Linking Cardiovascular Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): The Role of Cardiometabolic Drugs in MASLD Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiologic Association Between MASLD and CVD Incidence and Mortality
| Author | Study Design | Population | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mantovani et al. (2021) [15] | Systematic review and meta-analysis | 36 observational studies 5,802,226 adults 335,132 individuals with baseline MASLD (diagnosed with liver biopsy, imaging techniques, ICD 9/10 codes) Median follow-up period: 6.5 years | Increased risk of fatal or non-fatal CVD events in patients with MASLD vs. those without (pooled random-effects HR = 1.45, 95% CI 1.31–1.61). Even higher risk with more severe MASLD (pooled random-effects HR = 2.50, 95% CI 1.68–3.72). All risks were independent of other common cardiometabolic risk factors. |
| Wu et al. (2016) [16] | Systematic review and meta-analysis | 34 studies (21 cross-sectional studies, and 13 cohort studies) 164,494 participants 153,209 patients with MASLD (diagnosed by U/S, CT or liver biopsy) | Increased risk of prevalence (OR = 1.81, 95% CI: 1.23–2.66) and incidence (HR = 1.37, 95% CI: 1.10–1.72) of CVD in patients with MASLD vs. those without MASLD. Increased risk of prevalence (OR = 1.87, 95% CI: 1.47–2.37) and incidence (HR = 2.31, 95% CI: 1.46–3.65) coronary artery disease (CAD), prevalence (OR = 1.24, 95% CI: 1.14–1.36) and incidence (HR = 1.16, 95% CI: 1.06–1.27) of hypertension and prevalence (OR = 1.32, 95% CI: 1.07–1.62). atherosclerosis among patients with MASLD than those without MASLD. No statistically significant difference in CVD mortality between patients with MASLD and non-MASLD participants (HR = 1.10, 95% CI: 0.86–1.41). |
| Bisaccia et al. (2023) [20] | Systematic review and meta-analysis | 33 cohort studies 10,592,851 individuals 219,211 patients with MASLD (diagnosed by U/S, CT or liver biopsy) Mean follow-up time: 10 ± 6 years | Increased risk of MI (OR = 1.6, 95% CI: 1.5–1.7, p < 0.001), stroke (OR = 1.6, 95% CI, 1.2–2.1, p = 0.005), atrial fibrillation (OR = 1.7, 95% CI, 1.2–2.3, p = 0.001), and major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events (OR: 2.3, 95% CI, 1.3–4.2, p = 0.01) among patients with MASLD than those without MASLD. No statistically significant association between MASLD and CVD mortality (OR= 1.13, 95% CI, 0.57–2.23; p = 0.656) or all-cause mortality (OR= 1.14, 95% CI, 0.78–1.67, p = 0.459) between MASLD and non-MASLD patients. |
| Targher et al. (2016) [34] | Meta-analysis | 16 observational studies 34,043 adults 36.3% of individuals with baseline MASLD Median follow-up period: 6.9 years | Increased risk of fatal and/or non-fatal CVD events in patients with MASLD vs. those without MASLD (random effect OR = 1.64, 95% CI 1.26–2.13). Even higher risk in patients with more severe MASLD (random effect OR = 2.58; 95% CI 1.78–3.75). |
| Abosheaishaa et al. (2024) [35] | Systematic review and meta-analysis | 32 studies 5,610,990 individuals 567,729 patients with MASLD | Increased risk of angina (RR = 1.45, 95% CI: 1.17–1.79), CAD (RR = 1.21, 95% CI: 1.07–1.38), Coronary artery calcium (CAC) > 0 (RR = 1.39, 95% CI: 1.15–1.69), and calcified coronary plaques (RR = 1.55, 95% CI: 1.05–2.27). No statistically significant association between MASLD and CAC >100 (RR = 1.16, 95% CI: 0.97–1.38) and MI (RR = 1.70, 95% CI: 0.16–18.32). |
| Liu et al. (2019) [36] | Meta-analysis | 14 studies 498,501 individuals More of 95,111 patients with MASLD | Increased risk of all-cause mortality in patients with MASLD vs. those without (HR = 1.34, 95% CI 1.17–1.54). No statistically significant association of MASLD with CVD mortality (HR = 1.13, 95% CI 0.92–1.38). |
3. Pathophysiological Linkage of MASLD and CVD
3.1. Dyslipidemia
3.2. Inflammation–Oxidative Stress
3.3. Insulin Resistance (IR)
3.4. Hepatokines
3.5. Genetics
3.6. Gut Dysbiosis
3.7. Other Potential Mechanisms
4. Cardiometabolic Drugs and MASLD
4.1. Anti-Hypertensive Drugs
4.1.1. Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System (RAAS) Inhibitors
4.1.2. Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists (MRAs)
4.1.3. Calcium Channel Blockers
4.1.4. Beta Blockers
4.2. Anti-Hyperglycemic Agents
4.2.1. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1RAs)
4.2.2. Dual Glucagon-like Peptide-1/Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Peptide (glp-1/gip) Receptor Agonist
4.2.3. Sodium Glucose Transporter-2 Inhibitors (SGLT-2i)
4.2.4. Metformin
4.2.5. Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)
4.3. Lipid-Lowering Drugs
4.3.1. Statins
4.3.2. Ezetimibe
4.3.3. PCSK9 Inhibitors
4.3.4. Other Hypolipidemic Agents
4.4. THR-β Agonists-Resmetirom
4.5. Acetylsalicylic Acid (ASA)
| Drug Category | Drug | Reduction in Hepatic Steatosis | Reduction in Steatohepatitis | Reduction in Hepatic Fibrosis | Assessment Methods | References | Cardiovascular (CV) Risk | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-hypertensives | RAAS inhibitors (ACE Inhibitors, ARBs) | Controversial (SoE: IIa) | Controversial (SoE: IIa) | Controversial (SoE: IIa) | Histology, liver ultrasound (US) | [117,118] | Reduce CV risk (used in patients with HTN, HFrEF, post-MI) | |
| Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists | Controversial (SoE: Ib—limited data) | N/A | Not Effective (SoE Ib—limited data) | MRI-based techniques, NAFLD liver fat score, APRI score | [130,132] | Reduce CV risk in specific conditions (e.g., HFrEF) | Potential benefit in MASLD liver fat score when combined with vitamin E | |
| Glucose-lowering | GLP-1 Receptor Agonists | Effective (SoE: IIa) | Effective (SoE: IIa) | Not Effective (SoE: IIa) | Histology, MRI-based techniques, liver US | [157,158,159,160,161,162,163,164] | Reduce CV risk in high-risk patients with T2DM or obesity | Data in MASH patients without T2DM are scarce |
| SGLT-2 Inhibitors | Effective (SoE: Ib) | N/A | Effective (LoE: IIa—quantitively limited data) | Histology, MRI-based techniques, Fibrosis-4 Index score | [179,180,181,183] | Proven cardiovascular benefits, including a reduction in heart failure hospitalizations and cardiovascular mortality in HFrEF patients | Limited data in non-diabetic MASLD | |
| Dual GLP-1/GIP Receptor Agonist | Limited evidence showing effectiveness (SoE: IIb) | N/A | N/A | MRI | [169] | Potential to reduce cardiovascular risk | Ongoing trials are evaluating effects on MASH, fibrosis, and cardiovascular outcomes | |
| Thiazolidinediones | Effective (E.S: Ia) | Effective (E.S: Ia) | Effective (E.S: Ia) | Histology and MRI-based techniques | [202,203,204,205,206,207,208,209] | Mixed cardiovascular effects May reduce CV risk in T2DM patients but can increase risk of heart failure | Recommended in combination with vitamin E for the treatment of MASH with significant fibrosis | |
| Metformin | Not Effective (SoE: IIa) | Not effective (SoE: IIa) | Not Effective (SoE IIa) | Histology and US | [192,193] | May reduce CV risk in T2DM | Recent meta-analyses do not support liver benefits Not recommended as a specific MASLD treatment | |
| Lipid-lowering | Statins | Effective (SoE: IIb—limited data) | Effective (SoE: IIIa—limited data) | Effective (SoE IIIa—limited data) | Histology and US | [219,220,221,224] | Reduce CV risk | Fibrates |
| Ezetimibe | Controversial (LoE: IIb—limited data) | Effective (LoE: IIIb—limited data) | Controversial (LoE: IIb—limited data) | Histology and MRI-based techniques | [230,231,232,233,234,235] | Reduce CV risk when combined with statins | May worsen glycemic control in some patients Combined ezetimibe-rosuvastatin treatment significantly reduces liver fat compared to rosuvastatin monotherapy | |
| PCSK9 inhibitors | Effective—(LoE: IIIb limited data) | N/A | US, Computed tomography (CT), MRI | [240,241] | Reduce CV events in high-risk patients when added to statin therapy | Positive trend towards hepatic steatosis and fibrosis amelioration | ||
| N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Benefit in patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia when combined with statins | Preclinical studies suggest potential liver benefits | ||
| Ω-3 fatty acids | Effective (LoE IIa) | Controversial (LoE IIIa) | Controversial (LoE IIIa) | US, MRI | [250,251] | May reduce cardiovascular risk | Data mainly from small, non-randomized trials | |
| Others | ASA | Effective (LoE IIb—limited data) | Effective (LoE IIIa—limited data) | Effective (LoE: IIIa—quantitatively limited data) | MRI- based techniques, validated laboratory scores | [257,259] | Reduce CV risk |
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; LaVine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A systematic review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matteoni, C.A.; Younossi, Z.M.; Gramlich, T.; Boparai, N.; Liu∥, Y.C.; McCullough, A.J. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A spectrum of clinical and pathological severity. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, T.; Oakley, F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Day, C.P. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Pathogenesis and Disease Spectrum. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2016, 11, 451–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Dufour, J.-F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouwels, S.; Sakran, N.; Graham, Y.; Leal, A.; Pintar, T.; Yang, W.; Kassir, R.; Singhal, R.; Mahawar, K.; Ramnarain, D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A review of pathophysiology, clinical management and effects of weight loss. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1966–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flessa, C.-M.; Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Kyrou, I.; Leca, B.M.; Lianou, M.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Kaltsas, G.; Kassi, E.; Randeva, H.S. Genetic and Diet-Induced Animal Models for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Androutsakos, T.; Flessa, C.-M.; Kyrou, I.; Siasos, G.; Randeva, H.S.; Kassi, E.