Histamine H3 Receptor Isoforms: Insights from Alternative Splicing to Functional Complexity
Abstract
:1. Alternative Splicing to Increase GPCRome Diversity
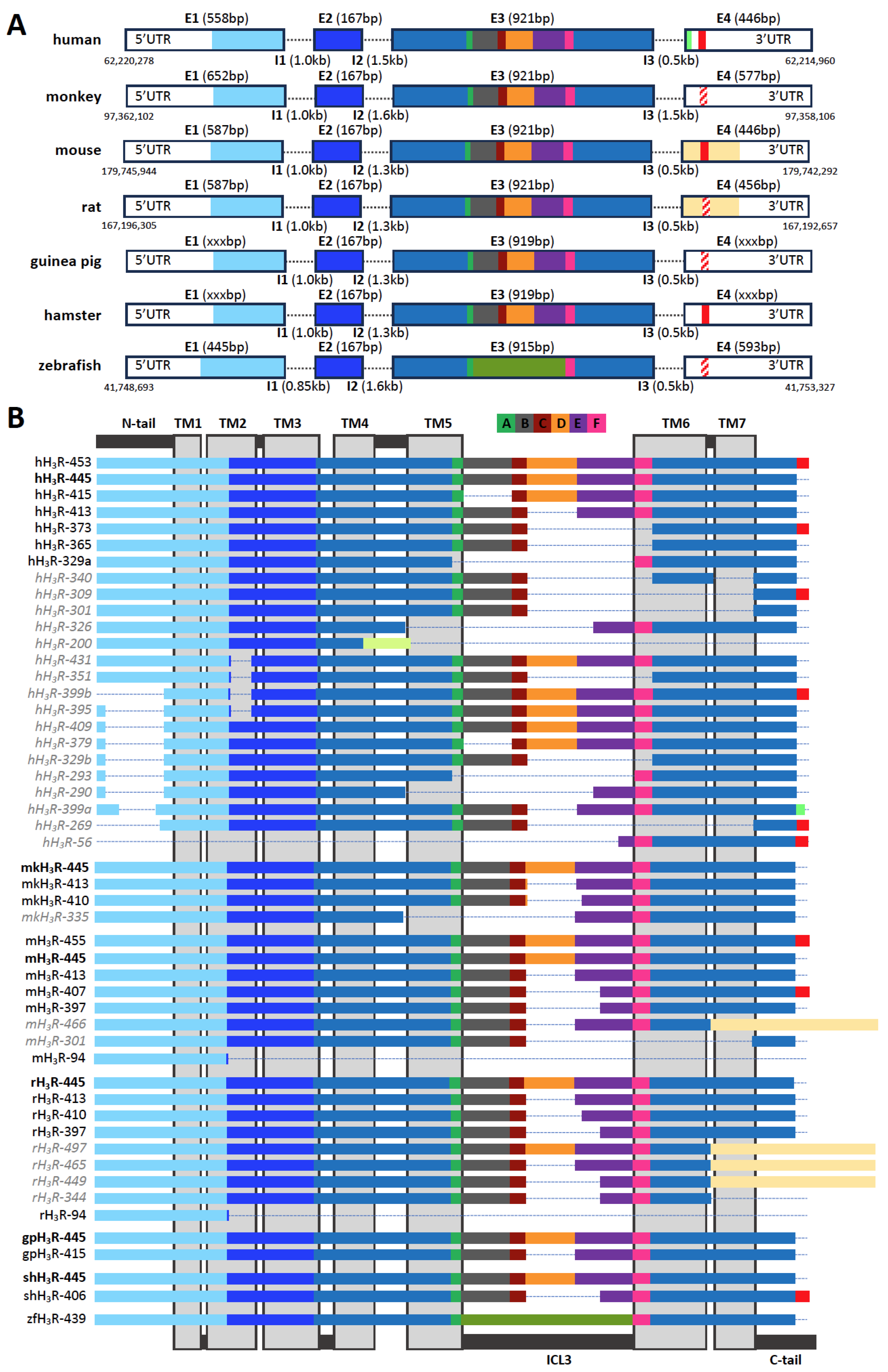
2. Histamine H3 Receptor (H3R) and Its Isoforms: Within and across Species
| Species | Isoform | Alternative Names | Genbank | Uniprot | RNA-seq | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | 453 | - | XP_054178891 | - | [16,22,45] | |
| 445 | Isoform 1; GPCR97 | NP_009163.2 | Q9Y5N1 | NSTRG_52062.3; ENST00000340177.9 | [13,15,20,22,48,49] | |
| 431 | H3(TM2,431AA) | - | - | [13] | ||
| 415 | H3(Δi3,415AA) | - | - | [13] | ||
| 413 | H3S | - | - | [17,49] | ||
| 409 | - | - | - | [14] | ||
| 399a | 399 | XP_016883112.1 | - | NSTRG_52062.8 | [22] | |
| 399b | 399 | XM_017027623.1 | - | [22] | ||
| 395 | - | - | - | [14] | ||
| 379 | - | - | - | [14] | ||
| 373 | Isoform 4 | AF321913 | Q8WXZ9 | NSTRG_52062.5; ENST00000317393.10 | [20,22] | |
| 365 | Isoform 2; H3S | AF321911 | Q8WY01 | [13,20,48,49] | ||
| 351 | - | - | - | [18] | ||
| 340 | - | - | - | [19] | ||
| 329a | H3(Δi3,329AA) | - | - | [13,49] | ||
| 329b | - | - | - | [14] | ||
| 326 | H3(Δi3+TM5,326AA) | AF346903 | - | [13] | ||
| 309 | Isoform 6 | AF346904 | Q8NI49 | [20] | ||
| 301 | Isoform 3 | AF321912 | Q8WY00 | [20] | ||
| 293 | - | - | - | [14] | ||
| 290 | - | - | - | [14] | ||
| 269 | - | - | - | NSTRG_52062.7 | [22] | |
| 200 | Isoform 5 | AF346903 | Q8NI50 | ENST00000611492.1 | [20,21] | |
| 56 | - | - | - | NSTRG_52062.6 | [22] | |
| Monkey (macaca) | 445 | - | AAO63757.1 | - | [36] | |
| 413 | - | - | - | [35] | ||
| 410 | - | - | - | [35] | ||
| 335 | - | - | - | [35] | ||
| Mouse | 466 | - | - | E9Q540 | ENSMUST00000163215 | [44] |
| 455 | - | - | - | ENSMUST00000165762 | [44] | |
| 445 | Isoform 1 | AY044153 | P58406 | ENSMUST00000056480 | [32,40,44] | |
| 413 | - | - | E9Q5S3 | ENSMUST00000164442 | [40,44] | |
| 407 | - | - | E9Q7T5 | ENSMUST00000165248 | [44] | |
| 397 | - | - | - | [40] | ||
| 301 | - | - | E9Q522 | ENSMUST00000171736 | [44] | |
| 94 | - | - | E9PZM9 | ENSMUST00000166724 | [44] | |
| Rat | 497 | H3D | NP_001257495 | Q2VJ18 | [41] | |
| 465 | H3E | NP_001257496 | - | [41] | ||
| 449 | H3F | - | - | [41] | ||
| 445 | H3L; H3A | AY009370 | Q9QYN8 | [37,38,42] | ||
| 413 | H3S; H3B | AY009371 | Q541U0 | [37,38,42] | ||
| 410 | isoform 7/8 | NP_001257498 | - | [38] | ||
| 397 | H3C | - | - | [38,50] | ||
| 344 | - | BAA88768 | - | [51] | ||
| 94 | H3(f1);H3T | - | - | [38] | ||
| Guinea pig | 445 | H3L | AF267537 | Q9JI35 | [39] | |
| 415 | H3S | AF267538 | Q9JI36 | [39] | ||
| Hamster | 445 | Long | AY855070 | - | [34] | |
| 406 | Short | AY855071 | - | [34] | ||
| Zebrafish | 439 | - | ABF71709 | - | [43] |
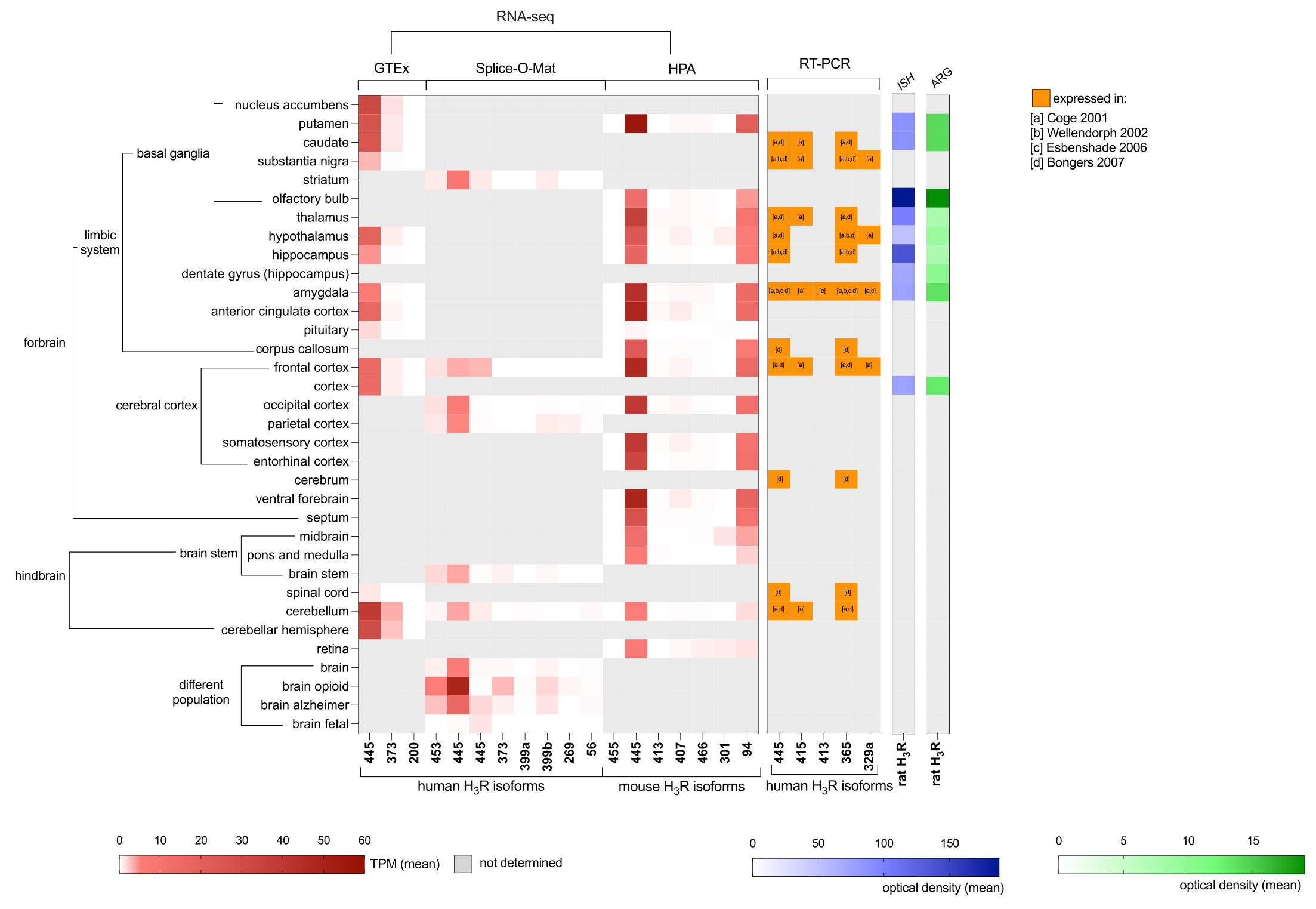
3. Localization of H3R Isoforms in the Central Nervous System
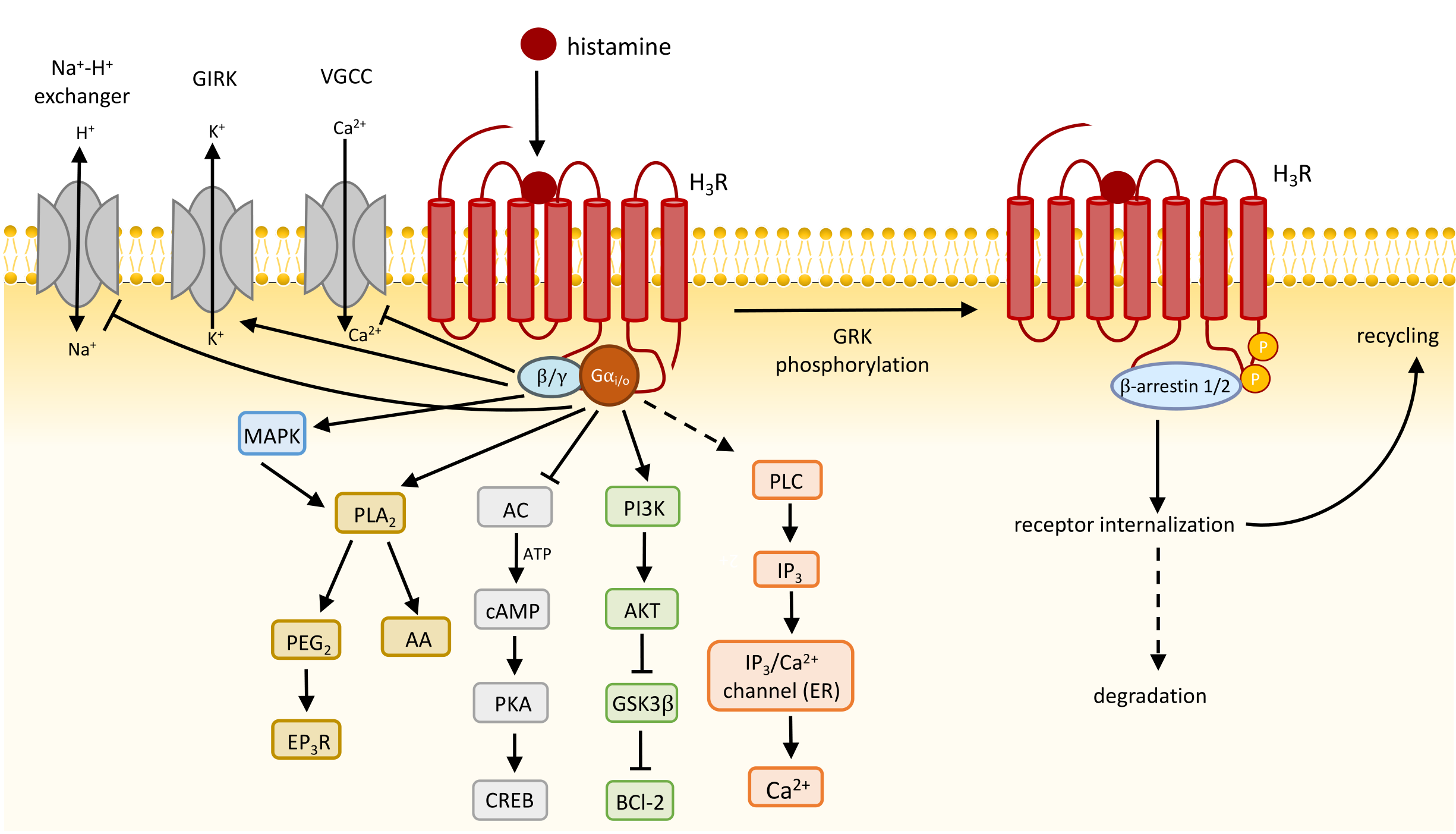
4. Function and Signaling Transduction of H3R
4.1. H3R Constitutively Activates Gi/o Proteins
4.2. Presynaptic H3R Inhibits Neurotransmitter Release and Synthesis
4.3. Postsynaptic H3R Function and Downstream Effects
4.4. H3R Dimerization
4.5. Regulation of H3R Signaling
4.6. Isoform Signaling Bias
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marasco, L.E.; Kornblihtt, A.R. The physiology of alternative splicing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, J.E.; Dehghannasiri, R.; Wang, P.L.; Jang, S.; de Morree, A.; Tan, S.Y.; Ming, J.; Ruohao Wu, A.; Tabula Sapiens, C.; Quake, S.R.; et al. RNA splicing programs define tissue compartments and cell types at single-cell resolution. eLife 2021, 10, e70692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, D.; Challiss, R.A. Alternative splicing of G protein-coupled receptors: Physiology and pathophysiology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 3337–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, A.S.; Attwood, M.M.; Rask-Andersen, M.; Schioth, H.B.; Gloriam, D.E. Trends in GPCR drug discovery: New agents, targets and indications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mele, M.; Ferreira, P.G.; Reverter, F.; DeLuca, D.S.; Monlong, J.; Sammeth, M.; Young, T.R.; Goldmann, J.M.; Pervouchine, D.D.; Sullivan, T.J.; et al. Human genomics. The human transcriptome across tissues and individuals. Science 2015, 348, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti-Solano, M.; Crilly, S.E.; Malinverni, D.; Munk, C.; Harris, M.; Pearce, A.; Quon, T.; Mackenzie, A.E.; Wang, X.; Peng, J.; et al. Combinatorial expression of GPCR isoforms affects signalling and drug responses. Nature 2020, 587, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panula, P.; Chazot, P.L.; Cowart, M.; Gutzmer, R.; Leurs, R.; Liu, W.L.; Stark, H.; Thurmond, R.L.; Haas, H.L. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCVIII. Histamine Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 601–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z. The Histaminergic System in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwell, V.; Fasinu, P.S. Pitolisant and Other Histamine-3 Receptor Antagonists-An Update on Therapeutic Potentials and Clinical Prospects. Medicines 2020, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Y.Y. Pitolisant: First Global Approval. Drugs 2016, 76, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligneau, X.; Perrin, D.; Landais, L.; Camelin, J.C.; Calmels, T.P.; Berrebi-Bertrand, I.; Lecomte, J.M.; Parmentier, R.; Anaclet, C.; Lin, J.S.; et al. BF2.649 [1-3-[3-(4-Chlorophenyl)propoxy]propylpiperidine, hydrochloride], a nonimidazole inverse agonist/antagonist at the human histamine H3 receptor: Preclinical pharmacology. