Heart Rate Variability, Microvascular Dysfunction, and Inflammation: Exploring the Potential of taVNS in Managing Heart Failure in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. T2DM and Cardiovascular Disease
2.1. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy (DCM)
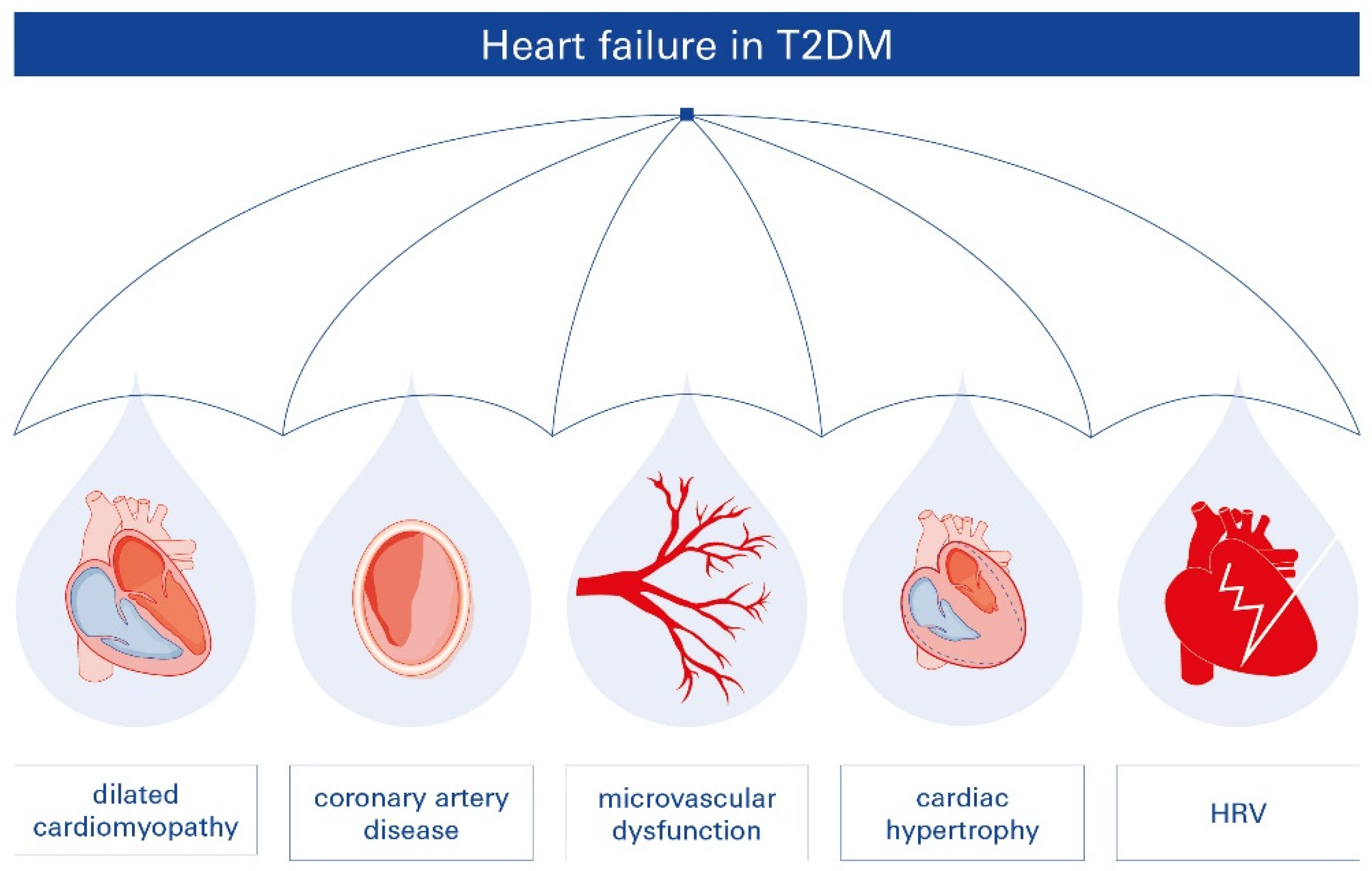
2.2. T2DM-Related Heart Failure (HF)
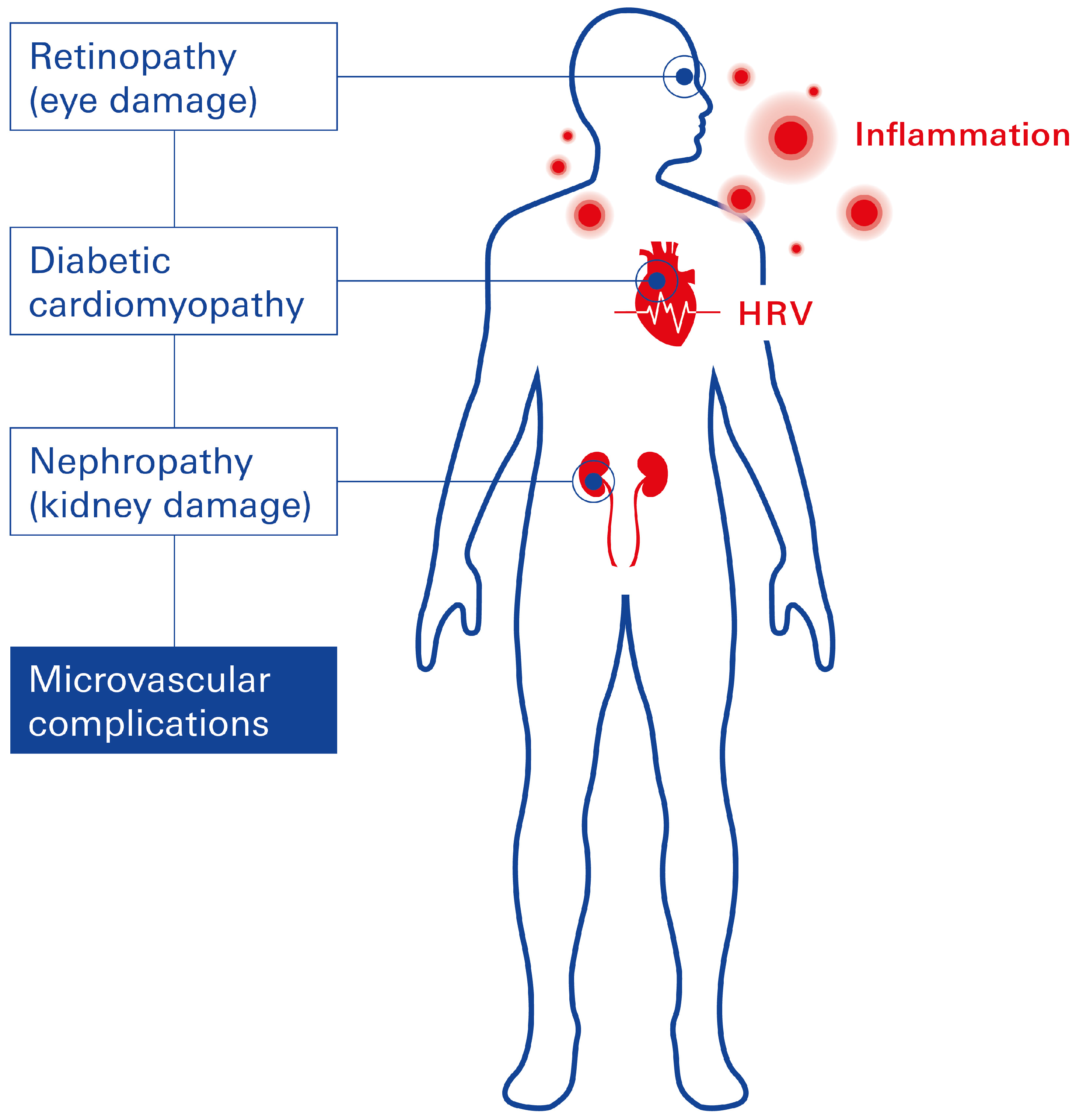
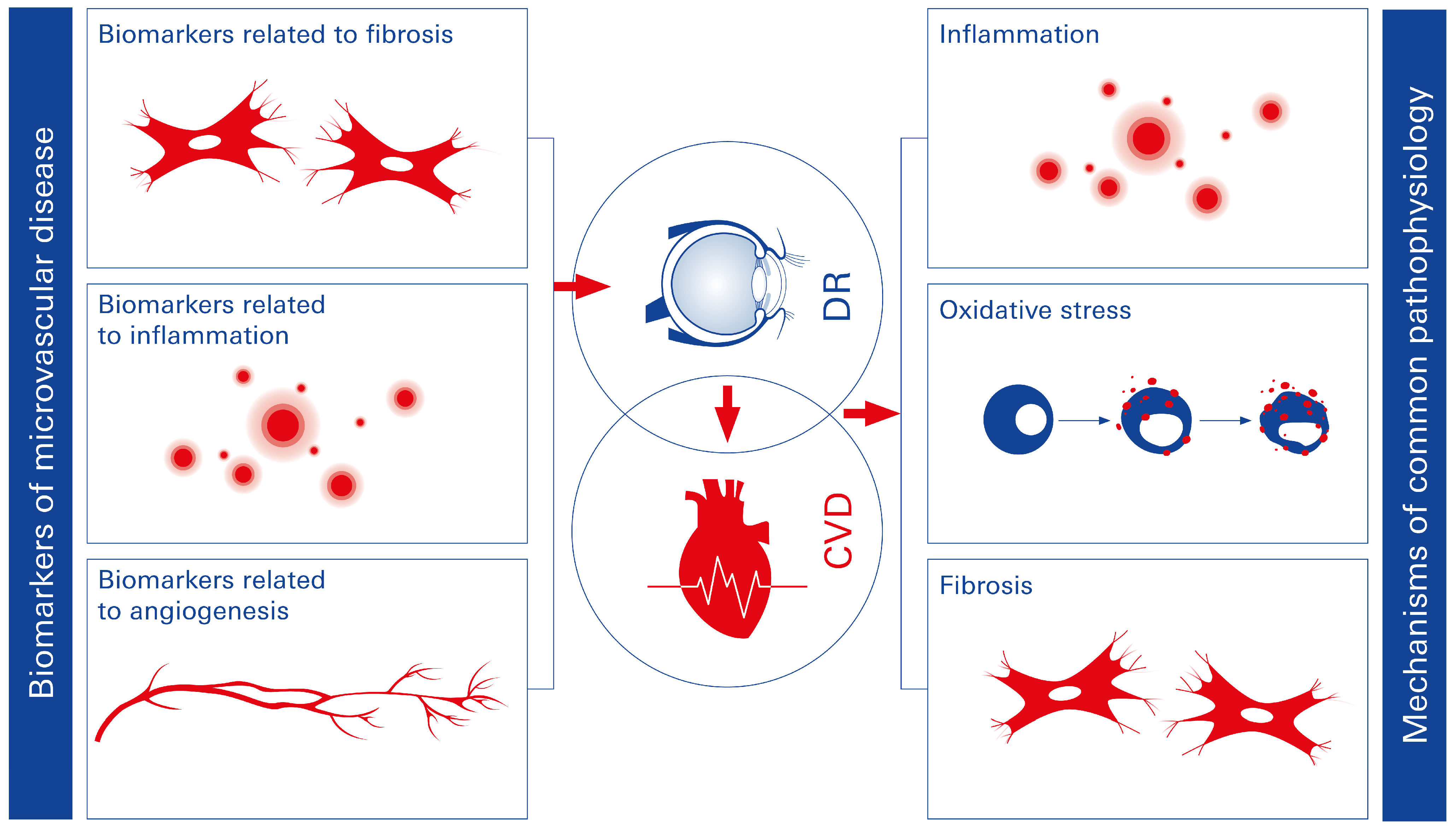
