Recent Progresses in Stable Isotope Analysis of Cellulose Extracted from Tree Rings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Challenges in Development of Stable Isotope Analysis Methods for Cellulose
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.1.1. Pre-Extraction Methods
2.1.2. Chemical Extraction Methods
2.2. Challenges in Developing EA-IRMS Methods for Hydrogen, Carbon, and Oxygen Isotopes
2.2.1. Hydrogen Isotope Analysis of Cellulose
2.2.2. Combustion of Cellulose for Carbon Isotope Analysis
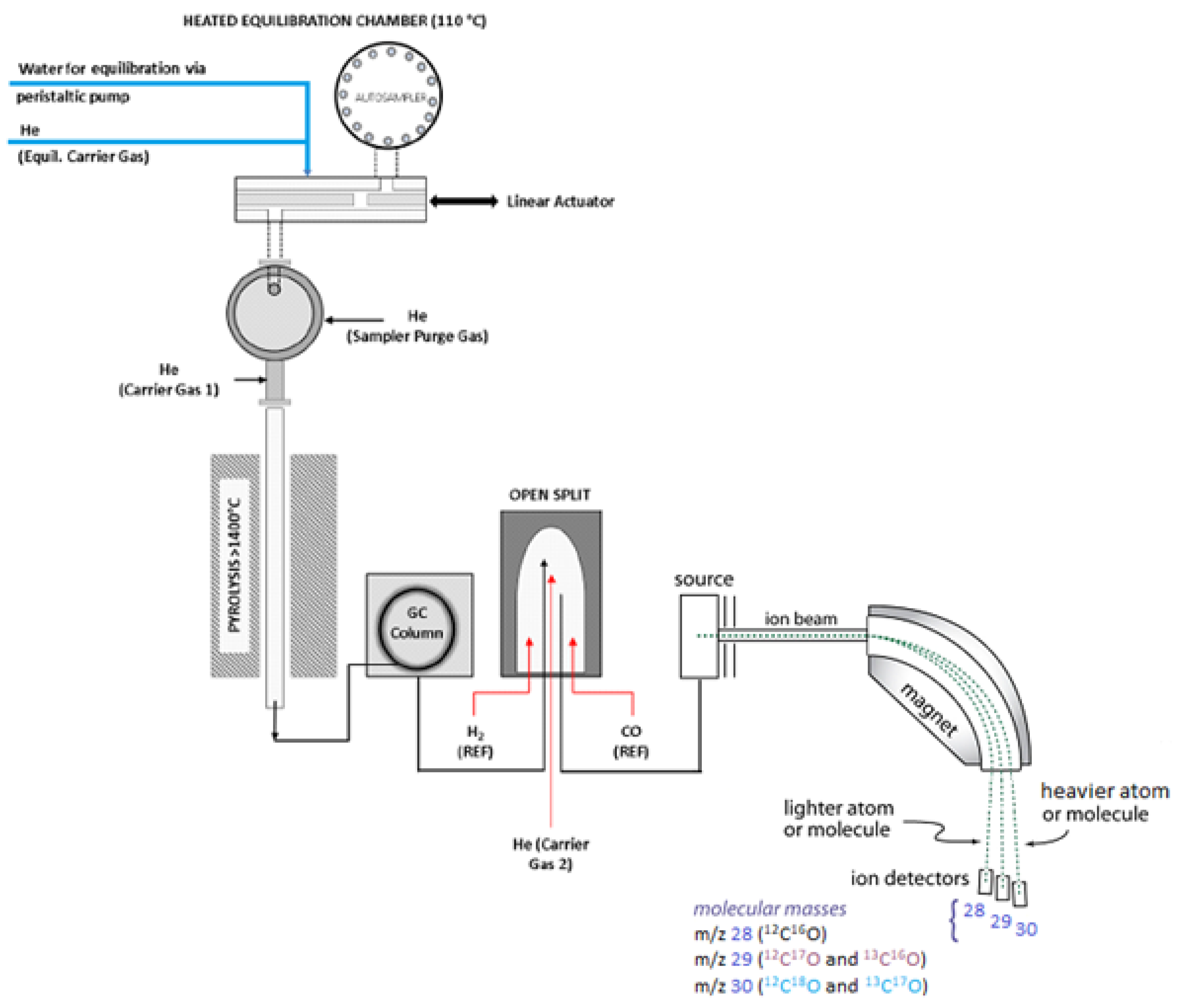
2.2.3. Pyrolysis of Cellulose to Carbon Monoxide for Oxygen Isotope Analysis
3. Assessing the Isotope Ratios of Hydrogen, Carbon, and Oxygen in Cellulose Extracted from Tree Rings and Its Correlation with Climate Variables
3.1. Assessing the Isotope Ratios of Hydrogen in Tree Rings-Cellulose and Its Correlation with Climate Variables
3.2. Assessing the Isotope Ratios of Carbon in Tree Rings-Cellulose and Its Correlation with Climate Variables
3.3. Assessing the Isotope Ratios of Oxygen in Tree Rings-Cellulose and Its Correlation with Climate Variables
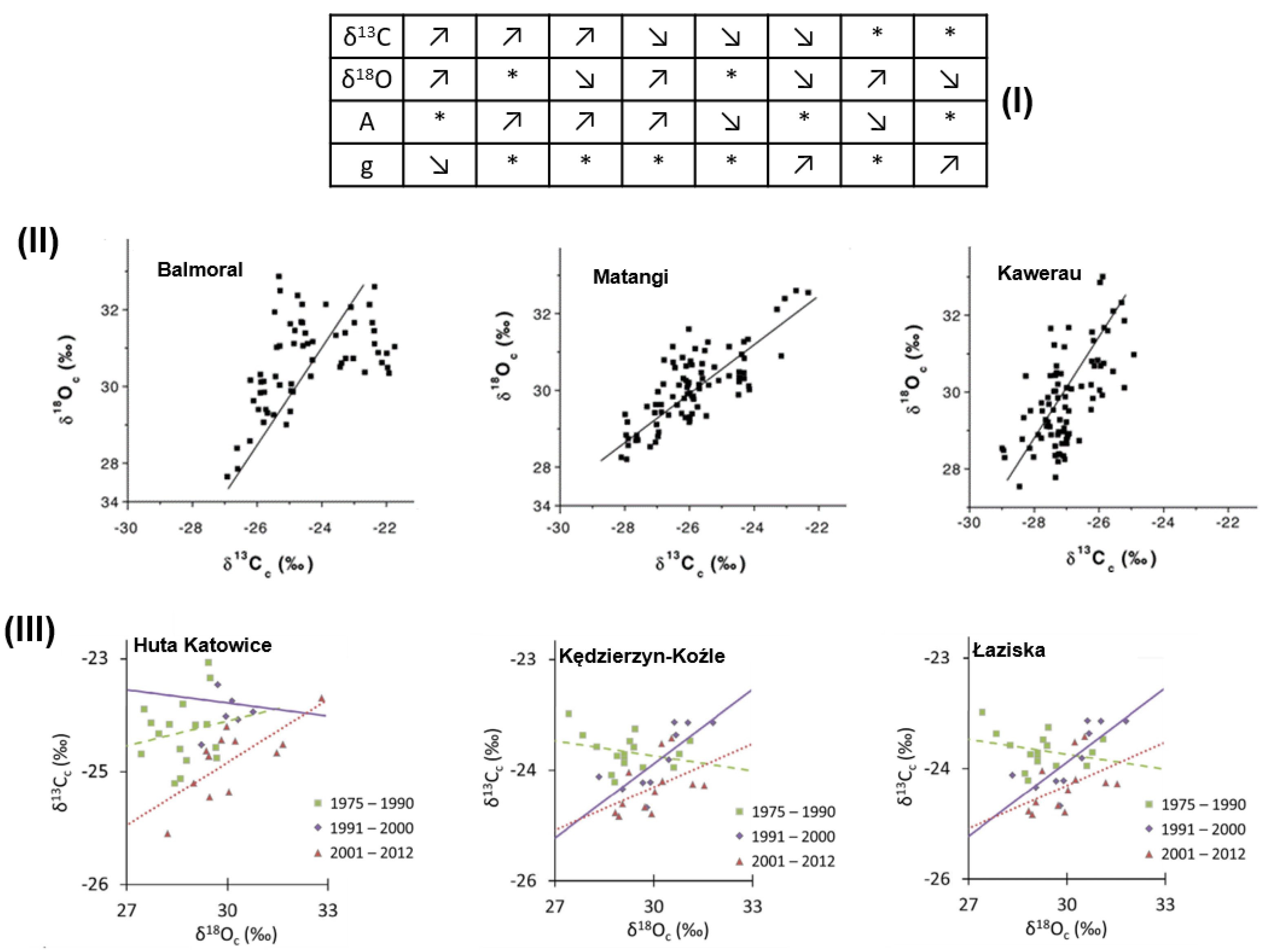
3.4. Multi-Element Isotope Analysis of Tree Rings-Cellulose
3.5. Assessing the Preservation of Isotope Ratios of Hydrogen, Carbon, and Oxygen in Cellulose during Wood Decay
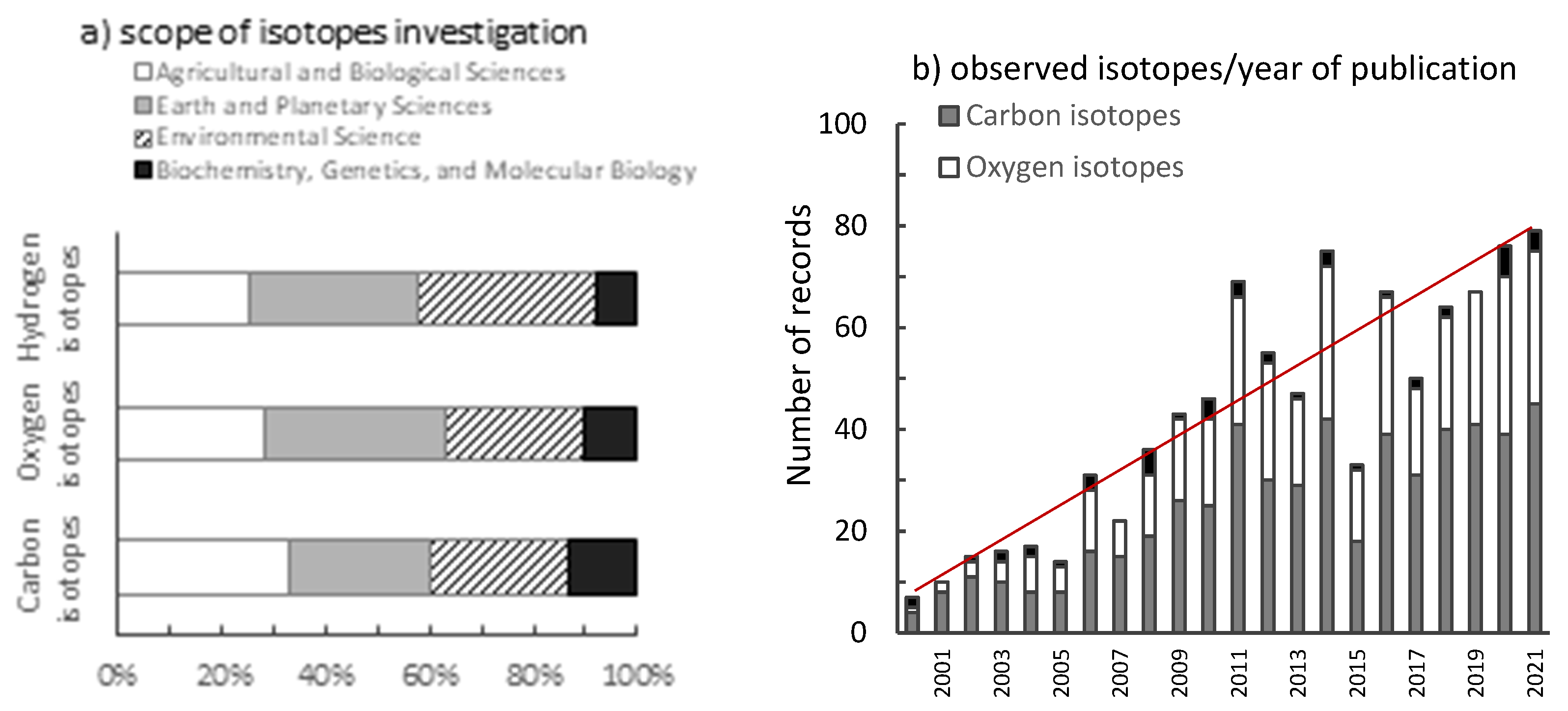
4. Research Trends Regarding Isotope Ratios of Hydrogen, Carbon, and Oxygen in Tree Rings
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; In Press. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Guerrero, A.; Doane, T. Chapter Seven—The Response of Forest Ecosystems to Climate Change. In Climate Change Impacts on Soil Processes and Ecosystem Properties; Horwath, W.R., Kuzyakov, Y.B.T.-D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 185–206. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Chiabai, A.; Silvestri, S.; Nunes, P.A.L.D. Valuing climate change impacts on European forest ecosystems. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 18, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, X.; Fahse, L.; Jactel, H.; Scherer-Lorenzen, M.; García-Valdés, R.; Bugmann, H. Long-term response of forest productivity to climate change is mostly driven by change in tree species composition. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arosio, T.; Ziehmer-Wenz, M.M.; Nicolussi, K.; Schlüchter, C.; Leuenberger, M. Larch Cellulose Shows Significantly Depleted Hydrogen Isotope Values With Respect to Evergreen Conifers in Contrast to Oxygen and Carbon Isotopes. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.C.; Poulter, B.; Saurer, M.; Esper, J.; Huntingford, C.; Helle, G.; Treydte, K.; Zimmermann, N.E.; Schleser, G.H.; Ahlström, A.; et al. Water-use efficiency and transpiration across European forests during the Anthropocene. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loader, N.J.; Robertson, I.; McCarroll, D. Comparison of stable carbon isotope ratios in the whole wood, cellulose and lignin of oak tree-rings. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2003, 196, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borella, S.; Leuenberger, M.C.; Saurer, M. Analysis of δ18O in tree rings: Wood-cellulose comparison and method dependent sensitivity. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 19267–19273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, T.E.; Ehleringer, J.R. Isotopic enrichment of water in the “woody” tissues of plants: Implications for plant water source, water uptake, and other studies which use the stable isotopic composition of cellulose. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 3487–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, A.; Castro, J.; Zamora, R.; Delgado-Huertas, A.; Querejeta, J.I. Growth and stable isotope signals associated with drought-related mortality in saplings of two coexisting pine species. Oecologia 2013, 173, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schollaen, K.; Baschek, H.; Heinrich, I.; Slotta, F.; Pauly, M.; Helle, G. A guideline for sample preparation in modern tree-ring stable isotope research. Dendrochronologia 2017, 44, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCarroll, D.; Loader, N.J. Stable isotopes in tree rings. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2004, 23, 771–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.-L.; Gleixner, G. Carbon isotope effects on key reactions in plant metabolism and 13C-patterns in natural compounds. Stable Isot. 2020, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.-L.; Werner, R.A.; Roßmann, A. 18O Pattern and biosynthesis of natural plant products. Phytochemistry 2001, 58, 9–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.; Thompson, P. Climatic information from 18O/16O analysis of cellulose, lignin and whole wood from tree rings. Nature 1977, 270, 708–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, M.M.; Andrews, T.J.; Farquhar, G.D. Correlations between oxygen isotope ratios of wood constituents of Quercus and Pinus samples from around the world. Funct. Plant Biol. 2001, 28, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.-L.; Grießinger, J.; Gebrekirstos, A.; Fan, Z.-X.; Bräuning, A. Earlywood and Latewood Stable Carbon and Oxygen Isotope Variations in Two Pine Species in Southwestern China during the Recent Decades. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Battipaglia, G.; Jäggi, M.; Saurer, M.; Siegwolf, R.T.W.; Cotrufo, M.F. Climatic sensitivity of δ18O in the wood and cellulose of tree rings: Results from a mixed stand of Acer pseudoplatanus L. and Fagus sylvatica L. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2008, 261, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak, S.; Joachimski, M.M.; Bräuning, A.; Hetzer, T.; Kuhlemann, J. Comparison of whole wood and cellulose carbon and oxygen isotope series from Pinus nigra ssp. laricio (Corsica/France). Dendrochronologia 2011, 29, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schollaen, K.; Heinrich, I.; Neuwirth, B.; Krusic, P.J.; D’Arrigo, R.D.; Karyanto, O.; Helle, G. Multiple tree-ring chronologies (ring width, δ13C and δ18O) reveal dry and rainy season signals of rainfall in Indonesia. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 73, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cullen, L.E.; Macfarlane, C. Comparison of cellulose extraction methods for analysis of stable isotope ratios of carbon and oxygen in plant material. Tree Physiol. 2005, 25, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brookman, T.; Whittaker, T. Experimental assessment of the purity of α-cellulose produced by variations of the Brendel method: Implications for stable isotope (δ13C, δ18O) dendroclimatology. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loader, N.J.; Robertson, I.; Barker, A.C.; Switsur, V.R.; Waterhouse, J.S. An improved technique for the batch processing of small wholewood samples to α-cellulose. Chem. Geol. 1997, 136, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagawa, A.; Sano, M.; Nakatsuka, T.; Ikeda, T.; Kubo, S. An optimized method for stable isotope analysis of tree rings by extracting cellulose directly from cross-sectional laths. Chem. Geol. 2015, 393–394, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaudinski, J.B.; Dawson, T.E.; Quideau, S.; Schuur, E.A.G.; Roden, J.S.; Trumbore, S.E.; Sandquist, D.R.; Oh, S.-W.; Wasylishen, R.E. Comparative Analysis of Cellulose Preparation Techniques for Use with 13C, 14C, and 18O Isotopic Measurements. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 7212–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tao, F.; Liu, Y.; An, N. On the necessity of organic solvent extraction for carbon isotopic analysis of α-cellulose: Implications for environmental reconstructions. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2010, 90, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Nakatsuka, T.; Tazuru-Mizuno, S.; Horikawa, Y.; Sugiyama, J.; Tsuda, T.; Tagami, T. Alpha-cellulose extraction procedure for the tropical tree sungkai (Peronema canescens Jack) by using an improved vessel for reliable paleoclimate reconstruction. Geochem. J. 2014, 48, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, W.; Noormets, A.; King, J.S.; Sun, G.; McNulty, S.; Domec, J.C. An extractive removal step optimized for a high-throughput α-cellulose extraction method for δ13C and δ18O stable isotope ratio analysis in conifer tree rings. Tree Physiol. 2017, 37, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mischel, M.; Esper, J.; Keppler, F.; Greule, M.; Werner, W. δ2H, δ13C and δ18O from whole wood, α-cellulose and lignin methoxyl groups in Pinus sylvestris: A multi-parameter approach. Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2015, 51, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagavciuc, V.; Kern, Z.; Perşoiu, A.; Kesjár, D.; Popa, I. Aerial decay influence on the stable oxygen and carbon isotope ratios in tree ring cellulose. Dendrochronologia 2018, 49, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, G.; O’Leary, M.H.; Berry, J. On the Relationship between Carbon Isotope Discrimination and the Intercellular Carbon Dioxide Concentration in Leaves. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 1982, 9, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, B.; Quilès, F.; Carteret, C.; Brendel, O. Infrared spectroscopy and multivariate analysis to appraise α-cellulose extracted from wood for stable carbon isotope measurements. Chem. Geol. 2014, 381, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harlow, B.A.; Marshall, J.D.; Robinson, A.P. A multi-species comparison of δ13C from whole wood, extractive-free wood and holocellulose. Tree Physiol. 2006, 26, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.M.; Renée Brooks, J.; Lachenbruch, B.; Morrell, J.J.; Voelker, S. Correlation of carbon isotope ratios in the cellulose and wood extractives of Douglas-fir. Dendrochronologia 2008, 26, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendel, O.; Iannetta, P.; Stewart, D. A Rapid and Simple Method to Isolate Pure Alpha-Cellulose. Phytochem. Anal. 2000, 11, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettger, T.; Haupt, M.; Knöller, K.; Weise, S.M.; Waterhouse, J.S.; Rinne, K.T.; Loader, N.J.; Sonninen, E.; Jungner, H.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; et al. Wood Cellulose Preparation Methods and Mass Spectrometric Analyses of δ13C, δ18O, and Nonexchangeable δ2H Values in Cellulose, Sugar, and Starch: An Interlaboratory Comparison. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4603–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNiro, M.J. The effects of different methods of preparing cellulose nitrate on the determination of the D/H ratios of non-exchangeable hydrogen of cellulose. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1981, 54, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Krishnamurthy, R.V.; Epstein, S. Determination of DH ratios of nonexchangeable hydrogen in cellulose: A method based on the cellulose-water exchange reaction. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 4249–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeshima, E.; Nakatsuka, T.; Kagawa, A.; Hiura, T.; Funada, R. Seasonal changes of δD and δ18O in tree-ring cellulose of Quercus crispula suggest a change in post-photosynthetic processes during earlywood growth. Tree Physiol. 2018, 38, 1829–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loader, N.J.; Street-Perrott, F.A.; Daley, T.J.; Hughes, P.D.M.; Kimak, A.; Levanič, T.; Mallon, G.; Mauquoy, D.; Robertson, I.; Roland, T.P.; et al. Simultaneous Determination of Stable Carbon, Oxygen, and Hydrogen Isotopes in Cellulose. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreu-Hayles, L.; Levesque, M.; Martin-Benito, D.; Huang, W.; Harris, R.; Oelkers, R.; Leland, C.; Martin-Fernández, J.; Anchukaitis, K.J.; Helle, G. A high yield cellulose extraction system for small whole wood samples and dual measurement of carbon and oxygen stable isotopes. Chem. Geol. 2019, 504, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badea, S.L.; Ionete, R.E.; Costinel, D.; Nechita, C.; Botu, M.; Botoran, O.R. Changes of carbon-isotope ratios in soil organic matter relative to parent vegetation and site specificity. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2020, 48, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuenberger, M.C.; Filot, M.S. Temperature dependencies of high-temperature reduction on conversion products and their isotopic signatures. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 21, 1587–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, M.M.; Vitali, V.; Schuler, P.; Leuenberger, M.; Saurer, M. More than climate: Hydrogen isotope ratios in tree rings as novel plant physiological indicator for stress conditions. Dendrochronologia 2021, 65, 125788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, M.A.; Werner, R.A.; Sauer, P.E.; Gröcke, D.R.; Leuenberger, M.C.; Wieloch, T.; Schleucher, J.; Kahmen, A. 2H-fractionations during the biosynthesis of carbohydrates and lipids imprint a metabolic signal on the δ2H values of plant organic compounds. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cernusak, L.A.; Barbour, M.M.; Arndt, S.K.; Cheesman, A.W.; English, N.B.; Feild, T.S.; Helliker, B.R.; Holloway-Phillips, M.M.; Holtum, J.A.M.; Kahmen, A.; et al. Stable isotopes in leaf water of terrestrial plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 1087–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, S.; Thompson, P.; Yapp, C.J. Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotopic Ratios in Plant Cellulose. Science 1977, 198, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, L.; DeNiro, M.J. Isotopic Composition of Cellulose from C 3, C 4, and CAM Plants Growing Near One Another. Science 1983, 220, 947–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbour, M.M. Stable oxygen isotope composition of plant tissue: A review. Funct. Plant Biol. 2007, 34, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimak, A.; Kern, Z.; Leuenberger, M. Qualitative Distinction of Autotrophic and Heterotrophic Processes at the Leaf Level by Means of Triple Stable Isotope (C–O–H) Patterns. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazany, T.; Lerman, J.C.; Long, A. Carbon-13 in tree-ring cellulose as an indicator of past climates. Nature 1980, 287, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, I.H.; Poulton, P.R.; Auerswald, K.; Schnyder, H. Intrinsic water-use efficiency of temperate seminatural grassland has increased since 1857: An analysis of carbon isotope discrimination of herbage from the Park Grass Experiment. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 1531–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battipaglia, G.; Saurer, M.; Cherubini, P.; Calfapietra, C.; Mccarthy, H.R.; Norby, R.J.; Francesca Cotrufo, M. Elevated CO2 increases tree-level intrinsic water use efficiency: Insights from carbon and oxygen isotope analyses in tree rings across three forest FACE sites. New Phytol. 