Screening of Secretory Proteins Linking Major Depressive Disorder with Heart Failure Based on Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis and Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
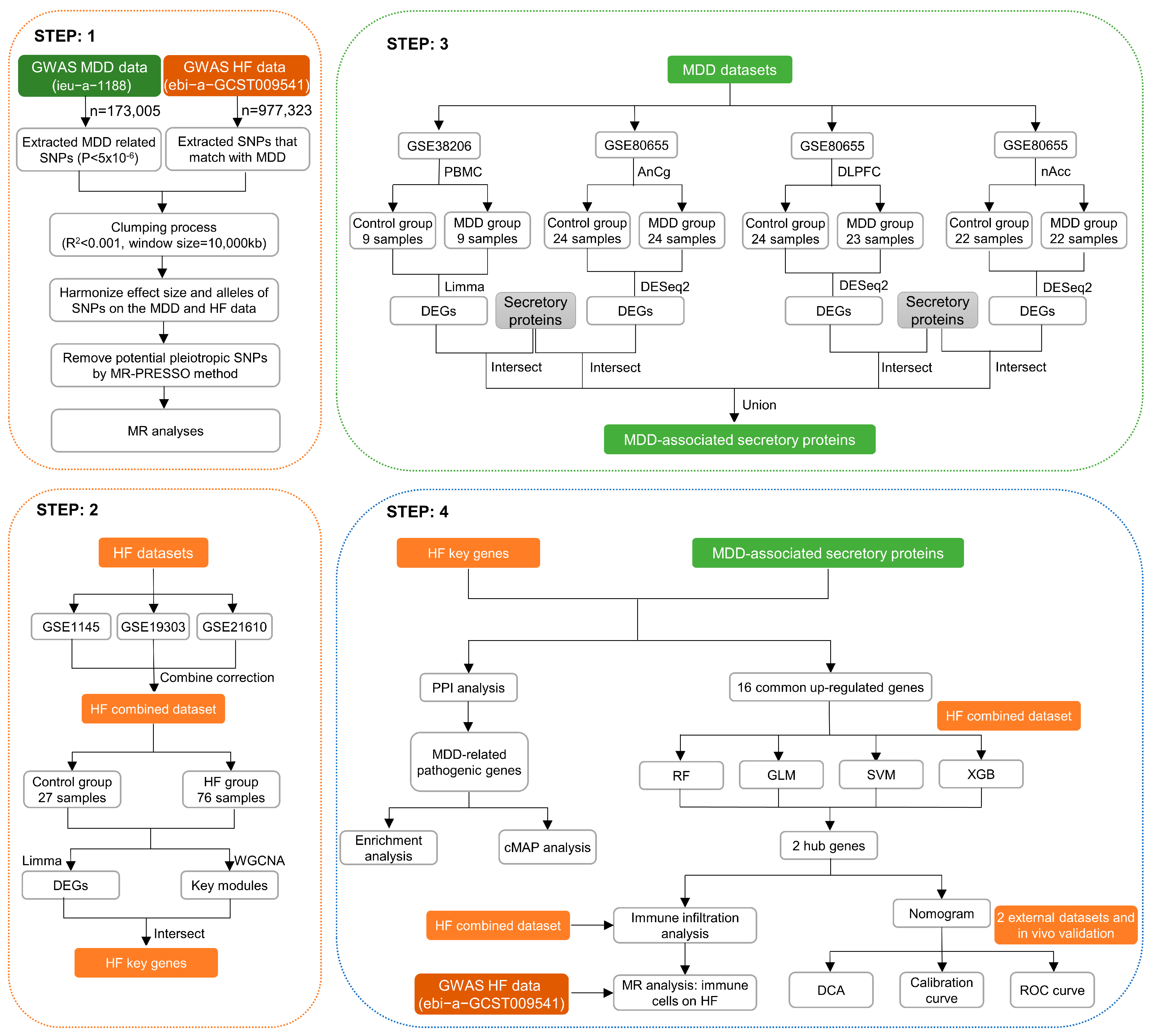
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MR Analysis of the Effect of MDD on HF
2.1.1. Instrumental Variable (IV) Selection Criteria
2.1.2. MR Analysis
2.1.3. Sensitivity Analysis
2.2. Expression Data Collection and Processing
2.3. Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) Analysis
2.4. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) and Key Module Gene Identification
2.5. Secretory Proteins Acquisition
2.6. The Construction of Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
2.7. Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.8. Connectivity Map (cMAP) Analysis
2.9. ML Algorithms for the Screening of HF Biomarkers in MDD
2.10. The Construction and Assessment of Diagnostic Model for HF
2.11. External Verification of Hub Genes Expression Pattern and Diagnostic Efficacy
2.12. Immune Cell Infiltration Measurement
2.13. MR Analysis of 731 Immune Cell Signatures on HF
2.14. In Vivo Experimental Protocols
2.15. Verification of the Expression of Hub Genes between Control and HF Groups
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
3.1. MR Analysis of MDD on HF
3.2. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes in HF
3.3. The Construction of the Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network and the Identification of Key Modules in HF
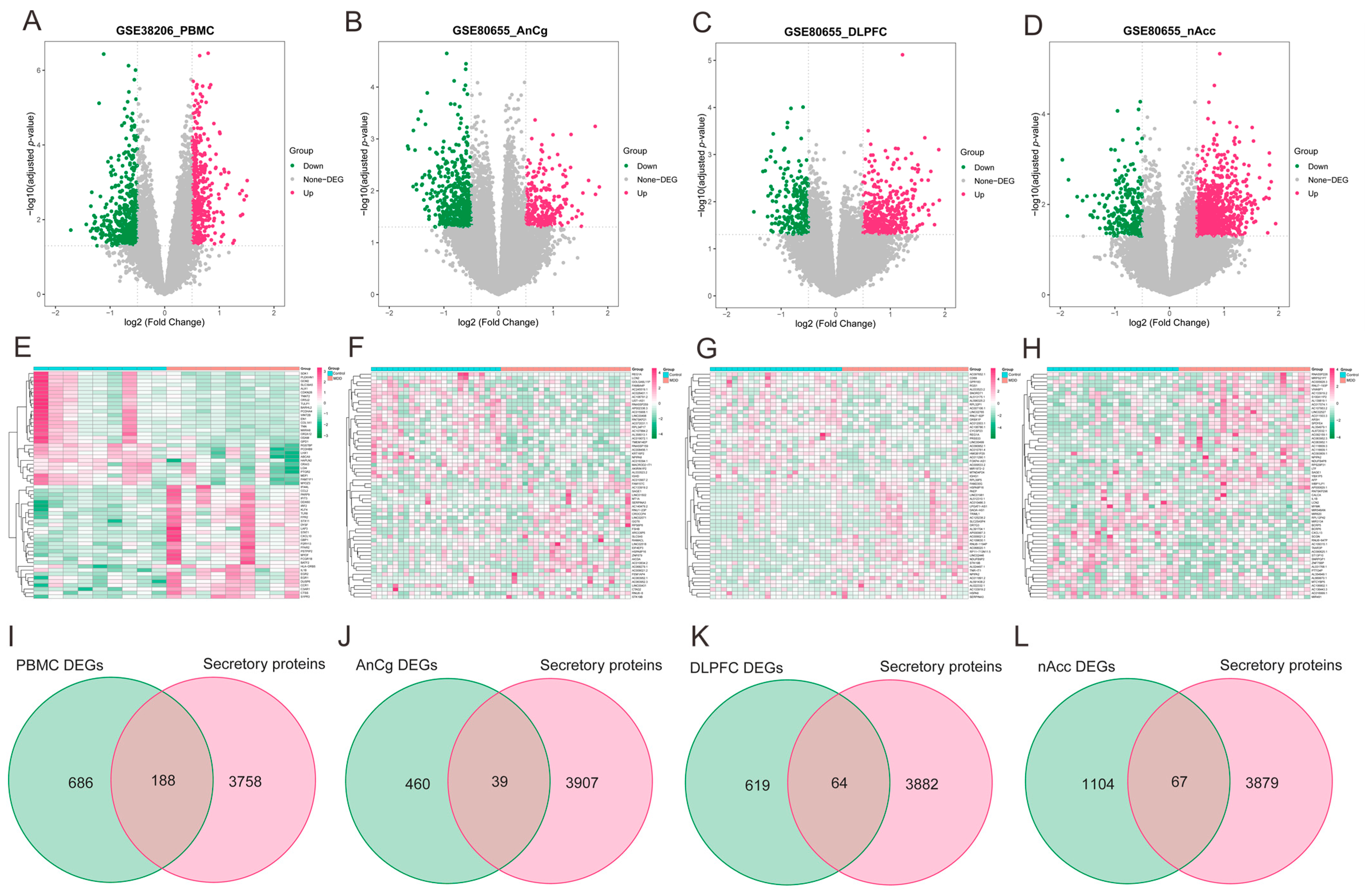
3.4. Identification of Differentially Expressed Secretory Proteins in MDD
3.5. Protein–Protein Interaction Network and Functional Enrichment and Drug Screening of the Pathogenic Genes Involved in MDD-Related HF
3.6. Screening of Hub Genes Harboring Diagnostic Value via ML and Development of a Diagnostic Model for MDD-Related HF
