Xylem Parenchyma—Role and Relevance in Wood Functioning in Trees
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Structure of the Secondary Xylem (Wood)
1.2. Xylem Parenchyma
2. Xylem Parenchyma as a Storage Tissue
2.1. Water Storage
2.2. Carbon Storage
3. Regulation of Xylem Hydraulic Conductivity by the Xylem Parenchyma
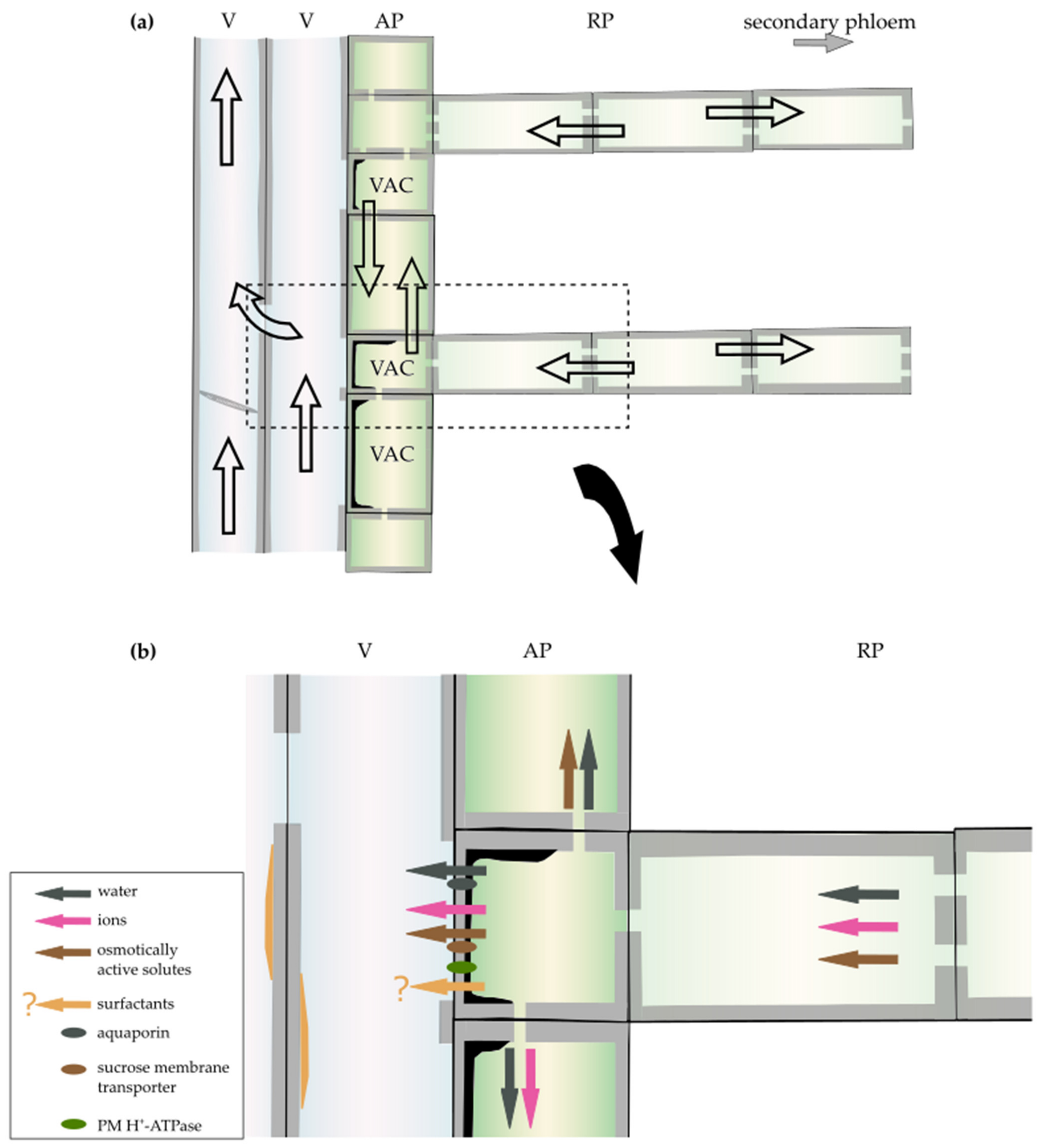
3.1. Embolism Repair
3.2. Ion-Mediated Increase in Xylem Hydraulic Conductance
3.3. Surfactants
4. Role of the Xylem Parenchyma in Defence Mechanism
4.1. Compartmentalisation of Decay in Trees (CODIT) Model
4.2. Heartwood Formation
5. Parenchyma Cells Contribute to the Mechanical Properties of Wood
5.1. Turgor Pressure of Xylem Parenchyma Cells
5.2. The Role of Xylem Rays for the Mechanical Properties of Wood
6. Final Notes
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evert, R.F.; Esau, K.; Esau, K. Esau’s Plant Anatomy: Meristems, Cells, and Tissues of the Plant Body: Their Structure, Function, and Development, 3rd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-471-73843-5. [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz, M.; Smith, R.; Ellis, B. Xylem tissue specification, patterning, and differentiation mechanisms. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H. Regulation of vascular cambium activity. Plant Sci. 2020, 291, 110322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Su, H.; Liu, S.; Du, X.; Xu, C.; Luo, K. Cytokinin signaling localized in phloem noncell-autonomously regulates cambial activity during secondary growth of Populus stems. New Phytol. 2021, 230, 1476–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyree, M.T.; Zimmermann, M.H. Hydraulic Architecture of Whole Plants and Plant Performance. In Xylem Structure and the Ascent of Sap; Springer Series in Wood Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 175–214. ISBN 978-3-642-07768-5. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, W.-G.; Miller, G.; Wallace, I.; Harper, J.; Mittler, R.; Gilroy, S. Orchestrating rapid long-distance signaling in plants with Ca2+, ROS and electrical signals. Plant J. 2017, 90, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lough, T.J.; Lucas, W.J. INTEGRATIVE PLANT BIOLOGY: Role of Phloem Long-Distance Macromolecular Trafficking. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 203–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notaguchi, M.; Okamoto, S. Dynamics of long-distance signaling via plant vascular tissues. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Schepper, V.; De Swaef, T.; Bauweraerts, I.; Steppe, K. Phloem transport: A review of mechanisms and controls. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 4839–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liesche, J.; Patrick, J. An update on phloem transport: A simple bulk flow under complex regulation. F1000Research 2017, 6, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liesche, J.; Schulz, A. Phloem transport in gymnosperms: A question of pressure and resistance. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 43, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, W.J.; Groover, A.; Lichtenberger, R.; Furuta, K.; Yadav, S.-R.; Helariutta, Y.; He, X.-Q.; Fukuda, H.; Kang, J.; Brady, S.; et al. The Plant Vascular System: Evolution, Development and FunctionsF. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2013, 55, 294–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, A.; Thompson, G.A. Phloem Structure and Function. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-0-470-01617-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hacke, U.G.; Sperry, J.S.; Pockman, W.; Davis, S.D.; McCulloh, K.A. Trends in wood density and structure are linked to prevention of xylem implosion by negative pressure. Oecologia 2001, 126, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittermann, J. The evolution of water transport in plants: An integrated approach. Geobiology 2010, 8, 112–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodersen, C.R.; Roddy, A.B.; Wason, J.W.; McElrone, A.J. Functional Status of Xylem through Time. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2019, 70, 407–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choat, B.; Cobb, A.R.; Jansen, S. Structure and function of bordered pits: New discoveries and impacts on whole-plant hydraulic function. New Phytol. 2008, 177, 608–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacke, U.G.; Lachenbruch, B.; Pittermann, J.; Mayr, S.; Domec, J.-C.; Schulte, P.J. The Hydraulic Architecture of Conifers. In Functional and Ecological Xylem Anatomy; Hacke, U., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2015; pp. 39–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacke, U.G.; Sperry, J.S. Functional and ecological xylem anatomy. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2001, 4, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, N.M.; Zwieniecki, M.A. Vascular Transport in Plants; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-1-280-62847-4. [Google Scholar]
- Brodersen, C.R.; McElrone, A.J.; Choat, B.; Matthews, M.A.; Shackel, K.A. The Dynamics of Embolism Repair in Xylem: In Vivo Visualizations Using High-Resolution Computed Tomography. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, J.J.; Iten, W.; Zimmermann, M.H. Studies on the release of sugar into the vessels of sugar maple (Acer saccharum). Can. J. Bot. 1973, 51, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, J.R. Cell-Cell Communication in Wood. In Cell-Cell Channels; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 135–147. ISBN 978-0-387-36058-4. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, H.; Plavcová, L.; Gorai, M.; Klepsch, M.M.; Kotowska, M.; Schenk, H.J.; Jansen, S. Vessel-associated cells in angiosperm xylem: Highly specialized living cells at the symplast–apoplast boundary. Am. J. Bot. 2018, 105, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decourteix, M.; Alves, G.; Brunel, N.; Améglio, T.; Guilliot, A.; Lemoine, R.; Pétel, G.; Sakr, S. JrSUT1, a putative xylem sucrose transporter, could mediate sucrose influx into xylem parenchyma cells and be up-regulated by freeze-thaw cycles over the autumn-winter period in walnut tree (Juglans regia L.). Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavcová, L.; Jansen, S. The Role of Xylem Parenchyma in the Storage and Utilization of Nonstructural Carbohydrates. In Functional and Ecological Xylem Anatomy; Hacke, U., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 209–234. ISBN 978-3-319-15782-5. [Google Scholar]
- Salleo, S.; Trifilò, P.; Esposito, S.; Nardini, A.; Gullo, M.A.L. Starch-to-sugar conversion in wood parenchyma of field-growing Laurus nobilis plants: A component of the signal pathway for embolism repair? Funct. Plant Biol. 2009, 36, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secchi, F.; Pagliarani, C.; Zwieniecki, M. The functional role of xylem parenchyma cells and aquaporins during recovery from severe water stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 40, 858–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, H.; Plavcová, L.; Cvecko, P.; Fichtler, E.; Gillingham, M.A.F.; Martínez-Cabrera, H.I.; McGlinn, D.J.; Wheeler, E.A.; Zheng, J.; Ziemińska, K.; et al. A global analysis of parenchyma tissue fractions in secondary xylem of seed plants. New Phytol. 2016, 209, 1553–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattaway, M.M. The sapwood-heartwood transition. Aust. For. 1952, 16, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrot, M.; Pazdrowski, W.; Szymanski, M. Dynamics of heartwood formation and axial and radial distribution of sapwood and heartwood in stems of European larch (Larix decidua Mill.). J. For. Sci. 2008, 54, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, J.R. Plasmodesmata and pit development in secondary xylem elements. Planta 1982, 155, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlquist, S. Bordered pits in ray cells and axial parenchyma: The histology of conduction, storage, and strength in living wood cells. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2007, 153, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chaffey, N.; Barlow, P. The cytoskeleton facilitates a three-dimensional symplasmic continuum in the long-lived ray and axial parenchyma cells of angiosperm trees. Planta 2001, 213, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedrov, G.B. Functioning Wood. Wulfenia 2012, 19, 57–95. [Google Scholar]
