Characterization of the Calmodulin/Calmodulin-like Protein (CAM/CML) Family in Ginkgo biloba, and the Influence of an Ectopically Expressed GbCML Gene (Gb_30819) on Seedling and Fruit Development of Transgenic Arabidopsis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of CAM/CML Homologs
2.2. Phylogenetic and Gene Structural Analysis of CAMs/CMLs
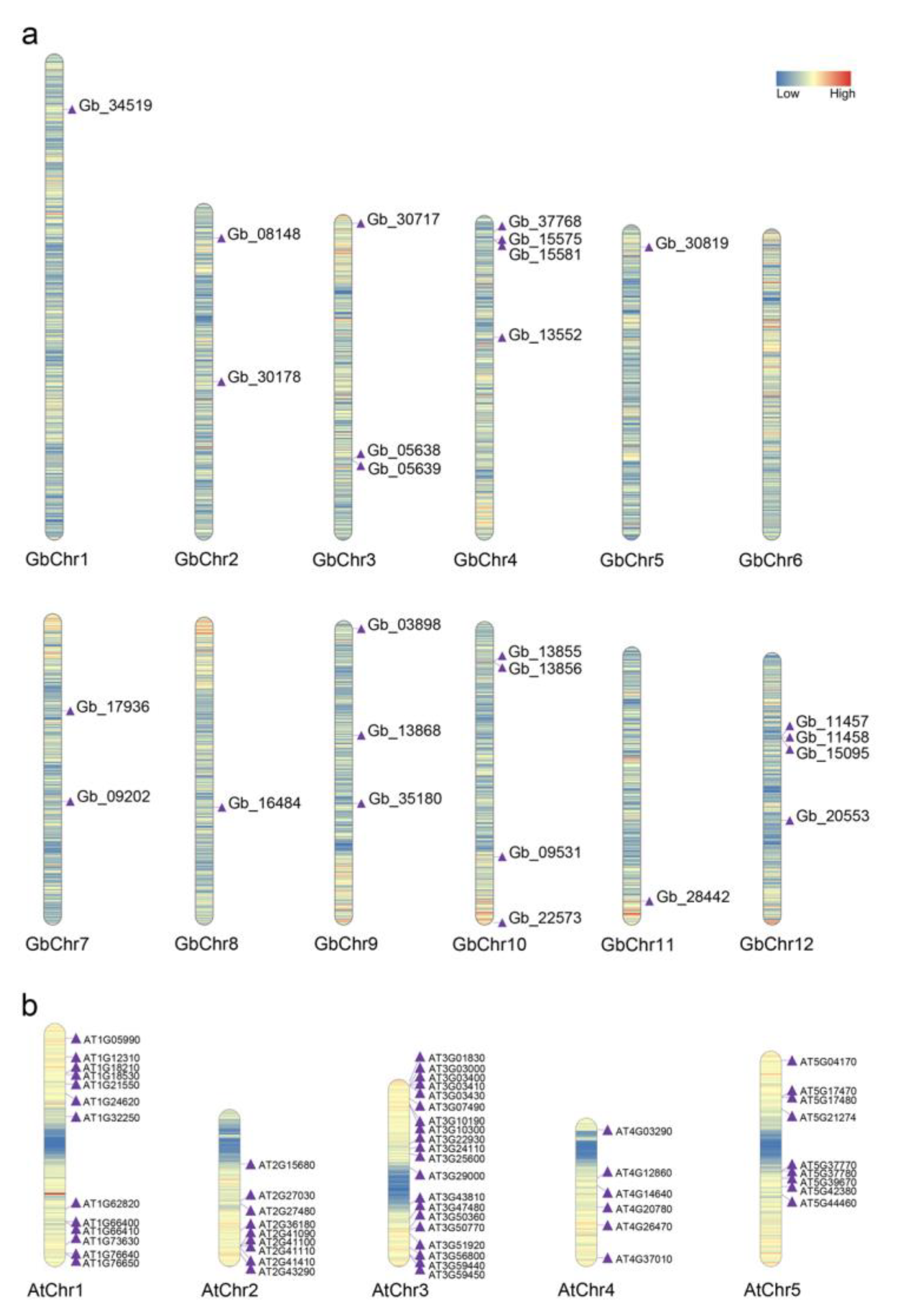
2.3. Collinearity Analysis of CAMs/CMLs
2.4. Quantitative Analysis of GbCAM/GbCML Expression in G. biloba
2.5. Analysis of Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements in GbCAM/GbCML Promotors
2.6. Transgenic Arabidopsis Plants Overexpressing Gb_30819
2.7. In Vitro Ca2+-Binding Activity of Gb_30819 Determined by Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. CAM/CML Gene Identification
4.2. Phylogenetic Tree Construction
4.3. Molecular Features, Gene Structures, and Conserved Motifs of CAM/CML Proteins
4.4. Chromosomal Distributions and Collinearity Relationships of CAM/CML Genes
4.5. Expression Analysis of GbCAMs/GbCMLs in G. biloba
4.6. Analysis of Regulatory Elements in GbCAM/GbCML Promotors
4.7. Construction of the Eukaryotic Expression Vector pCAMBIA1301a-Gb_30819 and Arabidopsis Transformation
4.8. Bacterial Expression of the Fusion Protein Gb_30819, and Protein Mobility Shift Electrophoresis Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis of Data
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanders, D.; Pelloux, J.; Brownlee, C.; Harper, J.F. Calcium at the crossroads of signaling. Plant Cell 2002, 14, S401–S417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dodd, A.N.; Kudla, J.; Sanders, D. The language of calcium signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 593–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudla, J.; Batistič, O.; Hashimoto, K. Calcium signals: The lead currency of plant information processing. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 541–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudd, J.J.; Franklin-Tong, V.E. Unravelling response-specificity in Ca2+ signaling pathways in plant cells. New Phytol. 2001, 151, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, I.S.; Reddy, V.S.; Shad Ali, G.; Reddy, A.S.N. Analysis of EF-hand-containing proteins in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, research0056.1–0056.24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.Q.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhang, X.J.; Pi, E.; Zhu, Y.Y. Analysis of EF-Hand Proteins in soybean genome suggests their potential roles in environmental and nutritional stress signaling. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snedden, W.A.; Fromm, H. Calmodulin as a versatile calcium signal transducer in plants. New Phytol. 2001, 151, 35–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCormack, E.; Braam, J. Calmodulins and related potential calcium sensors of Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2003, 159, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranty, B.; Aldon, D.; Galaud, J.P. Plant calmodulins and calmodulin-related proteins: Multifaceted relays to decode calcium signals. Plant Signal. Behav. 2006, 1, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCormack, E.; Tsai, Y.C.; Braam, J. Handling calcium signaling: Arabidopsis CaMs and CMLs. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonburapong, B.; Buaboocha, T. Genome-wide identification and analyses of the rice calmodulin and related potential calcium sensor proteins. BMC Plant Biol. 2007, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Yue, D.; Wei, W.; Hu, Y.; Feng, J.; Zou, Z. Characterization and functional analysis of calmodulin and calmodulin-like genes in Fragaria vesca. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munir, S.; Khan, M.R.G.; Song, J.W.; Munir, S.