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): A Concise Review. Cells 2022, 11, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Santillán, R.; López-Velázquez, J.A.; Chávez-Tapia, N.; Torres-Villalobos, G.; Uribe, M.; Méndez-Sánchez, N. Hepatic manifestations of metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2013; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, L.A.; Anstee, Q.M.; Tilg, H.; Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its relationship with cardiovascular disease and other extrahepatic diseases. Gut 2017, 66, 1138–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, A.; E Grobbee, D.; Dendale, P. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, a new and growing risk indicator for cardiovascular disease. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netala, V.R.; Teertam, S.K.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. A Comprehensive Review of Cardiovascular Disease Management: Cardiac Biomarkers, Imaging Modalities, Pharmacotherapy, Surgical Interventions, and Herbal Remedies. Cells 2024, 13, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Csermely, A.; Petracca, G.; Beatrice, G.; E Corey, K.; Simon, T.G.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wu, F.; Ding, Y.; Hou, J.; Bi, J.; Zhang, Z. Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with major adverse cardiovascular events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Wu, W.; Wen, W.; Xu, F.; Han, D.; Lyu, J.; Huang, Y. Association of NAFLD with cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality: A large-scale prospective cohort study based on UK Biobank. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2022, 13, 20406223221122478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-Y.; Zhou, X.-D.; Wu, S.-J.; Hu, X.-Q.; Tang, B.; van Poucke, S.; Pan, X.-Y.; Wu, W.-J.; Gu, X.-M.; Fu, S.-W.; et al. Synergistic increase in cardiovascular risk in diabetes mellitus with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 30, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-S.; Hong, S.; Han, K.; Park, C.-Y. Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Nationwide population based study. BMJ 2024, 384, e076388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisaccia, G.; Ricci, F.; Khanji, M.Y.; Sorella, A.; Melchiorre, E.; Iannetti, G.; Galanti, K.; Mantini, C.; Pizzi, A.D.; Tana, C.; et al. Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality Related to Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2023, 48, 101643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Zha, M.; Lv, Q.; Xie, Y.; Yuan, K.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and stroke: A Mendelian randomization study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 1534–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.Y.Z.; Yap, J.J.L.; Sultana, R.; Cheah, M.; Goh, G.B.B.; Yeo, K.K. Association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and subclinical atherosclerosis in Western and Asian cohorts: An updated meta-analysis. Open Heart 2021, 8, e001850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, K.; Qi, Y.; An, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Tang, Y.-D. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and subclinical atherosclerosis: A cross-sectional study on population over 40 years old. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2018, 18, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-H.; Liu, B.; Lei, F.; Liu, Y.-M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.-J.; She, Z.-G.; Cai, J.; et al. The Association Between Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Peripheral Arterial Disease in the Chinese Population. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardullo, S.; Bianconi, E.; Cannistraci, R.; Parmeggiani, P.; Marone, E.M.; Perseghin, G. Peripheral artery disease and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with NAFLD. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2022, 45, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Bai, W.; Mao, D.; Long, F.; Wang, N.; Wang, K.; Shi, Q. The relationship between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and incidence of chronic kidney disease for diabetic and non-diabetic subjects: A meta-analysis. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 32, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Song, J.; Xie, Y.; Huang, J.; Yang, J. The Role of Metabolic Dysfunction–Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Developing Chronic Kidney Disease: Longitudinal Cohort Study. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2023, 9, e45050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Petracca, G.; Beatrice, G.; Csermely, A.; Lonardo, A.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Tilg, H.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident chronic kidney disease: An updated meta-analysis. Gut 2022, 71, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustanti, N.; Soetedjo, N.N.M.; Damara, F.A.; Iryaningrum, M.R.; Permana, H.; Bestari, M.B.; Supriyadi, R. The association between metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2023, 17, 102780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Pei, X.; Jiang, W.; Zeng, Q.; Bai, L.; Zhou, T.; Lv, X.; Tang, H.; Wu, D. Non-obese non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the risk of chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PeerJ 2024, 12, e18459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Pang, J.; Huang, R.; Xue, H.; Chen, X. Association of MAFLD with end-stage kidney disease: A prospective study of 337,783 UK Biobank participants. Hepatol. Int. 2023, 17, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Lim, H.; Kim, Y.N.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.W.; Chang, T.I.; Han, S.H. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Its Association with Kidney and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Moderate to Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2024, 56, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamori, D.; Tanaka, M.; Sato, T.; Endo, K.; Mori, K.; Mikami, T.; Hosaka, I.; Hanawa, N.; Ohnishi, H.; Furuhashi, M. Coexistence of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Chronic Kidney Disease Is a More Potent Risk Factor for Ischemic Heart Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e030269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Lonardo, A.; Zoppini, G.; Barbui, C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abosheaishaa, H.; Hussein, M.; Ghallab, M.; Abdelhamid, M.; Balassiano, N.; Ahammed, R.; Baig, M.A.; Khan, J.; Elshair, M.; Soliman, M.Y.; et al. Association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and coronary artery disease outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2024, 18, 102938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhong, G.-C.; Tan, H.-Y.; Hao, F.-B.; Hu, J.-J. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and mortality from all causes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, E.P.; Dhindsa, D.S.; Lee, S.K.; Sandesara, P.B.; Chalasani, N.P.; Sperling, L.S. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Heart: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 948–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.; Leray, V.; Diez, M.; Serisier, S.; Le Bloc’h, J.; Siliart, B.; Dumon, H. Liver lipid metabolism. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2008, 92, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipsen, D.H.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic lipid accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 3313–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francque, S.M.; van der Graaff, D.; Kwanten, W.J. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular risk: Pathophysiological mechanisms and implications. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ference, B.A.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Graham, I.; Ray, K.K.; Packard, C.J.; Bruckert, E.; Hegele, R.A.; Krauss, R.M.; Raal, F.J.; Schunkert, H.; et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic, and clinical studies. A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2459–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, M.; Berneis, K.; Corrado, E.; Novo, S. The significance of low-density-lipoproteins size in vascular diseases. Int. Angiol. 2006, 25, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zewinger, S.; Reiser, J.; Jankowski, V.; Alansary, D.; Hahm, E.; Triem, S.; Klug, M.; Schunk, S.J.; Schmit, D.; Kramann, R.; et al. Apolipoprotein C3 induces inflammation and organ damage by alternative inflammasome activation. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latz, E.; Xiao, T.S.; Stutz, A. Activation and regulation of the inflammasomes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, M.S.; Lavrador, M.S.F.; Koike, M.K.; Cintra, D.E.; Ferreira, F.D.; Nunes, V.S.; Castilho, G.; Gioielli, L.A.; Bombo, R.P.; Catanozi, S.; et al. Dietary interesterified fat enriched with palmitic acid induces atherosclerosis by impairing macrophage cholesterol efflux and eliciting inflammation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 32, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.; Cabrera, D.; Arrese, M.; Feldstein, A.E. Triggering and resolution of inflammation in NASH. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoner, L.; Lucero, A.A.; Palmer, B.R.; Jones, L.M.; Young, J.M.; Faulkner, J. Inflammatory biomarkers for predicting cardiovascular disease. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 1353–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Chen, Q.; Wang, W.; Ling, Y.; Yan, Y.; Xia, P. Hepatocyte-derived extracellular vesicles promote endothelial inflammation and atherogenesis via microRNA-1. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braza-Boïls, A.; Marí-Alexandre, J.; Molina, P.; Arnau, M.A.; Barceló-Molina, M.; Domingo, D.; Girbes, J.; Giner, J.; Martínez-Dolz, L.; Zorio, E. Deregulated hepatic microRNAs underlie the association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and coronary artery disease. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacana, T.; Cazanave, S.; Verdianelli, A.; Patel, V.; Min, H.-K.; Mirshahi, F.; Quinlivan, E.; Sanyal, A.J. Dysregulated Hepatic Methionine Metabolism Drives Homocysteine Elevation in Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, A.; Alisi, A.; Di Giovamberardino, G.; Crudele, A.; Ceccarelli, S.; Panera, N.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Nobili, V. Plasma Levels of Homocysteine and Cysteine Increased in Pediatric NAFLD and Strongly Correlated with Severity of Liver Damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 21202–21214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distrutti, E.; Mencarelli, A.; Santucci, L.; Renga, B.; Orlandi, S.; Donini, A.; Shah, V.; Fiorucci, S. The methionine connection: Homocysteine and hydrogen sulfide exert opposite effects on hepatic microcirculation in rats. Hepatology 2008, 47, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batty, M.; Bennett, M.R.; Yu, E. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Atherosclerosis. Cells 2022, 11, 3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulman, G.I. Ectopic fat in insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and cardiometabolic disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itani, S.I.; Ruderman, N.B.; Schmieder, F.; Boden, G. Lipid-Induced Insulin Resistance in Human Muscle Is Associated with Changes in Diacylglycerol, Protein Kinase C, and IκB-α. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2005–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 2001, 414, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, P.; Martin, A.; Lang, S.; Kütting, F.; Goeser, T.; Demir, M.; Steffen, H.-M. NAFLD and cardiovascular diseases: A clinical review. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2021, 110, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, S.-H.; Dutcher, A.K.; Towle, H.C. Glucose and Insulin Function through Two Distinct Transcription Factors to Stimulate Expression of Lipogenic Enzyme Genes in Liver. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 9437–9445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, K.L.; Smith, C.I.; Schwarzenberg, S.J.; Jessurun, J.; Boldt, M.D.; Parks, E.J. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.C.L.; Hess, C.N.; Hiatt, W.R.; Goldfine, A.B. Clinical Update: Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation 2016, 133, 2459–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laakso, M.; Kuusisto, J. Insulin resistance and hyperglycaemia in cardiovascular disease development. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.K.; Norby, F.L.; Whitsel, E.A.; Soliman, E.Z.; Chen, L.Y.; Loehr, L.R.; Fuster, V.; Heiss, G.; Coresh, J.; Alonso, A. Cardiac Autonomic Dysfunction and Incidence of Atrial Fibrillation: Results From 20 Years Follow-Up. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, S.S.; Yi, Q.; Gerstein, H.; Lonn, E.; Jacobs, R.; Vuksan, V.; Teo, K.; Davis, B.; Montague, P.; Yusuf, S. Relationship of Metabolic Syndrome and Fibrinolytic Dysfunction to Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2003, 108, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meex, R.C.R.; Watt, M.J. Hepatokines: Linking nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.; Dasgupta, S.; Kundu, R.; Maitra, S.; Das, G.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Ray, S.; Majumdar, S.S.; Bhattacharya, S. Fetuin-A acts as an endogenous ligand of TLR4 to promote lipid-induced insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukeland, J.W.; Dahl, T.B.; Yndestad, A.; Gladhaug, I.P.; Løberg, E.M.; Haaland, T.; Konopski, Z.; Wium, C.; Aasheim, E.T.; Johansen, O.E.; et al. Fetuin A in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: In vivo and in vitro studies. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 166, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Häring, H.-U. The role of hepatokines in metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Xin, Y. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Circulating Fetuin-A Levels in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2021, 9, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weikert, C.; Stefan, N.; Schulze, M.B.; Pischon, T.; Berger, K.; Joost, H.-G.; Häring, H.-U.; Boeing, H.; Fritsche, A. Plasma Fetuin-A Levels and the Risk of Myocardial Infarction and Ischemic Stroke. Circulation 2008, 118, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kröger, J.; Meidtner, K.; Stefan, N.; Guevara, M.; Kerrison, N.D.; Ardanaz, E.; Aune, D.; Boeing, H.; Dorronsoro, M.; Dow, C.; et al. Circulating Fetuin-A and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ix, J.H. Fetuin-A and Incident Diabetes Mellitus in Older Persons. JAMA 2008, 300, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laughlin, G.A.; Cummins, K.M.; Wassel, C.L.; Daniels, L.B.; Ix, J.H. The association of fetuin-A with cardiovascular disease mortality in older community-dwelling adults: The Rancho Bernardo study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 1688–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Lloyd, D.J.; Hale, C.; Stanislaus, S.; Chen, M.; Sivits, G.; Vonderfecht, S.; Hecht, R.; Li, Y.-S.; Lindberg, R.A.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Reverses Hepatic Steatosis, Increases Energy Expenditure, and Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Diabetes 2009, 58, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Y.; Xu, C.; Lin, J.; Li, Y. Role of hepatokines in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Transl. Intern. Med. 2019, 7, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dong, K.; Fang, Q.; Hou, X.; Zhou, M.; Bao, Y.; Xiang, K.; Xu, A.; Jia, W. High serum level of fibroblast growth factor 21 is an independent predictor of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A 3-year prospective study in China. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanajak, P.; Sa-Nguanmoo, P.; Wang, X.; Liang, G.; Li, X.; Jiang, C.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Chattipakorn, N. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) therapy attenuates left ventricular dysfunction and metabolic disturbance by improving FGF21 sensitivity, cardiac mitochondrial redox homoeostasis and structural changes in pre-diabetic rats. Acta Physiol. 2016, 217, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miida, T.; Hirayama, S. Impacts of angiopoietin-like proteins on lipoprotein metabolism and cardiovascular events. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 21, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Wu, J.; Sun, X.; Huang, X.; Huang, W.; Weng, C.; Cai, J. The regulatory role of metabolic organ-secreted factors in the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1119005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, J. Circulating angiopoietin-like proteins in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2021, 20, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, Y.; Ulukaya, E.; Atug, O.; Dolar, E. Serum concentrations of human angiopoietin-like protein 3 in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Association with insulin resistance. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 21, 1247–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Z.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, J.-F.; Cheng, Z.-B.; Zhou, Z.-Y.; Tang, M.-Y.; Sun, J.-X.; Huang, L. Angiopoietin-like proteins in atherosclerosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 521, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Lebedy, D. Association of serum angiopoietin-like protein 2 with elevated risk of cardiovascular diseases in subjects with type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2019, 33, 107421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; He, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, J.; Qin, Y. Associations between circulating full-length angiopoietin-like protein 8 levels and severity of coronary artery disease in Chinese non-diabetic patients: A case–control study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, N.W.; Chong, B.; Ng, C.H.; Kong, G.; Chin, Y.H.; Xiao, W.; Lee, M.; Dan, Y.Y.; Muthiah, M.D.; Foo, R. The genetic interactions between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular diseases. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 971484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smagris, E.; BasuRay, S.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Ka-man, V.L.; Gromada, J.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Pnpla3I148M knockin mice accumulate PNPLA3 on lipid droplets and develop hepatic steatosis. Hepatology 2015, 61, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Mangia, A.; Berg, T.; Chan, H.L.Y.; Irving, W.L.; Dore, G.J.; Abate, M.L.; Bugianesi, E.; Adams, L.A.; Najim, M.A.; et al. Diverse impacts of the rs58542926 E167K variant in TM6SF2 on viral and metabolic liver disease phenotypes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stender, S.; Loomba, R. PNPLA3 Genotype and Risk of Liver and All-Cause Mortality. Hepatology 2020, 71, 777–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlitina, J.; Smagris, E.; Stender, S.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Zhou, H.H.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Vogt, T.F.; Hobbs, H.H.; Cohen, J.C. Exome-wide association study identifies a TM6SF2 variant that confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.J.; Peloso, G.M.; Yu, H.; Butterworth, A.S.; Wang, X.; Mahajan, A.; Saleheen, D.; Emdin, C.; Alam, D.; Alves, A.C.; et al. Exome-wide association study of plasma lipids in >300,000 individuals. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1758–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.; Rivera, L.; Furness, J.B.; Angus, P.W. The role of the gut microbiota in NAFLD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.W.; Bäckhed, F.; Landmesser, U.; Hazen, S.L. Intestinal Microbiota in Cardiovascular Health and Disease: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 2089–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.M.; Hazen, S.L. The Gut Microbial Endocrine Organ: Bacterially Derived Signals Driving Cardiometabolic Diseases. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Gregory, J.C.; Org, E.; Buffa, J.A.; Gupta, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y.; Mehrabian, M.; et al. Gut Microbial Metabolite TMAO Enhances Platelet Hyperreactivity and Thrombosis Risk. Cell 2016, 165, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandsma, E.; Kloosterhuis, N.J.; Koster, M.; Dekker, D.C.; Gijbels, M.J.; van der Velden, S.; Ríos-Morales, M.; van Faassen, M.J.; Loreti, M.G.; de Bruin, A.; et al. A Proinflammatory Gut Microbiota Increases Systemic Inflammation and Accelerates Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Belda, E.; Nielsen, T.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Chakaroun, R.; Forslund, S.K.; Assmann, K.; Valles-Colomer, M.; Nguyen, T.T.D.; et al. Statin Therapy Is Associated with Lower Prevalence of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis. Nature 2020, 581, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshvani, C.; Kopel, J.; Goyal, H. Obeticholic Acid—A Pharmacological and Clinical Review. Future Pharmacol. 2023, 3, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Lavine, J.E.; Van Natta, M.L.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Chalasani, N.; Dasarathy, S.; Diehl, A.M.; Hameed, B.; et al. Farnesoid X nuclear receptor ligand obeticholic acid for non-cirrhotic, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (FLINT): A multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacobellis, G.; Ribaudo, M.C.; Assael, F.; Vecci, E.; Tiberti, C.; Zappaterreno, A.; Di Mario, U.; Leonetti, F. Echocardiographic Epicardial Adipose Tissue Is Related to Anthropometric and Clinical Parameters of Metabolic Syndrome: A New Indicator of Cardiovascular Risk. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 5163–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Luo, A.; Ren, H.; She, Q. Association of epicardial adipose tissue with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. Hepatol. Int. 2019, 13, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M. Epicardial Adipose Tissue May Mediate Deleterious Effects of Obesity and Inflammation on the Myocardium. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2360–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdeva, O.; Uchasova, E.; Dyleva, Y.; Borodkina, D.; Akbasheva, O.; Antonova, L.; Matveeva, V.; Belik, E.; Ivanov, S.; Sotnikov, A.; et al. Adipocytes Directly Affect Coronary Artery Disease Pathogenesis via Induction of Adipokine and Cytokine Imbalances. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotronen, A.; Joutsi-Korhonen, L.; Sevastianova, K.; Bergholm, R.; Hakkarainen, A.; Pietiläinen, K.H.; Lundbom, N.; Rissanen, A.; Lassila, R.; Yki-Järvinen, H. Increased coagulation factor VIII, IX, XI and XII activities in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrijken, A.; Francque, S.; Mertens, I.; Prawitt, J.; Caron, S.; Hubens, G.; Van Marck, E.; Staels, B.; Michielsen, P.; Van Gaal, L. Prothrombotic factors in histologically proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2013, 59, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkorakis, M.; Boutari, C.; Hill, M.A.; Kotsis, V.; Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Resmetirom, the first approved drug for the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis: Trials, opportunities, and challenges. Metabolism 2024, 154, 155835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneni, E.C.; Oni, E.T.; Martin, S.S.; Blaha, M.J.; Agatston, A.S.; Feldman, T.; Veledar, E.; Conçeicao, R.D.; Carvalho, J.A.; Santos, R.D.; et al. Blood pressure is associated with the presence and severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease across the spectrum of cardiometabolic risk. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, J.; Suh, Y.J.; Shin, H.C.; Cho, Y.K.; Choi, J.; Park, S.K. Clinical association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the development of hypertension. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 1926–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, J.K.; Kaur, G.; Buttar, H.S.; Bagabir, H.A.; Bagabir, R.A.; Bagabir, S.A.; Haque, S.; Tuli, H.S.; Telessy, I.G. Role of the renin–angiotensin system in the pathophysiology of coronary heart disease and heart failure: Diagnostic biomarkers and therapy with drugs and natural products. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1034170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelton Correction to: 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2018, 71, e136–e139. [CrossRef]
- Hradec, J. Pharmacological therapy for chronic heart failure. Vnitr. Lek. 2018, 64, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturzeneker, M.C.S.; de Noronha, L.; Olandoski, M.; Wendling, L.U.; Precoma, D.B. Ramipril significantly attenuates the development of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in hyperlipidaemic rabbits. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 9, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.G.; Mok, J.S.; Han, Y.I.; Park, T.S.; Kang, K.W.; Choi, C.S.; Park, H.D.; Park, J. Connectivity mapping of angiotensin-PPAR interactions involved in the amelioration of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by Telmisartan. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapaksha, I.G.; Gunarathne, L.S.; Asadi, K.; Laybutt, R.; Andrikopoulous, S.; Alexander, I.E.; Watt, M.J.; Angus, P.W.; Herath, C.B. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-2 Therapy Improves Liver Fibrosis and Glycemic Control in Diabetic Mice With Fatty Liver. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 1056–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, S.C.; Pershadsingh, H.A.; Ho, C.I.; Chittiboyina, A.; Desai, P.; Pravenec, M.; Qi, N.; Wang, J.; Avery, M.A.; Kurtz, T.W. Identification of telmisartan as a unique angiotensin II receptor antagonist with selective PPARgamma-modulating activity. Hypertension 2004, 43, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enjoji, M.; Kotoh, K.; Kato, M.; Higuchi, N.; Kohjima, M.; Nakashima, M.; Nakamuta, M. Therapeutic effect of ARBs on insulin resistance and liver injury in patients with NAFLD and chronic hepatitis C: A pilot study. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 22, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wong, G.L.; Yip, T.C.; Tse, Y.; Liang, L.Y.; Hui, V.W.; Lin, H.; Li, G.; Lai, J.C.; Chan, H.L.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors prevent liver-related events in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2022, 76, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, T.; Tomita, K.; Kawai, T.; Yokoyama, H.; Shimada, A.; Kikuchi, M.; Hirose, H.; Ebinuma, H.; Irie, J.; Ojiro, K.; et al. Effect of Telmisartan or Losartan for Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Fatty Liver Protection Trial by Telmisartan or Losartan Study (FANTASY). Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 587140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Kabir, J.; Mustafa, G.; Gupta, U.; Hasan, S.; Alam, A. Effect of telmisartan on histological activity and fibrosis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A 1-year randomized control trial. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Wu, W.; Ye, J.; Fang, D.; Shi, D.; Li, L. Clinical application of angiotensin receptor blockers in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 24155–24167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.T. Aldosterone in congestive heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.; Yang, Y.F.; Pitt, B. Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists for Hypertension Management in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease BLOCK-CKD Trial. Hypertension 2020, 76, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, B.; Zannad, F.; Remme, W.J.; Cody, R.; Castaigne, A.; Perez, A.; Palensky, J.; Wittes, J. The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure. Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study Investigators. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, B.; Remme, W.; Zannad, F.; Neaton, J.; Martinez, F.; Roniker, B.; Bittman, R.; Hurley, S.; Kleiman, J.; Gatlin, M. Eplerenone, a Selective Aldosterone Blocker, in Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction after Myocardial Infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannad, F.; McMurray, J.J.; Krum, H.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Swedberg, K.; Shi, H.; Vincent, J.; Pocock, S.J.; Pitt, B. Eplerenone in Patients with Systolic Heart Failure and Mild Symptoms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapelios, C.J.; Murrow, J.R.; Nührenberg, T.G.; Lopez, M.N.M. Effect of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists on cardiac function in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Heart Fail. Rev. 2019, 24, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, B.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Assmann, S.F.; Boineau, R.; Anand, I.S.; Claggett, B.; Clausell, N.; Desai, A.S.; Diaz, R.; Fleg, J.L.; et al. Spironolactone for Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, M.; Solís, N.; Quintero, P.; Barrera, F.; Cabrera, D.; Santiago, P.R.; Arab, J.P.; Padilla, O.; Roa, J.C.; Moshage, H.; et al. Beneficial effects of mineralocorticoid receptor blockade in experimental non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 2129–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, J.; Chen, D.; Hulse, J.L.; Whaley-Connell, A.T.; Sowers, J.R.; Jia, G. Targeting mineralocorticoid receptors in diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2022, 322, R253–R262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, D.; Rao, I.; Raasch, F.; Solis, N.; Pizarro, M.; Freire, M.; De Urturi, D.S.; Ramírez, C.A.; Triantafilo, N.; León, J.; et al. Mineralocorticoid receptor modulation by dietary sodium influences NAFLD development in mice. Ann. Hepatol. 