- Sokołowska, K.; Zagórska-Marek, B. Symplasmic, long-distance transport in xylem and cambial regions in branches of Acer pseudoplatanus (Aceraceae) and Populus tremula × P. tremuloides (Salicaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, 1745–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicer, R. Symplasmic networks in secondary vascular tissues: Parenchyma distribution and activity supporting long-distance transport. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1829–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahn, A. Plant Anatomy, 4th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1995; ISBN 978-0-7506-2843-3. [Google Scholar]
- Metzner, R.; Thorpe, M.R.; Breuer, U.; Blümler, P.; Schurr, U.; Schneider, H.U.; Schroeder, W.H. Contrasting dynamics of water and mineral nutrients in stems shown by stable isotope tracers and cryo-SIMS. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 1393–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfautsch, S.; Renard, J.; Tjoelker, M.; Salih, A. Phloem as Capacitor: Radial Transfer of Water into Xylem of Tree Stems Occurs via Symplastic Transport in Ray Parenchyma. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, A.; Schatten, T.; Rennenberg, H. Exchange between phloem and xylem during long distance transport of glutathione in spruce trees [Picea abies [Karst.] L.). J. Exp. Bot. 1994, 45, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bel, A.J.E. Xylem-Phloem Exchange via the Rays: The Undervalued Route of Transport. J. Exp. Bot. 1990, 41, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlquist, S. Living Cells in Wood 3. Overview; Functional Anatomy of the Parenchyma Network. Bot. Rev. 2018, 84, 242–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAWA Committee. IAWA List of of Microscopic Features for Hardwood Identification. IAWA Bull. Ns 1989, 10, 219–332. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, H.; Jansen, S. Secondary Xylem Parenchyma—From Classical Terminology to Functional Traits. IAWA J. 2016, 37, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweingruber, F.H.; Baas, P. Anatomie Europäischer Hölzer: Ein Atlas zur Bestimmung Europäischer Baum-, Strauch- und Zwergstrauchhölzer = Anatomy of European Woods; Haupt: Bern, Switzerland, 1990; ISBN 978-3-258-04258-9. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, H.G.; Grosser, D.; Heinz, I.; Gasson, P.E. IAWA list of microscopic features for softwood identification. IAWA J. 2004, 25, 1–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, C.R.; Chalk, L. Anatomy of the Dicotyledons: Leaves, Stem, and Wood, in Relation to Taxonomy, with Notes on Economic Uses; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, H.; Gillingham, M.A.; Plavcová, L.; Gleason, S.M.; Olson, M.E.; Coomes, D.A.; Fichtler, E.; Klepsch, M.M.; Martínez-Cabrera, H.I.; McGlinn, D.J.; et al. Vessel diameter is related to amount and spatial arrangement of axial parenchyma in woody angiosperms. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 41, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavcová, L.; Hoch, G.; Morris, H.; Ghiasi, S.; Jansen, S. The amount of parenchyma and living fibers affects storage of nonstructural carbohydrates in young stems and roots of temperate trees. Am. J. Bot. 2016, 103, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olano, J.M.; Arzac, A.; García-Cervigón, A.I.; von Arx, G.; Rozas, V. New star on the stage: Amount of ray parenchyma in tree rings shows a link to climate. New Phytol. 2013, 198, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angyalossy, V.; Angeles, G.; Pace, M.R.; Lima, A.C.; Dias-Leme, C.L.; Lohmann, L.G.; Madero-Vega, C. An overview of the anatomy, development and evolution of the vascular system of lianas. Plant Ecol. Divers. 2012, 5, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapotin, S.M.; Razanameharizaka, J.H.; Holbrook, N.M.; Wu, X.; McSteen, P. A biomechanical perspective on the role of large stem volume and high water content in baobab trees (Adansonia spp.; Bombacaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2006, 93, 1251–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.; Miguel-Cha, R.S.; Terrazas, T. Xylem Conductivity and Anatomical Traits in Diverse Lianas and Small Tree Species from a Tropical Forest of Southwest Mexico. Int. J. Bot. 2009, 5, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlquist, S.J. Comparative Wood Anatomy: Systematic, Ecological, and Evolutionary Aspects of Dicotyledon Wood; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; ISBN 978-3-662-04578-7. [Google Scholar]
- Sauter, J.J.; Kloth, S. Plasmodesmatal frequency and radial translocation rates in ray cells of poplar (Populus × canadensis Moench ‘robusta’). Planta 1986, 168, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowska, K. Symplasmic Transport in Wood: The Importance of Living Xylem Cells. In Symplasmic Transport in Vascular Plants; Sokołowska, K., Sowiński, P., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 101–132. ISBN 978-1-4614-7764-8. [Google Scholar]
- Czaninski, Y. Vessel-associated Cells. Int. Assoc. Wood Anat. Bull. 1977, 3, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, H.J. Funktionelle Histologie Der Sekundären Sprossachse. Encyclopedia of Plant Anatomy, 2nd ed.; Gebrüder Borntraeger: Berlin, Germany, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, J.R.; Cooper, P.; Bonner, L.J. The Protective Layer as an Extension of the Apoplast. IAWA J. 1993, 14, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, K.; Wisniewski, M. Development of the Amorphous Layer (Protective Layer) in Xylem Parenchyma of cv. Golden Delicious Apple, cv. Loring Peach, and Willow. Am. J. Bot. 1989, 76, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słupianek, A.; Kasprowicz-Maluśki, A.; Myśkow, E.; Turzańska, M.; Sokołowska, K. Endocytosis acts as transport pathway in wood. New Phytol. 2018, 222, 1846–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essiamah, S.; Eschrich, W. Changes of Starch Content in the Storage Tissues of Deciduous Trees during Winter and Spring. IAWA J. 1985, 6, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, G.; Sauter, J.J.; Julien, J.-L.; Fleurat-Lessard, P.; Améglio, T.; Guillot, A.; Pétel, G.; Lacointe, A. Plasma membrane H+-ATPase, succinate and isocitrate dehydrogenases activities of vessel-associated cells in walnut trees. J. Plant Physiol. 2001, 158, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, G.; Decourteix, M.; Fleurat-Lessard, P.; Sakr, S.; Bonhomme, M.; Améglio, T.; Lacointe, A.; Julien, J.-L.; Petel, G.; Guilliot, A. Spatial activity and expression of plasma membrane H+-ATPase in stem xylem of walnut during dormancy and growth resumption. Tree Physiol. 2007, 27, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakr, S.; Alves, G.; Morillon, R.; Maurel, K.; Decourteix, M.; Guilliot, A.; Fleurat-Lessard, P.; Julien, J.-L.; Chrispeels, M.J. Plasma Membrane Aquaporins Are Involved in Winter Embolism Recovery in Walnut Tree. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Funada, R.; Sano, Y.; Ohtani, J. The Differentiation of Contact Cells and Isolation Cells in the Xylem Ray Parenchyma of Populus maximowiczii. Ann. Bot. 1999, 84, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nardini, A.; Gullo, M.A.L.; Salleo, S. Refilling embolized xylem conduits: Is it a matter of phloem unloading? Plant Sci. 2011, 180, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasella, M.; Petrussa, E.; Petruzzellis, F.; Nardini, A.; Casolo, V. The Possible Role of Non-Structural Carbohydrates in the Regulation of Tree Hydraulics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, N.M. Stem water storage. In Plant Stems: Physiology and Functional Morphology; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1995; pp. 151–174. [Google Scholar]
