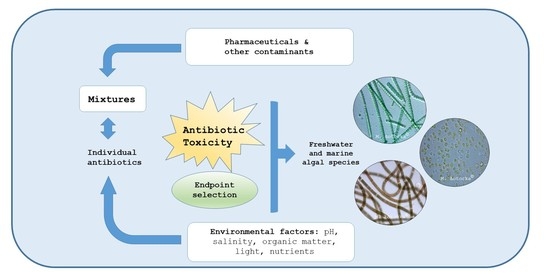
The Toxic Effects of Antibiotics on Freshwater and Marine Photosynthetic Microorganisms: State of the Art
Abstract
Share and Cite
Sharma, L.; Siedlewicz, G.; Pazdro, K. The Toxic Effects of Antibiotics on Freshwater and Marine Photosynthetic Microorganisms: State of the Art. Plants 2021, 10, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10030591
Sharma L, Siedlewicz G, Pazdro K. The Toxic Effects of Antibiotics on Freshwater and Marine Photosynthetic Microorganisms: State of the Art. Plants. 2021; 10(3):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10030591
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Lilianna, Grzegorz Siedlewicz, and Ksenia Pazdro. 2021. "The Toxic Effects of Antibiotics on Freshwater and Marine Photosynthetic Microorganisms: State of the Art" Plants 10, no. 3: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10030591
APA StyleSharma, L., Siedlewicz, G., & Pazdro, K. (2021). The Toxic Effects of Antibiotics on Freshwater and Marine Photosynthetic Microorganisms: State of the Art. Plants, 10(3), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10030591