Genome-Wide Identification of SMXL Gene Family in Soybean and Expression Analysis of GmSMXLs under Shade Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of SMXL Family Members in Soybean
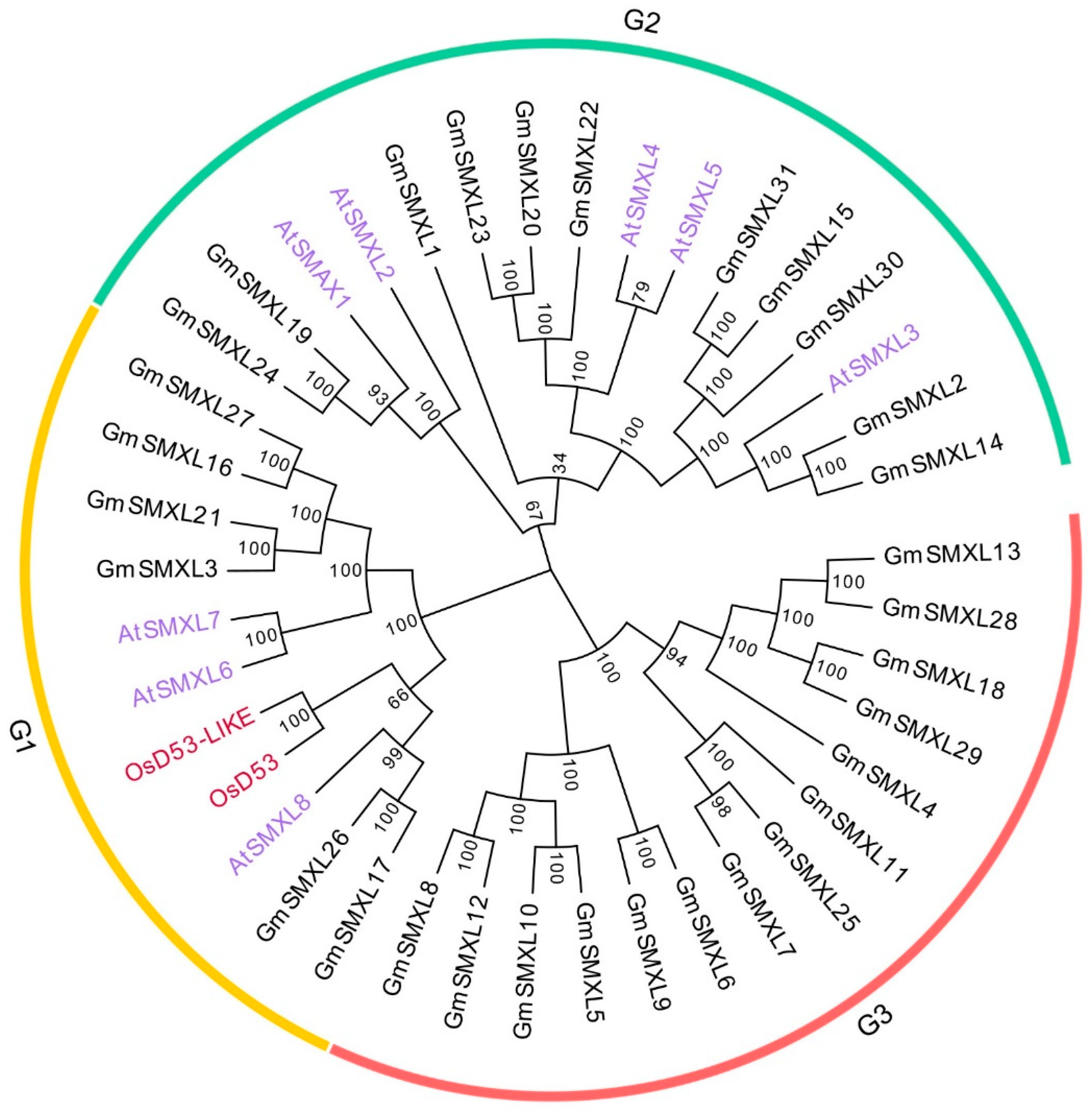
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of GmSMXL Gene Family
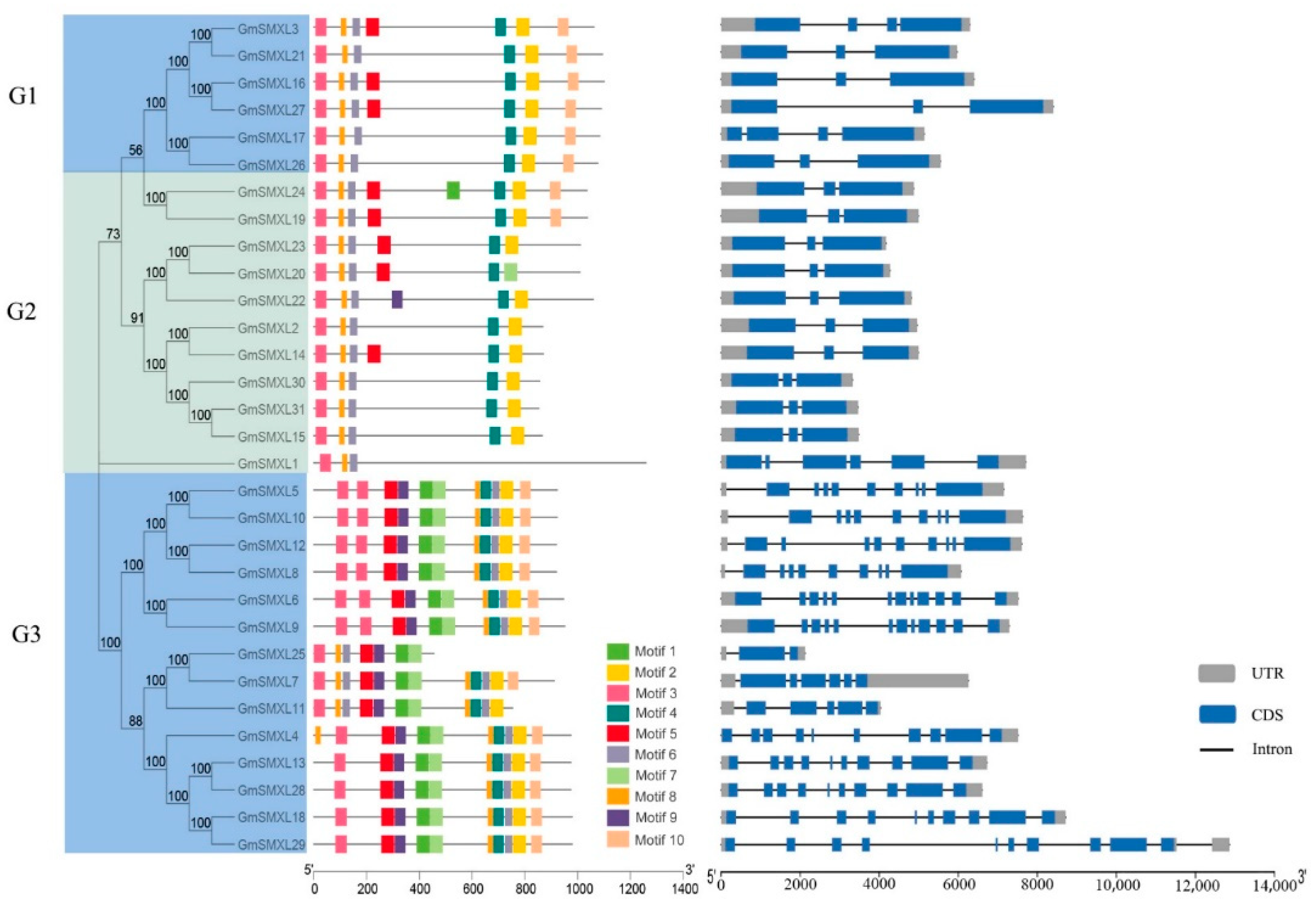
2.3. Gene Structures and Motif Patterns of GmSMXL Gene Members
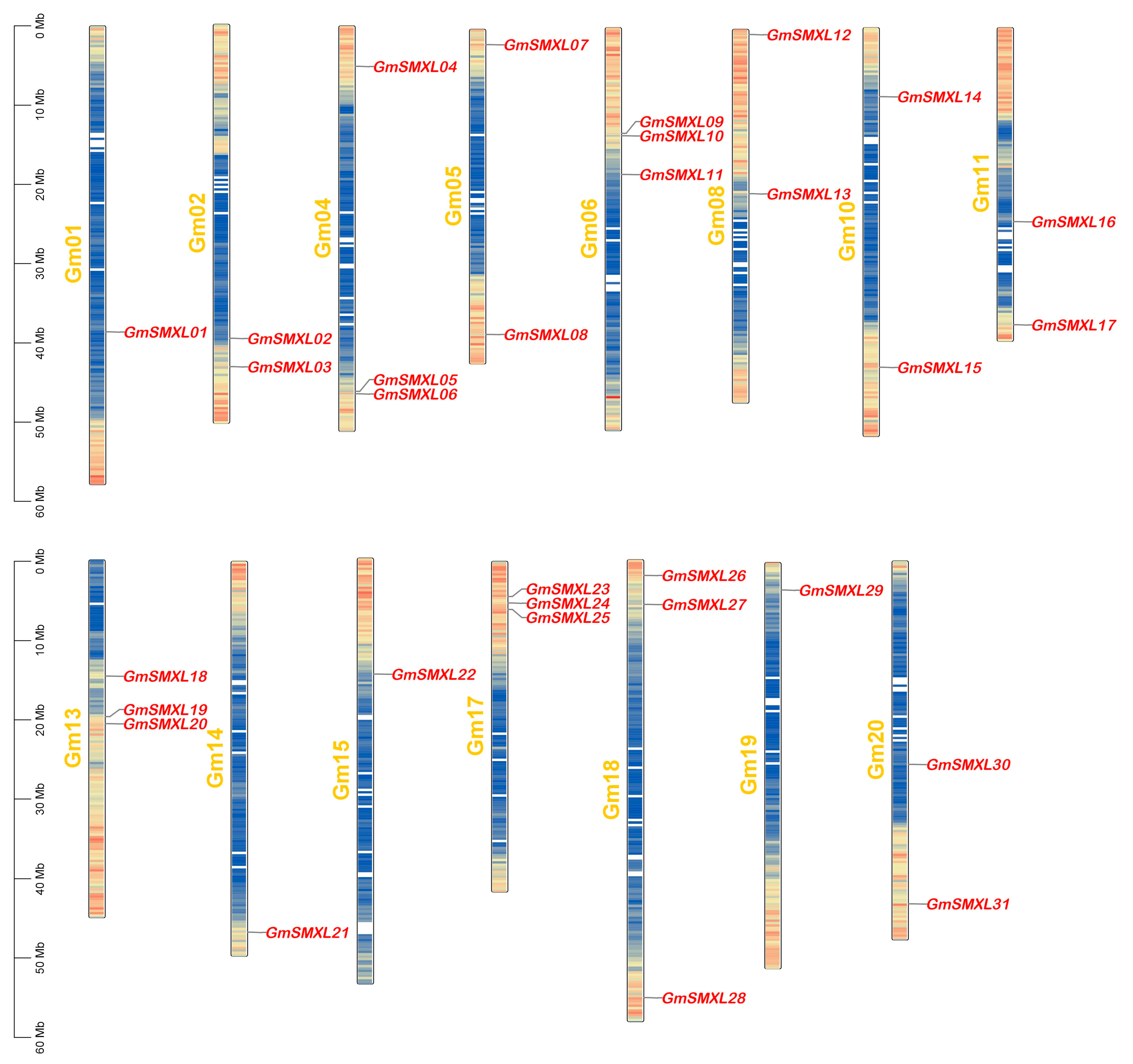
2.4. Chromosome Distributions of GmSMXL Gene Members
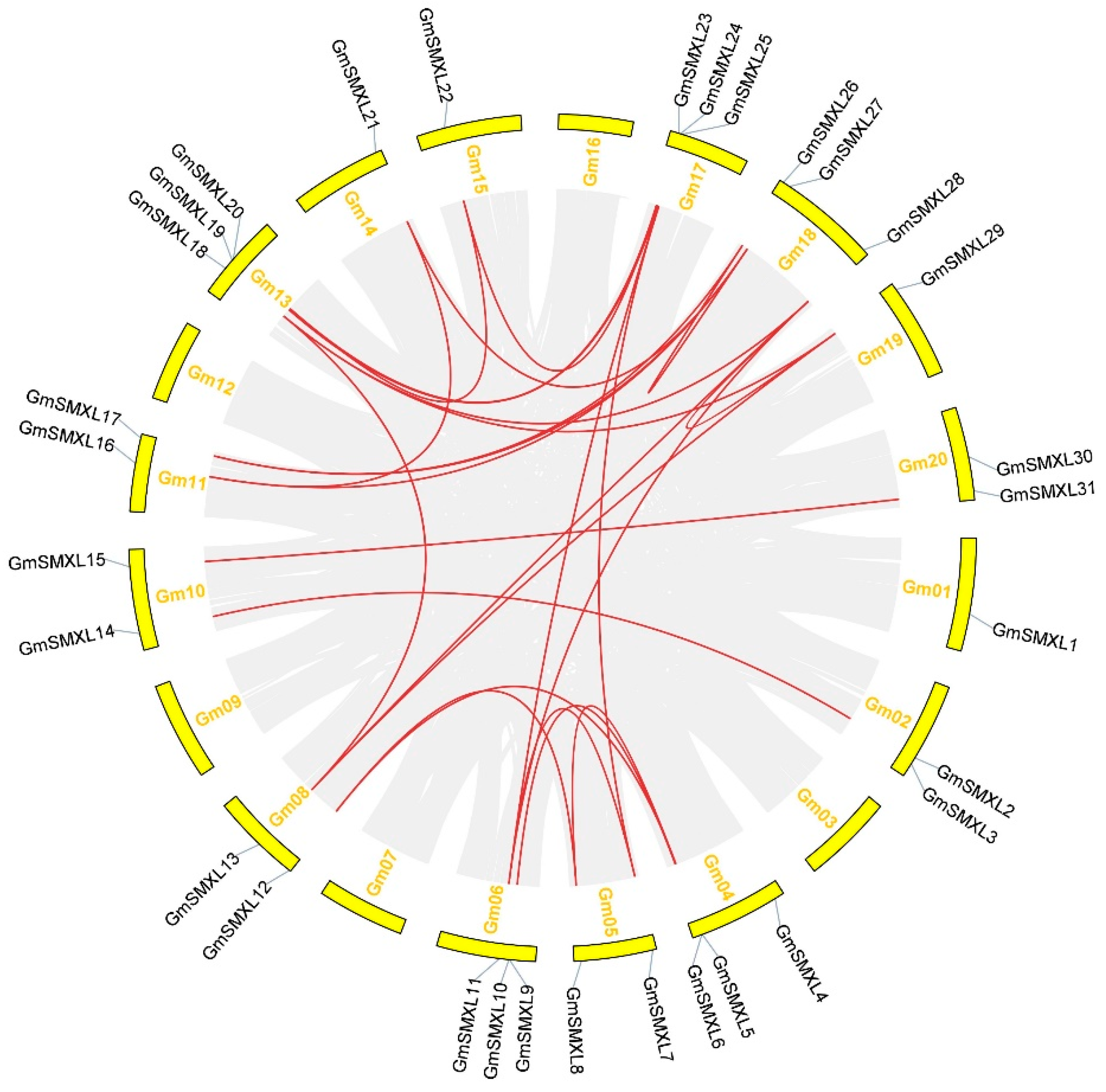
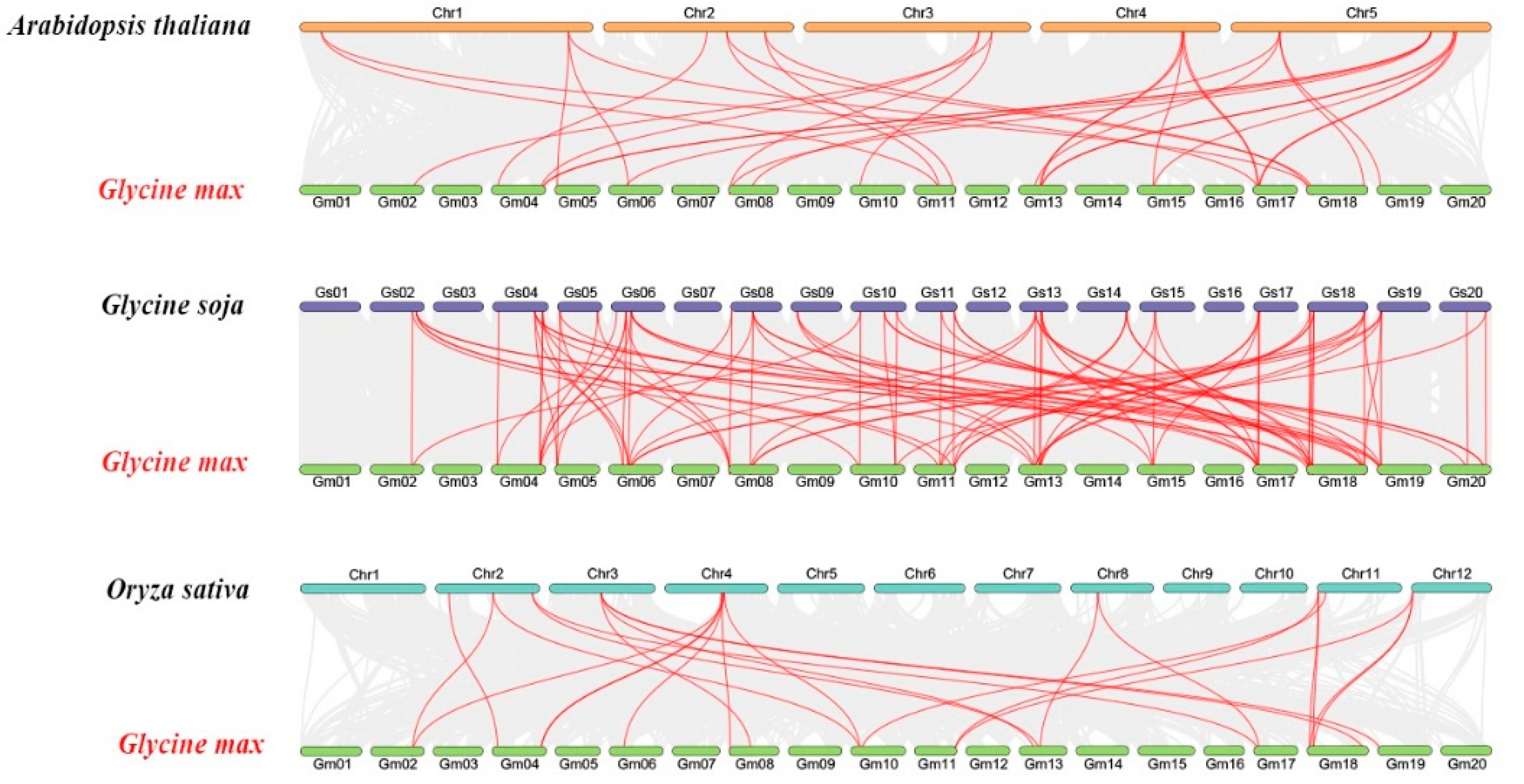
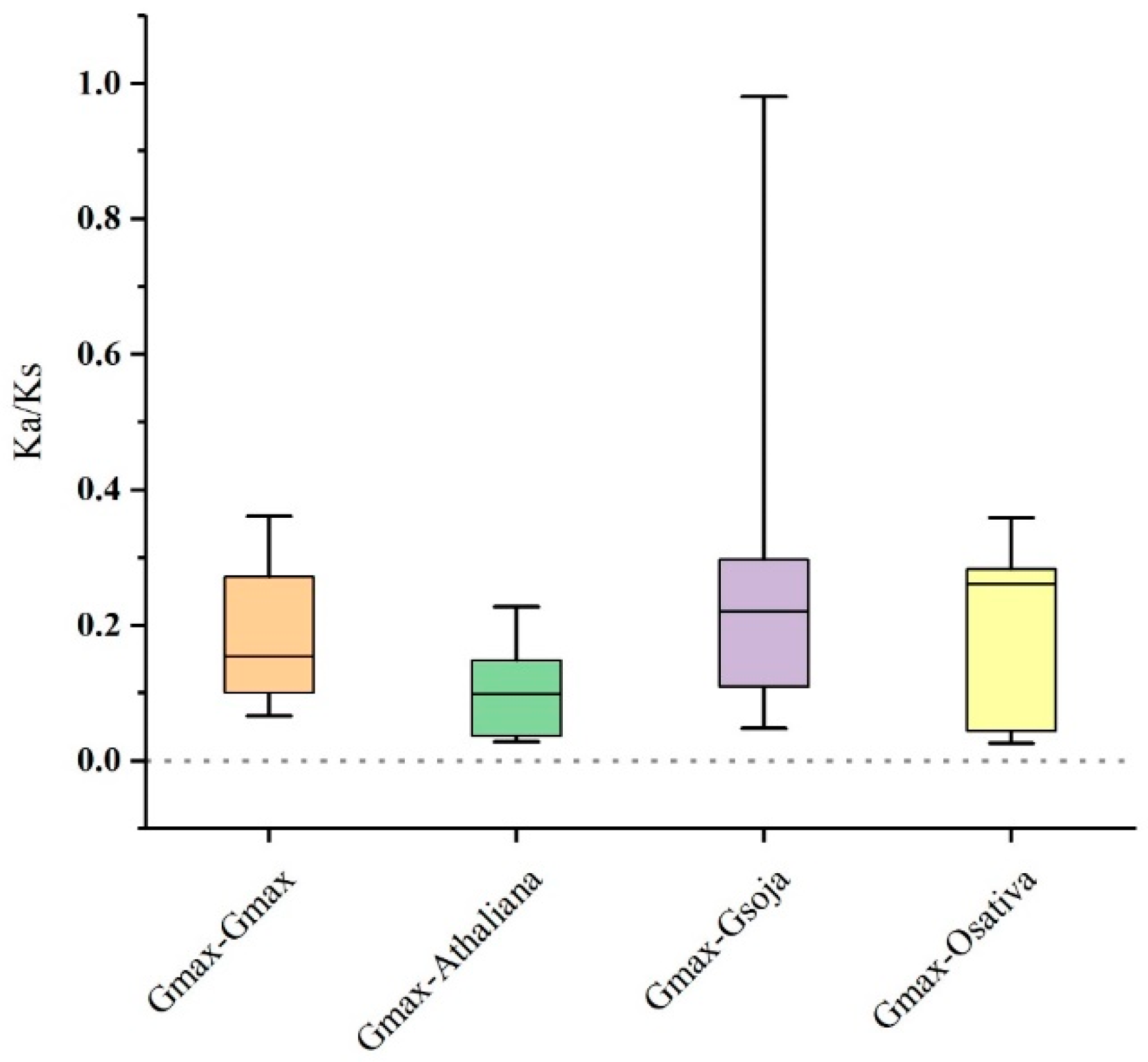
2.5. Synteny and Evolutionary Analyses of GmSMXL Gene Members
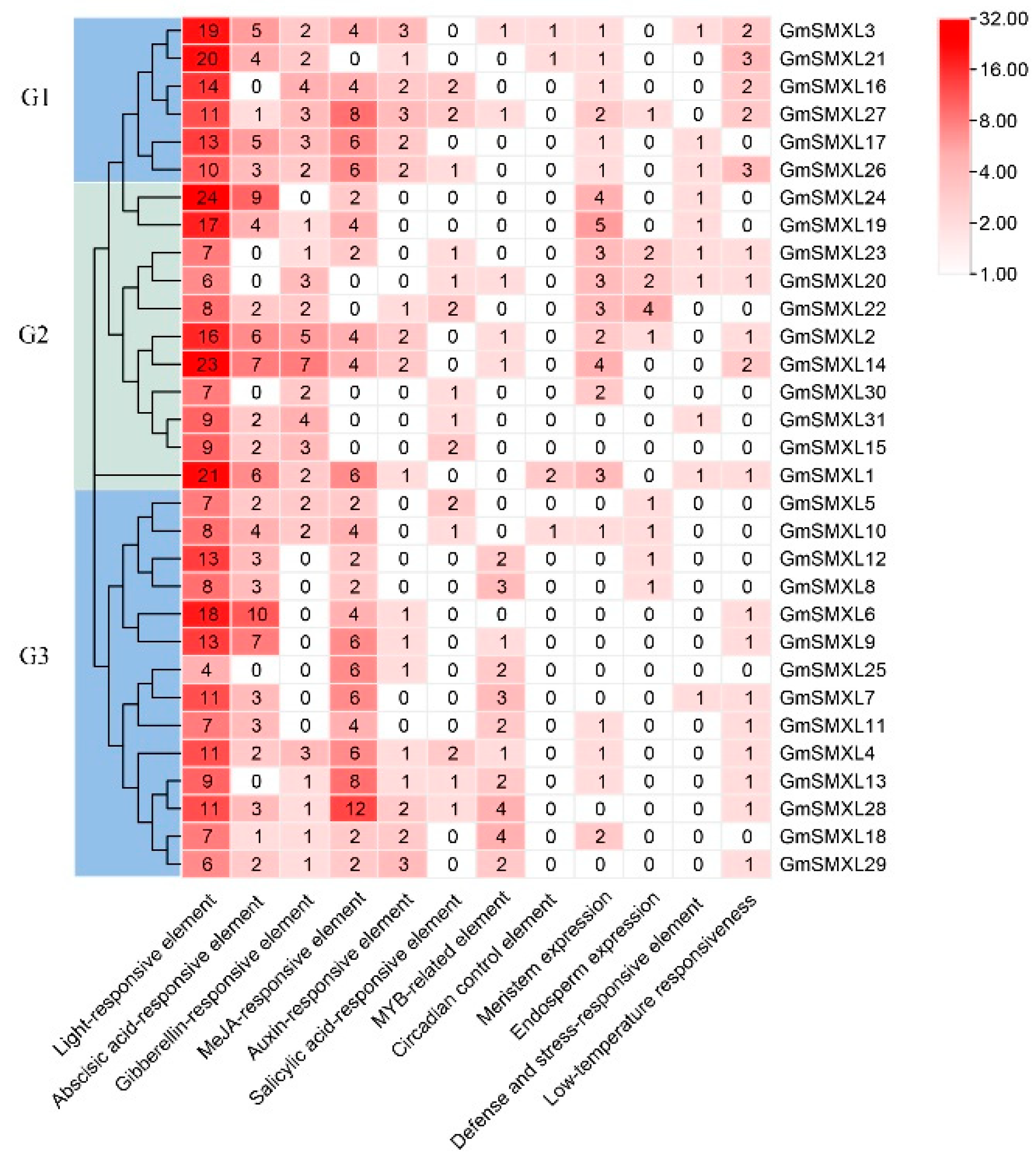
2.6. Cis-Element Analyses of Soybean GmSMXL Genes
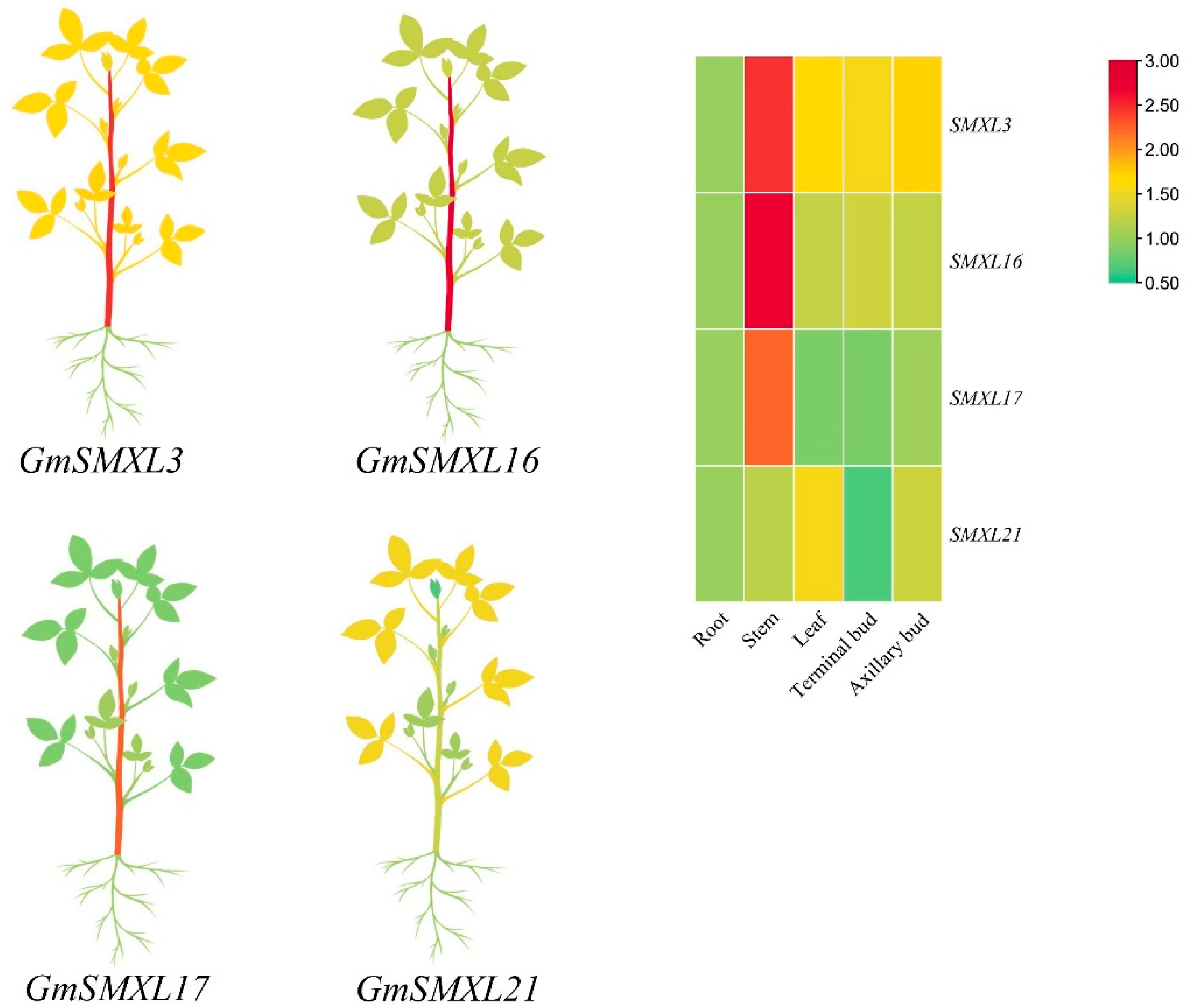
2.7. Expression Profile of GmSMXLs in Different Tissues
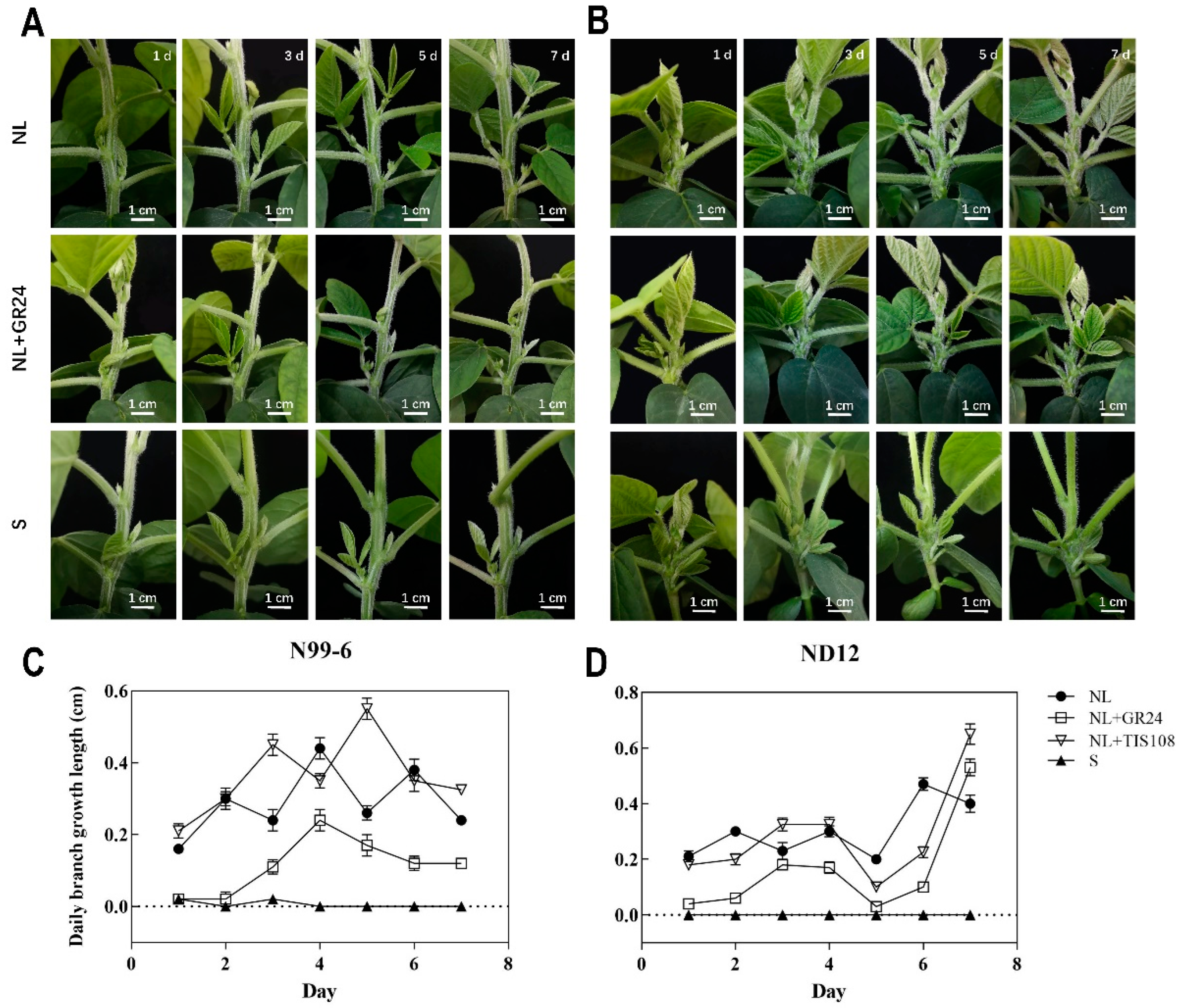
2.8. Growth and Development of Soybean Branches under Different Treatments
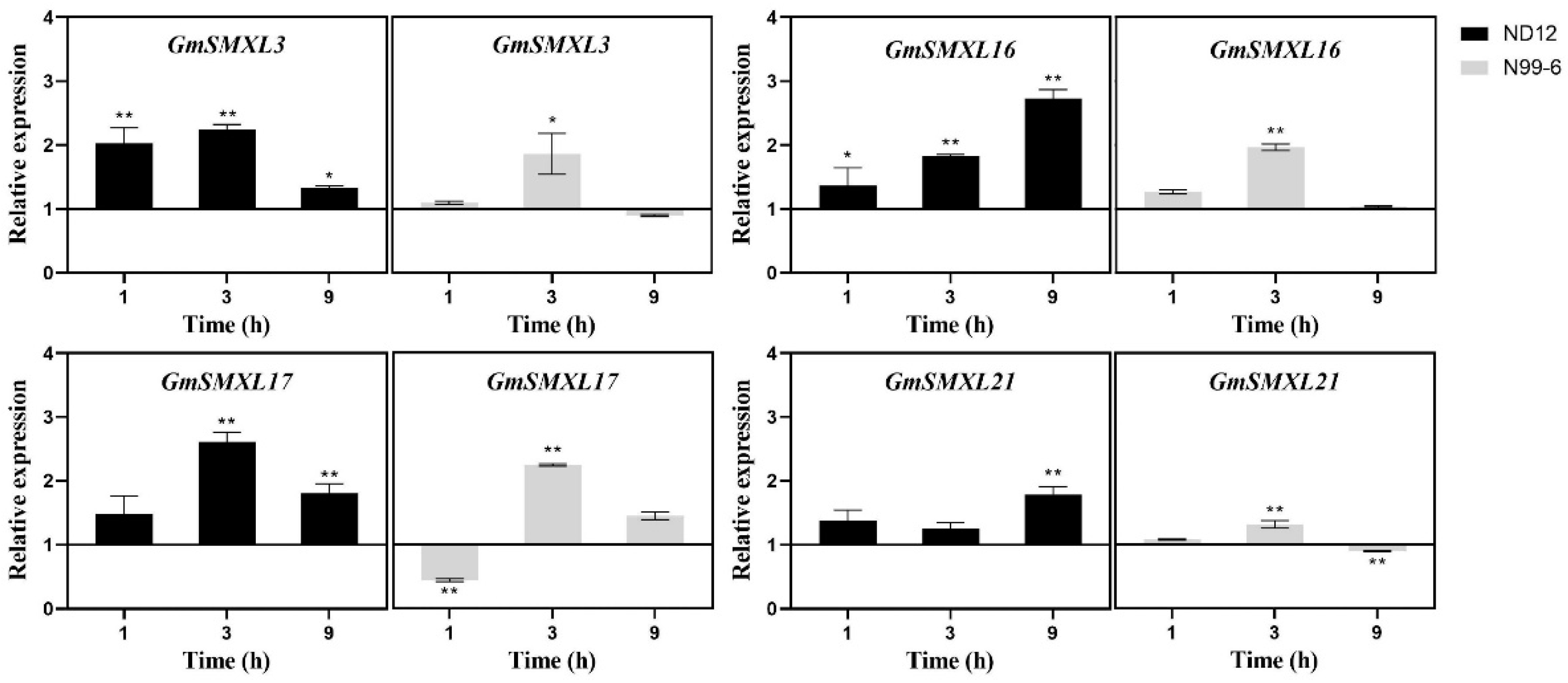
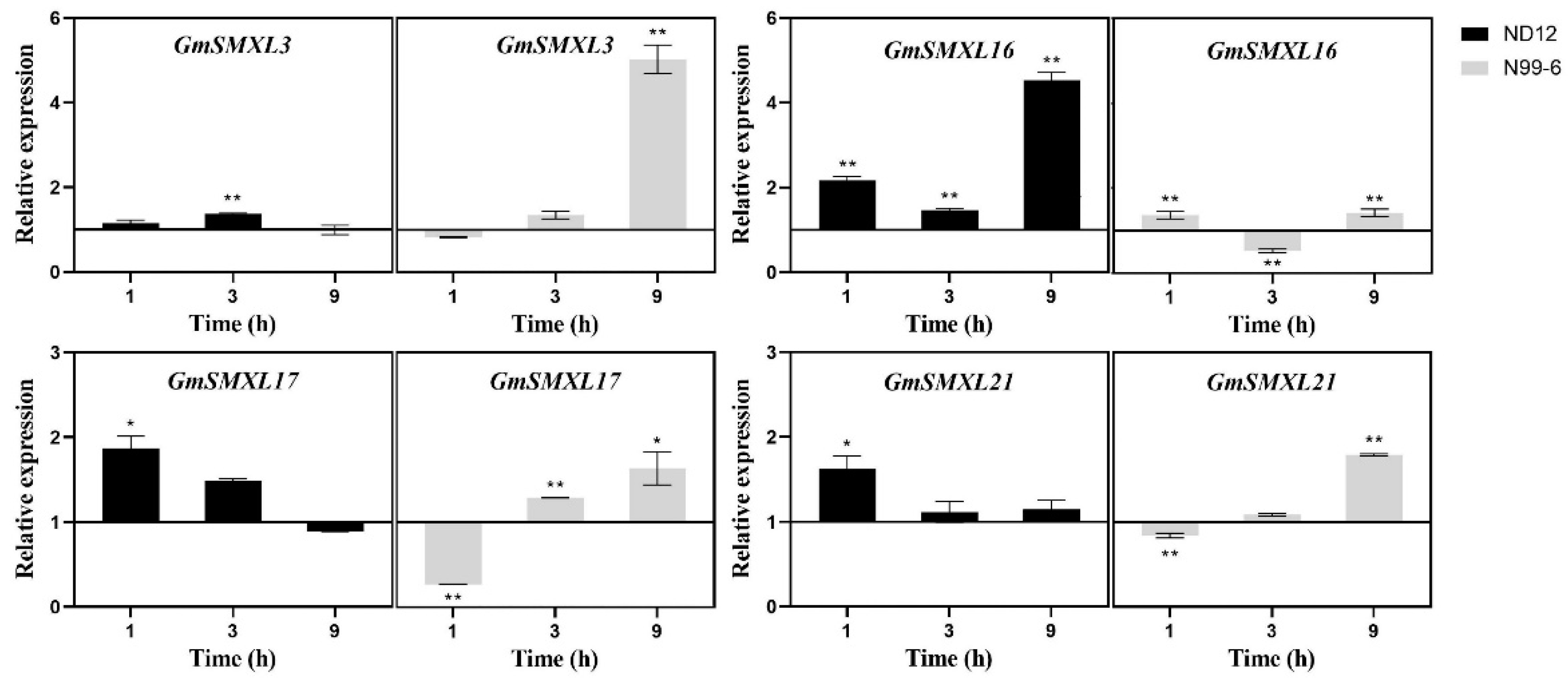
2.9. Expression Patterns of GmSMXL Genes under GR24 and Shading Treatments
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of GmSMXL Genes in Soybean
4.2. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis of GmSMXL Proteins
4.3. Gene Structures and Covered Motif Analyses of GmSMXLs
4.4. Chromosome Locations, Duplications and Synteny Analysis of GmSMXL Genes
4.5. Analysis of Cis-Elements in the Promoter Region of GmSMXL Genes
4.6. Prediction of Tertiary Structure of GmSMXL Proteins
4.7. Plant Materials, Growth Conditions and Shade Treatment
4.8. Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) for GmSMXL Genes
