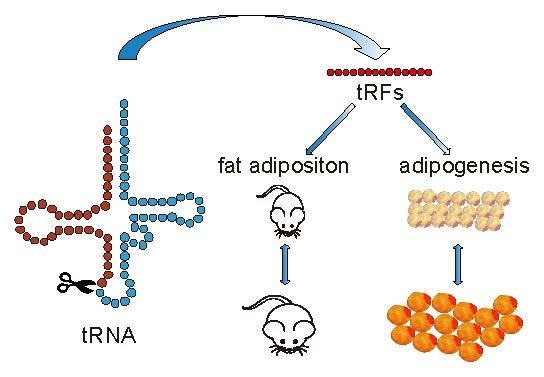
tRNA-Derived Small Non-Coding RNAs as Novel Epigenetic Molecules Regulating Adipogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
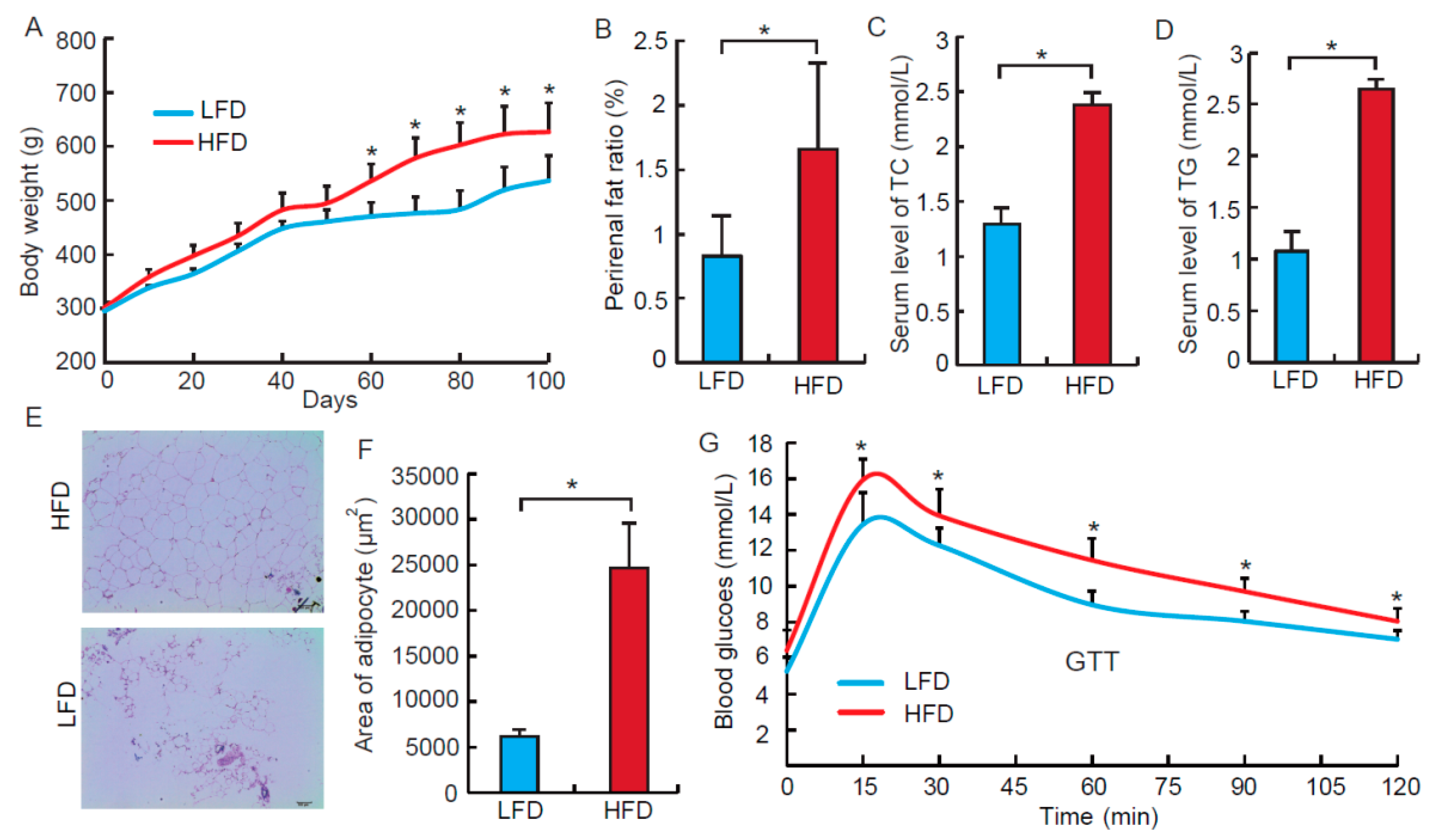
3.1. High Fat Diet Induces Obesity Phenotypes in the Rat Model
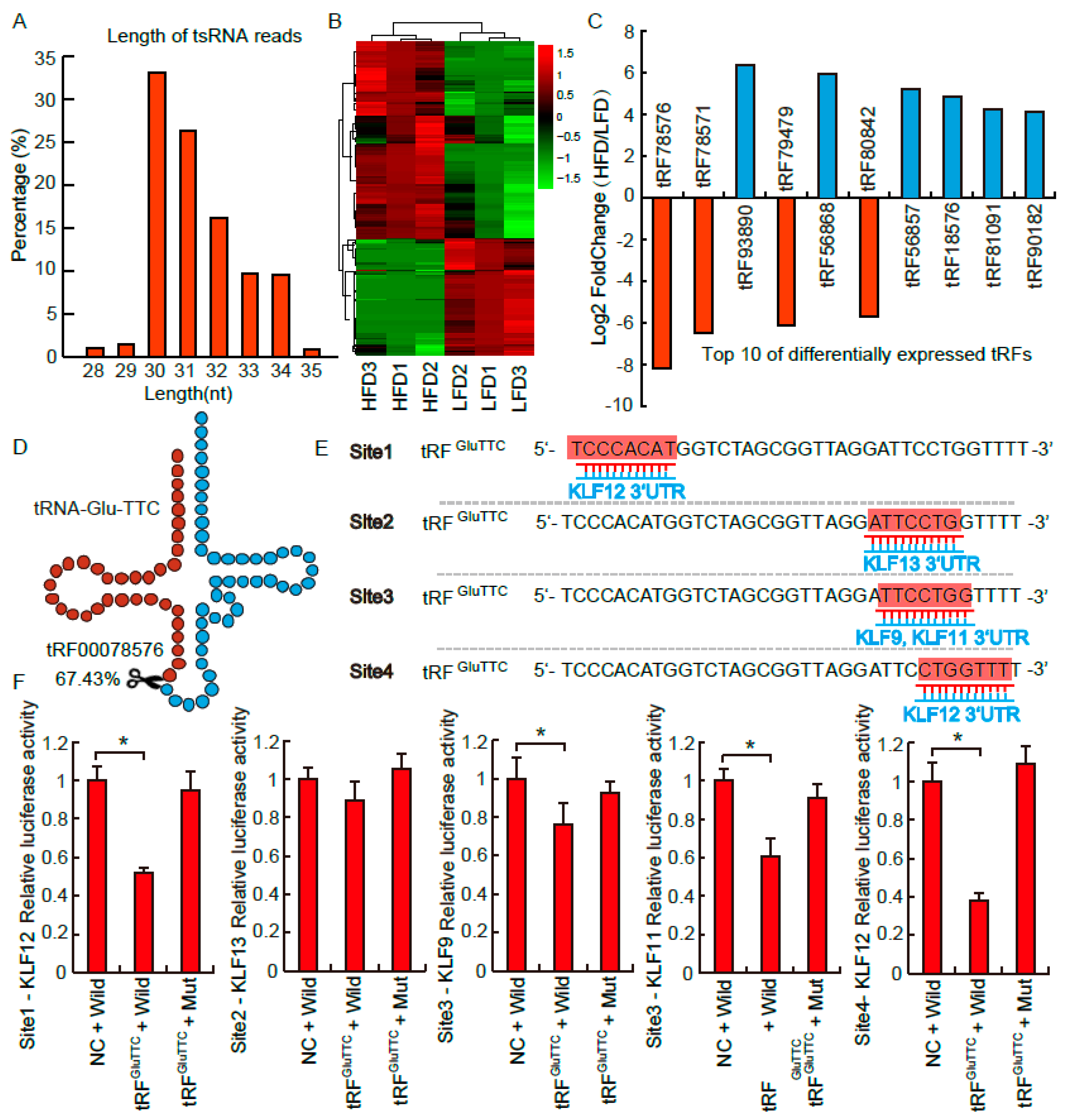
3.2. tRFs Profile Influenced by the Stress of Obesity
3.3. tRFGluTTC Directly Targets KLF Family
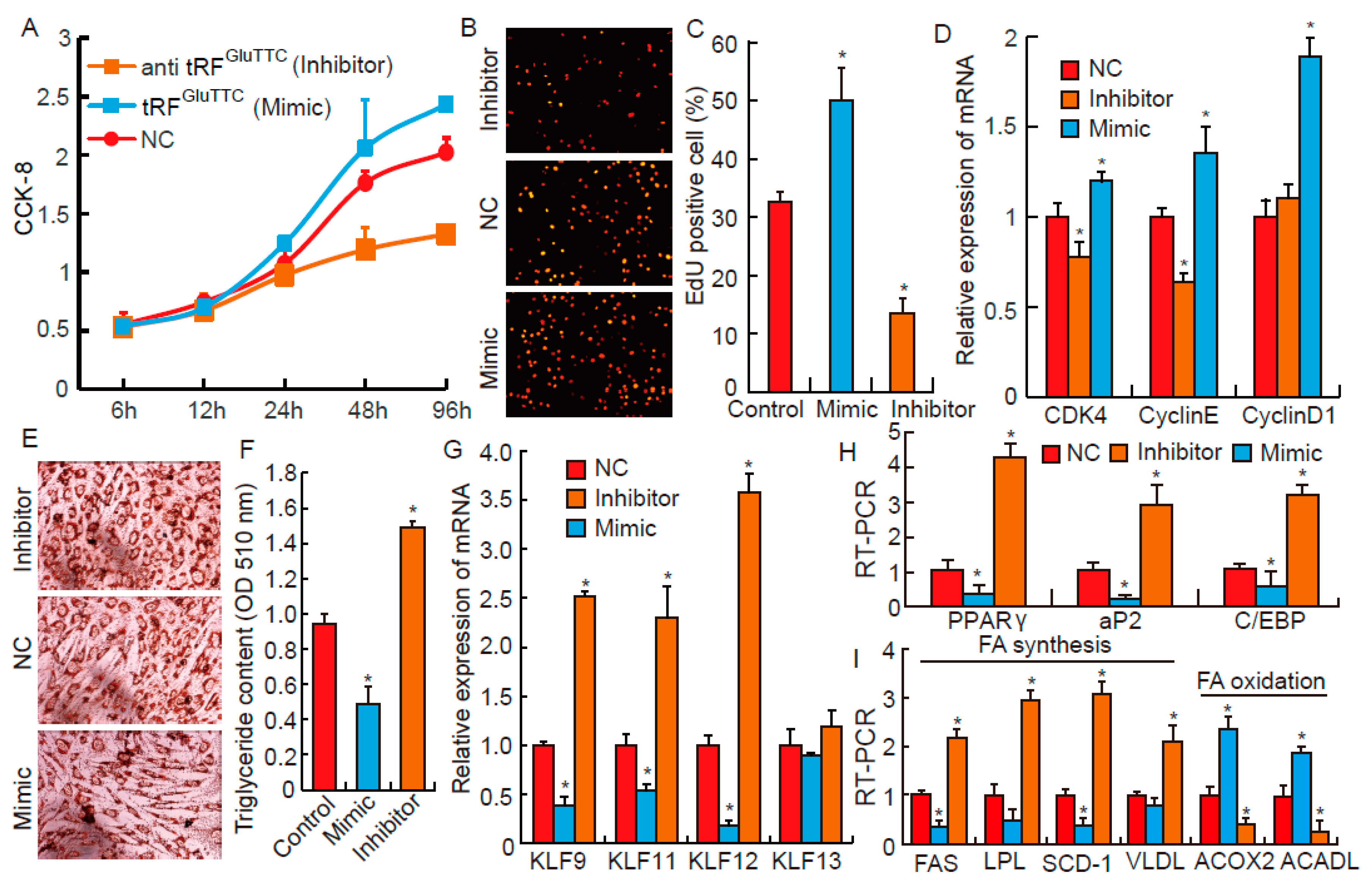
3.4. tRFGluTTC Regulates Proliferation and Differentiation of Preadipocytes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Apovian, C.M. The obesity epidemic-Understanding the disease and the treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaben, A.L.; Scherer, P.E. Adipogenesis and metabolic health. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2019, 20, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, R.; Fleetwood, J.; Eaton, S.; Crossley, M.; Bao, S. Krüppel-like transcription factors: A functional family. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2008, 40, 1996–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, L.; Bai, L.; Shuai, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, L. miR-144-3p Promotes Adipogenesis Through Releasing C/EBPα From Klf3 and CtBP2. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Du, M.; Jiang, Z.; Hausman, G.J.; Zhang, L.; Dodson, M.V. Long noncoding RNAs in regulating adipogenesis: New RNAs shed lights on obesity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 2079–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Gan, M.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, L. MicroRNA-200b regulates preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation by targeting KLF4. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, B.; Yu, J.; Zheng, P.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Luo, J.; Mao, X.; Yan, H.; He, J. Butyrate promotes slow-twitch myofiber formation and mitochondrial biogenesis in finishing pigs via inducing specific microRNAs and PGC-1α expression. J. Anim. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selitsky, S.R.; Baran-Gale, J.; Honda, M.; Yamane, D.; Masaki, T.; Fannin, E.E.; Guerra, B.; Shirasaki, T.; Shimakami, T.; Kaneko, S. Small tRNA-derived RNAs are increased and more abundant than microRNAs in chronic hepatitis B and C. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Gan, M.; Tan, Z.; Jiang, D.; Jiang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, L. A Novel Class of tRNA-Derived Small Non-Coding RNAs Respond to Myocardial Hypertrophy and Contribute to Intergenerational Inheritance. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megumi, S.; Yohei, K. tRNA-derived short non-coding RNA as interacting partners of argonaute proteins. Gen. Regul. Syst. Biol. 2015, 9, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Chen, Q. tsRNAs: The Swiss Army Knife for Translational Regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Shen, L.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Ma, J.; Jiang, A.; Tang, G. Betaine supplementation enhances lipid metabolism and improves insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet. Nutrients 2018, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liao, S.; Li, W.; Lei, L.; Han, C.; Ning, L.; Cao, Y. A novel class of tRNA-derived small RNAs extremely enriched in mature mouse sperm. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 1609–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjana, S.; Gene, F.; Barbara, T.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Bruna, B.; Karin, A.; Mary, S.; Vera, R.; Sara, T.; Gina, B. Prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance among children and adolescents with marked obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 802–810. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, U.; Conine, C.C.; Shea, J.M.; Boskovic, A.; Derr, A.G.; Bing, X.Y.; Belleannee, C.; Kucukural, A.; Serra, R.W.; Sun, F. Biogenesis and function of tRNA fragments during sperm maturation and fertilization in mammals. Science 2015, 351, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; He, F.; Luo, J.; Dou, S.; Wang, Y.; Guo, A.; Lu, J. Drosophila tsRNAs preferentially suppress general translation machinery via antisense pairing and participate in cellular starvation response. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 5250–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.G.; Reina, O.; Attolini, C.S.-O.; de Pouplana, L.R. Differential expression of human tRNA genes drives the abundance of tRNA-derived fragments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8451–8456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wei, H.; Song, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, J.; Jiang, S. KLF13 promotes porcine adipocyte differentiation through PPARγ activation. Cell Biosci. 2015, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, M.-Y.; Choi, H.; Lee, H.; Kim, J. Krüppel-like factor KLF8 plays a critical role in adipocyte differentiation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Fujimori, K. Activation of early phase of adipogenesis through Krüppel-like factor KLF9-mediated, enhanced expression of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β in 3T3-L1 cells. Gene 2014, 534, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.; Yao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liao, K.; Wu, J. Krüppel-like factor KLF9 regulates PPARγ transactivation at the middle stage of adipogenesis. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J. Expression analysis of transfer RNA-derived fragments in the blood of patients with moyamoya disease: A preliminary study. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 3564–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Li, Y.; Chu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, X.; Fu, Z.; Li, W.; Huang, X.; Yin, Y. Identification of tRNA-derived small noncoding RNA s as potential biomarkers for prediction of recurrence in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 5130–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnitzky, D.; Gossen, M.; Bujard, H.; Reed, S. Acceleration of the G1/S phase transition by expression of cyclins D1 and E with an inducible system. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Kotoshiba, S.; Berthet, C.; Hilton, M.B.; Kaldis, P. Rb/Cdk2/Cdk4 triple mutant mice elicit an alternative mechanism for regulation of the G1/S transition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, S.R. Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, L.; Tan, Z.; Gan, M.; Li, Q.; Chen, L.; Niu, L.; Jiang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; et al. tRNA-Derived Small Non-Coding RNAs as Novel Epigenetic Molecules Regulating Adipogenesis. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9070274
Shen L, Tan Z, Gan M, Li Q, Chen L, Niu L, Jiang D, Zhao Y, Wang J, Li X, et al. tRNA-Derived Small Non-Coding RNAs as Novel Epigenetic Molecules Regulating Adipogenesis. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(7):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9070274
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Linyuan, Zhendong Tan, Mailin Gan, Qiang Li, Lei Chen, Lili Niu, Dongmei Jiang, Ye Zhao, Jinyong Wang, Xuewei Li, and et al. 2019. "tRNA-Derived Small Non-Coding RNAs as Novel Epigenetic Molecules Regulating Adipogenesis" Biomolecules 9, no. 7: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9070274
APA StyleShen, L., Tan, Z., Gan, M., Li, Q., Chen, L., Niu, L., Jiang, D., Zhao, Y., Wang, J., Li, X., Zhang, S., & Zhu, L. (2019). tRNA-Derived Small Non-Coding RNAs as Novel Epigenetic Molecules Regulating Adipogenesis. Biomolecules, 9(7), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9070274