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 320, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urquhart, L. FDA new drug approvals in Q3 2019. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coge, F.; Guenin, S.P.; Audinot, V.; Renouard-Try, A.; Beauverger, P.; Macia, C.; Ouvry, C.; Nagel, N.; Rique, H.; Boutin, J.A.; et al. Genomic organization and characterization of splice variants of the human histamine H3 receptor. Biochem. J. 2001, 355, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, M.; Yates, S.L. Histamine H3 Receptor Polynucleotides. WO Patent 2003/042359, 22 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lovenberg, T.W.; Roland, B.L.; Wilson, S.J.; Jiang, X.; Pyati, J.; Huvar, A.; Jackson, M.R.; Erlander, M.G. Cloning and functional expression of the human histamine H3 receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999, 55, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Itadani, H.; Hidaka, Y.; Ohta, M.; Tanaka, K. Molecular cloning and characterization of a new human histamine receptor, HH4R. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 279, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardivel-Lacombe, J.; Morisset, S.; Gbahou, F.; Schwartz, J.C.; Arrang, J.M. Chromosomal mapping and organization of the human histamine H3 receptor gene. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, P. Human Histamine H3 Gene Variant-2. WO Patent 2001/068703, 20 September 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tsui, P. Human Histamine H3 Gene Variant-3. WO Patent 2001/068816, 20 September 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wellendorph, P.; Goodman, M.W.; Burstein, E.S.; Nash, N.R.; Brann, M.R.; Weiner, D.M. Molecular cloning and pharmacology of functionally distinct isoforms of the human histamine H(3) receptor. Neuropharmacology 2002, 42, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GTEx-Consortium. The GTEx Consortium atlas of genetic regulatory effects across human tissues. Science 2020, 369, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, C.K.; Stenzel, U.; Berndt, S.; Liebscher, I.; Schoneberg, T.; Horn, S. The repertoire and structure of adhesion GPCR transcript variants assembled from publicly available deep-sequenced human samples. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, 3823–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, M.M. Histamine in the regulation of wakefulness. Sleep Med. Rev. 2011, 15, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Xu, L.; Zheng, Y.; An, S.; Zhao, M.; Hu, W.; Li, M.; Dong, H.; Li, A.; Li, Y.; et al. Whole-brain mapping of histaminergic projections in mouse brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2216231120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panula, P.; Nuutinen, S. The histaminergic network in the brain: Basic organization and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 472–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khouma, A.; Moeini, M.M.; Plamondon, J.; Richard, D.; Caron, A.; Michael, N.J. Histaminergic regulation of food intake. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1202089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connelly, W.M.; Shenton, F.C.; Lethbridge, N.; Leurs, R.; Waldvogel, H.J.; Faull, R.L.; Lees, G.; Chazot, P.L. The histamine H4 receptor is functionally expressed on neurons in the mammalian CNS. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Q.; Xicoy, H.; Shen, J.; Luchetti, S.; Dai, D.; Zhou, P.; Qi, X.R.; Martens, G.J.M.; Huitinga, I.; Swaab, D.F.; et al. Histamine-4 receptor antagonist ameliorates Parkinson-like pathology in the striatum. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 92, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Martens, G.J.M.; Swaab, D.F. Histamine-4 Receptor: Emerging Target for the Treatment of Neurological Diseases. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 59, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, M.D.; Ghelardini, C.; Thurmond, R.L.; Masini, E.; Galeotti, N. Behavioural phenotype of histamine H(4) receptor knockout mice: Focus on central neuronal functions. Neuropharmacology 2017, 114, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrang, J.M.; Garbarg, M.; Schwartz, J.C. Auto-inhibition of brain histamine release mediated by a novel class (H3) of histamine receptor. Nature 1983, 302, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, C.; Lovenberg, T.W. Molecular and pharmacological characterization of the mouse histamine H3 receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 467, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovenberg, T.W.; Pyati, J.; Chang, H.; Wilson, S.J.; Erlander, M.G. Cloning of rat histamine H(3) receptor reveals distinct species pharmacological profiles. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 293, 771–778. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, P.; Ross, A.W.; Balik, A.; Littlewood, P.A.; Mercer, J.G.; Moar, K.M.; Sallmen, T.; Kaslin, J.; Panula, P.; Schuhler, S.; et al. Photoperiodic regulation of histamine H3 receptor and VGF messenger ribonucleic acid in the arcuate nucleus of the Siberian hamster. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 1930–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strakhova, M.I.; Fox, G.B.; Carr, T.L.; Witte, D.G.; Vortherms, T.A.; Manelli, A.M.; Miller, T.R.; Yao, B.B.; Brioni, J.D.; Esbenshade, T.A. Cloning and characterization of the monkey histamine H3 receptor isoforms. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 601, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, B.B.; Sharma, R.; Cassar, S.; Esbenshade, T.A.; Hancock, A.A. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of the monkey histamine H3 receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 482, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisset, S.; Rouleau, A.; Ligneau, X.; Gbahou, F.; Tardivel-Lacombe, J.; Stark, H.; Schunack, W.; Ganellin, C.R.; Schwartz, J.C.; Arrang, J.M. High constitutive activity of native H3 receptors regulates histamine neurons in brain. Nature 2000, 408, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisset, S.; Sasse, A.; Gbahou, F.; Heron, A.; Ligneau, X.; Tardivel-Lacombe, J.; Schwartz, J.C.; Arrang, J.M. The rat H3 receptor: Gene organization and multiple isoforms. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 280, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardivel-Lacombe, J.; Rouleau, A.; Heron, A.; Morisset, S.; Pillot, C.; Cochois, V.; Schwartz, J.C.; Arrang, J.M. Cloning and cerebral expression of the guinea pig histamine H3 receptor: Evidence for two isoforms. Neuroreport 2000, 11, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouleau, A.; Heron, A.; Cochois, V.; Pillot, C.; Schwartz, J.C.; Arrang, J.M. Cloning and expression of the mouse histamine H3 receptor: Evidence for multiple isoforms. J. Neurochem. 2004, 90, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, R.A.; Lozada, A.F.; van Marle, A.; Shenton, F.C.; Drutel, G.; Karlstedt, K.; Hoffmann, M.; Lintunen, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; van Rijn, R.M.; et al. Discovery of naturally occurring splice variants of the rat histamine H3 receptor that act as dominant-negative isoforms. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 69, 1194–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drutel, G.; Peitsaro, N.; Karlstedt, K.; Wieland, K.; Smit, M.J.; Timmerman, H.; Panula, P.; Leurs, R. Identification of rat H3 receptor isoforms with different brain expression and signaling properties. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peitsaro, N.; Sundvik, M.; Anichtchik, O.V.; Kaslin, J.; Panula, P. Identification of zebrafish histamine H1, H2 and H3 receptors and effects of histaminergic ligands on behavior. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjostedt, E.; Zhong, W.; Fagerberg, L.; Karlsson, M.; Mitsios, N.; Adori, C.; Oksvold, P.; Edfors, F.; Limiszewska, A.; Hikmet, F.; et al. An atlas of the protein-coding genes in the human, pig, and mouse brain. Science 2020, 367, eaay5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhurst, A.D.; Atkins, A.R.; Beresford, I.J.; Brackenborough, K.; Briggs, M.A.; Calver, A.R.; Cilia, J.; Cluderay, J.E.; Crook, B.; Davis, J.B.; et al. GSK189254, a novel H3 receptor antagonist that binds to histamine H3 receptors in Alzheimer’s disease brain and improves cognitive performance in preclinical models. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 321, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner-Link, D.; Madsen, J.S.; Gloriam, D.E.; Brauner-Osborne, H.; Hauser, A.S. Differential G protein activation by the long and short isoforms of the dopamine D(2) receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2024. online version of record. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadler, F.; Ma, N.; Ritt, M.; Sharma, Y.; Vaidehi, N.; Sivaramakrishnan, S. Autoregulation of GPCR signalling through the third intracellular loop. Nature 2023, 615, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongers, G.; Krueger, K.M.; Miller, T.R.; Baranowski, J.L.; Estvander, B.R.; Witte, D.G.; Strakhova, M.I.; van Meer, P.; Bakker, R.A.; Cowart, M.D.; et al. An 80-amino acid deletion in the third intracellular loop of a naturally occurring human histamine H3 isoform confers pharmacological differences and constitutive activity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 323, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esbenshade, T.A.; Strakhova, M.I.; Carr, T.L.; Sharma, R.; Witte, D.G.; Yao, B.B.; Miller, T.R.; Hancock, A.A. Differential CNS expression and functional activity of multiple human H(3) receptor isoforms. Inflamm. Res. 2006, 55 (Suppl. S1), S38–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrang, J.M.; Drutel, G.; Schwartz, J.C. Characterization of histamine H3 receptors regulating acetylcholine release in rat entorhinal cortex. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 114, 1518–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strausberg, R.L.; Feingold, E.A.; Grouse, L.H.; Derge, J.G.; Klausner, R.D.; Collins, F.S.; Wagner, L.; Shenmen, C.M.; Schuler, G.D.; Altschul, S.F.; et al. Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16899–16903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korte, A.; Myers, J.; Shih, N.Y.; Egan, R.W.; Clark, M.A. Characterization and tissue distribution of H3 histamine receptors in guinea pigs by N alpha-methylhistamine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990, 168, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rijn, R.M.; van Marle, A.; Chazot, P.L.; Langemeijer, E.; Qin, Y.; Shenton, F.C.; Lim, H.D.; Zuiderveld, O.P.; Sansuk, K.; Dy, M.; et al. Cloning and characterization of dominant negative splice variants of the human histamine H4 receptor. Biochem. J. 2008, 414, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillot, C.; Heron, A.; Cochois, V.; Tardivel-Lacombe, J.; Ligneau, X.; Schwartz, J.C.; Arrang, J.M. A detailed mapping of the histamine H(3) receptor and its gene transcripts in rat brain. Neuroscience 2002, 114, 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Bossers, K.; Unmehopa, U.; Bao, A.M.; Swaab, D.F. Alterations in the histaminergic system in Alzheimer’s disease: A postmortem study. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 2585–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.Y.; Anichtchik, O.; Panula, P. Altered histamine H3 receptor radioligand binding in post-mortem brain samples from subjects with psychiatric diseases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poveda, R.; Fernandez-Duenas, V.; Fernandez, A.; Sanchez, S.; Puig, M.M.; Planas, E. Synergistic interaction between fentanyl and the histamine H3 receptor agonist R-(alpha)-methylhistamine, on the inhibition of nociception and plasma extravasation in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 541, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlicker, E.; Kathmann, M. Role of the Histamine H(3) Receptor in the Central Nervous System. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 241, 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrang, J.M.; Garbarg, M.; Lancelot, J.C.; Lecomte, J.M.; Pollard, H.; Robba, M.; Schunack, W.; Schwartz, J.C. Highly potent and selective ligands for histamine H3-receptors. Nature 1987, 327, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, H.; Moreau, J.; Arrang, J.M.; Schwartz, J.C. A detailed autoradiographic mapping of histamine H3 receptors in rat brain areas. Neuroscience 1993, 52, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, F.P.; Mochizuki, T.; Maeyama, K.; Leurs, R.; Timmerman, H. Characterization of histamine H3 receptors in mouse brain using the H3 antagonist [125I]iodophenpropit. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 362, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Mir, M.I.; Pollard, H.; Moreau, J.; Arrang, J.M.; Ruat, M.; Traiffort, E.; Schwartz, J.C.; Palacios, J.M. Three histamine receptors (H1, H2 and H3) visualized in the brain of human and non-human primates. Brain Res. 1990, 526, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazot, P.L.; Hann, V.; Wilson, C.; Lees, G.; Thompson, C.L. Immunological identification of the mammalian H3 histamine receptor in the mouse brain. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sepúlveda, M.; Rosell, S.; Hoffmann, H.M.; Castillo-Ruiz, M.d.M.; Mignon, V.; Moreno-Delgado, D.; Vignes, M.; Díaz, J.; Sabriá, J.; Ortiz, J. Cellular distribution of the histamine H3 receptor in the basal ganglia: Functional modulation of dopamine and glutamate neurotransmission. Basal Ganglia 2013, 3, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino-Miranda, G.; Escamilla-Sanchez, J.; Gonzalez-Pantoja, R.; Bueno-Nava, A.; Arias-Montano, J.A. Histamine H3 receptor activation inhibits dopamine synthesis but not release or uptake in rat nucleus accumbens. Neuropharmacology 2016, 106, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Bossers, K.; Luchetti, S.; Balesar, R.; Lethbridge, N.; Chazot, P.L.; Bao, A.M.; Swaab, D.F. Alterations in the histaminergic system in the substantia nigra and striatum of Parkinson’s patients: A postmortem study. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 1488.e1–1488.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, S.; Lujan, K.S.; Rappaport, E.J.; Valenzuela, C.F.; Savage, D.D. Effect of moderate prenatal ethanol exposure on the differential expression of two histamine H3 receptor isoforms in different brain regions of adult rat offspring. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1192096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, E.A.; Hill, S.J. Sensitivity of histamine H3 receptor agonist-stimulated [35S]GTP gamma[S] binding to pertussis toxin. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 296, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, A.; Raimondi, F.; Kadji, F.M.N.; Singh, G.; Kishi, T.; Uwamizu, A.; Ono, Y.; Shinjo, Y.; Ishida, S.; Arang, N.; et al. Illuminating G-Protein-Coupling Selectivity of GPCRs. Cell 2019, 177, 1933–1947.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schihada, H.; Shekhani, R.; Schulte, G. Quantitative assessment of constitutive G protein-coupled receptor activity with BRET-based G protein biosensors. Sci. Signal 2021, 14, eabf1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouleau, A.; Ligneau, X.; Tardivel-Lacombe, J.; Morisset, S.; Gbahou, F.; Schwartz, J.C.; Arrang, J.M. Histamine H3-receptor-mediated [35S]GTP gamma[S] binding: Evidence for constitutive activity of the recombinant and native rat and human H3 receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 135, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallmen, T.; Lozada, A.F.; Anichtchik, O.V.; Beckman, A.L.; Leurs, R.; Panula, P. Changes in hippocampal histamine receptors across the hibernation cycle in ground squirrels. Hippocampus 2003, 13, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schihada, H.; Ma, X.; Zabel, U.; Vischer, H.F.; Schulte, G.; Leurs, R.; Pockes, S.; Lohse, M.J. Development of a Conformational Histamine H(3) Receptor Biosensor for the Synchronous Screening of Agonists and Inverse Agonists. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 1734–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Dekker, M.E.; Leurs, R.; Vischer, H.F. Pharmacological characterization of seven human histamine H(3) receptor isoforms. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 968, 176450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.N.; Imhaouran, F.; Leurs, R.; Christopoulos, A.; Valant, C.; Langmead, C.J. Ligand-directed biased agonism at human histamine H(3) receptor isoforms across Galpha(i/o)- and beta-arrestin2-mediated pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.N.; McNaught-Flores, D.A.; Huppelschoten, Y.; da Costa Pereira, D.; Christopoulos, A.; Leurs, R.; Langmead, C.J. Structural and Molecular Determinants for Isoform Bias at Human Histamine H(3) Receptor Isoforms. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staus, D.P.; Strachan, R.T.; Manglik, A.; Pani, B.; Kahsai, A.W.; Kim, T.H.; Wingler, L.M.; Ahn, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Masoudi, A.; et al. Allosteric nanobodies reveal the dynamic range and diverse mechanisms of G-protein-coupled receptor activation. Nature 2016, 535, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahlholm, K.; Nilsson, J.; Marcellino, D.; Fuxe, K.; Arhem, P. Voltage sensitivities and deactivation kinetics of histamine H(3) and H(4) receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 3081–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Tang, X.; Wen, X.; Cheng, S.; Xiao, P.; Zang, S.K.; Shen, D.D.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Molecular Determinant Underlying Selective Coupling of Primary G-Protein by Class A GPCRs. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2310120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesteros, J.A.; Jensen, A.D.; Liapakis, G.; Rasmussen, S.G.; Shi, L.; Gether, U.; Javitch, J.A. Activation of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor involves disruption of an ionic lock between the cytoplasmic ends of transmembrane segments 3 and 6. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 29171–29177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Segura, M.A.; Zarzycka, B.; Vischer, H.F.; Leurs, R. Analysis of Missense Variants in the Human Histamine Receptor Family Reveals Increased Constitutive Activity of E410(6.30x30)K Variant in the Histamine H(1) Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Zidek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betke, K.M.; Wells, C.A.; Hamm, H.E. GPCR mediated regulation of synaptic transmission. Prog. Neurobiol. 2012, 96, 304–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurawski, Z.; Yim, Y.Y.; Alford, S.; Hamm, H.E. The expanding roles and mechanisms of G protein-mediated presynaptic inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proft, J.; Weiss, N. G protein regulation of neuronal calcium channels: Back to the future. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 87, 890–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolphin, A.C.; Lee, A. Presynaptic calcium channels: Specialized control of synaptic neurotransmitter release. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 21, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshita, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Sakata, T.; Munakata, M.; Ishibashi, H.; Akaike, N. Histamine modulates high-voltage-activated calcium channels in neurons dissociated from the rat tuberomammillary nucleus. Neuroscience 1998, 87, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Li, M.; Yan, Y.; Qian, T.; Lin, Y.; Ma, X.; Vischer, H.F.; Liu, C.; Li, G.; Wang, H.; et al. Genetically encoded sensors for measuring histamine release both in vitro and in vivo. Neuron 2023, 111, 1564–1576.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrey, C.; Estephan, R.; Abbott, G.W.; Levi, R. Cardioprotective effect of histamine H3-receptor activation: Pivotal role of G beta gamma-dependent inhibition of voltage-operated Ca2+ channels. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 326, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedi, N.; Mackins, C.J.; Machida, T.; Reid, A.C.; Silver, R.B.; Levi, R. Histamine H3-receptor-induced attenuation of norepinephrine exocytosis: A decreased protein kinase a activity mediates a reduction in intracellular calcium. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 312, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeremic, D.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, I.; Jimenez-Diaz, L.; Navarro-Lopez, J.D. Therapeutic potential of targeting G protein-gated inwardly rectifying potassium (GIRK) channels in the central nervous system. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 223, 107808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Vázquez, H.; Gonzalez-Sandoval, C.; Vega, A.V.; Arias-Montaño, J.-A.; Barral, J. Histamine H3 Receptor Activation Modulates Glutamate Release in the Corticostriatal Synapse by Acting at CaV2.1 (P/Q-Type) Calcium Channels and GIRK (KIR3) Potassium Channels. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 42, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, R.; Seyedi, N.; Schaefer, U.; Estephan, R.; Mackins, C.J.; Tyler, E.; Silver, R.B. Histamine H3-receptor signaling in cardiac sympathetic nerves: Identification of a novel MAPK-PLA2-COX-PGE2-EP3R pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starke, K.; Gothert, M.; Kilbinger, H. Modulation of neurotransmitter release by presynaptic autoreceptors. Physiol. Rev. 1989, 69, 864–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerink, B.H.; Cremers, T.I.; De Vries, J.B.; Liefers, H.; Tran, N.; De Boer, P. Evidence for activation of histamine H3 autoreceptors during handling stress in the prefrontal cortex of the rat. Synapse 2002, 43, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hu, J.; Chen, Z.; Meng, J.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.; Luo, X. Evidence for histamine as a neurotransmitter in the cardiac sympathetic nervous system. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, H45–H51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundvik, M.; Kudo, H.; Toivonen, P.; Rozov, S.; Chen, Y.C.; Panula, P. The histaminergic system regulates wakefulness and orexin/hypocretin neuron development via histamine receptor H1 in zebrafish. