Abstract
Solanum glycoalkaloids are gaining increased scientific attention due to their bioactive potential in the defense of plants against pests and pathogens. The comprehensive glycoalkaloid profiling from the leaves, stems, and roots of seven underexploited Solanum species (S. caripense, S. melanocerasum, S. muricatum, S. nigrum, S. quitoense, S. retroflexum, and S. sisymbriifolium) was conducted using high-performance liquid chromatography–time-of-flight mass spectrometry. A total of 51 glycoalkaloids were shared among the studied Solanum species, with concentrations ranging from 7 to 5.63 × 105 ng g−1. Based on the glycoalkaloid composition, plants were separated into two clusters, Cluster 1 (S. melanocerasum, S. nigrum, and S. retroflexum) and Cluster 2 (S. caripense, S. muricatum, S. quitoense, and S. sisymbriifolium). The inhibition activity of glycoalkaloid extracts on acetylcholinesterase showed a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50), ranging from 0.4 (S. nigrum stems) to 344.9 µg mL−1 (S. sisymbriifolium leaves), that was not directly correlated to the total glycoalkaloid contents. This suggests that the composition of glycoalkaloids in the plant extract, rather than the total concentration, is a driver of biological activity. The study provides a framework for the bioprospecting of underexploited Solanum species for exploring bioactive glycoalkaloids and other compounds with potential pesticidal activities for the development of green bioformulation. This is the first comprehensive report on the glycoalkaloid profiles of S. retroflexum.
1. Introduction
The plants of the Solanaceae family contain a class of biologically active compounds called glycoalkaloids, which represent a wide class of chemical compounds composed of a C27 cholestane skeleton, to which a carbohydrate moiety of one to five monosaccharides is attached [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. Due to their pesticidal properties, glycoalkaloids have the potential to function well in the field of plant protection. For example, Solanum sisymbriifolium has been demonstrated to be an efficient trap crop for the control of potato cyst nematodes, making it one of the more promising feedstocks for the production of pesticides [10,11]. Glycoalkaloids are found in more than 350 plant species, and are present in all plant organs with concentrations varying depending on the plant growth stage, environmental conditions, and specific plant species, and they can range from 18 to 10,000 mg kg−1 [12,13]. While a significant effort was made to identify glycoalkaloids in commercial crops, such as tomatoes and potatoes, glycoalkaloid composition is unclear in noncommercial and weedy plants, such as S. sisymbriifolium and S. caripense [14]. Still, these underexploited plants contain many glycoalkaloids that can potentially have desirable pesticidal properties.
With the recent advance in hyphenated analytical techniques, such as high-performance liquid chromatography–time-of-flight mass spectrometry (HPLC TOF MS), the untargeted analysis of glycoalkaloids has become possible, and can facilitate the identification of novel or already-described glycoalkaloids in new plant species [15]. However, the data obtained via HPLC MS are very complex and contain a large amount of information. In combination with the lack of analytical and reference standards, this presents a challenge for identifying potential pesticidal candidates; thus, lengthy purification and isolation steps are required for activities screening. One of the approaches in analyzing the large amount of data produced through HPLC MS is the use of chemometric tools that can significantly reduce the data set and provide maximum amount of relevant chemical information, such as a subset of critical chemical compounds or a set of molecular features.
The objective of this study was to assess the applicability of a chemometrics analysis of HPLC TOF MS data for singling out chemical compounds or groups of chemical compounds with specific biological properties from underexploited Solanum species. HPLC TOF MS data for glycoalkaloid extracts from the roots, stems, and leaves of seven Solanum species (S. caripense, S. melanocerasum, S. muricatum, S. nigrum, S. quitoense, S. retroflexum, and S. sisymbriifolium) were analyzed, and their pesticidal potentials were assessed using the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE, EC 3.1.1.7), an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine [4].
