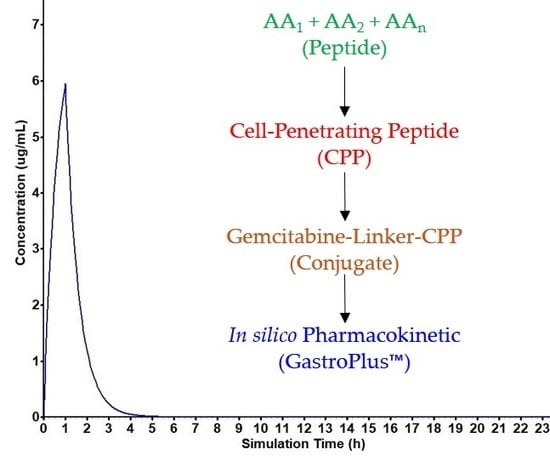
Combination of Gemcitabine with Cell-Penetrating Peptides: A Pharmacokinetic Approach Using in Silico Tools
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Amino Acids–Structure, Physicochemical Properties and Creation of a Z-Scale
2.2. Peptides
2.2.1. Datasets
2.2.2. Peptide Descriptors
2.3. Prediction Model Generation and Optimization
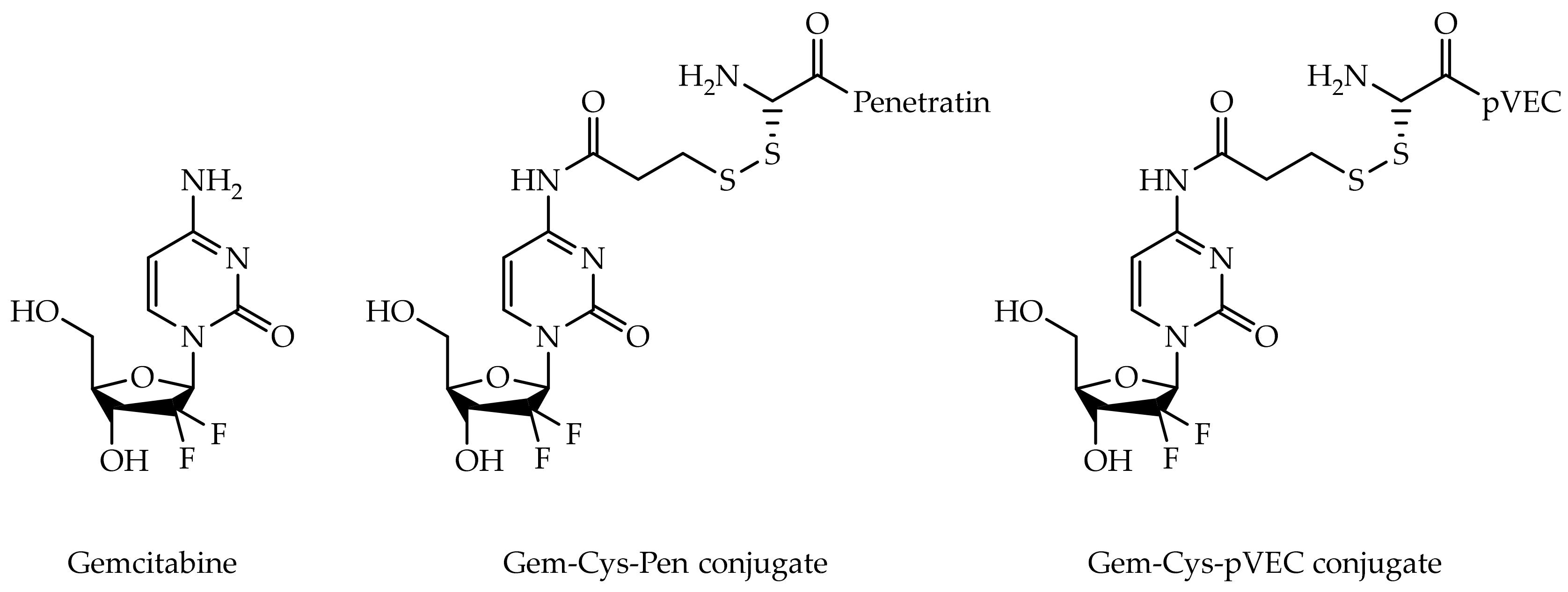
2.4. Pharmacokinetic Assessment of Gemcitabine, Cpp and Gemcitabine-Cpp Conjugates
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rybka, J.; Jurczak, W.; Giza, A.; Paszkiewicz-Kozik, E.; Kumiega, B.; Drozd-Sokolowska, J.; Butrym, A.; Kuliczkowski, K.; Wrobel, T. Gemcitabine-Based Treatment in Poor-Prognosis Patients with Relapsed and Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma--a Multicenter Polish Experience. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 24, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.; Soo, R.A.; Yong, W.P.; Innocenti, F. Clinical pharmacology and pharmacogenetics of gemcitabine. Drug Metab. Rev. 2009, 41, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mini, E.; Nobili, S.; Caciagli, B.; Landini, I.; Mazzei, T. Cellular pharmacology of gemcitabine. Ann. Oncol. 2006, 17, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccolini, J.; Mercier, C.; Dahan, L.; Andre, N. Integrating pharmacogenetics into gemcitabine dosing--time for a change? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marechal, R.; Mackey, J.R.; Lai, R.; Demetter, P.; Peeters, M.; Polus, M.; Cass, C.E.; Young, J.; Salmon, I.; Deviere, J.; et al. Human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 and human concentrative nucleoside transporter 3 predict survival after adjuvant gemcitabine therapy in resected pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2009, 15, 2913–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Chubb, S.; Hertel, L.W.; Grindey, G.B.; Plunkett, W. Action of 2’,2’-difluorodeoxycytidine on DNA synthesis. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 6110–6117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alvarellos, M.L.; Lamba, J.; Sangkuhl, K.; Thorn, C.F.; Wang, L.; Klein, D.J.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. PharmGKB summary: Gemcitabine pathway. Pharm. Genom. 2014, 24, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroep, J.; Van Moorsel, C.; Veerman, G.; Voorn, D.; Schultz, R.; Worzalla, J.; Tanzer, L.; Merriman, R.; Pinedo, H.; Peters, G. Role of Deoxycytidine Kinase (dCK), Thymidine Kinase 2 (TK2), and Deoxycytidine Deaminase (dCDA) in the Antitumor Activity of Gemcitabine (dFdC). Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism in Man Ix; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, N.; Ferreira, A.; Fernandes, I.; Alves, C.; Araujo, M.J.; Mateus, N.; Gomes, P. Gemcitabine anti-proliferative activity significantly enhanced upon conjugation with cell-penetrating peptides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 2898–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copolovici, D.M.; Langel, K.; Eriste, E.; Langel, U. Cell-penetrating peptides: Design, synthesis, and applications. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1972–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.H.; Park, I.S.; Hahm, K.S.; Shin, S.Y. Antimicrobial activity, bactericidal mechanism and LPS-neutralizing activity of the cell-penetrating peptide pVEC and its analogs. J. Pept. Sci. 2011, 17, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tai, L.; Zhang, W.; Wei, G.; Pan, W.; Lu, W. Penetratin, a potentially powerful absorption enhancer for noninvasive intraocular drug delivery. Mol Pharm 2014, 11, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reissmann, S. Cell penetration: Scope and limitations by the application of cell-penetrating peptides. J. Pept. Sci. 2014, 20, 760–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, S.; Almeida, A.J.; Vale, N. Combination of Cell-Penetrating Peptides with Nanoparticles for Therapeutic Application: A Review. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Guo, S.; Jin, F. Recent progress of cell-penetrating peptides as new carriers for intracellular cargo delivery. J. Control. Release 2014, 174, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regberg, J.; Srimanee, A.; Langel, U. Applications of cell-penetrating peptides for tumor targeting and future cancer therapies. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2012, 5, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, K.M.; Horton, K.L.; Kelley, S.O. Cell-penetrating peptides as delivery vehicles for biology and medicine. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 6, 2242–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Yin, L.; Kim, K.H.; Cheng, J. Helical Poly(arginine) Mimics with Superior Cell-Penetrating and Molecular Transporting Properties. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 3839–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, S. Pattern recognition by means of disjoint principal components models. Pattern Recognit 1976, 8, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner, G.L.; Kowalski, B.R. The application of pattern recognition to drug design. Drug Design 1978, 8, 73–131. [Google Scholar]
