Molecular Basis of Dipeptide Recognition in Drosophila melanogaster Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Homologue, AnCE
Abstract
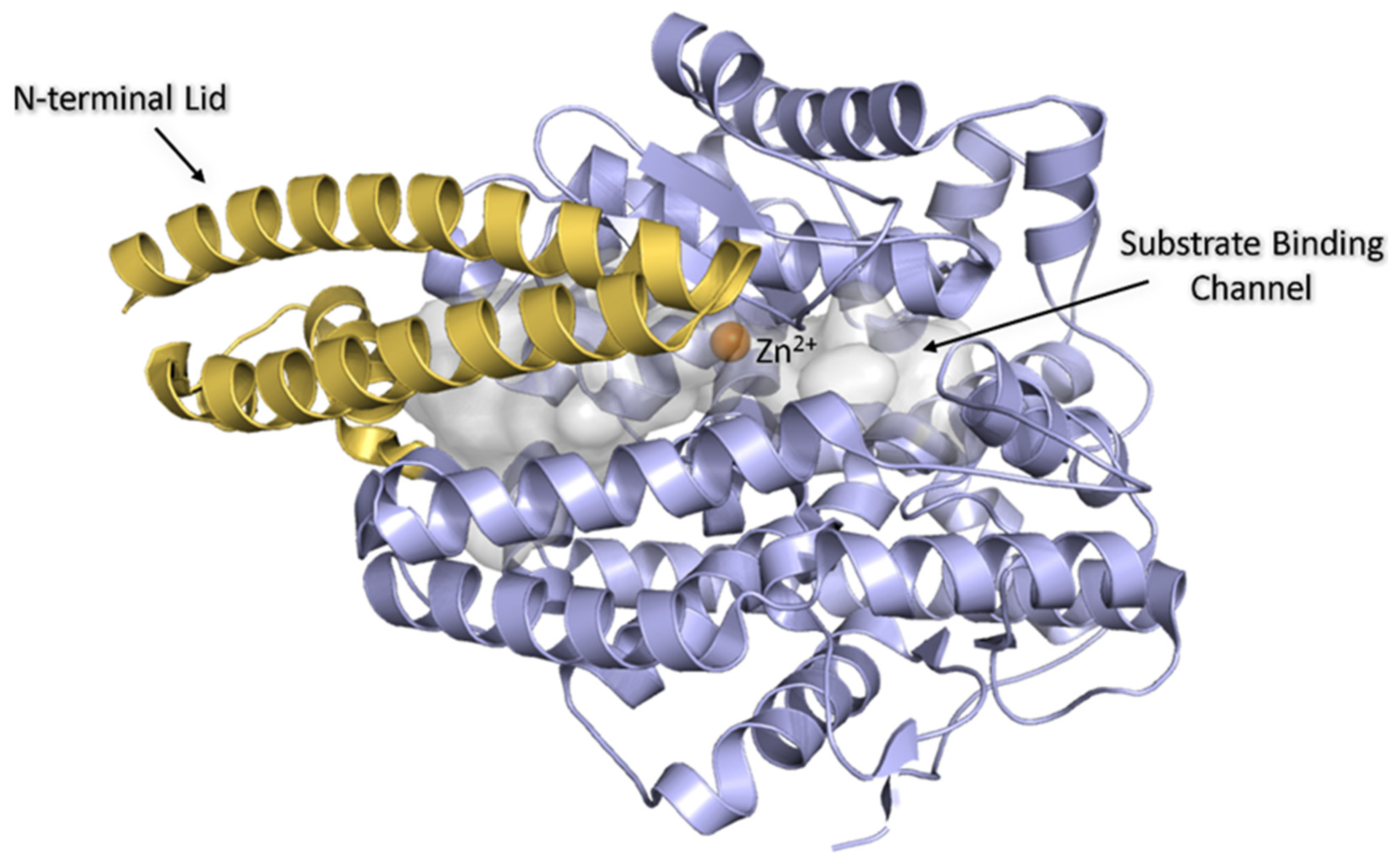
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. AnCE Expression and Purification
2.2. Crystallisation, X-Ray Diffraction Data Collection, and Structure Determination
2.3. Inhibition of AnCE Activity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Kinetic Analysis of AnCE Inhibition
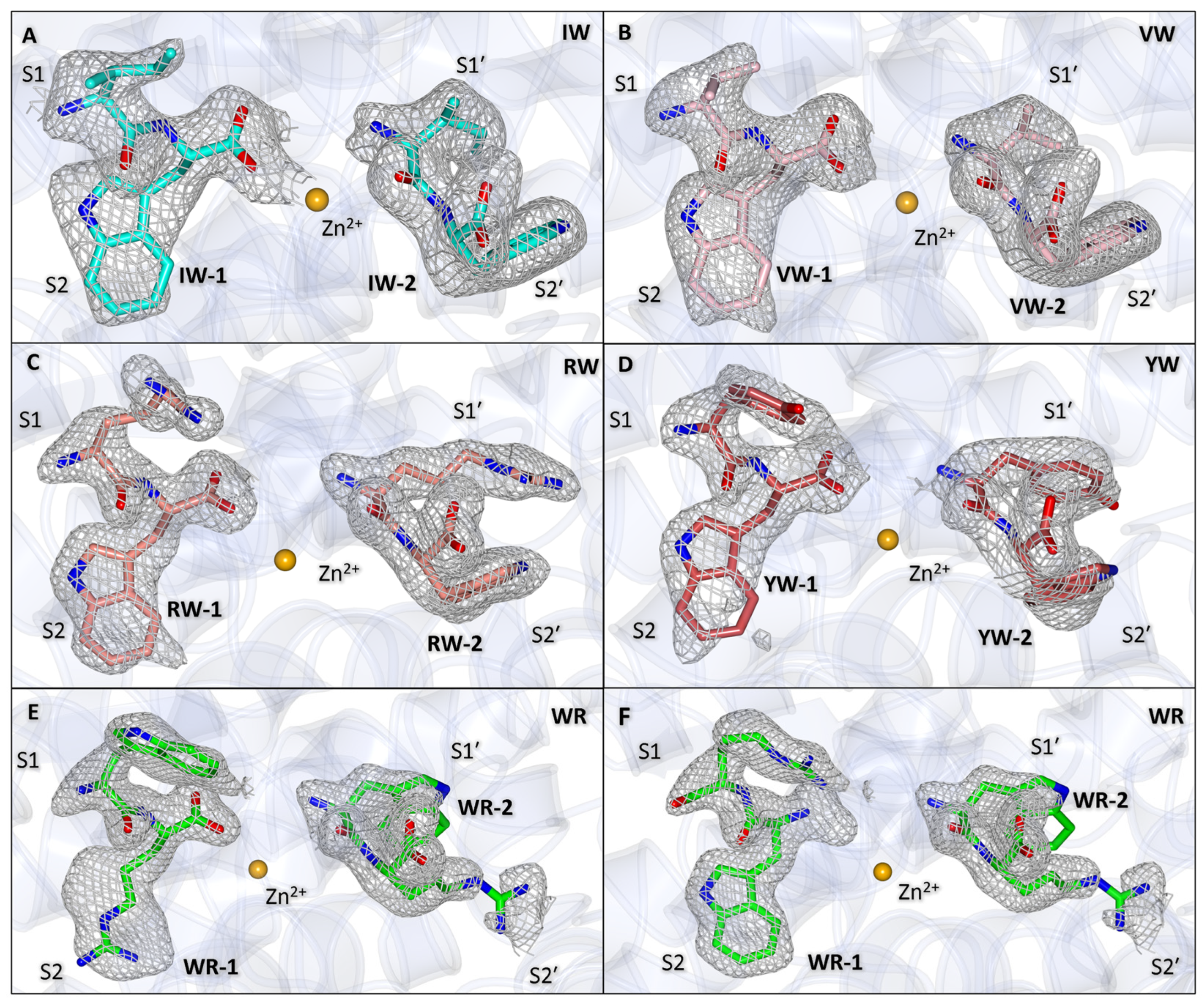
3.2. Crystal Structures of AnCE in Complex with Dipeptides IW, VW, YW, RW, and WR
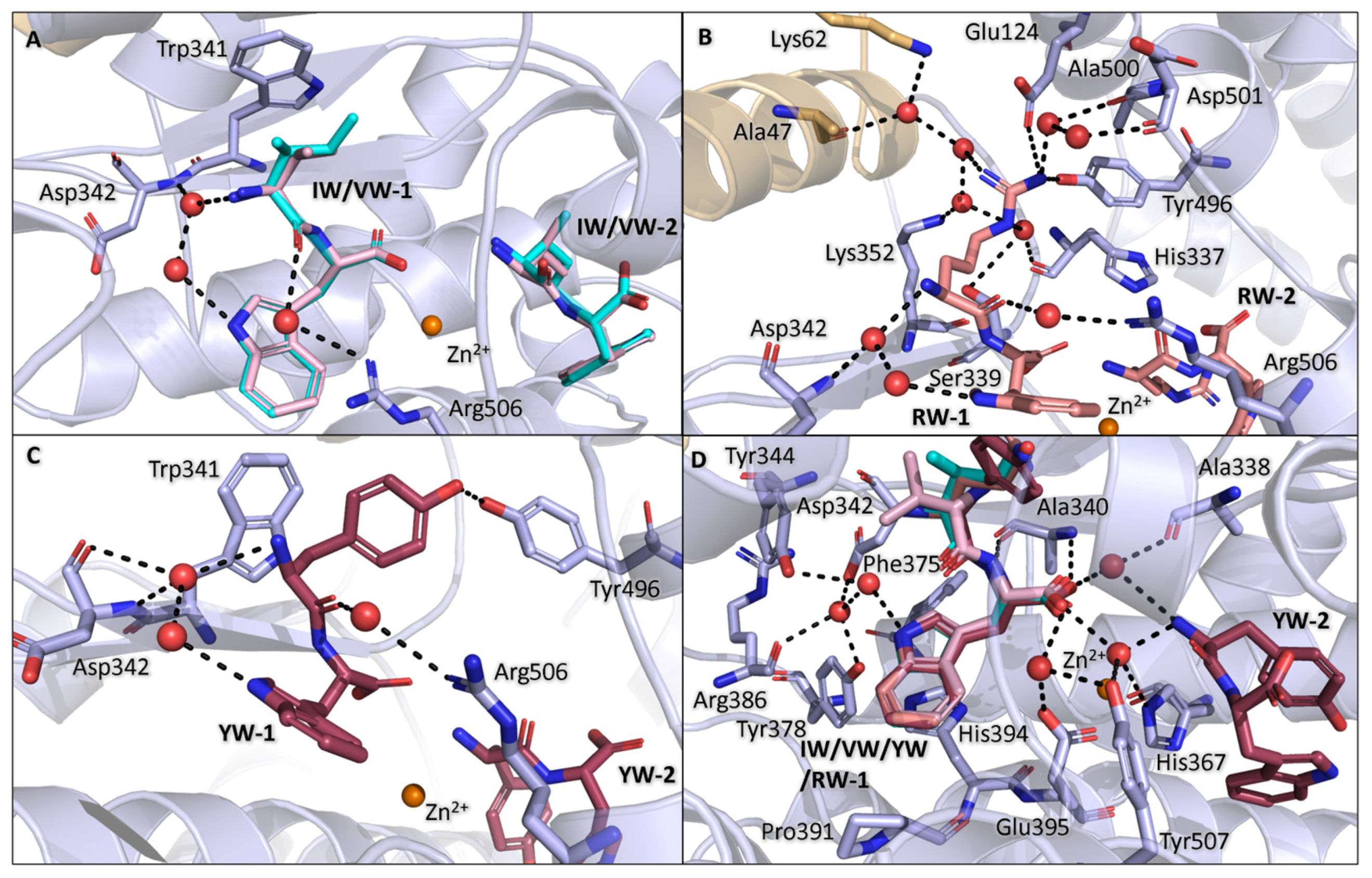
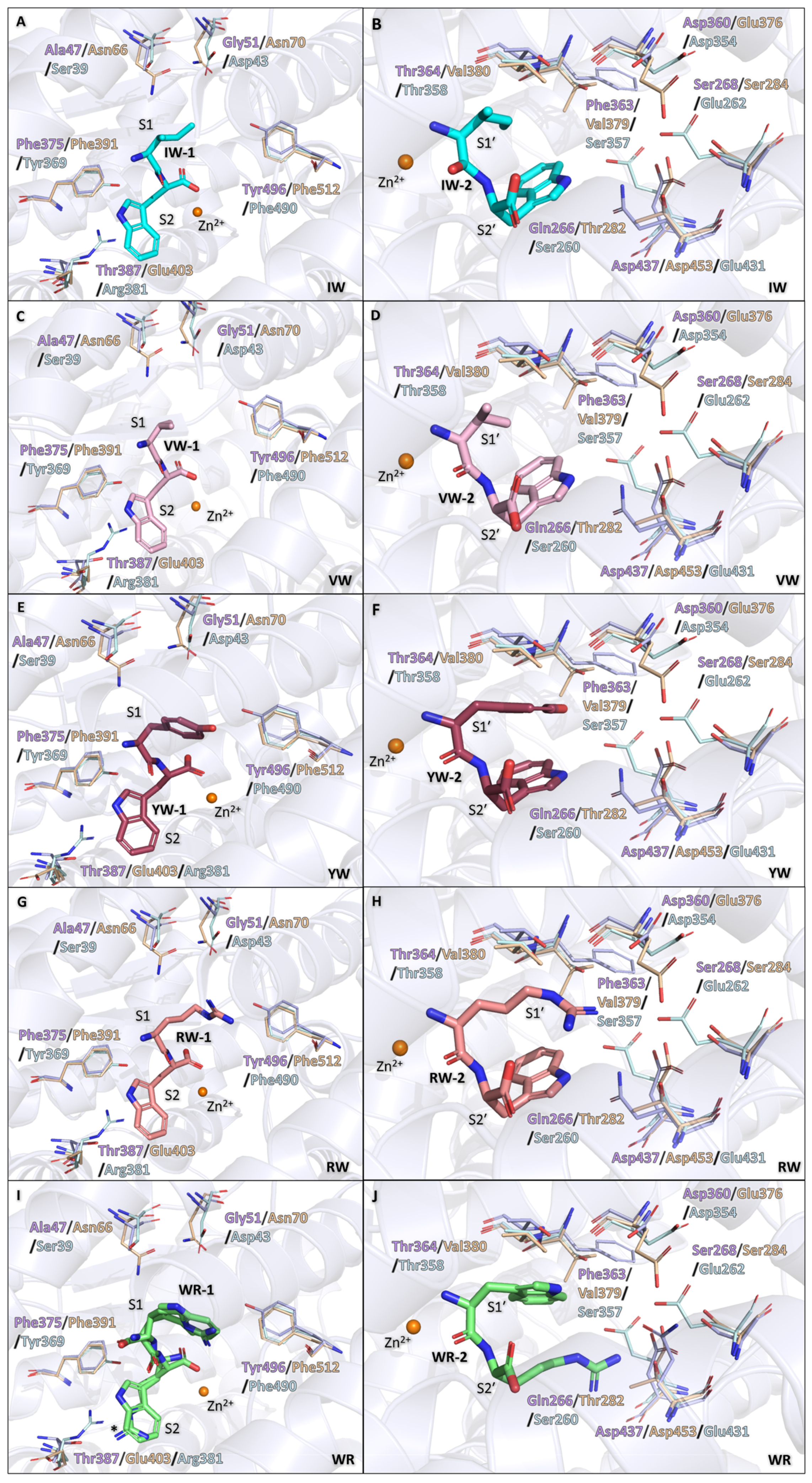
3.3. Binding of IW, VW, YW, and RW Within the Non-Prime Subsites
3.4. Binding of IW, VW, YW, and RW Within the Prime Subsites
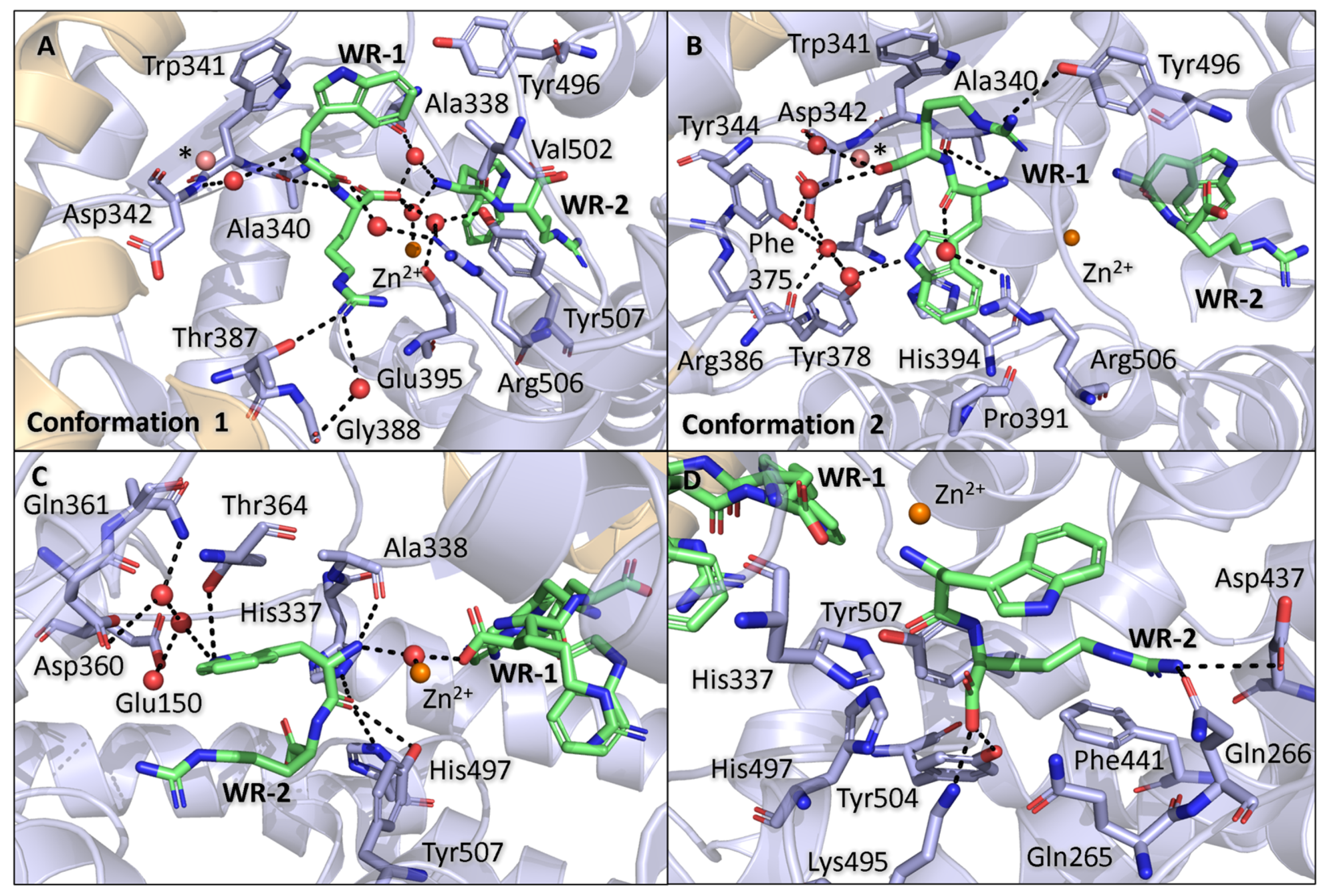
3.5. Binding of WR Within Non-Prime Subsite
3.6. Binding of WR Within Prime Subsite
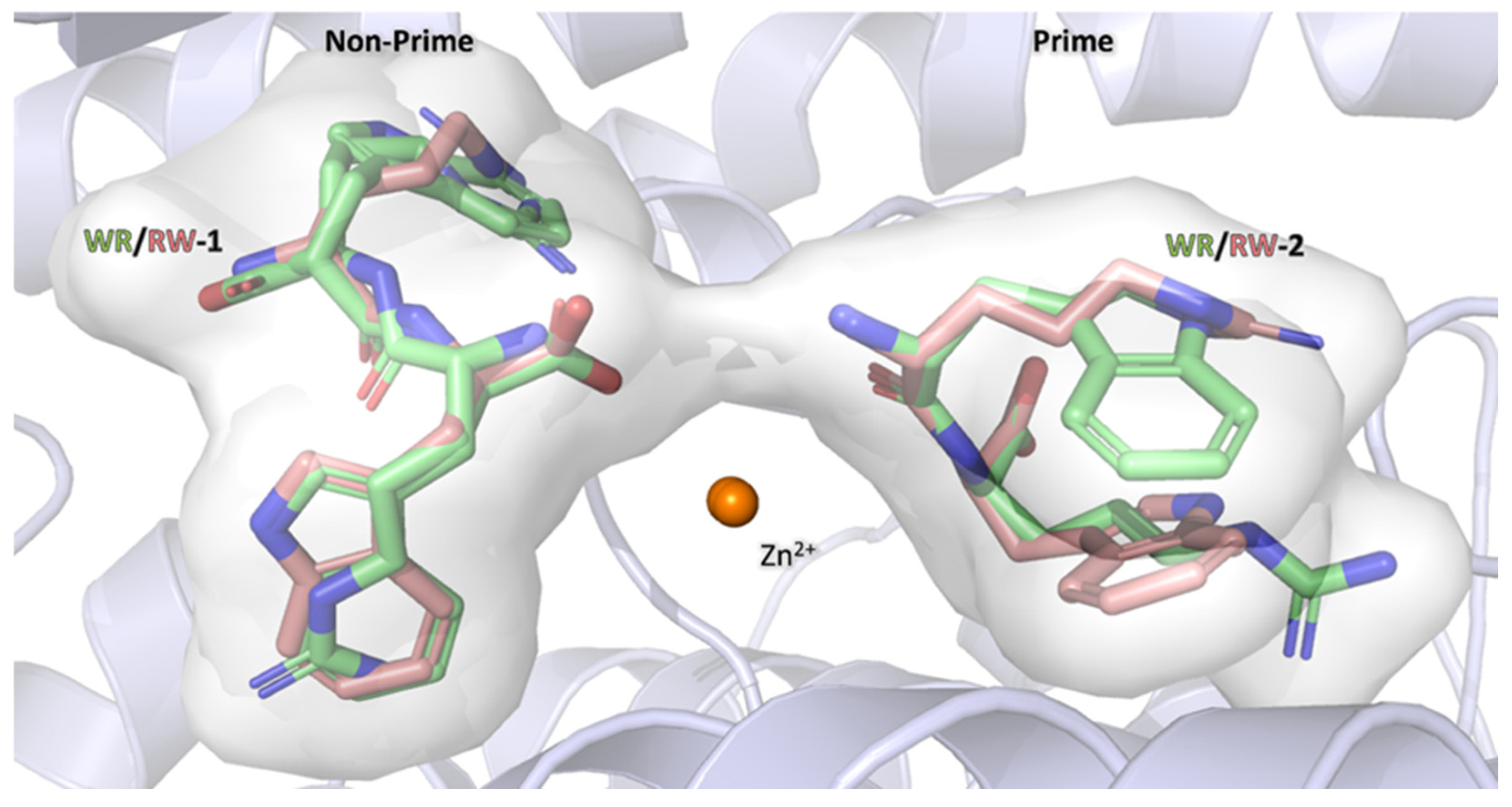
3.7. Comparison of RW and WR Binding
3.8. Dipeptides Modelled in cACE
3.9. Dipeptide Modelled in nACE
3.10. Comparison of Dipeptide Affinity to AnCE, cACE, and nACE
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Angiotensin-1-converting enzyme |
| AnCE | Angiotensin-1-converting enzyme from Drosophila melanogaster |
| cACE | C-terminal domain of ACE |
| nACE | N-terminal domain of ACE |
| PDB | Protein Data Bank |
| RMSD | Root mean square deviation |
References
- Watermeyer, J.M.; Kröger, W.L.; O’Neill, H.G.; Sewell, B.T.; Sturrock, E.D. Probing the Basis of Domain-Dependent Inhibition Using Novel Ketone Inhibitors of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 5942–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, C.S.; Masuyer, G.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. Structure Based Drug Design of Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme Inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, K.R.; Sturrock, E.D.; Riordan, J.F.; Ehlers, M.R.W. Ace Revisited: A New Target for Structure-Based Drug Design. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuyer, G.; Akif, M.; Czarny, B.; Beau, F.; Schwager, S.L.U.; Sturrock, E.D.; Isaac, R.E.; Dive, V.; Acharya, K.R. Crystal Structures of Highly Specific Phosphinic Tripeptide Enantiomers in Complex with the Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, K.R.; Gregory, K.S.; Sturrock, E.D. Advances in the Structural Basis for Angiotensin-1 Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors. Biosci. Rep. 2024, 44, BSR20240130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Bhat, S.A.; Shibata, T.; Giani, J.F.; Rader, F.; Bernstein, K.E.; Khan, Z. Diverse Biological Functions of the Renin-angiotensin System. Med. Res. Rev. 2024, 44, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natesh, R.; Schwager, S.L.U.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. Crystal Structure of the Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme–Lisinopril Complex. Nature 2003, 421, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradi, H.R.; Schwager, S.L.U.; Nchinda, A.T.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. Crystal Structure of the N Domain of Human Somatic Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Provides a Structural Basis for Domain-Specific Inhibitor Design. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 357, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polakovičová, M.; Jampílek, J. Advances in Structural Biology of ACE and Development of Domain Selective ACE-Inhibitors. Med. Chem. 2019, 15, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunow, D.; Kaiser, S.; Brückner, S.; Gotsch, A.; Henle, T. Selective Release of ACE-Inhibiting Tryptophan-Containing Dipeptides from Food Proteins by Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2013, 237, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczak, E.D.; Usui, H.; Fujita, H.; Yang, Y.; Yokoo, M.; Lipkowski, A.W.; Yoshikawa, M. New Antihypertensive Peptides Isolated from Rapeseed. Peptides 2003, 24, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.; Wellner, A.; Ossowski, I.; Henle, T. Identification and Quantification of Inhibitors for Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme in Hypoallergenic Infant Milk Formulas. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6333–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, S.; Lunow, D.; Kaiser, S.; Henle, T. Identification and Quantification of ACE-Inhibiting Peptides in Enzymatic Hydrolysates of Plant Proteins. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunow, D.; Kaiser, S.; Rückriemen, J.; Pohl, C.; Henle, T. Tryptophan-Containing Dipeptides Are C-Domain Selective Inhibitors of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, D.; Cuniasse, P.; Cotton, J.; Yiotakis, A.; Dive, V. Structural Determinants of RXPA380, a Potent and Highly Selective Inhibitor of the Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme C-Domain. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 8048–8054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almquist, R.G.; Chao, W.-R.; Ellis, M.E.; Johnson, H.L. Synthesis and Biological Activity of a Ketomethylene Analog of a Tripeptide Inhibitor of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme. J. Med. Chem. 1980, 23, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deddish, P.A.; Marcic, B.; Jackman, H.L.; Wang, H.-Z.; Skidgel, R.A.; Erdös, E.G. N-Domain–Specific Substrate and C-Domain Inhibitors of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme. Hypertension 1998, 31, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nchinda, A.T.; Chibale, K.; Redelinghuys, P.; Sturrock, E.D. Synthesis of