2.3. Microvascular Complications Linked to T2DM
2.3.1. Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)
2.3.2. Microvascular Dysfunction in the Diabetic Heart
2.3.3. Diabetic Nephropathy
2.4. Autonomic Dysfunction and Autonomic Neuropathy in T2DM
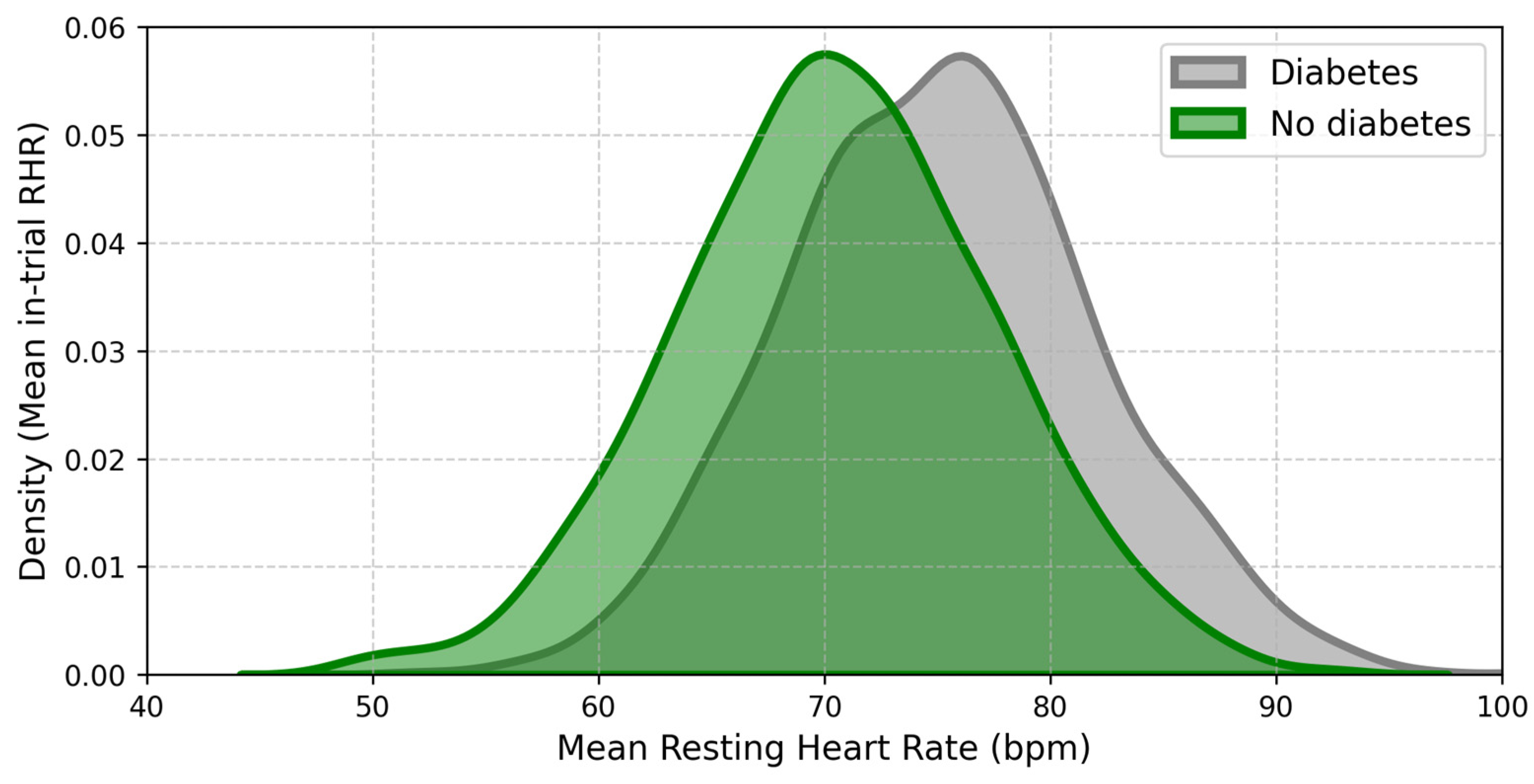
2.5. Heart Rate Variability (HRV)
2.6. T2DM and Chronic Inflammation
2.7. Myocardial Fibrosis
3. Impact of the Vagus Nerve on T2DM: Exploring the Connection