- Hällbrink, M.; Kilk, K.; Elmquist, A.; Lundberg, P.; Lindgren, M.; Jiang, Y.; Pooga, M.; Soomets, U.; Langel, Ü. Prediction of cell-penetrating peptides. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2005, 11, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, M.; Eriksson, L.; Jonsson, J.; Sjostrom, M.; Wold, S. New chemical descriptors relevant for the design of biologically active peptides. A multivariate characterization of 87 amino acids. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 2481–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellberg, S.; Sjostrom, M.; Skagerberg, B.; Wold, S. Peptide quantitative structure-activity relationships, a multivariate approach. J. Med. Chem. 1987, 30, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, J.; Norberg, T.; Carlsson, L.; Gustafsson, C.; Wold, S. Quantitative sequence-activity models (QSAM)—tools for sequence design. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, M.; Kilk, K.; Langel, U. Predicting cell-penetrating peptides. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2008, 60, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, A.; Chaudhary, K.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, A.; Kapoor, P.; Tyagi, A.; Open Source Drug Discovery Consortium; Raghava, G.P. In silico approaches for designing highly effective cell penetrating peptides. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lata, S.; Sharma, B.K.; Raghava, G.P. Analysis and prediction of antibacterial peptides. BMC Bioinformatics 2007, 8, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, W.S.; Johnston, C.I.; Bridges, S.M.; Burgess, S.C.; Willeford, K.O. Prediction of cell penetrating peptides by support vector machines. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, F.L.; Torres, R.; PolláN, R.R. Classification of Antimicrobial Peptides with Imbalanced Datasets. Proceedings of 11th International Symposium on Medical Information Processing and Analysis, Cuenca, Ecuador, 17–19 November 2015; Eduardo, R., Natasha, L., Juan, D.G.-A., Jorge, B., Eds.; SPIE—International Society For Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, Washington, DC, USA, 2015; p. 96810T. [Google Scholar]
