Agents Affecting the Plant Functional Traits in National Soil and Water Conservation Demonstration Park (China)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
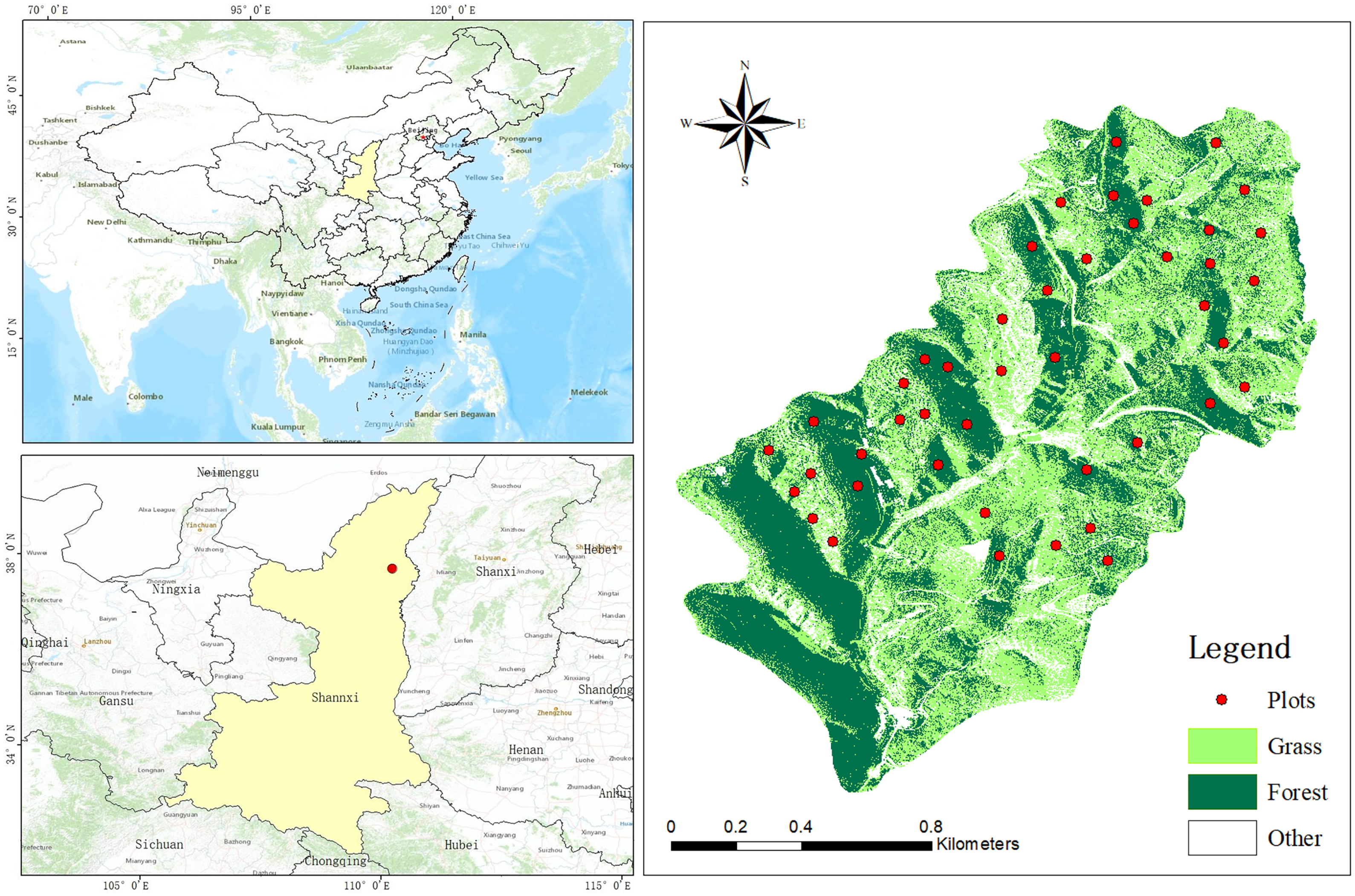
2.1. Study Area
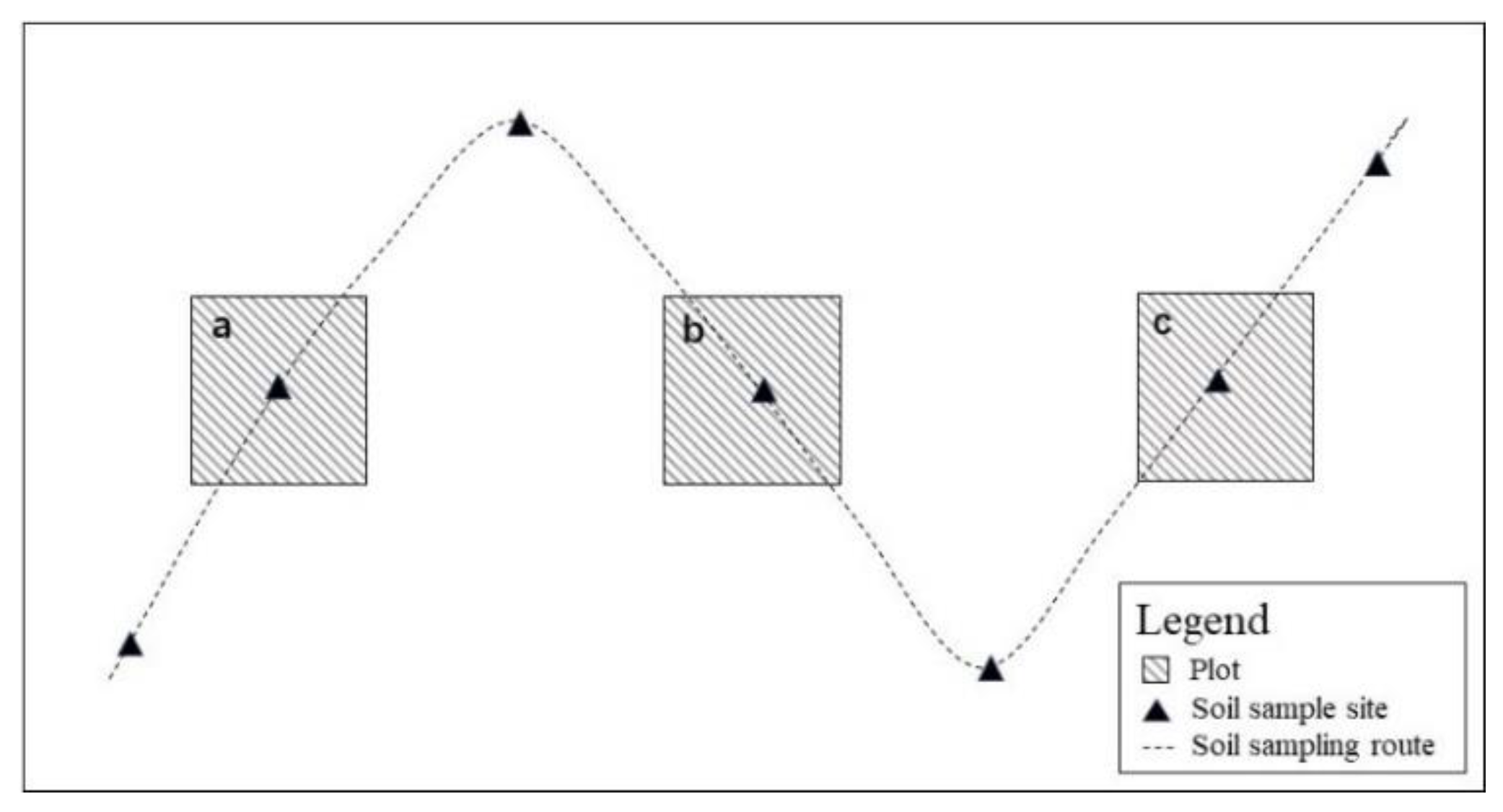
2.2. Plot Survey, Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Variables
2.4. Calculation of Variables
- (1)
- Margalef species richness index (MAR)
- (2)
- Shannon diversity index (SHA)
- (3)
- Simpson diversity index (SIM)
- (4)
- Pielou’s evenness index (PIE)
- (5)
- Gleason richness index (GLE)
- (6)
- Community weighted means (CWM)
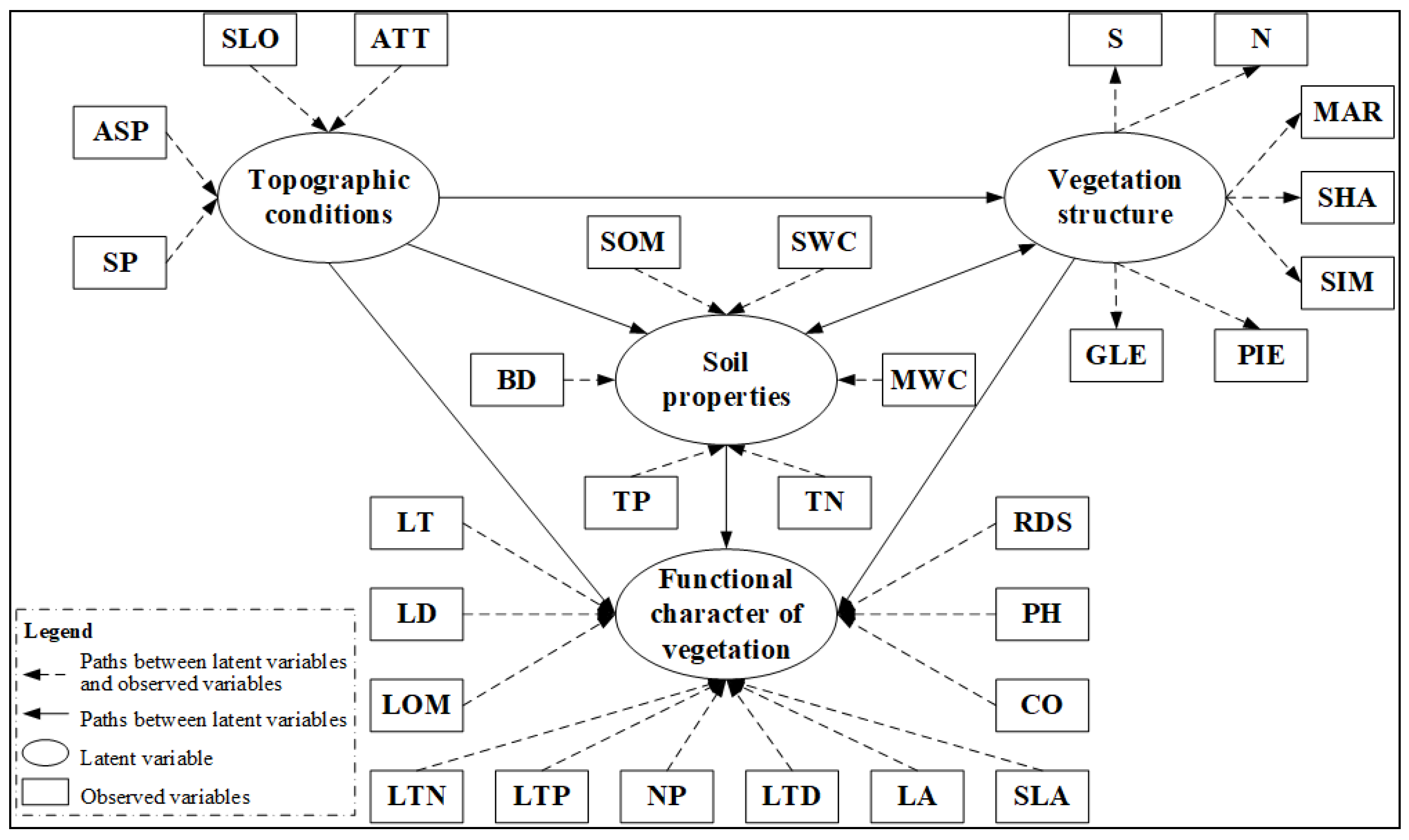
2.5. Selection of Variables
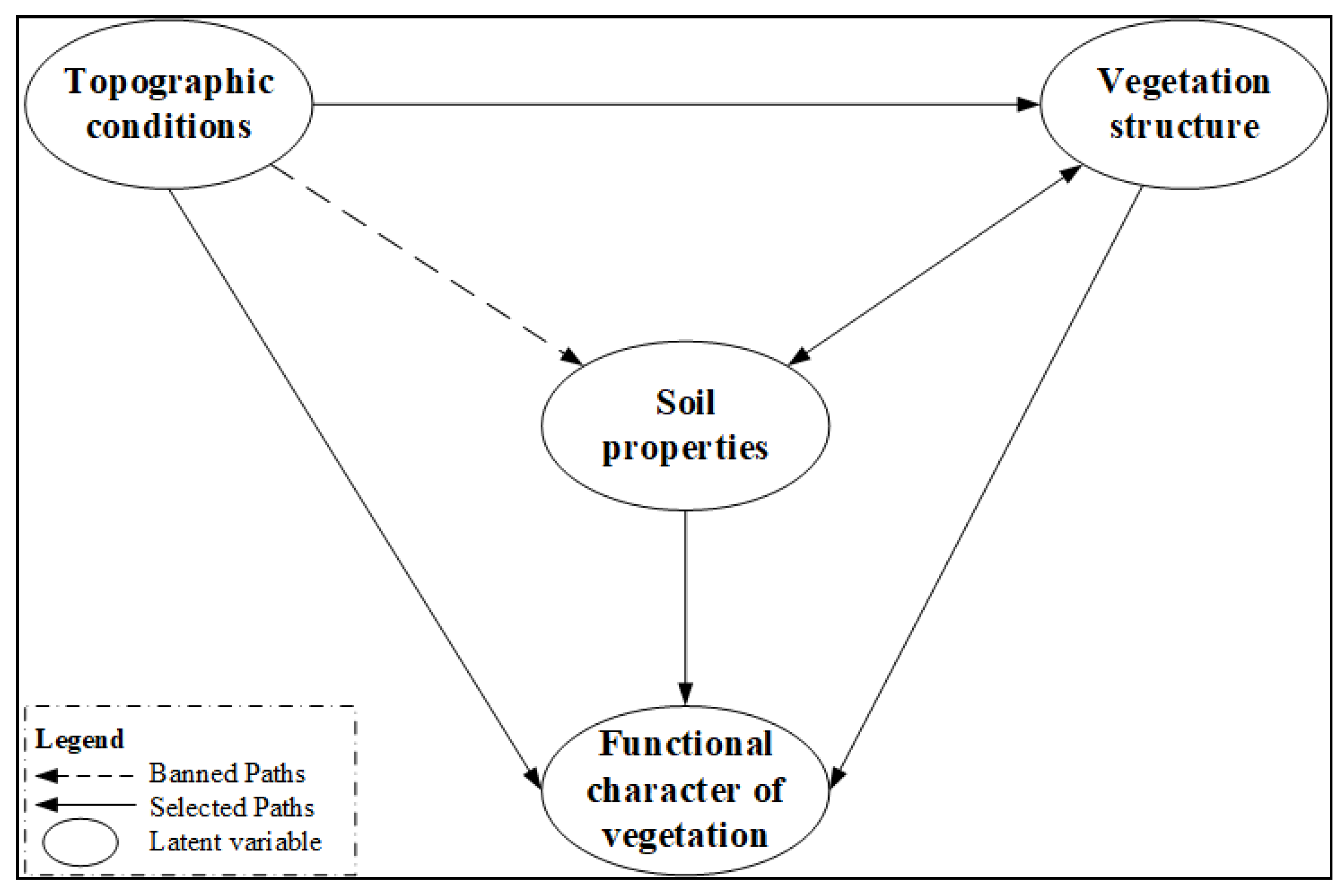
2.6. Establish of Preliminary Model and Paths Determination
2.7. Evaluation of PLS-SEM
3. Results
3.1. Observed Variables of Plant Functional Traits
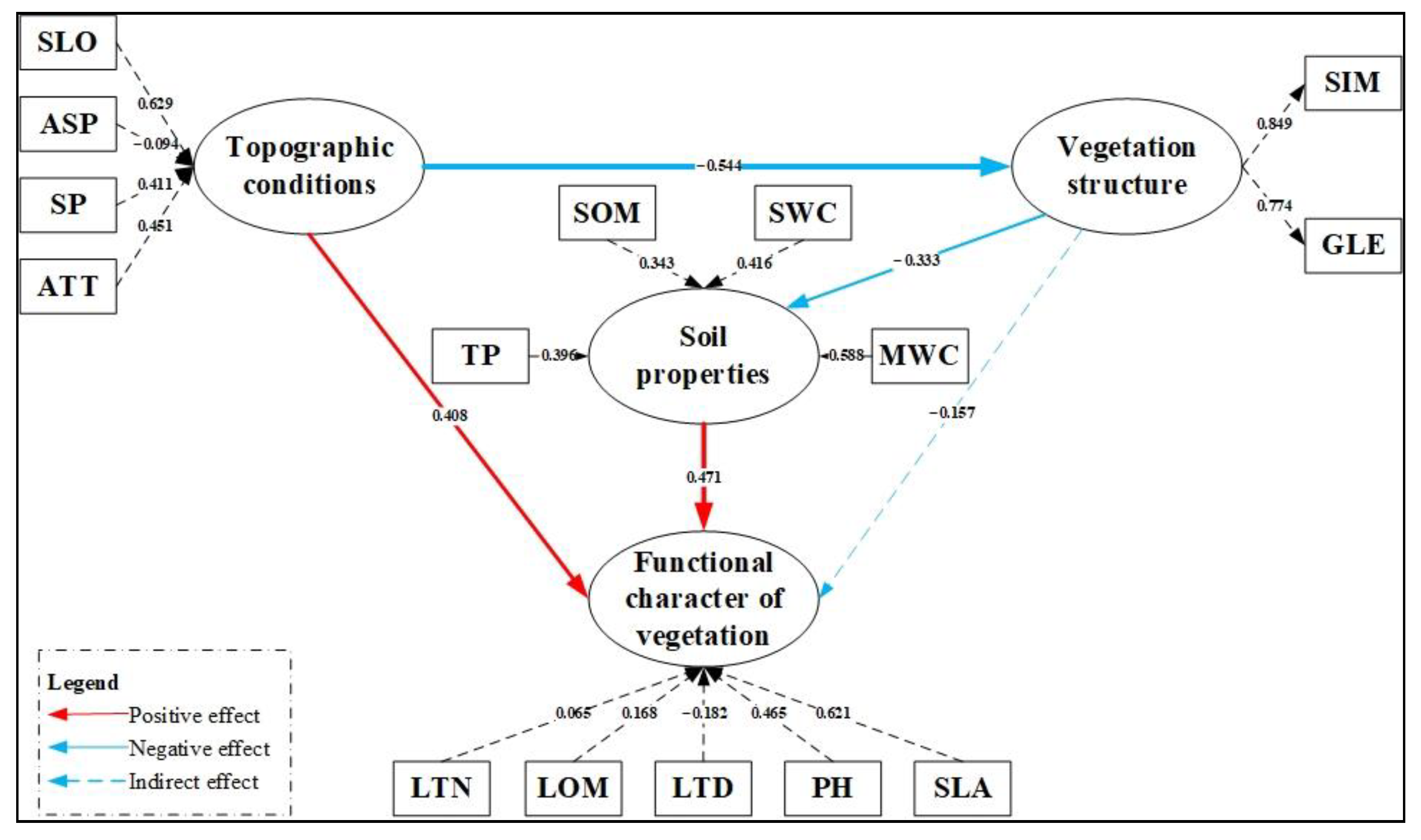
3.2. Possible Path and Model
3.3. Model Fit
3.4. Evaluation of Influencing Factors of Plant Functional Traits
4. Discussion
4.1. Results of Screening Plant Functional Traits by RF
4.2. Direct Effects of Topographic Conditions on Vegetation Structure and Plant Functional Traits
4.3. Direct Effects of Soil Properties on Plant Functional Traits
4.4. Indirect Effect of Vegetation Structure on Plant Functional Traits
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, Y.; Zhao, C.; Quan, Y.; Lu, H.; Rong, Y.; Wu, G. Interrelations of Ecosystem Services and Rural Population Wellbeing in an Ecologically-Fragile Area in North China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Violle, C.; Navas, M.L.; Vile, D.; Kazakou, E.; Fortunel, C.; Hummel, I.; Garnier, E. Let the concept of trait be functional! Oikos 2007, 116, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavorel, S.; McIntyre, S.; Landsberg, J.; Forbes, T. Plant functional classifications: From general groups to specific groups based on response to disturbance. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1997, 12, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, T.W.; Maynard, D.S.; Peccia, T.R.; Smith, J.R.; Bradford, M.A. Untangling the fungal niche: The trait-based approach. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seidel, H.; Matiu, M.; Menzel, A. Compensatory Growth of Scots Pine Seedlings Mitigates Impacts of Multiple Droughts Within and Across Years. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Geng, Y.; Ma, W.