Agronomic, Genetic and Quantitative Trait Characterization of Nightshade Accessions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Analysis of Variance
2.2. Variation among Accessions
2.3. Phenotypic Correlation for Quantitative Traits
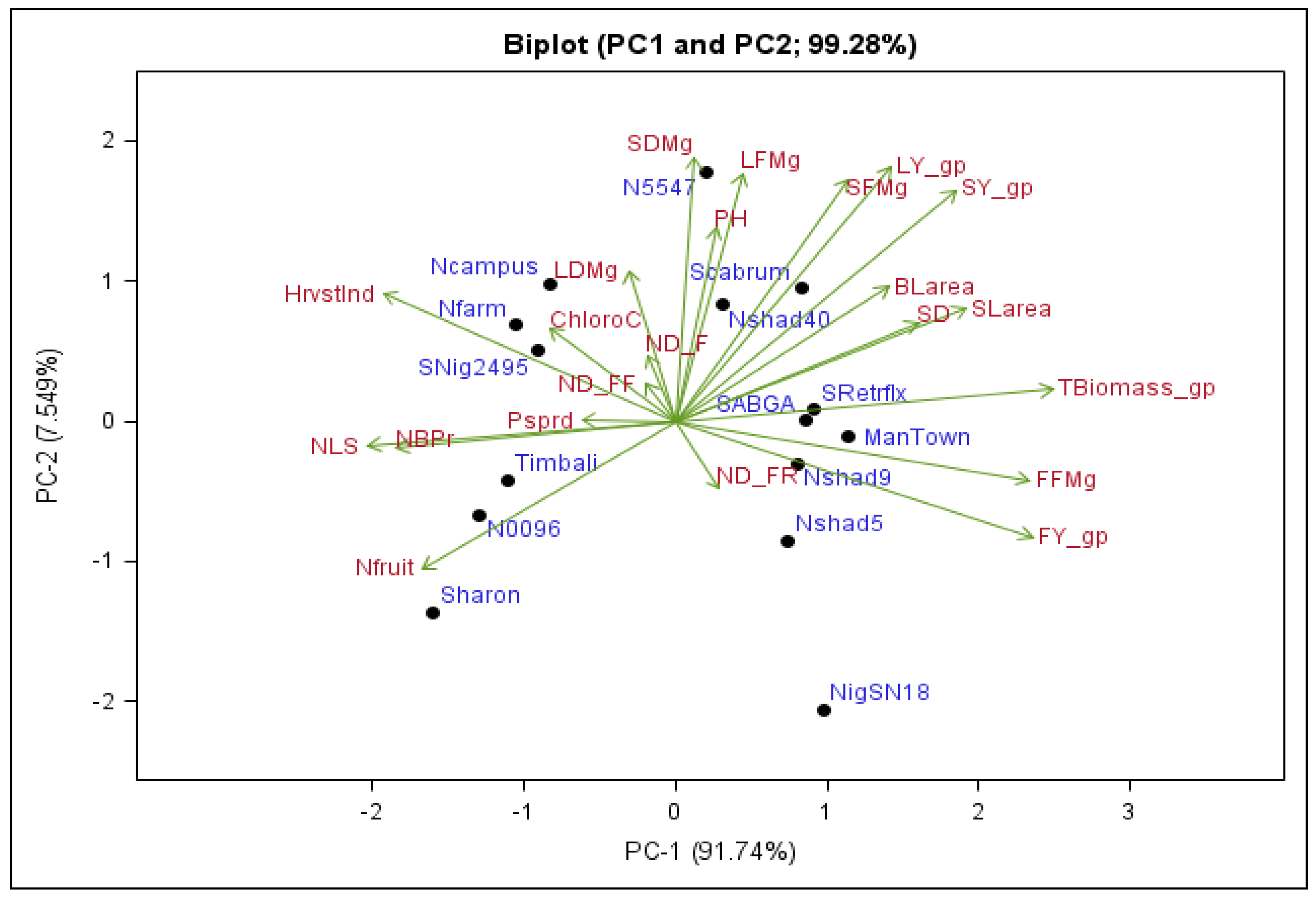
2.4. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
2.5. Principal Component Biplot
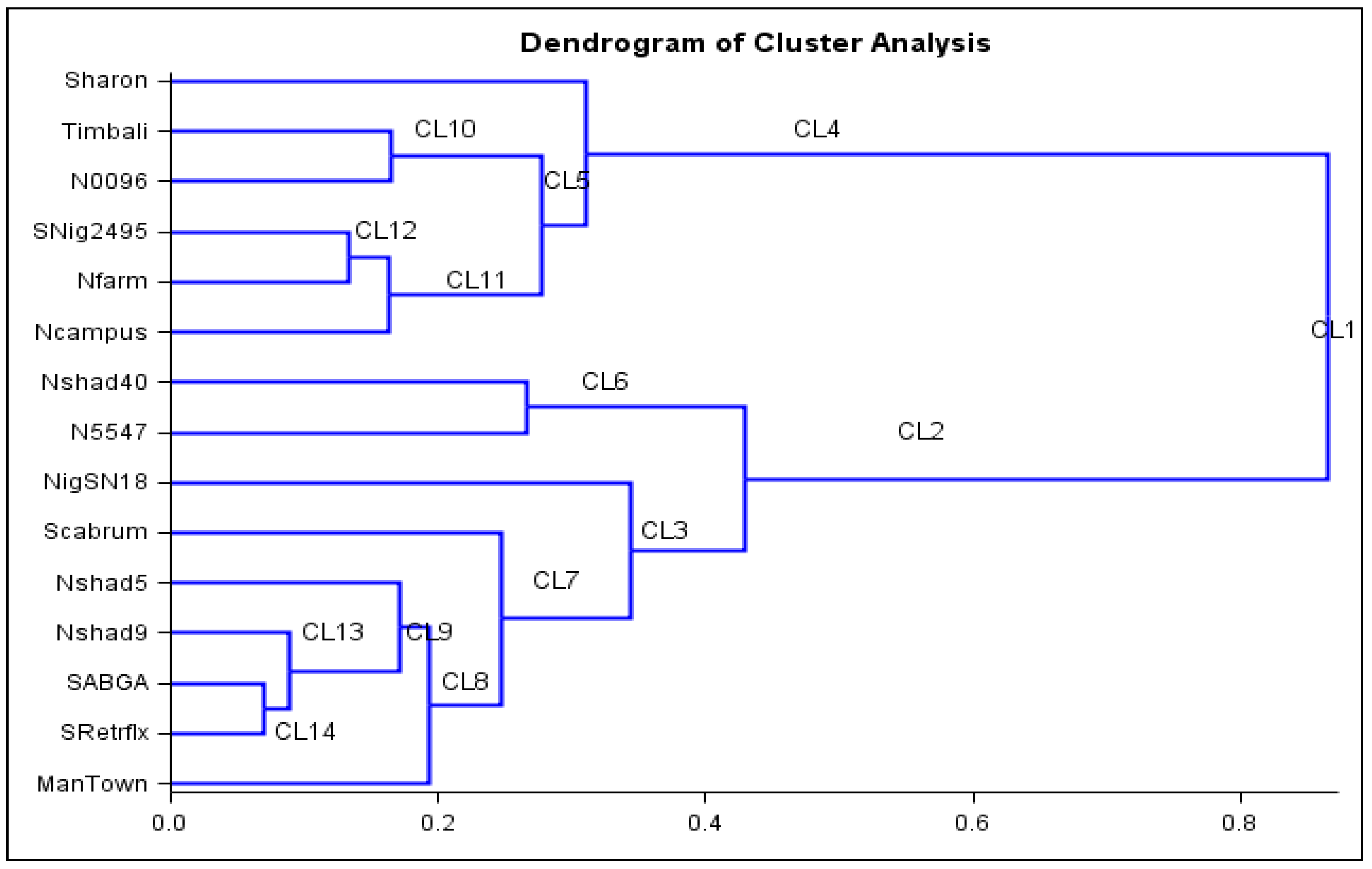
2.6. Cluster Analysis
2.7. Genetic Parameters
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Materials and Experimental Design and Treatments
3.2. Description of the Research Site, Trial Establishment and Maintenance
3.3. Data Collection
3.4. Data Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ronoh, R.; Linde, M.; Winkelmann, T.; Abukutsa-Onyango, M.; Dinssa, F.F.; Debener, T. Morphological characterization, genetic diversity and population structure of African nightshades (section Solanum L.). Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2018, 66, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagio, R.S. Assessing Diversity of Solanum nigrum L. Grown. Kenya Master’s Thesis, University of Kenyatta, Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nandhini, T.; Paramaguru, P.; Vajayakumar, A. Morphological characterization and genetic variability study on Makoi (Solanum nigrum L.) genotypes. Plant Arch. 2014, 14, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Jagatheeswari, D.; Bharathi, T.; Sheik Jahabar Ali, H. Black night shade (Solanum nigrum L.)—An updated review. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Arch. 2013, 4, 288–295. [Google Scholar]
- Ojiewo, C.O.; Mwai, G.N.; Abukutsa-Onyango, M.O.; Agong, S.G.; Nono-Womdim, R. Exploiting the genetic diversity of vegetable African nightshades. Bioremediat. Biodivers. Bioavailab. 2013, 7, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Abukutsa-Onyango, M.O.; Onyango, J.C. Crop, Conference Society, Conservation and seed production of African leafy vegetables at Maseno University botanic garden, Kenya. Afr. Crop Sci. Confress Proc. 2005, 7, 1201–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Schilling, E.E.; Andersen, R.N. The black nightshades (Solanum section Solanum) of the Indian subcontinent. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1990, 102, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyango, M. Effects of plant diversity and harvesting frequency on the yield of vegetable quality of four variant of black nightshades-Solanum nigrum. In African Crop Science Conference Proceedings; African Crop Science Society: Kampala, Uganda, 1993; pp. 1237–1240. [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds, J.M.; Chweya, J.A. Black Nightshades: Solanum nigrum L. and Related Species; Institute of plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research: Rome, Italy, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mwai, G.N.; Onyango, J.C.; Abukutsa-Onyango, M.O. Taxonomic Identification and Characterization of African Nightshades (Solanum L. Section Solanum). Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2007, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masinde, P.W.; Onyango, C.A.; Abukutsa-Onyango, M.; Wesonga, J.M.; Ojiewo, C.O.; Agong, S.G. Response of leaf yield and nutritive value of African nightshade (Solanum villosum) genotypes to nitrogen application. Afr. J. Hortic. Sci. 2010, 3, 34–47. [Google Scholar]