2013, 197, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ehleringer, J.R.; Field, C.B.; Lin, Z.F.; Kuo, C.Y. Leaf carbon isotope and mineral composition in subtropical plants along an irradiance cline. Oecologia 1986, 70, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessler, A.; Brandes, E.; Buchmann, N.; Helle, G.; Rennenberg, H.; Barnard, R.L. Tracing carbon and oxygen isotope signals from newly assimilated sugars in the leaves to the tree-ring archive. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 780–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, I.; Switsur, V.R.; Carter, A.H.C.; Barker, A.C.; Waterhouse, J.S.; Briffa, K.R.; Jones, P.D. Signal strength and climate relationships in 13C/12C ratios of tree ring cellulose from oak in east England. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 19507–19516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemming, D.I.; Switsur, V.R.; Waterhouse, J.S.; Heaton, T.H.E.; Carter, A.H.C. Climate variation and the stable carbon isotope composition of tree ring cellulose: An intercomparison of Quercus robur, Fagus sylvatica and Pinus silvestris. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 1998, 50, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kagawa, A.; Naito, D.; Sugimoto, A.; Maximov, T.C. Effects of spatial and temporal variability in soil moisture on widths and δ13C values of eastern Siberian tree rings. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazdur, A.; Nakamura, T.; Pawełczyk, S.; Pawlyta, J.; Piotrowska, N.; Rakowski, A.; Sensuła, B.; Szczepanek, M. Carbon Isotopes in Tree Rings: Climate and the Suess Effect Interferences in the Last 400 Years. Radiocarbon 2007, 49, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roden, J.S.; Lin, G.G.; Ehleringer, J.R. A mechanistic model for interpretation of hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios in tree-ring cellulose. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakir, D.; Sternberg, L.D.S.L. The use of stable isotopes to study ecosystem gas exchange. Oecologia 2000, 123, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternberg, L.; Ellsworth, P.F.V. Divergent Biochemical Fractionation, Not Convergent Temperature, Explains Cellulose Oxygen Isotope Enrichment across Latitudes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brienen, R.J.W.; Helle, G.; Pons, T.L.; Guyot, J.L.; Gloor, M. Oxygen isotopes in tree rings are a good proxy for Amazon precipitation and El Niño-Southern Oscillation variability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16957–16962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, M.; Stott, L.; Buckley, B.; Yoshimura, K.; Ra, K. Indo-Pacific Warm Pool convection and ENSO since 1867 derived from Cambodian pine tree cellulose oxygen isotopes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, 11307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, M.N.; Schrag, D.P. A stable isotope-based approach to tropical dendroclimatology. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 3295–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, T.J.; Pisaric, M.F.J.; Kokelj, S.V.; Edwards, T.W.D. Climatic Signals in δ13C and δ18O of Tree-rings from White Spruce in the Mackenzie Delta Region, Northern Canada. Arctic Antarct. Alp. Res. 2009, 41, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reynolds-Henne, C.E.; Siegwolf, R.T.W.; Treydte, K.S.; Esper, J.; Henne, S.; Saurer, M. Temporal stability of climate-isotope relationships in tree rings of oak and pine (Ticino, Switzerland). Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2007, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagavciuc, V.; Kern, Z.; Ionita, M.; Hartl, C.; Konter, O.; Esper, J.; Popa, I. Climate signals in carbon and oxygen isotope ratios of Pinus cembra tree-ring cellulose from the Călimani Mountains, Romania. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 2539–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, M.M.; Walcroft, A.S.; Farquhar, G.D. Seasonal variation in δ13C and δ18O of cellulose from growth rings of Pinus radiata. Plant Cell Environ. 2002, 25, 1483–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurer, M.; Aellen, K.; Siegwolf, R. Correlating δ13C and δ18O in cellulose of trees. Plant Cell Environ. 1997, 20, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidegger, Y.; Saurer, M.; Bahn, M.; Siegwolf, R. Linking stable oxygen and carbon isotopes with stomatal conductance and photosynthetic capacity: A conceptual model. Oecologia 2000, 125, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurer, M.; Siegwolf, R.T.W.; Schweingruber, F.H. Carbon isotope discrimination indicates improving water-use efficiency of trees in northern Eurasia over the last 100 years. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2004, 10, 2109–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roden, J.; Siegwolf, R. Is the dual-isotope conceptual model fully operational? Tree Physiol. 2012, 32, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sensuła, B.; Wilczyński, S. Tree-ring widths and the stable isotope composition of pine tree-rings as climate indicators in the most industrialised part of Poland during CO2 elevation. Geochronometria 2018, 45, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- English, N.B.; McDowell, N.G.; Allen, C.D.; Mora, C. The effects of α-cellulose extraction and blue-stain fungus on retrospective studies of carbon and oxygen isotope variation in live and dead trees. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 3083–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savard, M.M.; Bégin, C.; Marion, J.; Arseneault, D.; Bégin, Y. Evaluating the integrity of C and O isotopes in sub-fossil wood from boreal lakes. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2012, 348–349, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Carbon-13 Variations in Sequoia Rings and the Atmosphere. Science 1954, 119, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Extraction Method | Tree Species | δ13C [‰] Cellulose | δ18O [‰] Cellulose | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Extraction Methods | |||||