- Charrier, G.; Ngao, J.; Saudreau, M.; Améglio, T. Effects of environmental factors and management practices on microclimate, winter physiology, and frost resistance in trees. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.D.; Carbone, M.S.; Keenan, T.; Czimczik, C.I.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Murakami, P.; Schaberg, P.G.; Xu, X. Seasonal dynamics and age of stemwood nonstructural carbohydrates in temperate forest trees. New Phytol. 2013, 197, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tixier, A.; Gambetta, G.A.; Godfrey, J.; Orozco, J.; Zwieniecki, M.A. Non-structural Carbohydrates in Dormant Woody Perennials; The Tale of Winter Survival and Spring Arrival. Front. For. Glob. Chang. 2019, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, J. Respiratory and phosphatase activities in contact cells of wood rays and their possible role in sugar secretion. Z. Für Pflanzenphysiol. 1972, 67, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, T.; Cohen, S.; Paudel, I.; Preisler, Y.; Rotenberg, E.; Yakir, D. Diurnal dynamics of water transport, storage and hydraulic conductivity in pine trees under seasonal drought. iForest Biogeosci. For. 2016, 9, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, S.B.; Wullschleger, S.; Nosal, M. Diurnal and seasonal changes in stem increment and water use by yellow poplar trees in response to environmental stress. Tree Physiol. 2003, 23, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinzer, F.C.; James, S.A.; Goldstein, G.; Woodruff, D. Whole-tree water transport scales with sapwood capacitance in tropical forest canopy trees. Plant Cell Environ. 2003, 26, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinzer, F.C.; Johnson, D.M.; Lachenbruch, B.; McCulloh, K.A.; Woodruff, D.R. Xylem hydraulic safety margins in woody plants: Coordination of stomatal control of xylem tension with hydraulic capacitance. Funct. Ecol. 2009, 23, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweifel, R.; Item, H.; Häsler, R. Link between diurnal stem radius changes and tree water relations. Tree Physiol. 2001, 21, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.B. Wound Healing by Exposed Secondary Xylem in Adansonia (Bombacaceae). IAWA J. 1981, 2, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, E.T.; Sharifi, M.R.; Rundel, P.W.; Forseth, I.N.; Ehleringer, J.R. Water relations of stem succulent trees in north-central Baja California. Oecologia 1990, 82, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewers, F.W.; Fisher, J.B.; Fichtner, K. Water flux and xylem structure in vines. In The Biology of Vines; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991; pp. 127–160. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, J.B.; Ewers, F.W. Structural responses to stem injury in vines. In The Biology of Vines; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991; pp. 99–124. [Google Scholar]
- Borchert, R. Soil and Stem Water Storage Determine Phenology and Distribution of Tropical Dry Forest Trees. Ecology 1994, 75, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchert, R.; Hagnauer, W.; Rivera, G. Modification of Vegetative Phenology in a Tropical Semi-deciduous Forest by Abnormal Drought and Rain1. Biotropica 2002, 34, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchert, R.; Pockman, W. Water storage capacitance and xylem tension in isolated branches of temperate and tropical trees. Tree Physiol. 2005, 25, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baerdemaeker, N.J.F.; Hias, N.; Bulcke, J.V.D.; Keulemans, W.; Steppe, K. The effect of polyploidization on tree hydraulic functioning. Am. J. Bot. 2018, 105, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, H.; Trumbore, S. Understanding the roles of nonstructural carbohydrates in forest trees—From what we can measure to what we want to know. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 386–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, G.; Richter, A.; Körner, C. Non-structural carbon compounds in temperate forest trees. Plant Cell Environ. 2003, 26, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höll, W. Distribution, fluctuation and metabolism of food reserves in the wood of trees. In Cell & Molecular Biology of Wood Formation; Scientific Publishers Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2000; pp. 347–361. [Google Scholar]
- Pratt, R.B.; Jacobsen, A.L. Conflicting demands on angiosperm xylem: Tradeoffs among storage, transport and biomechanics. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, J.J.; Van Cleve, B. Storage, mobilization and interrelations of starch, sugars, protein and fat in the ray storage tissue of poplar trees. Trees 1994, 8, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifilò, P.; Kiorapostolou, N.; Petruzzellis, F.; Vitti, S.; Petit, G.; Gullo, M.A.L.; Nardini, A.; Casolo, V. Hydraulic recovery from xylem embolism in excised branches of twelve woody species: Relationships with parenchyma cells and non-structural carbohydrates. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 139, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.M.; McCulloh, K.A.; Woodruff, D.R.; Meinzer, F.C. Hydraulic safety margins and embolism reversal in stems and leaves: Why are conifers and angiosperms so different? Plant Sci. 2012, 195, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furze, M.E.; Huggett, B.A.; Aubrecht, D.M.; Stolz, C.D.; Carbone, M.S.; Richardson, A.D. Whole-tree nonstructural carbohydrate storage and seasonal dynamics in five temperate species. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 1466–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, A.D.; Carbone, M.S.; Huggett, B.A.; Furze, M.E.; Czimczik, C.I.; Walker, J.C.; Xu, X.; Schaberg, P.G.; Murakami, P. Distribution and mixing of old and new nonstructural carbon in two temperate trees. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, A.; Hoch, G. Height-related growth declines in ponderosa pine are not due to carbon limitation. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trumbore, S.; Czimczik, C.I.; Sierra, C.A.; Muhr, J.; Xu, X. Non-structural carbon dynamics and allocation relate to growth rate and leaf habit in California oaks. Tree Physiol. 2015, 35, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinnott, E.W. Factors Determining Character and Distribution of Food Reserve in Woody Plants. Int. J. Plant Sci. 1918, 66, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, G.; Popp, M.; Körner, C. Altitudinal increase of mobile carbon pools in Pinus cembra suggests sink limitation of growth at the Swiss treeline. Oikos 2002, 98, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Murata, N. Enhancement of tolerance of abiotic stress by metabolic engineering of betaines and other compatible solutes. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002, 5, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, M.; Leuzinger, S.; Philipson, C.; Tay, J.; Hector, A. Drought survival of tropical tree seedlings enhanced by non-structural carbohydrate levels. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwieniecki, M.A.; Holbrook, N.M. Confronting Maxwell’s demon: Biophysics of xylem embolism repair. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardini, A.; Salleo, S.; Jansen, S. More than just a vulnerable pipeline: Xylem physiology in the light of ion-mediated regulation of plant water transport. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4701–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroock, A.D.; Pagay, V.V.; Zwieniecki, M.; Holbrook, N.M. The Physicochemical Hydrodynamics of Vascular Plants. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2014, 46, 615–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochard, H.; Cruiziat, P.; Tyree, M.T. Use of Positive Pressures to Establish Vulnerability Curves. Plant Physiol. 1992, 100, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, S.; Kartusch, B.; Kikuta, S. Evidence for Air-Seeding: Watching the Formation of Embolism in Conifer Xylem. J. Plant Hydraul. 2014, 1, e004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyree, M.T. The Cohesion-Tension theory of sap ascent: Current controversies. J. Exp. Bot. 1997, 48, 1753–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickard, W.F. The ascent of sap in plants. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1981, 37, 181–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milburn, J.A. Cavitation. A review: Past, present and future. In Water Transport in Plants under Climatic Stress; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993; pp. 14–26. [Google Scholar]
- Tyree, M.T.; Salleo, S.; Nardini, A.; Gullo, M.A.L.; Mosca, R. Refilling of Embolized Vessels in Young Stems of Laurel. Do We Need a New Paradigm? Plant Physiol. 1999, 120, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochard, H.; Tyree, M.T. Xylem dysfunction in Quercus: Vessel sizes, tyloses, cavitation and seasonal changes in embolism. Tree Physiol. 1990, 6, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuta, S.B.; Gullo, M.A.L.; Nardini, A.; Richter, H.; Salleo, S. Ultrasound acoustic emissions from dehydrating leaves of deciduous and evergreen trees. Plant Cell Environ. 1997, 20, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencuccini, M.; Comstock, J.P. Vulnerability to cavitation in populations of two desert species, Hymenoclea salsola and Ambrosia dumosa, from different climatic regions. J. Exp. Bot. 1997, 48, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodribb, T.J.; Cochard, H. Hydraulic Failure Defines the Recovery and Point of Death in Water-Stressed Conifers. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Calcerrada, J.; Li, M.; López, R.; Cano, F.J.; Oleksyn, J.; Atkin, O.; Pita, P.; Aranda, I.; Gil, L. Drought-induced shoot dieback starts with massive root xylem embolism and variable depletion of nonstructural carbohydrates in seedlings of two tree species. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperry, J.S.; Adler, F.R.; Campbell, G.S.; Comstock, J.P. Limitation of plant water use by rhizosphere and xylem conductance: Results from a model. Plant Cell Environ. 1998, 21, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacke, U.G.; Sperry, J.S. Limits to xylem refilling under negative pressure in Laurus nobilis and Acer negundo. Plant Cell Environ. 2003, 26, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleo, S.; Gullo, M.A.L.; Paoli, D.; Zippo, M. Xylem recovery from cavitation-induced embolism in young plants of Laurus nobilis: A possible mechanism. New Phytol. 1996, 132, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneda, H.; Sperry, J.S. A case-study of water transport in co-occurring ring- versus diffuse-porous trees: Contrasts in water-status, conducting capacity, cavitation and vessel refilling. Tree Physiol. 2008, 28, 1641–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwieniecki, M.; Hutyra, L.; Thompson, M.V.; Holbrook, N.M. Dynamic changes in petiole specific conductivity in red maple (Acer rubrum L.), tulip tree (Liriodendron tulipifera L.) and northern fox grape (Vitis labrusca L.). Plant Cell Environ. 2000, 23, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleo, S.; Trifilò, P.; Gullo, M.A.L. Vessel wall vibrations: Trigger for embolism repair? Funct. Plant Biol. 2008, 35, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secchi, F.; Zwieniecki, M. Sensing embolism in xylem vessels: The role of sucrose as a trigger for refilling. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secchi, F.; Gilbert, M.E.; Zwieniecki, M. Transcriptome Response to Embolism Formation in Stems of Populus trichocarpa Provides Insight into Signaling and the Biology of Refilling. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, N.M.; Zwieniecki, M. Embolism Repair and Xylem Tension: Do We Need a Miracle? Plant Physiol. 1999, 120, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clearwater, M.J.; Goldstein, G. Embolism Repair and Long Distance Water Transport. In Vascular Transport in Plants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 375–399. ISBN 978-0-12-088457-5. [Google Scholar]
- Salleo, S.; Trifilò, P.; Gullo, M.A.L. Phloem as a possible major determinant of rapid cavitation reversal in stems of Laurus nobilis (laurel). Funct. Plant Biol. 2006, 33, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleo, S.; Gullo, M.A.L.; Trifilo, P.; Nardini, A. New evidence for a role of vessel-associated cells and phloem in the rapid xylem refilling of cavitated stems of Laurus nobilis L. Plant Cell Environ. 2004, 27, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secchi, F.; Zwieniecki, M. Patterns of PIP gene expression in Populus trichocarpa during recovery from xylem embolism suggest a major role for the PIP1 aquaporin subfamily as moderators of refilling process. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipfer, T.; Reyes, C.; Earles, J.M.; Berry, Z.C.; Johnson, D.M.; Brodersen, C.R.; McElrone, A.J. Spatiotemporal Coupling of Vessel Cavitation and Discharge of Stored Xylem Water in a Tree Sapling. Plant Physiol. 2019, 179, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canny, M.J. Vessel contents during transpiration-embolisms and refilling. Am. J. Bot. 1997, 84, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canny, M.J. Applications of the compensating pressure theory of water transport. Am. J. Bot. 1998, 85, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comstock, J.P. Why Canny’s Theory Doesn’t Hold Water. Am. J. Bot. 1999, 86, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westhoff, M.; Schneider, H.; Zimmermann, D.; Mimietz, S.; Stinzing, A.; Wegner, L.; Kaiser, W.; Krohne, G.; Shirley, S.; Jakob, P.; et al. The mechanisms of refilling of xylem conduits and bleeding of tall birch during spring. Plant Biol. 2008, 10, 604–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhoff, M.; Zimmermann, D.; Schneider, H.; Wegner, L.H.; Geßner, P.; Jakob, P.; Bamberg, E.; Shirley, S.; Bentrup, F.-W. Evidence for discontinuous water columns in the xylem conduit of tall birch trees. Plant Biol. 2009, 11, 307–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choat, B.; Brodersen, C.R.; McElrone, A.J. Synchrotron X-ray microtomography of xylem embolism in Sequoia sempervirens saplings during cycles of drought and recovery. New Phytol. 2015, 205, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, S.; Wolfschwenger, M.; Bauer, H. Winter-drought induced embolism in Norway spruce (Picea abies) at the Alpine timberline. Physiol. Plant. 2002, 115, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperry, J.S. Winter xylem embolism and spring recovery in Betula cordifolia, Fagus grandifolia, Abies balsamea and Picea rubens. In Water Transport in Plants under Climate Stress; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993; pp. 86–98. [Google Scholar]
