Environmental Heterogeneity Leads to Spatial Differences in Genetic Diversity and Demographic Structure of Acer caudatifolium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
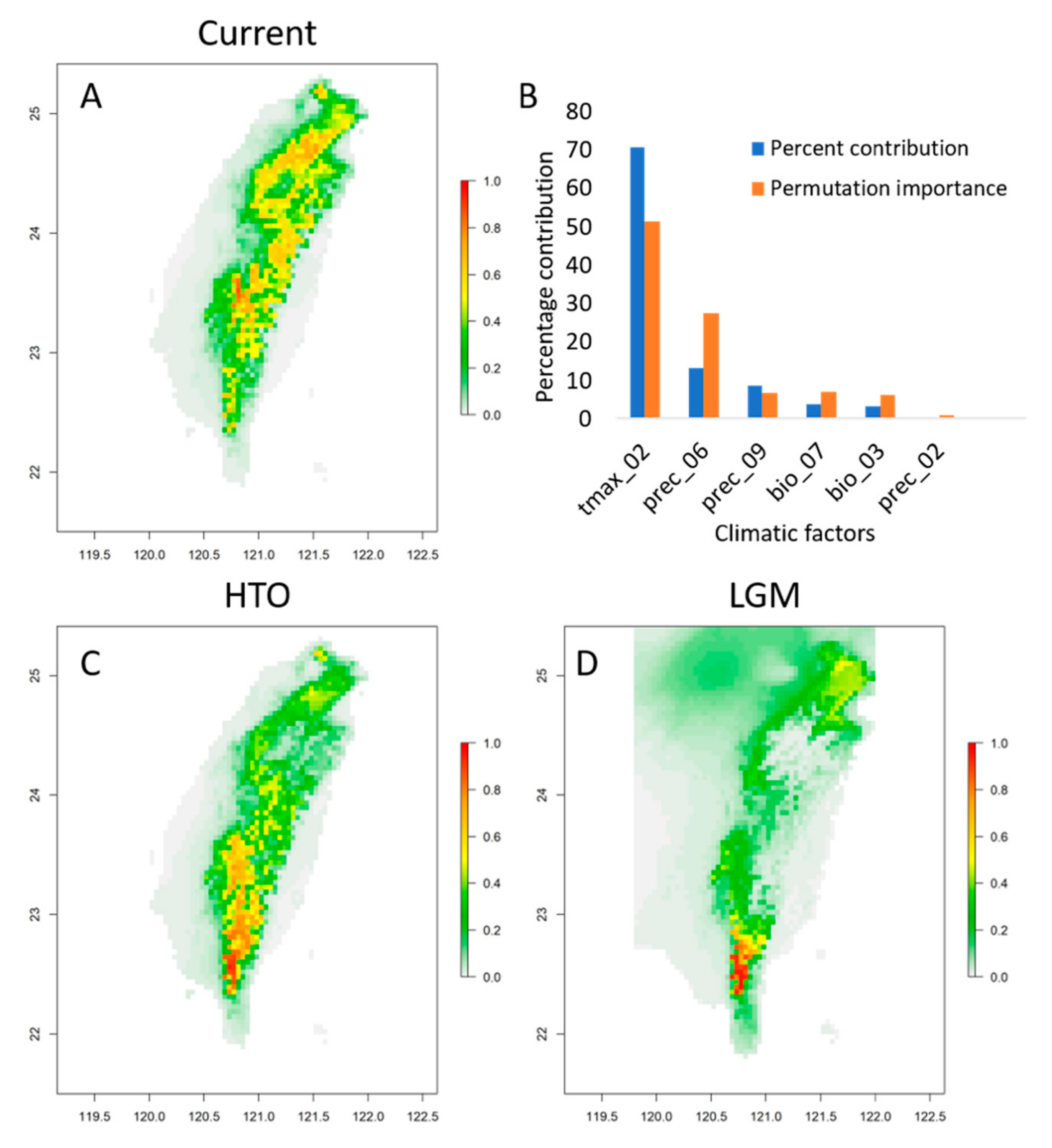
2.1. Ecological Niche Modeling
2.2. Sampling and Chloroplast DNA Sequences
2.3. Genetic Diversity and Haplotype Network
2.4. Mismatch Analysis
2.5. Genetic Barriers
2.6. Genetic Differentiation across Geography and Environment
2.7. Factors Affecting Demographic Dynamics
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure
3.2. Genetic Barriers
3.3. Geographic Distance as the Source of Population Differentiation
3.4. Demographic Dynamics Are Spatially and Environmentally Related
3.5. Upward and Northward Expansion of the Distribution Range
4. Discussion
4.1. Paleodistribution and Climate Change Affect the Geodistance-Related Genetic Structure
4.2. Climate Change Facilitates the Contact of Two Closely Related Maples with Divergent Grinnellian Niches
4.3. Environmentally Biased Dispersal Constrains the Northernmost Populations
4.4. Local Climate Heterogeneity Underlies Genetic Draft of Chlorotype Distribution
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grinnell, J. The niche-relationships of the California Thrasher. Auk 1917, 34, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fordham, D.A.; Resit Akçakaya, H.; Araújo, M.B.; Elith, J.; Keith, D.A.; Pearson, R.; Auld, T.D.; Mellin, C.; Morgan, J.W.; Regan, T.J.; et al. Plant extinction risk under climate change: Are forecast range shifts alone a good indicator of species vulnerability to global warming? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 1357–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, R.; Muller-Landau, H.C. Spatial patterns of seed dispersal, their determinants and consequences for recruitment. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2000, 15, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-Z.; Zhang, R.; Gao, R.-H.; Chai, M.-W.; Luo, M.-X.; Huang, B.-H.; Liao, P.-C. Heterocarpy diversifies diaspore propagation of the desert shrub Ammopiptanthus mongolicus. Plant Species Biol. 2021, 36, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamelon, M.; Grøtan, V.; Nilsson, A.L.K.; Engen, S.; Hurrell, J.W.; Jerstad, K.; Phillips, A.S.; Røstad, O.W.; Slagsvold, T.; Walseng, B.; et al. Interactions between demography and environmental effects are important determinants of population dynamics. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evans, L.M.; Allan, G.J.; DiFazio, S.P.; Slavov, G.T.; Wilder, J.A.; Floate, K.D.; Rood, S.B.; Whitham, T.G. Geographical barriers and climate influence demographic history in narrowleaf cottonwoods. Heredity 2015, 114, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, J.-T.; Luo, M.-X.; Lu, H.-P.; Tseng, Y.-T.; Liao, P.-C. Population genetics under the Massenerhebung effect: The influence of topography on the demography of Acer morrisonense. J. Biogeogr. 2021, 48, 1773–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironon, S.; Papuga, G.; Villellas, J.; Angert, A.L.; García, M.B.; Thompson, J.D. Geographic variation in genetic and demographic performance: New insights from an old biogeographical paradigm. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 1877–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sexton, J.P.; McIntyre, P.J.; Angert, A.L.; Rice, K.J. Evolution and Ecology of Species Range Limits. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 415–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angert, A.L.; Bontrager, M.G.; Ågren, J. What Do We Really Know About Adaptation at Range Edges? Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2020, 51, 341–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-L.; Lo, H.-C. Aceraceae. In Flora of Taiwan, 2nd ed.; Taiwan, Editorial Committee of the Flora of Taiwan, Ed.; National Science Council of the Republic of China: Taipei, Taiwan, 1993; Volume 3, pp. 589–598. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Li, J. Conflicting phylogenies of Section Macrantha (Acer, Aceroideae, Sapindaceae) based on chloroplast and nuclear DNA. Syst. Bot. 2010, 35, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liao, P.-C.; Huang, B.-H.; Yu, T.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Li, J.-Q. Historical biogeography of Acer L. (Sapindaceae): Genetic evidence for Out-of-Asia hypothesis with multiple dispersals to North America and Europe. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Areces-Berazain, F.; Hinsinger, D.D.; Strijk, J.S. Genome-wide supermatrix analyses of maples (Acer, Sapindaceae) reveal recurring inter-continental migration, mass extinction, and rapid lineage divergence. Genomics 2021, 113, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi, B.; Hamm, N.A.; Groen, T.A.; Skidmore, A.K.; Toxopeus, A.G. Where is positional uncertainty a problem for species distribution modelling? Ecography 2014, 37, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Dudík, M. Modeling of species distributions with Maxent: New extensions and a comprehensive evaluation. Ecography 2008, 31, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, T. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, W.S. Problems and cautions with sequence mismatch analysis and Bayesian skyline plots to infer historical demography. J. Hered. 2015, 106, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jombart, T.J.B. adegenet: A R package for the multivariate analysis of genetic markers. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1403–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, F. Genetic differentiation and estimation of gene flow from F-statistics under isolation by distance. Genetics 1997, 145, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team and Contributors Worldwide. The R Stats Package ver. 3.5.0; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ripley, B.; Venables, B.; Bates, D.M.; Hornik, K.; Gebhardt, A.; Firth, D.; Ripley, M.B. Package ‘mass’. Cran R 2013, 538, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Neher, R.A. Genetic draft, selective interference, and population genetics of rapid adaptation. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2013, 44, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orsini, L.; Vanoverbeke, J.; Swillen, I.; Mergeay, J.; De Meester, L. Drivers of population genetic differentiation in the wild: Isolation by dispersal limitation, isolation by adaptation and isolation by colonization. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 5983–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.-H.; Huang, C.-W.; Huang, C.-L.; Liao, P.