2021, 24, 100357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, M.L.; Schou, M.; Rossignol, P.; Holm, M.R.; Rasmussen, J.; Brandt, N.; Frandsen, M.; Chabanova, E.; Dela, F.; Faber, J.; et al. Effect of the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist eplerenone on liver fat and metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (MIRAD trial). Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 2305–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Polyzos, S.; Kountouras, J.; Zafeiriadou, E.; Patsiaoura, K.; Katsiki, E.; Deretzi, G.; Zavos, C.; Tsarouchas, G.; Rakitzi, P.; Slavakis, A. Effect of spironolactone and vitamin E on serum metabolic parameters and insulin resistance in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2011, 12, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Polymerou, V.; Katsinelos, P. Effects of combined low-dose spironolactone plus vitamin E vs vitamin E monotherapy on insulin resistance, non-invasive indices of steatosis and fibrosis, and adipokine levels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 1805–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, H.R. Calcium channel blockers in the treatment of hypertension and prevention of cardiovascular disease: Results from major clinical trials. Clin. Cornerstone 2004, 6, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, D.; Qian, M.; Liu, J.; Pan, C.; Duan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, W.; Wang, L. Amlodipine, an anti-hypertensive drug, alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating gut microbiota. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 2054–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozono, M.; Uto, H.; Ibusuki, R.; Arima, S.; Oda, K.; Taguchi, H.; Sasaki, F.; Nasu, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Setoyama, H.; et al. Antihypertensive therapy improves insulin resistance and serum levels of interleukin-6 and −10 in spontaneously hypertensive rats with steatohepatitis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 5385–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triposkiadis, F.; Karayannis, G.; Giamouzis, G.; Skoularigis, J.; Louridas, G.; Butler, J. The sympathetic nervous system in heart failure physiology, pathophysiology, and clinical implications. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 1747–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuuti, J.; Wijns, W.; Saraste, A.; Capodanno, D.; Barbato, E.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Prescott, E.; Storey, R.F.; Deaton, C.; Cuisset, T.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 407–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Byrne, R.; Rossello, X.; Coughlan, J.J.; Barbato, E.; Berry, C.; Chieffo, A.; Claeys, M.J.; Dan, G.-A.; Dweck, M.R.; Galbraith, M.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes: Developed by the task force on the management of acute coronary syndromes of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3720–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, C.; Soeda, J.; Asilmaz, E.; Sigalla, B.; Morgan, M.; Sinelli, N.; Roskams, T.; Oben, J.A. Propranolol, a β-adrenoceptor antagonist, worsens liver injury in a model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 437, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernon, G.; Baranova, A.; Younossi, Z.M. Systematic review: The epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Abraham, M.; Unalp, A.; Wilson, L.; Lavine, J.; Doo, E.; Bass, N.M.; The Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Association between diabetes, family history of diabetes, and risk of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis. Hepatology 2012, 56, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Adams, L.A.; Canbay, A.; Syn, W.-K. Extrahepatic complications of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1174–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaefer, C.F.; Kushner, P.; Aguilar, R. User’s guide to mechanism of action and clinical use of GLP-1 receptor agonists. Postgrad. Med. 2015, 127, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-Y.; Wang, Q.-W.; Yang, X.-Y.; Yang, W.; Li, D.-R.; Jin, J.-Y.; Zhang, H.-C.; Zhang, X.-F. GLP−1 receptor agonists for the treatment of obesity: Role as a promising approach. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1085799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, K.; Noyan-Ashraf, M.H.; Hoefer, J.; Bolz, S.-S.; Drucker, D.J.; Husain, M. Cardioprotective and Vasodilatory Actions of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Are Mediated Through Both Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor–Dependent and –Independent Pathways. Circulation 2008, 117, 2340–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marso, S.P.; Daniels, G.H.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Kristensen, P.; Mann, J.F.E.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Ravn, L.S.; et al. Liraglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Riddle, M.C.; Rydén, L.; et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattar, N.; Lee, M.M.Y.; Kristensen, S.L.; Branch, K.R.H.; Del Prato, S.; Khurmi, N.S.; Lam, C.S.P.; Lopes, R.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Pratley, R.E.; et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoff, A.M.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Colhoun, H.M.; Deanfield, J.; Emerson, S.S.; Esbjerg, S.; Hardt-Lindberg, S.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kahn, S.E.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Obesity without Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Shlomo, S.; Zvibel, I.; Shnell, M.; Shlomai, A.; Chepurko, E.; Halpern, Z.; Barzilai, N.; Oren, R.; Fishman, S. Glucagon-like peptide-1 reduces hepatic lipogenesis via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.A.; Mells, J.; Dunham, R.M.; Grakoui, A.; Handy, J.; Saxena, N.K.; Anania, F.A. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Is Present on Human Hepatocytes and Has A Direct Role in Decreasing Hepatic Steatosis in Vitro by Modulating Elements of the Insulin Signaling Pathway. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipsen, D.H.; Rolin, B.; Rakipovski, G.; Skovsted, G.F.; Madsen, A.; Kolstrup, S.; Schou-Pedersen, A.M.; Skat-Rørdam, J.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Liraglutide Decreases Hepatic Inflammation and Injury in Advanced Lean Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 123, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachou, M.; Flevari, P.; Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Varytimiadis, C.; Kalaitzakis, E.; Kassi, E.; Androutsakos, T. The role of anti-diabetic drugs in NAFLD. Have we found the Holy Grail? A narrative review. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 80, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Tian, W.; Lin, L.; Xu, X. Liraglutide or insulin glargine treatments improves hepatic fat in obese patients with type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in twenty-six weeks: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 170, 108487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, A.; Andersen, G.; Hockings, P.; Johansson, L.; Morsing, A.; Palle, M.S.; Vogl, T.; Loomba, R.; Plum-Mörschel, L. Randomised clinical trial: Semaglutide versus placebo reduced liver steatosis but not liver stiffness in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease assessed by magnetic resonance imaging. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 54, 1150–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frøssing, S.; Nylander, M.; Chabanova, E.; Frystyk, J.; Holst, J.J.; Kistorp, C.; Skouby, S.O.; Faber, J. Effect of liraglutide on ectopic fat in polycystic ovary syndrome: A randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderheiden, A.; Harrison, L.B.; Warshauer, J.T.; Adams-Huet, B.; Li, X.; Yuan, Q.; Hulsey, K.; Dimitrov, I.; Yokoo, T.; Jaster, A.W.; et al. Mechanisms of Action of Liraglutide in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Treated With High-Dose Insulin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Gaunt, P.; Aithal, G.P.; Barton, D.; Hull, D.; Parker, R.; Hazlehurst, J.M.; Guo, K.; Abouda, G.; A Aldersley, M.; et al. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet 2016, 387, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, P.N.; Buchholtz, K.; Cusi, K.; Linder, M.; Okanoue, T.; Ratziu, V.; Sanyal, A.J.; Sejling, A.-S.; Harrison, S.A. A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Subcutaneous Semaglutide in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, R.; Yin, H.; Yu, O.; Azoulay, L. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists and Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors and Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Petracca, G.; Beatrice, G.; Csermely, A.; Lonardo, A.; Targher, G. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Metabolites 2021, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Wharton, S.; Connery, L.; Alves, B.; Kiyosue, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, J.P.; Jastreboff, A.M.; le Roux, C.W.; Sattar, N.; Aizenberg, D.; Mao, H.; Zhang, S.; Ahmad, N.N.; Bunck, M.C.; Benabbad, I.; et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity in people with type 2 diabetes (SURMOUNT-2): A double-blind, randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, Y.Y. Tirzepatide: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Bhatt, D.L.; Buse, J.B.; Del Prato, S.; E Kahn, S.; Lincoff, A.M.; McGuire, D.K.; A Nauck, M.; E Nissen, S.; Sattar, N.; et al. Comparison of tirzepatide and dulaglutide on major adverse cardiovascular events in participants with type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: SURPASS-CVOT design and baseline characteristics. Am. Heart J. 2024, 267, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaldelli, A.; Cusi, K.; Landó, L.F.; Bray, R.; Brouwers, B.; Rodríguez, Á. Effect of tirzepatide versus insulin degludec on liver fat content and abdominal adipose tissue in people with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-3 MRI): A substudy of the randomised, open-label, parallel-group, phase 3 SURPASS-3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, M.L.; Sanyal, A.J.; Loomba, R.; Wilson, J.M.; Nikooienejad, A.; Bray, R.; Karanikas, C.A.; Duffin, K.L.; Robins, D.A.; Haupt, A. Effects of Novel Dual GIP and GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Tirzepatide on Biomarkers of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1352–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Correa, J.I.; Correa-Rotter, R. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Mechanisms of Action: A Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 777861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care 2021, 45 (Suppl. S1), S125–S143. [Google Scholar]