-H.; He, J.-S. Linkages of functional traits among plant organs in the dominant species of the inner mongolia grassland, China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2010, 34, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Propastin, P. Multiscale analysis of the relationship between topography and aboveground biomass in the tropical rainforests of Sulawesi, Indonesia. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2011, 25, 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yang, S.; Chu, B.; Ma, S.; Zhu, H.; Hua, L. The effects of topographical factors on the distribution of plant communities in a mountain meadow on the Tibetan Plateau as a foundation for target-oriented management. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106, 105532.1–105532.12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, K.; Vermeire, L. Power and limitation of soil properties as predictors of variation in peak plant biomass in a northern mixed-grass prairie. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 80, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, D.R.; Holmes, W.E.; White, D.C.; Peacock, A.D.; Tilman, D. Plant diversity, soil microbial communities, and ecosystem function: Are there any links? Ecology 2003, 84, 2042–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bui, N.E. Soil salinity: A neglected factor in plant ecology and biogeography. J. Arid. Environ. 2013, 92, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.J.; Waqas, A.; Mahmood, R. The Combined Effect of Vegetation and Soil Erosion in the Water Resource Management. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 3701–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bing, M.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Hai, X.; Li, A.; Wang, K.; Wu, P.; et al. Effects of vegetation restoration types on soil nutrients and soil erodibility regulated by slope positions on the Loess Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 302, 113985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Liang, W.; Yan, J.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. Effects of vegetation restoration on local microclimate on the Loess Plateau. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 291–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, S.; Cabido, M. Vive la différence: Plant functional diversity matters to ecosystem processes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2001, 16, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.K. Random Decision Forests. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–16 August 1995; Volume 1, pp. 278–282. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, D. Structural Equation Modeling: Foundations and Extensions; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2008; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Jiao, J.-Y.; Rayburg, S.; Wang, Q.-L.; Su, Y. Soil erosion resistance of “grain for green” vegetation types under extreme rainfall conditions on the loess plateau, China. Catena 2016, 141, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Bu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, P.; Yang, Y.; Qi, N.; Gou, R. Quantifying the Relationship among Impact Factors of Shrub Layer Diversity in Chinese Pine Plantation Forest Ecosystems. Forests 2019, 10, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Bello, F.; Carmona, C.P.; Dias, A.T.; Götzenberger, L.; Moretti, M.; Berg, M.P. Handbook of Trait-Based Ecology: From Theory to R Tools; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Harguindeguy, N.; Diaz, S.; Garnier, E.; Lavorel, S.; Poorter, H.; Jaureguiberry, P.; Bret-Harte, M.; Cornwell, W.; Craine, J.; Gurvich, D. New handbook for standardised measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust. Bot. 2013, 61, 167–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dane, J.H.; Topp, C.G. Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 4: Physical Methods; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, D.L.; Page, A.L.; Helmke, P.A.; Loeppert, R.H. Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3: Chemical Methods; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M. Nitrogen-Total. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3 Chemical Methods; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; Volume 5, pp. 1085–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson, J.A.; Allen, S.E. A wet oxidation procedure suitable for the determination of nitrogen and mineral nutrients in biological material. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1975, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyashevska, O.; Farnsworth, K.D. How many dimensions of biodiversity do we need? Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, E.; Cortez, J.; Billès, G.; Navas, M.