| 1 | Organic solvent pre-extraction of α-cellulose was processed in a Soxhlet system for 6 h with a 2:1 mixture of benzene to methanol, and another 6 h in acetone. Afterwards, extraction with acetic acid-acidified sodium chlorite solution followed by alkaline hydrolysis (modified Jayme-Wise method) | Pinus koraiensis |
| - | [26] |
| 2 | Pre-treatment with 300 + 200 mL acetone, 200 mL mixed solvent (100 mL toluene and 100 mL ethanol) and again 200 mL acetone | Peronema canescens Jack | - | Average values around +19‰ upon solvent extraction | [27] |
| 3 | Pre-treatment in a Soxhlet extractor using a 2:1 mixture of toluene and denatured alcohol, with 8 h of refluxing. Additionally, an acetone pretreatment that was completed by an overnight soaking in deionized water, followed by an 8-day-soaking in acetone (acetone was replaced every 2 days) | Loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.), Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.), Fraser fir (Abies fraseri (Pursh) Poir.), Ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa D.), Douglas fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.) Franco), Black spruce (Picea mariana Mill.) |
|
| [28] |
| Chemical Extraction Methods | |||||
| 4 | Modified Brendel method: hydrolysis with acetic and nitric acid, followed by extraction with ethanol and acetone | Pinus sylvestris | From −24.03 to −22.66‰ | From +32.73 to +34.33‰ | [29] |
| 5 | Dyglime-HCl method | E. maculata, E. botryoides, E. resinifera, P. pinaster C. glaucophylla (wood) |
|
| [21] |
| 6 | Jayme-Wise method with toluene/ethanol extraction, bleaching with NaClO2, and purification with NaOH | Pinus cembra |
|
| [30] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Badea, S.-L.; Botoran, O.R.; Ionete, R.E. Recent Progresses in Stable Isotope Analysis of Cellulose Extracted from Tree Rings. Plants 2021, 10, 2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10122743
Badea S-L, Botoran OR, Ionete RE. Recent Progresses in Stable Isotope Analysis of Cellulose Extracted from Tree Rings. Plants. 2021; 10(12):2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10122743
Chicago/Turabian StyleBadea, Silviu-Laurentiu, Oana Romina Botoran, and Roxana Elena Ionete. 2021. "Recent Progresses in Stable Isotope Analysis of Cellulose Extracted from Tree Rings" Plants 10, no. 12: 2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10122743
APA StyleBadea, S.-L., Botoran, O. R., & Ionete, R. E. (2021). Recent Progresses in Stable Isotope Analysis of Cellulose Extracted from Tree Rings. Plants, 10(12), 2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10122743






