How Does the Archaellum Work?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Archaellum Likely Assembles Using the Same Mechanism as Other Type IV Filament Superfamily Members
3. The Sole ATPase Must Switch from Assembly Function to Rotational Function Once the Archaellar Filament Is Fully Formed
4. Rotation Is Driven by the Same ATPase That Assembles the Archaellum
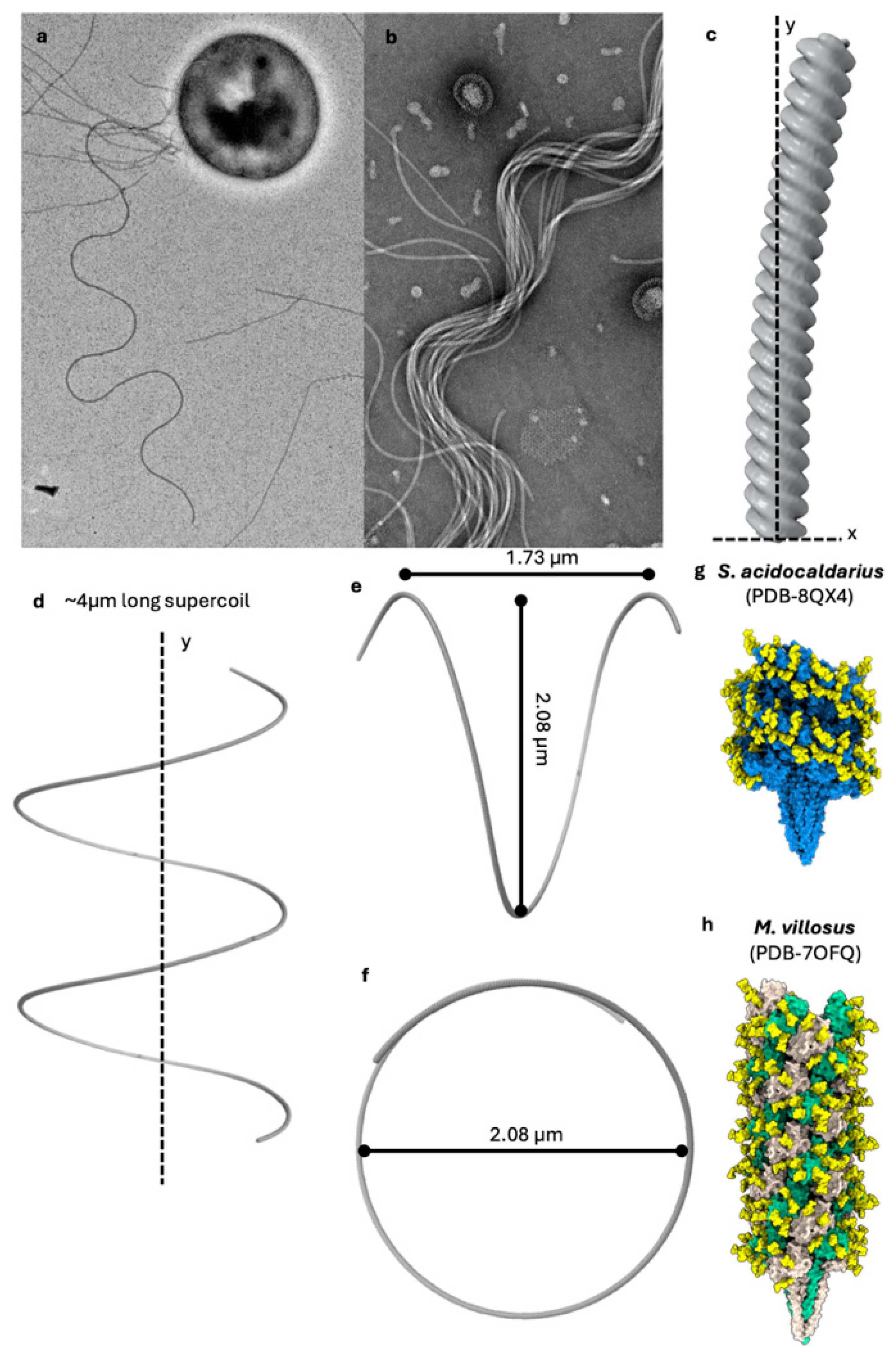
5. The Archaellum Is a Helical Propeller
6. What More Is Needed to Understand How the Archaellum Works?
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beeby, M.; Ferreira, J.L.; Tripp, P.; Albers, S.-V.; Mitchell, D.R. Propulsive Nanomachines: The Convergent Evolution of Archaella, Flagella and Cilia. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 253–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albers, S.V.; Jarrell, K.F. The Archaellum: How Archaea Swim. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrell, K.F.; Albers, S.-V.; Machado, J.N. de S. A Comprehensive History of Motility and Archaellation in Archaea. FEMS Microbes 2021, 2, xtab002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, J.-L.; Pelicic, V. Exceptionally Widespread Nanomachines Composed of Type IV Pilins: The Prokaryotic Swiss Army Knives. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 134–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeby, M. Evolution of a Family of Molecular Rube Goldberg Contraptions. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denise, R.; Abby, S.S.; Rocha, E.P.C. Diversification of the Type IV Filament Superfamily into Machines for Adhesion, Protein Secretion, DNA Uptake, and Motility. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skerker, J.M.; Berg, H.C. Direct Observation of Extension and Retraction of Type IV Pili. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6901–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reindl, S.; Ghosh, A.; Williams, G.J.; Lassak, K.; Neiner, T.; Henche, A.L.; Albers, S.V.; Tainer, J.A. Insights into FlaI Functions in Archaeal Motor Assembly and Motility from Structures, Conformations, and Genetics. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 1069–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Albers, S.-V. Assembly and Function of the Archaeal Flagellum. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, P.; Neiner, T.; D’Imprima, E.; Banerjee, A.; Reindl, S.; Ghosh, A.; Arvai, A.S.; Mills, D.J.; van der Does, C.; Tainer, J.A.; et al. The Nucleotide-Dependent Interaction of FlaH and FlaI Is Essential for Assembly and Function of the Archaellum Motor. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 99, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassak, K.; Neiner, T.; Ghosh, A.; Klingl, A.; Wirth, R.; Albers, S.V. Molecular Analysis of the Crenarchaeal Flagellum. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 83, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Tsai, C.-L.; Chaudhury, P.; Tripp, P.; Arvai, A.S.; Ishida, J.P.; Tainer, J.A.; Albers, S.-V. FlaF Is a β-Sandwich Protein That Anchors the Archaellum in the Archaeal Cell Envelope by Binding the S-Layer Protein. Structure 2015, 23, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.-L.; Tripp, P.; Sivabalasarma, S.; Zhang, C.; Rodriguez-Franco, M.; Wipfler, R.L.; Chaudhury, P.; Banerjee, A.; Beeby, M.; Whitaker, R.J.; et al. The Structure of the Periplasmic FlaG–FlaF Complex and Its Essential Role for Archaellar Swimming Motility. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Hartung, S.; van der Does, C.; Tainer, J.A.; Albers, S.-V. Archaeal Flagellar ATPase Motor Shows ATP-Dependent Hexameric Assembly and Activity Stimulation by Specific Lipid Binding. Biochem. J. 2011, 437, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, S.-V.; Szabó, Z.; Driessen, A.J.M. Protein Secretion in the Archaea: Multiple Paths towards a Unique Cell Surface. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmokoff, M.L.; Jarrell, K.F. Cloning and Sequencing of a Multigene Family Encoding the Flagellins of Methanococcus Voltae. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 7113–7125. [Google Scholar]
- Kalmokoff, M.L.; Karnauchow, T.M.; Jarrell, K.F. Conserved N-Terminal Sequences in the Flagellins of Archaebacteria. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990, 167, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlschroder, M.; Ghosh, A.; Tripepi, M.; Albers, S.V. Archaeal Type IV Pilus-like Structures-Evolutionarily Conserved Prokaryotic Surface Organelles. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 357–363. [Google Scholar]
- Szabó, Z.; Stahl, A.O.; Albers, S.V.; Kissinger, J.C.; Driessen, A.J.M.; Pohlschröder, M. Identification of Diverse Archaeal Proteins with Class III Signal Peptides Cleaved by Distinct Archaeal Prepilin Peptidases. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strom, M.S.; Nunn, D.N.; Lory, S. A Single Bifunctional Enzyme, PilD, Catalyzes Cleavage and N-Methylation of Proteins Belonging to the Type IV Pilin Family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 2404–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.Y.M.; Chaban, B.; Jarrell, K.F. Archaeal Flagella, Bacterial Flagella and Type IV Pili: A Comparison of Genes and Posttranslational Modifications. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 11, 167–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McCallum, M.; Tammam, S.; Khan, A.; Burrows, L.L.; Howell, P.L. The Molecular Mechanism of the Type IVa Pilus Motors. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, ncomms15091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohl, M.; Banks, E.J.; Manley, M.P.; Le, T.B.K.; Low, H.H. Bidirectional Pilus Processing in the Tad Pilus System Motor CpaF. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.E.; Saraste, M.; Runswick, M.; Gay, N.J. Distantly Related Sequences in the Alpha- and Beta-Subunits of ATP Synthase, Myosin, Kinases and Other ATP-Requiring Enzymes and a Common Nucleotide Binding Fold. EMBO J. 1982, 1, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraste, M.; Sibbald, P.R.; Wittinghofer, A. The P-Loop—A Common Motif in ATP- and GTP-Binding Proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1990, 15, 430–434. [Google Scholar]
- Takhar, H.K.; Kemp, K.; Kim, M.; Howell, P.L.; Burrows, L.L. The Platform Protein Is Essential for Type IV Pilus Biogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 9721–9728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abendroth, J.; Mitchell, D.D.; Korotkov, K.V.; Johnson, T.L.; Kreger, A.; Sandkvist, M.; Hol, W.G.J. The Three-Dimensional Structure of the Cytoplasmic Domains of EpsF from the Type 2 Secretion System of Vibrio cholerae. J. Struct. Biol. 2009, 166, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelicic, V. Mechanism of Assembly of Type 4 Filaments: Everything You Always Wanted to Know (but Were Afraid to Ask). Microbiology 2023, 169, 001311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Krausz, S.; Trachtenberg, S. The Flagellar Filament Structure of the Extreme Acidothermophile Sulfolobus Shibatae B12 Suggests That Archaeabacterial Flagella Have a Unique and Common Symmetry and Design. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 375, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Krausz, S.; Trachtenberg, S. The Structure of the Archeabacterial Flagellar Filament of the Extreme Halophile Halobacterium Salinarum R1M1 and Its Relation to Eubacterial Flagellar Filaments and Type IV Pili. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 321, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachtenberg, S.; Cohen-Krausz, S. The Archaeabacterial Flagellar Filament: A Bacterial Propeller with a Pilus-like Structure. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 11, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshcheryakov, V.A.; Wolf, M. Crystal Structure of the Flagellar Accessory Protein FlaH of Methanocaldococcus Jannaschii Suggests a Regulatory Role in Archaeal Flagellum Assembly. Protein Sci. 2016, 25, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa Machado, J.N.; Vollmar, L.; Schimpf, J.; Chaudhury, P.; Kumariya, R.; van der Does, C.; Hugel, T.; Albers, S.-V. Autophosphorylation of the KaiC-like Protein ArlH Inhibits Oligomerization and Interaction with ArlI, the Motor ATPase of the Archaellum. Mol. Microbiol. 2021, 116, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, P.I.; Whiteheart, S.W. AAA+ Proteins: Have Engine, Will Work. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Rodriguez-Franco, M.; Albers, S.-V.; Quax, T.E.F. The Switch Complex ArlCDE Connects the Chemotaxis System and the Archaellum. Mol. Microbiol. 2020, 114, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuno de Sousa Machado, J.; Albers, S.-V.; Daum, B. Towards Elucidating the Rotary Mechanism of the Archaellum Machinery. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 848597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaban, B.; Ng, S.Y.M.; Kanbe, M.; Saltzman, I.; Nimmo, G.; Aizawa, S.I.; Jarrell, K.F. Systematic Deletion Analyses of the Fla Genes in the Flagella Operon Identify Several Genes Essential for Proper Assembly and Function of Flagella in the Archaeon, Methanococcus Maripaludis. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 66, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umrekar, T.R.; Winterborn, Y.B.; Sivabalasarma, S.; Brantl, J.; Albers, S.-V.; Beeby, M. Evolution of Archaellum Rotation Involved Invention of a Stator Complex by Duplicating and Modifying a Core Component. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 773386. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, A.; Ghosh, A.; Mills, D.J.; Kahnt, J.; Vonck, J.; Albers, S.V. FlaX, a Unique Component of the Crenarchaeal Archaellum, Forms Oligomeric Ring-Shaped Structures and Interacts with the Motor ATPase FlaI. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 43322–43330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Oesterhelt, D. Morphology, Function and Isolation of Halobacterial Flagella. J. Mol. Biol. 1984, 176, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahapure, R.; Driessen, R.P.C.; Haurat, M.F.; Albers, S.V.; Dame, R.T. The Archaellum: A Rotating Type IV Pilus. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 91, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, S.; Kinosita, Y.; Uchida, N.; Nakane, D.; Nishizaka, T. Motor Torque Measurement of Halobacterium Salinarum Archaellar Suggests a General Model for ATP-Driven Rotary Motors. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinosita, Y.; Uchida, N.; Nakane, D.; Nishizaka, T. Direct Observation of Rotation and Steps of the Archaellum in the Swimming Halophilic Archaeon Halobacterium Salinarum. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Otaibi, N.S.; Bergeron, J.R.C. Structure and Assembly of the Bacterial Flagellum. In Macromolecular Protein Complexes IV; Subcellular Biochemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 99, pp. 395–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, C.B.; Lesich, K.A. The Mechanics of Cilia and Flagella: What We Know and What We Need to Know. Cytoskeleton 2024, 81, 648–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klena, N.; Pigino, G. Structural Biology of Cilia and Intraflagellar Transport. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 38, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Scholey, J.M. Assembly, Functions and Evolution of Archaella, Flagella and Cilia. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R278–R292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolley, D.M.; Vernon, G.G. A Study of Helical and Planar Waves on Sea Urchin Sperm Flagella, with a Theory of How They Are Generated. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 1333–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Minamino, T. Structure and Dynamics of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Complex. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Feng, H. Deciphering Bacterial Chemorepulsion: The Complex Response of Microbes to Environmental Stimuli. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutzberger, M.A.B.; Sonani, R.R.; Liu, J.; Chatterjee, S.; Wang, F.; Sebastian, A.L.; Biswas, P.; Ewing, C.; Zheng, W.; Poly, F.; et al. Convergent Evolution in the Supercoiling of Prokaryotic Flagellar Filaments. Cell 2022, 185, 3487–3500.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, W.R.; Doetsch, R.N. Effect of Viscosity on Bacterial Motility. J. Bacteriol. 1974, 117, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woese, C.R.; Kandler, O.; Wheelis, M.L. Towards a Natural System of Organisms: Proposal for the Domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 4576–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marwan, W.; Alam, M.; Oesterhelt, D. Rotation and Switching of the Flagellar Motor Assembly in Halobacterium Halobium. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 1971–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poweleit, N.; Ge, P.; Nguyen, H.H.; Loo, R.R.O.; Gunsalus, R.P.; Zhou, Z.H. CryoEM Structure of the Methanospirillum Hungatei Archaellum Reveals Structural Features Distinct from the Bacterial Flagellum and Type IV Pilus. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 2, 16222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daum, B.; Vonck, J.; Bellack, A.; Chaudhury, P.; Reichelt, R.; Albers, S.