An Inositol 1,3,4,5,6-Pentakisphosphate 2-Kinase 1 Mutant with a 33-nt Deletion Showed Enhanced Tolerance to Salt and Drought Stress in Rice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
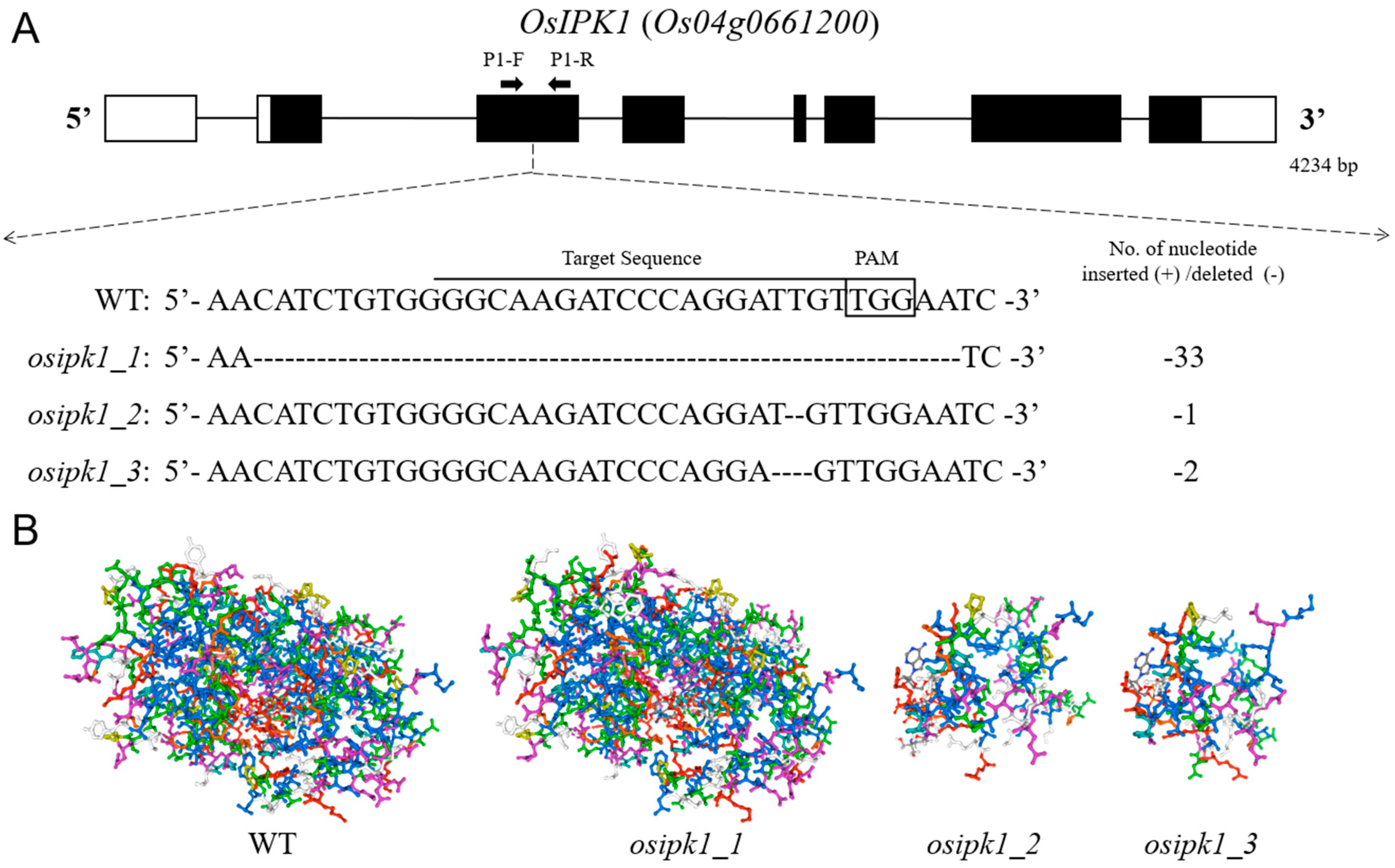
2.1. Mutations of OsIPK1 and Development of Homozygous Transgene-Free Mutant Lines
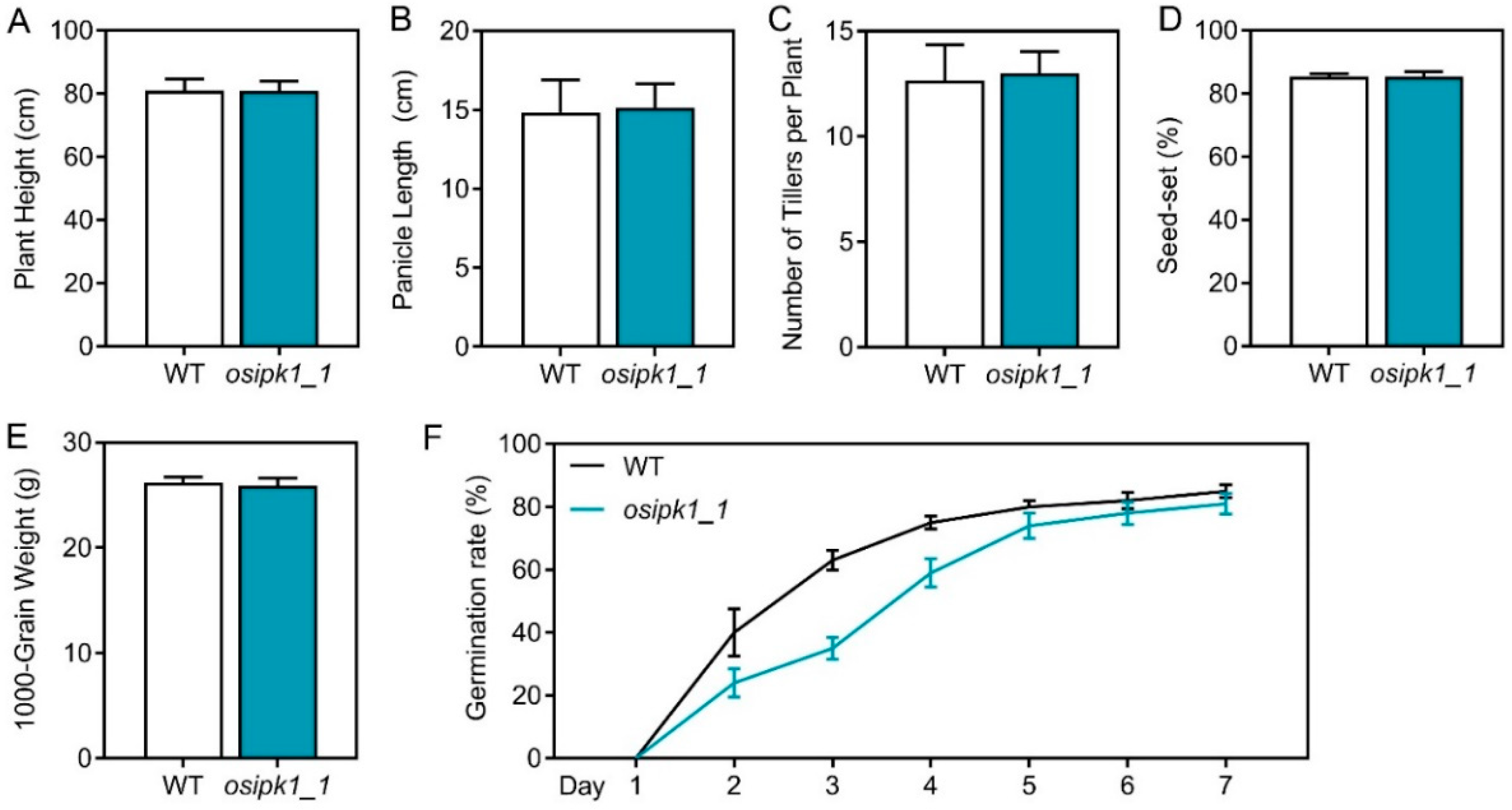
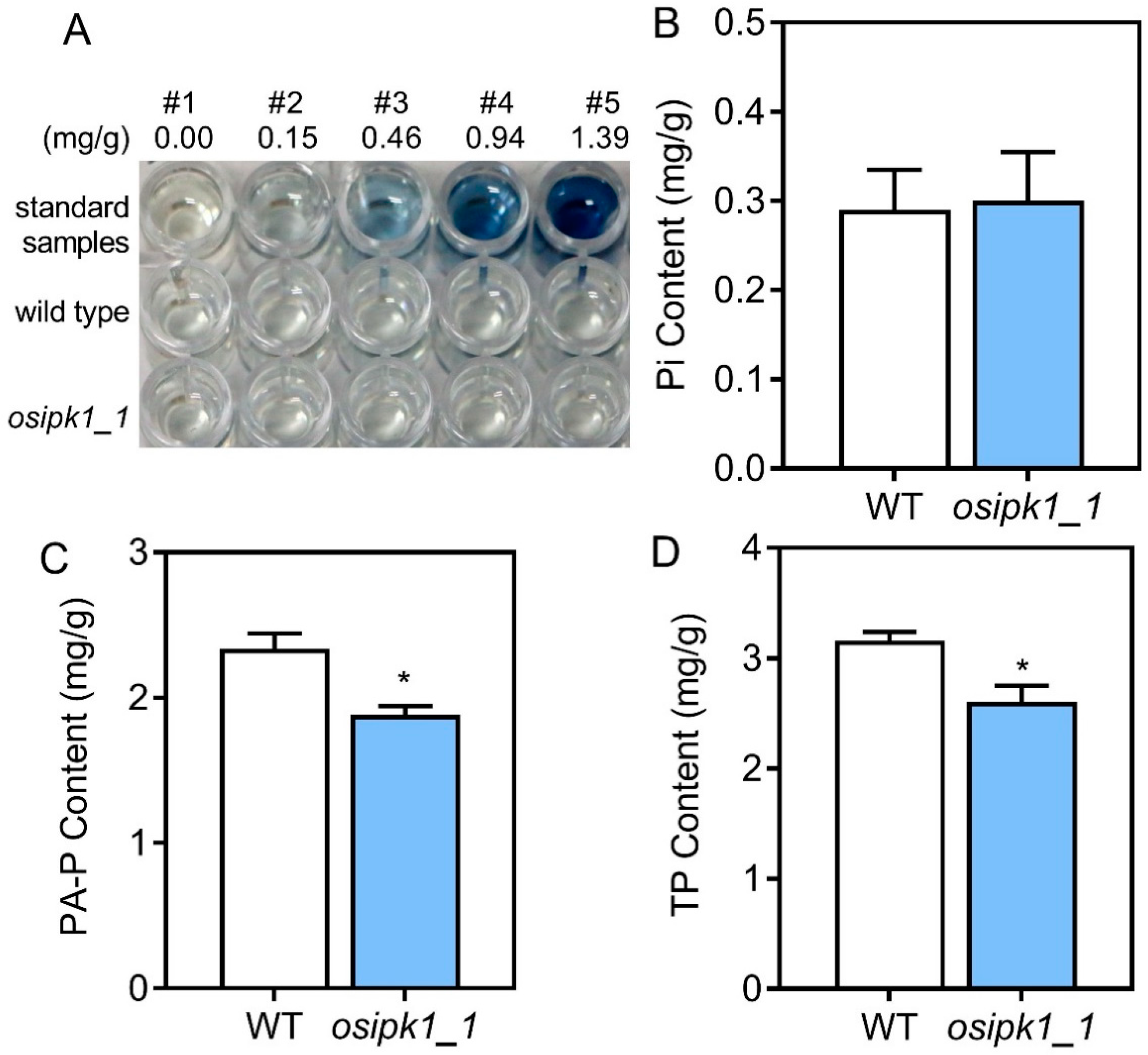
2.2. Plant Growth and Phosphorus Content of Osipk1_1 Mutant
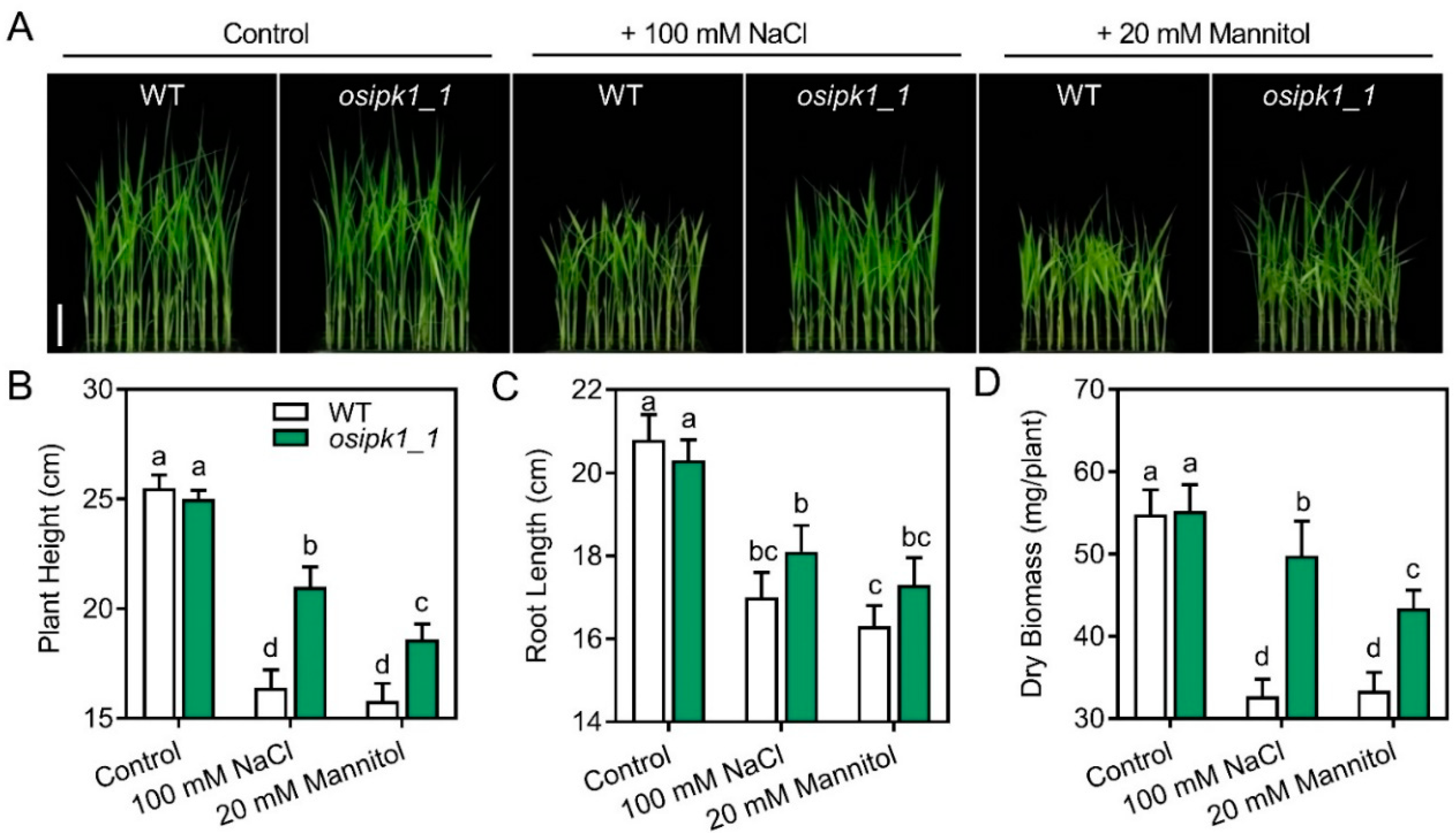
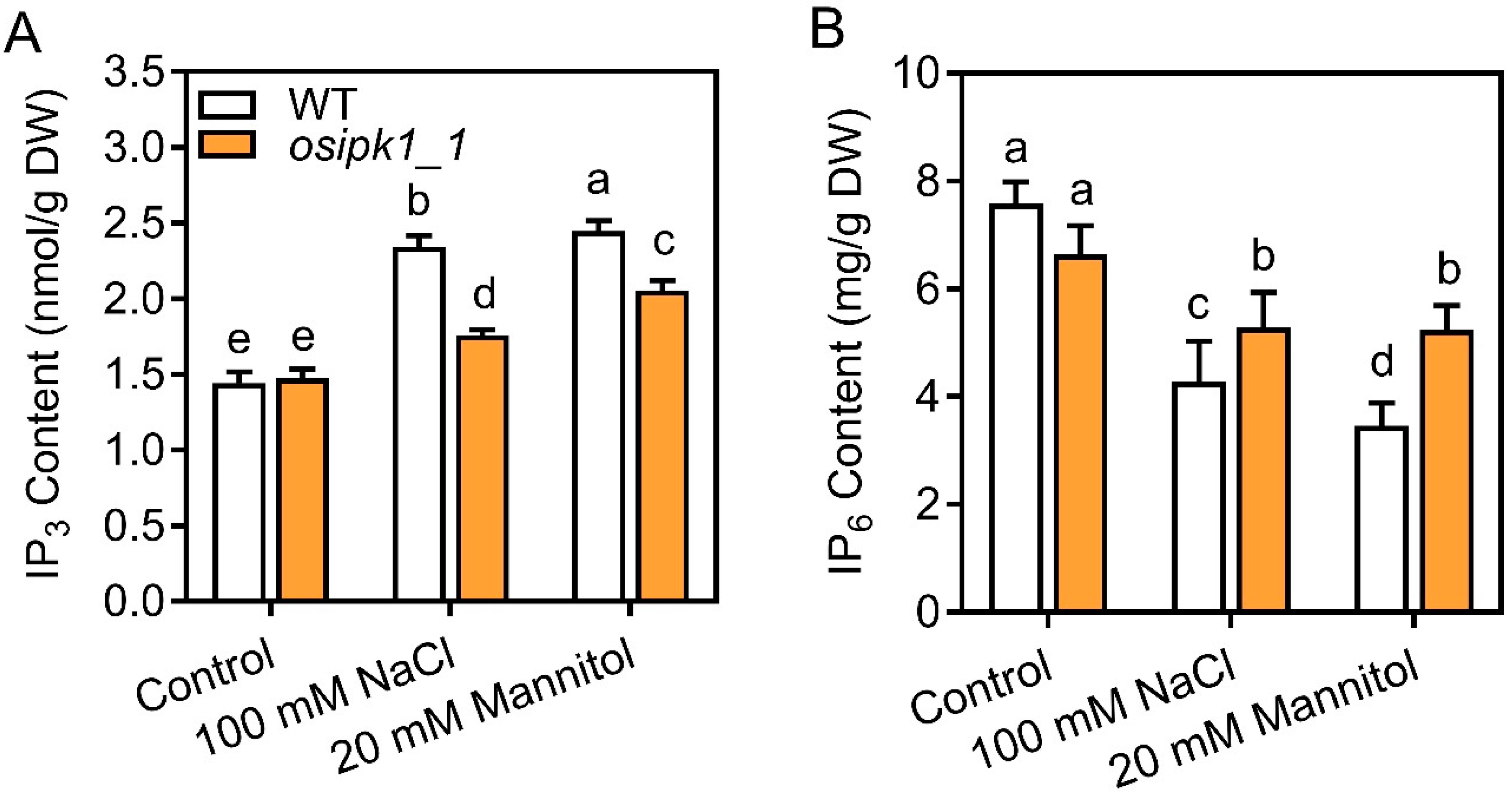
2.3. Mutant of Osipk1_1 Has a Better Tolerance against Drought or Salt Stress than Wild Type (WT)
2.4. The Osipk1_1 Mutant Accumulated Less Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) than WT under Salt and Drought Stresses
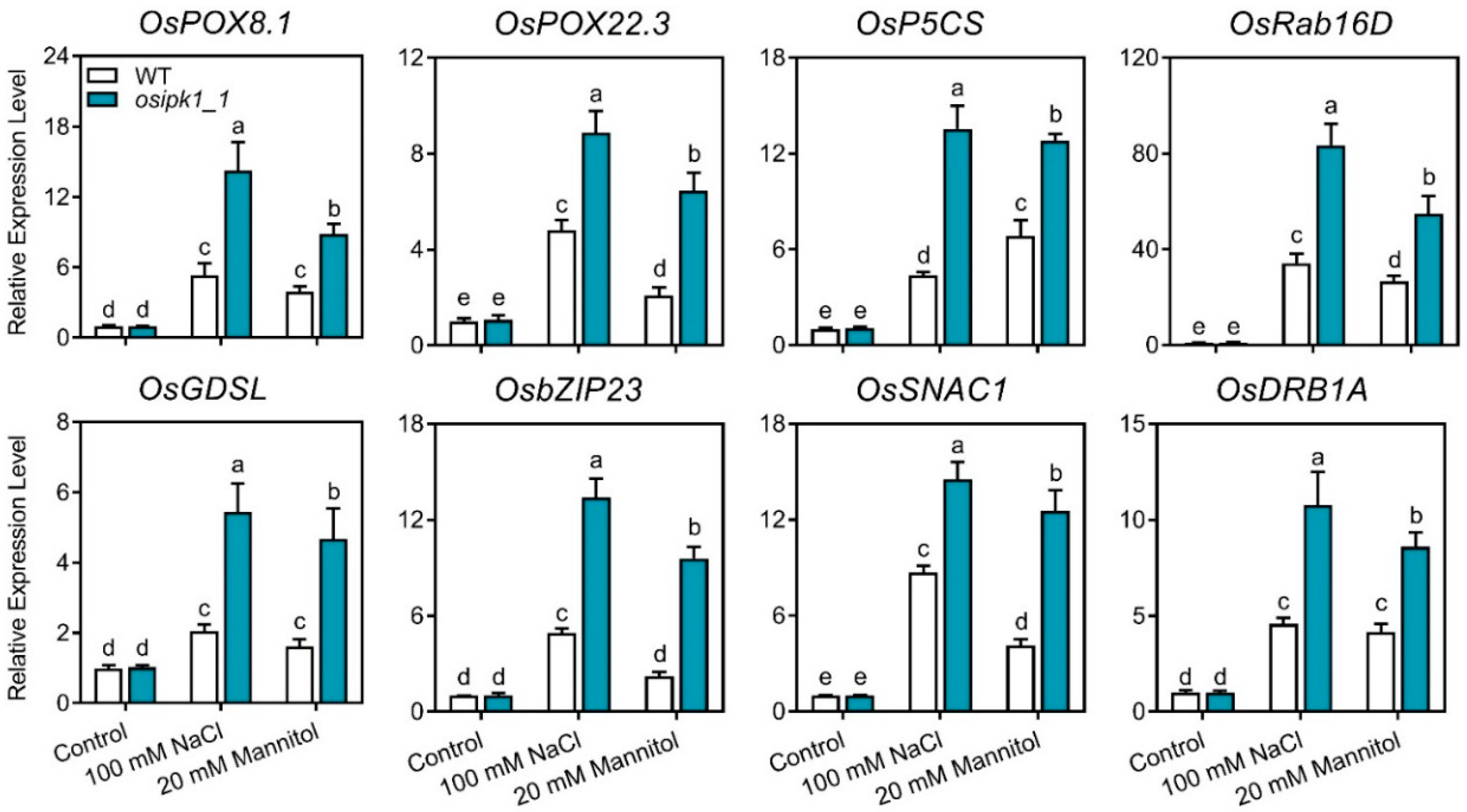
2.5. Transcription of Stress Response Genes Was Significantly Upregulated in the Osipk1_1 Mutant under Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Generation of Mutants Using Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) and CRISPR-Associated Protein (Cas9)
4.2. Growth and Identification of Mutants
4.3. Development of Transgene-Free Mutant Lines
4.4. Assay of Agronomic Traits
4.5. Assay of Seed Germination
4.6. Assay of Seed Phosphorus
4.7. Stresses Treatment
4.8. Measurement of Inositol Triphosphate (IP3) and Phytic Acid (IP6) Content
4.9. Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Content Measurement
4.10. Determination of Malondialdehyde (MDA)
4.11. Measurement of Free Proline (Pro)
4.12. Measurement of Anti-Oxidant Enzymes Activities
4.13. Analysis of Gene Expression
4.14. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lott, J.N.A.; Ockenden, I.; Raboy, V.; Batten, G.D. Phytic acid and phosphorus in crops seeds and fruits: A global estimate. Seed Sci. Res. 2000, 10, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.J.; Frank, T.; Tan, Y.Y.; Zhou, C.G.; Jabnoune, M.; Arpat, A.B.; Cui, H.R.; Huang, J.Z.; He, Z.H.; Poirier, Y.; et al. Disruption of OsSULTR3;3 reduces phytate and phosphorus concentrations and alters the metabolite profile in rice grains. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 926–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raboy, V.; Gerbasi, P.F.; Young, K.A.; Stoneberg, S.D.; Pickett, S.G.; Bauman, A.T.; Murthy, P.P.N.; Sheridan, W.F.; Ertlet, D.S. Origin and seed phenotype of maize low phytic acid 1-1 and low phytic acid 2-1. Plant Physiol. 2000, 124, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuwano, M.; Ohyama, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Mimura, T.; Takaiwa, F.; Yoshida, K.T. Molecular breeding for transgenic rice with low phytic acid phenotype through manipulating myo inositol 3 phosphate synthase gene. Mol. Breed. 