- Packer, M. SGLT2 Inhibitors Produce Cardiorenal Benefits by Promoting Adaptive Cellular Reprogramming to Induce a State of Fasting Mimicry: A Paradigm Shift in Understanding Their Mechanism of Action. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Im, K.; Goodrich, E.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.; Cahn, A.; Furtado, R.H.M.; et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet 2019, 393, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Bocchi, E.; Böhm, M.; Brunner–La Rocca, H.-P.; Choi, D.-J.; Chopra, V.; Chuquiure-Valenzuela, E.; et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jojima, T.; Tomotsune, T.; Iijima, T.; Akimoto, K.; Suzuki, K.; Aso, Y. Empagliflozin (an SGLT2 inhibitor), alone or in combination with linagliptin (a DPP-4 inhibitor), prevents steatohepatitis in a novel mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and diabetes. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2016, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, Y.; Imajo, K.; Kato, T.; Kessoku, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Tomeno, W.; Kato, S.; Mawatari, H.; Fujita, K.; Yoneda, M.; et al. The Selective SGLT2 Inhibitor Ipragliflozin Has a Therapeutic Effect on Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, A.; Kurosaki, E.; Yokono, M.; Yamajuku, D.; Kihara, R.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Takasu, T.; Imamura, M.; Li, Q.; Tomiyama, H.; et al. Effects of SGLT2 selective inhibitor ipragliflozin on hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, hepatic steatosis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and obesity in type 2 diabetic mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 715, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusi, K.; Bril, F.; Barb, D.; Polidori, D.; Sha, S.; Ghosh, A.; Farrell, K.; Sunny, N.E.; Kalavalapalli, S.; Pettus, J.; et al. Effect of canagliflozin treatment on hepatic triglyceride content and glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahl, S.; Gancheva, S.; Straßburger, K.; Herder, C.; Machann, J.; Katsuyama, H.; Kabisch, S.; Henkel, E.; Kopf, S.; Lagerpusch, M.; et al. Empagliflozin Effectively Lowers Liver Fat Content in Well-Controlled Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase 4, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhini, S.H.; Wahsh, E.A.; Elberry, A.A.; El Ameen, N.F.; Saedii, A.A.; Refaie, S.M.; Elsayed, A.A.; Rabea, H.M. The Impact of an SGLT2 Inhibitor versus Ursodeoxycholic Acid on Liver Steatosis in Diabetic Patients. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N.; Fitchett, D.; Hantel, S.; George, J.T.; Zinman, B. Empagliflozin is associated with improvements in liver enzymes potentially consistent with reductions in liver fat: Results from randomised trials including the EMPA-REG OUTCOME® trial. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Xu, X.; Guo, L.; Li, J.; Li, L. Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 635556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobita, H.; Yazaki, T.; Kataoka, M.; Kotani, S.; Oka, A.; Mishiro, T.; Oshima, N.; Kawashima, K.; Ishimura, N.; Naora, K.; et al. Comparison of dapagliflozin and teneligliptin in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients without type 2 diabetes mellitus: A prospective randomized study. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2021, 68, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Androutsakos, T.; Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Bakasis, A.-D.; Kyrou, I.; Efstathopoulos, E.; Randeva, H.S.; Kassi, E. SGLT-2 Inhibitors in NAFLD: Expanding Their Role beyond Diabetes and Cardioprotection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Shah, R.B.; Singhal, S.; Dutta, S.B.; Bansal, S.; Sinha, S.; Haque, M. Metformin: A Review of Potential Mechanism and Therapeutic Utility Beyond Diabetes. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2023, 17, 1907–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Peng, M.; Tang, X.; Xu, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, A.F.; Yang, X. Protective effects of metformin in various cardiovascular diseases: Clinical evidence and AMPK-dependent mechanisms. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 4886–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, W.; Dai, H.; Deng, Z. Cardiovascular risk following metformin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Results from meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 160, 108001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.M.; Sabry, N.; Farid, S. Effect of metformin on left ventricular mass and functional parameters in non-diabetic patients: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2022, 22, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, P.P.; Singh, A.G.; Murad, M.H.; Sanchez, W. Anti-Diabetic Medications and the Risk of Hepatocellular Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Desai, A.P.; Gawrieh, S.; Ghabril, M.; Saxena, R.; Cummings, O.W.; Chalasani, N. Long-term metformin use may improve clinical outcomes in diabetic patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and bridging fibrosis or compensated cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakoski, M.O.; Singal, A.G.; Rogers, M.A.M.; Conjeevaram, H. Meta-analysis: Insulin sensitizers for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 32, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Chen, D. Metformin in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed. Rep. 2013, 1, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebovitz, H.E. Thiazolidinediones: The Forgotten Diabetes Medications. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2019, 19, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, S.E.; Nicholls, S.J.; Wolski, K.; Nesto, R.; Kupfer, S.; Perez, A.; Jure, H.; De Larochellière, R.; Staniloae, C.S.; Mavromatis, K.; et al. Comparison of pioglitazone vs glimepiride on progression of coronary atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes: The PERISCOPE randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2008, 299, 1561–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormandy, J.A.; Charbonnel, B.; Eckland, D.J.A.; Erdmann, E.; Massi-Benedetti, M.; Moules, I.K.; Skene, A.M.; Tan, M.H.; Lefèbvre, P.J.; Murray, G.D.; et al. Secondary prevention of macrovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes in the PROactive Study (PROspective pioglitAzone Clinical Trial In macroVascular Events): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005, 366, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athyros, V.G.; Alexandrides, T.K.; Bilianou, H.; Cholongitas, E.; Doumas, M.; Ganotakis, E.S.; Goudevenos, J.; Elisaf, M.S.; Germanidis, G.; Giouleme, O.; et al. The use of statins alone, or in combination with pioglitazone and other drugs, for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and related cardiovascular risk. An Expert Panel Statement. Metabolism 2017, 71, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lincoff, A.M.; Wolski, K.; Nicholls, S.J.; Nissen, S.E. Pioglitazone and risk of cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. JAMA 2007, 298, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.E.; Wolski, K. Effect of rosiglitazone on the risk of myocardial infarction and death from cardiovascular causes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 2457–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Meng, Z.; Sun, A.; Yang, Z. Pioglitazone suppresses inflammation and fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by down-regulating PDGF and TIMP-2: Evidence from in vitro study. Cancer Biomark. 2017, 20, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalavalapalli, S.; Bril, F.; Koelmel, J.P.; Abdo, K.; Guingab, J.; Andrews, P.; Li, W.-Y.; Jose, D.; Yost, R.A.; Frye, R.F.; et al. Pioglitazone improves hepatic mitochondrial function in a mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 315, E163–E173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfort, R.; Harrison, S.A.; Brown, K.; Darland, C.; Finch, J.; Hardies, J.; Balas, B.; Gastaldelli, A.; Tio, F.; Pulcini, J.; et al. A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Pioglitazone in Subjects with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2297–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aithal, G.P.; Thomas, J.A.; Kaye, P.V.; Lawson, A.; Ryder, S.D.; Spendlove, I.; Austin, A.S.; Freeman, J.G.; Morgan, L.; Webber, J. Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Pioglitazone in Nondiabetic Subjects With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratziu, V.; Giral, P.; Jacqueminet, S.; Charlotte, F.; Hartemann–Heurtier, A.; Serfaty, L.; Podevin, P.; Lacorte, J.M.; Bernhardt, C.; Bruckert, E.; et al. Rosiglitazone for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: One-Year Results of the Randomized Placebo-Controlled Fatty Liver Improvement With Rosiglitazone Therapy (FLIRT) Trial. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusi, K.; Orsak, B.; Bril, F.; Lomonaco, R.; Hecht, J.; Ortiz-Lopez, C.; Tio, F.; Hardies, J.; Darland, C.; Musi, N.; et al. Long-Term Pioglitazone Treatment for Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 165, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.-F.; Dai, C.-Y.; Huang, C.-F.; Tsai, P.-C.; Hsu, P.-Y.; Huang, S.-F.; Bair, M.-J.; Hou, N.-J.; Huang, C.-I.; Liang, P.-C.; et al. First-in-Asian double-blind randomized trial to assess the efficacy and safety of insulin sensitizer in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients. Hepatol. Int. 2021, 15, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Chalasani, N.; Kowdley, K.V.; McCullough, A.; Diehl, A.M.; Bass, N.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Lavine, J.E.; Tonascia, J.; Unalp, A.; et al. Pioglitazone, Vitamin E, or Placebo for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boettcher, E.; Csako, G.; Pucino, F.; Wesley, R.; Loomba, R. Meta-analysis: Pioglitazone improves liver histology and fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, G.; Cassader, M.; Paschetta, E.; Gambino, R. Thiazolidinediones and Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 633–640. [Google Scholar]