3.1. The Vagus Nerve
3.2. Diabetic Syndrome and the Vagus Nerve
3.3. Diabetes Management and Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation (tVNS)
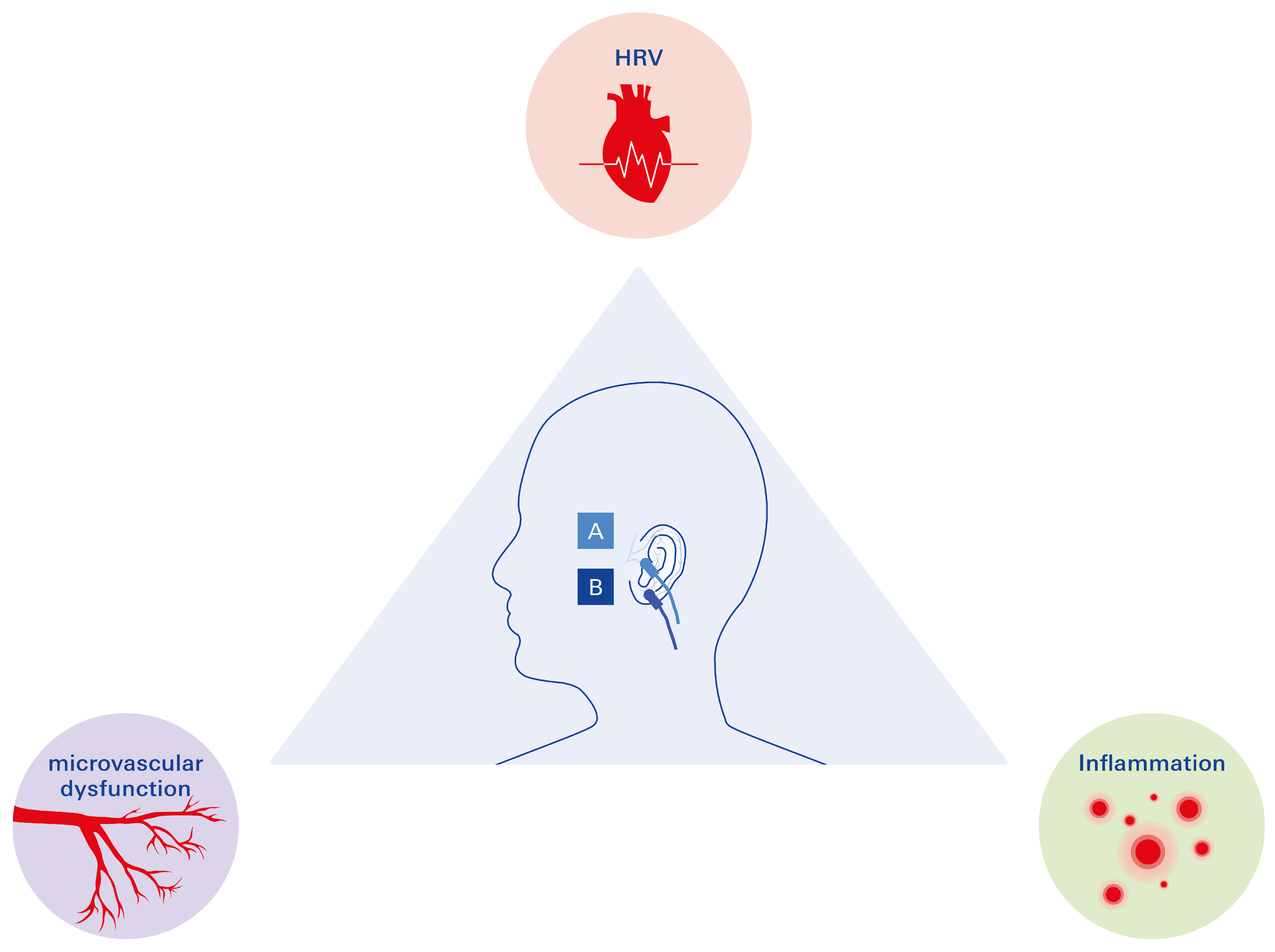
3.3.1. The Promising Triad in the Management of T2DM: HRV, Microvascular Disease, and Inflammation
3.3.2. Open Questions
Exploration of taVNS in Relation to T2DM-Associated HF—Is Clinical Translation Possible?