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 4338–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves-Rodrigues, A.; Timmerman, H.; Willems, E.; Lemstra, S.; Zuiderveld, O.P.; Leurs, R. Pharmacological characterisation of the histamine H3 receptor in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 1998, 788, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuder, H.; Muscholl, E. Heteroreceptor-mediated modulation of noradrenaline and acetylcholine release from peripheral nerves. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 126, 265–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlicker, E.; Werthwein, S.; Zentner, J. Histamine H3 receptor-mediated inhibition of noradrenaline release in the human brain. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 13, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlicker, E.; Malinowska, B.; Kathmann, M.; Gothert, M. Modulation of neurotransmitter release via histamine H3 heteroreceptors. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 1994, 8, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlicker, E.; Behling, A.; Lummen, G.; Gothert, M. Histamine H3A receptor-mediated inhibition of noradrenaline release in the mouse brain cortex. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1992, 345, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlicker, E.; Fink, K.; Hinterthaner, M.; Gothert, M. Inhibition of noradrenaline release in the rat brain cortex via presynaptic H3 receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1989, 340, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, R.P.; Mulder, A.H. Inhibitory effects of histamine on the release of serotonin and noradrenaline from rat brain slices. Neurochem. Int. 1991, 18, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, S.; Sperelakis, N. A novel class (H3) of histamine receptors on perivascular nerve terminals. Nature 1987, 327, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlicker, E.; Betz, R.; Gothert, M. Histamine H3 receptor-mediated inhibition of serotonin release in the rat brain cortex. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1988, 337, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, K.; Schlicker, E.; Neise, A.; Gothert, M. Involvement of presynaptic H3 receptors in the inhibitory effect of histamine on serotonin release in the rat brain cortex. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1990, 342, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlicker, E.; Fink, K.; Detzner, M.; Gothert, M. Histamine inhibits dopamine release in the mouse striatum via presynaptic H3 receptors. J. Neural Transm. Gen. Sect. 1993, 93, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Montano, J.A.; Floran, B.; Garcia, M.; Aceves, J.; Young, J.M. Histamine H(3) receptor-mediated inhibition of depolarization-induced, dopamine D(1) receptor-dependent release of [(3)H]-gamma-aminobutryic acid from rat striatal slices. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 133, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, T.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Huang, Z. UK-14,304, R(-)-alpha-methyl-histamine and SMS 201-995 block plasma protein leakage within dura mater by prejunctional mechanisms. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 224, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadou, V.; Rouleau, A.; Trung Tuong, M.D.; Newlands, G.J.; Miller, H.R.; Luffau, G.; Schwartz, J.C.; Garbarg, M. Functional relationships between sensory nerve fibers and mast cells of dura mater in normal and inflammatory conditions. Neuroscience 1997, 77, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Ramirez, J.; Ortiz, J.; Blanco, I. Presynaptic H3 autoreceptors modulate histamine synthesis through cAMP pathway. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 61, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrent, A.; Moreno-Delgado, D.; Gomez-Ramirez, J.; Rodriguez-Agudo, D.; Rodriguez-Caso, C.; Sanchez-Jimenez, F.; Blanco, I.; Ortiz, J. H3 autoreceptors modulate histamine synthesis through calcium/calmodulin- and cAMP-dependent protein kinase pathways. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbahou, F.; Rouleau, A.; Arrang, J.M. The histamine autoreceptor is a short isoform of the H(3) receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 1860–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, G.S.; Olivas, N.D.; Ikrar, T.; Sanathara, N.M.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Civelli, O.; Xu, X. Histamine inhibits the melanin-concentrating hormone system: Implications for sleep and arousal. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 2183–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.W.; Xu, J.J.; Zhao, Y.; LeDoux, M.S.; Zhou, F.M. Opposite functions of histamine H1 and H2 receptors and H3 receptor in substantia nigra pars reticulata. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 96, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundius, E.G.; Sanchez-Alavez, M.; Ghochani, Y.; Klaus, J.; Tabarean, I.V. Histamine influences body temperature by acting at H1 and H3 receptors on distinct populations of preoptic neurons. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 4369–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, J.; Sanchez-Alavez, M.; Tabarean, I.V. Kv4.2 mediates histamine modulation of preoptic neuron activity and body temperature. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Fan, L.; Fang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Z.; et al. Postsynaptic histamine H3 receptors in ventral basal forebrain cholinergic neurons modulate contextual fear memory. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ma, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H.; Jiang, S. Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist Enhances Neurogenesis and Improves Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion-Induced Cognitive Impairments. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Ye, L.; Liao, Y.; Jin, L.; Ma, Q.; Lu, B.; Sun, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, N. Agonist-induced activation of histamine H3 receptor signals to extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 through PKC-, PLD-, and EGFR-dependent mechanisms. J. Neurochem. 2016, 137, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariottini, C.; Scartabelli, T.; Bongers, G.; Arrigucci, S.; Nosi, D.; Leurs, R.; Chiarugi, A.; Blandina, P.; Pellegrini-Giampietro, D.E.; Passani, M.B. Activation of the histaminergic H3 receptor induces phosphorylation of the Akt/GSK-3 beta pathway in cultured cortical neurons and protects against neurotoxic insults. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongers, G.; Sallmen, T.; Passani, M.B.; Mariottini, C.; Wendelin, D.; Lozada, A.; Marle, A.; Navis, M.; Blandina, P.; Bakker, R.A.; et al. The Akt/GSK-3beta axis as a new signaling pathway of the histamine H(3) receptor. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Hernandez, A.; Nunez, A.; Arias-Montano, J.A. Histamine H3-receptor activation inhibits dopamine synthesis in rat striatum. Neuroreport 2000, 11, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Hernandez, A.; Nunez, A.; Sierra, J.J.; Arias-Montano, J.A. Histamine H3 receptor activation inhibits glutamate release from rat striatal synaptosomes. Neuropharmacology 2001, 41, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, E.; Hoffmann, H.; Gonzalez-Sepulveda, M.; Navarro, G.; Casado, V.; Cortes, A.; Mallol, J.; Vignes, M.; McCormick, P.J.; Canela, E.I.; et al. Dopamine D1-histamine H3 receptor heteromers provide a selective link to MAPK signaling in GABAergic neurons of the direct striatal pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 5846–5854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Pittenger, C. The histamine H3 receptor modulates dopamine D2 receptor-dependent signaling pathways and mouse behaviors. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, E.; Moreno-Delgado, D.; Navarro, G.; Hoffmann, H.M.; Fuentes, S.; Rosell-Vilar, S.; Gasperini, P.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.; Medrano, M.; Mallol, J.; et al. Cocaine disrupts histamine H3 receptor modulation of dopamine D1 receptor signaling: Sigma1-D1-H3 receptor complexes as key targets for reducing cocaine’s effects. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 3545–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Delgado, D.; Puigdellivol, M.; Moreno, E.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.; Botta, J.; Gasperini, P.; Chiarlone, A.; Howell, L.A.; Scarselli, M.; Casado, V.; et al. Modulation of dopamine D(1) receptors via histamine H(3) receptors is a novel therapeutic target for Huntington’s disease. Elife 2020, 9, e51093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrada, C.; Ferre, S.; Casado, V.; Cortes, A.; Justinova, Z.; Barnes, C.; Canela, E.I.; Goldberg, S.R.; Leurs, R.; Lluis, C.; et al. Interactions between histamine H3 and dopamine D2 receptors and the implications for striatal function. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrada, C.; Moreno, E.; Casado, V.; Bongers, G.; Cortes, A.; Mallol, J.; Canela, E.I.; Leurs, R.; Ferre, S.; Lluis, C.; et al. Marked changes in signal transduction upon heteromerization of dopamine D1 and histamine H3 receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, N.C.; Johnstone, E.K.M.; Pfleger, K.D.G. GPCR heteromers: An overview of their classification, function and physiological relevance. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 931573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferre, S.; Casado, V.; Devi, L.A.; Filizola, M.; Jockers, R.; Lohse, M.J.; Milligan, G.; Pin, J.P.; Guitart, X. G protein-coupled receptor oligomerization revisited: Functional and pharmacological perspectives. Pharmacol. Rev. 2014, 66, 413–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.; Moreno, E.; Moreno-Delgado, D.; Navarro, G.; Mallol, J.; Cortes, A.; Lluis, C.; Canela, E.I.; Casado, V.; McCormick, P.J.; et al. Heteroreceptor Complexes Formed by Dopamine D(1), Histamine H(3), and N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Glutamate Receptors as Targets to Prevent Neuronal Death in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 4537–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Gomez, R.; Robins, M.T.; Gutierrez-Rodelo, C.; Arias, J.M.; Olivares-Reyes, J.A.; van Rijn, R.M.; Arias-Montano, J.A. Functional histamine H(3) and adenosine A(2A) receptor heteromers in recombinant cells and rat striatum. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 129, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Figueroa, G.E.; Rivera-Ramirez, N.; Gonzalez-Pantoja, R.; Escamilla-Sanchez, J.; Garcia-Hernandez, U.; Galvan, E.J.; Arias-Montano, J.A. Adenosine A(2A) and histamine H(3) receptors interact at the cAMP/PKA pathway to modulate depolarization-evoked [(3)H]-GABA release from rat striato-pallidal terminals. Purinergic Signal. 