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists Collaboration; Fulcher, J.; O’Connell, R.; Voysey, M.; Emberson, J.; Blackwell, L.; Mihaylova, B.; Simes, J.; Collins, R.; Kirby, A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of LDL-lowering therapy among men and women: Meta-analysis of individual data from 174,000 participants in 27 randomised trials. Lancet 2015, 385, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Istvan, E.S.; Deisenhofer, J. Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Science 2001, 292, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oesterle, A.; Laufs, U.; Liao, J.K. Pleiotropic Effects of Statins on the Cardiovascular System. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaebel, J.H.; Skjødt, M.; Skat-Rørdam, J.; Rakipovski, G.; Ipsen, D.H.; Schou-Pedersen, A.M.V.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Atorvastatin and Vitamin E Accelerates NASH Resolution by Dietary Intervention in a Preclinical Guinea Pig Model. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, L.-W.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Lee, T.-F.; Lin, Y.; Chiu, Y.-T.; Yang, K.-C.; Wu, J.-C.; Huang, Y.-T. Fluvastatin attenuates hepatic steatosis-induced fibrogenesis in rats through inhibiting paracrine effect of hepatocyte on hepatic stellate cells. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, M.; Raurell, I.; Hide, D.; Fernández-Iglesias, A.; Gil, M.; Barberá, A.; Salcedo, M.T.; Augustin, S.; Genescà, J.; Martell, M. Restoration of liver sinusoidal cell phenotypes by statins improves portal hypertension and histology in rats with NASH. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athyros, V.G.; Tziomalos, K.; Gossios, T.D.; Griva, T.; Anagnostis, P.; Kargiotis, K.; Pagourelias, E.D.; Theocharidou, E.; Karagiannis, A.; Mikhailidis, D.P. Safety and efficacy of long-term statin treatment for cardiovascular events in patients with coronary heart disease and abnormal liver tests in the Greek Atorvastatin and Coronary Heart Disease Evaluation (GREACE) Study: A post-hoc analysis. Lancet 2010, 376, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikkanen, M.J.; Fayyad, R.; Faergeman, O.; Olsson, A.G.; Wun, C.-C.; Laskey, R.; Kastelein, J.J.; Holme, I.; Pedersen, T.R. Effect of intensive lipid lowering with atorvastatin on cardiovascular outcomes in coronary heart disease patients with mild-to-moderate baseline elevations in alanine aminotransferase levels. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 3846–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athyros, V.G.; Ganotakis, E.; Kolovou, G.D.; Nicolaou, V.; Achimastos, A.; Bilianou, E.; Alexandrides, T.; Karagiannis, A.; Paletas, K.; Liberopoulos, E.N.; et al. Assessing The Treatment Effect in Metabolic Syndrome Without Perceptible Diabetes (ATTEMPT): A Prospective-Randomized Study in Middle Aged Men and Women. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2011, 9, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athyros, V.G.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Didangelos, T.P.; Giouleme, O.I.; Liberopoulos, E.N.; Karagiannis, A.; Kakafika, A.I.; Tziomalos, K.; Burroughs, A.K.; Elisaf, M.S. Effect of multifactorial treatment on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in metabolic syndrome: A randomised study. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2006, 22, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.H.; Rha, S.W.; Kang, H.J.; Bae, J.W.; Choi, B.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Gwon, H.C.; Bae, J.H.; Hong, B.K.; Choi, D.H.; et al. Evaluation of short-term safety and efficacy of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors in hypercholesterolemic patients with elevated serum alanine transaminase concentrations: PITCH study (PITavastatin versus atorvastatin to evaluate the effect on patients with hypercholesterolemia and mild to moderate hepatic damage). J. Clin. Lipidol. 2012, 6, 340–351. [Google Scholar]
- Ekstedt, M.; Franzén, L.E.; Mathiesen, U.L.; Holmqvist, M.; Bodemar, G.; Kechagias, S. Statins in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and chronically elevated liver enzymes: A histopathological follow-up study. J. Hepatol. 2007, 47, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Toshiyoshi, M.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, Y.M.; Zhao, Y. Statins on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 14 RCTs. Medicine 2023, 102, e33981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Poly, T.N.; Walther, B.A.; Yang, H.-C.; Li, Y.-C.J. Statin Use and the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Cancers 2020, 12, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayada, I.; van Kleef, L.A.; Zhang, H.; Liu, K.; Li, P.; Abozaid, Y.J.; Lavrijsen, M.; Janssen, H.L.; van der Laan, L.J.; Ghanbari, M.; et al. Dissecting the multifaceted impact of statin use on fatty liver disease: A multidimensional study. EBioMedicine 2023, 87, 104392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, P.P.; Phan, B.A.P.; Dayspring, T.D. Ezetimibe therapy: Mechanism of action and clinical update. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2012, 8, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, C.P.; Blazing, M.A.; Giugliano, R.P.; McCagg, A.; White, J.A.; Théroux, P.; Darius, H.; Lewis, B.S.; Ophuis, T.O.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. Ezetimibe Added to Statin Therapy after Acute Coronary Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2387–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitouni, M.; Sabouret, P.; Kerneis, M.; Silvain, J.; Collet, J.-P.; Bruckert, E.; Montalescot, G. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for management of dyslipidaemia: Strengths and limitations. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2021, 7, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraoka, T.; Aoki, K.; Iwasaki, T.; Shinoda, K.; Nakamura, A.; Aburatani, H.; Mori, S.; Tokuyama, K.; Kubota, N.; Kadowaki, T.; et al. Ezetimibe decreases SREBP-1c expression in liver and reverses hepatic insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet. Metabolism 2011, 60, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Hoos, L.; Cook, J.; Tetzloff, G.; Davis, H.; van Heek, M.; Hwa, J.J. Ezetimibe improves high fat and cholesterol diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 584, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, M.; Fujita, K.; Nozaki, Y.; Endo, H.; Takahashi, H.; Hosono, K.; Suzuki, K.; Mawatari, H.; Kirikoshi, H.; Inamori, M.; et al. Efficacy of ezetimibe for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: An open-label, pilot study. Hepatol. Res. 2010, 40, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Shima, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Mitsuyoshi, H.; Minami, M.; Yasui, K.; Itoh, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Fukui, M.; Hasegawa, G.; et al. Efficacy of long-term ezetimibe therapy in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, Y.; Takamura, T.; Honda, M.; Kita, Y.; Zen, Y.; Kato, K.-I.; Misu, H.; Ota, T.; Nakamura, M.; Yamada, K.; et al. The effects of ezetimibe on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and glucose metabolism: A randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 878–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Sirlin, C.B.; Ang, B.; Bettencourt, R.; Jain, R.; Salotti, J.; Soaft, L.; Hooker, J.; Kono, Y.; Bhatt, A.; et al. Ezetimibe for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Assessment by Novel Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Magnetic Resonance Elastography in a Randomized Trial (MOZART Trial). Hepatology 2015, 61, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Jun, D.W.; Kim, H.J.; Oh, H.; Saeed, W.K.; Ahn, H.; Cheung, R.C.; Nguyen, M.H. Ezetimibe decreased nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score but not hepatic steatosis. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2019, 34, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Rhee, H.; Kim, Y.-E.; Lee, M.; Lee, B.-W.; Kang, E.S.; Cha, B.-S.; Choi, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-H. Ezetimibe combination therapy with statin for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An open-label randomized controlled trial (ESSENTIAL study). BMC Med. 2022, 20, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, E.M.; Davidson, M.H. PCSK9 Inhibitors: Mechanism of Action, Efficacy, and Safety. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 19, S31–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatine, M.S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Keech, A.C.; Honarpour, N.; Wiviott, S.D.; Murphy, S.