-C. Continuation of the genetic divergence of ecological speciation by spatial environmental heterogeneity in island endemic plants. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsiung, H.-Y.; Huang, B.-H.; Chang, J.-T.; Huang, Y.-M.; Huang, C.-W.; Liao, P.-C. Local climate heterogeneity shapes population genetic structure of two undifferentiated insular Scutellaria species. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.-L.; Chen, J.-H.; Chang, C.-T.; Chung, J.-D.; Liao, P.-C.; Wang, J.-C.; Hwang, S.-Y. Disentangling the effects of isolation-by-distance and isolation-by-environment on genetic differentiation among Rhododendron lineages in the subgenus Tsutsusi. Tree Genet. Genomes 2016, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-L.; Chen, J.-H.; Tsang, M.-H.; Chung, J.-D.; Chang, C.-T.; Hwang, S.-Y. Influences of environmental and spatial factors on genetic and epigenetic variations in Rhododendron oldhamii (Ericaceae). Tree Genet. Genomes 2014, 11, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, K.M.; Chang, C.T.; Chung, J.D.; Chiang, Y.C.; Hwang, S.Y. Adaptive genetic divergence despite significant isolation-by-distance in populations of Taiwan Cow-Tail Fir (Keteleeria davidiana var. formosana). Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krosby, M.; Wilsey, C.B.; McGuire, J.L.; Duggan, J.M.; Nogeire, T.M.; Heinrichs, J.A.; Tewksbury, J.J.; Lawler, J.J. Climate-induced range overlap among closely related species. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, B.G. Competitive interactions upon secondary contact drive elevational divergence in tropical birds. Am. Nat. 2015, 186, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Aparicio, L.; Gómez, J.M.; Zamora, R. Spatiotemporal patterns of seed dispersal in a wind-dispersed Mediterranean tree (Acer opalus subsp. granatense): Implications for regeneration. Ecography 2007, 30, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamantov, M.A.; Gibson-Reinemer, D.K.; Linck, E.B.; Sheldon, K.S. Climate-driven range shifts of montane species vary with elevation. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2021, 30, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang-Yang, C.-H.; Lu, C.-L.; Sun, I.F.; Hsieh, C.-F. Flowering and fruiting patterns in a subtropical rain forest, Taiwan. Biotropica 2013, 45, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-C.; Bain, A.; Chiu, Y.-T.; Ho, Y.-C.; Chen, W.-H.; Chou, L.-S.; Tzeng, H.-Y. Topographic effect on the phenology of Ficus pedunculosa var. mearnsii (Mearns fig) in its northern boundary distribution, Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sperry, J.S.; Donnelly, J.R.; Tyree, M.T. Seasonal occurrence of xylem embolism in sugar maple (Acer saccharum). Am. J. Bot. 1988, 75, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabot, B.F.; Hicks, D.J. The Ecology of Leaf Life Spans. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1982, 13, 229–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montserrat-Martí, G.; Camarero, J.J.; Palacio, S.; Pérez-Rontomé, C.; Milla, R.; Albuixech, J.; Maestro, M. Summer-drought constrains the phenology and growth of two coexisting Mediterranean oaks with contrasting leaf habit: Implications for their persistence and reproduction. Trees 2009, 23, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franco, A.M.A.; Hill, J.K.; Kitschke, C.; Collingham, Y.C.; Roy, D.B.; Fox, R.; Huntley, B.; Thomas, C.D. Impacts of climate warming and habitat loss on extinctions at species’ low-latitude range boundaries. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2006, 12, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, P.B.; Sendall, K.M.; Rice, K.; Rich, R.L.; Stefanski, A.; Hobbie, S.E.; Montgomery, R.A. Geographic range predicts photosynthetic and growth response to warming in co-occurring tree species. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Pop | Longitude (E) | Latitude (N) | Altitude (m) | N | Polym | avgFST | Θs * | SD(θs) * | Θπ * | SD(θπ) * | Tajima’s D | P | Fu’s Fs | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YMS | 121.539 | 25.181 | 762–1021 | 29 | 2 | 0.724 | 0.323 | 0.239 | 0.365 | 0.338 | 0.273 | 0.688 | 0.326 | 0.527 |
| RF | 121.787 | 25.065 | 381–484 | 9 | 1 | 0.432 | 0.233 | 0.233 | 0.141 | 0.207 | −1.088 | 0.198 | −0.263 | 0.190 |
| LLS | 121.401 | 24.687 | 1166–1317 | 7 | 0 | 0.462 | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. |
| JS | 121.27 | 24.667 | 1197–1468 | 17 | 8 | 0.223 | 1.499 | 0.721 | 1.402 | 0.910 | −0.229 | 0.461 | −0.295 | 0.454 |
| MC | 121.486 | 24.628 | 1106–1218 | 21 | 1 | 0.436 | 0.176 | 0.176 | 0.326 | 0.319 | 1.505 | 0.950 | 1.474 | 0.733 |
| SKR | 121.143 | 24.56 | 1546–1975 | 20 | 0 | 0.300 | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. |
| TPS | 121.521 | 24.523 | 1566–1764 | 14 | 1 | 0.238 | 0.199 | 0.199 | 0.278 | 0.297 | 0.842 | 0.850 | 0.944 | 0.572 |
| SY | 121.312 | 24.338 | 1848–2000 | 10 | 8 | 0.509 | 1.791 | 0.924 | 1.337 | 0.919 | −1.094 | 0.176 | 0.713 | 0.637 |
| DXS | 120.977 | 24.236 | 1680–2026 | 23 | 1 | 0.170 | 0.172 | 0.172 | 0.190 | 0.229 | 0.186 | 0.769 | 0.612 | 0.438 |
| TRK | 121.407 | 24.192 | 2336–2987 | 5 | 2 | 0.338 | 0.608 | 0.480 | 0.507 | 0.505 | −0.973 | 0.189 | −0.829 | 0.106 |
| MF | 121.176 | 24.093 | 2087–2283 | 26 | 8 | 0.329 | 1.328 | 0.611 | 0.435 | 0.380 | −2.115 | 0.002 | 0.610 | 0.586 |
| DD | 121.169 | 23.787 | 2196–2396 | 4 | 0 | 0.251 | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. |
| RL | 120.922 | 23.708 | 1362–1642 | 15 | 8 | 0.367 | 1.558 | 0.761 | 1.423 | 0.930 | −0.318 | 0.436 | 3.081 | 0.935 |
| TTC | 120.913 | 23.53 | 1604–2388 | 17 | 0 | 0.289 | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. |
| ALS | 120.855 | 23.482 | 1930–2404 | 15 | 0 | 0.886 | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. |
| LD | 120.995 | 23.245 | 2033–2309 | 26 | 0 | 0.339 | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. |
| TJ | 120.741 | 23.06 | 1467–1490 | 2 | 0 | 0.348 | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. |
| JBS | 120.757 | 22.726 | 1306–2040 | 21 | 0 | 0.264 | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | 0 | N.A. |
| JSY | 120.75 | 22.4 | 1257 | 13 | 1 | 0.352 | 0.204 | 0.204 | 0.097 | 0.163 | −1.149 | 0.169 | −0.537 | 0.128 |
| Model | Formula | npar | AIC | BIC | logLik | Deviance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IBD | gen~geo + (1 | pop) | 4 | 1103.3 | 1115.8 | −547.630 | 1095.3 |
| IBD + IBE | gen~geo + env + (1 | pop) | 5 | 1103.7 | 1119.4 | −546.860 | 1093.7 |
| IBD + IBAlt | gen~geo + alt + (1 | pop) | 5 | 1105.1 | 1120.8 | −547.540 | 1095.1 |
