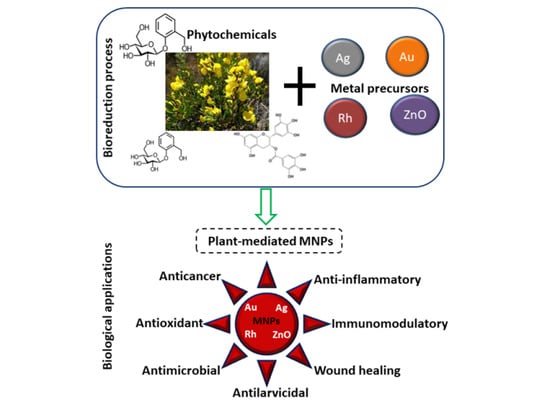
Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles Using Some Selected Medicinal Plants from Southern Africa and Their Biological Applications
Abstract
Share and Cite
Aboyewa, J.A.; Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Meyer, M.; Oguntibeju, O.O. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles Using Some Selected Medicinal Plants from Southern Africa and Their Biological Applications. Plants 2021, 10, 1929. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091929
Aboyewa JA, Sibuyi NRS, Meyer M, Oguntibeju OO. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles Using Some Selected Medicinal Plants from Southern Africa and Their Biological Applications. Plants. 2021; 10(9):1929. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091929
Chicago/Turabian StyleAboyewa, Jumoke A., Nicole R. S. Sibuyi, Mervin Meyer, and Oluwafemi O. Oguntibeju. 2021. "Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles Using Some Selected Medicinal Plants from Southern Africa and Their Biological Applications" Plants 10, no. 9: 1929. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091929
APA StyleAboyewa, J. A., Sibuyi, N. R. S., Meyer, M., & Oguntibeju, O. O. (2021). Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles Using Some Selected Medicinal Plants from Southern Africa and Their Biological Applications. Plants, 10(9), 1929. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091929