Optimization of Alfalfa-Based Mixed Cropping with Winter Wheat and Ryegrass in Terms of Forage Yield and Quality Traits
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
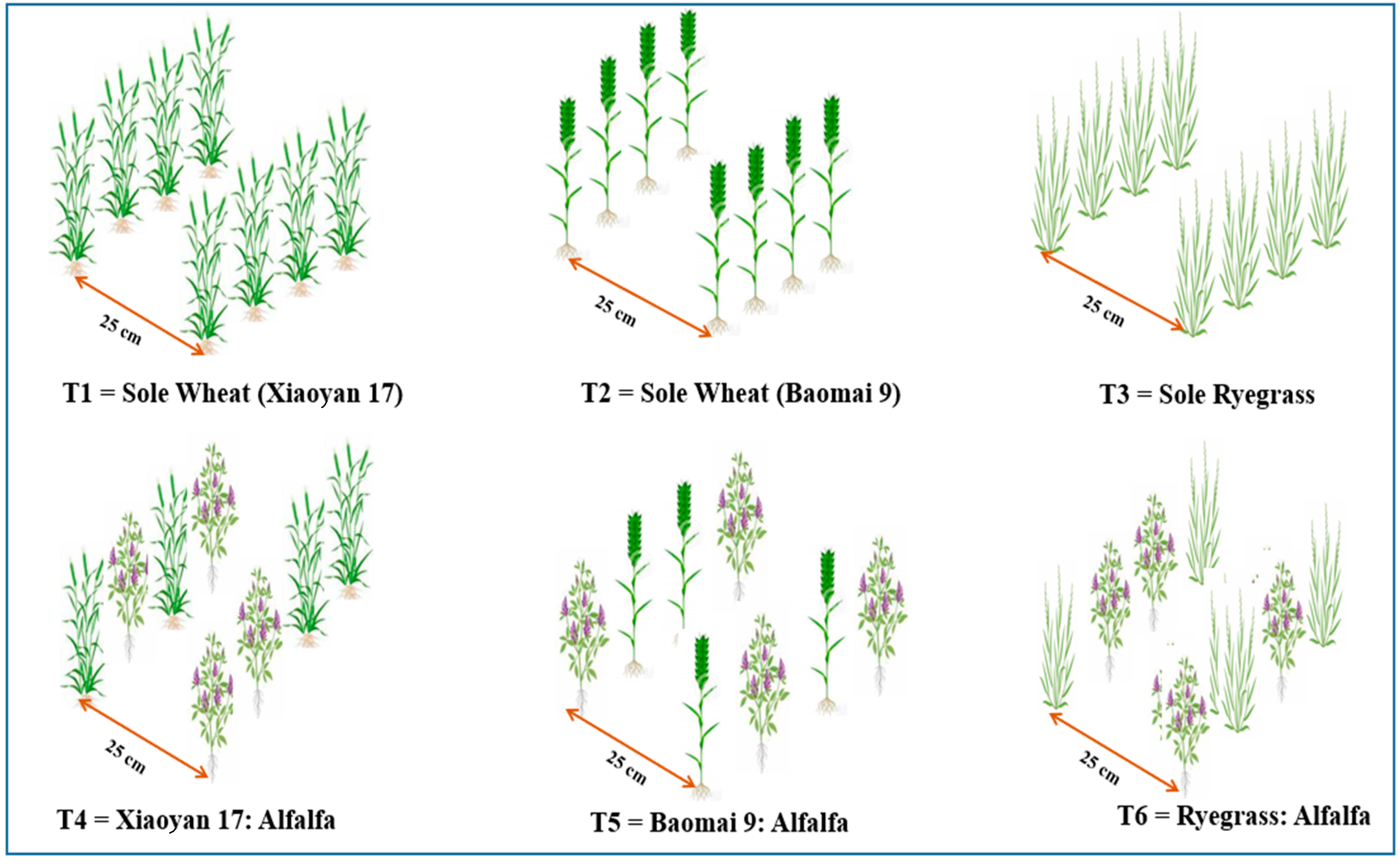
2.2. Experimental Treatments, Design and Forage Cultivation
2.3. Sample Collection and Sample Preparation
2.4. Proximate and Mineral Compositions and Amino Acid Profiles Determination
2.5. Laboratory Forage Quality Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fresh Biomass Yield
3.2. Dry Matter Yield
3.3. Crude Protein Yield
3.4. Scatterplot Matrix Analysis of the Forage of Wheat, Ryegrass Mono-Cropping and Wheat, Ryegrass Mixed Cropping with Alfalfa
3.5. Proximate and Mineral Composition Analysis
3.6. Amino Acid Profiles
3.7. Forage Quality Analysis
3.8. Correlation Analysis of Proximate Compositions and Forage Quality Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Assessment of FBY, Dry Forage Yield, and CPY
4.2. Evaluation of Nutritional Compositions (Proximate and Mineral) and Amino Acid Profiles
4.3. Forage Quality Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soussana, J.F.; Tallec, T.; Blanfort, V. Mitigating the greenhouse gas balance of ruminant production systems through carbon sequestration in grasslands. Animal 2010, 4, 334–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, Y.; Luan, W.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y. Environmental and economic benefits of carbon emission reduction in animal husbandry via the circular economy: A case study of pig farming in Liaoning China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamborg, C.; Sandøe, P. Sustainability in farm animal breeding: A review. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2005, 92, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raza, M.A.; Feng, L.Y.; van der Werf, W.; Iqbal, N.; Khan, I.; Hassan, M.J.; Ansar, M.; Chen, Y.K.; Xi, Z.J.; Shi, J.Y.; et al. Optimum leaf defoliation: A new agronomic approach for increasing nutrient uptake and land equivalent ratio of maize soybean relay intercropping system. Field Crops Res. 2019, 244, 107647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.A.; Gul, H.; Wang, J.; Yasin, H.S.; Qin, R.J.; Khalid, M.H.B.; Naeem, M.; Feng, L.Y.; Iqbal, N.; Gitari, H.; et al. Land productivity and water use efficiency of maize-soybean strip intercropping systems in semi-arid areas: A case study in Punjab Province, Pakistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 308, 127282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.I.; Ashraf, M.; Ahmad, K. Evaluation of Micro Minerals Composition of Different Grasses in Relation to Livestock Requirements. Pak. J. Bot. 2007, 39, 719–728. [Google Scholar]
- Rafińska, K.; Pomastowski, P.; Wrona, O. Medicago sativa as a source of secondary metabolites for agriculture and pharmaceutical industry. Phytochem. Lett. 2017, 20, 520–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahong, W.; Xuqing, W.; Sayre, K. Comparison of conventional, flood irrigated, flat planting with furrow irrigated, raised bed planting for winter wheat in China. Field Crops Res. 2004, 87, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; He, Z.; Sayre, K. Wheat cropping systems and technologies in China. Field Crops Res. 2009, 111, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, I.; Epplin, F.M.; Krenzer, E.G. Planting Date Influence on Dual-Purpose Winter Wheat Forage Yield, Grain Yield, and Test Weight. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, S.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Nishino, N. Effects of inoculation with lactic acid bacteria on the bacterial communities of Italian ryegrass, whole crop maize, guinea grass and Rhodes grass silages. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2010, 160, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avola, G.; Tuttobene, R.; Gresta, F.; Abbate, V. Weed control strategies for grain legumes. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.A.; Feng, L.Y.; Iqbal, N.; Ahmed, M.; Chen, Y.K.; Khalid, M.H.B.; Din, A.M.; Khan, A.; Ijaz, W.; Hussain, A.; et al. Growth and development of soybean under changing light environments in relay intercropping system. PeerJ 2019, 23, e7262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, M.A.; Feng, L.Y.; van der Werf, W.; Iqbal, N.; Khan, I.; Khan, A.; Din, A.M.U.; Naeem, M.; Meraj, T.A.; Hassan, M.J.; et al. Optimum strip width increases dry matter, nutrient accumulation, and seed yield of intercrops under the relay intercropping system. Food Energy Secur. 2020, 9, e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, L.; Raza, M.A.; Chen, Y.; Khalid, M.H.B.; Meraj, T.A.; Ahsan, F.; Fan, Y.; Du, J.; Wu, X.; Song, C.; et al. Narrow-wide row planting pattern improves the light environment and seed yields of intercrop species in relay intercropping system. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soe Htet, M.N.; Wang, H.; Yadav, V.; Sompouviseth, T.; Feng, B. Legume Integration Augments the Forage Productivity and Quality in Maize-Based System in the Loess Plateau Region. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Albrecht, K.A.; Muck, R.E. Spring Yield and Silage Characteristics of Kura Clover, Winter Wheat, and in Mixtures. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.-H.; Kim, K.-Y.; Jung, M.-W. Dry Matter Yield and Forage Quality at Mixture of Annual Legumes and Italian ryegrass on Paddy Field. J. Korean Soc. Grassl. Forage Sci. 2011, 31, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bélanger, G.; Castonguay, Y.; Lajeunesse, J. Benefits of mixing timothy with alfalfa for forage yield, nutritive value, and weed suppression in northern environments. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2014, 94, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Gooding, M.; Ambus, P. Pea-barley intercropping for efficient symbiotic N2-fixation, soil N acquisition and use of other nutrients in European organic cropping systems. Field Crops Res. 2009, 113, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amraei, S.; Jafari, A.; Nouri, F. The effect of intercropping and pure cropping of alfalfa with 3 rangeland grass species on forage dry matter and crude protein yield in dry land farming condition. Int. J. Agric. Crop Sci. 2012, 4, 1307–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, T.; Fang, L.; Wang, M. Intercropping of Gramineous Pasture Ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) and Leguminous Forage Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Increases the Resistance of Plants to Heavy Metals. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 7803408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raza, M.A.; Khalid, M.H.B.; Zhang, X.; Feng, L.Y.; Khan, I.; Hassan, M.J.; Ahmed, M.; Ansar, M.; Chen, Y.K.; Fan, Y.F.; et al. Effect of planting patterns on yield, nutrient accumulation and distribution in maize and soybean under relay intercropping systems. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacKown, C.T.; Heitholt, J.J.; Rao, S.C. Agronomic Feasibility of a Continuous Double Crop of Winter Wheat and Soybean Forage in the Southern Great Plains. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.E.; Moser, L.E.; Pitt, R.E. Postharvest factors affecting ensiling. In Agronomy Monographs; Buxton, D.R., Muck, R.E., Harrison, J.H., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy; Crop Science Society of America; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2015; pp. 251–304. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Wang, S.; Tian, X. Zinc and iron concentrations in grain milling fractions through combined foliar applications of Zn and macronutrients. Field Crops Res. 2016, 187, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, C.S. Soil and Plant Analysis; Scientific Publishers: Jodhpur, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis; The Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, R.P. A method for the extraction of plant samples and the determination of total soluble carbohydrates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1958, 9, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anil. L.; Park, J.; Phipps, R.H. The potential of forage—Maize intercrops in ruminant nutrition. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2000, 86, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Association of Official Analytical Chemists; International: Arlington, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.; Undersander, D. Relative forage quality: An alternative to relative feed value and quality index. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual Florida Ruminant Nutrition Symposium, Department of Animal Sciences, Best Western, Gainesville, FL, USA, 10–11 January 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Grabber, J.H. Prohexadione—Calcium Improves Stand Density and Yield of Alfalfa Interseeded into Silage Corn. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, M.T.; Lukaschewsky, J.; Samarappuli, D.P. Intercropping Alfalfa into Silage Maize Can Be More Profitable Than Maize Silage Followed by Spring-Seeded Alfalfa. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.-Z.; Hao, S.-G.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Kang, L. Strip cropping wheat and alfalfa to improve the biological control of the wheat aphid Macrosiphum avenae by the mite Allothrombium ovatum. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 119, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D. Yield and nutritive value of irrigated tall fescue compared with orchardgrass: In monocultures or mixed with alfalfa. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 93, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, N.S. Effects of Mix Cropping of Alfalfa and Annual Ryegrass on Forage Production. J. Rangel. Sci. 2015, 5, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Eskandari, H. Intercropping of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and bean (Vicia faba): Effects of complementarity and competition of intercrop components in resource consumption on dry matter production and weed growth. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 17755–17762. [Google Scholar]
- Berti, M.T.; Cecchin, A.; Samarappuli, D.P. Alfalfa Established Successfully in Intercropping with Corn in the Midwest US. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soe Htet, M.N.; Hai, J.-B.; Bo, P.T. Evaluation of Nutritive Values through Comparison of Forage Yield and Silage Quality of Mono-Cropped and Intercropped Maize-Soybean Harvested at Two Maturity Stages. Agriculture 2021, 11, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casler, M.D.; Van Santen, E. Breeding objectives in forages. In Fodder Crops and Amenity Grasses; Oller, B., Posselt, U.K., Veronesi, F., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 115–136. [Google Scholar]
- Francia, E.; Pecchioni, N.; Destri Nicosia, O.L. Dual-purpose barley and oat in a Mediterranean environment. Field Crops Res. 2006, 99, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.; McEniry, J.; Richardson, M.; O’Kiely, P. Yield and chemical composition of five common grassland species in response to nitrogen fertilizer application and phenological growth stage. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B–Soil Plant Sci. 2012, 62, 644–658. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Tang, G.; Tian, J. Effects of no-tillage sowing on soil properties and forage wheat and Italian ryegrass yields in winter fallow paddy fields. PeerJ 2021, 9, 10573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yin, B.; Xie, Y. Legume-Cereal Intercropping Improves Forage Yield, Quality and Degradability. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 0144813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithourgidis, A.S.; Vlachostergios, D.N.; Dordas, C.A.; Damalas, C.A. Dry matter yield, nitrogen content, and competition in pea–cereal intercropping systems. Eur. J. Agron. 2011, 34, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.M.; Villela, S.D.J.; Leonel, F.d.P. Intercropping of corn, brachialis grass and leguminous plants: Productivity, quality and composition of silages. Rev. Bras. de Zootec. 2012, 41, 2144–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sleugh, B.; Moore, K.J.; George, J.R.; Brummer, E.C. Binary Legume—Grass Mixtures Improve Forage Yield, Quality, and Seasonal Distribution. Agron. J. 2000, 92, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunelius, H.T.; Durr, G.H.; McRae, K.B.; Fillmore, S.A.E. Performance of Timothy-based Grass/Legume Mixtures in Cold Winter Region. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2006, 192, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, D.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, R. Evaluation of normal and specialty corn for fodder yield and quality traits. Range Manag. Agrofor. 