- Omondi, E.O.; Engels, C.; Nambafu, G.; Schreiner, M.; Neugart, S.; Abukutsa-Onyango, M.; Winkelmann, T. Nutritional compound analysis and morphological characterization of spider plant (Cleome gynandra)—An African indigenous leafy vegetable. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Genemey, B.; Amsala, A. Varaition and association of quality parameters in Ethopian Durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var. durum) genotypes. Int. J. Plant Breed. Genet. 2012, 6, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ravi, C.S.; Sreeramu, B.S.; Mallikarjuna Gowdal, A.P.; Smitha, G.R. Evaluation of makoi (Solanum nigrum L.) germplasm for growth, yield and quality. J. Appl. Hortic. 2013, 15, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, P.; Plazas, M.; Prohens, J.; Vilanova, S.; Gramazio, P. Diallel genetic analysis for multiple traits in eggplant and assessment of genetic distances for predicting hybrids performance. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, P.R.; Bhat, K.V. Analysis of agronomically important morphological traits diversity in Vigna radiata. Int. J. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 3, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi, G.; Nunes, J.; Parrella, R.; Teixeira, D.; Bruzi, A.; Durães, N.; Fagundes, T. Path analysis of agro-industrial traits in sweet sorghum. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 16392–16402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearsey, M.J.; Pooni, H.S. The Genetical Analysis of Quantitative Traits; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kisua, J.; Mwikamba, K.; Makobe, M.; Muigai, A. Genetic diversity of sweet and grain sorghum using phenotypic markers. Int. J. Biosci. 2015, 6, 34–46. [Google Scholar]
- Nundwe, M. Characterisation of Sweet Sorghum Germplasm Based on Agro-Morphological Traits, Molecular Markers and Juice Related Traits. Master’s Dissertation, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Pietermaritzburg, South Africa, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield, C.; Collins, A. Introduction to Multivariate Analysis; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.; Andreson, R.; Tatham, R.; Black, W. Multivariate Data Analysis, 5th ed.; Prentice-Hall Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Berinyuy, J.E.; Focho, D.A.; Fontem, D.A.; Shippers, R.R. Morphological diversity of Solanum scabrum accessions in Cameroon. Plant Genet. Res. Newsl. 2002, 131, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Fontem, D.A.; Schippers, R.R.; Fontem, D.A.; Schippers, R.R. Solanum scabrum Mill. In Plant Resources of Tropical Africa 2. Vegetables; Grubben, G.J.H., Denton, O.A., Eds.; PROTA Foundation Wageningen/CTAWageningen/Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 493–498. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffers, J.N.R. Two Case Studies in the Application of Principal Component Analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C 1967, 16, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkaya, A.; Yanmaz, R.; Ozbakir, M. Evaluation of variation in seed characters in Turkish winter squash (Cucurbita maxima Duch.) populations. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2009, 37, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, Z.; Balkaya, A.; Saribas, S.; Kandemir, D. The Morphological Diversity and Fruit Characterization of Turkish Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) Populations. Ekin J. Crop Breed. Genet. 