- Maccari, G.; Di Luca, M.; Nifosi, R.; Cardarelli, F.; Signore, G.; Boccardi, C.; Bifone, A. Antimicrobial peptides design by evolutionary multiobjective optimization. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosea, N.A.; Jones, H.M. Predicting pharmacokinetic profiles using in silico derived parameters. Mol Pharm 2013, 10, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GEMZAR®. (Gemcitabine HCl) for injection; FDA label. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/020509s069lbl.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- Gemcitabine on DrugBank Database. Available online: https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00441 (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z.; et al. DrugBank 5.0: A major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelen, K.; Coboeken, K.; Willmann, S.; Burghaus, R.; Dressman, J.B.; Lippert, J. Evolution of a detailed physiological model to simulate the gastrointestinal transit and absorption process in humans, part 1: Oral solutions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 5324–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thelen, K.; Coboeken, K.; Willmann, S.; Dressman, J.B.; Lippert, J. Evolution of a detailed physiological model to simulate the gastrointestinal transit and absorption process in humans, part II: Extension to describe performance of solid dosage forms. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 1267–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrott, N.J.; Yu, L.J.; Takano, R.; Nakamura, M.; Morcos, P.N. Physiologically Based Absorption Modeling to Explore the Impact of Food and Gastric pH Changes on the Pharmacokinetics of Alectinib. AAPS J. 2016, 18, 1464–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derossi, D.; Calvet, S.; Trembleau, A.; Brunissen, A.; Chassaing, G.; Prochiantz, A. Cell internalization of the third helix of the Antennapedia homeodomain is receptor-independent. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 18188–18193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmquist, A.; Lindgren, M.; Bartfai, T.; Langel, U. VE-cadherin-derived cell-penetrating peptide, pVEC, with carrier functions. Exp. Cell Res. 2001, 269, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsume, Y.; Drelich, A.J.; Smith, D.E.; Amidon, G.L. Potential Development of Tumor-Targeted Oral Anti-Cancer Prodrugs: Amino Acid and Dipeptide Monoester Prodrugs of Gemcitabine. Molecules 2017, 22, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, G.J.; Clavel, M.; Noordhuis, P.; Geyssen, G.J.; Laan, A.C.; Guastalla, J.; Edzes, H.T.; Vermorken, J.B. Clinical phase I and pharmacology study of gemcitabine (2′, 2′-difluorodeoxycytidine) administered in a two-weekly schedule. J. Chemother. 2007, 19, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/020509s077lbl.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2019).