2006, 18, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raboy, V. Approaches and challenges to engineering seed phytate and total phosphorus. Plant Sci. 2009, 177, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, L.; Meyer, A.S.; Rasmussen, S.K. Phytate: Impact on environment and human nutrition, a challenge for molecular breeding. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2008, 9, 165–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pilu, R.; Panzeri, D.; Gavazzi, G.; Rasmussen, S.K.; Consonni, G.; Nielsen, E. Phenotypic, genetic and molecular characterization of a maize low phytic acid mutant (lpa 241). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttieri, M.; Bowen, D.; Dorsch, J.A.; Raboy, V.; Souza, E. Identification and characterization of a low phytic acid wheat. Crop Sci. 2014, 44, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, S.R.; Rutger, J.N.; Young, K.A.; Raboy, V. Isolation and genetic mapping of a non-lethal rice (Oryza sativa L.) low phytic acid 1 mutation. Crop Sci. 2000, 40, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.L.; Xu, X.H.; Ren, X.L.; Fu, H.W.; Wu, D.X.; Shu, Q.Y. Generation and characterization of low phytic acid germplasm in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 114, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.I.; Andaya, C.B.; Newman, J.W.; Goyal, S.S.; Tai, T.H. Isolation and characterization of a low phytic acid rice mutant reveals a mutation in the rice orthologue of maize MIK. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 117, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.X.; Huang, J.Z.; Zhao, H.J.; Tan, Y.Y.; Cui, H.R.; Poirier, Y.; Shu, Q.Y. Production of low phytic acid rice by hairpin RNA- and artificial microRNA-mediated silencing of OsMIK in seeds. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. 2014, 119, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.X.; Zhao, H.J.; Pang, W.Q.; Cui, H.R.; Poirier, Y.; Shu, Q.Y. Seed-specific silencing of OsMRP5 reduces seed phytic acid and weight in rice. Transgenic Res. 2014, 23, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Tanaka, K.; Kuwano, M.; Yoshida, K.T. Expression pattern of inositol phosphate-related enzymes in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Implications for the phytic acid biosynthetic pathway. Gene 2007, 405, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, L.R.; Irvine, R.F. Stepwise phosphorylation of myo-inositol leading to myo-inositol hexakisphosphate in Dictyostelium. Nature 1990, 346, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brearley, C.A.; Hanke, D.E. Metabolic evidence for the order of addition of individual phosphate este rs to the myo-inositol moiety of inositol hexakisphosphate in the duckweed Spirodela polyrhiza L. Biochem. J. 1996, 314, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- York, J.D.; Odom, A.R.; Murphy, R.; Ives, E.B.; Wente, S.R. A phospholipase cdependent inositol polyphosphate kinase pathway required for efficient messenger RNA export. Science 1999, 285, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson-Paulik, J.; Bastidas, R.J.; Chiou, S.-T.; Frye, R.A.; York, J.D. Generation of phytate-free seeds in Arabidopsis through disruption of inositol polyphosphate kinases. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12612–12617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, N.; Paul, S.; Gayen, D.; Sarkar, S.N.; Datta, K.; Datta, S.K. Development of low phytate rice by RNAi mediated seed specific seed specific silencing of inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate 2-kinase gene (IPK1). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, F.J.; Zhao, H.J.; Ren, X.L.; Zhu, S.L.; Fu, X.J.; Shu, Q.Y. Generation and characterization of two novel low phytate mutations in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 115, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.J.; Zhu, D.H.; Tan, Y.Y.; Dong, D.K.; Fu, X.J.; Zhu, S.L.; Li, B.Q.; Shu, Q.Y. Identification and characterization of the soybean IPK1 ortholog of a low phytic acid mutant reveals an exon-excluding splice-site mutation. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.; Lee, B.; Ishitani, M.; Lee, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, J.K. FIERY1 encoding an inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase is a negative regulator of abscisic acid and stress signaling in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 1971–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DeWald, D.B.; Torabinejad, J.; Jones, C.A.; Shope, J.C.; Cangelosi, A.R.; Thompson, J.E.; Prestwich, G.D.; Hama, H. Rapid accumulation of phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate and inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate correlates with calcium mobilization in salt stressed Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Ye, X.; Guo, R.; Huang, J.; Wang, W.; Tang, J.; Tan, L.; Zhu, J.K.; Chu, C.; Qian, Y. Genome-wide targeted mutagenesis in rice using the crispr/cas9 system. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1242–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, C.; Capistrano-Gossmann, G.; Braatz, J.; Sashidhar, N.; Melzer, S. Recent developments in genome editing and applications in plant breeding. Plant Breed. 2017, 137, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Huang, J.; Shu, Q. Mutation of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate 5/6-kinase6 impairs plant growth and phytic acid synthesis in rice. Plants-Basel 2019, 8, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stevenson, J.M.; Perera, I.Y.; Heilmann, I.I.; Persson, S.; Boss, W.F. Inositol signaling and plant growth. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziolkowski, N.; Grover, A.K. Functional linkage as a direction for studies in oxidative stress: Alpha-adrenergic receptors. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2010, 88, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, H.; Hazebroek, J.; Ertl, D.S.; Harp, T. The maize low-phytic acid 3 encodes a myo-inositol kinase that plays a role in phytic acid biosynthesis in developing seeds. Plant J. 2005, 42, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodakovskaya, M.; Sword, C.; Wu, Q.; Perera, I.Y.; Boss, W.F.; Brown, C.S.; Sederoff, H.W. Increasing inositol (1, 4, 5)-trisphosphate metabolism affects drought tolerance, carbohydrate metabolism and phosphate-sensitive biomass increases in tomato. Plant Biotech. J. 2010, 8, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancey, P.H.; Clark, M.E.; Hand, S.C.; Bowlus, R.D.; Somero, G.N. Living with water stress: Evolution of osmolyte systems. Science 1982, 217, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Rudulier, D.; Strom, A.R.; Dandekar, A.M.; Smith, L.T.; Valentine, R.C. Molecular biology of osmoregulation. Science 1984, 224, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Lakkineni, K.; Zhang, Z.; Verma, D.P. Removal of feedback inhibition of delta(1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase results in increased proline accumulation and protection of plants from osmotic stress. Plant Physiol. 2000, 122, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mittler, R. Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, K.; Hirt, H. Reactive oxygen species: Metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 373–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graf, E.; Eaton, J.W. Antioxidant functions of phytic acid. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1990, 8, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enrico, D.; Luciano, G.; Lucia, C.; Calogero, P.; Roberto, P.; Elena, C.; Erik, N. Phytic acid prevents oxidative stress in seeds: Evidence from a maize (Zea mays L.) low phytic acid mutant. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 3, 967–978. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Liu, L.H.; You, L.; Yang, M.; He, Y.B.; Li, X.H.; Xiong, L.Z. Characterization of an inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate 5/6-kinase gene that is essential for drought and salt stress responses in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 77, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittoor, J.M.; Leach, J.E.; White, F.F. Differential induction of a peroxidase gene family during infection of rice by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 1997, 10, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; You, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Qi, Z.; Xiong, L. Characterization of transcription factor gene SNAC2 conferring cold and salt tolerance in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 67, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubouzet, J.G.; Sakuma, Y.; Ito, Y.; Kasuga, M.; Dubouzet, E.G.; Miura, S.; Seki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. OsDREB genes in rice, Oryza sativa L. encode transcription activators that function in drought-, high-salt- and cold-responsive gene expression. Plant J. 2003, 33, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Dai, M.; Yao, J.; Xiao, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, L. Overexpressing a NAM, ATAF, and CUC (NAC) transcription factor enhances drought resistance and salt tolerance in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12987–12992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiang, Y.; Tang, N.; Du, H.; Ye, H.; Xiong, L. Characterization of OsbZIP23 as a key player of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family for conferring abscisic acid sensitivity and salinity and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1938–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, X.; Xie, K.; Yao, J.; Qi, Z.; Xiong, L. A homolog of human skiinteracting protein in rice positively regulates cell viability and stress tolerance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6410–6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.T.; Shu, Q.Y.; Xia, Y.W. The biological effects of Pingyangmycin on rice. J. Zhejiang Agric. Univ. 1997, 23, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, Q.Y.; Cui, H.R.; Ye, G.Y.; Wu, D.X.; Xia, Y.W.; Gao, M.W.; Altosaar, I. Agronomic and morphological characterization of agrobacterium-transformed bt rice plants. Euphytica 2002, 127, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaeppler, S.M.; Kaeppler, H.F.; Rhee, Y. Epigenetic aspects of somaclonal variation in plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 43, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Lu, L.; Liu, H.Y.; Li, S.; Xing, F.; Chen, L.L. CRISPR-P: A web tool for synthetic single-guide RNA design of CRISPR-system in plants. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1494–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, H.P.; Liu, S.M.; Xu, S.L.; Chen, W.Y.; Zhou, X.; Tan, Y.Y.; Huang, J.Z.; Shu, Q.Y. CRISPR-S: An active interference element for a rapid and inexpensive selection of genome-edited, transgene-free rice plants. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 1371–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.F.; Li, H.; Qin, R.Y.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Wei, P.C.; Yang, J.B. Gene targeting using the Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated CRISPR-Cas system in rice. Rice 2014, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.X.; Wu, S.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Jin, G.L.; Zhao, H.J.; Fan, L.J.; Shu, Q.Y. Genome-wide profiling of genetic variation in Agrobacterium-transformed rice plants. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2016, 17, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.L.; Huang, J.Z.; Chen, X.Y.; Tan, Y.Y.; Shu, Q.Y. Competitive amplification of differentially melting amplicons facilitates efficient genotyping of photoperiod-and temperature-sensitive genic male sterility in rice. Mol. Breed. 2014, 34, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L.; Xu, B.B.; Song, Q.J.; Liu, X.M.; Xu, J.M.; Brookes, P.C. The identification of ‘hotspots’ of heavy metal pollution in soil-rice systems at a regional scale in eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liu, S.M.; Liu, Y.H.; Lu, H.P.; Tan, Y.Y.; Huang, J.Z.; Wei, P.C.; Shu, Q.Y. HRM-facilitated rapid identification and genotyping of mutations induced by CRISPR/Cas9 mutagenesis in rice. Crop Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2018, 18, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.Z.; Xie, X.R.; Ma, X.L.; Li, J.; Chen, J.H.; Liu, Y.G. DSDecode: Aweb-based tool for decoding of sequencing chromatograms for genotyping of targeted mutations. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1431–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.S.; Toribara, T.Y.; Warner, H. Micro determination of phosphorous. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 1756–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, J.R.; Premachandra, G.S.; Young, K.A.; Raboy, V. Isolation of high seed inorganic P, low-phytate soybean mutants. Crop Sci. 2000, 40, 1601–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raboy, V.; Young, K.A.; Dorsch, J.A.; Cook, A. Genetics and breeding of seed phosphorus and phytic acid. J. Plant Physiol. 