- Sperry, J.S.; Nichols, K.L.; Sullivan, J.E.M.; Eastlack, S.E. Xylem Embolism in Ring-Porous, Diffuse-Porous, and Coniferous Trees of Northern Utah and Interior Alaska. Ecology 1994, 75, 1736–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiorapostolou, N.; Da Sois, L.; Petruzzellis, F.; Savi, T.; Trifilò, P.; Nardini, A.; Petit, G. Vulnerability to xylem embolism correlates to wood parenchyma fraction in angiosperms but not in gymnosperms. Tree Physiol. 2019, 39, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascó, A.; Nardini, A.; Gortan, E.; Salleo, S. Ion-mediated increase in the hydraulic conductivity of Laurel stems: Role of pits and consequences for the impact of cavitation on water transport. Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 1946–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardini, A.; Gascó, A.; Trifilò, P.; Gullo, M.A.L.; Salleo, S. Ion-mediated enhancement of xylem hydraulic conductivity is not always suppressed by the presence of Ca2+ in the sap. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2609–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ieperen, W.; Van Meeteren, U.; Van Gelder, H. Fluid ionic composition influences hydraulic conductance of xylem conduits. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwieniecki, M.A. Hydrogel Control of Xylem Hydraulic Resistance in Plants. Science 2001, 291, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwieniecki, M.; Orians, C.M.; Melcher, P.J.; Holbrook, N.M. Ionic control of the lateral exchange of water between vascular bundles in tomato. J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zimmermann, M.H. Hydraulic architecture of some diffuse-porous trees. Can. J. Bot. 1978, 56, 2286–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Holbrook, N.M.; Zwieniecki, M.A. Ion Induced Changes in the Structure of Bordered Pit Membranes. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifilò, P.; Barbera, P.M.; Raimondo, F.; Nardini, A.; Gullo, M.A.L. Coping with drought-induced xylem cavitation: Coordination of embolism repair and ionic effects in three Mediterranean evergreens. Tree Physiol. 2014, 34, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, A.H.; Wegner, L.H. Regulatory mechanisms of ion channels in xylem parenchyma cells. J. Exp. Bot. 1997, 48, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromard, L.; Babin, V.; Fleurat-Lessard, P.; Fromont, J.C.; Serrano, R.; Bonnemain, J.L. Control of Vascular Sap pH by the Vessel-Associated Cells in Woody Species (Physiological and Immunological Studies). Plant Physiol. 1995, 108, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwieniecki, M.A.; Melcher, P.J.; Feild, T.S.; Holbrook, N.M. A potential role for xylem-phloem interactions in the hydraulic architecture of trees: Effects of phloem girdling on xylem hydraulic conductance. Tree Physiol. 2004, 24, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, K.; Yamane, K.; Itoh, Y. Radial Movement of Minerals in the Trunks of Standing Japanese Cedar (Cryptomeria Japonica D. Don) Trees in Summer by Tracer Analysis. Forests 2020, 11, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, H.J.; Espino, S.; Romo, D.M.; Nima, N.; Do, A.Y.; Michaud, J.M.; Papahadjopoulos-Sternberg, B.; Yang, J.; Zuo, Y.Y.; Steppe, K.; et al. Xylem Surfactants Introduce a New Element to the Cohesion-Tension Theory. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 1177–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, H.J.; Espino, S.; Rich-Cavazos, S.M.; Jansen, S. From the sap’s perspective: The nature of vessel surfaces in angiosperm xylem. Am. J. Bot. 2018, 105, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, H.J.; Michaud, J.M.; Mocko, K.; Espino, S.; Melendres, T.; Roth, M.R.; Welti, R.; Kaack, L.; Jansen, S. Lipids in xylem sap of woody plants across the angiosperm phylogeny. Plant J. 2021, 105, 1477–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochard, H.; Holtta, T.; Herbette, S.; Delzon, S.; Mencuccini, M. New Insights into the Mechanisms of Water-Stress-Induced Cavitation in Conifers. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hölttä, T.; Juurola, E.; Lindfors, L.; Porcar-Castell, A. Cavitation induced by a surfactant leads to a transient release of water stress and subsequent ‘run away’ embolism in Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) seedlings. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 63, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen-Dalsgaard, K.K.; Tyree, M.T.; Mussone, P.G. Surface tension phenomena in the xylem sap of three diffuse porous temperate tree species. Tree Physiol. 2011, 31, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losso, A.; Beikircher, B.; Dämon, B.; Kikuta, S.; Schmid, P.; Mayr, S. Xylem Sap Surface Tension May Be Crucial for Hydraulic Safety. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baerdemaeker, N.J.F.; Salomón, R.L.; De Roo, L.; Steppe, K. Sugars from woody tissue photosynthesis reduce xylem vulnerability to cavitation. New Phytol. 2017, 216, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigo, A.L. Compartmentalization: A Conceptual Framework for Understanding How Trees Grow and Defend Themselves. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1984, 22, 189–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigo, A.L.; Marx, H.G. Compartmentalization of Decay in Trees. Agric. Inf. Bull. 1977, 405, 1–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, H.; Brodersen, C.; Schwarze, F.; Jansen, S. The Parenchyma of Secondary Xylem and Its Critical Role in Tree Defense against Fungal Decay in Relation to the CODIT Model. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddy, L.; Rayner, A.D.M. Origins of decay in living deciduous trees: The role of moisture content and a re-appraisal of the expanded concept of tree decay. New Phytol. 1983, 94, 623–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liese, W.; Dujesiefken, D. Wundreaktionen bei Bäumen. In Proceedings of the Symposium Ausgewählte Probleme der Gehölzphysiologie—Gehölze, Mikroorganismen und Umwelt, Tagungsbericht, Tharandt, Germany, 13–16 June 1989; pp. 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Liese, W.; Dujesiefken, D. Wound reactions of trees. In Forest Trees and Palms: Diseases and Control; Science Publishers: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 21–35. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, H.; Hietala, A.M.; Jansen, S.; Ribera, J.; Rosner, S.; Salmeia, K.A.; Schwarze, F.W.M.R. Using the CODIT model to explain secondary metabolites of xylem in defence systems of temperate trees against decay fungi. Ann. Bot. 2019, 125, 701–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, U.; Liese, W. Response of xylem parenchyma by suberization in some hardwoods after mechanical injury. Trees 1993, 8, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippett, J.T.; Shigo, A.L. Barrier Zone Formation: A Mechanism of Tree Defense against Vascular Pathogens. IAWA J. 1981, 2, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Micco, V.; Balzano, A.; Wheeler, E.A.; Baas, P. Tyloses and gums: A review of structure, function and occurrence of vessel occlusions. IAWA J. 2016, 37, 186–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsen, K.J.M.; Kučera, L.J. Vessel Occlusions in Plants: Morphological, Functional and Evolutionary Aspects. IAWA J. 1990, 11, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillis, W.E. Heartwood and Tree Exudates; Springer Series in Wood Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987; Volume 4, ISBN 978-3-642-72536-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Rost, T.L.; Matthews, M.A. Wound-induced vascular occlusions in Vitis vinifera (Vitaceae): Tyloses in summer and gels in winter1. Am. J. Bot. 2008, 95, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattaway, M.M. The Development of Tyloses and Secretion of Gum in·Heartwood Formation. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 1949, 2, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouzoulet, J.; Pivovaroff, A.L.; Santiago, L.; Rolshausen, P.E. Can vessel dimension explain tolerance toward fungal vascular wilt diseases in woody plants? Lessons from Dutch elm disease and esca disease in grapevine. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rioux, D.; Chamberland, H.; Simard, M.; Ouellette, G. Suberized tyloses in trees: An ultrastructural and cytochemical study. Planta 1995, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Rost, T.L.; Matthews, M.A. Pruning-induced tylose development in stems of current-year shoots of Vitis vinifera (Vitaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2006, 93, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dute, R.R.R.R.; Duncan, K.M.; Duke, B. Tyloses in Abscission Scars of Loblolly Pinel. IAWA J. 1999, 20, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, W.J. Tylosis Formation in Pinus Tracheids. Int. J. Plant Sci. 1974, 135, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddy, L. Microenvironmental Aspects of Xylem Defenses to Wood Decay Fungi. In Defense Mechanisms of Woody Plants against Fungi; Blanchette, R.A., Biggs, A.R., Eds.; Springer Series in Wood Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 96–132. ISBN 978-3-662-01644-2. [Google Scholar]