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Glycoalkaloids Assignment
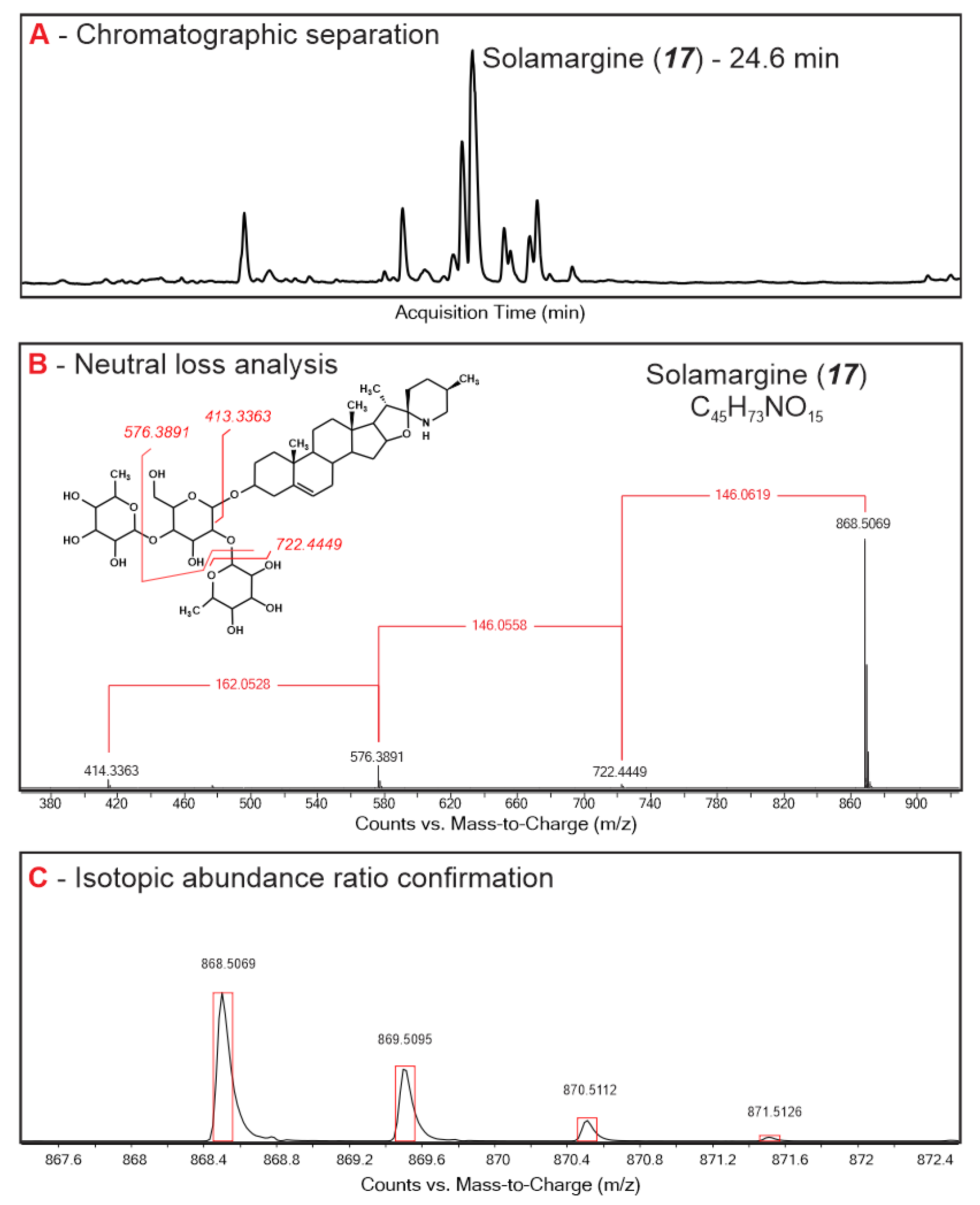
Root, leaf, and stem extracts from seven Solanum species were assessed using time-of-flight MS analysis for exact molecular mass assessment, and a characteristic neutral loss pattern analysis of typical sugar moieties (pentose, deoxyhexose, and hexose) for glycoalkaloid assignment [16]. A total of 51 compounds that were assigned as glycoalkaloids were shared among all Solanum plants and accounted for 97–99% of the peak area in the total ion chromatograms (Table 1). Chromatographic retention times for most of the glycoalkaloids clustered at around 22–25 min, suggesting that they had closely related chemical structures and polarities (Figure S1). The majority of the glycoalkaloids were baseline separated by the HPLC elution program; however, several coeluting or overlapping peaks were also present. In this case, mass spectra deconvolution was used to distinguish the mass spectra belonging to different compounds using the Agilent Profiler software package. For example, the spectra of two co-eluting glycoalkaloids at 25.67 min were resolved to obtain the individual fragmentation pattern of compounds 22 (m/z 1105.54) and 23 (m/z 1046.54).

Table 1.
Major glycoalkaloids identified in all Solanum plant extracts. Sugar moieties are proposed based on the neutral loss analysis of deconvoluted mass spectra. Pentose—Pen; deoxyhexose—DeoxyH; hexose—Hex; S. nigrum (OB)—SN(OB); S. nigrum (B)—SN(B); S. melanocerasum—SMe; S. retroflexum—SR; S. sisymbriifolium—SS; S. quitoense—SQ; S. caripense—SC; S. muricatum—SMu; roots—R; leaves—L; stems—S.
The molecular weight of the pseudo-molecular ions for the assigned glycoalkaloids ranged from 884.50 to 1563.75 m/z, with the majority of the compounds being in the 1000–1100 m/z range. Among the 51 compounds, eight isomeric pairs were identified. Similarities in fragmentation patterns and the relative abundances of fragments for the majority of isomeric pairs suggested that these are stereo rather than structural isomers. The glycoalkaloids 6 and 17 with the molecular ion [M + H]+ 868.50 detected at 22.19 and 24.67 min, respectively, is one such example. Similarly, compounds 1 and 15 with the molecular ion [M + H]+ 884.5042 eluting at 17.05 and 26.35 min, respectively, with the same fragmentation pattern and fragment abundance, are likely stereoisomers. The presence of multiple isomeric pairs is consistent with the previous findings for glycoalkaloids in plants where multiple isomers are usually reported for the same molecular weight compounds [33].
For the majority of the assigned glycoalkaloids, steroidal aglycone was identified based on the neutral sugar loss and the exact mass of the corresponding fragment present in the MS spectra (Figure 1, Table 1). A pseudo-molecular ion of 414.33, corresponding to solanidine aglycone, was present in the MS spectra of 13 assigned glycoalkaloids. Solanidine, also known as solatubin or solanid-5-en-3-ol, contains an oxazaspirodecane ring system and is present in solamargine- and solasonine-type glycoalkaloids [19,34]. An aglycone with a molecular mass of 430.33 was present in four assigned glycoalkaloids. This aglycone likely corresponds to the hydroxylated solanidine [19]. A fragment corresponding to jurubidine, a cyclized 3β-aminospirostane aglycone (m/z of 416.35) was present in three compounds. For the remaining assigned glycoalkaloids, the fragmentation pattern in the lower mass ranges was not strong enough to accurately identify the aglycone. Based on the neutral loss analysis (Table 1), 20 and 10 assigned glycoalkaloids were determined to contain a triose and teraose sugar moiety, respectively [16,35]. While the specific sugars and their linkage to the aglycone molecule cannot be accurately assigned, based on the consequent neutral loss mass, mono-, di-, tri-, and tetrameric sugar forms that could be obtained by combining pentose, hexose, and deoxyhexose were suggested (Table 1) [35].
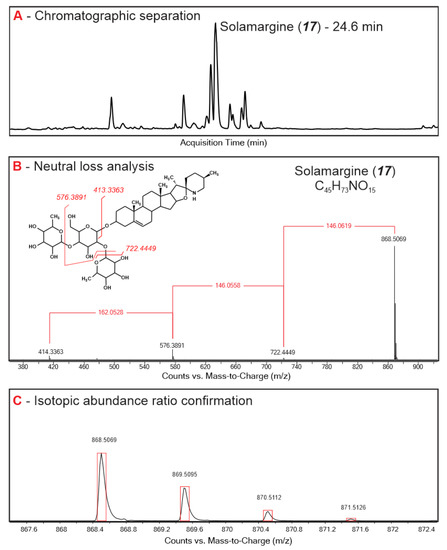
Figure 1.