2001, 158, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKie, V.A.; McCleary, B.V.A. Novel and rapid colorimetric method for measuring total phosphorus and phytic acid in foods and animal feeds. J. AOAC Int. 2016, 99, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.F.; McBride, M.B.; Cheng, H.; Wu, J.J.; Shi, J.C.; Xu, J.M.; Wu, L.S. Root-induced changes to cadmium speciation in the rhizosphere of two rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Zhong, L.B.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.M.; Tang, C.X.; Chen, H.L.; Xu, J.M. Contrasting effects of alkaline amendments on the bioavailability and uptake of Cd in rice plants in a Cd-contaminated acid paddy soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2018, 25, 8827–8835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plantarum 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campion, B.; Sparvoli, F.; Doria, E.; Tagliabue, G.; Galasso, I.; Fileppi, M.; Bollini, R.; Nielsen, E. Isolation and characterization of an lpa (low phytic acid) mutant in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Zheng, Y.; Fu, H.; Tan, Y.; Moller, I.M.; Fan, L.; Shu, Q.; Huang, J. A suppressor mutation partially reverts the xantha trait via lowered methylation in the promoter of genomes uncoupled 4 in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, G.A.; Youngs, V.L.; Oplinger, E.S. Environmental and cultivar effects on oat phytic acid concentration. Cereal Chem. 1980, 57, 189–191. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wen, F.; Yao, D.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Nan, L.; Zhang, A.; Tana, M.; Jiang, M. A novel rice C2H2-type zinc finger protein, ZFP36, is a key player involved in abscisic acid-induced antioxidant defence and oxidative stress tolerance in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 5795–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Jiang, J.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Tan, Y.Y.; Song, S.Y.; Shu, Q.Y.; Huang, J.Z. Glutamate alleviates cadmium toxicity in rice via suppressing cadmium uptake and translocation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Cai, H.; Ji, W.; Luo, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Cui, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Overexpression of GsZFP1 enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2013, 71, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Duan, Y.; Hua, D.; Fan, G.