- Rioux, D.; Nicole, M.; Simard, M.; Ouellette, G.B. Immunocytochemical Evidence that Secretion of Pectin Occurs During Gel (Gum) and Tylosis Formation in Trees. Phytopathology 1998, 88, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerivet, A.; Modafar, C. Vascular modifications in Platanus acerifolia seedlings inoculated with Ceratocystis fimbriata f. sp. platani. For. Pathol. 1994, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R.M.; Resende, M.L.V.; Flood, J.; Rowan, M.G.; Beale, M.H.; Potter, U. Detection and cellular localization of elemental sulphur in disease-resistant genotypes of Theobroma cacao. Nat. Cell Biol. 1996, 379, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubun, T. Phytoalexin induction in the sapwood of plants of the maloideae (rosaceae): Biphenyls or dibenzofurans. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Mueller, W.; Beckman, C. Vessel occlusion and secretory activities of vessel contact cells in resistant or susceptible cotton plants infected with Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vasinfectum. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1992, 40, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magel, E.; Jay-Allemand, C.; Ziegler, H. Formation of heartwood substances in the stemwood of Robinia pseudoacacia L. II. Distribution of nonstructural carbohydrates and wood extractives across the trunk. Trees 1994, 8, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shain, L. Dynamic Responses of Differentiated Sapwood to Injury and Infection. Phytopathology 1979, 69, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shain, L. Stem Defense against Pathogens. In Plant Stems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 383–406. [Google Scholar]
- Biggs, A.R. Occurrence and Location of Suberin in Wound Reaction Zones in Xylem of 17 Tree Species. Phytopathology 1987, 77, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, R.B. Occurrence of decay-associated xylem suberization in a range of woody species. For. Pathol. 1990, 20, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujesiefken, D.; Liese, W.; Shortle, W.; Minocha, R. Response of beech and oaks to wounds made at different times of the year. Eur. J. For. Res. 2005, 124, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarze, F.W.M.R.; Baum, S. Mechanisms of reaction zone penetration by decay fungi in wood of beech (Fagus sylvatica). New Phytol. 2000, 146, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarze, F.; Fink, S. Reaction zone penetration and prolonged persistence of xylem rays in London plane wood degraded by the basidiomycete Inonotus hispidus. Mycol. Res. 1997, 101, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, R.B. Antimicrobial defences in the wood of living trees. New Phytol. 1996, 132, 203–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortle, W.C. Mechanisms of Compartmentalization of Decay in Living Trees. Phytopathology 1979, 69, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buisman, C. The Anatomy of the Wood of Elms Infected with Graphium Ulmi. Plantenziekten 1935, 41, 104–120. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, R.; Holloway, P. Suberin in the sapwood of oak (Quercus robur L.): Its composition from a compartmentalization barrier and its occurrence in tyloses in undecayed wood. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1984, 24, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, R.; Rutherford, J. A wound-associated suberized barrier to the spread of decay in the sapwood of oak (Quercus robur L.). Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1981, 19, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarze, F.W.M.R.; Engels, J.; Mattheck, C. Fungal Strategies of Wood Decay in Trees; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; ISBN 978-3-642-57302-6. [Google Scholar]
- Eyles, A.; Davies, N.W.; Mohammed, C. Wound wood formation in Eucalyptus globulus and Eucalyptus nitens: Anatomy and chemistry. Can. J. For. Res. 2003, 33, 2331–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Tanabe, K.; Kato, T.; Fukushima, K. Localization of Ferruginol, a Diterpene Phenol, in Cryptomeria japonica Heartwood by Time-of-Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry. Planta 2005, 221, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, J.E.; McGinnes, E.A., Jr. Growth-Quality Evaluation of Black Walnut Wood. Part III—An Anatomical Study of Color Characteristics of Black Walnut Veneer. Wood Fiber Sci. 1983, 15, 212–218. [Google Scholar]
- Spicer, R. Senescence in Secondary Xylem. In Vascular Transport in Plants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 457–475. ISBN 978-0-12-088457-5. [Google Scholar]
- Spicer, R.; Holbrook, N.M. Parenchyma Cell Respiration and Survival in Secondary Xylem: Does Metabolic Activity Decline with Cell Age? Plant Cell Environ. 2007, 30, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niklas, K.J. Mechanical Behavior of Plant Tissues as Inferred from the Theory of Pressurized Cellular Solids. Am. J. Bot. 1989, 76, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklas, K.J. Plant Biomechanics: An Engineering Approach to Plant Form and Function; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1992; ISBN 978-0-226-58630-4. [Google Scholar]
- Baum, D.A. A Systematic Revision of Adansonia (Bombacaceae). Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1995, 82, 440–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickens, G.E. The Baobab: Africa’s Upside-Down Tree. Kew Bull. 1982, 37, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapotin, S.M.; Razanameharizaka, J.H.; Holbrook, N.M. Baobab Trees (Adansonia) in Madagascar Use Stored Water to Flush New Leaves but Not to Support Stomatal Opening before the Rainy Season. New Phytol. 2006, 169, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapotin, S.M.; Razanameharizaka, J.H.; Holbrook, N.M. Water Relations of Baobab Trees (Adansonia spp. L.) during the Rainy Season: Does Stem Water Buffer Daily Water Deficits? Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchert, R.; Rivera, G. Photoperiodic Control of Seasonal Development and Dormancy in Tropical Stem-Succulent Trees. Tree Physiol. 2001, 21, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgert, I.; Eckstein, D. The Tensile Strength of Isolated Wood Rays of Beech (Fagus Sylvatica L.) and Its Significance for the Biomechanics of Living Trees. Trees 2001, 15, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beery, W.H.; Ifju, G.; McLain, T.E. Quantitative Wood Anatomy—Relating Anatomy to Transverse Tensile Strength. Wood Fiber Sci. 1983, 15, 395–407. [Google Scholar]
- Youngs, R.L. The Perpendicular-to-Grain Mechanical Properties of Red Oak as Related to Temperature, Moisture Content, and Time. Rep. 2079; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory: Madison, WI, USA, 1957.
