Characterization of the Anti-Cancer Activity of the Probiotic Bacterium Lactobacillus fermentum Using 2D vs. 3D Culture in Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Cultures
2.2. Mammalian Cell Cultures
2.3. Spheroid Preparation
2.4. Preparation of Lactobacillus Cell-Free Supernatant (LCFS)
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
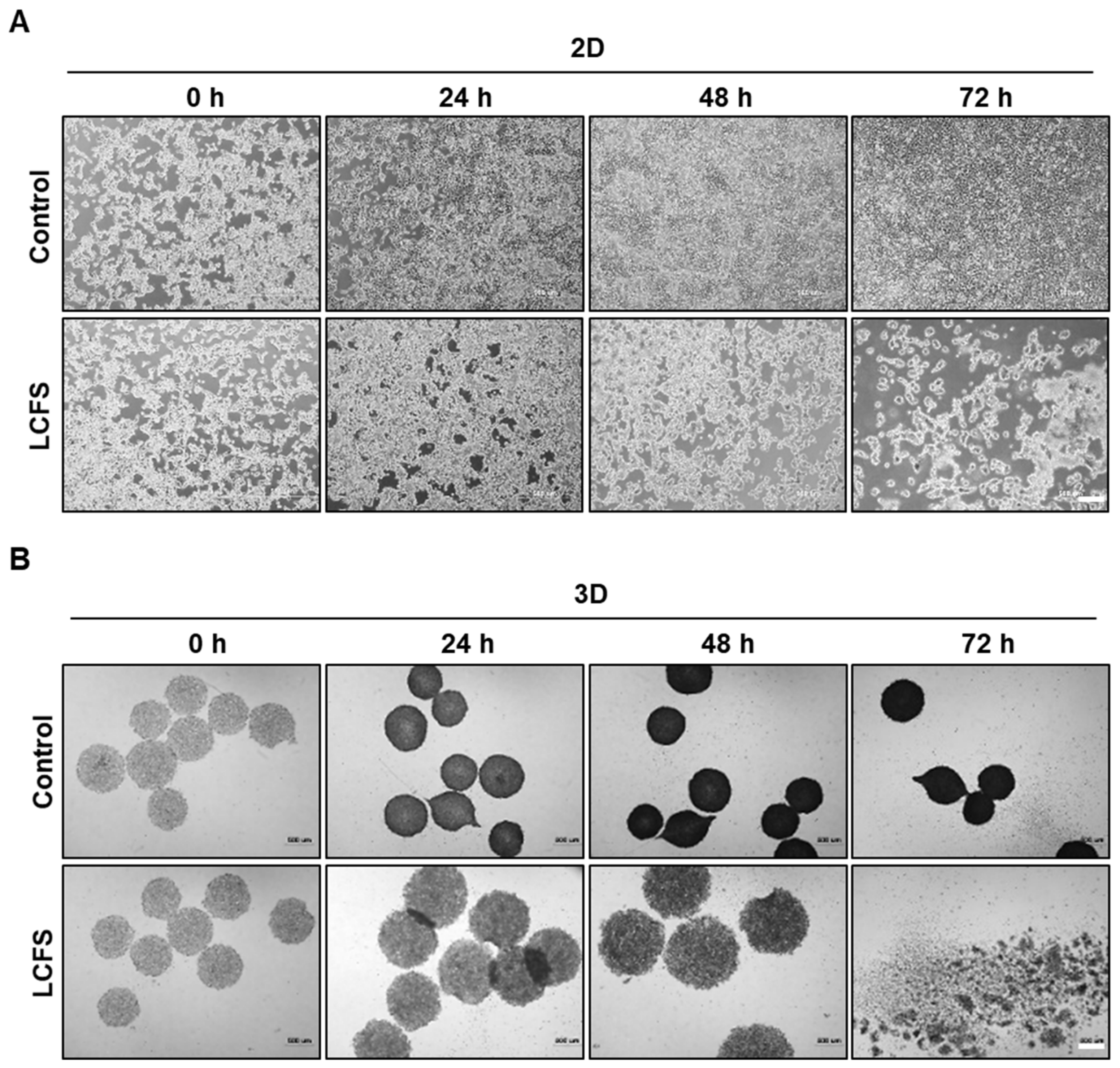
2.6. Microscopic Analysis
2.7. Apoptosis Assay
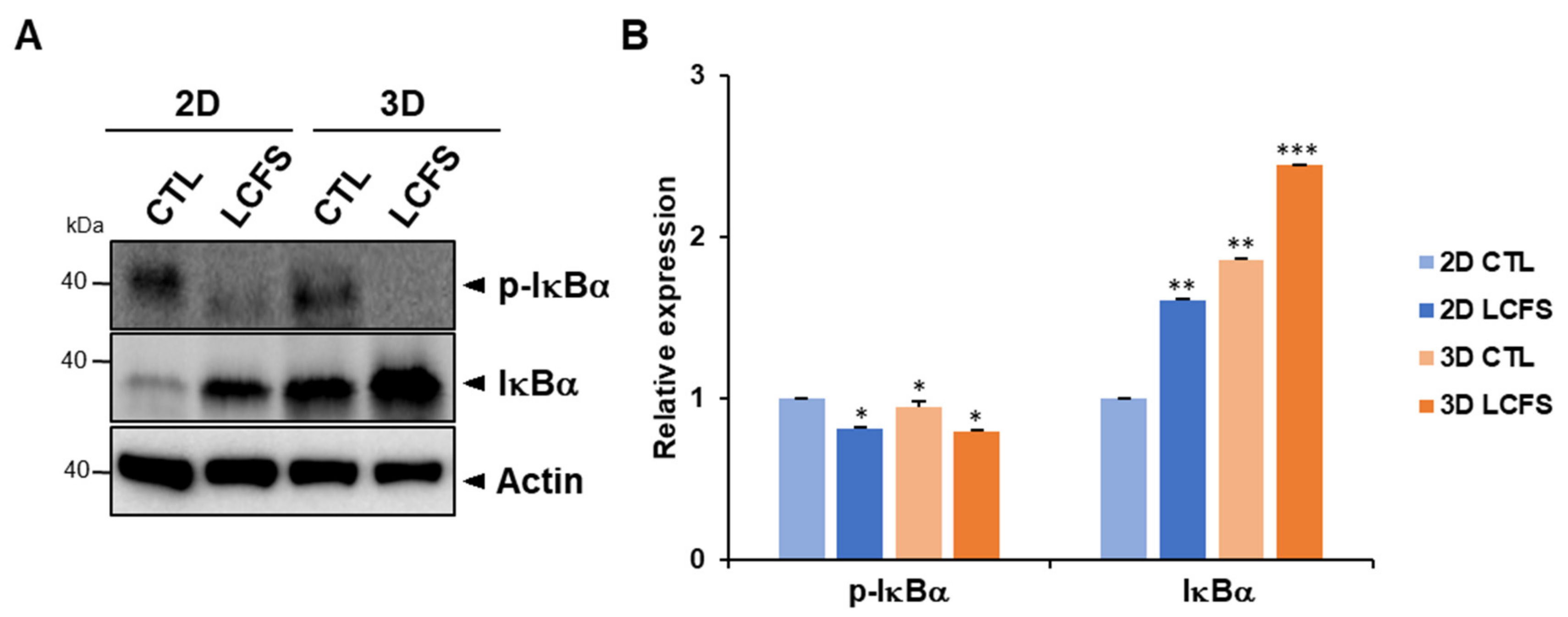
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. RT-PCR
2.10. Confocal Imaging
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
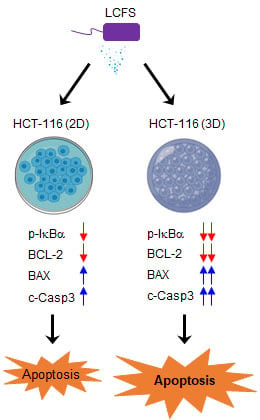
3.1. L. fermentum Cell-Free Supernatants (LCFS) Promote Cell Death in 3D HCT-116 Conditions rather than in 2D HCT-116 Conditions
3.2. LCFS Induces Apoptosis of HCT-116 Spheroids
3.3. LCFS Promotes Apoptotic Markers in Spheroids More Sensitive than in Monolayers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roy, S.; Trinchieri, G. Microbiota: A key orchestrator of cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Tang, W.; Fan, X.; Wu, G. OncoTargets and Therapy Dovepress intestinal microbiota: A novel perspective in colorectal cancer biotherapeutics. Oncotargets Ther. 2018, 11–4797. [Google Scholar]
- Kahouli, I.; Malhotra, M.; Westfall, S.; Alaoui-Jamali, M.A.; Prakash, S. Design and validation of an orally administrated active L. fermentum-L. acidophilus probiotic formulation using colorectal cancer Apc Min/+ mouse model. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1999–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Deeb, N.M.; Yassin, A.M.; Al-Madboly, L.A.; El-Hawiet, A. A novel purified Lactobacillus acidophilus 20079 exopolysaccharide, LA-EPS-20079, molecularly regulates both apoptotic and NF-κB inflammatory pathways in human colon cancer. Microb. Cell Factories 2018, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tukenmez, U.; Aktas, B.; Aslim, B.; Yavuz, S. The relationship between the structural characteristics of lactobacilli-EPS and its ability to induce apoptosis in colon cancer cells in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. Ca A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuipers, E.J.; Grady, W.M.; Lieberman, D.; Seufferlein, T.; Sung, J.J.; Boelens, P.G.; van de Velde, C.J.H.; Watanabe, T. Colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, S.; Syed, B.A. Colorectal cancer drugs market. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 525–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Zhang, X.; Covasa, M. Emerging roles of lactic acid bacteria in protection against colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7878–7886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiptiri-Kourpeti, A.; Spyridopoulou, K.; Santarmaki, V.; Aindelis, G.; Tompoulidou, E.; Lamprianidou, E.E.; Saxami, G.; Ypsilantis, P.; Lampri, E.S.; Simopoulos, C.; et al. Lactobacillus casei exerts anti-proliferative effects accompanied by apoptotic cell death and up-regulation