Blood Pressure Regulation in T2DM and taVNS
4. T2DM and the VN: Conclusions and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABNV | auricular branch of the nervus vagus |
| AGE | advanced glycation end products |
| AF | atrial fibrillation |
| Ang-1 | angiopoietin-1 |
| BDNF | brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| CAD | coronary artery disease |
| CAN | cardiac autonomic neuropathy |
| CD31 | platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule |
| CVD | cardiovascular disease |
| CCR2 | CC motif chemokine receptor 2 |
| DCM | diabetic cardiomyopathy |
| DR | diabetic retinopathy |
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| ECG | electrocardiogram |
| GAN | great auricular nerve |
| HbA1c | hemoglobin A1c |
| HF | heart failure |
| HFrEF | heart failure reduced ejection fraction |
| HFpEF | heart failure preserved ejection fraction |
| HRV | heart rate variability |
| iBRB | inner blood retinal barrier |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1 beta |
| LLTS | low-level transcutaneous electrical stimulation of the tragus |
| MCP-1 | monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| oxLDL | oxidized low-density lipoprotein |
| PWA | P-wave alternans |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor ‘kappa-light-chain-enhancer’ of activated B-cells |
| RAAS | renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SGLT2i | sodium-glucose transporter-2 inhibitor |
| taVNS | transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation |
| tVNS | transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation |
| T1DM | type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| T2DM | type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor α |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VNS | vagus nerve stimulation |
References
- Roden, M. Diabetes mellitus: Definition, classification and diagnosis. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2016, 128 (Suppl. S2), S37–S40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flannick, J.; Johansson, S.; Njolstad, P.R. Common and rare forms of diabetes mellitus: Towards a continuum of diabetes subtypes. Nature reviews. Endocrinology 2016, 12, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Monos, D.S.; Zmijewski, C.M. Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus as an autoimmune disease. In Vivo 1988, 2, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sapra, A.; Bhandari, P. Diabetes Mellitus. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.X.; Ma, X.N.; Guan, C.H.; Li, Y.D.; Mauricio, D.; Fu, S.B. Cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Progress toward personalized management. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarson, T.R.; Acs, A.; Ludwig, C.; Panton, U.H. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: A systematic literature review of scientific evidence from across the world in 2007–2017. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Sorski, L.; Gidron, Y. The Vagal Nerve, Inflammation, and Diabetes-A Holy Triangle. Cells 2023, 12, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelen, S.E.; van der Graaf, Y.; Stam-Slob, M.C.; Grobbee, D.E.; Cramer, M.J.; Kappelle, L.J.; de Borst, G.J.; Visseren, F.L.J.; Westerink, J. Incidence of cardiovascular events and vascular interventions in patients with type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 248, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Januzzi, J.L.; Bruemmer, D.; Butalia, S.; Green, J.B.; Horton, W.B.; Knight, C.; Levi, M.; Rasouli, N.; Richardson, C.R. Heart Failure: An Underappreciated Complication of Diabetes. A Consensus Report of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 1670–1690. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, R.H.; Abel, E.D. Basic Mechanisms of Diabetic Heart Disease. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1501–1525. [Google Scholar]
- Rubler, S.; Dlugash, J.; Yuceoglu, Y.Z.; Kumral, T.; Branwood, A.W.; Grishman, A. New type of cardiomyopathy associated with diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 1972, 30, 595–602. [Google Scholar]
- Murtaza, G.; Virk, H.U.H.; Khalid, M.; Lavie, C.J.; Ventura, H.; Mukherjee, D.; Ramu, V.; Bhogal, S.; Kumar, G.; Shanmugasundaram, M.; et al. Diabetic cardiomyopathy—A comprehensive updated review. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 62, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, M.; Tu, X.; Wu, R. Vascular endothelial dysfunction, a major mediator in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Simone, G.; Devereux, R.B.; Chinali, M.; Lee, E.T.; Galloway, J.M.; Barac, A.; Panza, J.A.; Howard, B.V. Diabetes and incident heart failure in hypertensive and normotensive participants of the Strong Heart Study. J. Hypertens. 2010, 28, 353–360. [Google Scholar]
- Holscher, M.E.; Bode, C.; Bugger, H. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Does the Type of Diabetes Matter? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, M.; Dihoum, A.; Mordi, I.R.; Choy, A.M.; Rena, G.; Lang, C.C. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: A Target for Intervention. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 746382. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.T.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.K.; Jiang, L.; Gao, Y.; Shi, R.; Yang, Z.G. Impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on left ventricular deformation in non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy patients assessed by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 94. [Google Scholar]
- Yancy, C.W.; Jessup, M.; Bozkurt, B.; Butler, J.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Drazner, M.H.; Fonarow, G.C.; Geraci, S.A.; Horwich, T.; Januzzi, J.L.; et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, e147–e239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryden, L.; Grant, P.J.; Anker, S.D.; Berne, C.; Cosentino, F.; Danchin, N.; Deaton, C.; Escaned, J.; Hammes, H.P.; Huikuri, H.; et al. ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD: The Task Force on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and developed in collaboration with the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 3035–3087. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M.; Shi, K.; Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Yan, W.F.; Gao, Y.; Shen, M.T.; Shi, R.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.J.; et al. Assessment of subclinical LV myocardial dysfunction in T2DM patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A cardiovascular magnetic resonance study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 217. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, P.; Piran, S.; Liu, P.P. Diastolic heart failure: Progress; treatment challenges, and prevention. Can. J. Cardiol. 2011, 27, 302–310. [Google Scholar]
- Galderisi, M. Diastolic dysfunction and diabetic cardiomyopathy: Evaluation by Doppler echocardiography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 1548–1551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kishi, S.; Gidding, S.S.; Reis, J.P.; Colangelo, L.A.; Venkatesh, B.A.; Armstrong, A.C.; Isogawa, A.; Lewis, C.E.; Wu, C.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; et al. Association of Insulin Resistance and Glycemic Metabolic Abnormalities With LV Structure and Function in Middle Age: The CARDIA Study. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, S.L.; Preiss, D.; Jhund, P.S.; Squire, I.; Cardoso, J.S.; Merkely, B.; Martinez, F.; Starling, R.C.; Desai, A.S.; Lefkowitz, M.P.; et al. Risk Related to Pre-Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetes Mellitus in Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction: Insights From Prospective Comparison of ARNI With ACEI to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure Trial. Circ. Heart Fail. 2016, 9, e002560. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oktay, A.A.; Akturk, H.K.; Esenboga, K.; Javed, F.; Polin, N.M.; Jahangir, E. Pathophysiology and Prevention of Heart Disease in Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2018, 43, 68–110. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Coranguez, M.; Ramos, C.; Antonetti, D.A. The inner blood-retinal barrier: Cellular basis and development. Vis. Res. 2017, 139, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabalgoitia, M.; Ismaeil, M.F.; Anderson, L.; Maklady, F.A. Prevalence of diastolic dysfunction in normotensive, asymptomatic patients with well-controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Cardiol. 2001, 87, 320–323. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, G.; Hill, M.A.; Sowers, J.R. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: An Update of Mechanisms Contributing to This Clinical Entity. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M. Differential Pathophysiological Mechanisms in Heart Failure With a Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction in Diabetes. JACC Heart Fail. 2021, 9, 535–549. [Google Scholar]