Typical HPLC TOF MS chromatogram of S. sisymbriifolium (A), fragmentation pattern and sugar moiety assignment (B), and stable isotope ratio analysis (C) of assigned glycoalkaloids.
The assigned glycoalkaloids were tentatively identified based on reference standards, the comparison of MS spectra with those reported in the literature, accurate mass data, and the chemical abstracts service database for the occurrence of the specific compounds [36]. Compounds 15 and 17 were identified against the analytical standards for solamarine and solamargine, respectively. Compounds 1 and 29 were identified as isomers of hydroxy-solamargine based on the molecular ion [M + H]+ of 884.50 and the aglycone fragment of 430.33, which corresponds to hydroxylated solasodine [19]. Hydroxy-solamargine was previously reported in the fruits of S. nigrum, as well as in S. melongena, in correlation with solamargine [17,18]. Compound 2 has been described in S. melongena previously as malonyl-solanandaine [20]. The high-resolution mass spectra of compound 2 suggests the presence of an aglycone fragment with an m/z of 430.33 that corresponds to solasodine. Compound 3 can be assigned as arudonine, which was previously detected in S. melongena and S. arundo [20,21,22]. Compound 6 is structurally similar to solamargine and is likely its stereoisomer. Compound 7, solaviaside B (C26H43O11), has been described previously in S. nigrum, as well as S. viarum [23,24]. Compound 9 is structurally similar to indioside D, which has been previously described in S. indicum and S. nigrum [25,26]. Compounds 12 and 13 have been reported in S. nigrum and can be assigned as isomers of solanigroside H [27]. Compound 16 and 21 has been reported in S. sycophanta, and were identified as sycophantine and hydroxy-sycophantine, respectively [21]. Compound 20, solanigroside Y5, was previously reported in S. nigrum [24]. Based on the previously reported composition of S. nigrum and the MS spectra of the detected compounds, compounds 26 and 28 were assigned as malonyl-solamargine and solanigroside E, respectively [20,28]. Compound 31 was described previously in the ripe fruits of S. lycocarpum; however, the structure was not assigned [37]. Compound 35 was described in S. nigrum, S. myriacanthum, and S. anguivi as anguivioside XI [29,30,31]. A compound with the same molecular mass as compound 36 was detected in S. nigrum and S. muricatum; however, no mass spectra were provided [38]. Compound 40 can be assigned as lyconoside II based on the glycoalkaloid composition of the S. lycocarpum fruit [32]. Compound 43 is structurally similar, based on the mass spectra, to solanigroside D, which has been detected in S. nigrum previously [27].
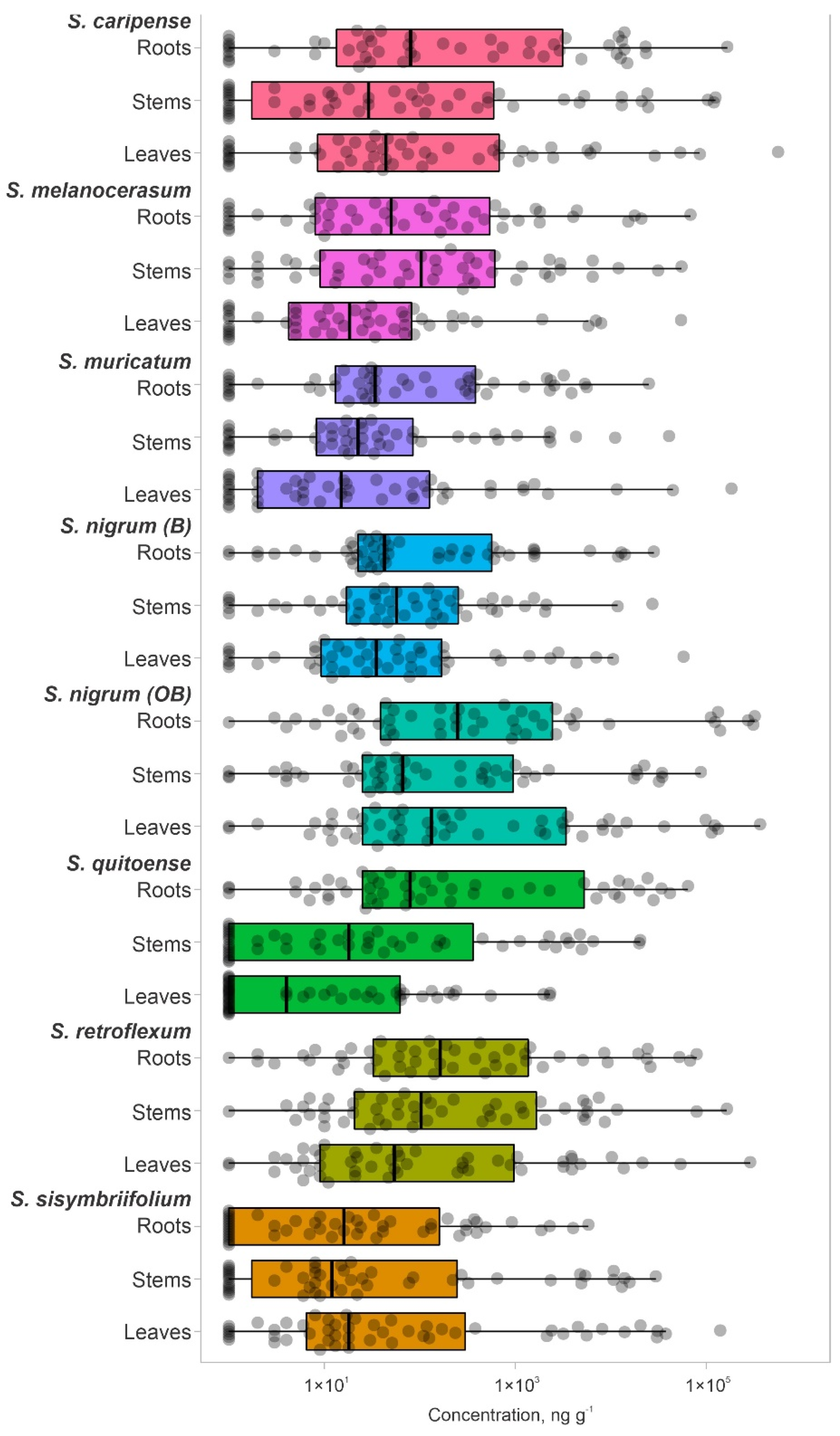
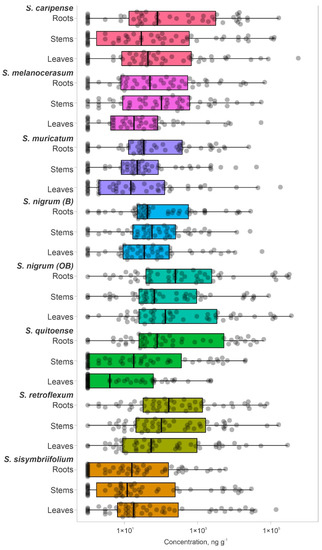
Since the exact glycoalkaloid composition of the analyzed plants is unknown, the total number of glycoalkaloids in the plant extracts could be higher. However, this subset of 51 glycoalkaloids is representative of the major glycoalkaloid constituents in the set of analyzed plants. Extracts of tested Solanum species were dominated by a small subset of glycoalkaloids (Figure 2, Table S1). Extracts from both shoots and roots contained glycoalkaloids with a similar detection frequency (Figure 2, Table S1). The cumulative amounts of glycoalkaloids in the shoots were significantly higher than in the roots, as reflected by total the peak areas for S. caripense, S. melanocerasum, S. muricatum, S. nigrum, S. retroflexum, and S. sisymbriifolium. For example, the amounts of glycoalkaloids in the shoots of S. sisymbriifolium and S. muricatum were 24.6- and 12-fold higher than in the roots, respectively. These data are consistent with the previously reported finding that glycoalkaloid concentrations are the highest in leaves and fruits. Solanum quitoense was the only species that had 30% higher total glycoalkaloid amounts present in the roots compared to the shoots. This was likely due to the higher amounts of four major glycoalkaloid compounds (14, 23, 31, and 32) that were detected in roots.