Novel Keto-ACE Analogues as Domain-Selective Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 4612–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redelinghuys, P.; Nchinda, A.T.; Chibale, K.; Sturrock, E.D. Novel Ketomethylene Inhibitors of Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE): Inhibition and Molecular Modelling. Biol. Chem. 2006, 387, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akif, M.; Ntai, I.; Sturrock, E.D.; Isaac, R.E.; Bachmann, B.O.; Acharya, K.R. Crystal Structure of a Phosphonotripeptide K-26 in Complex with Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Homologue (AnCE) from Drosophila Melanogaster. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, G. Xia2: An Expert System for Macromolecular Crystallography Data Reduction. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2010, 43, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, P.R. An Introduction to Data Reduction: Space-Group Determination, Scaling and Intensity Statistics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, P.R. Scaling and Assessment of Data Quality. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2006, 62, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, A.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Adams, P.D.; Winn, M.D.; Storoni, L.C.; Read, R.J. Phaser Crystallographic Software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C.; Acharya, K.R. A New High-resolution Crystal Structure of the Drosophila melanogaster Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Homologue, AnCE. FEBS Open Bio 2015, 5, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and Development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshudov, G.N.; Skubák, P.; Lebedev, A.A.; Pannu, N.S.; Steiner, R.A.; Nicholls, R.A.; Winn, M.D.; Long, F.; Vagin, A.A. REFMAC 5 for the Refinement of Macromolecular Crystal Structures. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshudov, G.N.; Vagin, A.A.; Dodson, E.J. Refinement of Macromolecular Structures by the Maximum-Likelihood Method. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1997, 53, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.B.; Arendall, W.B.; Headd, J.J.; Keedy, D.A.; Immormino, R.M.; Kapral, G.J.; Murray, L.W.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. MolProbity: All-Atom Structure Validation for Macromolecular Crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNicholas, S.; Potterton, E.; Wilson, K.S.; Noble, M.E.M. Presenting Your Structures: The CCP4Mg Molecular-Graphics Software. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung-Chi, C.; Prusoff, W.H. Relationship between the Inhibition Constant (KI) and the Concentration of Inhibitor Which Causes 50 per Cent Inhibition (I50) of an Enzymatic Reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1973, 22, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradi, H.R.; Chitapi, I.; Sewell, B.T.; Georgiadis, D.; Dive, V.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. The Structure of Testis Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme in Complex with the C Domain-Specific Inhibitor RXPA380. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 5473–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akif, M.; Georgiadis, D.; Mahajan, A.; Dive, V.; Sturrock, E.D.; Isaac, R.E.; Acharya, K.R. High-Resolution Crystal Structures of Drosophila Melanogaster Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme in Complex with Novel Inhibitors and Antihypertensive Drugs. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 400, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozier, G.E.; Arendse, L.B.; Schwager, S.L.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. Molecular Basis for Multiple Omapatrilat Binding Sites within the ACE C-Domain: Implications for Drug Design. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 10141–10154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozier, G.E.; Schwager, S.L.; Sharma, R.K.; Chibale, K.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. Crystal Structures of Sampatrilat and Sampatrilat-Asp in Complex with Human ACE—A Molecular Basis for Domain Selectivity. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 1477–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuyer, G.; Douglas, R.G.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. Structural Basis of Ac-SDKP Hydrolysis by Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuyer, G.; Schwager, S.L.U.; Sturrock, E.D.; Isaac, R.E.; Acharya, K.R. Molecular Recognition and Regulation of Human Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme (ACE) Activity by Natural Inhibitory Peptides. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, K.S.; Cozier, G.E.; Schwager, S.L.U.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. Structural Insights into the Inhibitory Mechanism of Angiotensin-I-converting Enzyme by the Lactotripeptides IPP and VPP. FEBS Lett. 2024, 598, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dipeptide | IC50 (mM) | Ki (mM) |
|---|---|---|
| IW | 0.34 | 0.08 |
| VW | 0.78 | 0.17 |
| YW | 3.40 | 0.75 |
| RW | 0.88 | 0.20 |
| WR | 3.78 | 0.84 |
| AnCE_IW | AnCE_VW | AnCE_YW | AnCE_RW | AnCE_WR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space group | H3 | H3 | H3 | H3 | H3 |
| Unit cell parameters: | |||||
| a (Å) | 173.2 | 172.5 | 172.4 | 172.9 | 172.9 |
| b (Å) | 173.2 | 172.5 | 172.4 | 172.9 | 172.9 |
| c (Å) | 103.1 | 103.7 | 103.5 | 103.6 | 103.0 |
| α (o) | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.0 |
| β (o) | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.0 |
| γ (o) | 120.00 | 120.00 | 120.00 | 120.00 | 120.0 |
