The ROMP: A Powerful Approach to Synthesize Novel pH-Sensitive Nanoparticles for Tumor Therapy
Abstract
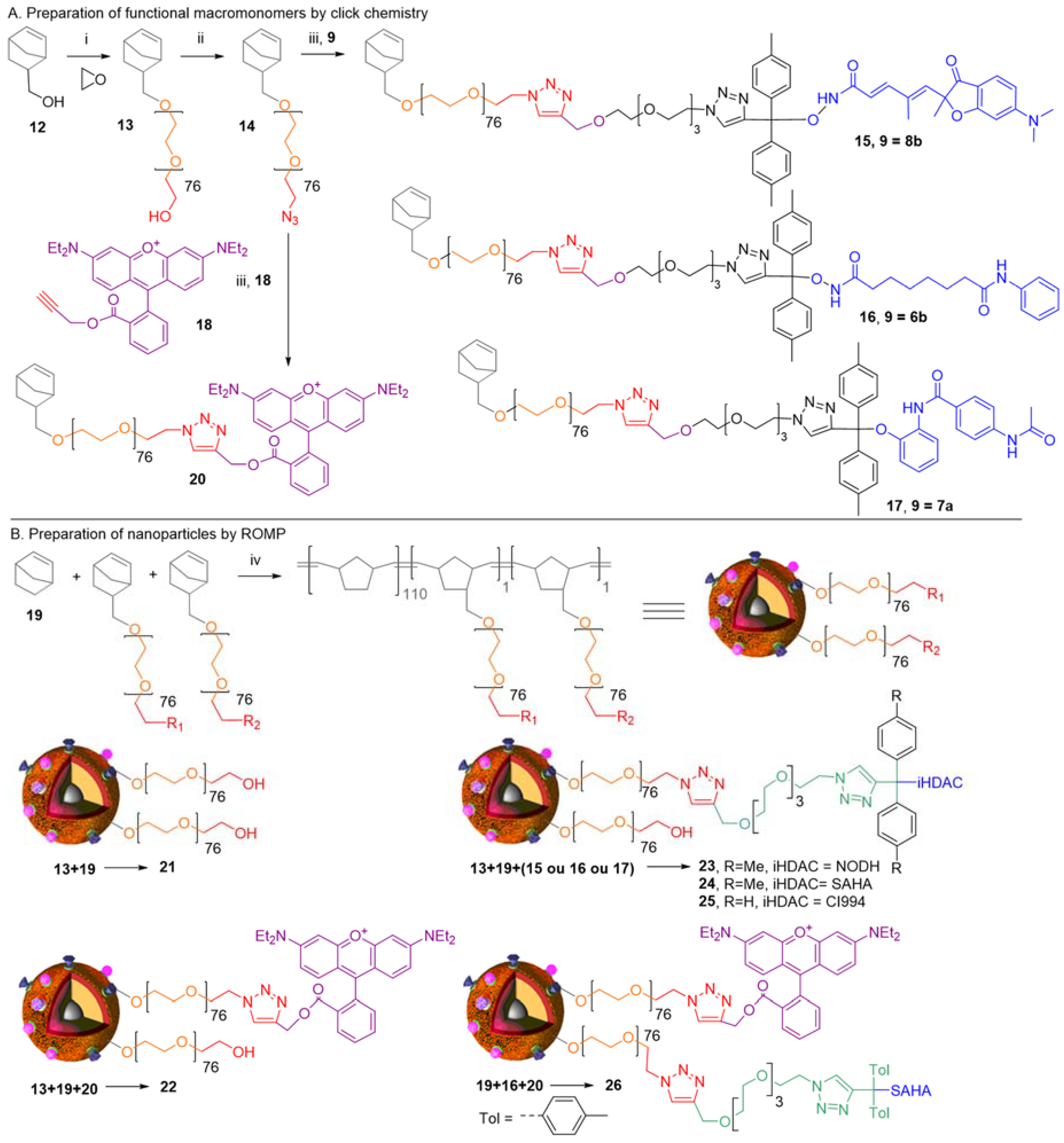
:1. Background
2. Concepts for Delivery of Epigenetic Modulators
3. Discussion
4. Biological Effects In Vitro and In Vivo
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary File 1Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Monneret, C.; Jacquesy, R.A. L’épigénétique: Enjeux scientifiques, éthiques et sociétaux. l’Actualité Chimique 2016, 407, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Arrowsmith, C.H.; Bountra, C.; Fish, P.V.; Lee, K.; Schapira, M. Epigenetic protein families: A new frontier for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvic, M.; Vu, J. Vorinostat: A new oral histone deacetylase inhibitor approved for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, C.; Rahman, F.; Piekarz, R.; Peer, C.; Frye, R.; Robey, R.W.; Gardner, E.R.; Figg, W.D.; Bates, S.E. Romidepsin: A new therapy for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and a potential therapy for solid tumors. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2010, 10, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, R. Belinostat: First Global Approval. Drugs 2014, 74, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenichel, M.P. FDA Approves New Agent for Multiple Myeloma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinet, N.; Bertrand, P. Interpreting clinical assays for histone deacetylase inhibitors. Cancer Manag. Res. 2011, 3, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H. Toward a full understanding of the EPR effect in primary and metastatic tumors as well as issues related to its heterogeneity. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 91, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, N.L.; Niimura, S.; Fujisawa, N.; Maeda, Y. Characterization of vascular permeability-increasing component isolated from solid tumors and the effect of highly polymerized dextran sulfate on its activity. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1986, 41, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y.; Hou, W.; Yang, Y.; Cai, R.; Cui, C.; Zhang, P.; Pan, X.; Li, X.; et al. Self-assembled aptamer-grafted hyperbranched polymer nanocarrier for targeted and photoresponsive drug delivery. Ang. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.; Zhao, Y.; Meshali, M.; Remsberg, C.; Borg, T.; Foda, A.; Takemoto, J.; Sayre, C.; Martinez, S.; Davies, N.; et al. Vorinostat with sustained exposure and high solubility in poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(DL-lactic acid) micelle nanocarriers: Characterization and effects on pharmacokinetics in rat serum and urine. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 3787–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.; Ramasamy, T.; Truong, D.; Shin, B.; Choi, H.; Yong, C.; Kim, J. Development of vorinostat-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles to enhance pharmacokinetics and efficacy against multidrug-resistant cancer cells. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 1978–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, R.; Ravikumar, V. Biocompatibility and biodistribution of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid loaded poly (DL-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery in cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2014, 68, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, R.; Karthik, S.; Subramanian, N.; Krishnaswami, V.; Sonnemann, J.; Ravikumar, V. Nanostructured delivery system for Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid against lung cancer cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 51, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.; Min, Y.; Palm, R.; Fiordalisi, J.; Wagner, K.; Hyder, N.; Cox, A.; Caster, J.; Tian, X.; Wang, A. Nanoparticle formulations of histone deacetylase inhibitors for effective chemoradiotherapy in solid tumors. Biomaterials 2015, 51, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.; Chu, D.; Truong, D.; Tak, J.; Jeong, J.; Hoang, V.; Yong, C.; Kim, J. Development of lipid nanoparticles for a histone deacetylases inhibitor as a promising anticancer therapeutic. Drug Deliv. 