Abstract
Radish is a typical self-incompatible crop. The rapid and accurate identification of S haplotypes can circumvent the blindness of the hybrid combination process, which is critical in radish heterosis utilization and the breeding of new varieties. In this study, based on the gene sequence which encodes the S-locus receptor kinase (SRK) of radish, and the polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) analysis, the S haplotypes were identified among 79 cultivated radish genotypes. The PCR results indicated that 79 radish genotypes could be divided into 48 Class I, 13 Class II, and 17 Class I/II S haplotypes. Sequence alignment confirmed that the Class I materials contained 19 S haplotypes, of which three haplotypes (‘NAU-S53’, ‘NAU-S54’ and ‘NAU-S55’) were identified for the first time in radish. After digestion using the Hinf I restriction endonuclease, the SRK domain of DNA fragments of different genotypes showed high polymorphism. Homozygous materials S haplotypes could be quickly distinguished by the differences in the digested bands. Molecular identification of the S haplotype was highly consistent with the field pollination and pollen tube germination results. These results would provide an important approach for the rapid identification of radish S haplotypes and the efficient utilization of self-incompatibility in heterosis breeding.
1. Introduction
Radish (Raphanus sativus L.) is an economically important root vegetable crop belonging to the Brassicaceae family. As a self-incompatibility (SI) plant, radish exhibits obvious heterosis in hybrid seeds production. The SI is an important mechanism that prevents self-fertilization and maintains genetic diversity in flowering plants. Based on the genetic mechanism controlling the SI phenotype of the pollen, the SI systems are generally classified into Gametophytic SI (GSI) and Sporophytic SI (SSI). The pollen phenotype of GSI systems is conferred by the S genotypes of haploid pollen, while the phenotype of pollen grains in plants with SSI is determined by the S genotype of the diploid parent that produces pollen [1,2]. The SSI is controlled by one highly polymorphic S-locus containing three tightly linked genes such as the S-locus receptor kinase (SRK), S-locus glycoprotein (SLG) and S-locus cysteine rich (SCR), which has been well described in Brassica crops such as B. rapa [3] and B. oleracea [4]. Among them, SRK localized in the stigmatic papilla cells as the female determinant, and the pollen coat protein SCR/SP11 controls the pollen determinant of SSI. On the basis of the SI phenotype and the sequence similarity of the S alleles, the S haplotypes in Brassica have been categorized into Class I and Class II. Class I haplotypes have a strong self-incompatible phenotypic effect and are generally considered dominant or co-dominant with other S haplotypes [5,6].
The SI system has been extensively used in F1 hybrid breeding of radish and other Brassica species, which has advantages including high efficiency and easy short-period breeding [7,8]. However, F1 seeds cannot be successfully produced at the anthesis stage if the parents share the same S-haplotype [6]. The rapid and accurate identification of S haplotypes can circumvent the blindness of the hybrid combination process, which is critical in radish heterosis utilization and the breeding of new varieties. In early studies, compatibility index analysis, pollen tube observation [9], fluorescence analysis [9,10] and isoelectric focusing gel examination [11] were often employed to conduct the S haplotype identification in Brassicaceae crops such as B. oleracea and R. sativus, however, it was difficult to widely apply for time consuming, labor costly and [12] complex operation. Polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) has been successfully implemented to identify S haplotypes in B. rapa [13], B. oleracea [14], and R. sativus [15,16], but it has some drawbacks and is limited by whether the material is homozygous in the application.
With the increasing report about S locus gene sequences information, the polymorphism analysis of SRK or SLG gene sequences was developed into a new approach for accurate and rapid identification of S haplotype in many crops such as R. sativus [6] and Chinese cabbage [17]. In addition, alignment analysis of the only female determinant SRK has been reported to be reliable as a method for S haplotype identification, and has been used for the identification of S haplotypes of breeding lines in broccoli and cabbage [18,19]. Previous studies have shown that S-locus gene sequences are not conserved among different S haplotypes [20,21]. The identification of the radish S haplotype focused on the gene sequence of the S locus and was carried out by different teams around the world [7,15,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. However, various groups use their own naming scheme for S haplotypes, which result in confusion of S haplotype names and limit the application of self-incompatibility of radish in heterosis breeding. Therefore, the unified naming of S haplotypes and the establishment of standard test lines are necessary for rapid and accurate identification of radish haplotypes.
In the present study, we firstly sorted out and named all of the currently published radish S haplotypes. Following, the S haplotypes of 79 cultivated radish genotypes were identified based on the gene sequence of SRK analysis, and also the PCR-RFLP marker was developed to rapidly classify the radish Class I S haplotype. In addition, the artificial pollination and pollen tube observation experiments were utilized to verify the accuracy of molecular identification. These results would provide an important theoretical basis for efficient utilization of self-incompatibility in heterosis breeding.
2. Results
2.1. Comparison and Unified Nomenclature of Published S haplotype in Radish (Raphanus sativus L.)
In previous reports, a total of 35 S haplotypes were found by Nishio [29] and Haseyama [30] in radish, but the results were incomplete. Therefore, comprehensive published information on radish S haplotypes [7,15,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30] were collected, and their nucleotide and amino acid sequences were futher compared in this study (Table S1). It was found that the S haplotypes identified by the teams intersected with each other (Figure S1). After removing the redundant members based on BLAST analysis of the reported S gene nucleotide and amino acid sequence, 52 S haplotypes have been identified in radish, which were numbered as ‘NAU-S1’-‘NAU-S52’ (Table 1).

Table 1.
Summary of S haplotypes in radish.