The major glycoalkaloid compounds detected in S. nigrum were 8, 15, 17, 19, 20, 26, 28, 46, and 47 (Table 1 and Table S1). Compounds 20, 28, and 46 were present in all parts of the plant at relatively high amounts. Shoots contained compounds 19 and 20 predominantly, while roots were dominated by compound 47. Solanum melanocerasum’s main glycoalkaloids were 20, 24, 25, 28, 32, 36, 38, 42, and 46, with compound 20 present in all plant parts. The roots contained only four major compounds, 20, 25, 38, and 46, while the shoots contained three major compounds, 20, 24, and 28. The major glycoalkaloids detected in S. retroflexum were 4, 15, 17, 20, 28, 38, and 46. Consistent glycoalkaloid diversity was observed throughout the plant, with most of the predominant glycoalkaloids present in all plant parts. Roots had compounds 15, 17, 20, 28, 38, and 46, while shoots contained three predominant compounds, 15, 17, 20, 28, and 46.
The main glycoalkaloids detected in S. caripense were 5, 8, 11, 12, 14–17, and 26. Compounds 5, 14, 17, and 26 were predominant in leaves. The roots contained three major compounds, 12, 16, and 26. The major glycoalkaloids detected in S. muricatum were 3, 8, 11–13, 15–18, 26, 32, 37, and 39. The roots had the highest glycoalkaloid diversity with compounds 8, 11–13, 15–18, 26, 32, and 37 present in relatively large amounts. The shoots had only four major glycoalkaloids, 15–17 and 26. Both solamargine and solasonine have previously been reported in S. muricatum [39]. The glycoalkaloid composition of S. quetoense was uniform across the detected compounds, with multiple assigned glycoalkaloids (4, 14, 16, 17, 23, 26, 31, 32, 40, 41, 45, and 48) being in the same level. Unlike other plant species, the roots had the highest diversity of glycoalkaloids, with compounds 14, 16, 17, 23, 32, 41, 45, and 48 being present in relatively large amounts. The major glycoalkaloids detected in S. sisymbriifolium were 1, 2, 6, 16, 17, 21, 26, 29, 32, 42, 49, and 50. The roots had four major compounds, 16, 32, 49, and 50. The shoots had compounds 1, 2, 16, 17, 26, and 42.
The glycoalkaloid concentrations, quantified based on the solamargine standard, were in the range of 7–5.63×105 ng g−1 (DW basis) (Figure 2). For most of the plants, the median glycoalkaloid concentration was similar for shoots and roots; however, the distribution of specific glycoalkaloid concentrations differed (Figure 2). For example, the S. sisymbriifolium median for glycoalkaloid concentrations was higher for shoots than for roots. The glycoalkaloid concentration in roots clustered close to the median, while in shoots, an additional cluster in the third quartile was observed. This is consistent with the lower total glycoalkaloid content for S. sisymbriifolium roots. Most of the S. caripense, S. quitoense, and S. sisymbriifolium glycoalkaloids concentrations were close to the median and third quartiles (Figure 2). The higher concentrations accounted for 97–98% of the total glycoalkaloid content, represented by 7–17 individual glycoalkaloids. The median for S. quitoense shoots was lower than for roots due to a large number of glycoalkaloids with low concentrations resulting in a longer plot. This is also reflected in the skewed data and relatively low first-quartile value. For the S. quitoense roots, an opposite trend was observed, with the majority of the glycoalkaloids having concentrations above the median value and relatively evenly distributed third and fourth quartiles.