- Kenny, H.C.; Abel, E.D. Heart Failure in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 121–141. [Google Scholar]
- Figtree, G.A.; Bubb, K.J.; Tang, O.; Kizana, E.; Gentile, C. Vascularized Cardiac Spheroids as Novel 3D in vitro Models to Study Cardiac Fibrosis. Cells Tissues Organs 2017, 204, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.; Garcia, M.; Sullivan, S.M.; Liu, C.; Moazzami, K.; Ko, Y.A.; Shah, A.J.; Kim, J.H.; Pearce, B.; Uphoff, I.; et al. Impaired Peripheral Microvascular Function and Risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nature reviews. Endocrinology 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Tao, L.; Lv, H.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, X. Risk factors of diabetic retinopathy and sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy: A cross-sectional study of 13 473 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in mainland China. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcao-Pires, I.; Hamdani, N.; Borbely, A.; Gavina, C.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; van der Velden, J.; van Heerebeek, L.; Stienen, G.J.; Niessen, H.W.; Leite-Moreira, A.F.; et al. Diabetes mellitus worsens diastolic left ventricular dysfunction in aortic stenosis through altered myocardial structure and cardiomyocyte stiffness. Circulation 2011, 124, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, F.; Campbell, M. The blood-retina barrier in health and disease. FEBS J. 2023, 290, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, B.E. Overview of epidemiologic studies of diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2007, 14, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, Z.L.; Tham, Y.C.; Yu, M.; Chee, M.L.; Rim, T.H.; Cheung, N.; Bikbov, M.M.; Wang, Y.X.; Tang, Y.; Lu, Y.; et al. Global Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy and Projection of Burden through 2045: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 1580–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980-2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1151–1210. [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Ikram, M.K.; Cotch, M.F.; Klein, B.; Varma, R.; Shaw, J.E.; Klein, R.; Mitchell, P.; Lamoureux, E.L.; Wong, T.Y. Association of Diabetic Macular Edema and Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy With Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017, 135, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, U.; Pajunpaa, H.; Koskela, P.; Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi, S. High cardiovascular disease mortality in subjects with visual impairment caused by diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlee, M. The pathobiology of diabetic complications: A unifying mechanism. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalfaoui, T.; Lizard, G.; Ouertani-Meddeb, A. Adhesion molecules (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) and diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes. J. Mol. Histol. 2008, 39, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Kanter, J.E.; Kramer, F.; Barnhart, S.; Averill, M.M.; Vivekanandan-Giri, A.; Vickery, T.; Li, L.O.; Becker, L.; Yuan, W.; Chait, A.; et al. Diabetes promotes an inflammatory macrophage phenotype and atherosclerosis through acyl-CoA synthetase 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E715–E724. [Google Scholar]
- Maack, C.; Lehrke, M.; Backs, J.; Heinzel, F.R.; Hulot, J.S.; Marx, N.; Paulus, W.J.; Rossignol, P.; Taegtmeyer, H.; Bauersachs, J.; et al. Heart failure and diabetes: Metabolic alterations and therapeutic interventions: A state-of-the-art review from the Translational Research Committee of the Heart Failure Association-European Society of Cardiology. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 4243–4254. [Google Scholar]
- Lundbaek, K. Diabetic angiopathy: A specific vascular disease. Lancet 1954, 266, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, S.V.; Wienand-Barnett, S.; Shepherd, M.; King, S.M.; Fox, C.; Khunti, K.; Oram, R.A.; Knight, B.A.; Hattersley, A.T.; Jones, A.G.; et al. Practical Classification Guidelines for Diabetes in patients treated with insulin: A cross-sectional study of the accuracy of diabetes diagnosis. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2016, 66, e315–e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.A.; Chakrabarti, S. MicroRNAs: The underlying mediators of pathogenetic processes in vascular complications of diabetes. Can. J. Diabetes 2013, 37, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borghetti, G.; von Lewinski, D.; Eaton, D.M.; Sourij, H.; Houser, S.R.; Wallner, M. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Current and Future Therapies. Beyond Glycemic Control. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1514. [Google Scholar]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Rooney, M.T.; Tuttle, K.R. Diabetic Kidney Disease: Challenges, Progress, and Possibilities. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2017, 12, 2032–2045. [Google Scholar]
- Afkarian, M.; Sachs, M.C.; Kestenbaum, B.; Hirsch, I.B.; Tuttle, K.R.; Himmelfarb, J.; de Boer, I.H. Kidney disease and increased mortality risk in type 2 diabetes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2013, 24, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, C.E. Microalbuminuria predicts clinical proteinuria and early mortality in maturity-onset diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 310, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manske, C.L.; Wilson, R.F.; Wang, Y.; Thomas, W. Prevalence of, and risk factors for, angiographically determined coronary artery disease in type I-diabetic patients with nephropathy. Arch. Intern. Med. 1992, 152, 2450–2455. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yudkin, J.S.; Forrest, R.D.; Jackson, C.A. Microalbuminuria as predictor of vascular disease in non-diabetic subjects. Islington Diabetes Survey. Lancet 1988, 2, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deckert, T.; Yokoyama, H.; Mathiesen, E.; Ronn, B.; Jensen, T.; Feldt-Rasmussen, B.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Jensen, J.S. Cohort study of predictive value of urinary albumin excretion for atherosclerotic vascular disease in patients with insulin dependent diabetes. BMJ 1996, 312, 871–874. [Google Scholar]
- Borch-Johnsen, K.; Kreiner, S. Proteinuria: Value as predictor of cardiovascular mortality in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed.) 1987, 294, 1651–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Dinneen, S.F.; Gerstein, H.C. The association of microalbuminuria and mortality in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. A systematic overview of the literature. Arch. Intern. Med. 1997, 157, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, J.H.; Stevens, L.K.; Wang, S.L. Risk factors for cardiovascular mortality and morbidity: The WHO Mutinational Study of Vascular Disease in Diabetes. Diabetologia 2001, 44 (Suppl. S2), S54–S64. [Google Scholar]
- Gruden, G.; Cavallo-Perin, P.; Bazzan, M.; Stella, S.; Vuolo, A.; Pagano, G. PAI-1 and factor VII activity are higher in IDDM patients with microalbuminuria. Diabetes 1994, 43, 426–429. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, G.; Cavallo-Perin, P.; Bargero, G.; Borra, M.; D’Errico, N.; Pagano, G. Association of fibrinogen with glycemic control and albumin excretion rate in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Ann. Intern. Med. 1996, 125, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulgari, C.; Papadogiannis, D.; Tentolouris, N. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: From the pathophysiology of the cardiac myocytes to current diagnosis and management strategies. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2010, 6, 883–903. [Google Scholar]