| Amino Acid | z1 | z2 | z3 | Amino Acid Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ala (A) | −3.4535 | −0.8314 | 0.8710 | Non-polar, aliphatic |
| Arg (R) | 5.9227 | −0.7707 | 1.9428 | Positively charged |
| Asn (N) | 0.4104 | −4.0436 | −0.5900 | Polar |
| Asp (D) | 0.1502 | −2.2592 | −1.7815 | Negatively charged |
| Cys (C) | −1.8132 | 0.7809 | −0.0062 | Polar |
| Gln (Q) | 2.5410 | −2.5906 | 0.0520 | Polar |
| Glu (E) | 1.4594 | −1.6961 | −1.7366 | Negatively charged |
| Gly (G) | −3.2706 | −1.7938 | 0.5308 | Non-polar, aliphatic |
| His (H) | 1.4195 | 0.2462 | 0.6037 | Positively charged |
| Ile (I) | −1.3560 | 1.8903 | 0.6660 | Non-polar, aliphatic |
| Leu (L) | −1.5348 | 1.8836 | 0.7144 | Non-polar, aliphatic |
| Lys (K) | 2.7685 | 0.6670 | 2.5607 | Positively charged |
| Met (M) | −0.0676 | 2.3168 | 0.4266 | Non-polar, aliphatic |
| Phe (F) | −0.0247 | 2.9087 | −1.2433 | Aromatic |
| Pro (P) | −3.3838 | −0.4244 | −0.0096 | Polar |
| Ser (S) | −1.6519 | −1.4774 | 0.3484 | Polar |
| Thr (T) | −1.3364 | −0.5600 | 0.3103 | Polar |
| Trp (W) | 1.7531 | 3.3182 | −1.7406 | Aromatic |
| Tyr (Y) | 2.0819 | 1.7453 | −1.1132 | Aromatic |
| Val (V) | −2.9262 | 0.7588 | 0.6271 | Non-polar, aliphatic |
| Peptide | z1 (Size and Shape) | z2 (Polarity) | z3 (Charge) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pen | 2.3233 | 0.4802 | 0.6731 |
| Cys-Pen | 2.0865 | 0.5016 | 0.6364 |
| pVEC | 1.0880 | 0.2586 | 1.0435 |
| Cys-pVEC | 0.9411 | 0.2895 | 0.9911 |
| Sequence | #AA1 | #Arg1 | #Lys1 | #His1 | HR2 (%) | Pred.3 | Exp.4 | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pen | RQIKIWFQNRRMKWKK | 16 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 63 | + | + | [38] |
| Cys-Pen | CRQIKIWFQNRRMKWKK | 17 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 59 | + | N.D. | |
| pVEC | LLIILRRRIRKQAHAHSK | 18 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 44 | + | + | [39] |
| Cys-pVEC | CLLIILRRRIRKQAHAHSK | 19 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 42 | + | N.D. |
| Compound | Caco-2 IC50/µM [9] | MKN-28 IC50/µM [9] | HT-29 IC50/µM [9] | t1/2 (PBS, 37 °C)/h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gem | >100 | >100 | >100 | >2 [40] |
| Cys-Pen | >100 | >100 | >100 | N.D. |
| Cys-pVEC | >100 | >100 | >100 | N.D. |
| Gem-Cys-Pen | 67.13 ± 2.92 | 46.99 ± 5.91 | 47.26 ± 11.3 | 230 [9] |