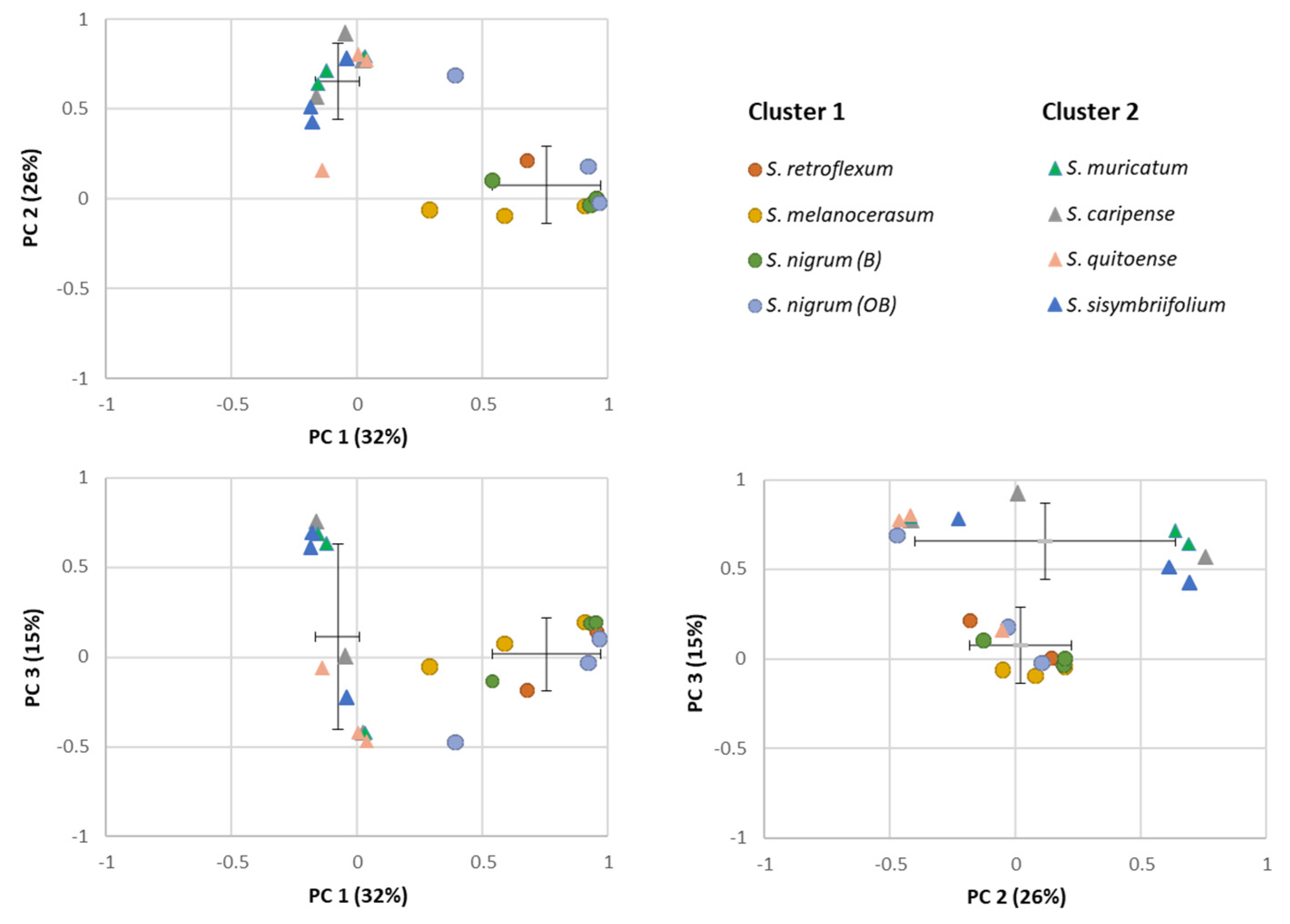
2.2. Glycoalkaloids Clustering in Solanum Plants
The similarities among the Solanum plants’ shoot and root extracts were assessed via PCA based on the composition and abundance of individual glycoalkaloids (Figure 3). Total variance (73%) was explained by first three principal components, with PC1, PC2, and PC3 accounting for 32, 26, and 15%, respectively. Based on the PCA loading plot, a separation of extracts on two clusters was observed: Cluster 1 included S. melanocerasum, S. nigrum, and S. retroflexum, and Cluster 2 included S. caripense, S. muricatum, S. quitoense, and S. sisymbriifolium. For the Cluster 1 plants (S. melanocerasum, S. nigrum, and S. retroflexum), the primary glycoalkaloids present in all plants were 15, 17, 20, 28, and 46. In the Cluster 2 plants, three predominant compounds (16, 17, and 26) that belong to solanidine-type glycoalkaloids were present across all the species [19,34]. The clustering is consistent with the fact that S. nigrum, S. retroflexum, and S. melanocerasum belong to the Morelloid clade and have been shown to be genetically related based on morphological and molecular data [40,41]. Cluster 2 plants do not belong to the same clade. However, S. muricatum has been shown to be related to wild-species S. caripense, and thus can share a similar glycoalkaloid composition [42]. The basis of its relationship to other Cluster 2 plants is not clear, as S. quitoense belongs to the Lasiocarpa clade and S. sisymbriifolium appears to be closely related to the Androceras/Crinitum clade [43,44]. While the clustering of Solanum plants based on the composition of their secondary metabolites profiles has been previously used for the chemotaxonomy of Solanum plants, to the best of our knowledge, the use of glycoalkaloids for Solanum biological activity clustering has not been investigated yet for the selected Solanum species [45].
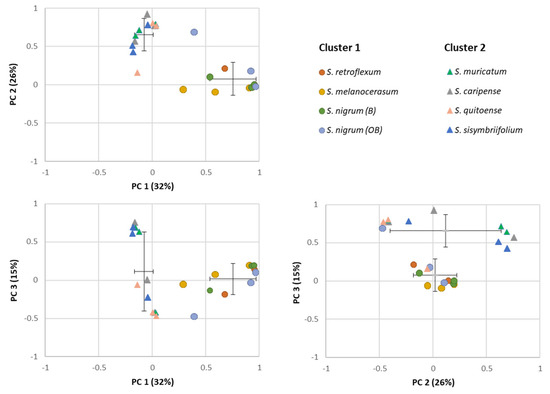
Figure 3.
Principal component analysis (PCA) plots for individual glycoalkaloids in the shoots and roots of Solanum plant extracts.