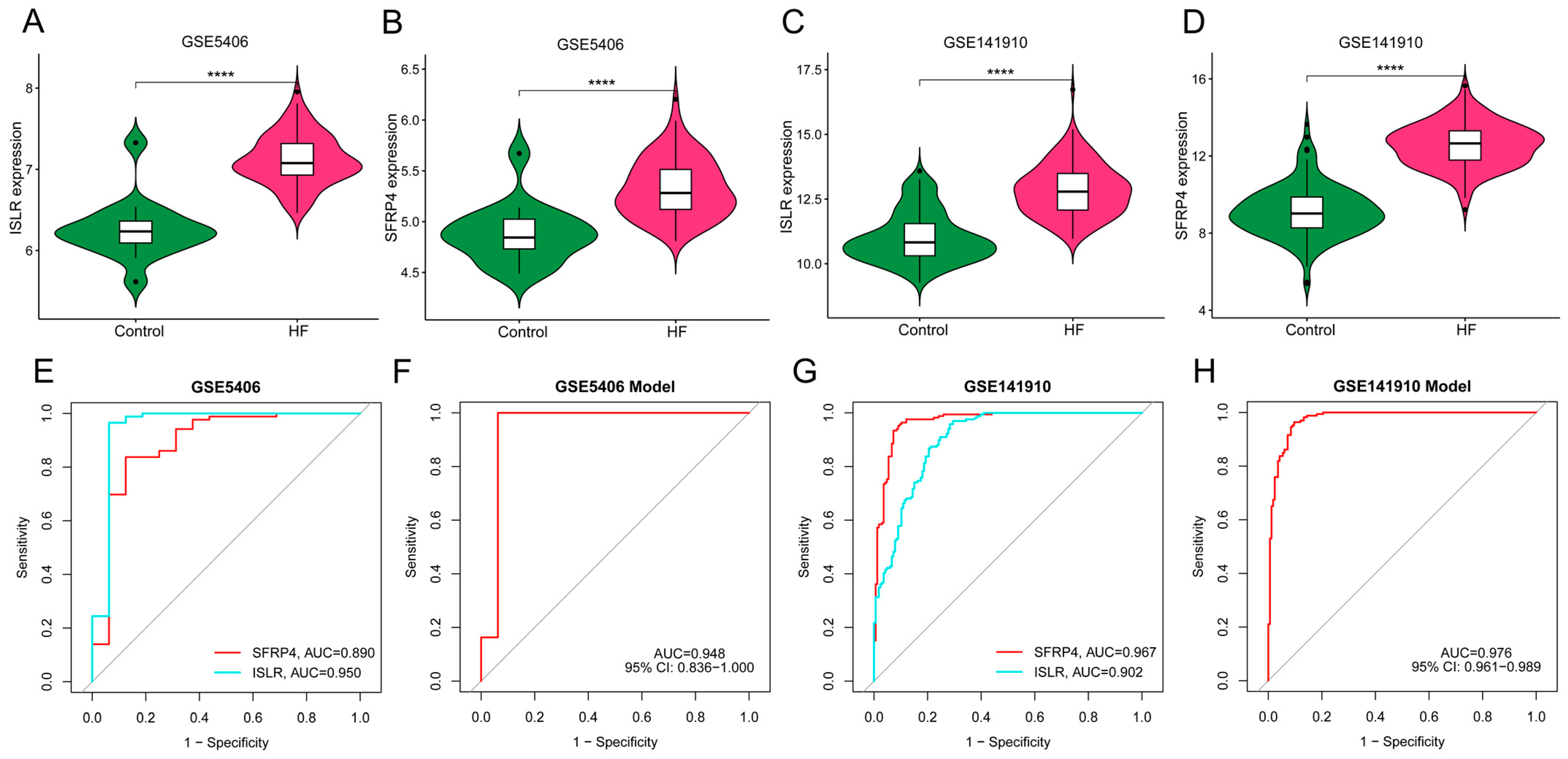
3.7. External Verification of Hub Genes Expression Pattern and Diagnostic Efficacy
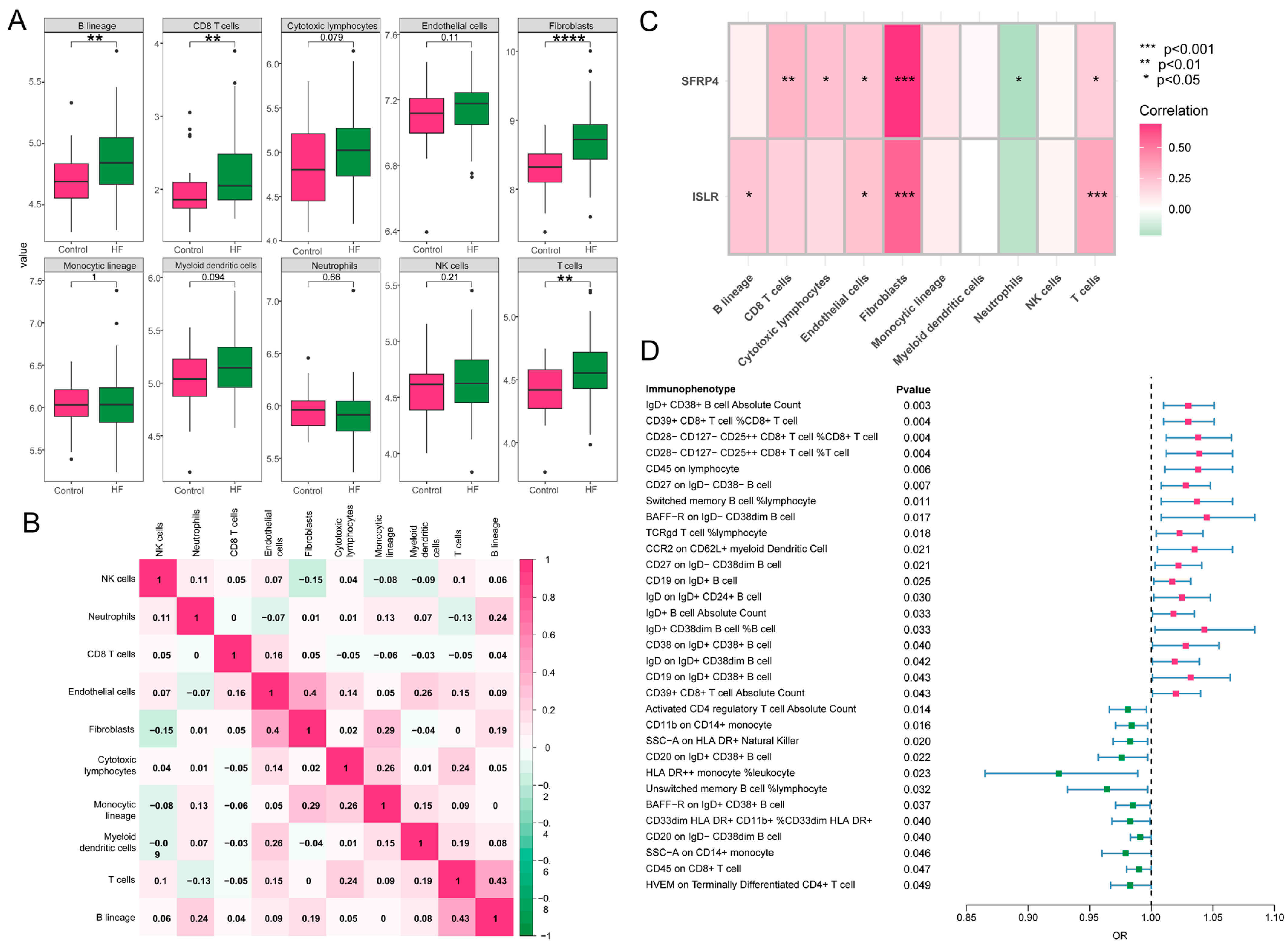
3.8. Immune Cell Infiltration and MR Analysis of 731 Immune Cell Signatures on HF
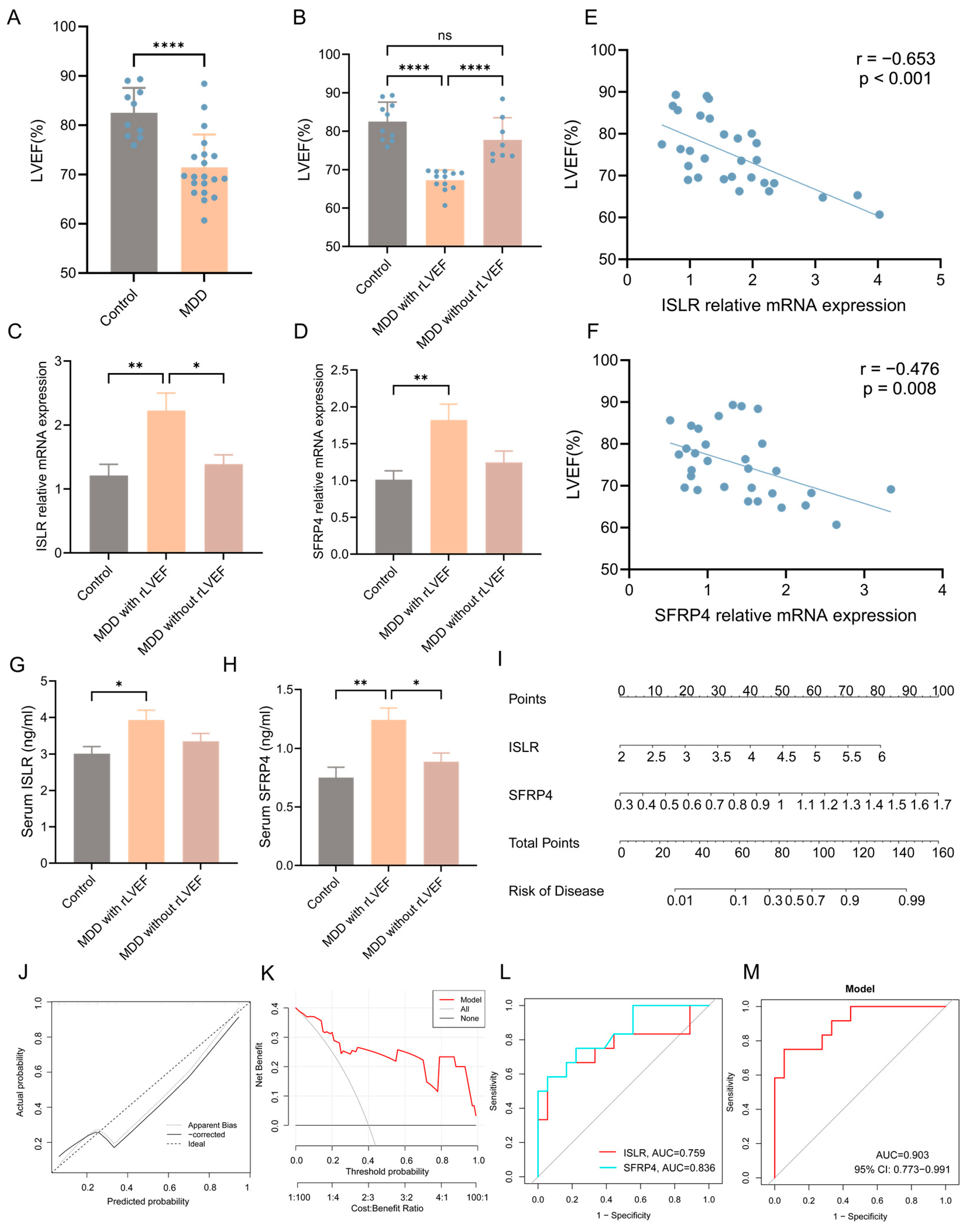
3.9. Validation of the Expression Pattern of Two Hub Genes and Evaluation of the Diagnostic Value of the Nomogram Model
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diseases, G.B.D.; Injuries, C. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, S.M.; Harkness, K.L. Major Depression and Its Recurrences: Life Course Matters. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2022, 18, 329–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; He, H.; Yang, J.; Feng, X.; Zhao, F.; Lyu, J. Changes in the global burden of depression from 1990 to 2017: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 126, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Bohm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Celutkiene, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustad, L.T.; Laugsand, L.E.; Janszky, I.; Dalen, H.; Bjerkeset, O. Symptoms of anxiety and depression and risk of heart failure: The HUNT Study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2014, 16, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garfield, L.D.; Scherrer, J.F.; Hauptman, P.J.; Freedland, K.E.; Chrusciel, T.; Balasubramanian, S.; Carney, R.M.; Newcomer, J.W.; Owen, R.; Bucholz, K.K.; et al. Association of anxiety disorders and depression with incident heart failure. Psychosom. Med. 2014, 76, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogilvie, R.P.; Everson-Rose, S.A.; Longstreth, W.T., Jr.; Rodriguez, C.J.; Diez-Roux, A.V.; Lutsey, P.L. Psychosocial Factors and Risk of Incident Heart