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foglietta, F.; Serpe, L.; Canaparo, R.; Vivenza, N.; Riccio, G.; Imbalzano, E.; Gasco, P.; Zara, G. Modulation of butyrate anticancer activity by solid lipid nanoparticle delivery: An in vitro investigation on human breast cancer and leukemia cell lines. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 17, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Choi, J.; Ramasamy, T.; Truong, D.; Nguyen, C.; Choi, H.; Yong, C.; Kim, J. Hyaluronic acid-coated solid lipid nanoparticles for targeted delivery of vorinostat to CD44 overexpressing cancer cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 114, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Ahmad, S.; Vu, M.; Kuma, K.; Cheng, Y.; Lam, K. Disulfide cross-linked micelles of novel HDAC inhibitor thailandepsin A for the treatment of breast cancer. Biomaterials 2015, 67, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Hoimes, C.; Kaimakliotis, H.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, K.; Liu, J.; Wheeler, M.; Kelly, W.; Tew, G.; Saltzman, W.; et al. Nanoparticles for urothelium penetration and delivery of the histone deacetylase inhibitor belinostat for treatment of bladder cancer. Nanomedicine 2013, 9, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, T.; Kim, D.; Jeong, Y.; Kang, D. Antitumor activity of vorinostat-incorporated nanoparticles against human cholangiocarcinoma cells. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran Rompicharla, S.; Trivedi, P.; Kumari, P.; Ghanta, P.; Ghosh, B.; Biswas, S. Polymeric micelles of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid to enhance the anticancer potential in vitro and in vivo. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Wang, T.; Wu, J.; Yin, X.; Fang, H.; Zhang, N. A facile route to form self-carried redox-responsive vorinostat nanodrug for effective solid tumor therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6003–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delatouche, R.; Bertrand, P.; Collette, F.; Héroguez, V.; Gueugnon, F.; Blanquart, C.; Grégoire, M. Nanovecteurs ou particules polymères et leur utilisation comme médicament et/ou agent de diagnostic. French Patent WO2013001244A1, 3 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Delatouche, R.; Denis, I.; Grinda, M.; El Bahhaj, F.; Baucher, E.; Collette, F.; Héroguez, V.; Grégoire, M.; Blanquart, C.; Bertrand, P. Design of pH responsive clickable prodrugs applied to histone deacetylases inhibitors: A new strategy for anticancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondon, M.; Delatouche, R.; Bachmann, C.; Frapper, G.; Len, C.; Bertrand, P. Triazolyl Derivatives for Acidic Release of Alcohols. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 11, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bahhaj, F.; Denis, I.; Pichavant, L.; Delatouche, R.; Collette, F.; Linot, C.; Pouliquen, D.; Grégoire, M.; Héroguez, V.; Blanquart, C.; et al. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Delivery using Nanoparticles with Intrinsic Passive Tumor Targeting Properties for Tumor Therapy. Theranostic 2016, 6, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueugnon, F.; Denis, I.; Pouliquen, D.; Collette, F.; Delatouche, R.; Héroguez, V.; Gregoire, M.; Bertrand, P.; Blanquart, C. Nanoparticles produced by ring-opening metathesis polymerization using norbornenyl-poly(ethylene oxide) as a ligand-free generic platform for highly selective in vivo tumor targeting. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 239–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collette, F.; Delatouche, R.; Blanquart, C.; Gueugnon, F.; Grégoire, M.; Bertrand, P.; Héroguez, V. An easy and effective method to produce functionalized particles for cellular uptake. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanquart, C.; Francois, M.; Charrier, C.; Bertrand, P.; Gregoire, M. Pharmacological characterization of histone deacetylase inhibitor and tumor cell-growth inhibition properties of new benzofuranone compounds. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets. 2011, 11, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, I.; El Bahhaj, F.; Collette, F.; Delatouche, R.; Gueugnon, F.; Pouliquen, D.; Pichavant, L.; Héroguez, V.; Grégoire, M.; Bertrand, P.; et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor-polymer conjugate nanoparticles for acid-responsive drug delivery. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 95, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, I.; El Bahhaj, F.; Collette, F.; Delatouche, R.; Gueugnon, F.; Pouliquen, D.; Pichavant, L.; Héroguez, V.; Gregoire, M.; Bertrand, P.; et al. Vorinostat-polymer conjugate nanoparticles for Acid-responsive delivery and passive tumor targeting. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 4534–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueugnon, F.; Cartron, P.; Charrier, C.; Bertrand, P.; Fonteneau, J.; Gregoire, M.; Blanquart, C. New histone deacetylase inhibitors improve cisplatin antitumor properties against thoracic cancer cells. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 4504–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq, S.; Gueugnon, F.; Boutin, B.; Guillot, F.; Blanquart, C.; Rogel, A.; Padieu, M.; Pouliquen, D.; Fonteneau, J.; Grégoire, M. A 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine/valproate combination induces cytotoxic T-cell response against mesothelioma. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charrier, C.; Clarhaut, J.; Gesson, J.; Estiu, G.; Wiest, O.; Roche, J.; Bertrand, P. Synthesis and modeling of new benzofuranone histone deacetylase inhibitors that stimulate tumor suppressor gene expression. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 3112–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, R.; Nguyen, H.; Jeong, J.; Shin, B.; Ku, S.; Choi, H.; Yong, C.; Kim, J. Synergistic anticancer activity of combined histone deacetylase and proteasomal inhibitor-loaded zein nanoparticles in metastatic prostate cancers. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Wasim, L.; Chopra, M.; Chhikara, A. Co-delivery of Vorinostat and Etoposide Via Disulfide Cross-Linked Biodegradable Polymeric Nanogels: Synthesis, Characterization, Biodegradation, and Anticancer Activity. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruttala, H.; Ramasamy, T.; Poudal, B.; Choi, Y.; Choi, J.; Kim, J.; Kwang, K.; Choi, H.; Soon, Y.; Oh Kim, J. Molecularly targeted co-delivery of a histone deacetylase inhibitor and paclitaxel by lipid-protein hybrid nanoparticles for synergistic combinational chemotherapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 14925–14940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhu, X.; Huang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, D. Supramolecular cisplatin-vorinostat nanodrug for overcoming drug resistance in cancer synergistic therapy. J. Control. Release 2017, 266, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Compound\pH | 3.0 | 4.3 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 7.3 |
| 6a | n.d. | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable |
| 6b | n.d. | 20 h | n.d. | 80 h (3.3 days) | 4 days |
| 6c | n.d. | 30 min | 80 min | 108 min | 34 min |
| 7a | n.d. | 30 min | 400 min | 48 h | 3.6 days |
| 7b | n.d. | <1 min | 12 min | 10 min | 2 h 30 |
| 7c | n.d. | <1 min | <5 min | <5 min | 2 h 30 |
| 8a * | n.d. | stable | stable | n.d. | Stable |
| 8b | 3 h | 13 h | 21 h | n.d | 3.2 days |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertrand, P.; Blanquart, C.; Héroguez, V. The ROMP: A Powerful Approach to Synthesize Novel pH-Sensitive Nanoparticles for Tumor Therapy. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9020060
Bertrand P, Blanquart C, Héroguez V. The ROMP: A Powerful Approach to Synthesize Novel pH-Sensitive Nanoparticles for Tumor Therapy. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(2):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9020060
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertrand, Philippe, Christophe Blanquart, and Valérie Héroguez. 2019. "The ROMP: A Powerful Approach to Synthesize Novel pH-Sensitive Nanoparticles for Tumor Therapy" Biomolecules 9, no. 2: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9020060
APA StyleBertrand, P., Blanquart, C., & Héroguez, V. (2019). The ROMP: A Powerful Approach to Synthesize Novel pH-Sensitive Nanoparticles for Tumor Therapy. Biomolecules, 9(2), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9020060





