CoCUN, a Novel Ubiquitin Binding Domain Identified in N4BP1
Abstract
1. Introduction
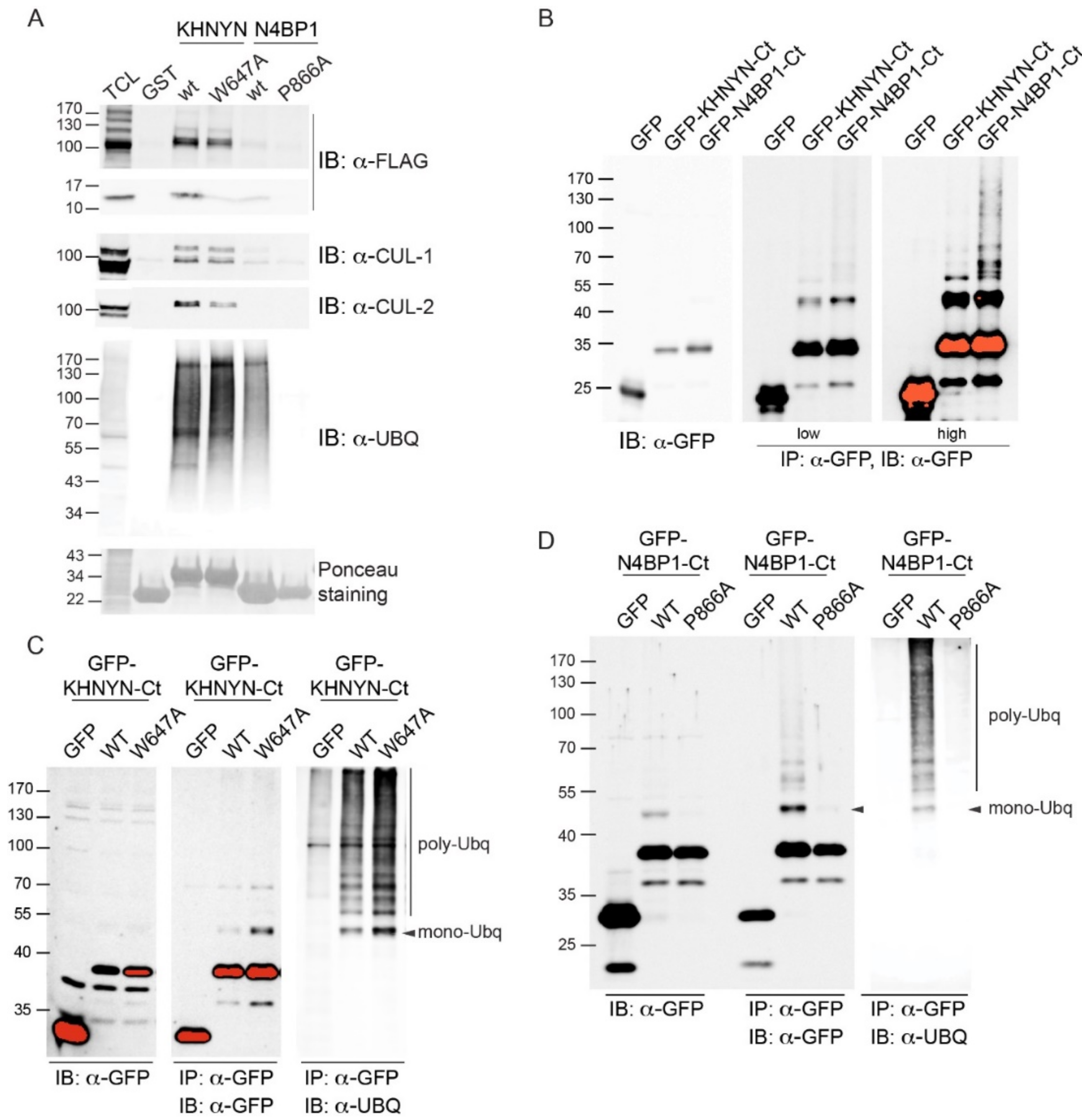
2. Results
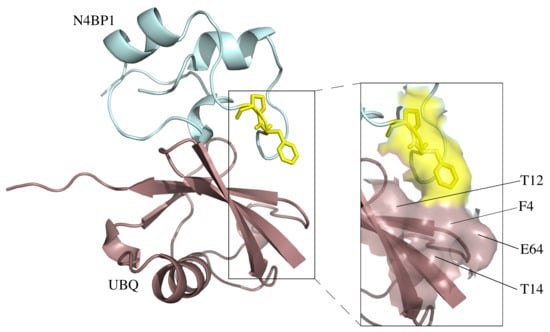
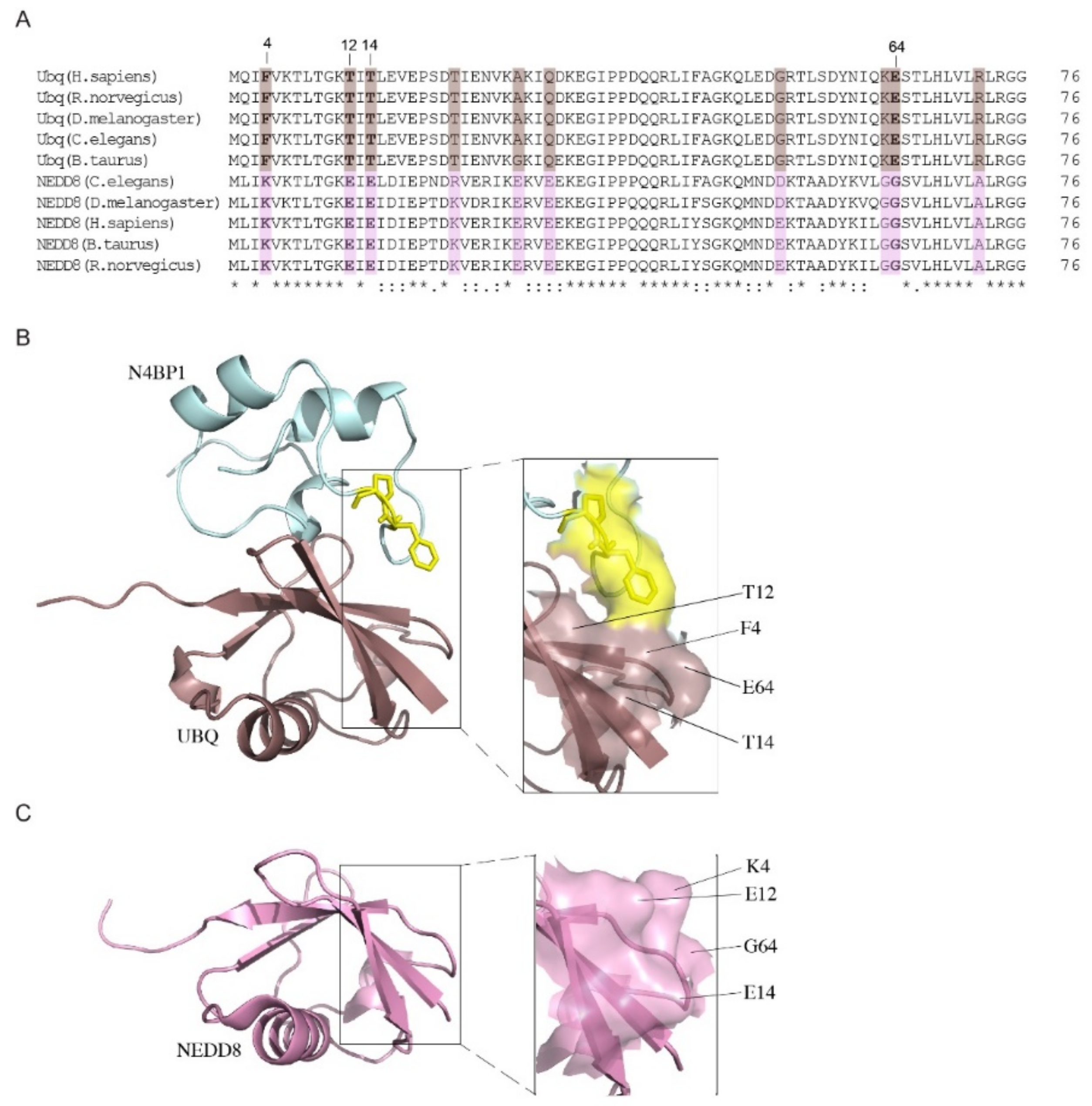
2.1. A Novel Ubiquitin-Binding Domain at the C-Terminal End of Human N4BP1
2.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Study of N4BP1 Ubiquitin Binding Domain
2.3. Conformational Studies of the CoCUN Domain in Complex with Either Ubiquitin or NEDD8 Performed by Circular Dichroism
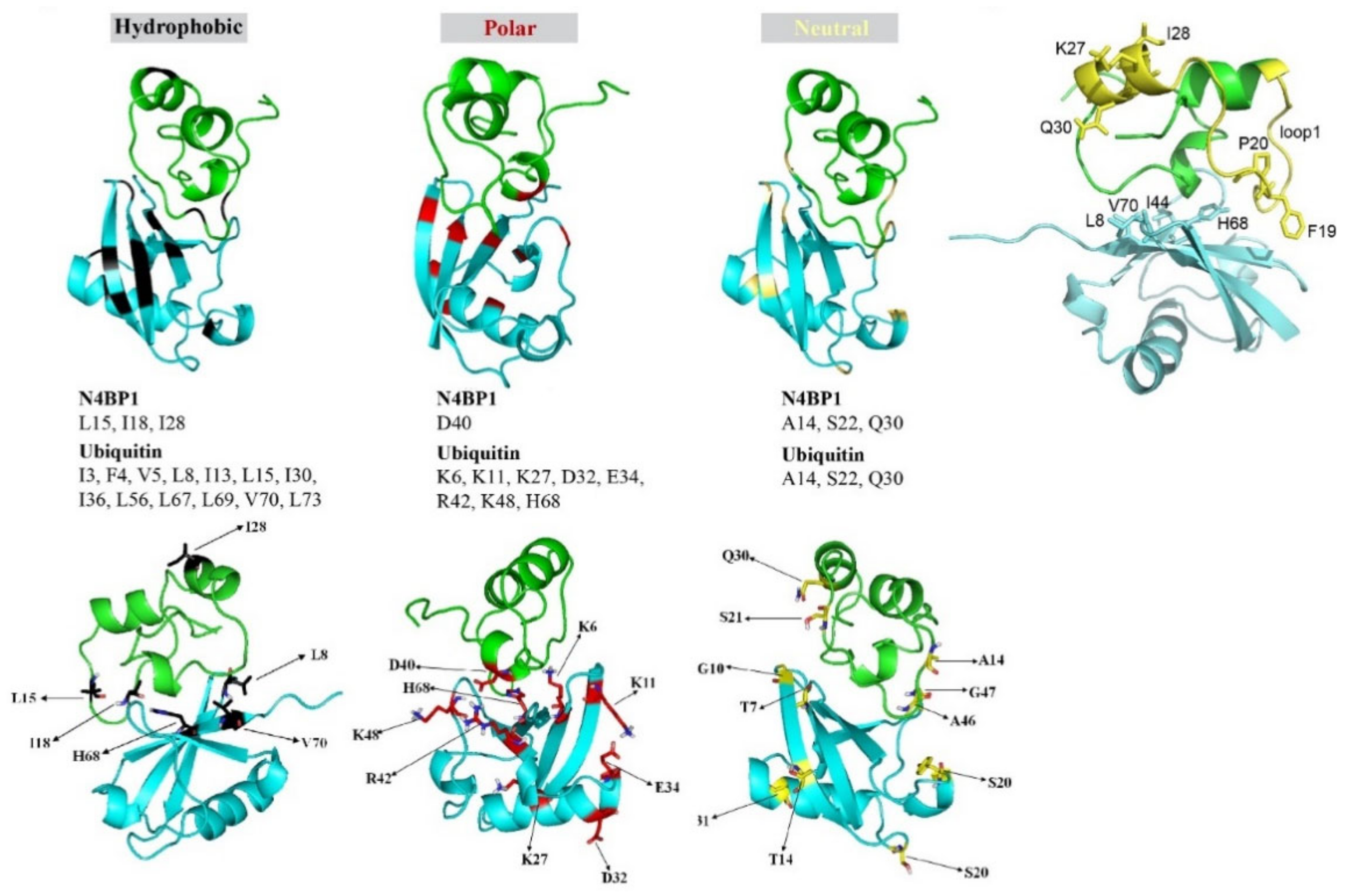
2.4. 15N The HSQC NMR Investigation of the CoCUN/Ubiquitin Complex by Chemical Shift Perturbation
2.5. The CoCUN Domain Binds Monoubiquitin, Albeit with Low Affinity
2.6. Differences and Similarities among CoCUN, CUE, and CUBAN
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swatek, K.N.; Komander, D. Ubiquitin modifications. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 399–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, J.H.; Lee, S.; Prag, G. Ubiquitin-binding domains. Biochem. J. 2006, 399, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husnjak, K.; Dikic, I. Ubiquitin-Binding Proteins: Decoders of Ubiquitin-Mediated Cellular Functions. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 291–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokratous, K.; Hadjisavvas, A.; Diamandis, E.P.; Kyriacou, K. The role of ubiquitin-binding domains in human pathophysiology. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2014, 51, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitby, F.G. Crystal Structure of the Human Ubiquitin-like Protein NEDD8 and Interactions with Ubiquitin Pathway Enzymes. J. Boil. Chem. 1998, 273, 34983–34991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murillas, R.; Simms, K.S.; Hatakeyama, S.; Weissman, A.M.; Kuehn, M.R. Identification of developmentally expressed proteins that functionally interact with Nedd4 ubiquitin ligase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 2897–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberst, A.; Malatesta, M.