Genetic Diversity Assessment and Cultivar Identification of Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Using the Fluidigm Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
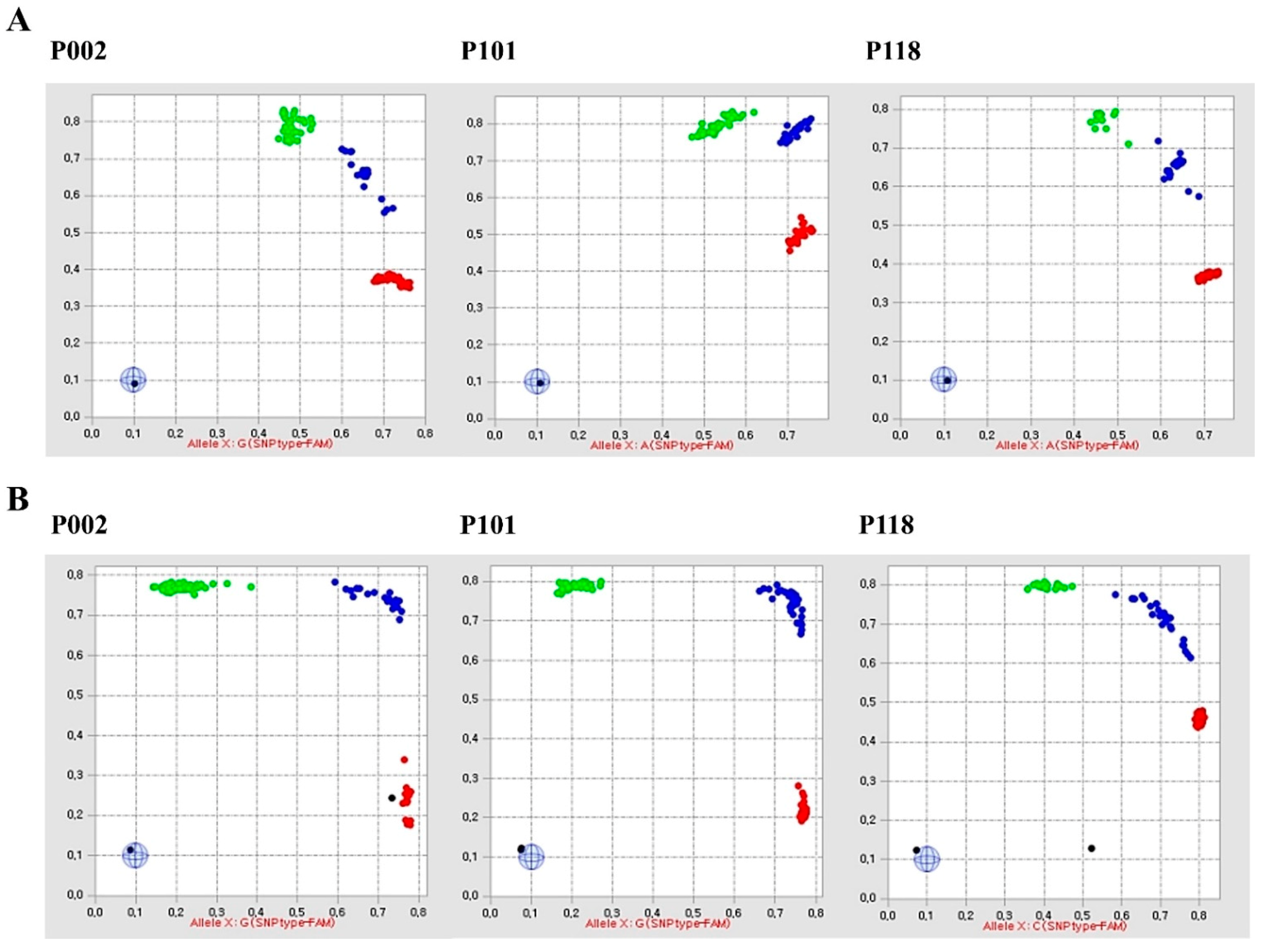
2.1. Fluidigm SNP Assay
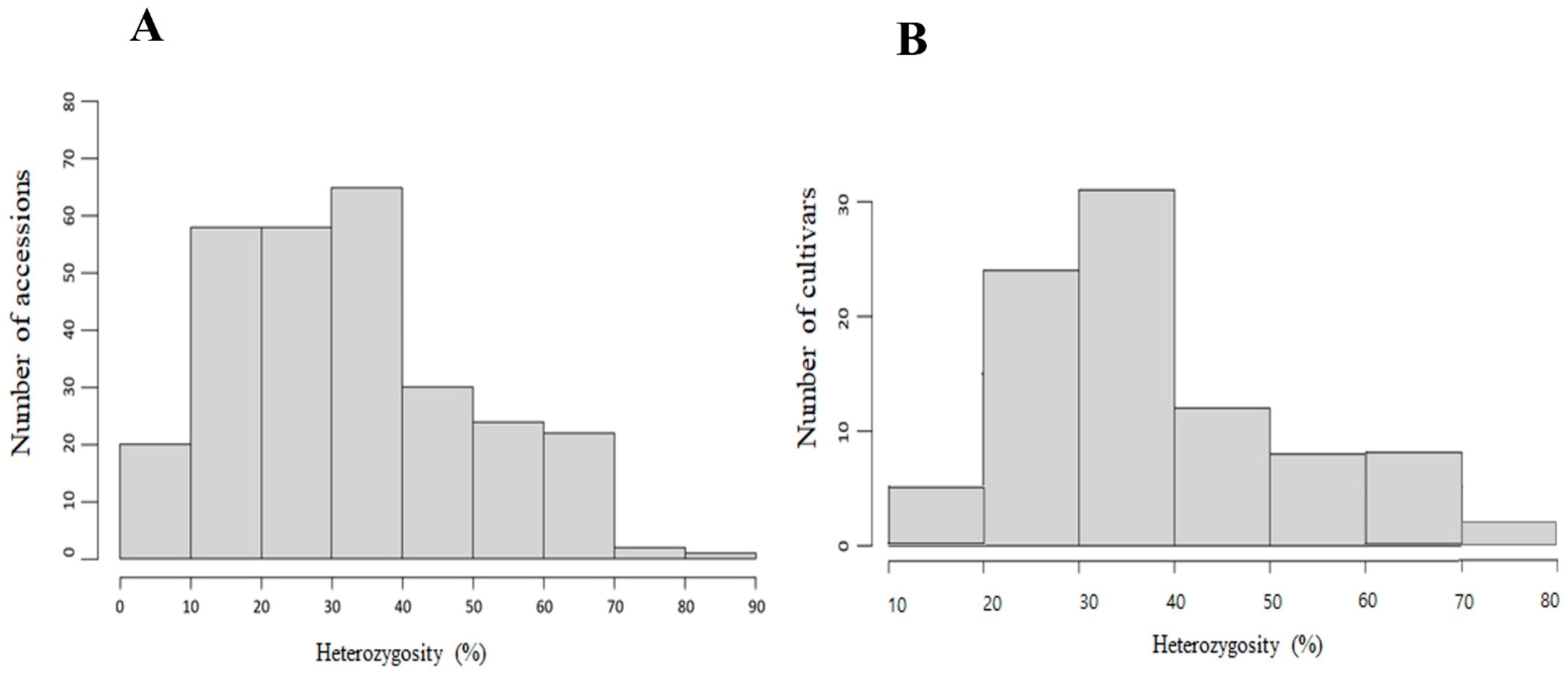
2.2. Population Genetics Analysis of 300 Accessions
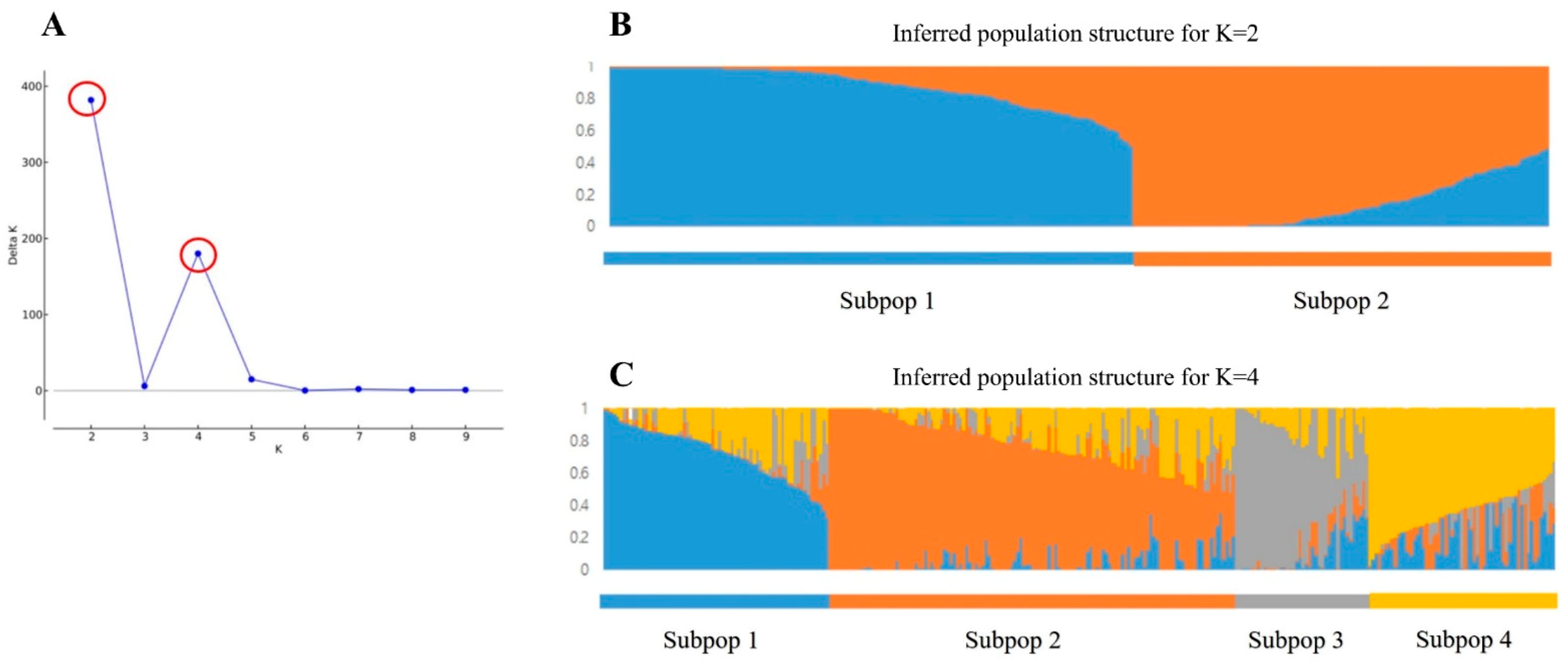
2.2.1. Population Structure
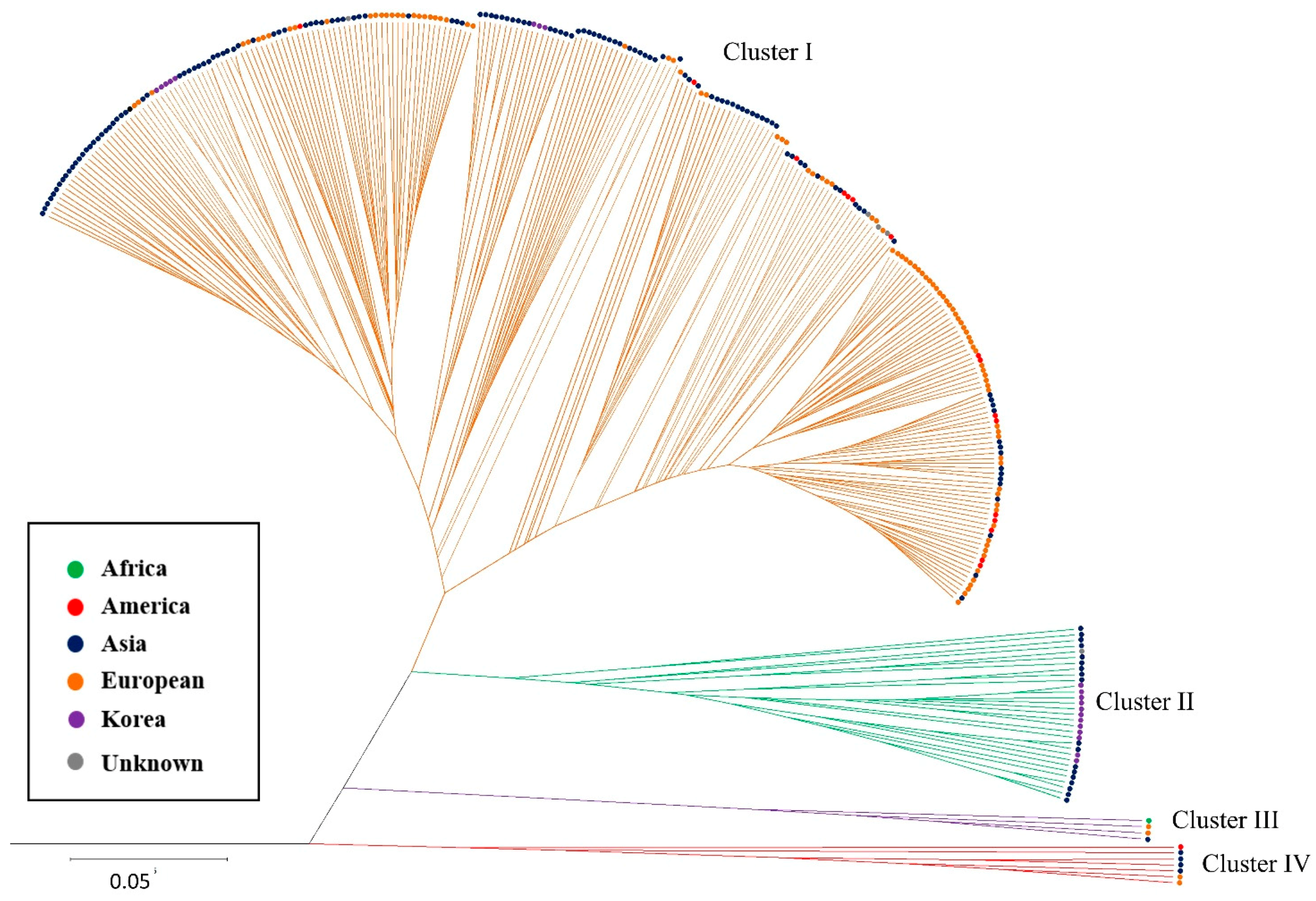
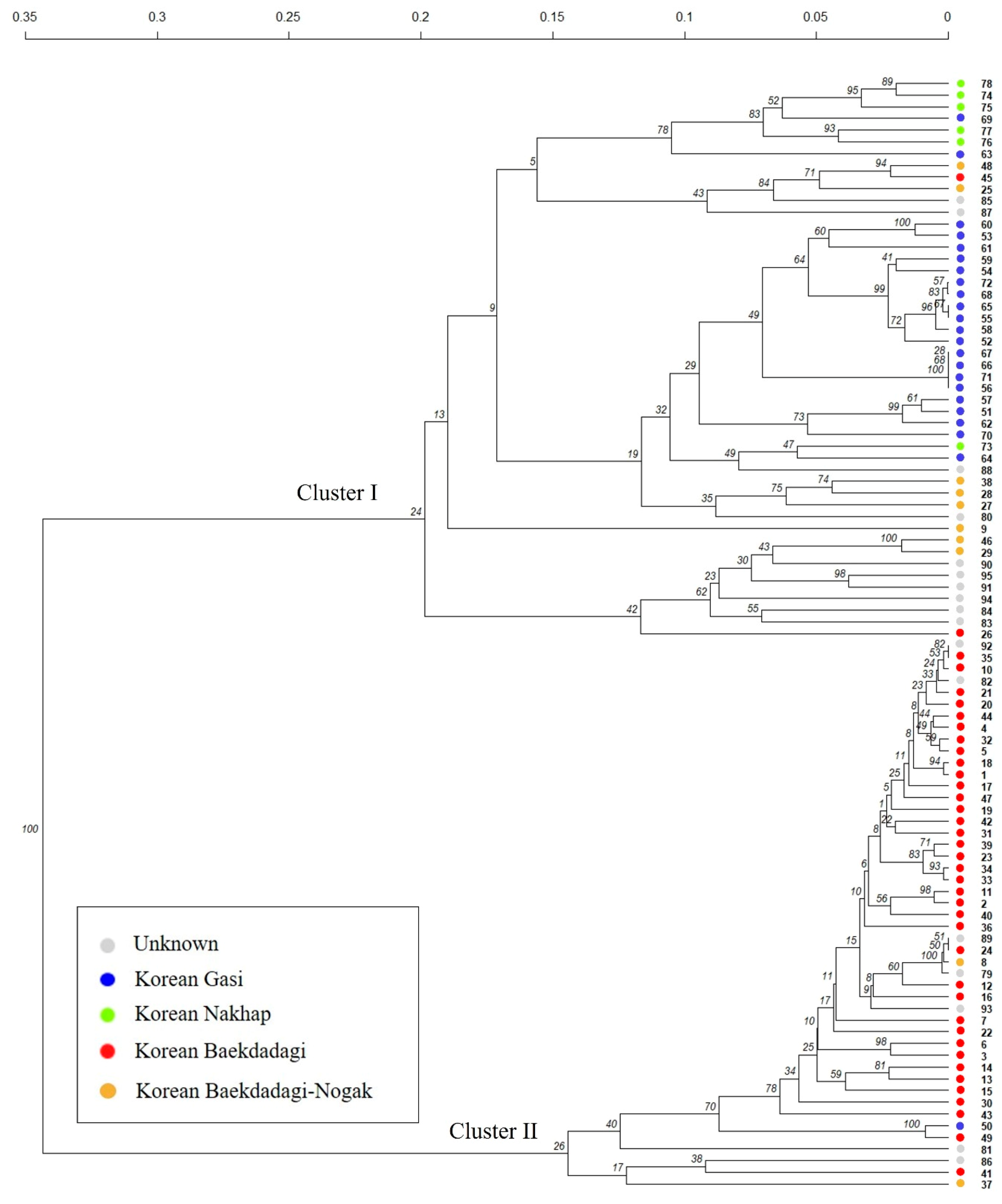
2.2.2. Hierarchical Clustering (HC) Analysis
2.3. Population Genetic Analysis of 95 Commercial F1 Hybrids
2.3.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
2.3.2. HC Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. DNA Extraction
4.3. Fluidigm SNP Assay
4.4. Population Genetics Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naegele, R.P.; Wehner, T.C. Genetic resources of cucumber. In Genetics and Genomics of Cucurbitaceae; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 61–86. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Gu, X.; Fan, W.; Lucas, W.J.; Wang, X.; Xie, B.; Ni, P. The genome of the cucumber, Cucumis sativus L. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Staub, J.E.; Han, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Li, X.; Lu, J.; Miao, H.; Kang, H. An integrated genetic and cytogenetic map of the cucumber genome. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zheng, Y.; Joung, J.-G.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Crasta, O.R.; Sobral, B.W.; Xu, Y.; Huang, S.; Fei, Z. Transcriptome sequencing and comparative analysis of cucumber flowers with different sex types. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitrat, M.; Chauvet, M.; Foury, C. Diversity, history and production of cultivated cucurbits. ISHS Acta Hortic. 1997, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. 2018. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- Dar, A.A.; Mahajan, R.; Lay, P.; Sharma, S. Genetic diversity and population structure of Cucumis sativus L. by using SSR markers. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meglic, V.; Serquen, F.; Staub, J.E. Genetic diversity in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.): I. A reevaluation of the US germplasm collection. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 1996, 43, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Liu, X.; Shen, D.; Miao, H.; Xie, B.; Li, X.; Zeng, P.; Wang, S.; Shang, Y.; Gu, X. A genomic variation map provides insights into the genetic basis of cucumber domestication and diversity. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Seed and Variety Service. 2019. Available online: http://www.seed.go.kr/seed_eng/index..do (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- Punetha, S.; Singh, D.; Singh, N. Genetic diversity assessment of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) genotypes using molecular markers. Electron. J. Plant Breed. 2017, 8, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, J.; Meglic, V. Molecular genetic markers and their legal relevance for cultivar discrimination: A case study in cucumber. HortTechnology 1993, 3, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.; Mackay, I. Implications of using genomic prediction within a high-density SNP dataset to predict DUS traits in barley. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, S.H.; Cockram, J.; Hickey, L.T. Insights into deployment of DNA markers in plant variety protection and registration. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.; Song, Q.; Choi, I.; Specht, J.E.; Hyten, D.; Cregan, P. BARCSoySNP23: A panel of 23 selected SNPs for soybean cultivar identification. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 114, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knerr, L.; Staub, J.; Holder, D.; May, B. Genetic diversity in Cucumis sativus L. assessed by variation at 18 allozyme coding loci. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1989, 78, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, J.E.; Serquen, F.C.; McCreight, J.D. Genetic diversity in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.): III. An evaluation of Indian germplasm. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 1997, 44, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meglic, V.; Staub, J.E. Genetic diversity in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.): II. An evaluation of selected cultivars released between 1846 and 1978. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 1996, 43, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkhuizen, A.; Kennard, W.C.; Havey, M.J.; Staub, J.E. RFLP variation and genetic relationships in cultivated cucumber. Euphytica 1996, 90, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horejsi, T.; Staub, J.E. Genetic variation in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) as assessed by random amplified polymorphic DNA1. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 1999, 46, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xixiang, L.; Dewei, Z.; Yongchen, D.; Di, S.; Qiusheng, K.; Jiangping, S. Studies on genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) germplasm by AFLP technique. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2004, 31, 309. [Google Scholar]
- Cavagnaro, P.F.; Senalik, D.A.; Yang, L.; Simon, P.W.; Harkins, T.T.; Kodira, C.D.; Huang, S.; Weng, Y. Genome-wide characterization of simple sequence repeats in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunziata, A.; Ruggieri, V.; Petriccione, M.; De Masi, L. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms as Practical Molecular Tools to Support European Chestnut Agrobiodiversity Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Luo, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Wen, C. A new Snp genotyping technology target Snp-seq and its application in genetic analysis of cucumber varieties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkel, J. SNP genotyping: Six technologies that keyed a revolution. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.-Y.; Lee, K.H. From SNPs to functional polymorphism: The insight into biotechnology applications. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 49, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhao, X.; Laroche, A.; Lu, Z.-X.; Liu, H.; Li, Z. Genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS), an ultimate marker-assisted selection (MAS) tool to accelerate plant breeding. Front. Plant. Sci. 2014, 5, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, M.J. High-throughput SNP genotyping to accelerate crop improvement. Plant. Breed. Biotechnol. 2014, 2, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, M.; Crenshaw, A.; Hutchinson, A.; Hicks, B.; Yeager, M.; Berndt, S.; Huang, W.-Y.; Hayes, R.B.; Chanock, S.J.; et al. High-throughput single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using nanofluidic Dynamic Arrays. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, M.; Pryor, R.; Palais, R.; Meadows, C.; Erali, M.; Lyon, E.; Wittwer, C. Genotyping of single-nucleotide polymorphisms by high-resolution melting of small amplicons. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Holme, J.; Anthony, J. SNP genotyping: The KASP assay. In Crop Breeding; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.; Park, G.; Jung, J.; Sim, E. SNP Marker Sets for Cultivar Identification in Cucumber and Its Use. Patent No. 10-20202-0126541, 26 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalli-Sforza, L.L.; Edwards, A.W. Phylogenetic analysis. Models and estimation procedures. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1967, 19, 233. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Kim, J.-G.; Kang, B.-C.; Song, K. Assessment of the Genetic Diversity of the Breeding Lines and a Genome Wide Association Study of Three Horticultural Traits Using Worldwide Cucumber (Cucumis spp.) Germplasm Collection. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Comparison of genomic SSR and EST-SSR markers for estimating genetic diversity in cucumber. Biol. Plant. 2011, 55, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M. Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics 1978, 89, 583–590. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Bao, K.; Reddy, U.K.; Bai, Y.; Hammar, S.A.; Jiao, C.; Wehner, T.C.; Ramírez-Madera, A.O.; Weng, Y.; Grumet, R. The USDA cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) collection: Genetic diversity, population structure, genome-wide association studies, and core collection development. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, D.A. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Muse, S.V. PowerMarker: An integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2128–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacklies, W.; Redestig, H.; Scholz, M.; Walther, D.; Selbig, J. pcaMethods—a bioconductor package providing PCA methods for incomplete data. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1164–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamvar, Z.N.; Tabima, J.F.; Grünwald, N.J. Poppr: An R package for genetic analysis of populations with clonal, partially clonal, and/or sexual reproduction. PeerJ 2014, 2, e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Pop1 | Pop2 | Pop3 | Pop4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pop1 | - | 0.3905 | 0.3476 | 0.4708 |
| Pop2 | 0.3905 | - | 0.3793 | 0.5128 |
| Pop3 | 0.3476 | 0.3793 | - | 0.4957 |
| Pop4 | 0.4708 | 0.5128 | 0.4957 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, G.; Choi, Y.; Jung, J.-K.; Shim, E.-J.; Kang, M.-y.; Sim, S.-C.; Chung, S.-M.; Lee, G.P.; Park, Y. Genetic Diversity Assessment and Cultivar Identification of Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Using the Fluidigm Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Assay. Plants 2021, 10, 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020395
Park G, Choi Y, Jung J-K, Shim E-J, Kang M-y, Sim S-C, Chung S-M, Lee GP, Park Y. Genetic Diversity Assessment and Cultivar Identification of Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Using the Fluidigm Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Assay. Plants. 2021; 10(2):395. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020395
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Girim, Yunseo Choi, Jin-Kee Jung, Eun-Jo Shim, Min-young Kang, Sung-Chur Sim, Sang-Min Chung, Gung Pyo Lee, and Younghoon Park. 2021. "Genetic Diversity Assessment and Cultivar Identification of Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Using the Fluidigm Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Assay" Plants 10, no. 2: 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020395
APA StylePark, G., Choi, Y., Jung, J.-K., Shim, E.-J., Kang, M.-y., Sim, S.-C., Chung, S.-M., Lee, G. P., & Park, Y. (2021). Genetic Diversity Assessment and Cultivar Identification of Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Using the Fluidigm Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Assay. Plants, 10(2), 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020395