- Coppola, A.; Conte, S.; Pastore, D.; Chiereghin, F.; Donadel, G. Multifractal Heart Rate Value Analysis: A Novel Approach for Diabetic Neuropathy Diagnosis. Healthcare 2024, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spallone, V.; Ziegler, D.; Freeman, R.; Bernardi, L.; Frontoni, S.; Pop-Busui, R.; Stevens, M.; Kempler, P.; Hilsted, J.; Tesfaye, S.; et al. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in diabetes: Clinical impact, assessment, diagnosis, and management. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2011, 27, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacre, J.W.; Franjic, B.; Jellis, C.L.; Jenkins, C.; Coombes, J.S.; Marwick, T.H. Association of cardiac autonomic neuropathy with subclinical myocardial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2010, 3, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinik, A.I.; Casellini, C.; Parson, H.K.; Colberg, S.R.; Nevoret, M.L. Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes: A Predictor of Cardiometabolic Events. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oost, L.J.; Kurstjens, S.; Ma, C.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Tack, C.J.; de Baaij, J.H.F. Magnesium increases insulin-dependent glucose uptake in adipocytes. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 986616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Malahi, O.; Mohajeri, D.; Bauerle, A.; Mincu, R.; Rothenaicher, K.; Ullrich, G.; Rammos, C.; Teufel, M.; Rassaf, T.; Lortz, J. The Effect of Stress-Reducing Interventions on Heart Rate Variability in Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life 2024, 14, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gathright, E.C.; Hughes, J.W.; Sun, S.; Storlazzi, L.E.; DeCosta, J.; Balletto, B.L.; Carey, M.P.; Scott-Sheldon, L.A.J.; Salmoirago-Blotcher, E. Effects of stress management interventions on heart rate variability in adults with cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Behav. Med. 2024, 47, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yugar, L.B.T.; Yugar-Toledo, J.C.; Dinamarco, N.; Sedenho-Prado, L.G.; Moreno, B.V.D.; Rubio, T.A.; Fattori, A.; Rodrigues, B.; Vilela-Martin, J.F.; Moreno, H. The Role of Heart Rate Variability (HRV) in Different Hypertensive Syndromes. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.T.H.; Tadesse, G.A.; Nhat, P.T.H.; Hao, N.V.; Prince, J.; Duong, T.D.; Kien, T.T.; Nhat, L.T.H.; Tan, L.V.; Pugh, C.; et al. Heart Rate Variability as an Indicator of Autonomic Nervous System Disturbance in Tetanus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 102, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, M.; Ito, C.; Sasaki, H.; Yamane, K.; Kohno, N. Low heart rate variability is a risk factor for sudden cardiac death in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2004, 64, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, M.; Schumacher, H.; Teo, K.K.; Lonn, E.M.; Mahfoud, F.; Ukena, C.; Mann, J.F.E.; Mancia, G.; Redon, J.; Schmieder, R.E.; et al. Resting heart rate and cardiovascular outcomes in diabetic and non-diabetic individuals at high cardiovascular risk analysis from the ONTARGET/TRANSCEND trials. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFuria, J.; Belkina, A.C.; Jagannathan-Bogdan, M.; Snyder-Cappione, J.; Carr, J.D.; Nersesova, Y.R.; Markham, D.; Strissel, K.J.; Watkins, A.A.; Zhu, M.; et al. B cells promote inflammation in obesity and type 2 diabetes through regulation of T-cell function and an inflammatory cytokine profile. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5133–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.P.; Kakkar, R.; McCarthy, C.P.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. Inflammation in Heart Failure: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 1324–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Hu, L.; Shu, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Du, M.; Sun, D.; Mao, X.; Deng, S.; Huang, K.; et al. Role of CCR2 in the Development of Streptozotocin-Treated Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Diabetes 2019, 68, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrocola, R.; Aragno, M.; Alloatti, G.; Collino, M.; Penna, C.; Pagliaro, P. Metaflammation: Tissue-Specific Alterations of the NLRP3 Inflammasome Platform in Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 1294–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloatti, G.; Penna, C.; Comita, S.; Tullio, F.; Aragno, M.; Biasi, F.; Pagliaro, P. Aging, sex and NLRP3 inflammasome in cardiac ischaemic disease. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 145, 107001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Shi, H.; Yu, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, R. NLRP3 inflammasome, an immune-inflammatory target in pathogenesis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, Z.; Lv, S.; Zhang, J. NLRP3 Inflammasome: A Novel Insight into Heart Failure. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2023, 16, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Buono, M.G.; Crea, F.; Versaci, F.; Biondi-Zoccai, G. NLRP3 Inflammasome: A New Promising Therapeutic Target to Treat Heart Failure. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2021, 77, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Li, X.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xie, C.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, K.; Shen, Y.; Tong, J. Recent advances in NLRP3 inflammasome in corneal diseases: Preclinical insights and therapeutic implications. Ocul. Surf. 2024, 34, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Sakimoto, T.; Yamagami, S. Pro-inflammatory role of NLRP3 inflammasome in experimental sterile corneal inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9596. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, E.; Warchol, I.; Mejza, M.; Mozdzan, M.; Strzeminska, M.; Bajer, A.; Madura, P.; Zak, J.; Plewka, M. Exploring Anti-Inflammatory Treatment as Upstream Therapy in the Management of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Yan, L.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Wu, X.; Gao, H.; Chen, Y.; Ma, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J. The relationship between atrial fibrillation and NLRP3 inflammasome: A gut microbiota perspective. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1273524. [Google Scholar]
- Ajoolabady, A.; Nattel, S.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Ren, J. Inflammasome Signaling in Atrial Fibrillation: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 2349–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirillo, A.; Norata, G.D.; Catapano, A.L. LOX-1, OxLDL, and atherosclerosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 152786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 2002, 420, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P. Current concepts of the pathogenesis of the acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 2001, 104, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.; Shityakov, S.; Smetak, M.; Hunkler, H.J.; Bar, C.; Schlegel, N.; Thum, T.; Forster, C.Y. Blood Biomarkers in Takotsubo Syndrome Point to an Emerging Role for Inflammaging in Endothelial Pathophysiology. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplin, A.C.; Gelati, M.; Fogel, E.; Carnevale, E.; Nicosia, R.F. Angiopoietin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor induce expression of inflammatory cytokines before angiogenesis. Physiol. Genom. 2006, 27, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J.; Chen, J.L. Inflammation may be a bridge connecting hypertension and atherosclerosis. Med. Hypotheses 2005, 64, 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, D.B., Jr.; Gamba, M.R.; Gonzalez-Jaramillo, N.; Gonzalez-Jaramillo, V.; Raguindin, P.F.N.; Minder, B.; Grani, C.; Wilhelm, M.; Stettler, C.; Doria, A.; et al. Diabetes and Myocardial Fibrosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 15, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, J.O.; DuBois, F.S. Quantitative studies of the vagus nerve in the cat. I. The ratio of sensory to motor fibers. J. Comp. Neurol. 1937, 67, 49–67. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Silberstein, S.D. Vagus Nerve and Vagus Nerve Stimulation, a Comprehensive Review: Part I. Headache 2016, 56, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Howland, R.H. Vagus Nerve Stimulation. Curr. Behav. Neurosci. Rep. 2014, 1, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berthoud, H.R.; Neuhuber, W.L. Functional and chemical anatomy of the afferent vagal system. Auton. Neurosci. 2000, 85, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Nemeroff, C.B.; Mayberg, H.S.; Krahl, S.E.; McNamara, J.; Frazer, A.; Henry, T.R.; George, M.S.; Charney, D.S.; Brannan, S.K. VNS therapy in treatment-resistant depression: Clinical evidence and putative neurobiological mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Tracey, K.J. Reflex control of immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 418–428. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A.H.; Raison, C.L. The role of inflammation in depression: From evolutionary imperative to modern treatment target. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 22–34. [Google Scholar]
