A Spatially Highly Resolved Ground Mounted and Rooftop Potential Analysis for Photovoltaics in Austria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model Framework
2.1.1. Ground Mounted Photovoltaics
2.1.2. Rooftop Photovoltaics
2.2. Input Data
2.2.1. Solar Radiation
2.2.2. Spatial Data
2.2.3. Parameters
2.3. Goals
3. Results
3.1. Ground Mounted Photovoltaics
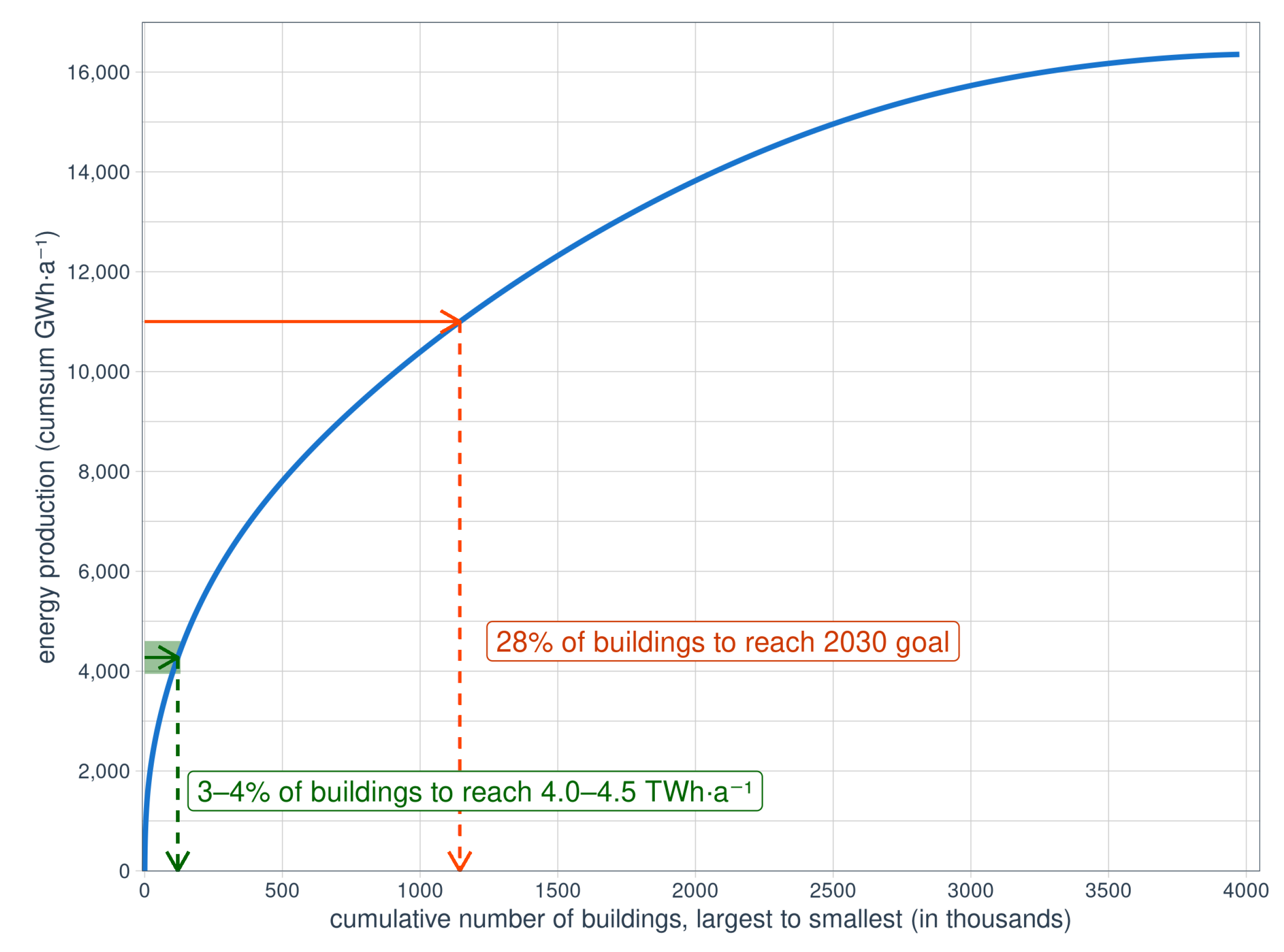
3.2. Rooftop Photovoltaics
3.3. Goals in Relation
4. Discussion
4.1. Ground Mounted Photovoltaics
4.2. Rooftop Photovoltaics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- REN21. Renewables 2020 Global Status Report; Technical Report; REN21 Secretariat: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Directive (Eu) 2018/2001 of the European Parliament and of the Council; The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Federal Ministry for Innovation. #mission 2030—Austrian Climate and Energy Strategy; Vienna, Austria. 2018. Available online: https://www.bundeskanzleramt.gv.at/dam/jcr:903d5cf5-c3ac-47b6-871c-c83eae34b273/20_18_beilagen_nb.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- e-Control. Ökostrombericht 2020; Technical Report; e-Control: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Österreichischer Nationalrat. Bundesgesetz über den Ausbau von Energie aus Erneuerbaren Quellen (Erneuerbaren-Ausbau-Gesetz—EAG) (Draft); Republic of Austria: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.bmk.gv.at/dam/jcr:f1017b8b-f77b-4613-aa79-e20a7786dee2/EAG-entwurf.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Fechner, H. Ermittlung des Flächenpotentials für den Photovoltaik-Ausbau in Österreich: Welche Flächenkategorien sind für die Erschließung von Besonderer Bedeutung, um das Ökostromziel Realisieren zu können; Endbericht: Vienna, Austria, 2020; p. 69. [Google Scholar]
- Ristic, B.; Mahlooji, M.; Gaudard, L.; Madani, K. The relative aggregate footprint of electricity generation technologies in the European Union (EU): A system of systems approach. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 143, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, P.; Nijs, W.; Tarvydas, D.; Sgobbi, A.; Zucker, A.; Pilli, R.; Jonsson, R.; Camia, A.; Thiel, C.; Hoyer-Klick, C.; et al. ENSPRESO—An open, EU-28 wide, transparent and coherent database of wind, solar and biomass energy potentials. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 26, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchelli, S.; Garegnani, G.; Geri, F.; Grilli, G.; Paletto, A.; Zambelli, P.; Ciolli, M.; Vettorato, D. Trade-off between photovoltaic systems installation and agricultural practices on arable lands: An environmental and socio-economic impact analysis for Italy. Land Use Policy 2016, 56, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nonhebel, S. Renewable energy and food supply: Will there be enough land? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2005, 9, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.; Macknick, J.; Lobell, D.; Field, C.; Ganesan, K.; Jain, R.; Elchinger, M.; Stoltenberg, B. Colocation opportunities for large solar infrastructures and agriculture in drylands. Appl. Energy 2016, 165, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinesh, H.; Pearce, J.M. The potential of agrivoltaic systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Šúri, M.; Huld, T.A.; Dunlop, E.D. PV-GIS: A web-based solar radiation database for the calculation of PV potential in Europe. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 2005, 24, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfenninger, S.; Staffell, I. Long-term patterns of European PV output using 30 years of validated hourly reanalysis and satellite data. Energy 2016, 114, 1251–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoefnagels, R.; Junginger, M.; Panzer, C.; Resch, G.; Held, A. Long Term Potentials and Costs of RES Part I: Potentials, Diffusion and Technological Learning. Available online: https://dspace.library.uu.nl/handle/1874/235228 (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Jacobson, M.Z.; Delucchi, M.A. Providing all global energy with wind, water, and solar power, Part I: Technologies, energy resources, quantities and areas of infrastructure, and materials. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 1154–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappa, W.; Junginger, M.; van den Broek, M. Is a 100% renewable European power system feasible by 2050? Appl. Energy 2019, 233–234, 1027–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trieb, F.; Schillings, C.; Sullivan, M.O.; Pregger, T.; Hoyer-klick, C. Global Potential of Concentrating Solar Power. In Proceedings of the SolarPaces Conference, Berlin, Germany, 15–18 September 2009; Number September. pp. 1–11. Available online: https://elib.dlr.de/60955/1/Solar_Paces_Paper_Trieb_Final_Colour.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Sun, Y.W.; Hof, A.; Wang, R.; Liu, J.; Lin, Y.J.; Yang, D.W. GIS-based approach for potential analysis of solar PV generation at the regional scale: A case study of Fujian Province. Energy Policy 2013, 58, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamasco, L.; Asinari, P. Scalable methodology for the photovoltaic solar energy potential assessment based on available roof surface area: Application to Piedmont Region (Italy). Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 1041–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeyringer, M.; Simoes, S.; Mayr, D.; Schmid, E.; Schmidt, J.; Lind, J.; Worrell, E. Solar buildings in Austria: Methodology to assess the potential for optimal PV deployment. In Proceedings of the 2013 10th International Conference on the European Energy Market (EEM), Stockholm, Sweden, 27–31 May 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainzer, K.; Fath, K.; McKenna, R.; Stengel, J.; Fichtner, W.; Schultmann, F. A high-resolution determination of the technical potential for residential-roof-mounted photovoltaic systems in Germany. Sol. Energy 2014, 105, 715–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, M.; Gomes, N.; Santos, T.; Tenedório, J. Photovoltaic potential in a Lisbon suburb using LiDAR data. Sol. Energy 2012, 86, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karteris, M.; Slini, T.; Papadopoulos, A.M. Urban solar energy potential in Greece: A statistical calculation model of suitable built roof areas for photovoltaics. Energy Build. 