Optimized RNA-Silencing Strategies for Rice Ragged Stunt Virus Resistance in Rice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
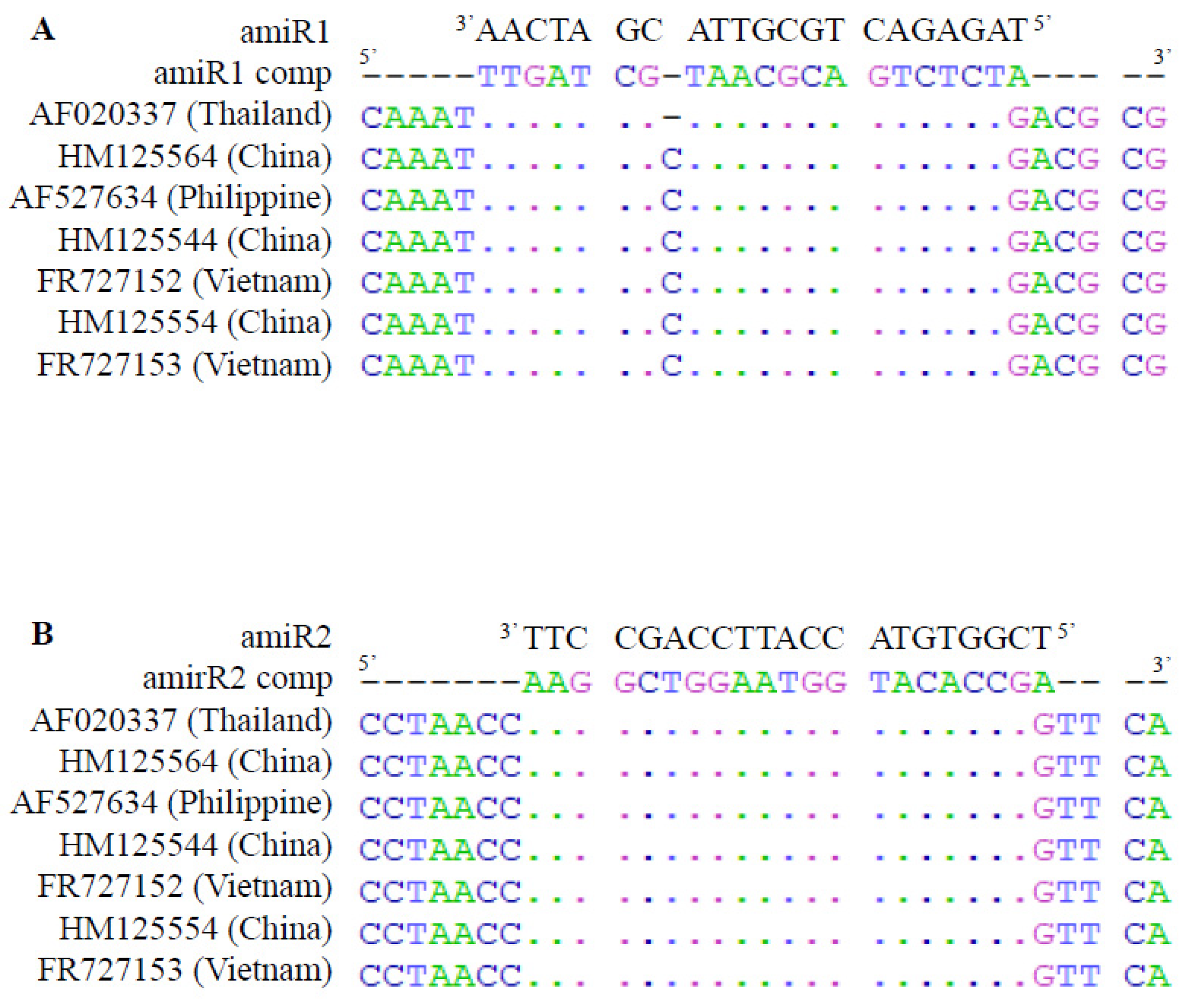
2.1. amiR Selection
2.2. Validation of the Functionality of the Rice miRNA Precursor to Produce Double Artificial miRNA
2.3. Selection of RRSV Sequences for siRNA Synthesis
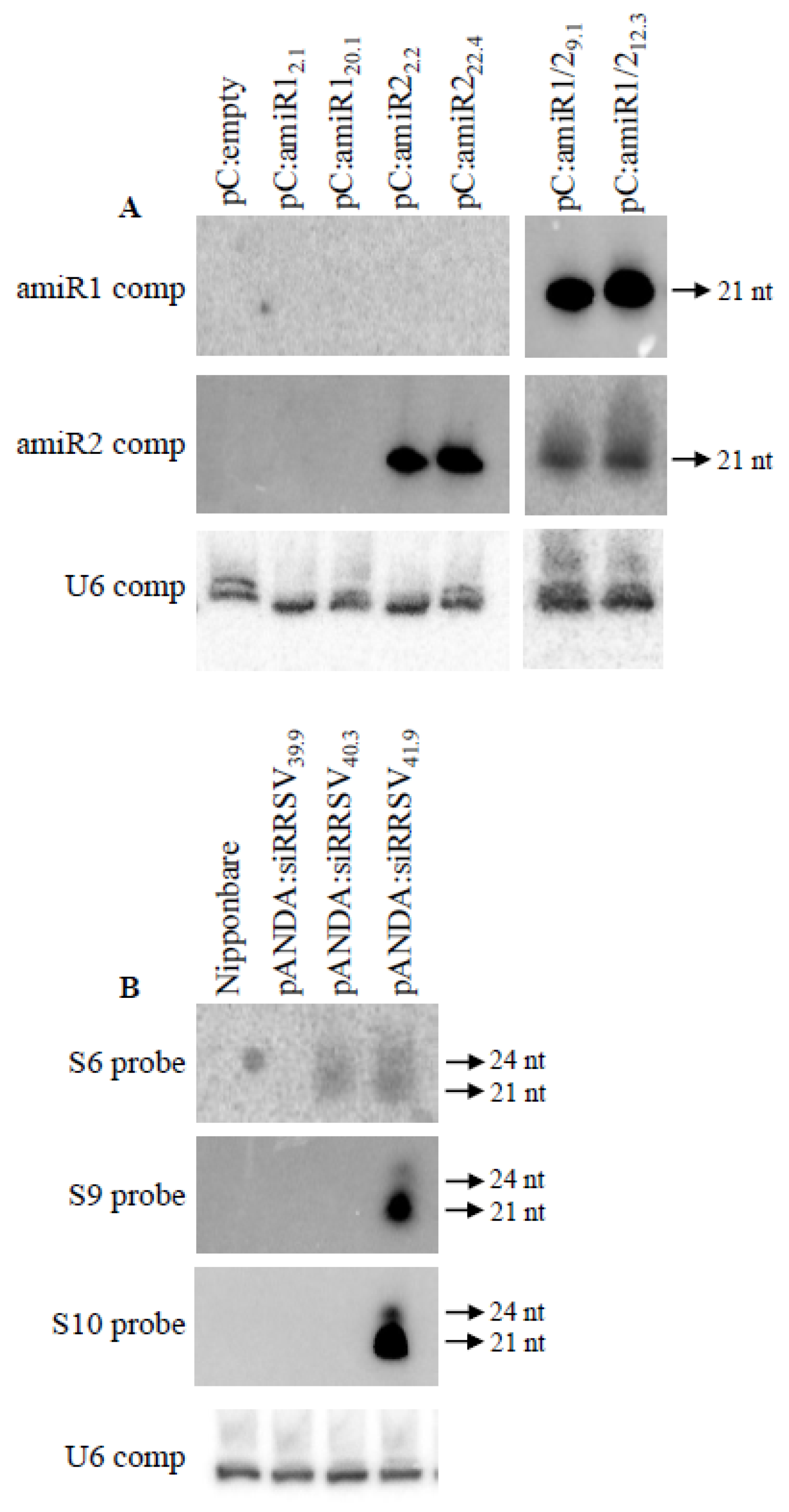
2.4. Accumulation of Expected amiR and siRNA in Transgenic Plants
2.5. Evaluation of RRSV Resistance
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Generation of RRSV amiR Precursor Constructs
4.2. Vector Construction for RRSV siRNA Production
4.3. Transient Expression Assay of amiR Precursors in Nicotiana Benthamiana
4.4. Rice Transformation Procedure
4.5. Selection of Homozygous Transgenic Rice Plants by PCR and Southern Blot
4.6. Small RNA Northern Blots
4.7. Evaluation for RRSV Resistance
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ling, K.C.; Tiongco, E.R.; Aguiero, V.M. Rice ragged stunt, a new virus disease. Plant Dis. Rep. 1978, 62, 701–705. [Google Scholar]
- Milne, R.G.; Boccasdo, G.; Ling, K.C. Rice ragged stunt virus. CMI/AAB Descr. Plant Viruses 1982, 16, 248. [Google Scholar]
- Vien, N.V.; Trung, H.M. Overview about rice virus and Rice grassy stunt virus, Rice ragged stunt virus protection in Mekong Delta. J. Agric. Agric. Dev. 2006, 18, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Boccardo, G.; Milne, R.G. Plant reovirus group. CMI/AAB Descr. Plant Viruses 1984, 294, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Omura, T.; Minobe, Y.; Kimura, I.; Hibino, H.; Tsuchizaki, T.; Saito, Y. Improved purification procedure and RNA segments of Rice ragged stunt virus. Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Jpn. 1983, 49, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Upadhyaya, N.M.; Zinkowsky, E.; Kositratana, W.; Waterhouse, P.M. The Mr 43K major capsid protein of rice ragged stunt Oryzavirus is a post-translationally processed product of a Mr 67,348 polypeptide encoded by genome segment 8. Arch. Virol. 1996, 141, 1689–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, N.M.; Ramm, K.; Gellatly, J.A.; Li, Z.; Kositratana, W.; Waterhouse, P.M. Rice ragged stunt oryzavirus genome segment S4 could encode an RNA dependent RNA polymerase and a second protein of unknown function. Arch. Virol. 1998, 143, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wu, J.; Adkins, S.; Xie, L.; Li, W. Rice ragged stunt virus segment S6-encoded nonstructural protein Pns6 complements cell-to-cell movement of Tobacco mosaic virus-based chimeric virus. Virus Res. 2010, 152, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Du, Z.; Wang, C.; Cai, L.; Hu, M.; Lin, Q.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Xie, L. Identification of Pns6, a putative movement protein of RRSV, as a silencing suppressor. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Lacombe, S.; Bangratz, M.; Ta, H.A.; Vinh, D.N.; Gantet, P.; Brugidou, C. p2 of Rice grassy stunt virus (RGSV) and p6 and p9 of Rice ragged stunt virus (RRSV) isolates from Vietnam exert suppressor activity on the RNA silencing pathway. Virus Genes 2015, 51, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaogang, S.; Jianhua, W.; Guoying, Z.; Gang, S.; Baozhen, P.; Juanli, L.; Dendi, J.; Shenxiang, C.; Upadhyaya, N.M.; Waterhouse, P.; et al. Ectopic expression of the spike protein of rice ragged stunt oryzavirus in transgenic rice plants inhibits transmission of the virus to insects. Mol. Breed. 2003, 11, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guoying, Z.; Xiongbin, L.; Huijuan, L.; Juanli, L.; Shengxiang, C.; Zuxun, G. Rice Ragged Stunt Oryzavirus: Role of the viral spike protein in transmission the insect vector. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1999, 135, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Upadhyaya, N.M.; Kositratana, W.; Gibbs, A.J.; Waterhouse, P.M. Genome segment 5 of rice ragged stunt virus encodes a virion protein. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 3155–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, N.M.; Ramm, K.; Gellatly, J.A.; Li, Z.; Kositratana, W.; Waterhouse, P.M. Rice ragged stunt oryzavirus genome segments S7 and S10 encode non-structural proteins of M(r) 68 025 (Pns7) and M(r) 32364 (Pns10). Arch. Virol. 1997, 142, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, K.; Minobe, Y.; Nozu, Y. Component proteins and structure of Rice ragged stunt virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1986, 67, 1711–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baulcombe, D. RNA silencing in plants. Nature 2004, 431, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodersen, P.; Voinnet, O. The Diversity of RNA Silencing Pathways in Plants. Trends Genet. 2006, 22, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, P.P.; Nelson, R.S.; De, B.; Hoffmann, N.; Rogers, S.G.; Fraley, R.T.; Beachy, R.N. Delay of disease development in transgenic plants that express the tobacco mosaic virus coat protein gene. Science 1986, 232, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, C.M.; Hall, R.M.; Mitter, N.; Cruickshank, A.; Dietzgen, R.G. Peanut stripe potyvirus resistance in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L) plants carrying viral coat protein gene sequences. Transgenic Res. 2004, 13, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindbo, J.A.; Dougherty, W.G. Untranslatable transcripts of the tobacco etch virus coat protein gene sequence can interfere with tobacco etch virus replication in transgenic plants and protoplasts. Virology 1992, 189, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorza, R.; Callahan, A.; Levy, L.; Damsteegt, V.; Webb, K.; Ravelonandro, M. Post-transcriptional gene silencing in plum pox virus resistant transgenic European plum containing the plum pox potyvirus coat protein gene. Transgenic Res. 2001, 10, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, M.; Millar, A.A.; Wood, C.C.; Larkin, P.J. Resistance to Wheat streak mosaic virus generated by expression of an artificial polycistronic microRNA in wheat. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2012, 10, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, T.; Nakazono-Nagaoka, E.; Akita, F.; Uehara-Ichiki, T.; Omura, T.; Sasaya, T. Immunity to Rice black streaked dwarf virus, a plant reovirus, can be achieved in rice plants by RNA silencing against the gene for the viroplasm component protein. Virus Res. 2011, 160, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, T.; Nakazono-Nagaoka, E.; Akita, F.; Wei, T.; Sasaya, T.; Omura, T.; Uehara-Ichiki, T. Hairpin RNA derived from the gene for Pns9, a viroplasm matrix protein of Rice gall dwarf virus, confers strong resistance to virus infection in transgenic rice plants. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 157, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tougou, M.; Furutani, N.; Yamagishi, N.; Shizukawa, Y.; Takahata, Y.; Hidaka, S. Development of resistant transgenic soybeans with inverted repeat-coat protein genes of soybean dwarf virus. Plant Cell Rep. 2006, 25, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.B.; Abbott, D.C.; Waterhouse, P.M. A single copy of a virus-derived transgene encoding hairpin RNA gives immunity to barley yellow dwarf virus. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2000, 1, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucher, E.; Lohuis, D.; van Poppel, P.M.J.A.; Geerts-Dimitriadou, C.; Goldbach, R.; Prins, M. Multiple virus resistance at a high frequency using a single transgene construct. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 3697–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kumar, G.; Dasgupta, I. Simultaneous resistance against the two viruses causing rice tungro disease using RNA interference. Virus Res. 2018, 255, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.X.; Song, Y.Z.; Yin, G.H.; Wen, F.J. Induction of RNA-mediated multiple virus resistance to Potato virus Y, Tobacco mosaic virus and Cucumber mosaic virus. J. Phytopathol. 2009, 157, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Yoshii, M.; Wei, T.; Hirochika, H.; Omura, T. Silencing by RNAi of the gene for Pns12, a viroplasm matrix protein of Rice dwarf virus, results in strong resistance of transgenic rice plants to the virus. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2009, 7, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanda, C.M.R.; Materatski, P.; Campos, M.D.; Clara, M.I.E.; Nolasco, G.; do Rosário Félix, M. Olive mild mosaic virus coat protein and P6 are suppressors of RNA silencing, and their silencing confers resistance against OMMV. Viruses 2018, 10, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Tanti, B.; Patil, B.L.; Mukherjee, S.K.; Sahoo, L. RNAi-derived transgenic resistance to Mungbean yellow mosaic India virus in cowpea. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, M.; Sharma, D.; Trivedi, P.K. Artificial microRNA mediated gene silencing in plants: Progress and perspectives. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 86, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Polydore, S.; Axtell, M.J. More than meets the eye? Factors that affect target selection by plant miRNAs and heterochromatic siRNAs. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 27, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ai, T.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Z.; Zhu, C.X.; Guo, X. Highly efficient virus resistance mediated by artificial microRNAs that target the suppressor of PVX and PVY in plants. Plant Biol. 2011, 13, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.W.; Lin, S.S.; Reyes, J.L.; Chen, K.C.; Wu, H.W.; Ye, S.D.; Chua, N.H. Expression of artificial microRNAs in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana confers virus resistance. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Ye, J.; Fang, R. Artificial microRNA-mediated virus resistance in plants. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6690–6699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Gong, P.; Ziaf, K.; Xiao, F.; Ye, Z. Expression of artificial microRNAs in tomato confers efficient and stable virus resistance in a cell-autonomous manner. Transgenic Res. 2011, 20, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.S.; Wu, H.W.; Elena, S.F.; Chen, K.C.; Niu, Q.W.; Yeh, S.D.; Chen, C.C.; Chua, N.H. Molecular evolution of a viral non-coding sequence under the selective pressure of amiRNA-mediated silencing. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simón-Mateo, C.; García, J.A. MicroRNA-guided processing impairs Plum pox virus replication, but the virus readily evolves to escape this silencing mechanism. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 2429–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lafforgue, G.; Martinez, F.; Niu, Q.W.; Chua, N.H.; Daros, J.A.; Elena, S.F. Improving the effectiveness of artificial MicroRNA (amiR)-mediated resistance against Turnip mosaic virus by combining two amiRs or by targeting highly conserved viral genomic regions. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 8254–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lacombe, S.; Nagasaki, H.; Santi, C.; Duval, D.; Piégu, B.; Bangratz, M.; Breitler, J.C.; Guiderdoni, E.; Brugidou, C.; Hirsch, J.; et al. Identification of precursor transcripts for 6 novel miRNAs expands the diversity on the genomic organisation and expression of miRNA genes in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2008, 8, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, S.; Zhou, X.X.; Xia, J.; Chellappan, P.; Zhou, X.X.; Zhang, X.; Jin, H. Multiple distinct small RNAs originate from the same microRNA precursors. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P. Computational identification of plant MicroRNAs and their targets, including a stress-induced miRNA. Mol. Cell 2004, 14, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butardo, V.M.; Fitzgerald, M.A.; Bird, A.R.; Gidley, M.J.; Flanagan, B.M.; Larroque, O.; Resurreccion, A.P.; Laidlaw, H.K.C.; Jobling, S.A.; Morel, M.K.; et al. Impact of down-regulation of starch branching enzyme IIb in rice by artificial microRNA-and hairpin RNA-mediated RNA silencing. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4927–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, J.; Lin, Y. Improving panicle exertion of rice cytoplasmic male sterile line by combination of artificial microRNA and artificial target mimic. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2013, 11, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Warthmann, N.; Chen, H.; Ossowski, S.; Weigel, D.; Hervé, P. Highly specific gene silencing by artificial miRNAs in rice. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Huang, Y.F.; Huang, S.H.; Kuang, Y.H.; Tung, C.W.; Liao, C.T.; Chuang, W.P. Genomic and phenotypic evaluation of rice susceptible check TN1 collected in Taiwan. Bot. Stud. 2019, 60, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kis, A.; Tholt, G.; Ivanics, M.; Várallyay, É.; Jenes, B.; Havelda, Z. Polycistronic artificial miRNA-mediated resistance to Wheat dwarf virus in barley is highly efficient at low temperature. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Lin, C.; Du, J.; Song, Y.; Jiang, M.; Liu, H.; Zhou, S.; Wen, F.; Zhu, C. Dimeric artificial microRNAs mediate high resistance to RSV and RBSDV in transgenic rice plants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ. Cult. 2016, 126, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecki, O.; Bryan, A.C.; Jawdy, S.S.; Yang, X.; Cheng, Z.M.; Chen, J.G.; Tuskan, G.A. Simultaneous knockdown of six non-family genes using a single synthetic RNAi fragment in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Methods 2016, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cisneros, A.E.; Carbonell, A. Artificial small RNA-based silencing tools for antiviral resistance in plants. Plants 2020, 9, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, D.; Shimamoto, K. Simple RNAi vectors for stable and transient suppression of gene function in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwach, F.; Vaistij, F.E.; Jones, L.; Baulcombe, D.C. An RNA-dependent RNA polymerase prevents meristem invasion by potato virus X and is required for the activity but not the production of a systemic silencing signal. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 1842–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sallaud, C.; Meynard, D.; Van Boxtel, J.; Gay, C.; Bès, M.; Brizard, J.P.; Larmande, P.; Ortega, D.; Raynal, M.; Portefaix, M.; et al. Highly efficient production and characterization of T-DNA plants for rice (Oryza sativa L.) functional genomics. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 1396–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coca, M.; Peñas, G.; Gómez, J.; Campo, S.; Bortolotti, C.; Messeguer, J.; San Segundo, B. Enhanced resistance to the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea conferred by expression of a cecropin A gene in transgenic rice. Planta 2006, 223, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herr, A.J. RNA Polymerase IV Directs Silencing of Endogenous DNA. Science 2005, 308, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Genotypes | Number of Transplanted Plants | Number of Dead Plants | Number of Observed Plants | Number of Symptomatic Plants | Proportion of Symptomatic Plants |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN1 | 110 | 1 | 109 | 49 | 44.95% |
| Nip | 106 | 3 | 103 | 38 | 36.89% |
| pC:empty | 110 | 11 | 99 | 39 | 39.39% |
| pC:amiR12.1 | 110 | 10 | 100 | 38 | 38% |
| pC:amiR120.1 | 110 | 14 | 96 | 39 | 40.63% |
| pC:amiR22.2 | 16 | 0 | 16 | 1 | 6.25% * |
| pC:amiR222.4 | 110 | 5 | 105 | 21 | 20% * |
| pC:amiR1/29.1 | 110 | 10 | 100 | 33 | 33% |
| pC:amiR1/212.3 | 108 | 2 | 106 | 35 | 33.02% |
| pANDA:siRRSV39.9 | 104 | 0 | 104 | 36 | 34.62% |
| pANDA:siRRSV40.3 | 105 | 0 | 105 | 7 | 6.67% * |
| pANDA:siRRSV41.9 | 103 | 4 | 99 | 2 | 2.02% * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lacombe, S.; Bangratz, M.; Ta, H.A.; Nguyen, T.D.; Gantet, P.; Brugidou, C. Optimized RNA-Silencing Strategies for Rice Ragged Stunt Virus Resistance in Rice. Plants 2021, 10, 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102008
Lacombe S, Bangratz M, Ta HA, Nguyen TD, Gantet P, Brugidou C. Optimized RNA-Silencing Strategies for Rice Ragged Stunt Virus Resistance in Rice. Plants. 2021; 10(10):2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102008
Chicago/Turabian StyleLacombe, Severine, Martine Bangratz, Hoang Anh Ta, Thanh Duc Nguyen, Pascal Gantet, and Christophe Brugidou. 2021. "Optimized RNA-Silencing Strategies for Rice Ragged Stunt Virus Resistance in Rice" Plants 10, no. 10: 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102008
APA StyleLacombe, S., Bangratz, M., Ta, H. A., Nguyen, T. D., Gantet, P., & Brugidou, C. (2021). Optimized RNA-Silencing Strategies for Rice Ragged Stunt Virus Resistance in Rice. Plants, 10(10), 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102008