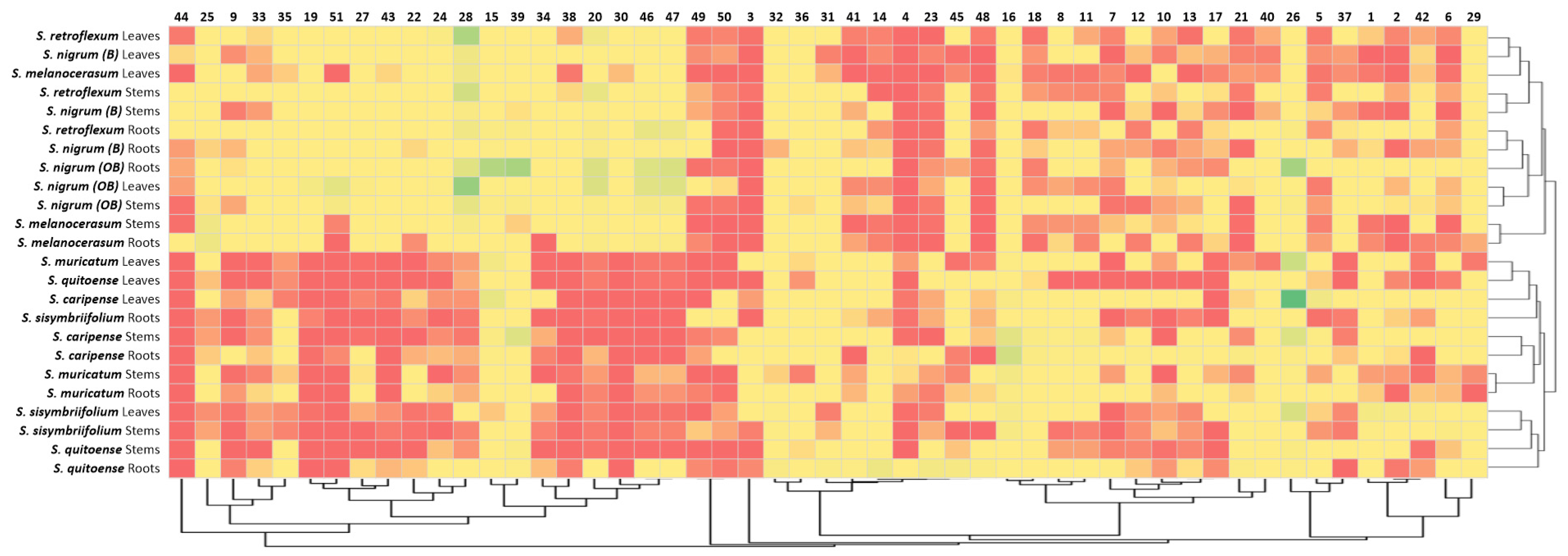
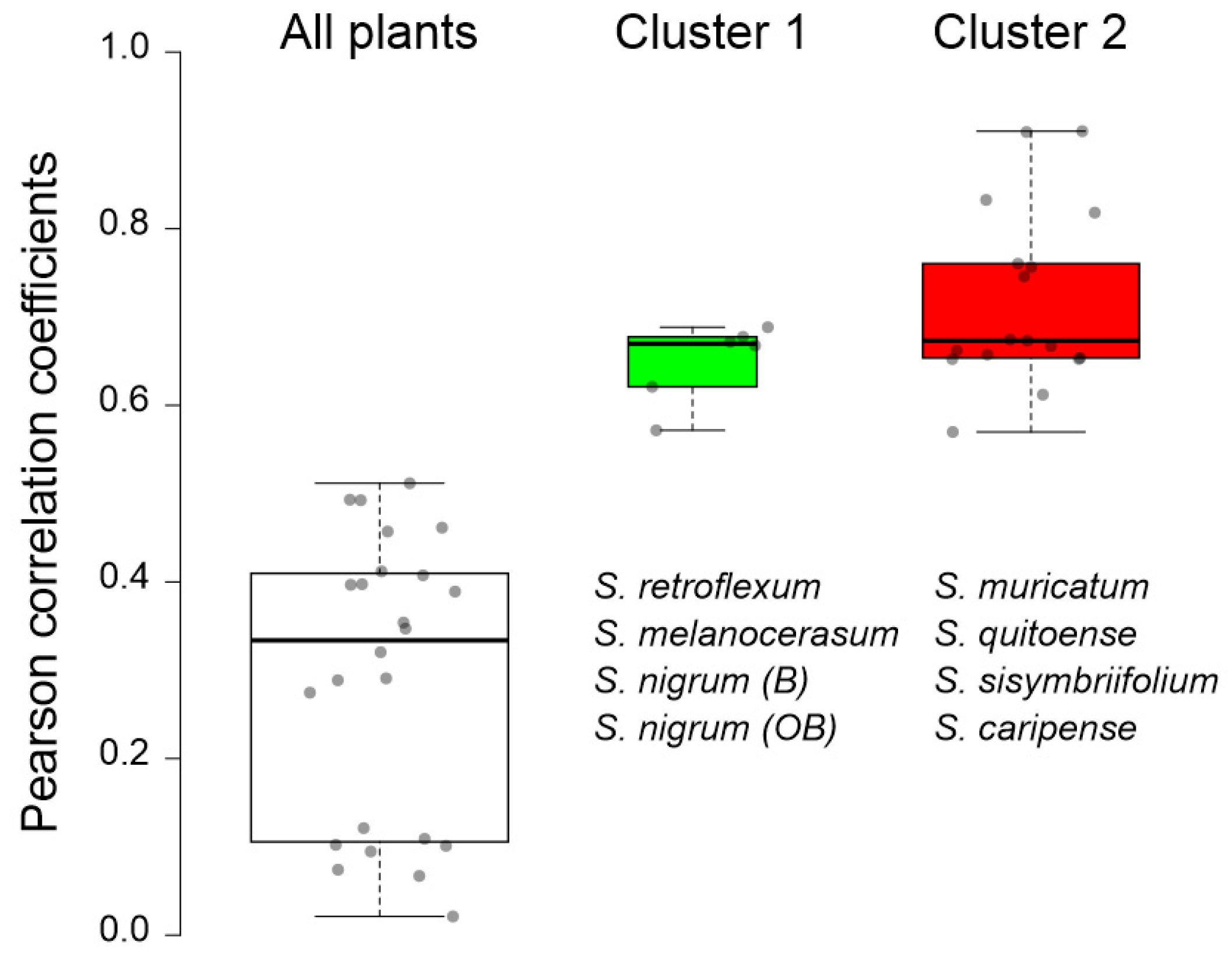
To confirm the observed clustering of Solanum plants based on their glycoalkaloid content, the Pearson’s correlations of the glycoalkaloid distributions in the shoots and roots were analyzed (Table 2). Strong correlation coefficients within the two clusters signify the applicability of glycoalkaloids as a chemical class for relating the species to the Solanum family. Specifically, the correlation coefficients for the Cluster 1 plants (S. melanocerasum, S. nigrum, and S. retroflexum) leaf glycoalkaloids ranged from 0.853 *** to 0.994 ***. For the Cluster 2 plants (S. caripense, S. muricatum, S. quitoense, and S. sisymbriifolium), the association amongst the glycoalkaloids in leaves was also strong, with coefficients ranging from 0.534 *** to 0.992 ***. Similarly, the association among root glycoalkaloids in the studied Solanum plants was present, though weaker, for the two identified clusters, with correlation coefficients ranging from 0.124 to 0.524 *** for Cluster 1 and from 0.037 to 0.966 *** for Cluster 2. A heat map analysis of the glycoalkaloids contributing to the Solanum species corroborate the presence of two distinct clusters (Figure 4).

