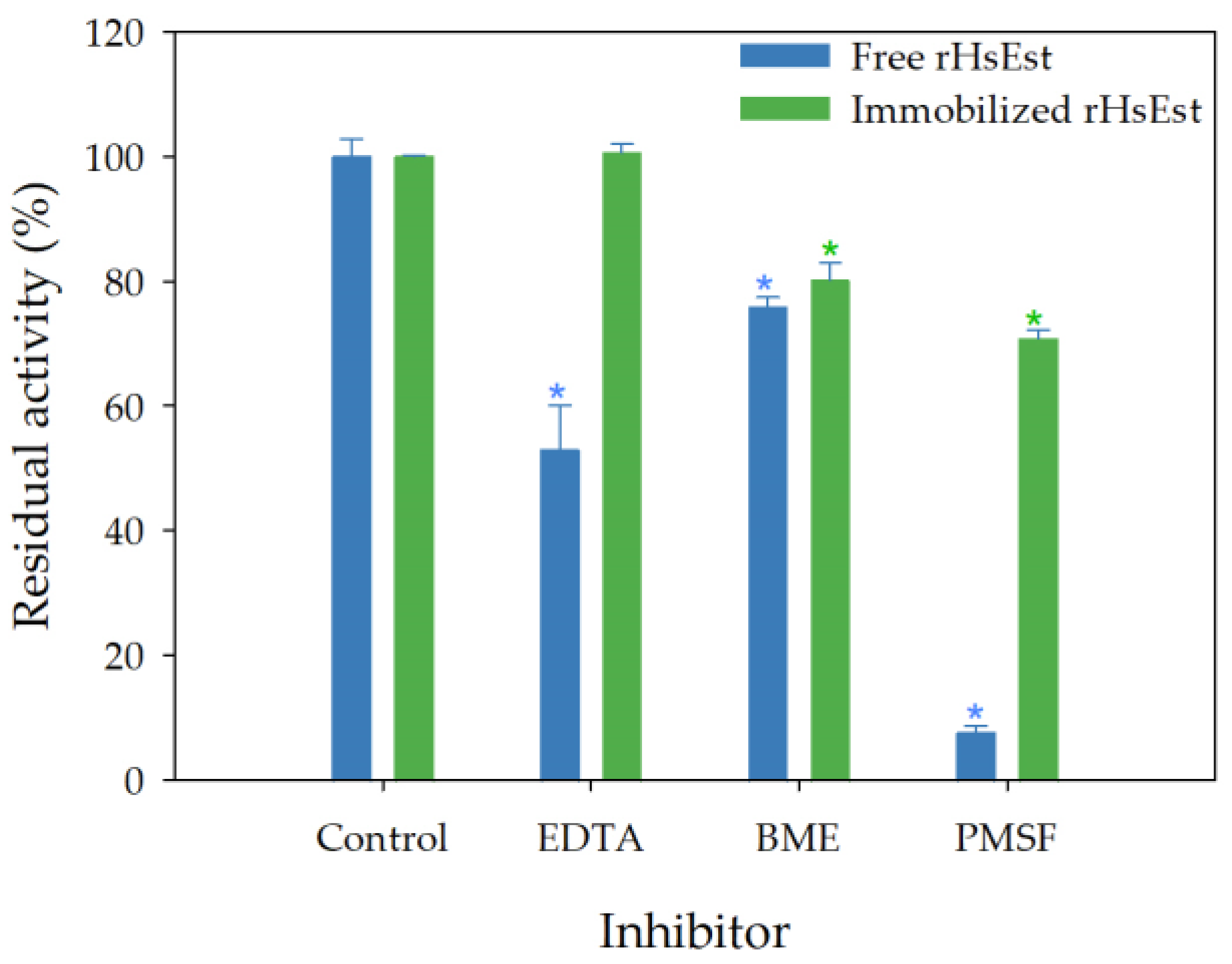
3.8.3. Effect of Inhibitors on Esterase Activity of Free and Immobilized rHsEst
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pfeifer, K.; Ergal, İ.; Koller, M.; Basen, M.; Schuster, B.; Rittmann, S.K.M.R. Archaea biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 47, 107668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meghwanshi, G.K.; Verma, S.; Srivastava, V.; Kumar, R. Archaeal lipolytic enzymes: Current developments and further prospects. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 61, 108054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litchfield, C.D. Potential for industrial products from the halophilic Archaea. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 38, 1635–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Sun, H.; Xu, C. Cloning, expression and characterization of a novel esterase from Bacillus pumilus. Ann. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, J.-E.; Tsai, C.-H.; Chou, C.-C.; Wu, C.; Wu, W.-F. Enzymatic characterization of a novel HSL family IV esterase EstD04 from Pseudomonas sp. D01 in Mealworm Gut Microbiota. Molecules 2023, 28, 5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeger, K.-E.; Dijkstra, B.W.; Reetz, M.T. Bacterial biocatalysts: Molecular Biology, Three-Dimensional Structures, and Biotechnological Applications of Lipases. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1999, 53, 315–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.; Xu, L.; Yan, Y. Biochemical characterization of a carboxylesterase from the Archaeon Pyrobaculum sp. 1860 and a rational explanation of its substrate specificity and thermostability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 16885–16910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Miyamoto, K.; Ohta, H. A Novel Thermostable esterase from the thermoacidophilic Archaeon Sulfolobus tokodaii strain 7. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 236, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.; Danso, D.; Ferrer, M.; Streit, W.R. The thaumarchaeon N. argensis carries functional bioABD genes and has a promiscuous E. coli ΔbioH-complementing esterase EstN1. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, R.M.; Mateos, J.C.; González-Reynoso, O.; Prado, L.A.; Córdova, J. Production and characterization of esterase and lipase from Haloarcula marismortui. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 36, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, M.; Katzer, M.; Antranikian, G. Extremely thermostable esterases from the thermoacidophilic euryarchaeon Picrophilus torridus. Extremophiles 2008, 12, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, R.M.; Mateos-Díaz, J.C.; Diaz-Montaño, D.M.; González-Reynoso, O.; Córdova, J. Carboxyl ester hydrolases production and growth of a halophilic Archaeon, Halobacterium sp. NRC-1. Extremophiles 2010, 14, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Espinosa, R.M. Heterologous and homologous expression of proteins from haloarchaea: Denitrification as case of study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allers, T. Overexpression and purification of halophilic proteins in Haloferax volcanii. Bioeng. Bugs 2010, 1, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allers, T.; Ngo, H.P.; Mevarech, M.; Lloyd, R.G. Development of additional selectable markers for the halophilic Archaeon Haloferax volcanii based on the LeuB and TrpA genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simossis, V.A.; Heringa, J. PRALINE: A Multiple Sequence Alignment Toolbox That Integrates Homology-Extended and Secondary Structure Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering Key Features in Protein Structures with the New ENDscript Server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 Web Portal for Protein Modeling, Prediction and Analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopalco, P.; Lobasso, S.; Babudri, F.; Corcelli, A. Osmotic shock stimulates de novo synthesis of two cardiolipins in an extreme halophilic Archaeon. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdova-García, G.; Esquivel, C.J.; Pérez-Staples, D.; Ruiz-May, E.; Herrera-Cruz, M.; Reyes-Hernández, M.; Abraham, S.; Aluja, M.; Sirot, L. Characterization of reproductive proteins in the mexican fruit fly points towards the evolution of novel functions. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2022, 289, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, L.; Menten, M.L. Die kinetik der invertinwirkung (The Kinetics of Invertase Action). Biochem. Z. 1913, 49, 333–369. [Google Scholar]
- del Campo, M.M.; Camacho, R.M.; Mateos-Díaz, J.C.; Müller-Santos, M.; Córdova, J.; Rodríguez, J.A. Solid-state Fermentation as a Potential Technique for Esterase/Lipase Production by Halophilic Archaea. Extremophiles 2015, 19, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boratyn, G.M.; Schäffer, A.A.; Agarwala, R.; Altschul, S.F.; Lipman, D.J.; Madden, T.L. Domain Enhanced Lookup Time Accelerated BLAST. Biol. Direct 2012, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollis, D.L.; Cheah, E.; Cygler, M.; Dijkstra, B.; Frolow, F.; Franken, S.M.; Harel, M.; Remington, S.J.; Silman, I.; Schrag, J.; et al. The α/β hydrolase fold. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1992, 5, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, C.; Finnigan, W.; Isupov, M.N.; Levisson, M.; Kengen, S.W.M.; van der Oost, J.; Harmer, N.J.; Littlechild, J.A. Structural and biochemical characterisation of Archaeoglobus fulgidus esterase reveals a bound CoA molecule in the vicinity of the active site. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the Expasy Server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Humana Press: Buckinghamshire, UK, 2005; pp. 571–608. [Google Scholar]
- Johan, U.U.M.; Rahman, R.N.Z.R.A.; Kamarudin, N.H.A.; Latip, W.; Ali, M.S.M. A new hyper-thermostable carboxylesterase from Anoxybacillus geothermalis D9. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 2486–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Rahman, Z.; Mubeen, H.; Makhdoom, J.; Tariq, J.; Mahjabeen, N.; Ali, Z.; Hamid, A.; Shafique, E.; Aftab, M.N. Heterologous expression, molecular studies and biochemical characterization of a novel alkaline esterase gene from Bacillus thuringiensis for detergent industry. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 34482–34495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Hao, W.; Xie, G.; Wang, Y.; Gao, R. Clone, purification and characterization of thermostable aminopeptidase ST1737 from Sulfolobus tokodaii. Chem. Res. Chinese Univ. 2015, 31, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Santos, M.; de Souza, E.M.; de O. Pedrosa, F.; Mitchell, D.A.; Longhi, S.; Carrière, F.; Canaan, S.; Krieger, N. First Evidence for the salt-dependent folding and activity of an esterase from the halophilic Archaea Haloarcula marismortui. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2009, 1791, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvaud, S.; Gabella, C.; Lisacek, F.; Stockinger, H.; Ioannidis, V.; Durinx, C. Expasy, the swiss bioinformatics resource portal, as designed by its users. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W216–W227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, J.; Maupin-Furlow, J. Post-translation modification in Archaea: Lessons from Haloferax volcanii and other haloarchaea. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 583–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alka, R.; Singh, V.; Kumar, R.; Bhardwaj, A. GlycoPP V2.0 A Webserver for Glycosite Prediction in Prokaryotes. Available online: http://datascience.imtech.res.in/alkarao/glycopp2/ (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Zong, W.; Su, W.; Xie, Q.; Gu, Q.; Deng, X.; Ren, Y.; Li, H. Expression, characterization, and immobilization of a novel SGNH esterase Est882 and its potential for pyrethroid degradation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1069754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, M.; Xing, S.; Wu, T.; He, H.; Bielicki, J.K.; Chen, J. Identification and biochemical characterization of a novel hormone-sensitive lipase family esterase Est19 from the antarctic bacterium Pseudomonas sp. E2-15. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, X.; Wu, Q.; Huang, Z.; Ding, J. A novel thermostable and salt-tolerant carboxylesterase involved in the initial aerobic degradation pathway for pyrethroids in Glycomyces salinus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 451, 131128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Reyes, A.L.; Valero, F.; Sandoval, G. Cloning, protein expression and biochemical characterization of Carica papaya esterase. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2023, 61, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wen, H.M.; Liu, X.L.; Fan, X.J. Cloning and rational modification of a cold-adapted esterase for phthalate esters and parabens degradation. Chemosphere 2023, 325, 138393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreini, C.; Bertini, I.; Cavallaro, G.; Holliday, G.L.; Thornton, J.M. Metal Ions in Biological Catalysis: From Enzyme Databases to General Principles. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 13, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarafeta, D.; Szabo, Z.; Moschidi, D.; Phan, H.; Chrysina, E.D.; Peng, X.; Ingham, C.J.; Kolisis, F.N.; Skretas, G. EstDZ3: A new esterolytic enzyme exhibiting remarkable thermostability. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, L.T.H.L.; Yoo, W.; Jeon, S.; Kim, K.K.; Kim, T.D. Characterization and immobilization of a novel SGNH family esterase (LaSGNH1) from Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Tang, X.; Yang, X.; Lin, L.; He, D.; Wei, W.; Wei, D. Immobilization of a novel ESTBAS esterase from Bacillus altitudinis onto an Epoxy Resin: Characterization and regioselective synthesis of chloramphenicol palmitate. Catalysts 2019, 9, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siódmiak, T.; Haraldsson, G.; Dulęba, J.; Ziegler-Borowska, M.; Siódmiak, J.; Marszałł, M.P. Evaluation of designed immobilized catalytic systems: Activity enhancement of lipase B from Candida antarctica. Catalysts 2020, 10, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grajales-Hernández, D.A.; Velasco-Lozano, S.; Armendáriz-Ruiz, M.A.; Rodríguez-González, J.A.; Camacho-Ruíz, R.M.; Asaff-Torres, A.; López-Gallego, F.; Mateos-Díaz, J.C. Carrier-bound and carrier-free immobilization of type A feruloyl esterase from Aspergillus niger: Searching for an operationally stable heterogeneous biocatalyst for the synthesis of butyl hydroxycinnamates. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 316, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamia, F.; Benouis, S.; Belafriekh, A.; Semache, N.; Rebbani, N.; Djeghaba, Z. Efficient Candida rugosa lipase immobilization on maghnite clay and application for the production of (1R)-(—)-Menthyl acetate. Chem. Pap. 2017, 71, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoh, C. Immobilization of lipases on Celite 545. Biotechnol. Technol. 1998, 12, 381–384. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, F.; Lin, L.; Wei, W.; Wei, D. Facile One—Pot immobilization of a novel esterase and its application in cinnamyl acetate synthesis. Catal. Lett. 2020, 150, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-H.; Park, Y.-J.; Yoon, S.-J.; Lee, H.-B. Purification and characterization of a new inducible thermostable extracellular lipolytic enzyme from the thermoacidophilic Archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus P1. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2016, 124, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Step | Total Activity (U) | Total Protein (mg) | Specific Activity (U mg−1) | Yield % | Purification Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude extract | 78.2 | 185 | 0.4 | 100.0 | 1.00 |
| HisTrap HP column | 63.0 | 13 | 5.0 | 80.5 | 11.90 |
| Substrate | VMAX (μM pNP s−1) | KM (µM) | kcat (s−1) | kcat/KM (s−1 mM−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pNPC2 | 0.68 ± 0.08 | 258 ± 51 | 0.02 | 0.07 |
| pNPC5 | 5.55 ± 0.21 | 78 ± 7 | 0.67 | 8.52 |
| pNPC8 | 3.33 ± 0.20 | 245 ± 26 | 0.09 | 0.37 |
| Supports | Free Protein (mg mL−1) | Adsorbed Protein (mg g−1 of Support) | Immobilization Yield of Protein % | Free Esterase Activity (U mL−1) | Immobilized Esterase Activity (U g−1) | Immobilization Yield of Esterase Activity % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celite 545 | 0.091 ± 0.013 | 0.96 ± 0.04 | 60 | 0.229 ± 0.004 | 0.318 ± 0.008 | 47 |
| Immobead 150P | 0.016 ± 0.007 | 1.50 ± 0.09 | 93 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0 | 0 |
| Lewatit VP OC1600 | 0.096 ± 0.010 | 0.93 ± 0.05 | 58 | 0.175 ± 0.005 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortega-de la Rosa, N.D.; Romero-Borbón, E.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Camacho-Ruiz, A.; Córdova, J. Cloning, Expression, Characterization and Immobilization of a Recombinant Carboxylesterase from the Halophilic Archaeon, Halobacterium salinarum NCR-1. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050534
Ortega-de la Rosa ND, Romero-Borbón E, Rodríguez JA, Camacho-Ruiz A, Córdova J. Cloning, Expression, Characterization and Immobilization of a Recombinant Carboxylesterase from the Halophilic Archaeon, Halobacterium salinarum NCR-1. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(5):534. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050534
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtega-de la Rosa, Nestor David, Evelyn Romero-Borbón, Jorge Alberto Rodríguez, Angeles Camacho-Ruiz, and Jesús Córdova. 2024. "Cloning, Expression, Characterization and Immobilization of a Recombinant Carboxylesterase from the Halophilic Archaeon, Halobacterium salinarum NCR-1" Biomolecules 14, no. 5: 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050534
APA StyleOrtega-de la Rosa, N. D., Romero-Borbón, E., Rodríguez, J. A., Camacho-Ruiz, A., & Córdova, J. (2024). Cloning, Expression, Characterization and Immobilization of a Recombinant Carboxylesterase from the Halophilic Archaeon, Halobacterium salinarum NCR-1. Biomolecules, 14(5), 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050534