Evolutionary Dynamics of Satellite DNA Repeats across the Tettigoniidae Family: Insights from Genomic Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection, Next-Generation Sequencing, and NCBI Data Retrieval
2.2. Pre-Processing of the Genomic Data
2.3. RepeatExplorer2 and TAREAN Clustering Analysis
2.4. Satellite DNA Homology Search and RepeatMasker Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Repetitive Sequences Composition and Distribution
3.2. Satellite DNA Repeat Diversity in Family Tettigoniidae
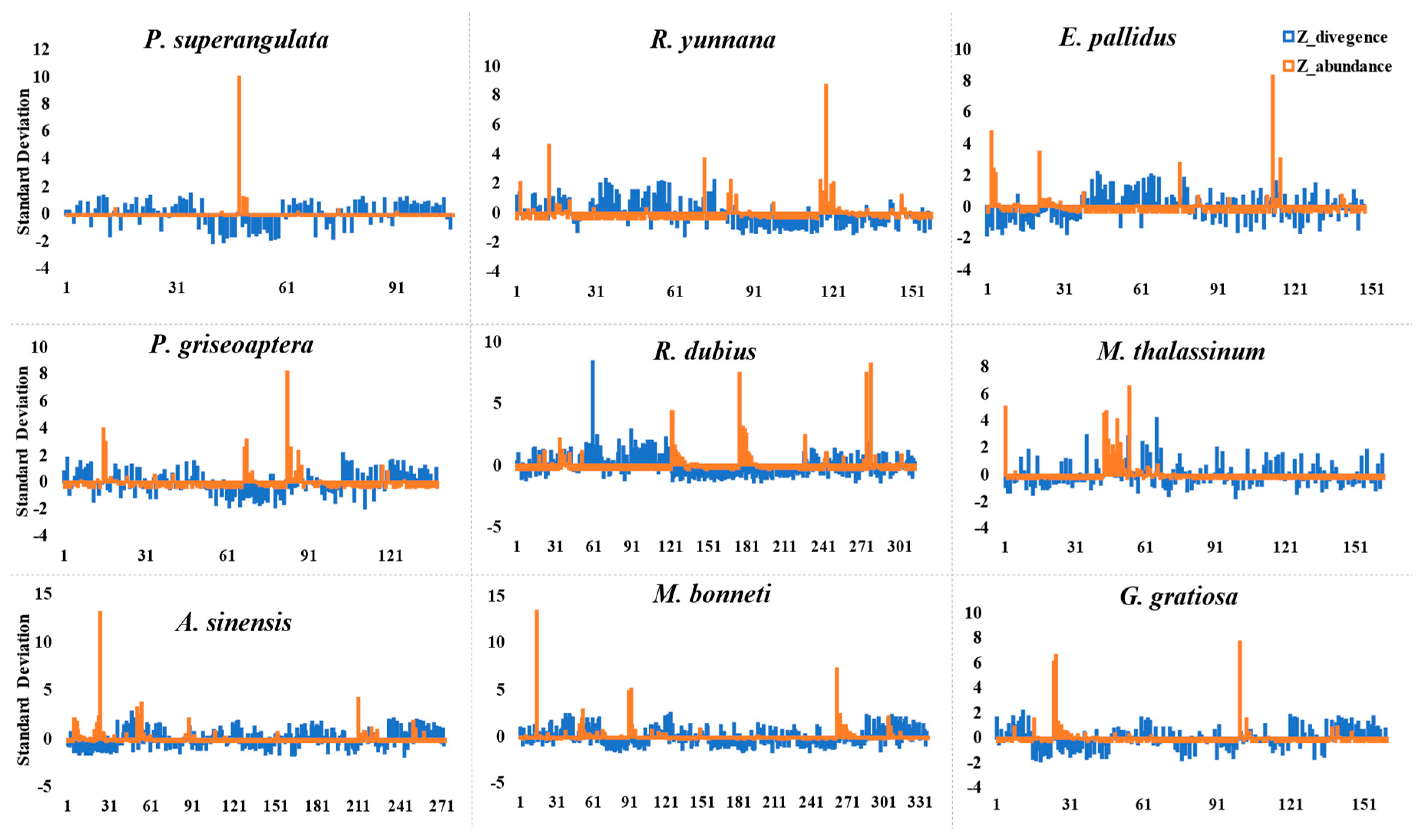
3.3. Satellite DNA Gain and Loss in Family Tettigoniidae
3.4. Satellitome Landscape of Species of the Tettigoniidae Family
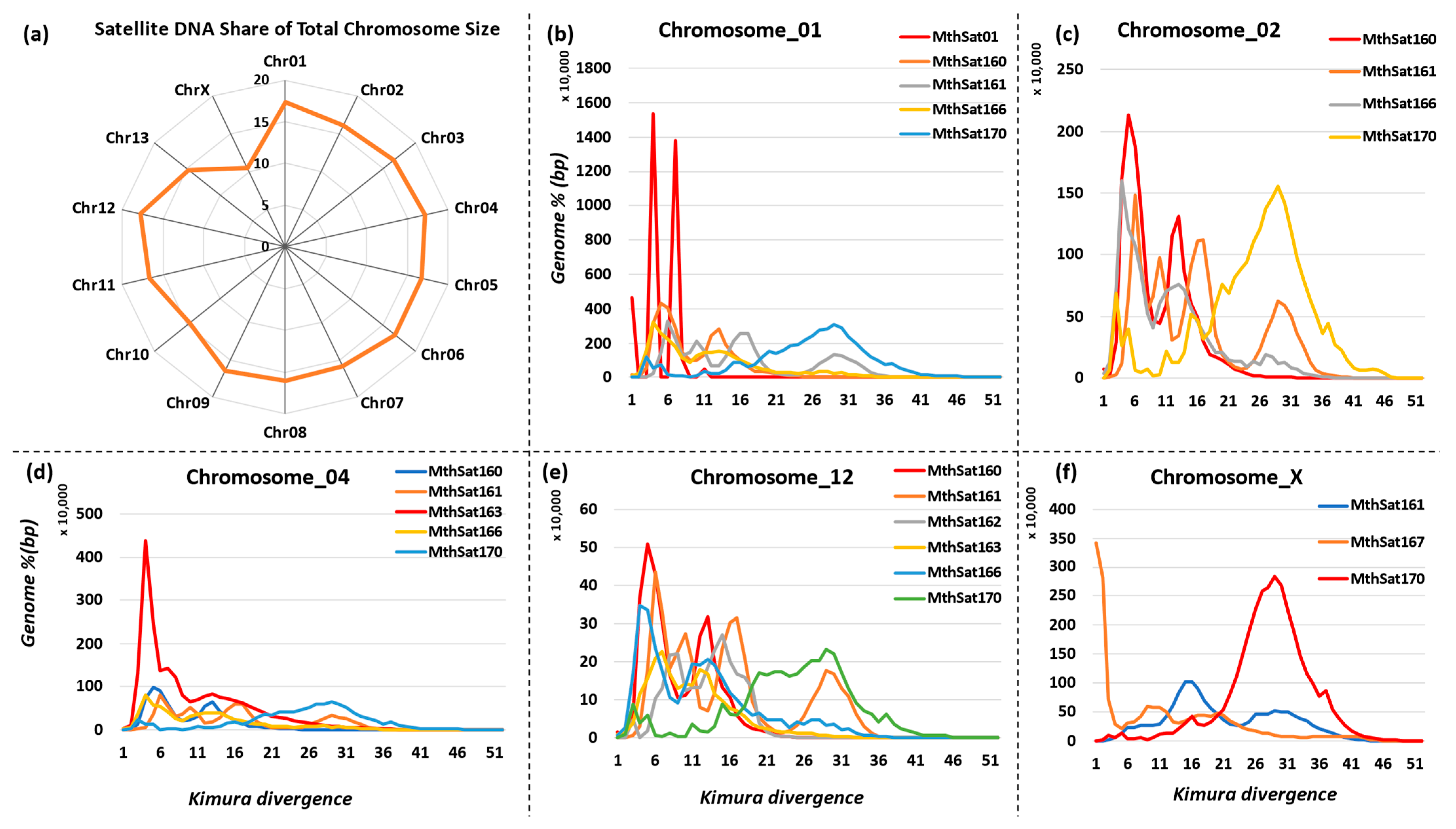
3.5. Chromosomal Distribution of Satellite DNA Repeats in M. thalassinum
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palomeque, T.; Lorite, P. Satellite DNA in insects: A review. Heredity 2008, 100, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sproul, J.S.; Hotaling, S.; Heckenhauer, J.; Powell, A.; Marshall, D.; Larracuente, A.M.; Kelley, J.L.; Pauls, S.U.; Frandsen, P.B. Analyses of 600+ insect genomes reveal repetitive element dynamics and highlight biodiversity-scale repeat annotation challenges. Genome Res. 2023, 33, 1708–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, J.; Packiaraj, J.; Henikoff, S. Sequence, Chromatin and Evolution of Satellite DNA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plohl, M.; Luchetti, A.; Meštrović, N.; Mantovani, B. Satellite DNAs between selfishness and functionality: Structure, genomics and evolution of tandem repeats in centromeric (hetero)chromatin. Gene 2008, 409, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louzada, S.; Lopes, M.; Ferreira, D.; Adega, F.; Escudeiro, A.; Gama-Carvalho, M.; Chaves, R. Decoding the Role of Satellite DNA in Genome Architecture and Plasticity-An Evolutionary and Clinical Affair. Genes 2020, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral-de-Mello, D.C.; Zrzavá, M.; Kubíčková, S.; Rendón, P.; Marec, F. The Role of Satellite DNAs in Genome Architecture and Sex Chromosome Evolution in Crambidae Moths. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 661417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, I.U.; Muhammad, M.; Yuan, H.; Ali, S.; Abbasi, A.; Asad, M.; Ashraf, H.J.; Khurshid, A.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Satellitome Analysis and Transposable Elements Comparison in Geographically Distant Populations of Spodoptera frugiperda. Life 2022, 12, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, L.M.; Cummings, M.P. Satellite DNA repeat sequence variation is low in three species of burying beetles in the genus Nicrophorus (Coleoptera: Silphidae). Mol. Biol. Evol. 1997, 14, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, A.; Nakata, A.; Mito, T.; Noji, S. The characteristics of karyotype and telomeric satellite DNA sequences in the cricket, Gryllus bimaculatus (Orthoptera, Gryllidae). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2006, 112, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Hoffman, J.I.; Schielzeth, H. Comparative Analysis of Genomic Repeat Content in Gomphocerine Grasshoppers Reveals Expansion of Satellite DNA and Helitrons in Species with Unusually Large Genomes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 1180–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, L.G.; Ruiz-Ruano, F.J. In-depth satellitome analyses of 37 Drosophila species illuminate repetitive DNA evolution in the Drosophila genus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2022, 14, evac064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majid, M.; Yuan, H. Comparative Analysis of Transposable Elements in Genus Calliptamus Grasshoppers Revealed That Satellite DNA Contributes to Genome Size Variation. Insects 2021, 12, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Majid, M.; Yuan, H.; Chang, H.; Zhao, L.; Nie, Y.; He, L.; Liu, X.; He, X.; Huang, Y. Transposable element expansion and low-level piRNA silencing in grasshoppers may cause genome gigantism. BMC Biol. 2022, 20, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbert, P.B.; Henikoff, S. The genetics and epigenetics of satellite centromeres. Genome Res. 2022, 32, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, G.; O’Neill, R.J. Centromere repeats: Hidden gems of the genome. Genes 2019, 10, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plohl, M.; Meštrović, N.; Mravinac, B. Centromere identity from the DNA point of view. Chromosoma 2014, 123, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestrović, N.; Plohl, M.; Mravinac, B.; Ugarković, D. Evolution of satellite DNAs from the genus Palorus—Experimental evidence for the “library” hypothesis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1998, 15, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mravinac, B.; Plohl, M.; Mestrović, N.; Ugarković, Đ. Sequence of PRAT Satellite DNA “Frozen” in Some Coleopteran Species. J. Mol. Evol. 2002, 54, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mravinac, B.; Plohl, M.; Ugarković, Ð. Preservation and high sequence conservation of satellite DNAs suggest functional constraints. J. Mol. Evol. 2005, 61, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliciello, I.; Chinali, G.; Ugarković, Đ. Structure and population dynamics of the major satellite DNA in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum. Genetica 2011, 139, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Gimenez, O.M.; Milani, D.; Song, H.; Marti, D.A.; López-León, M.D.; Ruiz-Ruano, F.J.; Camacho, J.P.M.; Cabral-de-Mello, D.C. Eight Million Years of Satellite DNA Evolution in Grasshoppers of the Genus Schistocerca Illuminate the Ins and Outs of the Library Hypothesis. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lower, S.S.; McGurk, M.P.; Clark, A.G.; Barbash, D.A. Satellite DNA evolution: Old ideas, new approaches. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2018, 49, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Ramos, M.A. Satellite DNA: An evolving topic. Genes 2017, 8, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plohl, M.; Meštrović, N.; Mravinac, B. Satellite DNA evolution. Repetitive DNA 2012, 7, 126–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lorite, P.; Muñoz-Lopez, M.; Carrillo, J.; Sanllorente, O.; Vela, J.; Mora, P.; Tinaut, A.; Mi, T.; Palomeque, T. Concerted evolution, a slow process for ant satellite DNA: Study of the satellite DNA in the Aphaenogaster genus (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Org. Divers. Evol. 2017, 17, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí, E.; Milani, D.; Bardella, V.B.; Albuquerque, L.; Song, H.; Palacios-Gimenez, O.M.; Cabral-de-Mello, D.C. Cytogenomic analysis unveils mixed molecular evolution and recurrent chromosomal rearrangements shaping the multigene families on Schistocerca grasshopper genomes. Evolution 2021, 75, 2027–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, D.; Ramos, É.; Loreto, V.; Martí, D.A.; Cardoso, A.L.; de Moraes, K.C.M.; Martins, C.; Cabral-de-Mello, D.C. The satellite DNA AflaSAT-1 in the A and B chromosomes of the grasshopper Abracris flavolineata. BMC Genet. 2017, 18, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teruel, M.; Ruíz-Ruano, F.J.; Marchal, J.A.; Sánchez, A.; Cabrero, J.; Camacho, J.P.; Perfectti, F. Disparate molecular evolution of two types of repetitive DNAs in the genome of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Heredity 2014, 112, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Gimenez, O.M.; Koelman, J.; Palmada-Flores, M.; Bradford, T.M.; Jones, K.K.; Cooper, S.J.B.; Kawakami, T.; Suh, A. Comparative analysis of morabine grasshopper genomes reveals highly abundant transposable elements and rapidly proliferating satellite DNA repeats. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ruano, F.J.; López-León, M.D.; Cabrero, J.; Camacho, J.P.M. High-throughput analysis of the satellitome illuminates satellite DNA evolution. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, P.; Vela, J.; Ruiz-Ruano, F.J.; Ruiz-Mena, A.; Montiel, E.E.; Palomeque, T.; Lorite, P. Satellitome analysis in the ladybird beetle Hippodamia variegata (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae). Genes 2020, 11, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montiel, E.E.; Panzera, F.; Palomeque, T.; Lorite, P.; Pita, S. Satellitome analysis of Rhodnius prolixus, one of the main Chagas disease vector species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsunomia, R.; Silva, D.M.Z.d.A.; Ruiz-Ruano, F.J.; Goes, C.A.G.; Melo, S.; Ramos, L.P.; Oliveira, C.; Porto-Foresti, F.; Foresti, F.; Hashimoto, D.T. Satellitome landscape analysis of Megaleporinus macrocephalus (Teleostei, Anostomidae) reveals intense accumulation of satellite sequences on the heteromorphic sex chromosome. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boštjančić, L.L.; Bonassin, L.; Anušić, L.; Lovrenčić, L.; Besendorfer, V.; Maguire, I.; Grandjean, F.; Austin, C.M.; Greve, C.; Hamadou, A.B. The Pontastacus leptodactylus (Astacidae) repeatome provides insight into genome evolution and reveals remarkable diversity of satellite DNA. Front. Genet. 