2013, 62, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukač, N.; Seme, S.; Žlaus, D.; Štumberger, G.; Žalik, B. Buildings roofs photovoltaic potential assessment based on LiDAR (Light Detection And Ranging) data. Energy 2014, 66, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, I.; Hellweger, F.L.; Fritch, T.G. Fractal generation of artificial sewer networks for hydrologic simulations. In Proceedings of the 2006 ESRI International User Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–11 August 2006; Number 617. pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pillai, I.R.; Banerjee, R. Methodology for estimation of potential for solar water heating in a target area. Sol. Energy 2007, 81, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, S.; Rodrigues, M.; Fueyo, N. A method for estimating the geographical distribution of the available roof surface area for large-scale photovoltaic energy-potential evaluations. Sol. Energy 2008, 82, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaita-Pradas, I.; Marques-Perez, I.; Gallego, A.; Segura, B. Analyzing territory for the sustainable development of solar photovoltaic power using GIS databases. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, J.; Schönhart, M.; Biberacher, M.; Guggenberger, T.; Hausl, S.; Kalt, G.; Leduc, S.; Schardinger, I.; Schmid, E. Regional energy autarky: Potentials, costs and consequences for an Austrian region. Energy Policy 2012, 47, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudermann, T.; Reinsberger, K.; Orthofer, A.; Kislinger, M.; Posch, A. Photovoltaics in agriculture: A case study on decision making of farmers. Energy Policy 2013, 61, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes, S.; Zeyringer, M.; Mayr, D.; Huld, T.; Nijs, W.; Schmidt, J. Impact of different levels of geographical disaggregation of wind and PV electricity generation in large energy system models: A case study for Austria. Renew. Energy 2017, 105, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defaix, P.R.; van Sark, W.G.; Worrell, E.; de Visser, E. Technical potential for photovoltaics on buildings in the EU-27. Sol. Energy 2012, 86, 2644–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seidl, R. Photovoltaik-Ausbaupotential im Versorgungsgebiet Wien Netz—Plausibilitätscheck, Endergebnisse; Technical Report; ÖIR: Austrian Institute for Regional Studies; Austria and Austrian Institute for Regional Studies: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kjellsson, E. Potential for building integrated photovoltaics. IEA PVPS Task 2002, 2002, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Streicher, W.; Schnitzer, H.; Heimrath, R.; Titz, M. Energieautarkie für Österreich 2050. 2010. Available online: https://www.klimafonds.gv.at/wp-content/uploads/sites/16/Energieautarkie205012pt20110308Final.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Huld, T.; Müller, R.; Gambardella, A. A new solar radiation database for estimating PV performance in Europe and Africa. Sol. Energy 2012, 86, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrarmarkt Austria. INVEKOS Schläge Österreich. 2018. Available online: https://www.data.gv.at/katalog/dataset/f7691988-e57c-4ee9-bbd0-e361d3811641 (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Umweltbundesamt; Sentinel-2 Bodenbedeckung Österreich: Vienna, Austria, 2016.