| Gem-Cys-pVEC | >100 | 20.68 ± 6.81 | 45.20 ± 1.04 | 42 [9] |
| Parameter | Value | Reference/Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| Solubility | 5.01 mg/mL at pH 7.92 | ADMET PredictorTM |
| pKa | 3.54 (DrugBanka: 3.6) | ADMET PredictorTM |
| LogP | −1.32 (DrugBanka: 1.4) | ADMET PredictorTM |
| Dose | 1250 mg | FDA (Ref. ID: 3503046)b |
| Effective permeability, Peff | 0.59 cm/s × 10−4 | Caco-2 (Nuno Vale Lab) |
| Blood/plasma ratio | 1.12 | ADMET PredictorTM |
| Clearance | 168 L/h | [41] |
| Physiology | Human, fasting conditions | FDA (Ref. ID: 3503046)b |
| Body weight (Kg) | 70 | FDA (Ref. ID: 3503046)b |
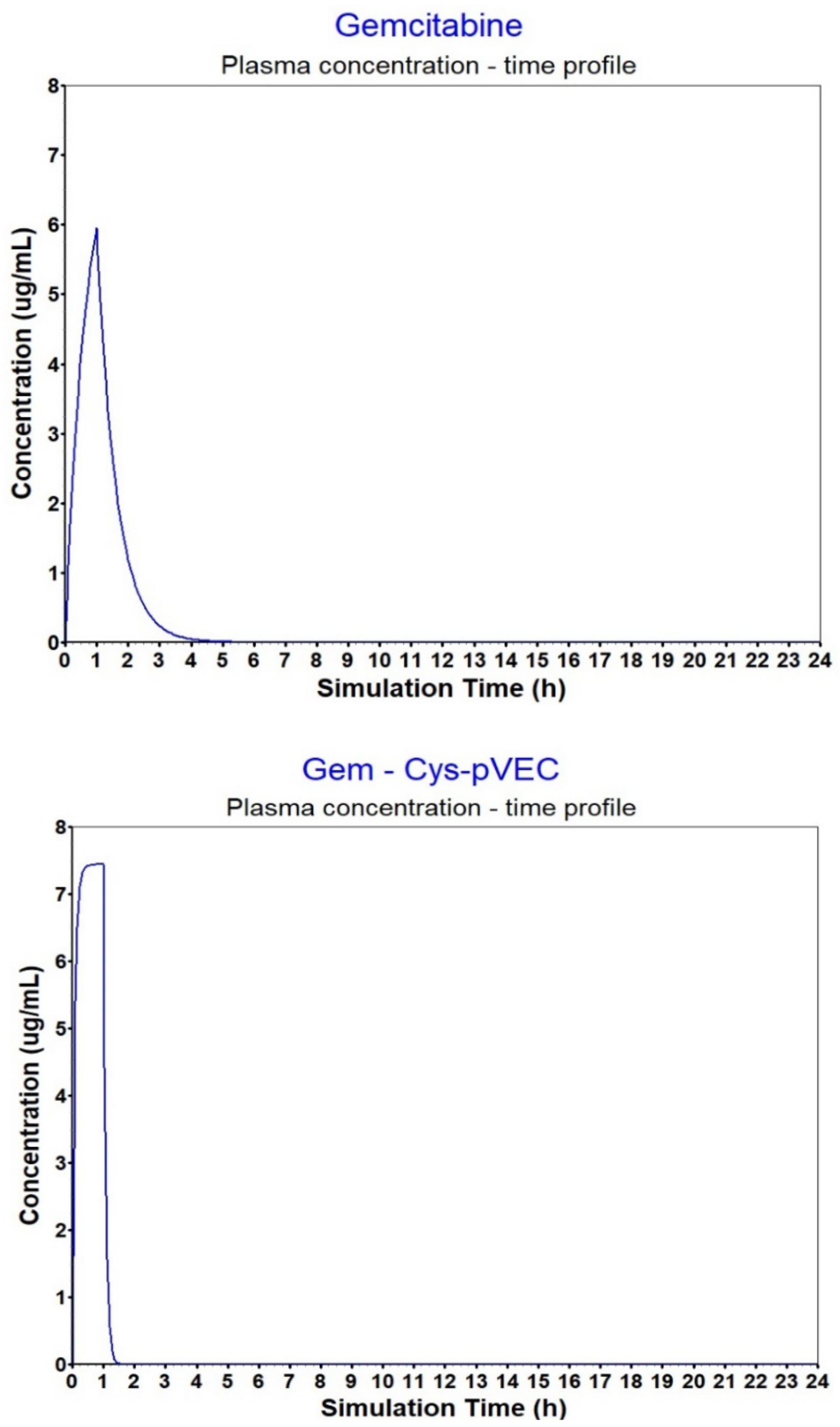
| Compound | Fup 1 (%) | B/P ratio2 | Vc 3 | F (%) 4 | Fa (%) 5 | AUC 0-inf 6 | AUC 0-t 7 | Cmax 8 | Cmax liver 9 | Sol. 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gem | 84.61 | 1.12 | 1.45 | 99.949 | 99.949 | 7.4368 | 7.4367 | 5.9505 | 5.8709 | 5.01 |
| Pen | 22.50 | 0.93 | 0.14 | 99.999 | 99.999 | 7.4404 | 7.4404 | 7.4403 | 7.4398 | 1.83 |
| Cys-Pen | 26.72 | 0.92 | 0.11 | 99.999 | 99.999 | 7.4404 | 7.4404 | 7.4401 | 7.4394 | 4.66 |
| Gem-Cys-Pen | 12.91 | 0.98 | 0.17 | 100.000 | 100.000 | 7.4405 | 7.4404 | 7.4404 | 7.4403 | 1.26 |
| pVEC | 13.35 | 1.13 | 0.16 | 100.000 | 100.000 | 7.4405 | 7.4405 | 7.4404 | 7.4403 | 28.94 |
| Cys-pVEC | 15.53 | 1.12 | 0.11 | 100.000 | 100.000 | 7.4405 | 7.4404 | 7.4404 | 7.4403 | 17.34 |
| Gem-Cys-pVEC | 42.89 | 1.20 | 0.18 | 99.998 | 99.999 | 7.4404 | 7.4403 | 7.4400 | 7.4393 | 5.39 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, A.; Lapa, R.; Vale, N. Combination of Gemcitabine with Cell-Penetrating Peptides: A Pharmacokinetic Approach Using in Silico Tools. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9110693
Ferreira A, Lapa R, Vale N. Combination of Gemcitabine with Cell-Penetrating Peptides: A Pharmacokinetic Approach Using in Silico Tools. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(11):693. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9110693
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Abigail, Rui Lapa, and Nuno Vale. 2019. "Combination of Gemcitabine with Cell-Penetrating Peptides: A Pharmacokinetic Approach Using in Silico Tools" Biomolecules 9, no. 11: 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9110693
APA StyleFerreira, A., Lapa, R., & Vale, N. (2019). Combination of Gemcitabine with Cell-Penetrating Peptides: A Pharmacokinetic Approach Using in Silico Tools. Biomolecules, 9(11), 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9110693