2017, 3, 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Mwadzingeni, L.; Shimelis, H.; Tesfay, S.; Tsilo, T.J. Screening of Bread Wheat Genotypes for Drought Tolerance Using Phenotypic and Proline Analyses. Front. Plant. Sci. 2016, 7, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mary, S.S.; Gopalan, A. Dissection of genetic attributes yield traits of fodder cowpea in F3 and F4. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2006, 2, 805–808. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Tabbal, J.A.; Al-Fraihat, A.H. Heritability Studies of Yield and Yield Associated Traits in Wheat Genotypes. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 4, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tabbal, J.A.; Al-Fraihat, A.H. Genetic Variation, Hetitability, Phenotypic and Genotypic Correlation Studies for Yield and Yield Components in Promising Barley Genotypes. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 4, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Upadhyay, K.K.; Mishra, B.K. Genetic Relationship Between Foliage Yield and its Biochemical Components in Vegetable Amaranth. Int. J. Veg. Sci. 2015, 22, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, O.P.; Singh, T.P.; Yadav, A.L.; Yadav, P.N. Genetic variability, genotypic and phenotypic correlation in germplasm of opium poppy (Papaver somniferum L.). Adv. Plant Sci. 2000, 13, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, O.P.; Singh, T.P. Genetic variability among some genotypes for morphological characters in lemongrass (Cymbopogon flexuosus L. Stapf). Indian Perfum. 1999, 43, 35–36. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.D. Plant Breeding: Principles and Methods; Kalyani Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bilgin, O.; Korkut, Z.N.; Baser, I.; Dalioglu, O.; Ozturk, I.; Kahraman, T.; Balkan, A. Variation and heritability for some semolina characteristics and grain yield and their relations in Durum Wheat (Triticum durum Desf.). World J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 6, 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Nyadana, D.; Dikera, E. Exploring variation, relationships and heritability of traits among selected accessions of sorghum (Sorghum bicolour L. Moench) in the upper east region of Ghana. J. Plant Breed. Genet. 2014, 2, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, H.W.; Robinson, H.F.; Comstock, R.E. Estimates of Genetic and Environmental Variability in Soybeans. Agron. J. 1955, 47, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, H.E.G.; Khidir, M.O. Estimates of Genetic and Environmental Variability in Sesame. Exp. Agric. 1974, 10, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Natera, J.R.; Rondo’n, A.; Hernandez, J.; Merazo-Pinto, J.F. Genetic studies in upland cotton. III. Genetic parameters, correlation and path analysis. SABRAO J. Breed. Genet. 2012, 44, 112–128. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, K.; Semwal, C.S.; Uniyal, S.P. Genetic variability and character association analysis in Bell pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). J. Hortic. For. 2010, 2, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Adeniji, O. Genetic variation and heritability for foliage yield and yield component traits in edible Amaranthus cruentus [L.] Genotypes. Bangladesh J. Agric. Res. 2018, 43, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.M. Variability Study in F4 Populations Obtained through Intervarietal Crosses of Brassica Rapa. Master’s Thesis, Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Saifullah, M. Variability Study among the F2 Segregants of the Intervarietal Crosses of Brassica Rapa. Master’s Thesis, Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Sher-eBangla Agricultural University, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, M.; Sharma, P.P.; Sharma, H.; Meghawal, D.R. Genetic variability in cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.] Germplasm lines. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2017, 6, 1384–1387. [Google Scholar]
- Suganthi, S.; Rajamani, K.; Renuka, R.; Suresh, J.; Joel, A.J.; Suganthan, R.N. Genetic diversity analysis using ISSR markers in Black nightshade (Solanum nigrum L. Complex). Med. Plants Int. J. Phytomed. Relat. Ind. 2018, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.H.L.; Walter, T.L. Heritability Estimates and Gene Effects for Agronomic Traits in Grain Sorghum, Sorghum vulgate Pers.1. Crop. Sci. 1968, 8, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panse, V.G. Genetics of quantitative characters in relation to plant breeding. Indian J. Genet. 1957, 17, 318–328. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.K.; Narayanan, S.S. Biometrical Techniques in Plant Breeding; Kalyani Publishers: New Delhi, India, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, O.P.; Kumar, Y.; Verma, P.K. Genetic variability, association among metric traits and path coefficient analysis in Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera). Haryana Agric. Univ. J. Res. 2008, 38, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sanexa, M.C.; Singh, Y. A note on leaf area estimation of intact maize leaves. Indian J. Agron. 1965, 10, 437–439. [Google Scholar]
- Bvenura, C.; Afolayan, A.J. The role of wild vegetables in household food security in South Africa: A review. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institution. The SAS System for Windows Version 9.4; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, K.A.; Gomez, A.A. Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Falconer, D.S. Introduction to Quantitative Genetics, 3rd ed.; Longman Scientific and Technical, Longman House, Burnt Mill: Harlow, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Falconer, D.; Mackay, T.F.C. Introduction to Quantitative Genetics, 4th ed.; Benjamin Cummings: London, UK, 1996; ISBN 0582243025. [Google Scholar]
- Piepho, H.-P.; MöHring, J. Computing Heritability and Selection Response From Unbalanced Plant Breeding Trials. Genetics 2007, 177, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, H.F.; Comstock, R.E.; Harvey, P.H. Estimates of Heritability and the Degree of Dominance in Corn. Agron. J. 1949, 41, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangena, P. Genetic Diversity Assessment and Evaluation of the Concentration and Stage of Application of a Male Gametocide for Hybrid Development in Sweet Stem Sorghum for Bioethanol Production. Ph.D. Thesis, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban, South Africa, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Comstock, R.R.; Robinson, H.F. Genetic Parameters, Their Estimation and Significance. In Proceedings of the 6th International Grassland Congress, State College, PA, USA, 17–23 August 1952; pp. 248–291. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.K.; Chaudhary, B.D. Biometric Methods in Quantitative Analysis; Kalayani Publishers: New Delhi, India, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Allard, R.W. Principles of Plant Breeding; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1960; p. 485. [Google Scholar]
| Mean Squares | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source of Variance | SEASON | Rep | Access | S*Access | Residual Error | CV% | GM |
| DF | 1 | 2 | 14 | 14 | 508 | ||
| PH cm | 37,500.00 | 2272.20 | 1541.61 | 972.97 | 170.12 | 23.48 | 55.54 |
| NLS | 386,082.81 | 126,599.01 | 28,148.89 | 6127.77 | 3822.37 | 50.35 | 122.77 |
| NBPr | 18.51 | 31.57 | 56.33 | 13.14 | 5.70 | 30.93 | 7.72 |
| SD mm | 941.84 | 13.59 | 152.50 | 105.78 | 57.79 | 70.19 | 10.83 |
| ChloroC nm | 171.92 | 682.19 | 857.30 | 375.56 | 120.26 | 39.69 | 27.63 |
| Psprd mm | 180,950.41 | 332,508.37 | 52,391.55 | 38,209.14 | 8513.04 | 21.15 | 436.26 |
| Nfruit | 1,803,360.06 | 16,647.53 | 145,177.30 | 75,054.82 | 17,846.65 | 81.52 | 163.87 |
| FFM g | 471,865.09 | 24,732.61 | 73,300.68 | 31,490.02 | 4823.89 | 87.72 | 79.18 |
| LFM g | 41,018.36 | 3167.15 | 4806.58 | 2650.23 | 1434.49 | 69.21 | 54.73 |
| LDM g | 4411.95 | 269.51 | 337.36 | 109.12 | 91.66 | 71.36 | 13.42 |
| SFM g | 209,762.49 | 54,980.50 | 15,658.43 | 16,752.00 | 3511.77 | 69.05 | 85.82 |
| SDM g | 16,668.55 | 2718.57 | 456.95 | 617.37 | 179.64 | 69.30 | 19.34 |
| SLarea cm2 | 22.97 | 38.43 | 154.27 | 17.61 | 57.79 | 35.14 | 5.80 |
| BLarea cm2 | 998.11 | 2009.37 | 23,268.50 | 5545.11 | 433.21 | 66.22 | 31.43 |
| ND_F | 4611.26 | 270.06 | 481.20 | 148.12 | 12.29 | 11.56 | 30.32 |
| ND_FF | 10,454.40 | 131.40 | 357.28 | 91.40 | 11.75 | 7.62 | 45.00 |
| ND_FR | 1092.26 | 168.80 | 314.17 | 112.83 | 6.63 | 4.97 | 51.80 |
| Source of Variance | SEASON | Rep | Access | S*Access | Residual Error | CV% | GM |
| DF | 1 | 2 | 14 | 14 | 58 | ||
| LY_gp | 1,224,365.41 | 64,213.01 | 90,383.08 | 83,521.08 | 43,006.78 | 34.95 | 593.19 |
| SY_gp | 5,775,868.26 | 1,220,950.45 | 419,336.89 | 338,286.70 | 136,080.38 | 37.91 | 972.99 |
| FY_gp | 14,048,539.10 | 545,708.29 | 1,944,116.32 | 1,003,041.28 | 147,601.51 | 44.10 | 871.17 |
| TBiomass_gp | 52,677,869.68 | 4,210,043.66 | 3,895,404.18 | 2,601,992.42 | 693,867.4 | 34.17 | 2437.36 |
| HrvstInd% | 785.40 | 289.58 | 224.65 | 101.48 | 31.46 | 20.13 | 27.85 |
| Accession | PH (cm) | NLS | NBPr | SD (mm) | ChloroC nm | Psprd mm | Nfruit | FFM (g) | LFM (g) | LDM (g) | SFM (g) | SDM (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ManTown | 61.33 ab | 94.67 df | 6.41 de | 12.16 ab | 23.59 c | 418.89 bd | 136.47 c e | 123.41 a | 48.82 ac | 10.38 bc | 83.70 ad | 16.67 bc |
| NigSN18 | 43.50 d | 104.14 de | 7.78 ad | 11.58 ab | 24.95 bc | 443.61 ac | 161.42 be | 111.17 ab | 43.01 bc | 10.68 bc | 52.20 d | 11.34 c |
| SRetrflx | 56.11 bc | 101.28 de | 6.97 be | 11.57 ab | 26.50 bc | 453.33 ac | 116.42 de | 120.97 ab | 49.21 ac | 10.89 bc | 91.15 ad | 19.09 ac |
| Nshad9 | 59.83 ac | 101.19 de | 8.31 ac | 10.82 ab | 25.71 bc | 457.22 ac | 155.39 be | 130.68 a | 52.85 ac | 11.12 bc | 94.61 ad | 19.79 ac |