- Conrad, O.; Bechtel, B.; Bock, M.; Dietrich, H.; Fischer, E.; Gerlitz, L.; Wehberg, J.; Wichmann, V.; Böhner, J. System for Automated Geoscientific Analyses (SAGA) v. 2.1.4. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 1991–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geoland.at. Digital Terrain Model of Austria, Based on Airborne Laserscanning. Available online: https://www.data.gv.at/auftritte/?organisation=geoland (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Krutzler, T.; Wiesenberger, H.; Heller, C.; Gössl, M.; Stranner, G.; Storch, A.; Heinfellner, H.; Winter, R.; Kellner, M.; Schindler, I. Szenario Erneuerbare Energie 2030 und 2050; Technical report; Umweltbundesamt Österreich: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Veigl, A. Energie- und Klimazukunft österreich Szenario für 2030 und 2050; Technical Report, Global 2000; Greenpeace und WWF: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Auer, H.; Crespo del Granado, P.; Oei, P.Y.; Hainsch, K.; Löffler, K.; Burandt, T.; Huppmann, D.; Grabaak, I. Development and modelling of different decarbonization scenarios of the European energy system until 2050 as a contribution to achieving the ambitious 1.5 °C climate target -establishment of open source/data modelling in the European H2020 project openENT. Elektrotechnik Informationstechnik 2020, 137, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z.; Delucchi, M.A.; Bauer, Z.A.; Goodman, S.C.; Chapman, W.E.; Cameron, M.A.; Bozonnat, C.; Chobadi, L.; Clonts, H.A.; Enevoldsen, P.; et al. 100% Clean and Renewable Wind, Water, and Sunlight All-Sector Energy Roadmaps for 139 Countries of the World. Joule 2017, 1, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The Federal Republic of Germany; The French Republic; The Italian Republic; The Republic of Slovenia; The Principality of Liechtenstein; The Republic of Austria; The Swiss Federation.; The European Economic Community. Convention on the protection of the Alps (Alpine Convention). Off. J. Eur. Communities. 1996. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/convention/1996/191/oj (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Biermayr, P.; Dißauer, C.; Eberl, M.; Enigl, M.; Leonhartsberger, K.; Maringer, F.; Moidl, S.; Schmidl, C.; Strasser, C.; Weiss, W.; et al. Innovative Energietechnologien in Österreich-Marktentwicklung 2019, Biomasse, Photovoltaik, Solarthermie, Wärmepumpen und Windkraft. In Berichte aus Energie-und Umweltforschung; Im Auftrag des Bundesministerium für Wissenschaft und Verkehr 100 Seiten: Klagenfurt, Austria, 2020; pp. 1–266. [Google Scholar]
- Mikovits, C. Rooftop and open space PV data for Austria. Zenodo 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, T.W.; Lobell, D.B. Agricultural adaptation to climate change in rich and poor countries: Current modeling practice and potential for empirical contributions. Energy Econ. 2014, 46, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IPCC. IPCC, 2014: Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Technical Report; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Karpić, J.; Sharma, E.; Khatib, T.; Elmenreich, W. Comparison of solar power measurements in alpine areas using a mobile dual-axis tracking system. Energy Informatics 2019, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michel, A.H.; Buchecker, M.; Backhaus, N. Renewable Energy, Authenticity, and Tourism: Social Acceptance of Photovoltaic Installations in a Swiss Alpine Region. Mt. Res. Dev. 2015, 35, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastik, R.; Basso, S.; Geitner, C.; Haida, C.; Poljanec, A.; Portaccio, A.; Vrščaj, B.; Walzer, C. Renewable energies and ecosystem service impacts. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 48, 608–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.L. Renewable energy vs. biodiversity: Policy conflicts and the future of nature conservation. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2011, 21, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Száz, D.; Mihályi, D.; Farkas, A.; Egri, A.; Barta, A.; Kriska, G.; Robertson, B.; Horváth, G. Polarized light pollution of matte solar panels: Anti-reflective photovoltaics reduce polarized light pollution but benefit only some aquatic insects. J. Insect Conserv. 2016, 20, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fthenakis, V.; Blunden, J.; Green, T.; Krueger, L.; Turney, D. Large photovoltaic power plants: Wildlife impacts and benefits. In Proceedings of the 2011 37th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 19–24 June 2011; pp. 2011–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| grid resolution | 250 |
| maximum altitude | 1950 |
| maximum slope | 35 |
| ground mounted density | 20 m2/p |
| rooftop density | 8 m2/p |
| Scenario | PV Land-Use |
|---|---|
| All Open | Agricultural fields and pastures |
| Crops & Vegetables | Cropland & vegetable fields |
| Pastures | Pastures and greenland |
| Cereals | Only cereal cropland |
| Vegetables | Only vegetable fields |
| Coefficient | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0.60 | rooftop: pitches | |
| 0.65 | features: chimneys/windows | |
| 0.55 | self-shading | |
| 0.75 | structural conditions | |
| 0.95 | historic preservation | |
| 0.15 | total |
| Scenario | Grid Points | Area (km2) | Median () | Mean (−2) | Total Potential () |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austria | 1,336,286 | 83,518 | - | - | - |
| All Open | 505,794 | 31,612 | 1029 | 51.06 | 1614 |
| Crops & Vegetables | 230,142 | 14,384 | 1042 | 52.34 | 753 |
| Pastures | 194,179 | 12,136 | 1011 | 49.75 | 604 |
| Cereals | 163,321 | 10,208 | 1038 | 52.17 | 533 |
| Vegetables | 50,120 | 3133 | 1052 | 52.65 | 165 |
| Source | Mission 2030 [3] | UBA [42] | NGOs [43] | Auer et al. [44] | Jacobsen et al. [45] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 2030 | 2050 | 2050 | 2050 | 2050 |
| Goal (in ) | 11.0 | 21.8 | 31.3 | 48.3 | 109.3 |
| Rooftop PV (in ) | 4.5 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 |
| Ground Mounted PV Area (in ha) | 12,600 | 22,900 | 41,300 | 74,200 | 195,800 |
| All Open | 0.40 | 0.73 | 1.32 | 2.37 | 6.26 |
| Crops & Vegetables | 0.88 | 1.57 | 2.83 | 5.09 | 13.41 |
| Pastures | 1.08 | 1.95 | 3.53 | 6.34 | 16.72 |
| Cereals | 1.22 | 2.21 | 4.00 | 7.19 | 18.95 |
| Vegetables | 3.94 | 7.15 | 12.91 | 23.21 | 61.21 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mikovits, C.; Schauppenlehner, T.; Scherhaufer, P.; Schmidt, J.; Schmalzl, L.; Dworzak, V.; Hampl, N.; Sposato, R.G. A Spatially Highly Resolved Ground Mounted and Rooftop Potential Analysis for Photovoltaics in Austria. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10060418
Mikovits C, Schauppenlehner T, Scherhaufer P, Schmidt J, Schmalzl L, Dworzak V, Hampl N, Sposato RG. A Spatially Highly Resolved Ground Mounted and Rooftop Potential Analysis for Photovoltaics in Austria. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2021; 10(6):418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10060418
Chicago/Turabian StyleMikovits, Christian, Thomas Schauppenlehner, Patrick Scherhaufer, Johannes Schmidt, Lilia Schmalzl, Veronika Dworzak, Nina Hampl, and Robert Gennaro Sposato. 2021. "A Spatially Highly Resolved Ground Mounted and Rooftop Potential Analysis for Photovoltaics in Austria" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 10, no. 6: 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10060418
APA StyleMikovits, C., Schauppenlehner, T., Scherhaufer, P., Schmidt, J., Schmalzl, L., Dworzak, V., Hampl, N., & Sposato, R. G. (2021). A Spatially Highly Resolved Ground Mounted and Rooftop Potential Analysis for Photovoltaics in Austria. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 10(6), 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10060418