-L.; Roumet, C.; Debussche, M.; Laurent, G.; Blanchard, A.; Aubry, D.; Bellmann, A. Plant functional markers capture ecosystem properties during secondary succession. Ecology 2004, 85, 2630–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, S.; Lavorel, S.; de Bello, F.; Quétier, F.; Grigulis, K.; Robson, T.M. Incorporating plant functional diversity effects in ecosystem service assessments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20684–20689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, K.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Sheng, Z.; Chen, H. Effects of nitrogen addition on vegetation and soil and its linkages to plant diversity and productivity in a semi-arid steppe. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuv, E.; Borisov, A.; Runger, G.; Torkkola, K. Feature selection with ensembles, artificial variables, and redundancy elimination. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2009, 10, 1341–1366. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Anderson, R.E.; Tatham, R.L.; Black, W.C. Multivariate Data Analysis, 5th ed.; Prentice Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kursa, M.B.; Rudnicki, W.R. Feature selection with the boruta package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grace, J.B. Structural Equation Modeling and Natural Systems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Samani, S.A. Steps in research process (partial least square of structural equation modeling (pls-sem)). Int. J. Soc. Sci. Bus. 2016, 1, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.K.-K. Partial least squares structural equation modeling (pls-sem) techniques using smartpls. Mark. Bull. 2013, 24, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bacon, L.D. Using Lisrel and Pls to Measure Customer Satisfaction. In Proceedings of the Sawtooth Software Conference Proceedings, La Jolla, CA, USA, 2–5 February 1999; pp. 305–306. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K. Handling small survey sample size and skewed dataset with partial least square path modelling. Vue Mag. Mark. Res. Intell. Assoc. 2010, 20, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F., Jr. Successful Strategies for Teaching Multivariate Statistics; Kennesaw State University: Kennesaw, GA, USA, 2006; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. Pls-sem: Indeed a silver bullet. J. Mark. Theory Pract. 2011, 19, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Dijkstra, T.K.