-V.; Rachel, R.; Kühlbrandt, W. Structure and in Situ Organisation of the Pyrococcus Furiosus Archaellum Machinery. eLife 2017, 6, e27470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshcheryakov, V.A.; Shibata, S.; Schreiber, M.T.; Villar-Briones, A.; Jarrell, K.F.; Aizawa, S.-I.; Wolf, M. High-resolution Archaellum Structure Reveals a Conserved Metal-binding Site. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e46340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambelli, L.; McLaren, M.; Conners, R.; Sanders, K.; Gaines, M.C.; Clark, L.; Gold, V.A.M.; Kattnig, D.; Sikora, M.; Hanus, C.; et al. Structure of the Two-Component S-Layer of the Archaeon Sulfolobus Acidocaldarius. eLife 2024, 13, e84617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, M.C.; Isupov, M.N.; McLaren, M.; Mollat, C.L.; Haque, R.U.; Stephenson, J.K.; Sivabalasarma, S.; Hanus, C.; Kattnig, D.; Gold, V.A.M.; et al. Towards a Molecular Picture of the Archaeal Cell Surface. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinosita, Y.; Nishizaka, T. Cross-Kymography Analysis to Simultaneously Quantify the Function and Morphology of the Archaellum. Biophys. Physicobiol 2018, 15, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambelli, L.; Isupov, M.N.; Conners, R.; McLaren, M.; Bellack, A.; Gold, V.; Rachel, R.; Daum, B. An Archaellum Filament Composed of Two Alternating Subunits. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.H.; Birich, A.; Albers, S.-V. N-Glycosylation of the Archaellum Filament Is Not Important for Archaella Assembly and Motility, Although N-Glycosylation Is Essential for Motility in Sulfolobus Acidocaldarius. Biochimie 2015, 118, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofer, S.; Vershinin, Z.; Mashni, L.; Zalk, R.; Shahar, A.; Eichler, J.; Grossman-Haham, I. Perturbed N-Glycosylation of Halobacterium Salinarum Archaellum Filaments Leads to Filament Bundling and Compromised Cell Motility. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvette, J.; Liu, H.-F.; Du, X.; Zhou, Y.; Sikkema, A.P.; da Fonseca Rezende e Mello, J.; Klemm, B.P.; Huang, R.; Schaaper, R.M.; Borgnia, M.J.; et al. Beam Image-Shift Accelerated Data Acquisition for near-Atomic Resolution Single-Particle Cryo-Electron Tomography. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenstein, F.; Danev, R.; Pilhofer, M. Improved Applicability and Robustness of Fast Cryo-Electron Tomography Data Acquisition. J. Struct. Biol. 2019, 208, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.; DiMaio, F.; Anishchenko, I.; Dauparas, J.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Lee, G.R.; Wang, J.; Cong, Q.; Kinch, L.N.; Schaeffer, R.D.; et al. Accurate Prediction of Protein Structures and Interactions Using a Three-Track Neural Network. Science 2021, 373, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beeby, M.; Daum, B. How Does the Archaellum Work? Biomolecules 2025, 15, 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040465
Beeby M, Daum B. How Does the Archaellum Work? Biomolecules. 2025; 15(4):465. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040465
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeeby, Morgan, and Bertram Daum. 2025. "How Does the Archaellum Work?" Biomolecules 15, no. 4: 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040465
APA StyleBeeby, M., & Daum, B. (2025). How Does the Archaellum Work? Biomolecules, 15(4), 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040465