| Molecules per asymmetric unit | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Resolution range (Å) | 50.01–2.20 (2.26–2.20) | 43.13–2.20 (2.26–2.20) | 86.22–2.20 (2.26–2.20) | 86.45–1.90 (1.93–1.90) | 86.47–1.85 (1.88–1.85) |
| Rmerge (%) | 19.2 (177.6) | 31.9 (383.0) | 23.5 (213.0) | 12.3 (142.5) | 7.9 (90.6) |
| Rpim (%) | 6.2 (57.2) | 7.0 (84.8) | 7.7 (69.2) | 4.0 (46.4) | 2.6 (32) |
| Mean I/σ (I) | 8.3 (1.3) | 8.6 (1.4) | 7.0 (1.8) | 10.2 (1.5) | 15.6 (2.2) |
| Completeness (%) | 100.0 (100.0) | 100.0 (99.8) | 100.0 (100.0) | 100.0 (100.0) | 100.0 (100.0) |
| Number of reflections: | |||||
| Total | 619,139 | 1,266,516 | 596,397 | 959,889 | 1,014,896 |
| Unique | 58,565 | 58,412 | 58,227 | 91,012 | 98,093 |
| CC 1/2 | 0.997 (0.704) | 0.997 (0.824) | 0.994 (0.599) | 0.998 (0.793) | 0.999 (0.886) |
| Multiplicity | 10.6 (10.6) | 21.7 (21.1) | 10.2 (10.2) | 10.5 (10.4) | 10.3 (8.9) |
| Average B factor (Å2) | |||||
| Protein | 40.50 | 40.46 | 35.94 | 32.73 | 30.26 |
| Ligand | 91.75 | 81.13 | 66.93 | 62.16 | 61.84 |
| Zinc ion | 34.90 | 32.61 | 28.95 | 28.15 | 25.55 |
| Solvent | 38.20 | 39.46 | 36.24 | 40.21 | 41.54 |
| Dipeptide-1 | 57.41 | 58.93 | 70.91 | 54.71 | 44.16 |
| Dipeptide-2 | 33.76 | 44.15 | 48.91 | 40.01 | 54.09 |
| Rwork/Rfree (%) | 0.17/0.21 | 0.17/0.21 | 0.16/0.21 | 0.16/0.20 | 0.15/0.18 |
| R.M.S deviation from ideal values | |||||
| Bond lengths (Å) | 0.014 | 0.008 | 0.015 | 0.010 | 0.011 |
| Bond angles (o) | 2.463 | 1.729 | 2.560 | 1.904 | 1.909 |
| Ramachandran plot statistics (%) | |||||
| Favoured | 97.48 | 98.32 | 98.32 | 98.83 | 98.83 |
| Allowed | 2.52 | 1.51 | 1.68 | 1.00 | 1.17 |
| Disallowed | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.00 |
| Number of non-hydrogen atoms | |||||
| Amino acids | 4923 | 4908 | 4927 | 4929 | 4955 |
| Ions | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Ligand | 113 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 137 |
