Cryo-EM Structure of the Flagellar Motor Complex from Paenibacillus sp. TCA20
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Plasmids
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Cryo-EM Acquisition
2.4. Image Processing
2.5. Model Building
3. Results
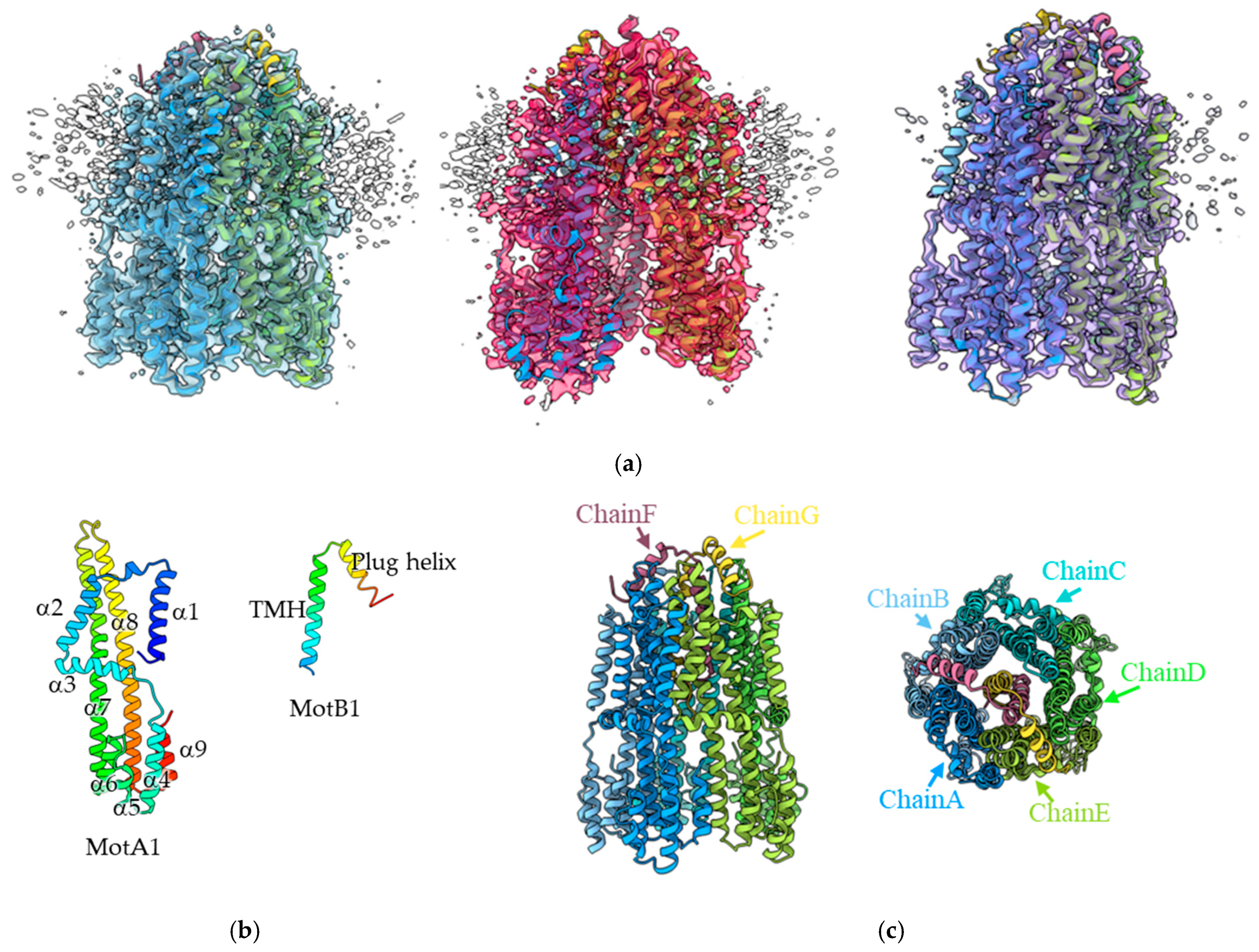
3.1. Structural Analysis of the MotA1/MotB1 Complex
3.2. Mechanism of Rotor Rotation by MotA1 in E. coli
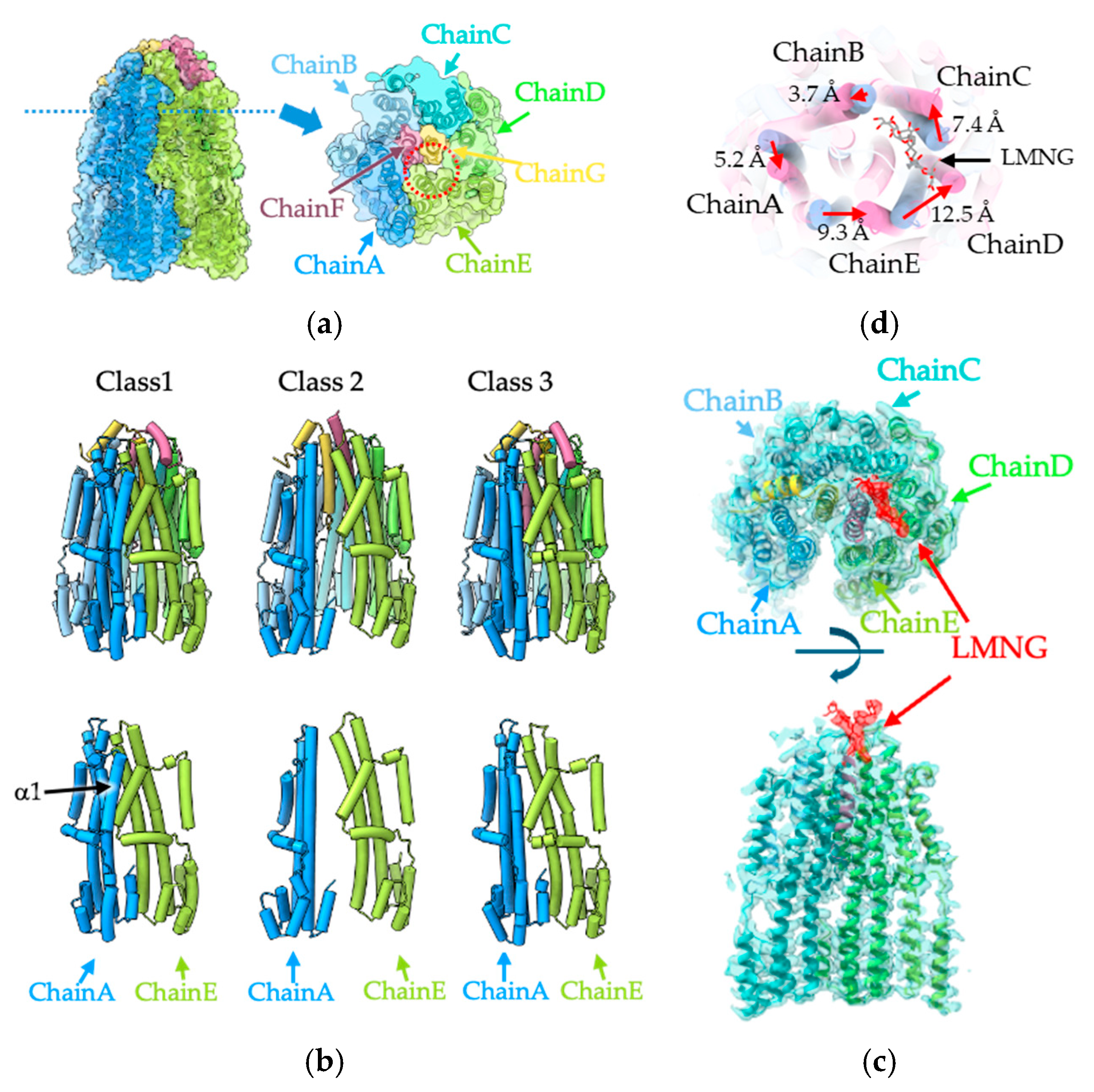
3.3. Structural Comparison of the Three MotA1 Rings
3.4. The Plug Helix of MotB1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berg, H. The rotary motor of bacterial flagella. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 19–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Minamino, T. Flagella-Driven Motility of Bacteria. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homma, M.; Nishikino, T.; Kojima, S. Achievements in bacterial flagellar research with focus on Vibrio species. Microbiol. Immunol. 2022, 66, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, D.F. Flagellar movement driven by proton translocation. FEBS Lett. 2003, 545, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, Y.; Kojima, S.; Kato, H.; Nishioka, N.; Kawagishi, I.; Homma, M. Putative channel components for the fast-rotating sodium-driven flagellar motor of a marine bacterium. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 5104–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Hicks, D.; Henkin, T.; Guffanti, A.; Powers, B.; Zvi, L.; Uematsu, K.; Krulwich, T. MotPS is the stator-force generator for motility of alkaliphilic Bacillus, and its homologue is a second functional Mot in Bacillus subtilis. Molecular. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 1035–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikino, T.; Takekawa, N.; Kishikawa, J.; Hirose, M.; Kojima, S.; Homma, M.; Kato, T.; Imada, K. Structural insight into sodium ion pathway in the bacterial flagellar stator from marine Vibrio. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2415713122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deme, J.C.; Johnson, S.; Vickery, O.; Aron, A.; Monkhouse, H.; Griffiths, T.; James, R.H.; Berks, B.C.; Coulton, J.W.; Stansfeld, P.J.; et al. Structures of the stator complex that drives rotation of the bacterial flagellum. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiveri, M.; Roa-Eguiara, A.; Kühne, C.; Wadhwa, N.; Hu, H.; Berg, H.C.; Erhardt, M.; Taylor, N.M.I. Structure and Function of Stator Units of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor. Cell 2020, 183, 244–257.e216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Santiveri, M.; Wadhwa, N.; Berg, H.C.; Erhardt, M.; Taylor, N.M.I. Structural basis of torque generation in the bi-directional bacterial flagellar motor. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2022, 47, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Popp, P.F.; Santiveri, M.; Roa-Eguiara, A.; Yan, Y.; Martin, F.J.O.; Liu, Z.; Wadhwa, N.; Wang, Y.; Erhardt, M.; et al. Ion selectivity and rotor coupling of the Vibrio flagellar sodium-driven stator unit. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Fazzio, R.T.; Blair, D.F. Membrane topology of the MotA protein of Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 251, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Lloyd, S.A.; Blair, D.F. Electrostatic interactions between rotor and stator in the bacterial flagellar motor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6436–6441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, S.A.; Blair, D.F. Charged residues of the rotor protein FliG essential for torque generation in the flagellar motor of Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 266, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorimitsu, T.; Mimaki, A.; Yakushi, T.; Homma, M. The conserved charged residues of the C-terminal region of FliG, a rotor component of the Na+-driven flagellar motor. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 334, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashima, H.; Kojima, S.; Homma, M. Site-directed crosslinking identifies the stator-rotor interaction surfaces in a hybrid bacterial flagellar motor. J. Bacteriol. 2021, 203, e00016-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Sharp, L.L.; Tang, H.L.; Lloyd, S.A.; Billings, S.; Braun, T.F.; Blair, D.F. Function of protonatable residues in the flagellar motor of Escherichia coli: A critical role for Asp 32 of MotB. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 2729–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosking, E.; Vogt, C.; Bakker, E.; Manson, M. The Escherichia coli MotAB proton channel unplugged. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 364, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenzinger, S.; Dewenter, L.; Delalez, N.J.; Leicht, O.; Berndt, V.; Paulick, A.; Berry, R.M.; Thanbichler, M.; Armitage, J.P.; Maier, B.; et al. Mutations targeting the plug-domain of the Shewanella oneidensis proton-driven stator allow swimming at increased viscosity and under anaerobic conditions. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 102, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Kojima, S.; Homma, M. Characterization of the Periplasmic Region of PomB, a Na+-Driven Flagellar Stator Protein in Vibrio alginolyticus. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 3773–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, M.; Terashima, H.; Koiwa, H.; Kojima, S. Putative Spanner Function of the. J. Bacteriol. 2021, 203, e0015921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, Y.V.; Che, Y.S.; Minamino, T.; Namba, K. Proton-conductivity assay of plugged and unplugged MotA/B proton channel by cytoplasmic pHluorin expressed in Salmonella. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imazawa, R.; Takahashi, Y.; Aoki, W.; Sano, M.; Ito, M. A novel type bacterial flagellar motor that can use divalent cations as a coupling ion. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoe, S.; Yoshida, M.; Terahara, N.; Sowa, Y. Coupling Ion Specificity of the Flagellar Stator Proteins MotA1/MotB1 of Paenibacillus SP. TCA20. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoue, Y.; Iwaki, M.; Shinobu, A.; Nishihara, Y.; Iwatsuki, H.; Terashima, H.; Kitao, A.; Kandori, H.; Homma, M. Essential ion binding residues for Na. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastronarde, D.N. Automated electron microscope tomography using robust prediction of specimen movements. J. Struct. Biol. 2005, 152, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punjani, A.; Rubinstein, J.L.; Fleet, D.J.; Brubaker, M.A. cryoSPARC: Algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-EM structure determination. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bepler, T.; Morin, A.; Rapp, M.; Brasch, J.; Shapiro, L.; Noble, A.J.; Berger, B. Positive-unlabeled convolutional neural networks for particle picking in cryo-electron micrographs. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.; Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D-Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, K.; Palmer, C.M.; Burnley, T.; Murshudov, G.N. Cryo-EM single particle structure refinement and map calculation using Servalcat. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D-Struct. Biol. 2021, 77, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, V.B.; Arendall, W.B.; Headd, J.J.; Keedy, D.A.; Immormino, R.M.; Kapral, G.J.; Murray, L.W.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. MolProbity: All-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66 Pt 1, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.; Goddard, T.; Huang, C.; Meng, E.; Couch, G.; Croll, T.; Morris, J.; Ferrin, T. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, M.L.; Young, J.W.; Zhao, Z.; Fabre, L.; Jun, D.; Li, J.; Dhupar, H.S.; Wason, I.; Mills, A.T.; Beatty, J.T.; et al. The Peptidisc, a simple method for stabilizing membrane proteins in detergent-free solution. eLife 2018, 7, e34085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Deme, J.C.; Furlong, E.J.; Caesar, J.J.E.; Chevance, F.F.V.; Hughes, K.T.; Lea, S.M. Structural Basis of Directional Switching by the Bacterial Flagellum. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 20249, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Onoe, S.; Nishikino, T.; Kinoshita, M.; Takekawa, N.; Minamino, T.; Imada, K.; Namba, K.; Kishikawa, J.-i.; Kato, T. Cryo-EM Structure of the Flagellar Motor Complex from Paenibacillus sp. TCA20. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030435
Onoe S, Nishikino T, Kinoshita M, Takekawa N, Minamino T, Imada K, Namba K, Kishikawa J-i, Kato T. Cryo-EM Structure of the Flagellar Motor Complex from Paenibacillus sp. TCA20. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(3):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030435
Chicago/Turabian StyleOnoe, Sakura, Tatsuro Nishikino, Miki Kinoshita, Norihiro Takekawa, Tohru Minamino, Katsumi Imada, Keiichi Namba, Jun-ichi Kishikawa, and Takayuki Kato. 2025. "Cryo-EM Structure of the Flagellar Motor Complex from Paenibacillus sp. TCA20" Biomolecules 15, no. 3: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030435
APA StyleOnoe, S., Nishikino, T., Kinoshita, M., Takekawa, N., Minamino, T., Imada, K., Namba, K., Kishikawa, J.-i., & Kato, T. (2025). Cryo-EM Structure of the Flagellar Motor Complex from Paenibacillus sp. TCA20. Biomolecules, 15(3), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030435