| IBD + IBE + IBAlt | gen~geo + env + alt + (1 | pop) | 6 | 1105.7 | 1124.5 | −546.850 | 1093.7 |
| IBE | gen~env + (1 | pop) | 4 | 1110.7 | 1123.3 | −551.350 | 1102.7 |
| IBAlt | gen~alt + (1 | pop) | 4 | 1111.5 | 1124.0 | −551.740 | 1103.5 |
| IBE + IBAlt | gen~env + alt + (1 | pop) | 5 | 1112.6 | 1128.3 | −551.300 | 1102.6 |
| Demographic Expansion | Spatial Expansion | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pop | τ | θ0 | θ1 | SSD | Rag | τ | θ | M | SSD | Rag |
| YMS | 0.744 | 0 | 999 | 0.026 | 0.199 | 0.742 | 0.003 | 999 | 0.026 | 0.199 |
| RF | 2.930 | 0.900 | 3.600 | 0.307 | 0.358 | 0.260 | 0.008 | 999 | 0.0005 | 0.358 |
| JS | 8.350 | 0 | 1.642 | 0.043 | 0.112 | 7.099 | 1.381 | 0.31 | 0.035 | 0.112 |
| MC | 0.789 | 0.002 | 999 | 0.025 | 0.265 | 0.785 | 0.006 | 999 | 0.025 | 0.265 |
| TPS | 0.643 | 0 | 999 | 0.012 | 0.208 | 0.645 | 0.001 | 999 | 0.012 | 0.208 |
| SY | 1.031 | 0.004 | 999 | 0.037 | 0.129 | 7.897 | 1.69 | 0.159 | 0.063 | 0.129 |
| DXS | 2.982 | 0.900 | 3.600 | 0.238 | 0.250 | 0.387 | 0.003 | 999 | 0.002 | 0.250 |
| TRK | 1.037 | 0 | 999 | 0.065 | 0.350 | 1.035 | 0.003 | 999 | 0.065 | 0.350 |
| MF | 3 | 0 | 0.247 | 0.007 | 0.439 | 7.646 | 0.208 | 0.079 | 0.005 | 0.439 |
| RL | 0.725 | 0.010 | 999 | 0.058 | 0.166 | 7.924 | 1.009 | 0.326 | 0.057 | 0.166 |
| JSY | 2.965 | 0.450 | 0.450 | 0.028 | 0.503 | 0.135 | 0.110 | 2.705 | 0.0002 | 0.503 |
| Tajima’s D | Spatial Expansion Time (τ) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | SE | t | P | Estimate | SE | t | P | |
| Lat | 2.856 | 0.741 | 3.853 | 0.003 * | −6.626 | 3.613 | −1.834 | 0.090 |
| Long | −2.681 | 1.697 | −1.580 | 0.143 | 17.710 | 8.358 | 2.119 | 0.054 |
| Alt | NA | NA | NA | NA | −0.006 | 0.003 | −1.955 | 0.072 |
| prec10 | 0.013 | 0.004 | 3.279 | 0.007 * | −0.051 | 0.017 | −3.025 | 0.010 * |
| srad6 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 2.691 | 0.021 * | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| srad7 | −0.004 | 0.001 | −3.220 | 0.008 * | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| AET | −0.015 | 0.005 | −2.972 | 0.013 * | −0.035 | 0.028 | −1.250 | 0.233 |
| GAI | −0.0001 | 0.00004 | −1.775 | 0.104 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, M.-X.; Lu, H.-P.; Chai, M.-W.; Chang, J.-T.; Liao, P.-C. Environmental Heterogeneity Leads to Spatial Differences in Genetic Diversity and Demographic Structure of Acer caudatifolium. Plants 2021, 10, 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081646
Luo M-X, Lu H-P, Chai M-W, Chang J-T, Liao P-C. Environmental Heterogeneity Leads to Spatial Differences in Genetic Diversity and Demographic Structure of Acer caudatifolium. Plants. 2021; 10(8):1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081646
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Min-Xin, Hsin-Pei Lu, Min-Wei Chai, Jui-Tse Chang, and Pei-Chun Liao. 2021. "Environmental Heterogeneity Leads to Spatial Differences in Genetic Diversity and Demographic Structure of Acer caudatifolium" Plants 10, no. 8: 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081646
APA StyleLuo, M.-X., Lu, H.-P., Chai, M.-W., Chang, J.-T., & Liao, P.-C. (2021). Environmental Heterogeneity Leads to Spatial Differences in Genetic Diversity and Demographic Structure of Acer caudatifolium. Plants, 10(8), 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081646