2016, 37, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Pirhofer-Walzl, K.; Søegaard, K.; Høgh-Jensen, H. Forage herbs improve mineral composition of grassland herbage: Forage herbs improve mineral composition of grassland herbage. Grass Forage Sci. 2011, 66, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kammes, K.L.; Bals, B.D.; Dale, B.E.; Allen, M.S. Grass leaf protein, a coproduct of cellulosic ethanol production, as a source of protein for livestock. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2011, 164, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Mahmood, K. Nutrient Composition and Protein Extractability of Oat Forage Harvested at Different Maturity Stages as Compared to Grain. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borreani, G.; Cavallarin, L.; Antoniazzi, S.; Tabacco, E. Effect of the stage of growth, wilting and inoculation in field pea (Pisum sativum L.) silages. I. Herbage composition and silage fermentation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, I.; Radu-Rusu, C.; Simeanu, D. Characterization of The Nutritional Value of Alfalfa Harvested at Different Stages of Vegetation Using Cell Walls Content Based Methods. Lucr. Ştiinţifice-Ser. Zooteh. 2022, 53, 350–354. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, J.L.; Ward, G.N. Effect of intercropping forage peas (Pisum sativum L.) with winter wheat (Tritium vulgare L.) or triticale (Triticale hexaploide L.) on DM yield, nutritive characteristics when harvested at different stages of growth. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2012, 52, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbester, U.; Akkaya, M.R.; Yucel, C.; Gorgulu, M. Comparison of Yield, Nutritive Value, and In Vitro Digestibility of Monocrop and Intercropped Corn-Soybean Silages Cut at Two Maturity Stages. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 14, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, A.; Dev, I.; Kumar, V. Potential Role of Maize-Legume Intercropping Systems to Improve Soil Fertility Status under Smallholder Farming Systems for Sustainable Agriculture in India. Int. J. Life Sci. Biotechnol. Pharma Res. 2015, 4, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarthi, M.; Reddy, Y.; Reddy, K.; Ravi, A. A Study on Nutritive Value and Chemical Composition of Sorghum Fodder. Int. J. Sci. Environ. Technol. 2018, 6, 104–109. [Google Scholar]
- Lanyasunya, T.P.; Rong, W.H.; Mukisira, E.A.; Abdulrazak, S.A.; Ayako, W.O. Influence of manure and inorganic fertilizer on yield and quality of Vicia villosa intercropped with Sorghum almum in Ol-joro-orok, Kenya. Livest. Res. Rural Dev. 2006, 18, 10. [Google Scholar]







| Forage Species | Harvesting Stage | Harvested Date |
|---|---|---|
| Wheat 1 (Xiaoyan 17) | Flowering stage | 20 March |
| Wheat 2 (Baomai 9) | Flowering stage | 20 March |
| Ryegrass | Booting stage | 20 March |
| Alfalfa | Late vegetative stage | 20 March |
| Wheat 1 (Xiaoyan 17) | Milk stage | 3 April |
| Wheat 2 (Baomai 9) | Milk stage | 3 April |
| Ryegrass | Flowering stage | 3 April |
| Alfalfa | Early bud stage | 3 April |
| Wheat 1 (Xiaoyan 17) | Soft dough stage | 18 April |
| Wheat 2 (Baomai 9) | Soft dough stage | 18 April |
| Ryegrass | Early heading stage | 18 April |
| Alfalfa | Late bud stage | 18 April |