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Diamantopoulos, A.; Straub, D.W.; Ketchen, D.J., Jr.; Hair, J.F.; Hult, G.T.M.; Calantone, R.J. Common beliefs and reality about pls: Comments on rönkkö and evermann (2013). Organ. Res. Methods 2014, 17, 182–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schöb, C.; Armas, C.; Guler, M.; Prieto, I.; Pugnaire, F.I. Variability in functional traits mediates plant interactions along stress gradients. J. Ecol. 2013, 101, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-González, M.; Stiti, B.; Chaar, H.; Cañellas, I. Dynamic dominant height growth model for spanish and tunisian cork oak (Quercus suber L.) forest. For. Syst. 2010, 19, 285–298. [Google Scholar]
- Bruns, T.D.; Kennedy, P.G. Individuals, populations, communities and function: The growing field of ectomycorrhizal ecology. New Phytol. 2009, 182, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, R.H.; Niering, W.A. Vegetation of the Santa Catalina Mountains, Arizona. V. Biomass, production, and diversity along the elevation gradient. Ecology 1975, 56, 771–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutiel, P.; Lavee, H. Effect of slope aspect on soil and vegetation properties along an aridity transect. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 1999, 47, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-P.; Wang, J.; Gu, H.-L.; Zhang, Z.-G.; Wang, Q. Effects of continuous slope gradient on the dominance characteristics of plant functional groups and plant diversity in alpine meadows. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Z.; He, S.; Wu, F. Effects of soil surface roughness on sheet erosion and change under different rainfall conditions. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wen, Z.M.; Miao, L.P. Source of variation of plant functional traits in the yanhe river watershed: The influence of environment and phylogenetic background. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 6543–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvet, J.-C.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Mougin, E.; Kerr, Y.; Brito, J. Plant water content and temperature of the Amazon forest from satellite microwave radiometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.I. The Effects of Microtopography on Environmental Conditions, Plant Performance, and Plant Community Structure in Fens of the New Jersey Pinelands; Rutgers The State University of New Jersey: New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Lal, R.; Owens, L.; Izaurralde, R.; Post, W.; Hothem, D. Effect of cropland management and slope position on soil organic carbon pool at the North Appalachian Experimental Watersheds. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 68, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Bai, H.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Gan, Z.; Huang, A. Differences in growth response of larix chinensis to climate change at the upper timberline of southern and northern slopes of mt. Taibai in central qinling mountains, china. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 5333–5342. [Google Scholar]
- Bennie, J.; Huntley, B.; Wiltshire, A.; Hill, M.O.; Baxter, R. Slope, aspect and climate: Spatially explicit and implicit models of topographic microclimate in chalk grassland. Ecol. Model. 2008, 216, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-M.; Liu, D.; An, S.-S. Effects of slope aspect on soil nitrogen and microbial properties in the chinese loess region. Catena 2015, 125, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, J.; Dutoit, T.; Saatkamp, A.; Bucher, S.F.; Leiterer, M.; Rmermann, C. Recovery of Mediterranean Steppe Vegetation after Cultivation: Legacy Effects on Plant Composition, Soil Properties and Functional Traits; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sadiq, S.A.; Baloch, D.M.; Ahmed, N. Role of coal-derived humic acid in the availability of nutrients and growth of sunflower under calcareous soil. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2014, 24, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Vilagrosa, A.; Chirino, E.; Peguero-Pina, J.-J.; Barigah, T.S.; Cochard, H.; Gil-Pelegrin, E. Xylem Cavitation and Embolism in Plants Living in Water-Limited Ecosystems. In Plant Responses to Drought Stress; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 63–109. [Google Scholar]
- Rosado, B.H.P.; Joly, C.A.; Burgess, S.S.O.; Oliveira, R.; Aidar, M.P.M. Changes in plant functional traits and water use in Atlantic rainforest: Evidence of conservative water use in spatio-temporal scales. Trees 2015, 30, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkin, O.K.; Bloomfield, K.J.; Reich, P.B.; Tjoelker, M.G.; Asner, G.P.; Bonal, D.; Bönisch, G.; Bradford, M.G.; Cernusak, L.A.; Cosio, E.G. Global variability in leaf respiration in relation to climate, plant functional types and leaf traits. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 614–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elgala, A.M.; Amberger, A. Effect OP PH, orgrnic matter and plant growth on the movement of iron in soils. J. Plant Nutr. 1982, 5, 841–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Vargas, G.; Sánchez-Velásquez, L.R.; López-Acosta, J.C.; Noa-Carrazana, J.C.; Perroni, Y. Relationship between soil properties and leaf functional traits in early secondary succession of tropical montane cloud forest. Ecol. Res. 2019, 34, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I. Land-use effects on organic matter and physical properties of soil in a southern Mediterranean highland of Turkey. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 83, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goderya, F.S. Field Scale Variations in Soil Properties for Spatially Variable Control: A Review. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 1998, 7, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, H.I.F. Effects of Land Use Change on Plant Composition and Ecosystem Functioning in an Extensive Agro-Pastoral System: Plant Functional Traits and Ecosystems Processes; Universidade de Coimbra: Coimbra, Portugal, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, S.; Negi, V.S.; Dhyani, R.; Bhatt, I.; Yadava, A. Influence of environmental factors on tree species diversity and composition in the Indian western Himalaya. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 503, 119746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittelson, P.; Maron, J.; Marler, M. An invader differentially affects leaf physiology of two natives across a gradient in diversity. Ecology 2008, 89, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.J.; Kroon, H.; Visser, E.J.W.; Buchmann, T.; Ebeling, A.; Eisenhauer, N.; Fischer, C.; Hildebrandt, A.; Ravenek, J.; Roscher, C.; et al. Plants are less negatively affected by flooding when growing in species-rich plant communities. New Phytol. 2016, 213, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Liu, G.; Xu, M. Above- and belowground dynamics of plant community succession following abandonment of farmland on the Loess Plateau, China. Plant Soil 2008, 316, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Meng, M.; Li, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhai, L.; Liu, X.; Ma, S.