2.2. SRK Kinase Domain-Based Classification and Identification of S haplotypes
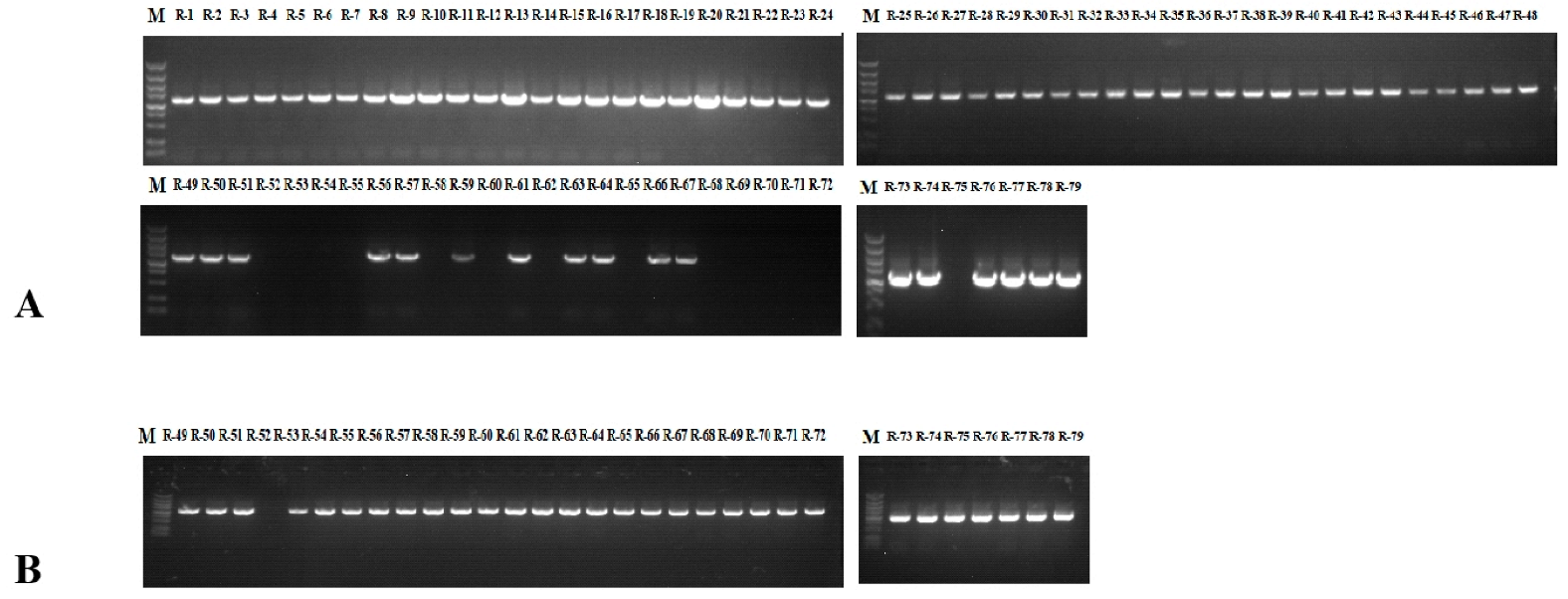
Class Ⅰ and Class Ⅱ primers were designed based on the sequence of the SRK kinase region, which can be applied to classify the compatibility of different genotypes. Class Ⅰ exhibits strong self-incompatibility, while Class Ⅱ exhibits weak self-incompatibility. Incompatibility Classes I and II show a dominant relationship [31,32]. The primers KD (I)-F/R and KD4/KD7 can respectively generate 1200 (Figure 1A) and 1000 bp (Figure 1B) bands among the radish materials. PCR results shown that the 79 radish genotypes could be divided into Class I (48), Class II (13) and Class I/II (17) groups. Homozygous Class I and II S haplotype materials are found in 60.76% and 16.46% of radish, respectively. Strong self-incompatibility occurs more frequently (Table 2).
Figure 1.
PCR amplification of SRK kinase domain in radish. (A) PCR amplification results of KD(I)-F/R in NAU-R1-NAU-R79; (B) PCR amplification results of KD4/KD7 in NAU-R49-NAU-R79.

Table 2.
The classification of S haplotypes in radish.
The types and frequencies of S haplotypes in the tested radish materials were analyzed according to the S haplotype system established in this study. The 48 Class I materials contained 19 sequence types, of which 16 indicated high similarities to known S haplotypes. Among them, the nucleotide sequences of eight lines were highly similar to Okamoto (S22, S7), Lim (S16), and Kim D (S13) and were identified as ‘NAU-S16’, with a frequency of up to 16.67%. Likewise, seven lines were ‘NAU-S25’, with a frequency of 14.58% as well as five lines were ‘NAU-S17’, with a frequency of 10.41%. There were four materials of ‘NAU-S51’ type, with a frequency of 8.33%. The ‘NAU-S04’ and ‘NAU-S44’ types comprised three materials, and the frequency was 6.25%. The ‘NAU-S02’ and ‘NAU-S14’ types appeared twice, and the other S haplotypes appeared only once in the tested materials (Table 3). The predicted amino acid sequence was used in a protein BLAST search. The SRK sequence information of NAU-Rs46, NAU-Rs47, and NAU-Rs48, has not been found in the NCBI database. It was thus preliminarily inferred that there were three new S haplotypes, which were respectively named as ‘NAU-S53’, ‘NAU-S54’, and ‘NAU-S55’ (The nucleotide sequences of new S haplotypes are listed in Table S2).

Table 3.
S haplotypes frequencies among 48 Class I radish materials.
The S haplotypes of the 13 Class II radish genotypes identified were focused on four types including ‘NAU-S38’, ‘NAU-S39’, ‘NAU-S43’, and ‘NAU-S52’ (Table 4). In addition, the ClassI/II SRK gene could be simultaneously amplified by the primer of KD (D)-F/R and KD4/KD7 among 17 materials which maybe heterozygous at the S locus (Table 5).

Table 4.
S haplotypes frequencies among 13 Class II radish materials.

Table 5.
Distribution of S haplotype in 17 Class I/II radish materials.