- Neurath, M.F. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 329–342. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.S.; Oomura, Y.; Fujino, T.; Akashi, K. Glucose signaling in the brain and periphery to memory. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 110, 100–113. [Google Scholar]
- Benichou, T.; Pereira, B.; Mermillod, M.; Tauveron, I.; Pfabigan, D.; Maqdasy, S.; Dutheil, F. Heart rate variability in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, M.F.; Albusoda, A.; Farmer, A.D.; Aziz, Q. The anatomical basis for transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation. J. Anat. 2020, 236, 588–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peuker, E.T.; Filler, T.J. The nerve supply of the human auricle. Clin Anat 2002, 15, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, P.; Rodriguez, M.; Slavíčková, A.; Hanka, J. The application of vagus nerve stimulation and deep brain stimulation in depression. Neuropsychobiology 2011, 64, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.H.; Nahas, Z.; Lomarev, M.; Denslow, S.; Lorberbaum, J.P.; Bohning, D.E.; George, M.S. A review of functional neuroimaging studies of vagus nerve stimulation (VNS). J. Psychiatr. Res. 2003, 37, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, T.R.; Bakay, R.A.; Votaw, J.R.; Pennell, P.B.; Epstein, C.M.; Faber, T.L.; Grafton, S.T.; Hoffman, J.M. Brain blood flow alterations induced by therapeutic vagus nerve stimulation in partial epilepsy: I. Acute effects at high and low levels of stimulation. Epilepsia 1998, 39, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, E.; Nowak, M.; Kiess, O.; Biermann, T.; Bayerlein, K.; Kornhuber, J.; Kraus, T. Auricular transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in depressed patients: A randomized controlled pilot study. J. Neural. Transm. 2013, 120, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, R.; Fang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Vangel, M.; Sun, S.; et al. Effect of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation on major depressive disorder: A nonrandomized controlled pilot study. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 195, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, T.R. Therapeutic mechanisms of vagus nerve stimulation. Neurology 2002, 59, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahl, S.E.; Clark, K.B. Vagus nerve stimulation for epilepsy: A review of central mechanisms. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2012, 3, S255–S259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrosu, F.; Serra, A.; Maleci, A.; Puligheddu, M.; Biggio, G.; Piga, M. Correlation between GABA(A) receptor density and vagus nerve stimulation in individuals with drug-resistant partial epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2003, 55, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machetanz, K.; Berelidze, L.; Guggenberger, R.; Gharabaghi, A. Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation and heart rate variability: Analysis of parameters and targets. Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin. 2021, 236, 102894. [Google Scholar]
- Forte, G.; Favieri, F.; Leemhuis, E.; De Martino, M.L.; Giannini, A.M.; De Gennaro, L.; Casagrande, M.; Pazzaglia, M. Ear your heart: Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation on heart rate variability in healthy young participants. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Szeles, J.C.; Kampusch, S.; Thurk, F.; Clodi, C.; Thomas, N.; Fichtenbauer, S.; Schwanzer, C.; Schwarzenberger, S.; Neumayer, C.; Kaniusas, E. Bursted auricular vagus nerve stimulation alters heart rate variability in healthy subjects. Physiol. Meas. 2021, 42, 105002. [Google Scholar]
- Gianlorenco, A.C.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Daibes, M.; Camargo, L.; Choi, H.; Song, J.J.; Fregni, F. Age as an Effect Modifier of the Effects of Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation (taVNS) on Heart Rate Variability in Healthy Subjects. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spallone, V. Update on the Impact, Diagnosis and Management of Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes: What Is Defined, What Is New, and What Is Unmet. Diabetes Metab. J. 2019, 43, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.M.; Eleftheriadou, A.; Alam, U.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Wilding, J.P.H. Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy in Obesity, the Metabolic Syndrome and Prediabetes: A Narrative Review. Diabetes Ther. Res. Treat. Educ. Diabetes Relat. Disord. 2019, 10, 1995–2021. [Google Scholar]
- Buccelletti, E.; Gilardi, E.; Scaini, E.; Galiuto, L.; Persiani, R.; Biondi, A.; Basile, F.; Silveri, N.G. Heart rate variability and myocardial infarction: Systematic literature review and metanalysis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 13, 299–307. [Google Scholar]
- Im, S.I.; Kim, S.J.; Bae, S.H.; Kim, B.J.; Heo, J.H.; Kwon, S.K.; Cho, S.P.; Shim, H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; et al. Real-time heart rate variability according to ambulatory glucose profile in patients with diabetes mellitus. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1249709. [Google Scholar]
- Kornum, D.S.; Bertoli, D.; Kufaishi, H.; Wegeberg, A.M.; Okdahl, T.; Mark, E.B.; Hoyer, K.L.; Frokjaer, J.B.; Brock, B.; Krogh, K.; et al. Transcutaneous vagal nerve stimulation for treating gastrointestinal symptoms in individuals with diabetes: A randomised, double-blind, sham-controlled, multicentre trial. Diabetologia 2024, 67, 1122–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.L.; Sun, J.B.; Yang, X.J.; Deng, H.; Qin, W.; Du, M.Y.; Meng, L.X.; Li, N.; Guo, X.Y.; Qiao, W.Z.; et al. Reassessment of the Effect of Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation Using a Novel Burst Paradigm on Cardiac Autonomic Function in Healthy Young Adults. Neuromodulation 2022, 25, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.R.; Su, W.S.; Lin, K.D.; Lin, I.M. Effect of Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback on Cardiac Autonomic Activation and Diabetes Self-Care in Patients with Type II Diabetes Mellitus. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback, 2024; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Xin, C.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhang, K.Q.; Li, L.; Rong, P.J.; Li, S.Y. Mechanism of melatonin-mediated antihyperglycemic effect of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu = Acupunct. Res. 2023, 48, 812–817. [Google Scholar]
- Thayer, J.F.; Fischer, J.E. Heart rate variability, overnight urinary norepinephrine and C-reactive protein: Evidence for the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in healthy human adults. J. Intern. Med. 2009, 265, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frank, N.; Nagai, M.; Förster, C.Y. Exploration of transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation as a treatment option for adjuvant cancer and heart failure therapy. Explor. Neuroprotective Ther. 2023, 3, 363–397. [Google Scholar]
- Borovikova, L.V.; Ivanova, S.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; Botchkina, G.I.; Watkins, L.R.; Wang, H.; Abumrad, N.; Eaton, J.W.; Tracey, K.J. Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 2000, 405, 458–462. [Google Scholar]