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Rossi, M.; Salomoni, P.; Murillas, R.; Sharma, P.; Kuehn, M.R.; Oren, M.; Croce, C.M.; et al. The Nedd4-binding partner 1 (N4BP1) protein is an inhibitor of the E3 ligase Itch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2007, 104, 11280–11285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spel, L.; Nieuwenhuis, J.; Haarsma, R.; Stickel, E.; Bleijerveld, O.B.; Altelaar, M.; Boelens, J.J.; Brummelkamp, T.R.; Nierkens, S.; Boes, M. Nedd4 Binding Protein 1 (N4BP1) and TNFAIP3 Interacting Protein 1 (TNIP1) control MHC-1 display in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6621–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenner, B.J.; Scannell, M.; Prehn, J.H. Identification of polyubiquitin binding proteins involved in NF-κB signaling using protein arrays. BBA-Proteins Proteom. 2009, 1794, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnoli, L.; Mandaliti, W.; Nepravishta, R.; Valentini, E.; Mattioni, A.; Procopio, R.; Iannuccelli, M.; Polo, S.; Paci, M.; Cesareni, G.; et al. Selectivity of the CUBAN domain in the recognition of ubiquitin and NEDD8. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 653–677. [Google Scholar]
- Santonico, E.; Nepravishta, R.; Mandaliti, W.; Castagnoli, L.; Cesareni, G.; Paci, M. CUBAN, a Case Study of Selective Binding: Structural Details of the Discrimination between Ubiquitin and NEDD8. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicke, L.; Schubert, H.L.; Hill, C.P. Ubiquitin-binding domains. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Boil. 2005, 6, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, S.C.; Prag, G.; Francis, S.A.; Sutanto, M.A.; Hurley, J.H.; Hicke, L. A ubiquitin-binding motif required for intramolecular monoubiquitylation, the CUE domain. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prag, G.; Misra, S.; Jones, E.A.; Ghirlando, R.; Davies, B.A.; Horazdovsky, B.F.; Hurley, J.H. Mechanism of Ubiquitin Recognition by the CUE Domain of Vps9p. Cell 2003, 113, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.S.; Daniels, C.M.; Francis, S.A.; Shih, S.C.; Salerno, W.J.; Hicke, L.; Radhakrishnan, I. Solution Structure of a CUE-Ubiquitin Complex Reveals a Conserved Mode of Ubiquitin Binding. Cell 2003, 113, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Sykes, B.D. The 13C chemical-shift index: A simple method for the identification of protein secondary structure using 13C chemical-shift data. J. Biomol. NMR 1994, 4, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brünger, A.T. Assessment of phase accuracy by cross validation: the free R value. Methods and applications. Acta Crystallogr. 1993, D49, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omichinski, J.G.; Pedone, P.V. The solution structure of a specific GAGA factor-DNA complex reveals a modular binding mode. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1997, 4, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis-Jeune, C.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A.; Perez-Iratxeta, C.; Louis-Jeune, C.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A.; Perez-Iratxeta, C. Prediction of protein secondary structure from circular dichroism using theoretically derived spectra. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2012, 80, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobley, A.; Whitmore, L.; Wallace, B.A. DICHROWEB: An interactive website for the analysis of protein secondary structure from circular dichroism spectra. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 211–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreerama, N.; Woody, R.W. Estimation of Protein Secondary Structure from Circular Dichroism Spectra: Comparison of CONTIN, SELCON, and CDSSTR Methods with an Expanded Reference Set. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 287, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, V.; Serrano, L. Local versus nonlocal interactions in protein folding and stability–An experimentalist’s point of view. Fold. Des. 1996, 1, R71–R77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, N.J. Circular dichroism analysis for protein-protein interactions. Methods Mol. Biol. 2004, 261, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodero, V.I.; Quirolo, Z.B.; Sequeira, M.A. Biomolecular studies by circular dichroism. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011, 16, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamburro, A.M.; Lorusso, M.; Ibris, N.; Pepe, A.; Bochicchio, B. Investigating by circular dichroism some amyloidogenic elastin-derived polypeptides. Chirality 2010, 22, E56–E66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, S.J.; Van Dijk, M.; Bonvin, A.M. The HADDOCK web server for data-driven biomolecular docking. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polo, S.; Sigismund, S.; Faretta, M.; Guidi, M.; Capua, M.R.; Bossi, G.; Chen, H.; De Camilli, P.; Di Fiore, P.P. A single motif responsible for ubiquitin recognition and monoubiquitination in endocytic proteins. Nature 2002, 416, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haglund, K.; Stenmark, H. Working out coupled monoubiquitination. Nature 2006, 8, 1218–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.C.; Chen, J.H.; Chang, S.C. The molecular determinants for distinguishing between ubiquitin and NEDD8 by USP. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Murillas, R.; Zhang, H.; Kuehn, M.R. N4BP1 is a newly identified nucleolar protein that undergoes SUMO-regulated polyubiquitylation and proteasomal turnover at promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaman, V.; Aravind, L. The NYN Domains: Novel Predicted RNAses with a PIN Domain-Like Fold. RNA Boil. 2006, 3, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santonico, E.; Panni, S.; Falconi, M.; Castagnoli, L.; Cesareni, G. Binding to DPF-motif by the POB1 EH domain is responsible for POB1-Eps15 interaction. BMC Biochem. 2007, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, D.J.; Gittis, A.G.; Mullen, G.P.; Abeygunawardana, C.; Lattman, E.E.; Mildvan, A.S. NMR docking of a substrate into the X-ray structure of staphylococcal nuclease. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 1992, 13, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bax, A.; Davis, D.G. MLEV-17-based two-dimensional homonuclear magnetization transfer spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. (1969) 1985, 65, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, D.; Wüthrich, K. Application of phase sensitive two-dimensional correlated spectroscopy (COSY) for measurements of 1H-1H spin-spin coupling constants in proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1983, 113, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunschweiler, L.; Ernst, R.R. Coherence transfer by isotopic mixing: Application to proton correlation spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 1983, 53, 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich, K. NMR of Proteins and Nucleic Acids; A Wiley-Intersci. Publication: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1986; ISBN 978-0-471-82893-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bodenhausen, G.; Ruben, D.J. Natural abundance nitrogen-15 NMR by enhanced heteronuclear spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1980, 69, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.D.; Meng, X.; Donovan, K.J.; Shaka, A. SOGGY: Solvent-optimized double gradient spectroscopy for water suppression. A comparison with some existing techniques. J. Magn. Reson. 