| Nshad5 | 49.61 cd | 113.31 be | 5.97 de | 10.18 b | 28.25 bc | 359.17 d | 98.39 e | 108.15 ab | 50.55 ac | 12.01 bc | 81.72 ad | 17.53 ac |
| N5547 | 66.83 a | 138.22 ae | 7.61 ad | 10.94 ab | 25.29 bc | 405.28 bd | 82.67 e | 67.20 ac | 59.83 ac | 13.34 ac | 109.87 ab | 22.72 ab |
| Nshad40 | 57.89 ac | 90.39 ef | 7.08 cd | 16.42 a | 22.20 c | 460.00 ac | 210.67 ad | 100.65 ac | 71.33 ab | 17.82 ab | 114.10 ab | 21.22 ac |
| Ncampus | 51.83 bd | 127.08 be | 8.86 ab | 9.83 b | 39.34 a | 469.72 ab | 188.47 be | 24.03 d | 74.88 a | 15.97 ac | 82.07 ad | 21.32 ac |
| Nfarm | 53.67 bd | 150.08 ac | 9.31 a | 9.84 b | 33.69 ab | 459.44 ac | 119.36 de | 18.74 d | 54.67 ac | 14.20 ac | 81.70 ad | 19.16 ac |
| N0096 | 61.63 ab | 135.06 be | 8.33 ac | 8.03 b | 25.62 bc | 390.56 cd | 241.94 ac | 30.88 d | 39.24 c | 9.62 c | 57.77 cd | 16.66 bc |
| Scabrum | 56.81 ac | 85.47f | 5.06 e | 12.54 ab | 22.92 c | 433.06 bd | 122.03 de | 107.43 ab | 73.49 a | 19.91 a | 122.97 a | 27.75 a |
| SNig2495 | 50.39 cd | 140.33 ad | 8.81 ab | 9.39 b | 32.68 ab | 446.25 ac | 150.97 be | 26.36 d | 55.55 ac | 12.59 ac | 73.32 bd | 18.16 ac |
| Sharon | 45.28 d | 153.92 ab | 8.39 ab | 9.33 b | 23.25 c | 516.94 a | 300.06 a | 45.14 cd | 49.31 ac | 17.11 ac | 76.85 ad | 19.09 ac |
| SABGA | 56.14 bc | 121.14 be | 7.53 ad | 11.63 ab | 32.60 ab | 432.22 bd | 115.81 de | 140.32 a | 60.31 ac | 13.98 ac | 105.00 ad | 21.28 ac |
| Timbali | 62.31 ab | 185.36 a | 9.42 a | 8.18 b | 27.86 bc | 398.33 bd | 257.94 ab | 32.58 d | 37.85 c | 11.65 bc | 60.31 cd | 18.33 ac |
| HSD | ** | *** | *** | ** | ** | ** | *** | *** | ** | * | ** | ** |
| Fpr | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 00.0010 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0016 |
| GM | 55.54 | 122.77 | 7.72 | 10.83 | 27.63 | 436.27 | 163.87 | 79.18 | 54.73 | 13.42 | 85.82 | 19.34 |
| Accession | SLarea (cm2) | BLarea (cm2) | ND_F | ND_FF | ND_FR | LY_gp | SY_gp | FY_gp | TBiomass_gp | HrvstInd (%) | ||
| ManTown | 6.10 b | 51.61 c | 28.33 bc | 43.83 cf | 52.17 cf | 651.90 ab | 1187.30 ac | 1507.90 ab | 3347.20 a | 20.77 ed | ||
| NigSN18 | 6.50 b | 22.36 de | 28.50 bc | 44.67 be | 53.33 be | 532.60 ab | 765.10 ac | 1782.00 a | 3079.70 ab | 21.86 ce | ||
| SRetrflx | 6.68 b | 33.26 d | 30.16 b | 45.83 bd | 52.33 cf | 611.70 ab | 1206.60 ac | 1354.20 ac | 3172.60 ab | 19.60 e | ||
| Nshad9 | 6.24 b | 24.66 de | 27.83 bc | 43.83 cf | 51.67 df | 612.50 ab | 1086.90 ac | 1363.70 ac | 3063.10 ab | 21.29 ed | ||
| Nshad5 | 6.14 b | 23.19 de | 27.83 bc | 42.83 ef | 49.17gh | 580.20 ab | 956.10 ac | 1433.70 ac | 2970.00 ac | 26.30 be | ||
| N5547 | 6.64 b | 23.40 de | 35.33 a | 51.50 a | 55.33 b | 685.50 ab | 1376.90 a | 657.10 ce | 2719.50 ad | 26.47 be | ||
| Nshad40 | 9.72 a | 70.31 b | 36.50 a | 47.00 b | 53.50 bd | 679.00 ab | 1192.80 ac | 879.80 be | 2751.60 ac | 29.42 ae | ||
| Ncampus | 4.14 c | 20.49 de | 28.17 bc | 43.67 df | 47.67h | 718.60 ab | 911.60 ac | 228.20 e | 1858.40 ad | 37.68 ab | ||
| Nfarm | 4.00 c | 14.30 e | 26.33 c | 41.83f | 48.17h | 612.00 ab | 856.80 ac | 173.40 e | 1642.20 bd | 38.87 a | ||
| N0096 | 3.38 c | 10.17 e | 29.83 b | 41.83f | 51.17fg | 425.80 ab | 615.30 bc | 304.80 e | 1346.00 cd | 30.41 ae | ||
| Scabrum | 9.77 a | 101.84 a | 34.67 a | 46.00 bd | 53.83 bc | 805.30 a | 1252.00 ab | 1132.70 ad | 3190.10 ab | 30.19 ae | ||
| SNig2495 | 4.41 c | 20.63 de | 26.33 c | 41.83f | 48.17h | 573.40 ab | 880.30 ac | 289.80 e | 1743.50 ad | 33.22 ac | ||