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ye, Z.B.; Wang, T.T. Genome-wide identification, characterization and expression analysis of calmodulin-like (CML) proteins in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 102, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of calmodulin-like (CML) genes in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandelle, E.; Vannozzi, A.; Wong, D.; Danzi, D.; Digby, A.E.; Santo, S.D.; Astegno, A. Identification, characterization, and expression analysis of calmodulin and calmodulin-like genes in grapevine (Vitis vinifera) reveal likely roles in stress responses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 129, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Meng, D.; Zhang, J.H.; Cheng, L.L. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of calmodulin and calmodulin-like genes in apple (Malus × domestica). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 139, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Dunand, C.; Snedden, W.; Galaud, J.P. CaM and CML emergence in the green lineage. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushwaha, R.; Singh, A.; Chattopadhyay, S. Calmodulin7 plays an important role as transcriptional regulator in Arabidopsis seedling development. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landoni, M.; De Francesco, A.; Galbiati, M.; Tonelli, C. A loss-of-function mutation in Calmodulin2 gene affects pollen germination in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol. Biol. 2010, 74, 235–247. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L.Q.; Poovaiah, B.W. Ca2+/calmodulin is critical for brassinosteroid biosynthesis and plant growth. Nature 2005, 437, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnan, F.; Ranty, B.; Charpenteau, M.; Sotta, B.; Galaud, J.P.; Aldon, D. Mutations in AtCML9, a calmodulin-like protein from Arabidopsis thaliana, alter plant responses to abiotic stress and abscisic acid. Plant J. 2008, 56, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galon, Y.; Aloni, R.; Nachmias, D.; Snir, O.; Feldmesser, E.; Scrase-Field, S.; Boyce, J.M.; Bouché, N.; Knight, M.R.; Fromm, H. Calmodulin-binding transcription activator 1 mediates auxin signaling and responds to stresses in Arabidopsis. Planta 2010, 232, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFalco, T.A.; Bender, K.W.; Snedden, W.A. Breaking the code: Ca2+ sensors in plant signaling. Biochem. J. 2010, 425, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobney, S.; Chiasson, D.; Lam, P.; Smith, S.P.; Snedden, W.A. The calmodulin-related calcium sensor CML42 plays a role in trichome branching. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 31647–31657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Wang, S.S.; Wang, M.; Qiao, Z.; Bao, C.C.; Zhang, W. Arabidopsis thaliana calmodulin-like protein CML24 regulates pollen tube growth by modulating the actin cytoskeleton and controlling the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 86, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiasson, D.; Ekengren, S.K.; Martin, G.B.; Dobney, S.L.; Snedden, W.A. Calmodulin-like proteins from Arabidopsis and tomato are involved in host defense against Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 58, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.W.; Lee, D.H.; Hwang, B.K. The pepper calmodulin gene CaCaM1 is involved in reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide generation required for cell death and the defense response. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, R.G.; Gao, Y.J.; Zheng, S.Z.; Xu, P.; Zhang, S.Q.; Sun, D.Y. Molecular and genetic evidence for the key role of AtCaM3 in heat-shock signal transduction in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 1773–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.J.; Lin, Z.W.; Huang, G.J.; Lin, Y.H. Sweet potato calmodulin SPCAM is involved in salt stress mediated leaf senescence, H₂O₂ elevation and senescence-associated gene expression. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 1892–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Sun, X.; Duanmu, H.; Zhu, D.; Yu, Y.; Cao, L.; Liu, A.; Jia, B.