2007, 184, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.A.; Blevins, R.A. NMR View: A computer program for the visualization and analysis of NMR data. J. Biomol. NMR 1994, 4, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuiderweg, E.R.P. Mapping Protein−Protein Interactions in Solution by NMR Spectroscopy. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, M.P. Using chemical shift perturbation to characterise ligand binding. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2013, 73, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


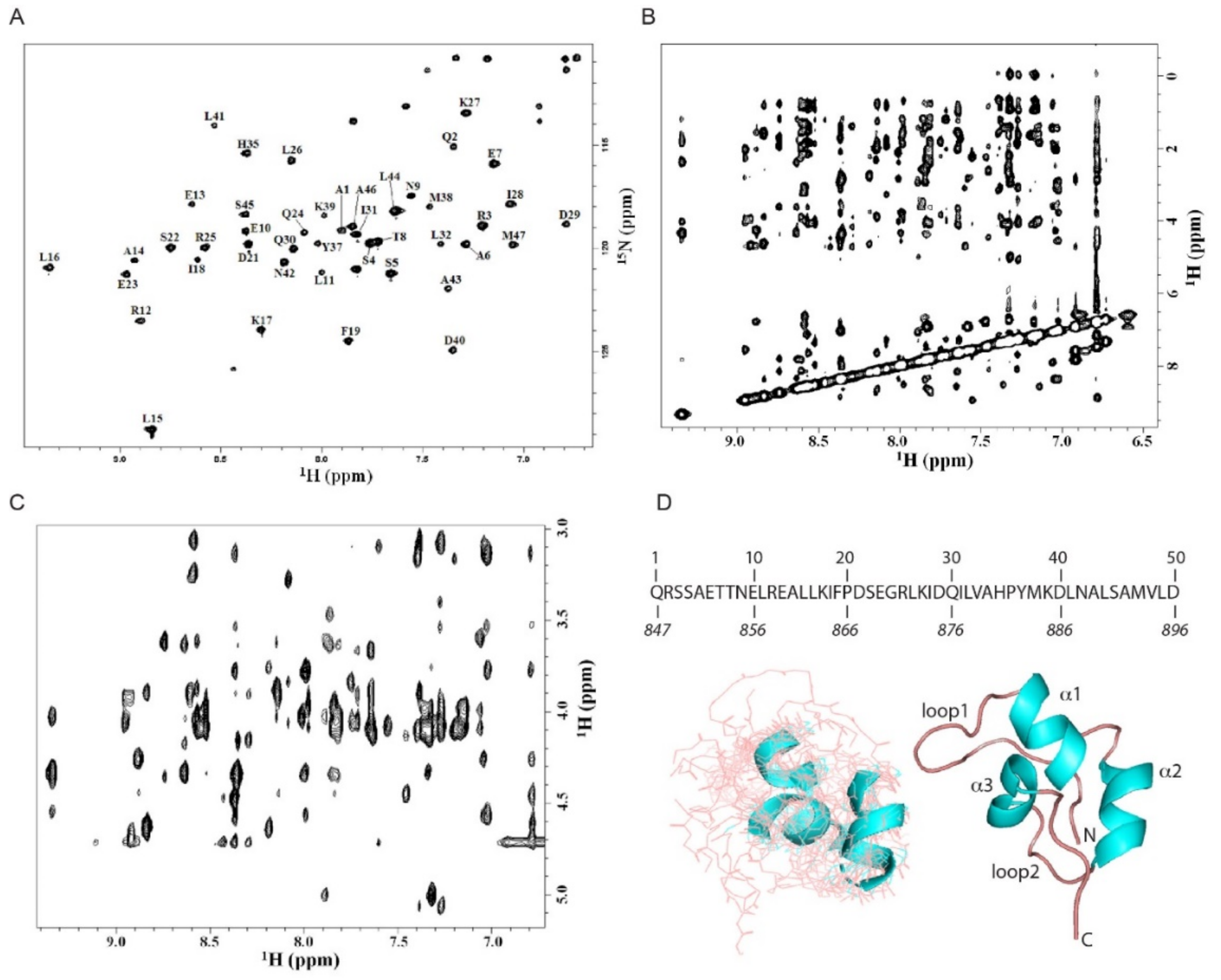




| N | HN | Hα | Hβ1,2 | Hγ | Hδ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 119.11 | 7.90 | ||||
| Q2 | 115.05 | 7.34 | 4.35 | 1.96 | ||
| R3 | 118.85 | 7.20 | 4.00 | 1.68 | ||
| S4 | 119.71 | 7.76 | 4.70 | 3.85 | ||
| S5 | 121.19 | 7.66 | 4.15 | 3.95 | ||
| A6 | 119.78 | 7.29 | 4.06 | 1.48 | ||
| E7 | 115.90 | 7.15 | 4.00 | _ | ||
| T8 | 119.64 | 7.72 | 4.07 | 4.05 | 1.20 | |
| N9 | 117.40 | 7.56 | 4.10 | 2.70 | ||
| E10 | 119.06 | 8.43 | 3.97 | 1.88 | ||
| L11 | 121.01 | 8.00 | 4.37 | 1.70 | ||
| R12 | 123.40 | 8.91 | 4.60 | 1.61 | ||
| E13 | 117.83 | 8.64 | 3.80 | 1.90 | ||
| A14 | 121.51 | 8.96 | 4.60 | _ | ||
| L15 | 128.80 | 8.82 | 4.60 | 2.04 | ||
| L16 | 120.89 | 9.30 | 4.60 | _ | ||
| K17 | 123.89 | 8.31 | 4.24 | 1.59 | ||
| I18 | 120.30 | 8.60 | 4.13 | _ | 1.00 | |
| F19 | 124.40 | 7.80 | 4.38 | 3.06 | ||
| D21 | 119.80 | 8.43 | 4.38 | 2.74 | ||
| S22 | 119.90 | 8.73 | _ | 3.79 | ||
| E23 | 121.33 | 9.10 | 4.60 | 2.08 | ||
| Q24 | 119.20 | 8.08 | 4.10 | 2.07 | ||
| R25 | 119.90 | 8.59 | 4.13 | 1.85 | ||
| L26 | 115.70 | 8.13 | 4.30 | _ | ||
| K27 | 113.42 | 7.26 | 4.06 | 1.91 | ||
| I28 | 118.24 | 7.17 | 3.79 | 1.45 | 0.83 | 0.04 |
| D29 | 118.87 | 6.87 | 4.70 | 2.93 | ||