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, J. Rock-Solubilizing Microbial Inoculums Have Enormous Potential as Ecological Remediation Agents to Promote Plant Growth. Forests 2021, 12, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Weg, M.J.; Meir, P.; Grace, J.; Atkin, O.K. Altitudinal variation in leaf mass per unit area, leaf tissue density and foliar nitrogen and phosphorus content along an Amazon-Andes gradient in Peru. Plant Ecol. Divers. 2009, 2, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Latent Variables Group | Canonical Correlations 1 | Eigenvalue | p-Value | Wilk’s | DF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetation structure vs. Soil properties | 0.660 | 0.771 | 0.028 * | 0.285 | 42 |
| Topographic conditions vs. Vegetation structure | 0.651 | 0.737 | 0.042 * | 0.430 | 28 |
| Topographic conditions vs. Soil properties | 0.551 | 0.435 | 0.101 | 0.518 | 24 |
| Vegetation structure vs. Functional character of vegetation | 0.612 | 0.600 | 0.002 ** | 0.226 | 42 |
| Topographic conditions vs. Functional character of vegetation | 0.592 | 0.540 | 0.024 * | 0.457 | 24 |
| Soil properties vs. Functional character of vegetation | 0.668 | 0.808 | 0.012 * | 0.309 | 36 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, G.; Wen, Z.; Xue, W.; Bu, Y.; Lu, J.; Wen, B.; Wang, B.; Chen, S. Agents Affecting the Plant Functional Traits in National Soil and Water Conservation Demonstration Park (China). Plants 2022, 11, 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11212891
Duan G, Wen Z, Xue W, Bu Y, Lu J, Wen B, Wang B, Chen S. Agents Affecting the Plant Functional Traits in National Soil and Water Conservation Demonstration Park (China). Plants. 2022; 11(21):2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11212891
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Gaohui, Zhongming Wen, Wei Xue, Yuankun Bu, Jinxin Lu, Bojin Wen, Boheng Wang, and Sihui Chen. 2022. "Agents Affecting the Plant Functional Traits in National Soil and Water Conservation Demonstration Park (China)" Plants 11, no. 21: 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11212891
APA StyleDuan, G., Wen, Z., Xue, W., Bu, Y., Lu, J., Wen, B., Wang, B., & Chen, S. (2022). Agents Affecting the Plant Functional Traits in National Soil and Water Conservation Demonstration Park (China). Plants, 11(21), 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11212891