2.3. PCR-RFLP Analysis of SRK Alleles
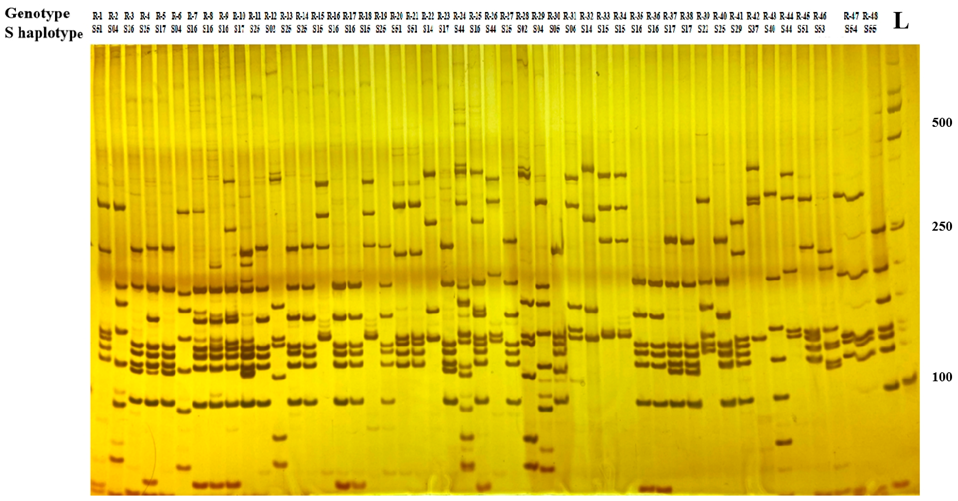
Compared with the sequence alignment analysis, the utilization of PCR-RFLP technology to identify the S haplotype of radish materials does not require sequencing and has the advantages of a faster and higher identification efficiency and lower cost. To identify and classify the S haplotypes from genotypes with SI phenotypes, the PCR reaction was performed with the Class I SRK specific primer, and then digestion of the PCR products with Hinf I restriction endonucleases and subsequent polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis revealed polymorphism of the amplified DNA fragments. There were 19 types of electrophoretic profiles found in 48 genotypes (Figure 2). The size of the electronic restriction fragments of the PCR product is attached in Table S3. The PCR-RFLP result was the same as the nucleotide sequence analysis. All the different S genotypes showed different electrophoretic profiles, while lines with the same S genotype had the same electrophoretic profiles. These results showed that the self-incompatibility and S haplotype of radish homozygous genotypes could be quickly discovered through employing PCR-RFLP markers to analyze SRK gene polymorphisms.
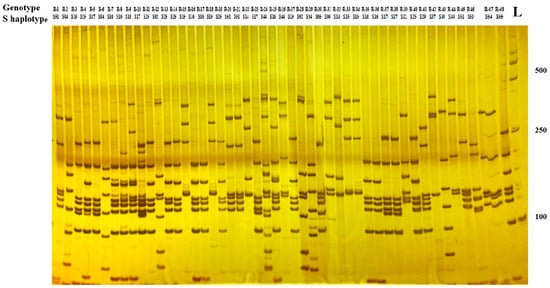
Figure 2.
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of PCR products after cleavage with Hinf I. L: 2000-bp ladders.
2.4. Pollen Germination and Tube Growth
The germination and growth of pollen tube would be inhibited on the stigma of those self-incompatible lines belonging to same S haplotypes. Consequently, fertilization does not occur and no seeds are produced. To verify the molecular identification results of the S haplotype, different S haplotype materials were prepared for pollination, and pollen tube germination after hybridization/self-pollination at the flowering stage was analyzed.
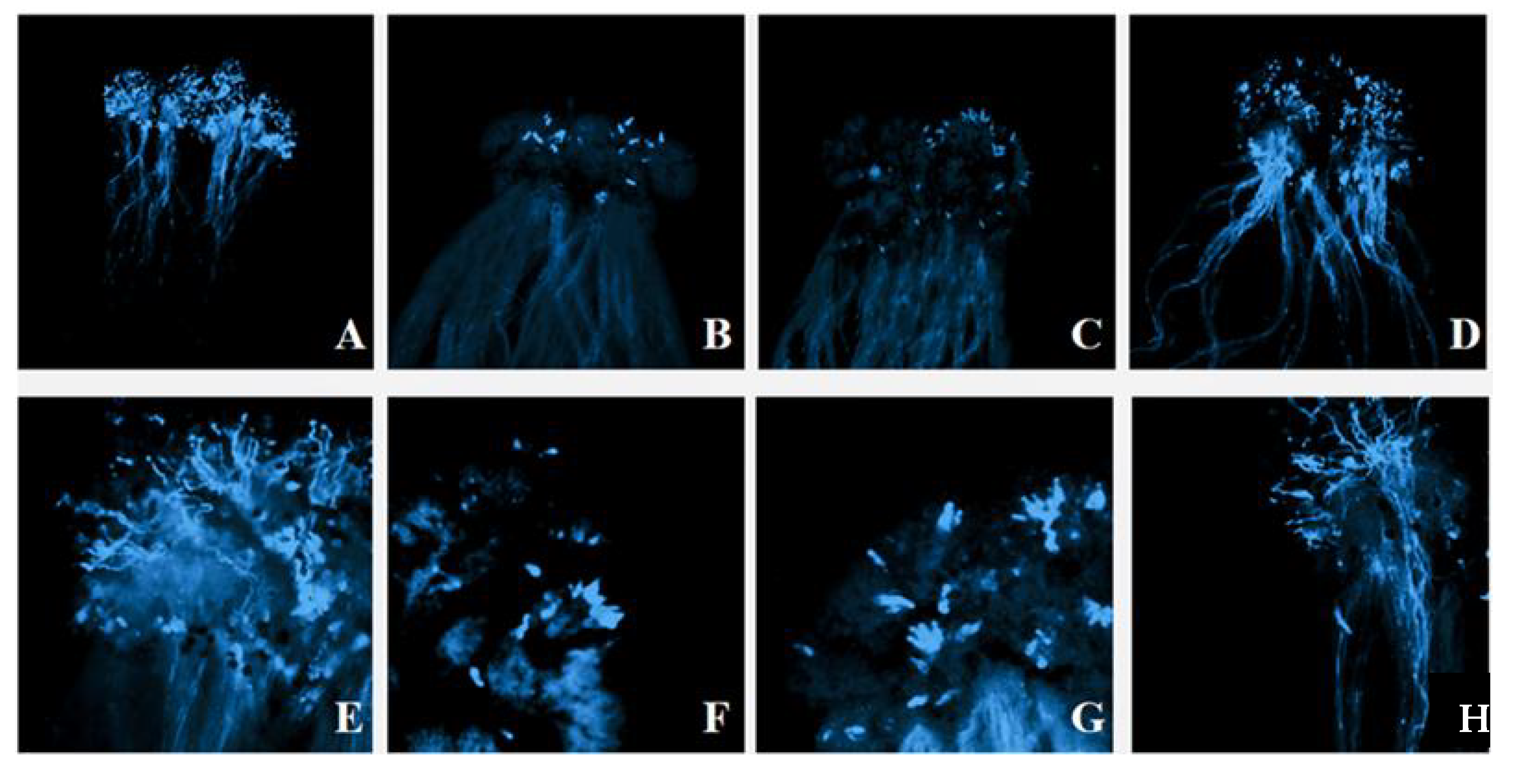
The strong self-incompatibility radish line ‘NAU-Rs4’ was employed as an example to explore the behavior of pollen tube in the stigma, and the germination of self-pollinated pollen tubes at the bud stage was normal (Figure 3A,E). When the same material was self-pollinated during flowering, it was obvious that pollen grains germinated less at the stigma and failed to produce pollen tubes that extended to the style (Figure 3B,F). This was similar to the result after cross-pollination of the same S haplotype material NAU-Rs4 × NAU-Rs40 (‘NAU-S25’), which induced the callose response (Figure 3C,G). In contrast, different S haplotype materials ‘NAU-Rs4’ × ’NAU-Rs32’ (‘NAU-S25’ × ‘NAU-S14’) were cross-pollinated at the flowering stage, which resulted in a large number of pollen grains germinating, and pollen tube elongation was observed (Figure 3D,H). These results of the fluorescence microscope observation of pollen tube germination verified the accuracy of S haplotypes identification.
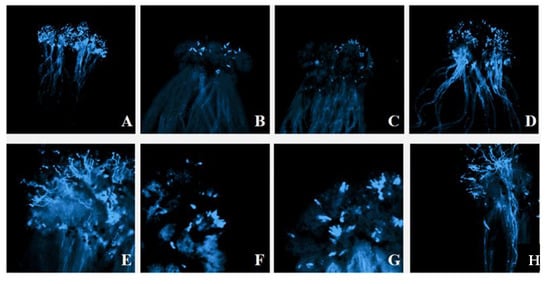
Figure 3.
The germination of pollen tubes of different pollination combinations. (A). NAU-Rs4 (‘NAU-S25’) Bud pollination⊗ (4×); (B). NAU-Rs4 (‘NAU-S25’) Flower pollination⊗ (4×); (C). NAU-Rs4 × NAU-Rs40 (‘NAU-S25’) (4×); (D). NAU-Rs4 × NAU-Rs32 (‘NAU-S25’ × ‘NAU-S14’) (4×); (E). NAU-Rs4 (‘NAU-S25’) Bud pollination⊗ (10×); (F). NAU-Rs4 (‘NAU-S25’) Flower pollination⊗ (10×); (G). NAU-Rs4 × NAU-Rs40 (‘NAU-S25’) (10×); (H). NAU-Rs4 × NAU-Rs32 (‘NAU-S25’ × ‘NAU-S14’) (10×).
2.5. Compatibility Index Analysis
To verify the molecular identification results of the S haplotype, different cross combinations were conducted, and the compatibility was analyzed after pollination.
Cross combinations included the same S haplotype material: NAU-Rs5 × NAU-Rs38 (‘NAU-S17’), NAU-Rs44 × NAU-Rs24 (‘NAU-S44’), NAU-Rs7 × NAU-Rs9 (‘NAU-S16’), NAU-Rs7 × NAU-Rs16 (‘NAU-S16’), NAU-Rs4 × NAU-Rs40 (‘NAU-S25’, orthogonal), NAU-Rs40 × NAU-Rs4 (‘NAU-S25’, reverse cross); and different S haplotype material: NAU-Rs1 × NAU-Rs40, NAU-Rs44 × NAU-Rs30, NAU-Rs34 × NAU-Rs40, NAU-Rs7 × NAU-Rs18, and NAU-Rs7 × NAU-Rs1. At the same time, four materials of NAU-Rs1 (‘NAU-S51’), NAU-Rs45 (‘NAU-S05’), NAU-Rs33 (‘NAU-S15’), and NAU-Rs30 (‘NAU-S51’) were used as controls during the flowering stage.
The seed production of the F1 generation depends on whether the parents have the same S haplotype. After 40–50 days of pollination, the hybridization of the same S haplotype was almost sterile. The compatibility index was less than 1, and the reciprocal cross results were consistent, which was similar to the self-pollinating result of SI material in the flowering period. In contrast, the compatibility indexes of different S haplotypes materials are all larger than two, showing compatibility (Table 6, Figure 4). The results of self- and cross-pollination tests were consistent with the prediction of S haplotypes by PCR analysis.

Table 6.
Compatibility index and podding rate of different pollination combinations.