- Ozden, S.; Ennos, A.R. Understanding the Function of Rays and Wood Density on Transverse Fracture Behavior of Green Wood of Three Species. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 731–743. [Google Scholar]
- Reiterer, A.; Burgert, I.; Sinn, G.; Tschegg, S. The Radial Reinforcement of the Wood Structure and Its Implication on Mechanical and Fracture Mechanical Properties—A Comparison between Two Tree Species. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattheck, C. Wood—The internal optimization of trees. Arboric. J. 1995, 19, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodner, J.; Schlag, M.G.; Grüll, G. Fracture Initiation and Progress in Wood Specimens Stressed in Tension. Part I. Clear Wood Specimens Stressed Parallel to the Grain. Holzforschung 1997, 51, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgert, I.; Bernasconi, A.; Eckstein, D. Evidence for the Strength Function of Rays in Living Trees. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 1999, 57, 397–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, A.H.; Volkov, V. Logistics of Water and Salt Transport through the Plant: Structure and Functioning of the Xylem: Structural and Functional Features of Xylem. Plant Cell Environ. 2003, 26, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ache, P.; Fromm, J.; Hedrich, R. Potassium-Dependent Wood Formation in Poplar: Seasonal Aspects and Environmental Limitations: Potassium-Dependent Wood Formation in Poplar. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larisch, C.; Dittrich, M.; Wildhagen, H.; Lautner, S.; Fromm, J.; Polle, A.; Hedrich, R.; Rennenberg, H.; Müller, T.; Ache, P. Poplar Wood Rays Are Involved in Seasonal Remodeling of Tree Physiology. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauter, J.J.; Wisniewski, M.; Witt, W. Interrelationships between Ultrastructure, Sugar Levels, and Frost Hardiness of Ray Parenchyma Cells during Frost Acclimation and Deacclimation in Poplar (Populus × Canadensis Moench ‹robusta›) Wood. J. Plant Physiol. 1996, 149, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascó, A.; Salleo, S.; Gortan, E.; Nardini, A. Seasonal Changes in the Ion-Mediated Increase of Xylem Hydraulic Conductivity in Stems of Three Evergreens: Any Functional Role? Physiol. Plant. 2007, 129, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, R.; Fukatsu, E. Seasonal Variation of Heartwood Formation in Larix kaempferi. Tree Physiol. 2012, 32, 1497–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, G.; Ameglio, T.; Guilliot, A.; Fleurat-Lessard, P.; Lacointe, A.; Sakr, S.; Petel, G.; Julien, J.-L. Winter Variation in Xylem Sap PH of Walnut Trees: Involvement of Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase of Vessel-Associated Cells. Tree Physiol. 2004, 24, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essiamah, S.K. Spring Sap of Trees. Berichte Dtsch. Bot. Ges. 1980, 93, 257–267. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, A.R.; Eiseman, J.A.; Leonard, J.A. Xylem Sap from Actinidia Chinensis: Seasonal Changes in Composition. Ann. Bot. 1983, 51, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losso, A.; Nardini, A.; Damon, B.; Mayr, S. Xylem Sap Chemistry: Seasonal Changes in Timberline Conifers Pinus cembra, Picea abies, and Larix decidua. Biol. Plant. 2018, 62, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, J.J.; Ambrosius, T. Changes in the Partitioning of Carbohydrates in the Wood during Bud Break in Betula Pendula Roth. J. Plant Physiol. 1986, 124, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, J.J. Seasonal Changes in the Efflux of Sugars from Parenchyma Cells into the Apoplast in Poplar Stems (Populus × canademis ‘robusta’). Trees 1988, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbellay, E.; Fonti, P.; Stoffel, M. Duration and Extension of Anatomical Changes in Wood Structure after Cambial Injury. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 3271–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myśkow, E.; Zagórska-Marek, B. Vertical Migration of Rays Leads to the Development of a Double-Storied Phenotype in the Cambium of Aesculus Turbinata. Botany 2008, 86, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słupianek, A.; Wojtuń, B.; Myśkow, E. Origin, Activity and Environmental Acclimation of Stem Secondary Tissues of the Polar Willow (Salix Polaris) in High-Arctic Spitsbergen. Polar Biol. 2019, 42, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerttula, S.; Groover, A. Immunolocalization in Secondary Xylem of Populus. In Xylem; de Lucas, M., Etchhells, J.P., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1544, pp. 83–90. ISBN 978-1-4939-6720-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.S.; Awano, T.; Yoshinaga, A.; Takabe, K. Immunolocalization of β-1-4-Galactan and Its Relationship with Lignin Distribution in Developing Compression Wood of Cryptomeria japonica. Planta 2010, 232, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, R.B.; Jacobsen, A.L. Identifying Which Conduits Are Moving Water in Woody Plants: A New HRCT-Based Method. Tree Physiol. 