Table 2.
Pearson’s correlations for tested Solanum plant extracts based on their glycoalkaloid composition and content. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
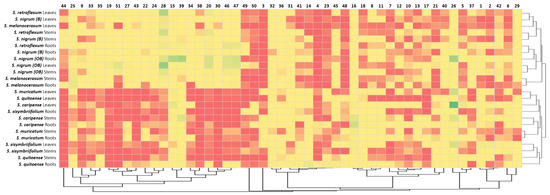
Figure 4.
Heat map analysis of assigned glycoalkaloids (Table 1) in the extracts of Solanum Spp, roots, stems, and leaves.
The clustering of plants based on their glycoalkaloid composition was confirmed using a Czekanowski similarity analysis (Table 3). Several strong correlations were noted, as reflected by the correlation indices close to 1. Generally, S. nigrum, S. melanocerasum, and S. retroflexum were more closely correlated, with indices averaging at 0.33. In fact, the glycoalkaloid composition of S. melanocerasum leaves was very close to S. nigrum (B) leaves in terms of the amount and distribution of glycoalkaloids (0.83). S. nigrum (OB) leaves were very similar to S. retroflexum leaves (0.68). Plant extracts from S. caripense, S. muricatum, S. quitoense, and S. sisymbriifolium were similar based on their glycoalkaloid composition. However, the similarity indices were lower than for the first set of plants, with the highest being 0.63.

Table 3.
Czekanowski similarity coefficients for tested Solanum plant extracts based on their glycoalkaloid composition and content.
2.3. Glycoalkaloids Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition Activity
To evaluate the correlation between plant clustering, based on the glycoalkaloid content and composition, and the pesticidal potential, plant methanolic extracts were tested for the inhibition of AChE (Table 4). The inhibition of AChE results in the disruption of neurotransmission, and, in the case of nematodes, the cessation of nerve impulses and, ultimately, death [4,46]. Inhibition, as reflected by IC50 values, ranged from 39 to 93% when extracts were used at the nominal concentration of glycoalkaloids (as calculated on a solamargine basis). The corresponding IC50, calculated on the total glycoalkaloid basis, varied from 0.4 to 344.9 µg total glycoalkaloid mL−1. These values are in the same order of magnitude as for the previously reported IC50, where crude extracts of eleven Solanums spp. were tested [20,47]. Generally, the extracts of leaves exhibited the highest inhibition potential, while extracts from roots had the lowest inhibition of AChE. This trend can partially be explained by a concentration-dependent effect because, for most of the tested species, leaves contained the highest concentrations of glycoalkaloids. However, the correlation between the total glycoalkaloid concentration in the plant tissue extracts and half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values was not strong (r = 0.1520), and as a result, the total glycoalkaloid concentration cannot be used as a predictor of the pesticidal potential (Figure 5). Separating plants into two groups (Group 1 and Group 2) based on the similarity of their glycoalkaloid composition resulted in significantly better correlation and pesticidal potential prediction (Figure 5). Particularly, the strong correlation between seven major glycoalkaloids and the IC50 values was observed for S. caripense, S. muricatum, S. quitoense, and S. sisymbriifolium (Cluster 2). The concentration of 19 other GAs also exhibited a strong correlation with the S. melanocerasum, S. nigrum (B), S. nigrum (OB), and S. retroflexum (Cluster 1) IC50 values. These results indicate that not all glycoalkaloids contribute equally to the overall pesticidal potential. In fact, the strong correlations between the IC50 values and glycoalkaloid concentrations were not observed for the most abundant glycoalkaloid. This suggests that structure, rather than the total amount of glycoalkaloids, plays the primary role in determining the pesticidal potential. These results are consistent with previously reported findings that both aglycone type and the sugar moiety of glycoalkaloids have a significant effect on AChE inhibition [48]. For example, α-solamargine has a chacotriose sugar moiety and α-solasonine has a solatriose sugar moiety, and the inhibitory activity of α-solasonine was at least 10 times lower [48].

Table 4.
AChE inhibition of Solanum plants root, stem, and leaf extracts expressed as percentage, and the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) relative to the total glycoalkaloid and plant mass basis.
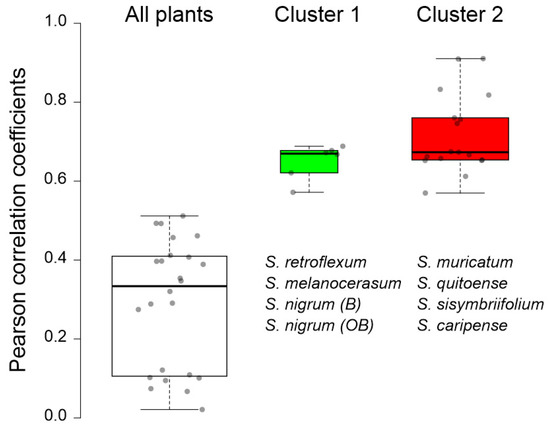
Figure 5.