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Han, L.; Qu, L.J.; Gong, Z. DEXH Box RNA Helicase-mediated mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production in Arabidopsis mediates crosstalk between abscisic acid and auxin signaling. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 1815–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Method Enzymol. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, F.; Raziuddin, R.; Gong, H.; Yang, Z.; Lu, L.; Ye, Q.; Zhou, W. Effects of 5-aminolevulinic acid on oilseed rape seedling growth under herbicide toxicity stress. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2008, 27, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Fujita, M. Up-regulation of antioxidant and glyoxalase systems by exogenous glycinebetaine and proline in mung bean confer tolerance to cadmium stress. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2010, 16, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, J.X.; Rui, M.M.; Yang, L.J.; Shen, J.; Chu, H.W.; Song, S.Y.; Chen, Y. OsFTIP7 determines metallic oxide nanoparticles response and tolerance by regulating auxin biosynthesis in rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 403, 123946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Wu, X.J.; Song, Y.; Shen, H.Z.; Cui, H.R. Effects of OsMSH6 mutations on microsatellite stability and homeologous recombination in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta c (t)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Li, S.; Tan, Y.; Huang, J.; Shu, Q. An Inositol 1,3,4,5,6-Pentakisphosphate 2-Kinase 1 Mutant with a 33-nt Deletion Showed Enhanced Tolerance to Salt and Drought Stress in Rice. Plants 2021, 10, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10010023
Jiang M, Liu Y, Li R, Li S, Tan Y, Huang J, Shu Q. An Inositol 1,3,4,5,6-Pentakisphosphate 2-Kinase 1 Mutant with a 33-nt Deletion Showed Enhanced Tolerance to Salt and Drought Stress in Rice. Plants. 2021; 10(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Meng, Yanhua Liu, Ruiqing Li, Shan Li, Yuanyuan Tan, Jianzhong Huang, and Qingyao Shu. 2021. "An Inositol 1,3,4,5,6-Pentakisphosphate 2-Kinase 1 Mutant with a 33-nt Deletion Showed Enhanced Tolerance to Salt and Drought Stress in Rice" Plants 10, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10010023
APA StyleJiang, M., Liu, Y., Li, R., Li, S., Tan, Y., Huang, J., & Shu, Q. (2021). An Inositol 1,3,4,5,6-Pentakisphosphate 2-Kinase 1 Mutant with a 33-nt Deletion Showed Enhanced Tolerance to Salt and Drought Stress in Rice. Plants, 10(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10010023