| Treatment | Parameters (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM | CP | WSC | EE | CF | Ash | NDF | ADF | |
| T1 | 29.36 b | 10.20 d | 10.23 e | 2.43 e | 31.92 b | 7.72 c | 47.56 f | 26.13 e |
| T2 | 30.05 b | 10.67 c | 11.20 d | 2.48 d | 31.79 c | 7.62 c | 49.35 e | 28.01 d |
| T3 | 20.81 d | 12.62 a | 13.24 c | 2.55 c | 27.32 e | 10.31 b | 54.66 b | 32.71 b |
| T4 | 30.32 b | 10.56 c | 13.52 b | 2.48 d | 32.20 a | 7.55 c | 50.31 d | 29.45 c |
| T5 | 30.77 a | 11.29 b | 13.40 b | 2.61 b | 32.30 a | 7.79 c | 53.58 c | 29.47 c |
| T6 | 23.16 c | 12.86 a | 13.67 a | 2.75 a | 30.17 d | 10.47 a | 57.06 a | 34.27 a |
| SEM | 0.27 | 0.11 | 0.71 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.44 | 0.30 |
| LOS | * | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | ** | ** |
| Harvest Stage | ||||||||
| Flowering Stage | 20.18 c | 14.28 a | 15.60 a | 2.61 a | 34.12 a | 9.10 a | 55.06 a | 32.55 a |
| Milk Stage | 25.66 b | 10.33 b | 12.64 b | 2.50 c | 30.35 b | 8.41 b | 52.86 b | 30.35 b |
| Soft Dough Stage | 36.39 a | 9.49 c | 9.41 c | 2.53 b | 28.38 c | 8.22 b | 48.35 c | 27.10 c |
| SEM | 0.19 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.31 | 0.21 |
| LOS | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | ** | ** |
| Year | ||||||||
| 2020 | 28.49 a | 11.62 a | 12.63 a | 3.08 a | 31.24 a | 8.64 a | 53.22 a | 31.25 a |
| 2021 | 26.33 b | 11.12 b | 12.47 b | 2.02 b | 30.66 b | 8.52 b | 50.95 a | 28.76 b |
| SEM | 0.16 | 0.50 | 0.04 | 0.29 | 0.53 | 0.33 | 1.38 | 0.91 |
| LOS | ** | ** | ns | * | ns | ns | ns | * |
| Treatment | Parameters (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca | Na | K | P | Mg | |
| T1 | 0.20 c | 0.03 c | 2.03 c | 0.27 b | 0.08 d |
| T2 | 0.21 c | 0.04 c | 2.01 c | 0.26 b | 0.07 d |
| T3 | 0.31 b | 0.14 b | 2.02 c | 0.27 b | 0.30 b |
| T4 | 0.21 c | 0.04 c | 2.06 c | 0.27 b | 0.10 c |
| T5 | 0.31 b | 0.14 b | 2.13 b | 0.27 b | 0.30 b |
| T6 | 0.40 a | 0.20 a | 2.46 a | 0.32 a | 0.50 a |
| SEM | 0.001 | 0.008 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.001 |
| LOS | * | * | * | * | * |
| Harvest Stage | |||||
| Flowering Stage | 0.27 a | 0.08 a | 2.48 a | 0.33 a | 0.22 a |
| Milk Stage | 0.26 a | 0.09 a | 2.06 b | 0.27 b | 0.19 b |
| Soft Dough Stage | 0.23 b | 0.07 a | 1.82 c | 0.23 c | 0.15 c |
| SEM | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.001 |
| LOS | * | ns | ** | ** | ** |
| Year | |||||
| 2020 | 0.25 a | 0.06 a | 2.10 a | 0.28 a | 0.18 a |
| 2021 | 0.26 a | 0.09 a | 2.14 a | 0.28 a | 0.20 a |
| SEM | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.05 |
| LOS | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Treatment | Amino Acid Profile (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arg | His | Ile | Leu | Lys | Met | Phe | The | Val | |
| T1 | 7.1 d | 2.5 c | 4.0 e | 7.1 e | 5.6 d | 1.3 c | 5.6 c | 5.0 c | 4.9 d |
| T2 | 7.3 c | 2.6 b | 4.0 e | 7.1 e | 5.7 d | 1.0 d | 6.2 b | 5.4 b | 6.5 b |
| T3 | 7.7 a | 2.6 b | 5.1 b | 8.7 c | 6.0 c | 1.9 b | 6.2 b | 5.1 c | 6.3 c |
| T4 | 7.2 c | 2.5 c | 4.2 d | 8.5 d | 6.4 b | 1.5 c | 6.2 b | 5.0 c | 6.3 c |
| T5 | 7.5 b | 2.8 a | 4.5 c | 9.8 a | 6.4 b | 2.7 a | 7.0 a | 6.0 a | 7.0 a |
| T6 | 7.1 d | 2.7 a | 5.5 a | 9.0 b | 6.8 a | 1.8 b | 7.1 a | 5.6 b | 6.8 a |