| Water | 236 | 243 | 309 | 520 | 769 |
| Dipeptide-1 | 23 | 22 | 27 | 26 | 52 |
| Dipeptide-2 | 23 | 22 | 27 | 26 | 26 |
| PDB code | 9QA0 | 9QA1 | 9QA3 | 9QA2 | 9QA4 |
| Subsite | AnCE | cACE | nACE |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Ala47 | Asn66 | Ser39 |
| Gly51 | Asn70 | Asp43 | |
| Tyr496 | Phe512 | Phe490 | |
| S2 | Phe375 | Phe391 | Tyr369 |
| Thr387 | Glu403 | Arg381 | |
| S1′ | Asp360 | Glu376 | Asp354 |
| Phe363 | Val379 | Ser357 | |
| Thr364 | Val380 | Thr358 | |
| S2′ | Gln266 | Thr282 | Ser260 |
| Ser268 | Ser284 | Glu262 | |
| Asp437 | Asp453 | Glu431 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Żukowska, J.; Gregory, K.S.; Robinson, A.; Isaac, R.E.; Acharya, K.R. Molecular Basis of Dipeptide Recognition in Drosophila melanogaster Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Homologue, AnCE. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040591
Żukowska J, Gregory KS, Robinson A, Isaac RE, Acharya KR. Molecular Basis of Dipeptide Recognition in Drosophila melanogaster Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Homologue, AnCE. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(4):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040591
Chicago/Turabian StyleŻukowska, Joanna, Kyle S. Gregory, Adam Robinson, R. Elwyn Isaac, and K. Ravi Acharya. 2025. "Molecular Basis of Dipeptide Recognition in Drosophila melanogaster Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Homologue, AnCE" Biomolecules 15, no. 4: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040591
APA StyleŻukowska, J., Gregory, K. S., Robinson, A., Isaac, R. E., & Acharya, K. R. (2025). Molecular Basis of Dipeptide Recognition in Drosophila melanogaster Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Homologue, AnCE. Biomolecules, 15(4), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040591