4.9. Statitical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teichmann, T.; Muhr, M. Shaping plant architecture. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Smith, S.M.; Li, J. Genetic Regulation of Shoot Architecture. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 437–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, M.T.; Gutjahr, C.; Bennett, T.; Nelson, D.C. Strigolactone Signaling and Evolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2017, 68, 291–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, C.E.; Whichard, L.P.; Turner, B.; Wall, M.E.; Egley, G.H. Germination of witchweed (Striga lutea Lour.): Isolation and properties of a potent stimulant. Science 1966, 154, 1189–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besserer, A.; Puech-Pages, V.; Kiefer, P.; Gomez-Roldan, V.; Jauneau, A.; Roy, S.; Portais, J.C.; Roux, C.; Becard, G.; Sejalon-Delmas, N. Strigolactones stimulate arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi by activating mitochondria. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, K.; Matsuzaki, K.; Hayashi, H. Plant sesquiterpenes induce hyphal branching in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Nature 2005, 435, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Roldan, V.; Fermas, S.; Brewer, P.B.; Puech-Pages, V.; Dun, E.A.; Pillot, J.P.; Letisse, F.; Matusova, R.; Danoun, S.; Portais, J.C.; et al. Strigolactone inhibition of shoot branching. Nature 2008, 455, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umehara, M.; Hanada, A.; Yoshida, S.; Akiyama, K.; Arite, T.; Takeda-Kamiya, N.; Magome, H.; Kamiya, Y.; Shirasu, K.; Yoneyama, K.; et al. Inhibition of shoot branching by new terpenoid plant hormones. Nature 2008, 455, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagalska, M.A.; Leyser, O. Signal integration in the control of shoot branching. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Ming, Z.; Yan, L.; Li, S.; Wang, F.; Ma, S.; Yu, C.; Yang, M.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.; et al. DWARF14 is a non-canonical hormone receptor for strigolactone. Nature 2016, 536, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, T.; Liang, Y.; Seale, M.; Ward, S.; Muller, D.; Leyser, O. Strigolactone regulates shoot development through a core signalling pathway. Biol. Open 2016, 5, 1806–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arite, T.; Umehara, M.; Ishikawa, S.; Hanada, A.; Maekawa, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kyozuka, J. d14, a strigolactone-insensitive mutant of rice, shows an accelerated outgrowth of tillers. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, L.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, K.; Shabek, N.; Wu, F.; Mao, H.; Dong, W.; Gan, L.; et al. D14-SCF(D3)-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling. Nature 2013, 504, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Lu, Z.; Meng, X.; Wang, Y.; Smith, S.M.; Li, J. Strigolactone Signaling in Arabidopsis Regulates Shoot Development by Targeting D53-Like SMXL Repressor Proteins for Ubiquitination and Degradation. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 3128–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.H.; Zhou, X.E.; Yi, W.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Y.; Hou, L.; de Waal, P.W.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Destabilization of strigolactone receptor DWARF14 by binding of ligand and E3-ligase signaling effector DWARF3. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 1219–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundappan, I.; Bennett, T.; Morffy, N.; Liang, Y.; Stanga, J.P.; Abbas, A.; Leyser, O.; Nelson, D.C. SMAX1-LIKE/D53 Family Members Enable Distinct MAX2-Dependent Responses to Strigolactones and Karrikins in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 3143–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Ward, S.; Li, P.; Bennett, T.; Leyser, O. SMAX1-LIKE7 Signals from the Nucleus to Regulate Shoot Development in Arabidopsis via Partially EAR Motif-Independent Mechanisms. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 1581–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhang, M.; Ding, Z. D53: The missing link in strigolactone signaling. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 761–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stanga, J.P.; Smith, S.M.; Briggs, W.R.; Nelson, D.C. SUPPRESSOR OF MORE AXILLARY GROWTH2 1 controls seed germination and seedling development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moturu, T.R.; Thula, S.; Singh, R.K.; Nodzynski, T.; Varekova, R.S.; Friml, J.; Simon, S. Molecular evolution and diversification of the SMXL gene family. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 2367–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunsick, M.; Toh, S.; Wong, C.; Xu, Z.; Ly, G.; McErlean, C.S.P.; Pescetto, G.; Nemrish, K.E.; Sung, P.; Li, J.D.; et al. SMAX1-dependent seed germination bypasses GA signalling in Arabidopsis and Striga. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Xie, W.; Yue, X.; Zhu, H.; Chen, S.; Sun, X. Arabidopsis SMAX1 overaccumulation suppresses rosette shoot branching and promotes leaf and petiole elongation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 553, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Yu, H.; Guo, H.; Lin, T.; Kou, L.; Wang, A.; Shao, N.; Ma, H.; Xiong, G.