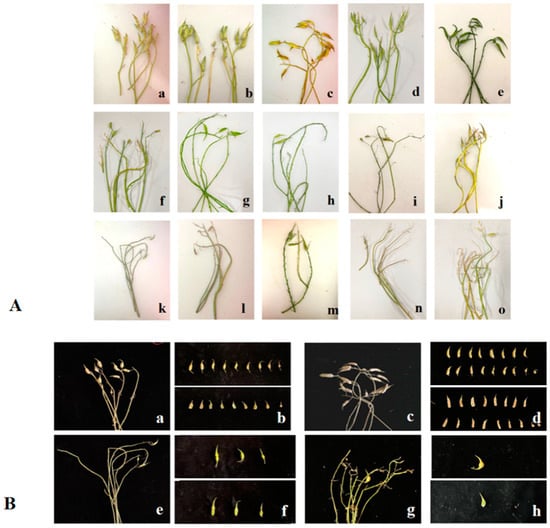

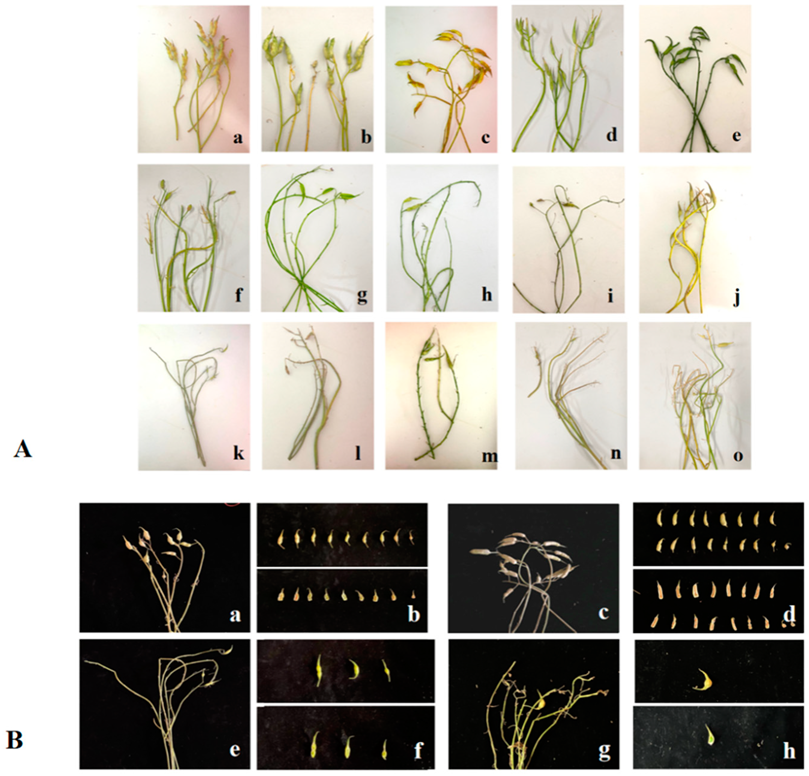
Figure 4.
The pod setting and seed setting of different pollination combinations. (A). (a). NAU-Rs1 × NAU-Rs40 (‘NAU-S51’ × ‘NAU-S25’); (b). NAU-Rs34 × NAU-Rs40 (‘NAU-S15’ × ‘NAU-S25’); (c). NAU-Rs7 × NAU-Rs18 (‘NAU-S16’ × ‘NAU-S15’); (d). NAU-Rs44 × NAU-Rs30 (‘NAU-S44’ × ‘NAU-S05’); (e). NAU-Rs7 × NAU-Rs1 (‘NAU-S16’ × ‘NAU-S51’); (f). NAU-Rs5 × NAU-Rs38 (‘NAU-S17’); (g). NAU-Rs40 × NAU-Rs4 (‘NAU-S25’); (h). NAU-Rs7 × NAU-Rs9 (‘NAU-S16’); (i). NAU-Rs7 × NAU-Rs16 (‘NAU-S16’); (j). NAU-Rs44 × NAU-Rs24 (‘NAU-S44’); (k). NAU-Rs4 × NAU-Rs40 (‘NAU-S25’); (l). NAU-Rs1⊗ (‘NAU-S51’); (m). NAU-Rs30⊗ (‘NAU-S05’); (n). NAU-Rs3⊗ (‘NAU-S15’); (o). NAU-Rs45⊗ (‘NAU-S51’). (B). (a,b). NAU-Rs7 × NAU-Rs18 (‘NAU-S16’ × ‘NAU-S15’); (c,d). NAU-Rs7 × NAU-Rs1 (‘NAU-S16’ × ‘NAU-S51’); (e,f). NAU-Rs4 × NAU-Rs40 (‘NAU-S25’); (g,h). NAU-Rs7 × NAU-Rs16 (‘NAU-S16’).
3. Discussion
As a self-incompatibility (SI) plant, radish exhibits high heterosis in hybrid seed production. However, F1 seeds cannot be produced at the anthesis stage because the parents share the same S haplotype [6]. To ensure rational hybridization and guarantee the purity and yield of the hybrid, it is necessary to rapidly and accurately identify the S haplotype of the radish hybrid parent.