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Wasserman, S.M.; et al. Evolocumab and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.G.; Steg, P.G.; Szarek, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bittner, V.A.; Diaz, R.; Edelberg, J.M.; Goodman, S.G.; Hanotin, C.; Harrington, R.A.; et al. Alirocumab and Cardiovascular Outcomes after Acute Coronary Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharidou, E.; Papademetriou, M.; Reklou, A.; Sachinidis, A.; Boutari, C.; Giouleme, O. The Role of PCSK9 in the Pathogenesis of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Effect of PCSK9 Inhibitors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 3654–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimakopoulou, A.; Sfikas, G.; Athyros, V. PCSK9 administration ameliorates non alcoholic fatty disease in patients with heterozygous familial hyperlipidemia. Hell. J. Atheroscler 2018, 9, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiq, M.; Walmann, T.; Nutalapati, V.; Gibson, C.; Zafar, Y. Effects of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type-9 inhibitors on fatty liver. World J. Hepatol. 2020, 12, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staels, B.; Dallongeville, J.; Auwerx, J.; Schoonjans, K.; Leitersdorf, E.; Fruchart, J.-C. Mechanism of Action of Fibrates on Lipid and Lipoprotein Metabolism. Circulation 1998, 98, 2088–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harano, Y.; Yasui, K.; Toyama, T.; Nakajima, T.; Mitsuyoshi, H.; Mimani, M.; Hirasawa, T.; Itoh, Y.; Okanoue, T. Fenofibrate, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α agonist, reduces hepatic steatosis and lipid peroxidation in fatty liver Shionogi mice with hereditary fatty liver. Liver Int. 2006, 26, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Meng, F.L.; Lu, R.J.; Jia, X.Q.; Zhao, X.C. Therapy effects of fenofibrate on alcoholic fatty liver and drug-induced fatty liver in rats. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2003, 11, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmoneim, D.; El-Adl, M.; El-Sayed, G.; El-Sherbini, E.S. Protective effect of fenofibrate against high-fat-high-fructose diet induced non-obese NAFLD in rats. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 35, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamoorthi, A.; Arias, N.; Basta, J.; Lee, R.G.; Baldán, Á. Amelioration of diet-induced steatohepatitis in mice following combined therapy with ASO-Fsp27 and fenofibrate. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 2127–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbrini, E.; Mohammed, B.S.; Korenblat, K.M.; Magkos, F.; McCrea, J.; Patterson, B.W.; Klein, S. Effect of Fenofibrate and Niacin on Intrahepatic Triglyceride Content, Very Low-Density Lipoprotein Kinetics, and Insulin Action in Obese Subjects with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 2727–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghoubi, M.; Jafari, S.; Sajedi, B.; Gohari, S.; Akbarieh, S.; Heydari, A.H.; Jameshoorani, M. Comparison of fenofibrate and pioglitazone effects on patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 29, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Steg, P.G.; Miller, M.; Brinton, E.A.; Jacobson, T.A.; Ketchum, S.B.; Doyle, R.T., Jr.; Juliano, R.A.; Jiao, L.; Granowitz, C.; et al. Cardiovascular Risk Reduction with Icosapent Ethyl for Hypertriglyceridemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spooner, M.H.; Jump, D.B. Omega-3 fatty acids and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adults and children: Where do we stand? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2019, 22, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-H.; Fu, Y.; Yang, S.-J.; Chi, C.-C. Effects of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.A.; Bruinstroop, E.; Singh, B.K.; Yen, P.M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hypercholesterolemia: Roles of Thyroid Hormones, Metabolites, and Agonists. Thyroid 2019, 29, 1173–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bedossa, P.; Guy, C.D.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Loomba, R.; Taub, R.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Neff, G.W.; Rinella, M.E.; et al. A Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Resmetirom in NASH with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Taub, R.; Neff, G.W.; Lucas, K.J.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Alkhouri, N.; Bashir, M.R. Resmetirom for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2919–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antithrombotic Trialists’ Collaboration. Collaborative meta-analysis of randomised trials of antiplatelet therapy for prevention of death, myocardial infarction, and stroke in high risk patients. BMJ 2002, 324, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.-M.; Lee, Y.-J.; Jang, Y.-N.; Kim, H.-M.; Seo, H.S.; Jung, T.W.; Jeong, J.H. Aspirin Improves Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Atherosclerosis through Regulation of the PPARδ-AMPK-PGC-1αPathway in Dyslipidemic Conditions. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 7806860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.G.; Henson, J.; Osganian, S.; Masia, R.; Chan, A.T.; Chung, R.T.; Corey, K.E. Daily Aspirin Use Associated With Reduced Risk For Fibrosis Progression In Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 2776–2784.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.-Y.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Ho, H.J.; Lin, J.-T.; Chen, Y.-J.; Wu, C.-Y. Daily aspirin associated with a reduced risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A population-based cohort study. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 61, 102065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.G.; Wilechansky, R.M.; Stoyanova, S.; Grossman, A.; Dichtel, L.E.; Lauer, G.M.; Miller, K.K.; Hoshida, Y.; Corey, K.E.; Loomba, R.; et al. Aspirin for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Without Cirrhosis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 331, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ali, L.; van de Vegte, Y.J.; Said, M.A.; Groot, H.E.; Hendriks, T.; Yeung, M.W.; Lipsic, E.; van der Harst, P. Fetuin-A and its genetic association with cardiometabolic disease. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Schick, F.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Häring, H.-U.; White, M.F. The role of hepatokines in NAFLD. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 236–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Martinez-Perez, Y.; Calzadilla-Bertot, L.; Torres-Gonzalez, A.; Gra-Oramas, B.; Gonzalez-Fabian, L.; Friedman, S.L.; Diago, M.; Romero-Gomez, M. Weight Loss Through Lifestyle Modification Significantly Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 367–378.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsarou, A.; Tsioulos, G.; Kassi, E.; Chatzigeorgiou, A. Current and experimental pharmacotherapy for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hormones 2024, 23, 621–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raptis, D.D.; Mantzoros, C.S.; A Polyzos, S. Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 as a Potential Therapeutic Target of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2023, 19, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genua, I.; Cusi, K. Pharmacological Approaches to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Current and Future Therapies. Diabetes Spectr. 2024, 37, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Nikolopoulou, C.; Papoutsi, K.; Kyrou, I.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Kyriakopoulos, G.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Kalotychou, V.; Randeva, M.S.; Chatha, K.; et al. Empagliflozin Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in High Fat Diet Fed ApoE((-/-)) Mice by Activating Autophagy and Reducing ER Stress and Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Kessoku, T.; Kawanaka, M.; Nonaka, M.; Hyogo, H.; Fujii, H.; Nakajima, T.; Imajo, K.; Tanaka, K.; Kubotsu, Y.; et al. Ipragliflozin Improves the Hepatic Outcomes of Patients With Diabetes with NAFLD. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, Y.; Honda, M.; Harada, K.; Kita, Y.; Takata, N.; Tsujiguchi, H.; Tanaka, T.; Goto, H.; Nakano, Y.; Iida, N.; et al. Comparison of Tofogliflozin and Glimepiride Effects on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Participants with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, 48-Week, Open-Label, Active-Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 2064–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Van Natta, M.L.; Clark, J.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Diehl, A.; Dasarathy, S.; Loomba, R.; Chalasani, N.; Kowdley, K.; Hameed, B.; et al. Prospective Study of Outcomes in Adults with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1559–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
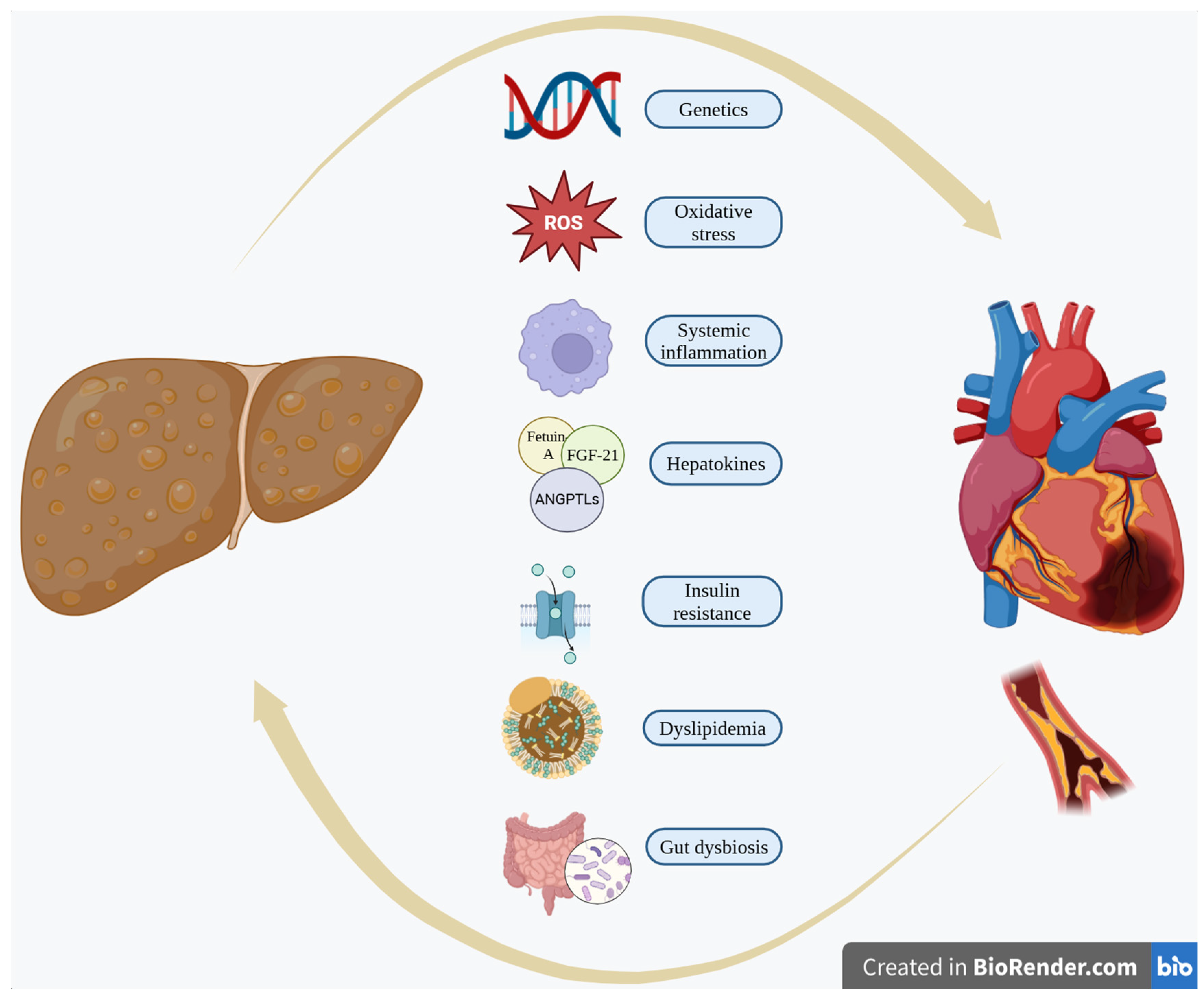
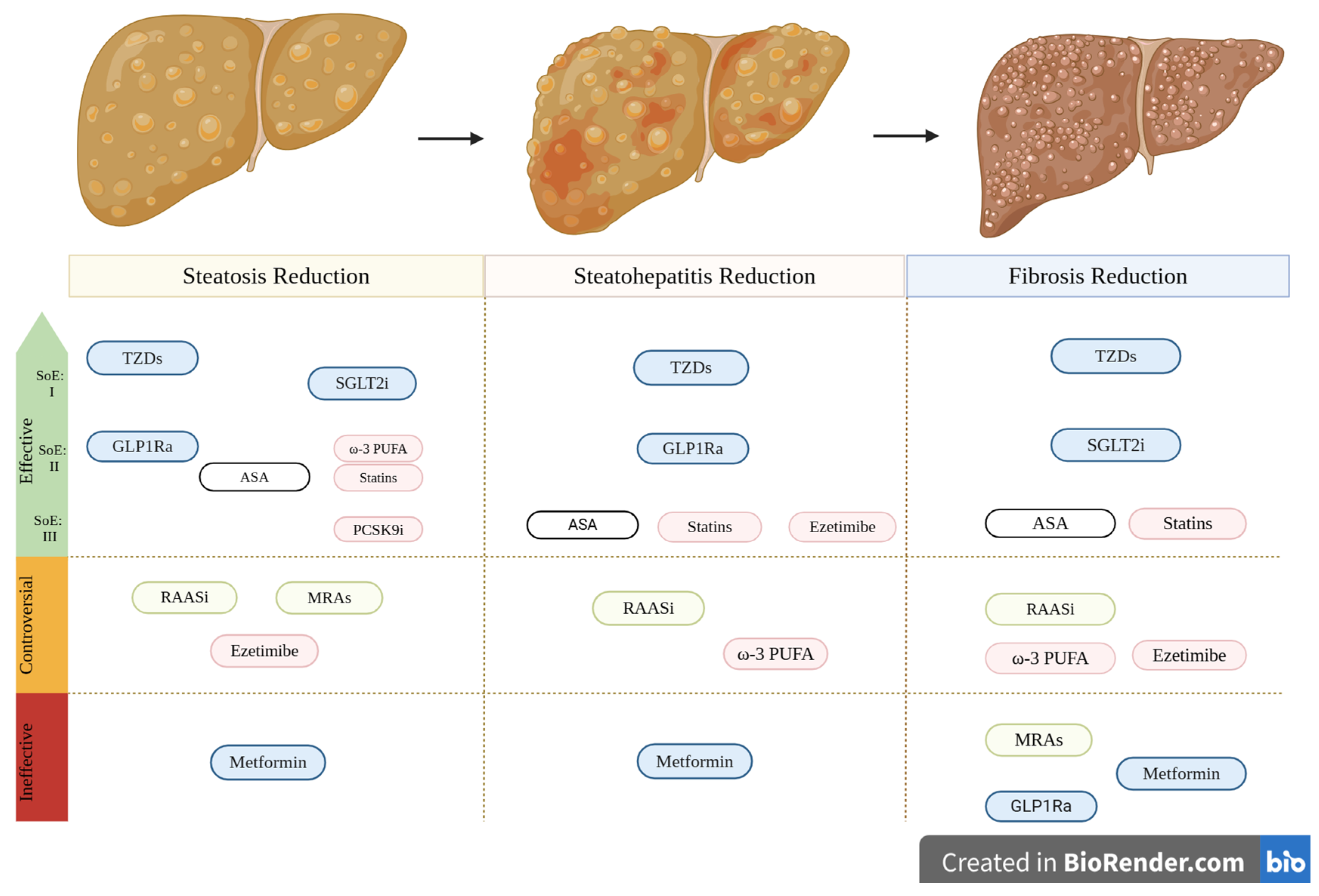
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zisis, M.; Chondrogianni, M.E.; Androutsakos, T.; Rantos, I.; Oikonomou, E.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Kassi, E. Linking Cardiovascular Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): The Role of Cardiometabolic Drugs in MASLD Treatment. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030324
Zisis M, Chondrogianni ME, Androutsakos T, Rantos I, Oikonomou E, Chatzigeorgiou A, Kassi E. Linking Cardiovascular Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): The Role of Cardiometabolic Drugs in MASLD Treatment. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(3):324. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030324
Chicago/Turabian StyleZisis, Marios, Maria Eleni Chondrogianni, Theodoros Androutsakos, Ilias Rantos, Evangelos Oikonomou, Antonios Chatzigeorgiou, and Eva Kassi. 2025. "Linking Cardiovascular Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): The Role of Cardiometabolic Drugs in MASLD Treatment" Biomolecules 15, no. 3: 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030324
APA StyleZisis, M., Chondrogianni, M. E., Androutsakos, T., Rantos, I., Oikonomou, E., Chatzigeorgiou, A., & Kassi, E. (2025). Linking Cardiovascular Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): The Role of Cardiometabolic Drugs in MASLD Treatment. Biomolecules, 15(3), 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030324