2021, 11, 611745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, P.; Pita, S.; Montiel, E.E.; Rico-Porras, J.M.; Palomeque, T.; Panzera, F.; Lorite, P. Making the genome huge: The case of Triatoma delpontei, a Triatominae species with more than 50% of its genome full of satellite DNA. Genes 2023, 14, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, B.S.M.L.; Picorelli, A.C.R.; Kuhn, G.C.S. In Silico Identification and Characterization of Satellite DNAs in 23 Drosophila Species from the Montium Group. Genes 2023, 14, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.A.; Cabral-de-Mello, D.C.; Lopes, D.M. The Satellite DNAs Populating the Genome of Trigona hyalinata and the Sharing of a Highly Abundant satDNA in Trigona Genus. Genes 2023, 14, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gržan, T.; Dombi, M.; Despot-Slade, E.; Veseljak, D.; Volarić, M.; Meštrović, N.; Plohl, M.; Mravinac, B. The Low-Copy-Number Satellite DNAs of the Model Beetle Tribolium castaneum. Genes 2023, 14, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjos, A.; Milani, D.; Bardella, V.B.; Paladini, A.; Cabral-de-Mello, D.C. Evolution of satDNAs on holocentric chromosomes: Insights from hemipteran insects of the genus Mahanarva. Chromosome Res. 2023, 31, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, G.; Campbell, P.; Leiva-Neto, J.T.; Markow, T.A. Analysis of Drosophila species genome size and satellite DNA content reveals significant differences among strains as well as between species. Genetics 2007, 177, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlesworth, B.; Sniegowski, P.; Stephan, W. The evolutionary dynamics of repetitive DNA in eukaryotes. Nature 1994, 371, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios-Gimenez, O.M.; Bardella, V.B.; Lemos, B.; Cabral-de-Mello, D.C. Satellite DNAs are conserved and differentially transcribed among Gryllus cricket species. DNA Res. 2017, 25, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, A.P.; Amorim, I.C.d.; Milani, D.; Cabral-de-Mello, D.C.; Moura, R.C. Differential amplification and contraction of satellite DNAs in the distinct lineages of the beetle Euchroma gigantea. Gene 2024, 927, 148723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Dou, L.; Yue, B.; Xing, J.; Li, J. Transposable Elements Shape the Genome Diversity and the Evolution of Noctuidae Species. Genes 2023, 14, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, A.; Chen, J.; Schaack, S. ‘Junk’ that matters: The role of transposable elements in bumblebee genome evolution. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2023, 59, 101103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, M.; Armisén, D.; Gibbs, R.A.; Hering, L.; Khila, A.; Mayer, G.; Richards, S.; Niehuis, O.; Misof, B. Diversity and evolution of the transposable element repertoire in arthropods with particular reference to insects. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2019, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Liu, X.-Z.; Yuan, H.; Dai, Y.; Zheng, Y.-N.; Zhao, L.-N.; Ma, L.