2019, 15, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khamlichi, C.; Cobret, L.; Arrang, J.M.; Morisset-Lopez, S. BRET Analysis of GPCR Dimers in Neurons and Non-Neuronal Cells: Evidence for Inactive, Agonist, and Constitutive Conformations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coge, F.; Guenin, S.P.; Renouard-Try, A.; Rique, H.; Ouvry, C.; Fabry, N.; Beauverger, P.; Nicolas, J.P.; Galizzi, J.P.; Boutin, J.A.; et al. Truncated isoforms inhibit [3H]prazosin binding and cellular trafficking of native human alpha1A-adrenoceptors. Biochem. J. 1999, 343 Pt 1, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wess, J.; Oteng, A.B.; Rivera-Gonzalez, O.; Gurevich, E.V.; Gurevich, V.V. beta-Arrestins: Structure, Function, Physiology, and Pharmacological Perspectives. Pharmacol. Rev. 2023, 75, 854–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, O.; Haider, R.S.; Sanchez, J.; Canals, M. Arrestin-centred interactions at the membrane and their conformational determinants. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2024. online version of record. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Garcia, C.; Morales, L.; Alguacil, L.F. Histamine H3 receptor desensitization in the guinea-pig ileum. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 341, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garduno-Torres, B.; Arias-Montano, J.A. Homologous down-regulation of histamine H3 receptors in rat striatal slices. Synapse 2006, 60, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio-Espinoza, A.; Escamilla-Sanchez, J.; Aquino-Jarquin, G.; Arias-Montano, J.A. Homologous desensitization of human histamine H(3) receptors expressed in CHO-K1 cells. Neuropharmacology 2014, 77, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Galvez, A.M.; Escamilla-Sanchez, J.; Flores-Maldonado, C.; Contreras, R.G.; Arias, J.M.; Arias-Montano, J.A. Differential homologous desensitization of the human histamine H(3) receptors of 445 and 365 amino acids expressed in CHO-K1 cells. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 112, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montejo-Lopez, W.; Rivera-Ramirez, N.; Escamilla-Sanchez, J.; Garcia-Hernandez, U.; Arias-Montano, J.A. Heterologous, PKC-Mediated Desensitization of Human Histamine H3 Receptors Expressed in CHO-K1 Cells. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 2415–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddy, D.M.; Cook, A.E.; Diepenhorst, N.A.; Bosnyak, S.; Brady, R.; Mannoury la Cour, C.; Mocaer, E.; Summers, R.J.; Charman, W.N.; Sexton, P.M.; et al. Isoform-Specific Biased Agonism of Histamine H3 Receptor Agonists. Mol. Pharmacol. 2017, 91, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giros, B.; Sokoloff, P.; Martres, M.P.; Riou, J.F.; Emorine, L.J.; Schwartz, J.C. Alternative splicing directs the expression of two D2 dopamine receptor isoforms. Nature 1989, 342, 923–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Y.; Liu, Z.C.; Sun, Y.G.; Ross, M.; Kim, S.; Tsai, F.F.; Li, Q.F.; Jeffry, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Loh, H.H.; et al. Unidirectional cross-activation of GRPR by MOR1D uncouples itch and analgesia induced by opioids. Cell 2011, 147, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Liu, N.J.; Gintzler, A.R. Relevance of Mu-Opioid Receptor Splice Variants and Plasticity of Their Signaling Sequelae to Opioid Analgesic Tolerance. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 41, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piltonen, M.; Parisien, M.; Gregoire, S.; Chabot-Dore, A.J.; Jafarnejad, S.M.; Berube, P.; Djambazian, H.; Sladek, R.; Geneau, G.; Willett, P.; et al. Alternative Splicing of the Delta-Opioid Receptor Gene Suggests Existence of New Functional Isoforms. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2855–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Transmitter | Species | Tissue | Pathway | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histamine | Human | Neocortex | ↓AC, ↓cAMP | [94] |
| Mouse | Neocortex | [37] | ||
| Rat | Neocortex | [37,94,95] | ||
| Guinea pig | Cardiac synaptosomes | [96] | ||
| Hamster | Hypothalamus | [34] | ||
| Zebrafish | Hypothalamus | [97] | ||
| Acetylcholine | Rat | Cortex | ↓VGCC | [50,98] |
| Guinea pig | Ileum | [99] | ||
| Noradrenaline | Human | Neocortex | [100] | |
| Mouse | Neocortex | [101,102] | ||
| Rat | Neocortex | [103,104] | ||
| Guinea pig | Cardiac synaptosomes | ↓AC/↓PKA/↓VGCC; ↑MAPK/↑PLA2/↑PEG2/↑EP3R/↓VGCC | [90,93] | |
| Serotonin | Guinea pig | Mesenteric artery | ↓PKA/↓VGCC | [105] |
| Rat | Neocortex | ↓AC, ↓cAMP | [104,106,107] | |
| Dopamine | Mouse | Striatum | ↓AC, ↓cAMP | [108] |
| Glutamate | Rat | Striatum | ↑GIRK, ↓VGCC | [92] |
| GABA | Rat | Striatum | ↓AC, ↓cAMP ↓PKA/↓VGCC | [109] |
| Neuropeptides | Rat | Dura mater | ↓AC, ↓cAMP ↓PKA/↓VGCC | [110,111] |
| Guinea pig | Dura mater | [110] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, M.; Ooms, J.F.; Leurs, R.; Vischer, H.F. Histamine H3 Receptor Isoforms: Insights from Alternative Splicing to Functional Complexity. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070761
Gao M, Ooms JF, Leurs R, Vischer HF. Histamine H3 Receptor Isoforms: Insights from Alternative Splicing to Functional Complexity. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(7):761. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070761
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Meichun, Jasper F. Ooms, Rob Leurs, and Henry F. Vischer. 2024. "Histamine H3 Receptor Isoforms: Insights from Alternative Splicing to Functional Complexity" Biomolecules 14, no. 7: 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070761
APA StyleGao, M., Ooms, J. F., Leurs, R., & Vischer, H. F. (2024). Histamine H3 Receptor Isoforms: Insights from Alternative Splicing to Functional Complexity. Biomolecules, 14(7), 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070761