of TRAIL in colon carcinoma cells. Plos ONE 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, H.; Fujiya, M.; Tanaka, H.; Ueno, N.; Moriichi, K.; Sasajima, J.; Ikuta, K.; Akutsu, H.; Tanabe, H.; Kohgo, Y. Probiotic-derived ferrichrome inhibits colon cancer progression via JNK-mediated apoptosis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, C.; Millette, M.; Oth, D.; Ruiz, M.T.; Luquet, F.M.; Lacroix, M. Probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus and L. casei mix sensitize colorectal tumoral cells to 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis. Nutr. Cancer 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zitvogel, L.; Daillère, R.; Roberti, M.P.; Routy, B.; Kroemer, G. Anticancer effects of the microbiome and its products. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamir, E.R.; Ewald, A.J. Three-dimensional organotypic culture: Experimental models of mammalian biology and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 647–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melissaridou, S.; Wiechec, E.; Magan, M.; Jain, M.V.; Chung, M.K.; Farnebo, L.; Roberg, K. The effect of 2D and 3D cell cultures on treatment response, EMT profile and stem cell features in head and neck cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedl, A.; Schlederer, M.; Pudelko, K.; Stadler, M.; Walter, S.; Unterleuthner, D.; Unger, C.; Kramer, N.; Hengstschläger, M.; Kenner, L.; et al. Comparison of cancer cells in 2D vs. 3D culture reveals differences in AKT–mTOR–S6K signaling and drug responses. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.E.; Jeon, H.J.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.Y.; Hong, J.; Maeng, P.J.; Kim, K.R.; Kang, D. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of 2D and 3D Cultured Colorectal Cancer Cells: Profiling of Tankyrase Inhibitor XAV939-Induced Proteome. Sci. Rep. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, J.; Ekawa, T.; Endo, H.; Yamazaki, K.; Tanaka, N.; Kukita, Y.; Okuyama, H.; Okami, J.; Imamura, F.; Ohue, M.; et al. High-throughput screening in colorectal cancer tissue-originated spheroids. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KIM, Y.; WHANG, J.Y.; WHANG, K.Y.; OH, S.; KIM, S.H. Characterization of the Cholesterol-Reducing Activity in a Cell-Free Supernatant of Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 43121. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhans, S.A. Three-dimensional in vitro cell culture models in drug discovery and drug repositioning. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katt, M.E.; Placone, A.L.; Wong, A.D.; Xu, Z.S.; Searson, P.C. In Vitro Tumor Models: Advantages, Disadvantages, Variables, and Selecting the Right Platform. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahouli, I.; Tomaro-Duchesneau, C.; Prakash, S. Probiotics in colorectal cancer (CRC) with emphasis on mechanisms of action and current perspectives. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 1107–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinić, M.; Lukić, J.; Djokić, J.; Milenković, M.; Strahinić, I.; Golić, N.; Begović, J. Lactobacillus fermentum postbiotic-induced autophagy as potential approach for treatment of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirabunyanon, M.; Boonprasom, P.; Niamsup, P. Probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria isolated from fermented dairy milks on antiproliferation of colon cancer cells. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichim, G.; Tait, S.W.G. A fate worse than death: Apoptosis as an oncogenic process. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danial, N.N. BCL-2 family proteins: Critical checkpoints of apoptotic cell death. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 7254–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios De La Rosa, J.M.; Wubetu, J.; Tirelli, N.; Tirella, A. Colorectal tumor 3D in vitro models: Advantages of biofabrication for the recapitulation of early stages of tumour development. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liverani, C.; De Vita, A.; Minardi, S.; Kang, Y.; Mercatali, L.; Amadori, D.; Bongiovanni, A.; La Manna, F.; Ibrahim, T.; Tasciotti, E. A biomimetic 3D model of hypoxia-driven cancer progression. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, H.; Vervloessem, T.; Kiviluoto, S.; Bittremieux, M.; Parys, J.B.; De Smedt, H.; Bultynck, G. A dual role for the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein in cancer: Mitochondria versus endoplasmic reticulum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1843, 2240–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Tamaki, H.; Harada, M. Docetaxel induces Bcl-2- and pro-apoptotic caspase-independent death of human prostate cancer DU145 cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 2330–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.S.; Barros, A.S.; Costa, E.C.; Moreira, A.F.; Correia, I.J. 3D tumor spheroids as in vitro models to mimic in vivo human solid tumors resistance to therapeutic drugs. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 116, 206–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimkiewicz, K.; Weglarczyk, K.; Collet, G.; Paprocka, M.; Guichard, A.; Sarna, M.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J.; Sarna, T.; Grillon, C.; et al. A 3D model of tumour angiogenic microenvironment to monitor hypoxia effects on cell interactions and cancer stem cell selection. Cancer Lett. 2017, 396, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschhaeuser, F.; Menne, H.; Dittfeld, C.; West, J.; Mueller-Klieser, W.; Kunz-Schughart, L.A. Multicellular tumor spheroids: An underestimated tool is catching up again. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 148, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piqué, N.; Berlanga, M.; Miñana-Galbis, D.; Piqué, N.; Berlanga, M.; Miñana-Galbis, D. Health Benefits of Heat-Killed (Tyndallized) Probiotics: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoni, M.; Piccinini, F.; Arienti, C.; Zamagni, A.; Santi, S.; Polico, R.; Bevilacqua, A.; Tesei, A. 3D tumor spheroid models for in vitro therapeutic screening: A systematic approach to enhance the biological relevance of data obtained. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puls, T.J.; Tan, X.; Husain, M.; Whittington, C.F.; Fishel, M.L.; Voytik-Harbin, S.L. Development of a Novel 3D Tumor-tissue Invasion Model for High-throughput, High-content Phenotypic Drug Screening. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampaloni, F.; Reynaud, E.G.; Stelzer, E.H.K. Most of the cell-based data-harvesting efforts that drive the integration of cell biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A. Cell culture: Biology’s new dimension. Nature 2003, 424, 870–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, L.G.; Swartz, M.A. Capturing complex 3D tissue physiology in vitro. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, R.E.; Raleigh, J.A. Identification of nonproliferating but viable hypoxic tumor cells in vivo. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 3547–3550. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, C.T.; Wang, J.Y.; Lin, Y.F.; Wo, A.M.; Chen, B.P.C.; Lee, H. Three-dimensional spheroid culture targeting versatile tissue bioassays using a PDMS-based hanging drop array. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Park, D.Y.; Yang, L.; Kim, E.J.; Ahrberg, C.D.; Lee, K.B.; Chung, B.G. Generation of uniform-sized multicellular tumor spheroids using hydrogel microwells for advanced drug screening. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-E.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, N.; Lee, S.H.; Park, S.B.; Koh, B.; Kang, D.; Kim, S.; Yoo, H.M. Characterization of the Anti-Cancer Activity of the Probiotic Bacterium Lactobacillus fermentum Using 2D vs. 3D Culture in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9100557
Lee J-E, Lee J, Kim JH, Cho N, Lee SH, Park SB, Koh B, Kang D, Kim S, Yoo HM. Characterization of the Anti-Cancer Activity of the Probiotic Bacterium Lactobacillus fermentum Using 2D vs. 3D Culture in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(10):557. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9100557
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Joo-Eun, Jina Lee, Ji Hyun Kim, Namki Cho, Sung Hoon Lee, Sung Bum Park, Byumseok Koh, Dukjin Kang, Seil Kim, and Hee Min Yoo. 2019. "Characterization of the Anti-Cancer Activity of the Probiotic Bacterium Lactobacillus fermentum Using 2D vs. 3D Culture in Colorectal Cancer Cells" Biomolecules 9, no. 10: 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9100557
APA StyleLee, J.-E., Lee, J., Kim, J. H., Cho, N., Lee, S. H., Park, S. B., Koh, B., Kang, D., Kim, S., & Yoo, H. M. (2019). Characterization of the Anti-Cancer Activity of the Probiotic Bacterium Lactobacillus fermentum Using 2D vs. 3D Culture in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Biomolecules, 9(10), 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9100557