| SEM | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| LOS | * | * | ** | ** | * | * | * | * | * |
| Harvest Time | |||||||||
| Flowering Stage | 7.5 a | 2.9 a | 4.9 a | 11.6 a | 6.3 a | 1.8 b | 6.9 a | 5.9 a | 6.5 a |
| Milk Stage | 7.1 b | 2.4 b | 4.6 b | 9.2 b | 6.2 a | 2.1 a | 6.2 b | 4.9 c | 6.2 b |
| Soft Dough Stage | 7.5 a | 2.5 b | 4.2 c | 9.2 b | 5.5 b | 1.2 c | 6.0 c | 5.3 b | 6.1 b |
| SEM | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| LOS | * | * | ** | * | * | ** | ** | ** | * |
| Year | |||||||||
| 2020 | 7.1 b | 2.6 a | 4.7 a | 10.3 a | 6.6 a | 1.7 a | 6.3 a | 5.4 a | 6.6 a |
| 2021 | 7.6 a | 2.6 a | 4.4 b | 9.4 b | 5.6 b | 1.7 a | 6.4 a | 5.3 a | 5.9 b |
| SEM | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| LOS | ** | ns | * | * | ** | ns | ns | ns | * |
| Treatment | Quality Indexes (Values) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMI | DDM | RFV | TDN | RFQ | QI | |
| T1 | 2.11 f | 62.21 e | 101.59 f | 47.30 f | 81.08 f | 1.11 f |
| T2 | 2.20 e | 63.42 d | 108.13 e | 50.98 e | 91.24 e | 1.24 e |
| T3 | 2.39 c | 65.96 c | 122.65 c | 55.92 c | 109.42 c | 1.46 c |
| T4 | 2.27 d | 65.94 c | 116.83 d | 54.00 d | 101.34 d | 1.36 d |
| T5 | 2.56 a | 68.54 a | 136.49 a | 60.50 a | 127.41 a | 1.69 a |
| T6 | 2.46 b | 67.08 b | 128.71 b | 57.08 b | 115.52 b | 1.54 b |
| SEM | 0.03 | 0.24 | 2.05 | 0.48 | 2.57 | 0.03 |
| LOS | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Harvest Stage | ||||||
| Flowering Stage | 2.52 a | 67.79 a | 134.91 a | 59.59 a | 124.02 a | 1.65 a |
| Milk Stage | 2.28 b | 65.25 b | 115.93 b | 54.38 b | 101.39 b | 1.36 b |
| Soft Dough Stage | 2.19 c | 63.54 c | 108.33 c | 48.92 c | 87.59 c | 1.19 c |
| SEM | 0.21 | 0.17 | 1.45 | 0.34 | 1.82 | 0.02 |
| LOS | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Year | ||||||
| 2020 | 2.38 a | 66.50 a | 123.33 a | 55.64 a | 109.04 a | 1.46 a |
| 2021 | 2.28 a | 64.56 b | 114.81 b | 52.95 b | 99.62 b | 1.34 b |
| SEM | 0.06 | 0.71 | 4.48 | 1.16 | 4.98 | 0.06 |
| LOS | ns | * | * | * | * | * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bo, P.T.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, R.; Soe Htet, M.N.; Hai, J. Optimization of Alfalfa-Based Mixed Cropping with Winter Wheat and Ryegrass in Terms of Forage Yield and Quality Traits. Plants 2022, 11, 1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11131752
Bo PT, Dong Y, Zhang R, Soe Htet MN, Hai J. Optimization of Alfalfa-Based Mixed Cropping with Winter Wheat and Ryegrass in Terms of Forage Yield and Quality Traits. Plants. 2022; 11(13):1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11131752
Chicago/Turabian StyleBo, Poe Thinzar, Yongli Dong, Ruifang Zhang, Maw Ni Soe Htet, and Jiangbo Hai. 2022. "Optimization of Alfalfa-Based Mixed Cropping with Winter Wheat and Ryegrass in Terms of Forage Yield and Quality Traits" Plants 11, no. 13: 1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11131752
APA StyleBo, P. T., Dong, Y., Zhang, R., Soe Htet, M. N., & Hai, J. (2022). Optimization of Alfalfa-Based Mixed Cropping with Winter Wheat and Ryegrass in Terms of Forage Yield and Quality Traits. Plants, 11(13), 1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11131752