| Sharon | 3.16 c | 9.16 e | 36.83 a | 51.50 a | 58.67 a | 301.60 b | 466.50 c | 275.90 e | 1044.00 d | 29.39 ae | ||
| SABGA | 6.53 b | 35.13 cd | 27.83 bc | 42.33 ef | 51.33 ef | 622.30 ab | 1161.50 ac | 1331.70 ac | 3115.50 ab | 21.00 ed | ||
| Timbali | 3.52 c | 10.99 e | 30.33 b | 46.50 bc | 50.50fg | 485.50 ab | 679.10 ac | 352.50 de | 1517.20 bd | 31.33 ad | ||
| HSD | ** | *** | * | *** | *** | * | ** | *** | *** | *** | ||
| Fpr | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0250 | 0.0013 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||
| GM | 5.80 | 31.43 | 30.32 | 45.00 | 51.80 | 593.19 | 972.99 | 871.16 | 2437.37 | 27.85 | ||
| Eigenvectors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 |
| PH (cm) | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.65 |
| NLS | −0.27 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.24 |
| NBPr | −0.27 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.00 |
| SD (mm) | 0.28 | 0.06 | −0.04 | −0.18 |
| ChloroC | −0.14 | −0.02 | 0.42 | −0.14 |
| Psprd (mm) | −0.02 | 0.25 | −0.07 | −0.46 |
| Nfruit | −0.19 | 0.20 | −0.24 | −0.10 |
| FFM g/plant | 0.26 | −0.22 | −0.14 | −0.09 |
| LFM g/plant | 0.19 | 0.26 | 0.27 | −0.16 |
| LDM g/plant | 0.12 | 0.40 | 0.07 | −0.20 |
| SFM g/plant | 0.27 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| SDM g/plant | 0.17 | 0.31 | 0.18 | 0.20 |
| SLarea cm2 | 0.31 | 0.02 | −0.01 | −0.05 |
| BLarea cm2 | 0.28 | 0.11 | 0.04 | −0.06 |
| ND_F | 0.11 | 0.34 | −0.29 | 0.13 |
| ND_FF | 0.05 | 0.28 | −0.32 | 0.17 |
| ND_FR | 0.10 | 0.18 | −0.44 | 0.03 |
| LY_gp | 0.24 | 0.02 | 0.32 | 0.06 |
| SY_gp | 0.28 | −0.04 | 0.15 | 0.21 |
| FY_gp | 0.22 | −0.31 | −0.14 | −0.15 |
| TBiomass_gp | 0.28 | −0.22 | −0.00 | −0.03 |
| HrvstInd (%) | −0.16 | 0.28 | 0.28 | −0.03 |
| Eigenvalue (explained variance) | 9.25 | 4.41 | 3.61 | 1.83 |
| Proportion of total variance (%) | 42.03 | 20.07 | 16.41 | 8.31 |
| Cumulative variance (%) | 42.03 | 62.10 | 78.51 | 86.82 |
| Variables | Mean Range | X | σ2g | σ2p | H2 (%) | GCV (%) | PCV (%) | GA at 5% | GAM (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH cm | 43.50–66.83 | 55.54 | 94.77 | 609.62 | 15.55 | 17.53 | 44.45 | 7.91 | 14.24 |
| NLS | 85.47–185.36 | 122.77 | 3670.19 | 7371.14 | 49.79 | 49.35 | 69.93 | 88.06 | 71.73 |
| NBPr | 5.06–9.41 | 7.72 | 7.20 | 14.72 | 48.88 | 34.75 | 49.70 | 3.86 | 50.05 |
| SD mm | 8.03–16.42 | 10.83 | 7.79 | 70.31 | 11.08 | 25.79 | 77.50 | 1.91 | 17.68 |
| ChloroC | 22.20–39.34 | 27.63 | 80.29 | 288.12 | 27.87 | 32.43 | 61.43 | 9.74 | 35.27 |
| Psprd mm | 359.17–515.94 | 436.27 | 2363.73 | 22,888.89 | 10.33 | 11.14 | 34.68 | 32.19 | 7.38 |
| Nfruit | 82.67–300.06 | 163.87 | 11,687.08 | 52,188.94 | 22.39 | 65.97 | 139.41 | 105.39 | 64.31 |
| FFM g | 18.74–140.32 | 79.18 | 6968.44 | 23,517.40 | 29.63 | 105.43 | 193.68 | 93.61 | 118.22 |
| LFM g | 37.85–74.88 | 54.73 | 359.39 | 1923.59 | 18.68 | 34.64 | 80.14 | 16.88 | 30.84 |
| LDM g | 9.62–19.91 | 13.42 | 38.04 | 107.88 | 35.26 | 45.96 | 77.39 | 7.54 | 56.22 |
| SLarea cm2 | 3.16–9.77 | 5.80 | 22.78 | 32.27 | 70.59 | 82.28 | 97.95 | 8.26 | 142.40 |
| BLarea cm2 | 9.16–101.84 | 31.43 | 2953.90 | 5798.66 | 50.94 | 172.92 | 242.28 | 79.91 | 254.25 |
| ND_F | 26.33–36.83 | 30.32 | 55.52 | 131.62 | 42.18 | 24.57 | 37.84 | 9.97 | 32.88 |
| ND_FF | 41.43–51.50 | 45.00 | 44.32 | 91.97 | 48.18 | 14.79 | 21.31 | 9.52 | 21.15 |