- Tracey, K.J. Physiology and immunology of the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniusas, E.; Kampusch, S.; Tittgemeyer, M.; Panetsos, F.; Gines, R.F.; Papa, M.; Kiss, A.; Podesser, B.; Cassara, A.M.; Tanghe, E.; et al. Current Directions in the Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation I—A Physiological Perspective. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 854. [Google Scholar]
- Okdahl, T.; Bertoli, D.; Brock, B.; Krogh, K.; Knop, F.K.; Brock, C.; Drewes, A.M. Study protocol for a multicentre, randomised, parallel group, sham-controlled clinical trial investigating the effect of transcutaneous vagal nerve stimulation on gastrointestinal symptoms in people with diabetes complicated with diabetic autonomic neuropathy: The DAN-VNS Study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e038677. [Google Scholar]
- Stratton, I.M.; Adler, A.I.; Neil, H.A.; Matthews, D.R.; Manley, S.E.; Cull, C.A.; Hadden, D.; Turner, R.C.; Holman, R.R. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): Prospective observational study. BMJ 2000, 321, 405–412. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, G.; Whaley-Connell, A.; Sowers, J.R. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: A hyperglycaemia-; insulin-resistance-induced heart disease. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M.; Guo, F.; Song, L.; Tan, W.; Han, X.; Xu, S.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, X.; et al. Noninvasive neuromodulation protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and inhibits tumor growth. iScience 2024, 27, 109163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazoukis, G.; Stavrakis, S.; Armoundas, A.A. Vagus Nerve Stimulation and Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease: A State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e030539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellocchi, C.; Carandina, A.; Della Torre, A.; Turzi, M.; Arosio, B.; Marchini, M.; Vigone, B.; Scata, C.; Beretta, L.; Rodrigues, G.D.; et al. Transcutaneous auricular branch vagal nerve stimulation as a non-invasive add-on therapeutic approach for pain in systemic sclerosis. RMD Open 2023, 9, e003265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischer, J.; Yderstraede, K.; Gulichsen, E.; Jakobsen, P.E.; Lervang, H.H.; Eldrup, E.; Nygaard, H.; Tarnow, L.; Ejskjaer, N. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy is associated with macrovascular risk factors in type 2 diabetes: New technology used for routine large-scale screening adds new insight. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2014, 8, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Kong, Z.; Wang, X.; Lv, W.; Geng, Z.; Wang, Y. The renoprotective effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes with or without prevalent kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, P.S.; Parente, J.; Rebello-Sanchez, I.; Marduy, A.; Gianlorenco, A.C.; Kim, C.K.; Choi, H.; Song, J.J.; Fregni, F. Understanding the Neuroplastic Effects of Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Animal Models of Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2023, 37, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafeiropoulos, S.; Ahmed, U.; Bikou, A.; Mughrabi, I.T.; Stavrakis, S.; Zanos, S. Vagus nerve stimulation for cardiovascular diseases: Is there light at the end of the tunnel? Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 34, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malpas, S.C. Sympathetic nervous system overactivity and its role in the development of cardiovascular disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 513–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, K.; Cummings, M.; Bernatik, M.; Brinkhaus, B.; Usichenko, T.; Dietzel, J. Cardiovascular effects of auricular stimulation -a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1227858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usichenko, T.; Hacker, H.; Lotze, M. Transcutaneous auricular vagal nerve stimulation (taVNS) might be a mechanism behind the analgesic effects of auricular acupuncture. Brain Stimul. 2017, 10, 1042–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, M.Z.; He, J.K.; Zhang, J.L.; Zhao, B.; Hou, L.W.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation: From Concept to Application. Neurosci. Bull. 2021, 37, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhnau, P.; Zaehle, T. Transcranial Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation (taVNS) and Ear-EEG: Potential for Closed-Loop Portable Non-invasive Brain Stimulation. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 699473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carandina, A.; Rodrigues, G.D.; Di Francesco, P.; Filtz, A.; Bellocchi, C.; Furlan, L.; Carugo, S.; Montano, N.; Tobaldini, E. Effects of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation on cardiovascular autonomic control in health and disease. Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin. 2021, 236, 102893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Jiao, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.N.; Zhang, S.; He, J.; Rong, P. Optimizing the modulation paradigm of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation in patients with disorders of consciousness: A prospective exploratory pilot study protocol. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1145699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Filiberti, A.; Humphrey, M.B.; Fleming, C.D.; Scherlag, B.J.; Po, S.S.; Stavrakis, S. Low-level transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation attenuates cardiac remodelling in a rat model of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Exp. Physiol. 2019, 104, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liao, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, S.; Chen, M. Chronic vagus nerve stimulation in patients with heart failure: Challenge or failed translation? Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1052471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.R.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Hauptman, P.J.; Borggrefe, M.; Kubo, S.H.; Lieberman, R.A.; Milasinovic, G.; Berman, B.J.; Djordjevic, S.; Neelagaru, S.; et al. Vagus Nerve Stimulation for the Treatment of Heart Failure: The INOVATE-HF Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrakis, S.; Elkholey, K.; Morris, L.; Niewiadomska, M.; Asad, Z.U.A.; Humphrey, M.B. Neuromodulation of Inflammation to Treat Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e023582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, K.; Po, S.S.; Stavrakis, S. Non-invasive Neuromodulation of Arrhythmias. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2024, 16, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkholey, K.; Niewiadomska, M.; Morris, L.; Whyte, S.; Houser, J.; Humphrey, M.B.; Stavrakis, S. Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation Ameliorates the Phenotype of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction Through Its Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Circ. Heart Fail. 2022, 15, e009288. [Google Scholar]
- Forster, C.Y.; Kunzel, S.R.; Shityakov, S.; Stavrakis, S. Synergistic Effects of Weight Loss and Catheter Ablation: Can microRNAs Serve as Predictive Biomarkers for the Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thal, S.C.; Shityakov, S.; Salvador, E.; Förster, C.Y. Heart Rate Variability, Microvascular Dysfunction, and Inflammation: Exploring the Potential of taVNS in Managing Heart Failure in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040499
Thal SC, Shityakov S, Salvador E, Förster CY. Heart Rate Variability, Microvascular Dysfunction, and Inflammation: Exploring the Potential of taVNS in Managing Heart Failure in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(4):499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040499
Chicago/Turabian StyleThal, Serge C., Sergey Shityakov, Ellaine Salvador, and Carola Y. Förster. 2025. "Heart Rate Variability, Microvascular Dysfunction, and Inflammation: Exploring the Potential of taVNS in Managing Heart Failure in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Biomolecules 15, no. 4: 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040499
APA StyleThal, S. C., Shityakov, S., Salvador, E., & Förster, C. Y. (2025). Heart Rate Variability, Microvascular Dysfunction, and Inflammation: Exploring the Potential of taVNS in Managing Heart Failure in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomolecules, 15(4), 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040499