The unified naming of S haplotypes and the establishment of standard test lines are necessary for rapid and accurate identification of radish haplotypes. Haseyama [30] determined the reported SRK, SLG, and SCR/SP11 gene sequences and found that there were 35 S haplotypes in radish, of which there were 26 ones in South Korea radish and 24 ones in Japanese radish. A BLAST analysis revealed that 15 S haplotypes are widespread in Japanese and South Korean radish. However, the results failed to cover all current radish haplotype information. Therefore, in this study, all published S gene nucleotide sequences were collected for BLAST alignment. On the basis research of Haseyama [30], the S haplotype reported by Kim [28], Wang [6] and other teams was added. It was concluded that a total of 52 S haplotypes were reported in radish and they were uniformly named ‘NAU-S1’-‘NAU-S52’ (Table 1). Exchanges of plant materials between researchers and breeders and the establishment of a unified nomenclature of S haplotypes are necessary to avoid confusion regarding the identity of S haplotypes in radish. The S haplotype is an important agronomic trait of cruciferous crops that varies greatly among different species. Thus far, more than 50 S haplotypes have been found in B. oleracea crops [5], which is comparable to the number of radish S haplotypes determined in the present study. And more than 100 S haplotypes have been identified in Brassica [32,33,34]. There are many SRK and SP11/SCR alleles having highly similar sequences between B. oleracea and B. rapa. Similar interspecific pairs of S haplotypes also exist in radish. Due to the large number of S haplotypes, traditional pollination methods are complicated to distinguish S haplotypes [27]. Establishing an efficient and simple S haplotype identification system is important for the breeding work.
To establish a reliable S haplotyping system in radish, we designed specific primers to analyze the SRK kinase domain sequence. The PCR results indicated that 79 radish genotypes could be divided into 48 Class I, 13 Class II, and 17 Class I/II S genotypes. Sequence alignment confirmed that the Class I materials contained 19 S haplotypes. Among them, the S sequences of the three materials were not registered in NCBI, and hence, there were new members identified for the first time in radish, named ‘NAU-S53’, ‘NAU-S54’, and ‘NAU-S55’. In general, Class I S haplotypes predominate over Class II S haplotypes. In the study, the S haplotypes of Class II materials were only concentrated in four types, such as ‘NAU-S38’ and the types and numbers are significantly less than those of Class I S haplotypes. It is convincing that strong self-incompatibility lines are more common. In previous reports, this phenomenon was also found in B. campestris [35] and B. pekinensis Rupr [36,37,38]. Directional selection, either natural or through breeding, increases the frequency of favorable S alleles resulting in the differences of S haplotype frequencies.
The publication of S locus gene sequence details has enabled the identification of S haplotypes based on gene sequences and BLAST analyses. However, in breeding practice, when conducting large-scale screening of parents to prepare hybrid combinations, all parent materials need to be sequenced. This entails low throughput and high cost, which are unsuitable for batch identification of S haplotypes. In contrast, PCR-RFLP markers have the characteristics of high polymorphism, good reproducibility and codominance, which are easily used to develop efficient, simple and practical molecular markers [39], and successfully detect S haplotypes in crops such as B. campestris and Chinese cabbage, as well as fruit plants such as apple and pear [14,40,41,42]. The S haplotype of 48 Class I materials was identified using the PCR-RFLP technique here, and their PCR products showed a polymorphism depending on their genotypes. Therefore, the PCR-RFLP analysis of S-locus allele is adequate for the S haplotypes identification.
The PCR-RFLP method has proven useful for the identification of S alleles in genotypes and listing S haplotypes in radish [16]. Of course, the limitation of this method is that some S haplotypes have a significant degree of sequence similarity or the same restriction site, making the PCR-RFLP approach ineffective. Furthermore, it is difficult to identify individual haplotypes for heterozygotes or new S haplotypes [36,37]. Thus, for materials with complex bands are difficult to distinguish accurately. PCR-RFLP analysis, combined with the cloning analysis of the S locus gene, permits rapid and efficient identification of the radish S haplotype.
In addition, the compatibility relationships in pollen between same S haplotypes of radish by pollination tests and aniline blue tests were analyzed. The results of molecular identification of the S haplotype were highly consistent with the field pollination and pollen tube germination. It will become an essential tool based on the combination of radish SRK gene sequence analysis and the PCR-RFLP in radish breeding, which would provide an important theoretical basis for efficient utilization of self-incompatibility in heterosis breeding.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
The 79 cultivated radish genotypes were provided by the Radish Genetics and Breeding Laboratory, School of Horticulture, Nanjing Agricultural University (Table 7). Pollination experiments were conducted in 2019–2021 at Jiangpu Horticultural Experimental Station and Baima Experimental Base of Nanjing Agricultural University.

Table 7.
Materials of radish used in this study.
4.2. Amplification and Sequencing of the PCR Products
4.2.1. Extraction of Genomic DNA and Amplification of the SRK Gene
Total genomic DNA was extracted from the seedling leaves of each genotype using the modified CTAB (Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide) method. Degenerate primers were designed based on the nucleotide sequence (exons 4–7) of the radish SRK gene (kinase domain) published by Lim [16], Okamoto [23] et al. The sequences encoding the kinase domains of Class I and Class II S haplotype SRK were amplified with KD (I)-F/R and KD4/KD7. The primer sequences were shown in Table 8.

Table 8.
Specific primers of SRK gene.
PCR amplification was performed in a 20 μL reaction mixture containing 0.1 μg template, 1 μL forward primer (10 μM), 1 μL reverse primer (10 μM), and 10 μL polymerase mix (2 × Taq Master Mix, Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China). PCR amplification consisted of an initial denaturation step at 94 °C for 5 min, 35 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 59 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 1 min 40 s, and a final 10 min extension at 72 °C.
4.2.2. Determination of Nucleotide Sequences
The PCR products were visualized on 1.2% agarose gel. The FastPure Plant DNA Isolation Mini Kit® (Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China) was used for product purification. Then, it was ligated with the cloning vector pMD19-T and transformed into E. coli (Escherichia coli) competent DH5α. Sequencing reactions were performed by Spokane Biotech Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China). The obtained nucleotide sequences of the SRK gene of the respective cross lines were compared in the NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) database to determine the corresponding haplotype.
4.3. PCR-RFLP Analysis
DNA fragments corresponding to the SRK kinase domain were amplified by PCR with a Class I specific primer pair, KD (I)-F and KD (I)-R. The reaction conditions and system were identical to those described in Section 4.2. The PCR products were subjected to restriction digestion using Hinf I restriction enzyme at 37 °C for 1 h, and 65 °C for 20 min. The digested product was electrophoresed on a 6% non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel at a constant voltage 120 V for 2 h, and DNA bands were detected by silver staining.