| ND_FR | 47. 67–58.67 | 51.80 | 33.56 | 91.08 | 36.84 | 11.18 | 18.42 | 7.25 | 13.98 |
| LY_gp | 301.60–805.30 | 593.19 | 1143.67 | 50,072.00 | 2.28 | 5.70 | 37.72 | 10.53 | 1.77 |
| SY_gp | 466.50–1376.90 | 972.99 | 13,508.37 | 205,331.78 | 6.58 | 11.95 | 46.57 | 61.41 | 6.31 |
| FY_gp | 173.40–1782.00 | 871.16 | 156,845.84 | 682,966.73 | 22.97 | 45.46 | 94.86 | 390.97 | 44.88 |
| TBiomass_gp | 1044.00–3347.60 | 2437.37 | 215,568.63 | 1,632,209.40 | 13.07 | 19.05 | 52.42 | 347.59 | 14.26 |
| HrvstInd (%) | 19.60–38.88 | 27.85 | 20.53 | 76.51 | 26.83 | 16.27 | 31.41 | 4.83 | 17.36 |
| Entry No. | Given Codes | Accessions | Source of Origin in South Africa |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ManTown | ManTown | ARC |
| 2 | NigSN18 | NigSN18 | ARC |
| 3 | SRetrflx | Solanum retroflexum | ARC |
| 4 | Nshad9 | Nshad9 | ARC |
| 5 | Nshad5 | Nshad5 | ARC |
| 6 | Nshad40 | Nshad40 | ARC |
| 7 | Scabrum | Solanum scabrium (Unizulu) | University of Zululand |
| 8 | SNig2495 | S. nigrum 2495 | DAFF |
| 9 | Ncapmus | Nshad NWU | NWU Mafikeng-campus |
| 10 | Nfarm | Nshad NWU | NWU Farm |
| 11 | Timbali | NshadTimbali | Komatiport- Mpumalanga |
| 12 | N0096 | Nshad 0096 | Naas- Mpumalanga |
| 13 | N5547 | N5547 | ARC |
| 14 | SABGA | SABGA | ARC |
| 15 | Sharon | Sharon | ARC |
| Month | Year | Minimum | Maximum | Rainfall (mm) | Relative Humidity (%) Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | |||||
| Season 1 | |||||
| January | 2020 | 20 | 30 | 179.3 | 51 |
| February | 2020 | 20 | 30 | 95.7 | 49 |
| March | 2020 | 18 | 29 | 97.2 | 45 |
| April | 2020 | 15 | 26 | 59.2 | 45 |
| November | 2020 | 20 | 30 | 229.5 | 46 |
| Season 2 | |||||
| December | 2020 | 20 | 29 | 168.2 | 52 |
| January | 2021 | 17.4 | 30.8 | 335.8 | 58 |
| February | 2021 | 16.8 | 29.5 | 259.3 | 63 |
| Soil Properties | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 |
|---|---|---|
| Sample density g/mL | 1.14 | 1.17 |
| P mg/L | 1 | 1 |
| K mg/L | 244 | 279 |
| Ca mg/L | 2961 | 1857 |
| Mg mg/L | 680 | 478 |
| Zn mg/L | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| Mn mg/L | 14 | 16 |
| Cu mg/L | 2.2 | 2.5 |
| pH- (KCI) | 6.24 | 6.07 |
| Exchangeable acidity cmol/L | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| Total cations cmol/L | 21.07 | 13.98 |
| Acid saturation (%) | 0 | 1 |
| Soil Organic Carbon (%) | 1.5 | 1.3 |
| N (%) | 0.08 | 0.09 |
| Clay (%) | 20 | 19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mabuza, N.M.; Mavengahama, S.; Mokolobate, M. Agronomic, Genetic and Quantitative Trait Characterization of Nightshade Accessions. Plants 2022, 11, 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111489
Mabuza NM, Mavengahama S, Mokolobate M. Agronomic, Genetic and Quantitative Trait Characterization of Nightshade Accessions. Plants. 2022; 11(11):1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111489
Chicago/Turabian StyleMabuza, Ntombifuthi Msewu, Sydney Mavengahama, and Motlogeloa Mokolobate. 2022. "Agronomic, Genetic and Quantitative Trait Characterization of Nightshade Accessions" Plants 11, no. 11: 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111489
APA StyleMabuza, N. M., Mavengahama, S., & Mokolobate, M. (2022). Agronomic, Genetic and Quantitative Trait Characterization of Nightshade Accessions. Plants, 11(11), 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111489