Failure: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Circ. Heart Fail. 2016, 9, e002243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokoreli, I.; de Vries, J.J.G.; Pauws, S.C.; Steyerberg, E.W. Depression and anxiety as predictors of mortality among heart failure patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Fail. Rev. 2016, 21, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelborg, K.; Schmidt, M.; Sundboll, J.; Pedersen, L.; Videbech, P.; Botker, H.E.; Egstrup, K.; Sorensen, H.T. Mortality Risk among Heart Failure Patients with Depression: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e004137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladwig, K.H.; Baghai, T.C.; Doyle, F.; Hamer, M.; Herrmann-Lingen, C.; Kunschitz, E.; Lemogne, C.; Beresnevaite, M.; Compare, A.; von Kanel, R.; et al. Mental health-related risk factors and interventions in patients with heart failure: A position paper endorsed by the European Association of Preventive Cardiology (EAPC). Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022, 29, 1124–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, E.; Shu, X.; Xu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guan, H.; Zhong, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.Z.; et al. Screening of immune-related secretory proteins linking chronic kidney disease with calcific aortic valve disease based on comprehensive bioinformatics analysis and machine learning. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hare, D.L.; Toukhsati, S.R.; Johansson, P.; Jaarsma, T. Depression and cardiovascular disease: A clinical review. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Shi, X.Q.; Shui, J.W.; Liu, X.Y.; Bu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yin, L.P. Exploring the causal factor effects of hypothyroidism on ischemic stroke: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1322472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, C.; Chen, Z.; Chai, Y.; Liu, P.; Yu, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Assessing the relationship between gut microbiota and endometriosis: A bidirectional two-sample mendelian randomization analysis. BMC Womens Health 2024, 24, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, D.; Zuo, X.; Yao, L.; Liu, T.; Ge, X.; He, C.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, Z. Causal role of immune cells in schizophrenia: Mendelian randomization (MR) study. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willner, P. The chronic mild stress (CMS) model of depression: History, evaluation and usage. Neurobiol. Stress 2017, 6, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penninx, B.W. Depression and cardiovascular disease: Epidemiological evidence on their linking mechanisms. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 74, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Kooy, K.; van Hout, H.; Marwijk, H.; Marten, H.; Stehouwer, C.; Beekman, A. Depression and the risk for cardiovascular diseases: Systematic review and meta analysis. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2007, 22, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, A.; Kuper, H.; Hemingway, H. Depression as an aetiologic and prognostic factor in coronary heart disease: A meta-analysis of 6362 events among 146 538 participants in 54 observational studies. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 2763–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bauersachs, J.; Langer, H.F. Immune mechanisms in heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasubramanian, N.; Coker, M.L.; Kurrelmeyer, K.M.; MacLellan, W.R.; DeMayo, F.J.; Spinale, F.G.; Mann, D.L. Left ventricular remodeling in transgenic mice with cardiac restricted overexpression of tumor necrosis factor. Circulation 2001, 104, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartupee, J.; Mann, D.L. Positioning of inflammatory biomarkers in the heart failure landscape. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2013, 6, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.A.; Yang, D.; Zhu, W.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.A.; Xiang, M. Interleukin-17A mediates cardiomyocyte apoptosis through Stat3-iNOS pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 2784–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, G.L.; Li, D.S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.M.; Li, C.Z.; Li, X.D.; Ma, J.D.; Zhang, M.M.; Lu, Y.J.; et al. Interleukin-17 upregulation participates in the pathogenesis of heart failure in mice via NF-kappaB-dependent suppression of SERCA2a and Cav1.2 expression. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaitre, R.N.; Sitlani, C.; Song, X.; King, I.B.; McKnight, B.; Spiegelman, D.; Sacks, F.M.; Djousse, L.; Rimm, E.B.; Siscovick, D.S.; et al. Circulating and dietary alpha-linolenic acid and incidence of congestive heart failure in older adults: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazaro, I.; Lupon, J.; Cediel, G.; Codina, P.; Fito, M.; Domingo, M.; Santiago-Vacas, E.; Zamora, E.; Sala-Vila, A.; Bayes-Genis, A. Relationship of Circulating Vegetable Omega-3 to Prognosis in Patients with Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 1751–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi Saravi, S.S.; Bonetti, N.R.; Vukolic, A.; Vdovenko, D.; Lee, P.; Liberale, L.; Basso, C.; Rizzo, S.; Akhmedov, A.; Luscher, T.F.; et al. Long-term dietary n3 fatty acid prevents aging-related cardiac diastolic and vascular dysfunction. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2023, 150, 107175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Metra, M.; Lund, L.H.; Milicic, D.; Costanzo, M.R.; Filippatos, G.; Gustafsson, F.; Tsui, S.; Barge-Caballero, E.; De Jonge, N.; et al. Advanced heart failure: A position statement of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 1505–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nag, A.; Gerritsen, A.; Doeppke, C.; Harman-Ware, A.E. Machine Learning-Based Classification of Lignocellulosic Biomass from Pyrolysis-Molecular Beam Mass Spectrometry Data. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, S.; Khan, A.; Hossain, M.E.; Moni, M.A. Comparing different supervised machine learning algorithms for disease prediction. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevers, T.; Salvador, A.M.; Grodecki-Pena, A.; Knapp, A.; Velazquez, F.; Aronovitz, M.; Kapur, N.K.; Karas, R.H.; Blanton, R.M.; Alcaide, P. Left Ventricular T-Cell Recruitment Contributes to the Pathogenesis of Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2015, 8, 776–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallikourdis, M.; Martini, E.; Carullo, P.; Sardi, C.; Roselli, G.; Greco, C.M.; Vignali, D.; Riva, F.; Ormbostad Berre, A.M.; Stolen, T.O.; et al. T cell costimulation blockade blunts pressure overload-induced heart failure. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroumanie, F.; Douin-Echinard, V.; Pozzo, J.; Lairez, O.; Tortosa, F.; Vinel, C.; Delage, C.; Calise, D.; Dutaur, M.; Parini, A.; et al. CD4+ T cells promote the transition from hypertrophy to heart failure during chronic pressure overload. Circulation 2014, 129, 2111–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouggari, Y.; Ait-Oufella, H.; Bonnin, P.; Simon, T.; Sage, A.P.; Guerin, C.; Vilar, J.; Caligiuri, G.; Tsiantoulas, D.; Laurans, L.; et al. B lymphocytes trigger monocyte mobilization and impair heart function after acute myocardial infarction. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero-Reyes, A.M.; Youker, K.A.; Trevino, A.R.; Celis, R.; Hamilton, D.J.; Flores-Arredondo, J.H.; Orrego, C.M.; Bhimaraj, A.; Estep, J.D.; Torre-Amione, G. Full Expression of Cardiomyopathy Is Partly Dependent on B-Cells: A Pathway That Involves Cytokine Activation, Immunoglobulin Deposition, and Activation of Apoptosis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, Z.; Leib, C.; Katus, H.A. Autoantibodies in heart failure and cardiac dysfunction. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Song, Y.; Cen, L.; Huang, C.; Zhou, J.; Lian, J. Screening of Secretory Proteins Linking Major Depressive Disorder with Heart Failure Based on Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis and Machine Learning. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070793
Zhang C, Song Y, Cen L, Huang C, Zhou J, Lian J. Screening of Secretory Proteins Linking Major Depressive Disorder with Heart Failure Based on Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis and Machine Learning. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(7):793. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070793
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chuanjing, Yongfei Song, Lichao Cen, Chen Huang, Jianqing Zhou, and Jiangfang Lian. 2024. "Screening of Secretory Proteins Linking Major Depressive Disorder with Heart Failure Based on Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis and Machine Learning" Biomolecules 14, no. 7: 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070793
APA StyleZhang, C., Song, Y., Cen, L., Huang, C., Zhou, J., & Lian, J. (2024). Screening of Secretory Proteins Linking Major Depressive Disorder with Heart Failure Based on Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis and Machine Learning. Biomolecules, 14(7), 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070793