| Q30 | 119.40 | 8.11 | 3.90 | 2.00 | ||
| I31 | 119.30 | 7.83 | 4.10 | _ | 0.08 (Hγ2) | −0.08 |
| L32 | 119.75 | 7.41 | 3.31 | _ | ||
| V33 | 115.36 | 8.37 | 4.57 | 2.90 | ||
| H35 | 115.36 | 8.37 | 3.14 | 3.14 | ||
| Y37 | 119.73 | 8.01 | 5.10 | 3.01 | ||
| M38 | 117.95 | 7.47 | 4.10 | 2.70 | ||
| K39 | 118.38 | 8.04 | 4.08 | _ | ||
| D40 | 124.90 | 7.46 | 4.36 | 2.66 | ||
| L41 | 113.90 | 8.55 | 4.05 | _ | ||
| N42 | 120.64 | 8.20 | 4.70 | 2.86 | ||
| A43 | 121.92 | 7.37 | 4.67 | 1.40 | ||
| L44 | 118.16 | 7.64 | 4.15 | _ | ||
| S45 | 118.32 | 8.37 | 4.58 | 3.97 | 0.9 (Hδ1,2) | |
| A46 | 119.77 | 7.29 | 4.05 | 1.40 | ||
| M47 | 119.80 | 7.05 | 4.27 | 2.04 | 2.52 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nepravishta, R.; Ferrentino, F.; Mandaliti, W.; Mattioni, A.; Weber, J.; Polo, S.; Castagnoli, L.; Cesareni, G.; Paci, M.; Santonico, E. CoCUN, a Novel Ubiquitin Binding Domain Identified in N4BP1. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9070284
Nepravishta R, Ferrentino F, Mandaliti W, Mattioni A, Weber J, Polo S, Castagnoli L, Cesareni G, Paci M, Santonico E. CoCUN, a Novel Ubiquitin Binding Domain Identified in N4BP1. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(7):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9070284
Chicago/Turabian StyleNepravishta, Ridvan, Federica Ferrentino, Walter Mandaliti, Anna Mattioni, Janine Weber, Simona Polo, Luisa Castagnoli, Gianni Cesareni, Maurizio Paci, and Elena Santonico. 2019. "CoCUN, a Novel Ubiquitin Binding Domain Identified in N4BP1" Biomolecules 9, no. 7: 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9070284
APA StyleNepravishta, R., Ferrentino, F., Mandaliti, W., Mattioni, A., Weber, J., Polo, S., Castagnoli, L., Cesareni, G., Paci, M., & Santonico, E. (2019). CoCUN, a Novel Ubiquitin Binding Domain Identified in N4BP1. Biomolecules, 9(7), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9070284