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, Y. GsCML27, a gene encoding a calcium-binding EF-hand protein from Glycine soja, plays differential roles in plant responses to bicarbonate, salt and osmotic stresses. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, H.; Chung, P.J.; Park, S.H.; Redillas, M.C.F.R.; Kim, Y.S.; Suh, J.W.; Kim, J.K. Overexpression of OsERF48 causes regulation of OsCML16, a calmodulin-like protein gene that enhances root growth and drought tolerance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 1295–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.H.; Wu, D.; Li, S.Z.; Guo, N.; Gao, J.S.; Sun, X.; Cai, Y.P. Transcriptomic profiling identifies differentially expressed genes associated with programmed cell death of nucellar cells in Ginkgo biloba L. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, A. Selection and gene duplication: A view from the genome. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, reviews1012.1–1012.3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruge, H.; Flosdorff, S.; Ebersberger, I.; Chigri, F.; Vothknecht, U.C. The calmodulin-like proteins AtCML4 and AtCML5 are single-pass membrane proteins targeted to the endomembrane system by an N-terminal signal anchor sequence. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 3985–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Snedden, W.A.; Fromm, H. Calmodulin, calmodulin-related proteins and plant responses to the environment. Trends Plant Sci. 1998, 3, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2—Approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; DeBarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.H.; Wu, D.; Li, S.Z.; Dai, Y.; Cao, Y.P. Evolutionary and functional analysis of the plant-specific NADPH oxidase gene family in Brassica rapa L. Roy. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 181727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.H.; Yang, X.; Cui, X.; Cui, K.M.; Li, Z.L. Early development of pollen chamber in Ginkgo biloba ovule. Acta Bot. Sin. 2002, 44, 757–763. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆Ct method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielinski, R.E. Characterization of three new members of the Arabidopsis thaliana calmodulin gene family: Conserved and highly diverged members of the gene family functionally complement a yeast calmodulin null. Planta 2002, 214, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Tian, J.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Feng, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, D. Characterization of the Calmodulin/Calmodulin-like Protein (CAM/CML) Family in Ginkgo biloba, and the Influence of an Ectopically Expressed GbCML Gene (Gb_30819) on Seedling and Fruit Development of Transgenic Arabidopsis. Plants 2022, 11, 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111506
Zhang X, Tian J, Li S, Liu Y, Feng T, Wang Y, Li Y, Huang X, Li D. Characterization of the Calmodulin/Calmodulin-like Protein (CAM/CML) Family in Ginkgo biloba, and the Influence of an Ectopically Expressed GbCML Gene (Gb_30819) on Seedling and Fruit Development of Transgenic Arabidopsis. Plants. 2022; 11(11):1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111506
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinxin, Juan Tian, Sai Li, Yuying Liu, Ting Feng, Yunyun Wang, Yuanjin Li, Xinxin Huang, and Dahui Li. 2022. "Characterization of the Calmodulin/Calmodulin-like Protein (CAM/CML) Family in Ginkgo biloba, and the Influence of an Ectopically Expressed GbCML Gene (Gb_30819) on Seedling and Fruit Development of Transgenic Arabidopsis" Plants 11, no. 11: 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111506
APA StyleZhang, X., Tian, J., Li, S., Liu, Y., Feng, T., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Huang, X., & Li, D. (2022). Characterization of the Calmodulin/Calmodulin-like Protein (CAM/CML) Family in Ginkgo biloba, and the Influence of an Ectopically Expressed GbCML Gene (Gb_30819) on Seedling and Fruit Development of Transgenic Arabidopsis. Plants, 11(11), 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111506