-B.; Huang, Y. Evolutionary dynamics of genome size and transposable elements in crickets (Ensifera: Gryllidea). Syst. Entomol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisot, N.; Vargas-Chávez, C.; Goubert, C.; Baa-Puyoulet, P.; Balmand, S.; Beranger, L.; Blanc, C.; Bonnamour, A.; Boulesteix, M.; Burlet, N.; et al. The transposable element-rich genome of the cereal pest Sitophilus oryzae. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maumus, F.; Fiston-Lavier, A.-S.; Quesneville, H. Impact of transposable elements on insect genomes and biology. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 7, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ruano, F.J.; Cabrero, J.; López-León, M.D.; Sánchez, A.; Camacho, J.P.M. Quantitative sequence characterization for repetitive DNA content in the supernumerary chromosome of the migratory locust. Chromosoma 2018, 127, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila Robledillo, L.; Koblížková, A.; Novák, P.; Böttinger, K.; Vrbová, I.; Neumann, P.; Schubert, I.; Macas, J. Satellite DNA in Vicia faba is characterized by remarkable diversity in its sequence composition, association with centromeres, and replication timing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios-Gimenez, O.M.; Dias, G.B.; De Lima, L.G.; Kuhn, G.C.e.S.; Ramos, E.; Martins, C.; Cabral-de-Mello, D.C. High-throughput analysis of the satellitome revealed enormous diversity of satellite DNAs in the neo-Y chromosome of the cricket Eneoptera surinamensis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- João Da Silva, M.; Gazoni, T.; Haddad, C.F.B.; Parise-Maltempi, P.P. Analysis in Proceratophrys boiei genome illuminates the satellite DNA content in a frog from the Brazilian Atlantic forest. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1101397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melters, D.P.; Bradnam, K.R.; Young, H.A.; Telis, N.; May, M.R.; Ruby, J.G.; Sebra, R.; Peluso, P.; Eid, J.; Rank, D.; et al. Comparative analysis of tandem repeats from hundreds of species reveals unique insights into centromere evolution. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Majid, M.; Khan, H.; Liu, X.; Shaheer, M.; Huang, Y. Evolutionary Dynamics of Satellite DNA Repeats across the Tettigoniidae Family: Insights from Genomic Analysis. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14080915
Majid M, Khan H, Liu X, Shaheer M, Huang Y. Evolutionary Dynamics of Satellite DNA Repeats across the Tettigoniidae Family: Insights from Genomic Analysis. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(8):915. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14080915
Chicago/Turabian StyleMajid, Muhammad, Hashim Khan, Xuanzeng Liu, Muhammad Shaheer, and Yuan Huang. 2024. "Evolutionary Dynamics of Satellite DNA Repeats across the Tettigoniidae Family: Insights from Genomic Analysis" Biomolecules 14, no. 8: 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14080915
APA StyleMajid, M., Khan, H., Liu, X., Shaheer, M., & Huang, Y. (2024). Evolutionary Dynamics of Satellite DNA Repeats across the Tettigoniidae Family: Insights from Genomic Analysis. Biomolecules, 14(8), 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14080915