4.4. Pollination Tests
The traditional compatibility index method was used to verify the molecular identification results of the S haplotype. Based on the results of the SRK gene sequence comparison, artificial cross-pollination was carried out within the same haplotype and among different haplotypes at the flowering stage to determine whether the materials belonged to the same S haplotype according to the compatibility index and pod setting rate among different hybrid combinations.
Pod setting rate = number of pods/number of pollinated flowers × 100%.
Compatibility index = number of seeds/number of pollinated flowers.
In the field pollination statistics of radish, the compatibility index less than 0.5 indicates strong self-incompatibility, a value greater than 2.0 indicates compatibility, and compatibility index from 0.5 to 2.0 indicates weak self-incompatibility [7].
4.5. Aniline Blue Assays
Aniline blue assays were performed as previously described. Based on the molecular identification results of the S haplotype, the pistils after hybridization with the same or different S haplotypes were fixed in FAA (Formalin-Aceto-Alcohol) fixative (50% Ethanol:Glacial Acetic Acid:Ormaldehyde = V18:V1:V1) at least 4 h and then transferred to 10 M NaOH at 42 °C for 0.5 h. The pistils were washed with distilled water and stained with 0.1% basic aniline blue (1% K3PO3, PH = 11) [43,44]. The stained samples were mounted in 70% glycerol and the growth of pollen tubes in the styles was observed under a BX53® Olympus fluorescence microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/plants11172304/s1, Table S1: Summary of the publicly published radish S haplotypes; Table S2: Novel S haplotype gene sequence; Table S3: Size of restriction fragment of PCR product of Class I SRK gene; Figure S1: Venn diagram of radish S haplotypes determined by groups.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.N. and Y.W.; methodology, M.N. and Q.W.; validation, M.N., X.Y. and S.W.; formal analysis, M.N. and J.W.; investigation, M.N., X.Y. and Q.W.; resources, L.L. and L.X.; writing—original draft preparation, M.N. and Y.W.; funding acquisition, Y.W. and L.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by Jiangsu Seed Industry Revitalization Project [JBGS(2021)071], Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (KYZZ2022004), Guidance Foundation, the Hainan Institute of Nanjing Agricultural University(NAUSY-MS02), and the Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Stone, S.L.; Goring, D.R. The molecular biology of self-incompatibility systems in flowering plants. Plant Cell. Tissue Organ Culture. 2001, 67, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Suwabe, K.; Suzuki, G. Molecular genetics, physiology and biology of self-incompatibility in Brassicaceae. Proc. Jpn. Acad. 2012, 88, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatakeyama, K.; Takasaki, T.; Watanabe, M.; Hinata, K. High sequence similarity between SLG and the receptor domain of SRK is not necessarily involved in higher dominance relationships in stigma in self-incompatible Brassica rapa L. Sex. Plant Reprod. 1998, 11, 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J. Dissecting pistil responses to incompatible and compatible pollen in self-incompatibility Brassica oleracea using comparative proteomics. Protein J. 2017, 36, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ockendon, D.J. The S-allele collection of Brassica oleracea. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2000, 539, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, L. Identification and classification of S haplotypes in radish (Raphanus sativus L). Plant Breed. 2019, 138, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.R. Detection of self-Incompatibility of Radish and Identification of Related Genes. Master’s Dissertation, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.M.; Li, C.Y.; Lan, C.Y.; Zou, M.; Ren, X.S.; Si, J.; Li, C.Q.; Song, H.Y. Effects of transgenic MLPK antisense gene on self-incompatibility of cabbage. Chin. J. Hortic. 2015, 2, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, E.H. Determination of cabbage self-incompatibility by fluorescence microscopy. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 1989, 1, 6–7. Available online: https://CNKI:SUN:SNKX.0.1989-01-003 (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Fang, Z.Y.; Sun, P.T.; Liu, Y.M. Several issues on utilization of heterosis and selection of self-incompatible lines in cabbage. Chin. Agric. Sci. 1983, 3, 51–62. Available online: https://www.chinaagrisci.com/CN/Y1983/V16/I03/51 (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Pastuglia, M.; Ruffio, C.V.; Delorme, V.; Gaude, T.; Cock, J.M. A functional S locus anther gene is not required for the self-incompatibility response in Brassica oleracea. Plant Cell. 1997, 9, 2065. [Google Scholar]
- Kitashiba, H.; Nasrallah, J.B. Self-incompatibility in Brassicaceae crops: Lessons for interspecific incompatibility. Breed Sci. 2014, 64, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishio, T.; Kusaba, M.; Watanabe, M.; Hinata, K. Registration of S alleles in Brassica campestris L. by the restriction fragment sizes of SLGs. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1996, 92, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brace, J.; Ockendon, D.J.; King, G.J. Development of a method for the identification of S alleles in Brassica oleracea based on digestion of PCR-amplified DNA with restriction endonucleases. Sex. Plant Reprod. 1993, 6, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.; Kusaba, M.; Nishio, T. Polymorphism of the S-locus glycoprotein gene (SLG) and the S-locus related gene (SLR1) in Raphanus sativus L. and self-incompatible ornamental plants in the Brassicaceae. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1998, 258, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.H.; Cho, H.; Lee, S.; Cho, Y.H.; Kim, B.D. Identification and classification of S haplotypes in Raphanus sativus by PCR-RFLP of the S locus glycoprotein (SLG) gene and the S locus receptor kinase (SRK) gene. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 104, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Kawanabe, T.; Shimizu, M. Genetic characterization of inbred lines of Chinese cabbage by DNA markers; towards the application of DNA markers to breeding of F1 hybrid cultivars. Data Brief. 2015, 6, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.F.; Wang, J.S.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Sheng, X.G.; Gu, H.H. Identification of the S Haplotype of the Self-Incompatible DH Line in Broccoli; Chinese Horticultural Society: LiJiang, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.F.; Li, Y.; Gao, S.Y.; Shi, G.J.; Hou, X.L. Identification of self-incompatible S haplotypes in non-heading Chinese cabbage. Northwestern J. Bot. 2008, 28, 1720–1727. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Brugiere, N.; Jackman, L.; Bi, Y.M.; Rothstein, S.J. Structural and transcriptional comparative analysis of the S locus regions in two self-incompatible Brassica napus lines. Plant Cell. 1999, 11, 2217–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fukai, E.; Fujimoto, R.; Nishio, T. Genomic organization of the S core region and the S flanking regions of a Class-II S haplotype in Brassica rapa. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2003, 269, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.K.; Gong, Y.Q.; Liu, L.W.; Ma, E.L.; Song, L.J.; Wang, L.Z. Rapid Identification of Self-Incompatibility between Radish and Broccoli; The Second Council and Academic Symposium of the Tenth Chinese Horticultural Society: Nanjing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, S.; Sato, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Nishio, T. Distribution of similar self-incompatibility (S) haplotypes in different genera, Raphanus and Brassica. Sex. Plant Reprod. 2004, 17, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.K.; Shao, W.T.; Gong, Y.Q.; Zhu, X.W.; Ma, E.L.; Zhao, T.R. Radish RsSRK-a gene cDNA cloning and expression characteristics analysis. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2010, 33, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, J.C.O.; Hoebee, S.E.; Newbigin, E.J. Sporophytic Self-Incompatability; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 334–340. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Jung, J.; Choi, Y.; Kim, S. Development of a system for S locus haplotyping based on the polymorphic SLL2 gene tightly linked to the locus determining self-incompatibility in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Euphytica 2016, 209, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, S. Identification of the S locus core sequences determining self-incompatibility and S multigene family from draft genome sequences of radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Euphytica 2018, 214, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, S. Development of a new S locus haplotyping system based on three tightly linked genes in the S locus controlling self-incompatibility in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Sci. Hortic. 2019, 243, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, T.; Sakamoto, K. Polymorphism of self-incompatibility genes. In The Radish Genome; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Haseyama, Y.; Kitashiba, H.; Okamoto, S.; Tonouchi, E.; Sakamoto, K.; Nishio, A. Nucleotide sequence analysis of S-locus genes to unify S haplotype nomenclature in radish. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrallah, J.B.; Nasrallah, M.E. Pollen-stigma signaling in the sporophytic self-incompatibility response. Plant Cell. 1993, 5, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.C.; Yao, Q.J.; Yuan, Y.X.; Wei, F.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.Y.; Jiang, W.S.; Zhang, X.W. Distribution of S haplotypes in Chinese cabbage high-generation inbred lines. Henan Agric. Sci. 2015, 44, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrallah, J.B. Evolution of the Brassica self-incompatibility locus: A look into S-locus gene polymorphisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9516–9519. Available online: https://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.94.18.9516 (accessed on 10 June 2022). [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, Z.H.; Zhou, G.L.; Wang, A.H. Molecular identification of self-incompatible S haplotypes in four non-heading Chinese cabbage. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2015, 54, 948–3951. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.H. Inheritance and SSR Markers of Self-Compatibility in Brassica campestris L.; Gansu Agricultural University: Lanzhou, China, 2009; Available online: https://CNKI:CDMD:2.2009.253310 (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Tian, L.; Miao, W.W.; Liu, J.S.; Fang, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Yang, L.M.; Zhuang, M. Identification of S haplotypes in cabbage inbred lines (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.). Sci. Hortic. 2013, 164, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhuang, M.; Miao, W.W.; Fang, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Yang, L.M.; Zhang, Y.Y. The rapid classification and identification of S haplotypes in cabbage inbred lines. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2011, 38, 2545. Available online: http://www.ahs.ac.cn/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=3405 (accessed on 1 August 2011).
- Zheng, M.; Zhu, C.Z.; Liu, M.C.; Xu, B.B.; Ma, C.F.; Li, Q.F.; Ren, X.S.; Si, J.; Song, H.Y. Haplotype identification and verification of self-incompatible cabbage lines based on SRK gene sequence analysis. Chin. Veg. 2018, 3, 32–39. Available online: http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94878X/201803/674591563.html (accessed on 24 December 2017).
- Park, S.H.; Kim, K.T.; Lim, S.H.; Yoon, M.K.; Park, H.G. Classification and identification of S-haplotypes using PCR-RFLP and measuring the self-incompatibility activity in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). HortScience 2005, 40, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitahara, K.; Matsumoto, S. Cloning of the S25 cDNA from ′McIntosh′ apple and an S25-allele identification method. J. Hortic. Sci. 2002, 77, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zisovich, A.H.; Stern, R.A.; Shafir, S.; Goldway, M. Identification of seven S-alleles from the European pear (Pyrus communis) and the determination of compatibility among cultivars. J. Pomol. Hortic. Sci. 2004, 79, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.I.; Lee, S.S.; Watanabe, M.; Takahata, Y.; Nou, S.I. Identification of S-alleles using polymerase chain reaction-cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence of the S-locus receptor kinase in inbreeding lines of Brassica oleracea. Plant Breed. 2002, 121, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.H.; Kita, D.; Johnson, E.A.; Aggarwal, M.; Gates, L.; Wu, H.M.; Cheung, A.Y. Reactive oxygen species mediate pollen tube rupture to release sperm for fertilization in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 547–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.Q.; Dai, H.M.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, C.; Zeng, W.Q.; Huang, J.B.; Duan, Q.H. Ethylene negatively mediates self-incompatibility response in Brassica rapa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 525, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).