2018, 38, 1200–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzker, M.L. Sequencing Technologies—the next Generation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuskan, G.A.; DiFazio, S.; Jansson, S.; Bohlmann, J.; Grigoriev, I.; Hellsten, U.; Putnam, N.; Ralph, S.; Rombauts, S.; Salamov, A.; et al. The Genome of Black Cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa (Torr. & Gray). Science 2006, 313, 1596–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundell, D.; Street, N.R.; Kumar, M.; Mellerowicz, E.J.; Kucukoglu, M.; Johnsson, C.; Kumar, V.; Mannapperuma, C.; Delhomme, N.; Nilsson, O.; et al. AspWood: High-Spatial-Resolution Transcriptome Profiles Reveal Uncharacterized Modularity of Wood Formation in Populus Tremula. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 1585–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, I.M.; Zinkgraf, M.S.; Groover, A.T.; Comai, L. A System for Dosage-Based Functional Genomics in Poplar. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 2370–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokhina, O.; Valerio, C.; Sokołowska, K.; Zhao, L.; Kärkönen, A.; Niittylä, T.; Fagerstedt, K. Laser Capture Microdissection Protocol for Xylem Tissues of Woody Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokhina, O.; Laitinen, T.; Hatakeyama, Y.; Delhomme, N.; Paasela, T.; Zhao, L.; Street, N.R.; Wada, H.; Kärkönen, A.; Fagerstedt, K. Ray Parenchymal Cells Contribute to Lignification of Tracheids in Developing Xylem of Norway Spruce. Plant Physiol. 2019, 181, 1552–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, I.N.; Johansson, A.I.; Sokołowska, K.; Niittylä, T.; Sundberg, B.; Hvidsten, T.R.; Street, N.R.; Moritz, T. A Metabolite Roadmap of the Wood-forming Tissue in Populus Tremula. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 1559–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Sztojka, B.; Escamez, S.; Vanholme, R.; Hedenström, M.; Wang, Y.; Turumtay, H.; Gorzsás, A.; Boerjan, W.; Tuominen, H. PIRIN2 Suppresses S-type Lignin Accumulation in a Noncell-autonomous Manner in Arabidopsis Xylem Elements. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1923–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragni, L.; Greb, T. Secondary Growth as a Determinant of Plant Shape and Form. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 79, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffey, N.; Cholewa, E.; Regan, S.; Sundberg, B. Secondary Xylem Development in Arabidopsis: A Model for Wood Formation. Physiol. Plant. 2002, 114, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demura, T.; Fukuda, H. Transcriptional Regulation in Wood Formation. Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.A.; Schuetz, M.; Roach, M.; Mansfield, S.D.; Ellis, B.; Samuels, L. Neighboring Parenchyma Cells Contribute to Arabidopsis Xylem Lignification, While Lignification of Interfascicular Fibers Is Cell Autonomous. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 3988–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Craig, J.C.; Petzold, H.E.; Dickerman, A.W.; Beers, E.P. The Xylem and Phloem Transcriptomes from Secondary Tissues of the Arabidopsis Root-Hypocotyl. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

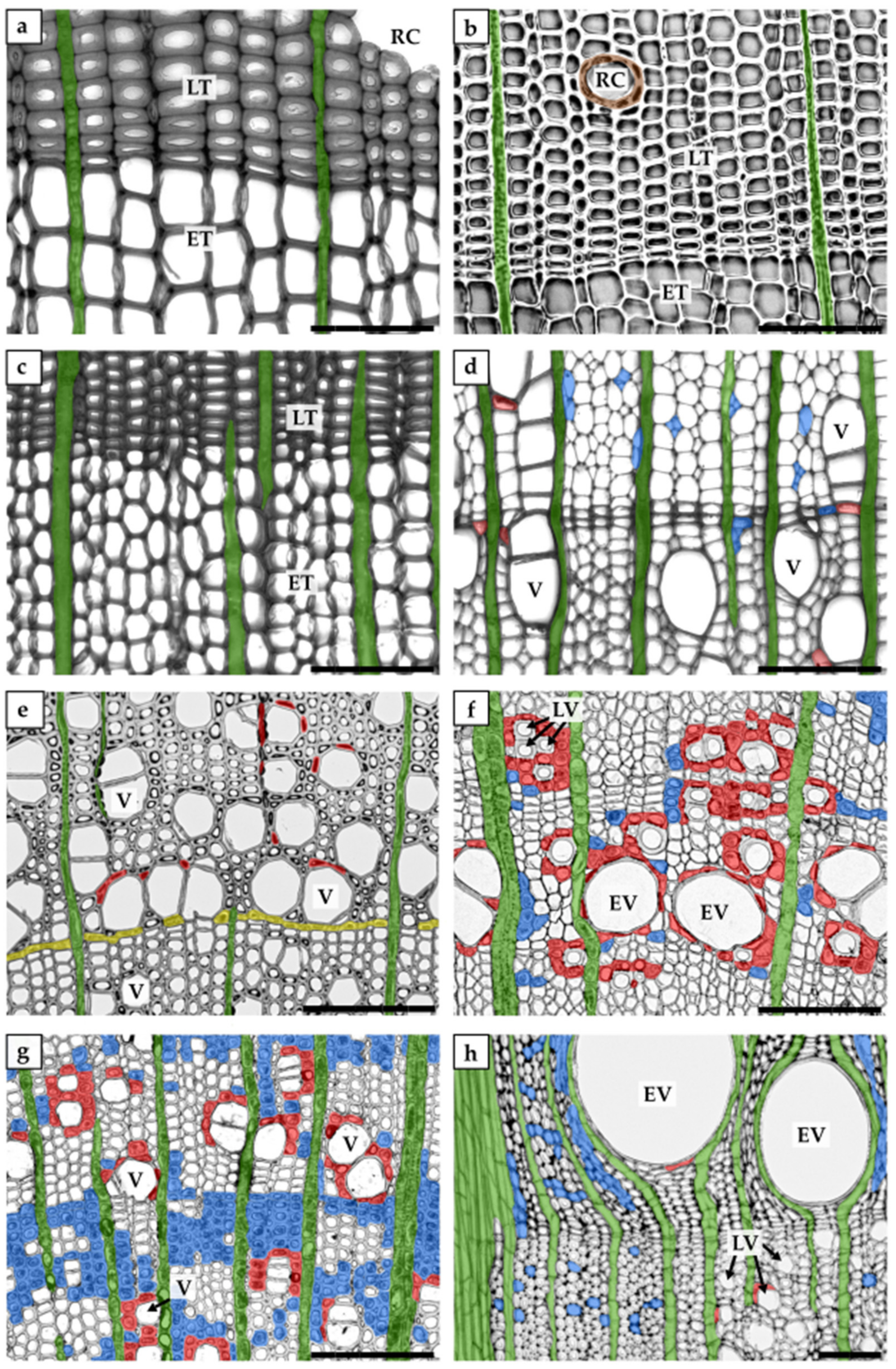
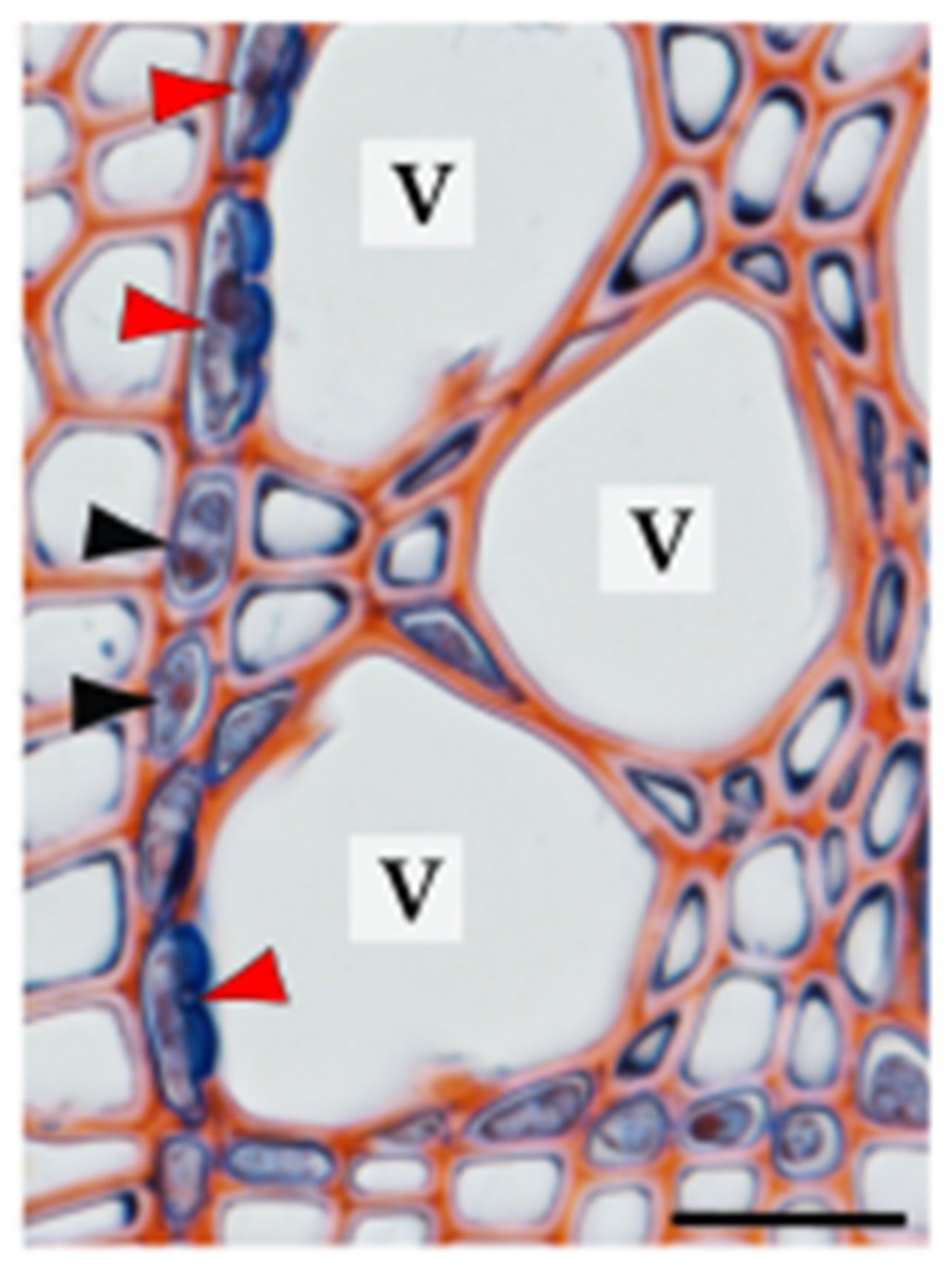
| axial parenchyma | parenchyma cells of a longitudinal system; usually form strands of axially elongated cells |
| paratracheal parenchyma | axial parenchyma neighbouring tracheary elements |
| apotracheal parenchyma | axial parenchyma not neighbouring tracheary elements |
| ray parenchyma | parenchyma cells of a radial system, grouped into radially oriented rays |
| marginal parenchyma | parenchyma bands at the ends of growth rings; associated with the end (terminal parenchyma) or with the beginning (initial parenchyma) of a ring |
| contact cell | axial or ray parenchyma cell in direct contact with tracheary elements via specialized pits (contact pits) |
| vessel-associated cell (VAC) | contact cell in direct contact with vessel elements |
| isolation cell | axial or ray parenchyma cell without direct contact with tracheary elements |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Słupianek, A.; Dolzblasz, A.; Sokołowska, K. Xylem Parenchyma—Role and Relevance in Wood Functioning in Trees. Plants 2021, 10, 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10061247
Słupianek A, Dolzblasz A, Sokołowska K. Xylem Parenchyma—Role and Relevance in Wood Functioning in Trees. Plants. 2021; 10(6):1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10061247
Chicago/Turabian StyleSłupianek, Aleksandra, Alicja Dolzblasz, and Katarzyna Sokołowska. 2021. "Xylem Parenchyma—Role and Relevance in Wood Functioning in Trees" Plants 10, no. 6: 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10061247
APA StyleSłupianek, A., Dolzblasz, A., & Sokołowska, K. (2021). Xylem Parenchyma—Role and Relevance in Wood Functioning in Trees. Plants, 10(6), 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10061247






