- Article
Anatomical, Molecular–Genetic, and Phytochemical Study of Species from the Genus Equisetum in Bulgaria
- Krasimir Todorov,
- Ginka Antova and
- Zhana Petkova
- + 9 authors
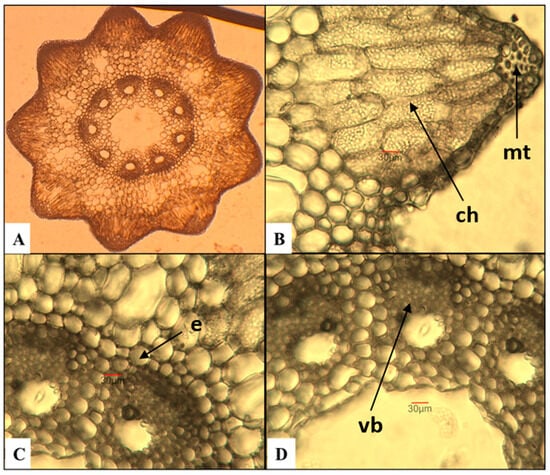
Five species of the genus Equisetum distributed in Bulgaria were studied: four species from the subgenus Equisetum (Equisetum arvense, E. telmateia, E. sylvaticum, and E. palustre) and one from the subgenus Hippochaete (E. ramosissimum). The anatomical, taxonomic, and phylogenetic characteristics of the selected species were established. In species belonging to the subgenus Equisetum, the endodermis was arranged in the form of a continuous ring, while in the representatives of the subgenus Hippochaete, a two-layered endodermis surrounding each vascular bundle was observed. The results from the DNA barcoding supported the taxonomic treatment of the studied species. The chemical and lipid compositions of the plants were also investigated. The Equisetum species had a similar chemical composition and a high content of sterols and phospholipids. In the glyceride oils, palmitic acid predominated, ranging from 69.5% to 78.7%. β-sitosterol was the main component in the sterol fraction, while the tocopherol content was found to be remarkably low in two of the samples (37.6–82.8 mg/kg), with α-tocopherol being predominant. In the phospholipid fraction, the major classes were phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylinositol, and phosphatidic acids. The chemical composition of the studied species and their high biologically active lipid constituents suggested that they were suitable for application in various directions.
20 December 2025