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of strigolactone signalling in Arabidopsis. Nature 2020, 583, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, B.; Wei, H.; Wang, H. Arabidopsis FHY3 and FAR1 integrate light and strigolactone signaling to regulate branching. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seale, M.; Bennett, T.; Leyser, O. BRC1 expression regulates bud activation potential but is not necessary or sufficient for bud growth inhibition in Arabidopsis. Development 2017, 144, 1661–1673. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, C.H.; Siu-Ting, K.; Taylor, A.; O’Connell, M.J.; Bennett, T. Strigolactone synthesis is ancestral in land plants, but canonical strigolactone signalling is a flowering plant innovation. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Martin-Fontecha, E.S.; Khosla, A.; White, A.R.F.; Chang, S.; Cubas, P.; Nelson, D.C. The strigolactone receptor D14 targets SMAX1 for degradation in response to GR24 treatment and osmotic stress. Plant Commun. 2022, 3, 100303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.L.; Klueva, N.Y.; Zheng, H.G.; Nieto-Sotelo, J.; Ho, T.D.; Nguyen, H.T. Cloning of new members of heat shock protein HSP101 gene family in wheat (Triticum aestivum (L.) Moench) inducible by heat, dehydration, and ABA. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2001, 1517, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trosch, R.; Muhlhaus, T.; Schroda, M.; Willmund, F. ATP-dependent molecular chaperones in plastids-More complex than expected. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1847, 872–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, S.C.; Patil, S.B.; de Saint Germain, A.; Pillot, J.P.; Saffar, J.; Ligerot, Y.; Aubert, G.; Citerne, S.; Bellec, Y.; Dun, E.A.; et al. Integration of the SMXL/D53 strigolactone signalling repressors in the model of shoot branching regulation in Pisum sativum. Plant J. 2021, 107, 1756–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.L.; Duan, J.B.; Ke, J.Y.; He, Y.Z.; Gu, X.; Xu, T.H.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.H.; Brunzelle, J.S.; Jiang, Y.; et al. A D53 repression motif induces oligomerization of TOPLESS corepressors and promotes assembly of a corepressor-nucleosome complex. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1601217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Lian, Y.; Kang, J.; Bian, Z.; Xuan, L.; Gao, Z.; Wang, X.; Deng, J.; Wang, C. The SUPPRESSOR of MAX2 1 (SMAX1)-Like SMXL6, SMXL7 and SMXL8 Act as Negative Regulators in Response to Drought Stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2020, 61, 1477–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.b.; Han, T.f.; Gai, J.y.; Yong, T.w.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.c.; Yang, F.; Liu, J.; Shu, K.; Liu, W.g.; et al. Maize-soybean strip intercropping: Achieved a balance between high productivity and sustainability. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Rahman, T.; Song, C.; Yang, F.; Su, B.; Cui, L.; Bu, W.; Yang, W. Relationships among light distribution, radiation use efficiency and land equivalent ratio in maize-soybean strip intercropping. Field Crops Res. 2018, 224, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.A.; Feng, L.Y.; Iqbal, N.; Ahmed, M.; Chen, Y.K.; Khalid, M.H.B.; Mohi Ud Din, A.; Khan, A.; Ijaz, W.; Hussain, A.; et al. Growth and development of soybean under changing light environments in relay intercropping system. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maere, S.; De, B.S.; Raes, J.; Casneuf, T.; Van, M.M.; Kuiper, M.; Van, D.P.Y. Modeling gene and genome duplications in eukaryotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5454–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, N.N.; Song, W.L.; Yin, G.J.; Qin, Y.J.; Yan, Y.M.; Hu, Y.K. Soybean (Glycine max) expansin gene superfamily origins: Segmental and tandem duplication events followed by divergent selection among subfamilies. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelderen, K.; Kang, C.; Pierik, R. Light Signaling, Root Development, and Plasticity. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldissera, T.C.; Frak, E.; Carvalho, P.C.; Louarn, G. Plant development controls leaf area expansion in alfalfa plants competing for light. Ann. Bot. 2014, 113, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundel, P.E.; Pierik, R.; Mommer, L.; Ballare, C.L. Competing neighbors: Light perception and root function. Oecologia 2014, 176, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Xiong, G.; Liu, H.; Chen, F.; Wang, L.; Meng, X.; Liu, G.; Yu, H.; Yuan, Y.; et al. DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice. Nature 2013, 504, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmutz, J.; Cannon, S.B.; Schlueter, J.; Ma, J.X.; Mitros, T.; Nelson, W.; Hyten, D.L.; Song, Q.J.; Thelen, J.J.; Cheng, J.L.; et al. Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. Nature 2010, 463, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner, E.S.; Lopez-Salmeron, V.; Belevich, I.; Poschet, G.; Jung, I.; Grunwald, K.; Sevilem, I.; Jokitalo, E.; Hell, R.; Helariutta, Y.; et al. Strigolactone- and Karrikin-Independent SMXL Proteins Are Central Regulators of Phloem Formation. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.B.; Barbier, F.F.; Zhao, J.; Zafar, S.A.; Uzair, M.; Sun, Y.; Fang, J.; Perez-Garcia, M.D.; Bertheloot, J.; Sakr, S.; et al. Sucrose promotes D53 accumulation and tillering in rice. New Phytol. 2021, 234, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Gao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, N.; Xu, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Liu, W.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification of SMXL Gene Family in Soybean and Expression Analysis of GmSMXLs under Shade Stress. Plants 2022, 11, 2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11182410
Zhang H, Wang L, Gao Y, Guo Y, Zheng N, Xu X, Xu M, Wang W, Liu C, Liu W, et al. Genome-Wide Identification of SMXL Gene Family in Soybean and Expression Analysis of GmSMXLs under Shade Stress. Plants. 2022; 11(18):2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11182410
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Han, Li Wang, Yang Gao, Yukai Guo, Naiwen Zheng, Xiangyao Xu, Mei Xu, Wenyan Wang, Chunyan Liu, Weiguo Liu, and et al. 2022. "Genome-Wide Identification of SMXL Gene Family in Soybean and Expression Analysis of GmSMXLs under Shade Stress" Plants 11, no. 18: 2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11182410
APA StyleZhang, H., Wang, L., Gao, Y., Guo, Y., Zheng, N., Xu, X., Xu, M., Wang, W., Liu, C., Liu, W., & Yang, W. (2022). Genome-Wide Identification of SMXL Gene Family in Soybean and Expression Analysis of GmSMXLs under Shade Stress. Plants, 11(18), 2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11182410