Correlation (expressed as Pearson correlation coefficients) between the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of Solanum plant extracts and the concentrations of selected glycoalkaloids (Table 1). The IC50 values for Cluster 1 plants were correlated with the concentrations of compounds 9, 10, 12, 13, 17, 35, and 51; the IC50 values for Cluster 2 plants were correlated with the concentrations of compounds 1, 2, 6, 14, 15, 20, 21, 23, 26, 29, 30, 34, 38, 39, 41, 43, 46, and 47 (Table 1).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Solanum spp.
Seeds for S. caripense (Tzimbalo Melon Pear), S. muricatum (Pepino Melon), S. melanocerasum (S. scabrum, Garden Huckleberry), S. nigrum (Blackberry), S. quitoense (Naranjilla), S. retroflexum (S. burbankii, Wonderberry), and S. nigrum (Otricoli Orange Berry) were obtained from Baker Creek Heirloom Seeds (Mansfield, MO, USA). Plants were germinated on Petri dishes, transplanted to potting soil, and kept under greenhouse conditions 18 ± 2 °C (daytime), 14 ± 2 °C (nighttime), with a 16:8 h light–dark period. S. sisymbriifolium plants were obtained from Dr. Joseph Kuhl as 6-week-old plants. At 6 weeks after transplanting, plants were harvested by gently separating them from the soil. After washing in DI water, plants were sectioned into roots, leaves, stems, and flowers, and buds when these were present. The separated plant parts were pat dried, frozen in liquid nitrogen, and freeze dried. Dry tissues were pulverized using a cyclone mill (UDY Corporation, Fort Collins, CO, USA) and kept at −20 °C until extraction.
3.2. Extraction of Glycoalkaloids
Plants tissues (0.2 g) were homogenized with 10 mL of 90% methanol in Omni Prep homogenizer (Omni Int, Kennesaw GA, USA) at 10 K rpm for 10 min. The suspension was centrifuged at 4000× g rpm and 18 °C for 10 min. The extraction was repeated, and all extracts were combined. Chlorophyll was removed via liquid–liquid extraction with hexane (10 mL) using an end-to-end shaker (10 min). The hexane fraction containing chlorophyll was removed by aspirating the top layer after centrifuging the solution at 2400× g rpm at 18 °C for 5 min. The hexane extraction was repeated. The methanolic fraction of the extract was then diluted with DI water (600 mL) to obtain less than 3% methanol content. The diluted extract was subjected to solid-phase extraction on an Oasis HLB (3 mL, 60 mg, 30 µm) (Waters Corp., Milford, MA, USA). The cartridges were preconditioned with 3 mL of methanol and equilibrated with 3 mL of water. The samples were loaded into the column at 25 mm Hg negative pressure, and cartridges were washed with water and eluted with 3 mL 85% methanol using gravity.
3.3. HPLC TOF MS Analysis of Glycoalkaloids
The analysis of the GAs was performed using an Agilent 1200 Series HPLC coupled to an Agilent G6230 ESI TOF MS (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The chromatographic separation of glycoalkaloids was performed on an Extend-C18 3.5 µm, 2.1 mm × 100 mm (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) reversed-phase chromatographic column. The mobile phase consisted of 0.1% formic acid in water (solvent A) and 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile (solvent B). The gradient program started with isocratic elution using 5% B for 2 min, followed by a linear gradient to 35% B from 2 to 35 min, followed by a linear gradient to 98% over 10 min, kept at 98% for 5 min, and re-equilibrated back to the initial mobile phase composition over 10 min. The column was maintained at 30 °C. The injection volume was 5 μL. The flow rate was 0.2 mL min−1.
Electrospray ionization was operated in positive mode. The absolute value for electrospray ionization potential was 3500 V. The collision-induced dissociation potential was set at 150 and 250 V to analyze the spectra for molecular ion and fragmentation patterns, respectively. The gas temperature was 350 °C, the drying gas (N2) flow rate was 10 L min−1, and the nebulizer pressure was 2.4 × 105 Pa. The analyses were conducted in a centroid mode within an m/z range from 100 to 1700 amu. The quantification of the total glycoalkaloid concentration was performed based on the external calibration curve constructed for solamargine based on the pseudo-molecular ion [M + H]+.
HPLC TOF MS chromatograms were processed in MassHunter B.08.00 Agilent Profinder software (Agilent Technologies Inc, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The assignment of glycoalkaloids was performed based on neutral loss analysis using fragmentation and isotopic patterns for each compound [16,35]. Neutral loss corresponding to mono-, di-, tri-, and tetrameric sugar moieties that could be obtained by combining pentose, hexose, and deoxyhexose units were considered to be with the error of less than 3 ppm.
3.4. Acetylcholinesterase Assay
The measurement of acetylcholinesterase (EC number 3.1.1.7) activity was conducted in a 96-well microplate format according to a method previously described, with some modifications [49]. Different volumes (5–1000 µL) of plant extracts in 85% methanol samples were added to microplate wells, evaporated to dryness, and reconstituted in 200 µL of sodium phosphate buffer (100 mM, pH 7.4). Then, 50 µL of Ellman’s reagent (1 mM acetylthiocholine and 0.3 mM 5,5′-dithiobis (2-nitrobenzoic acid) in (100 mM pH 7.4 phosphate buffer) was added to each well. Prior to start of the analysis, 50 µL of acetylcholinesterase from Electrophorus electricus (1 unit mL−1) was added to each well. The absorbance at 405 nm was measured every minute for 15 min using SpectraMax M Series Multi-Mode Microplate Readers (Molecular Devices, LLC., San Jose, CA, USA). The rate of the reaction was calculated as a slope of the kinetics curve over the linear range. A negative control was run with each batch, substituting the plant extract for 85% methanol and treating it in a similar manner. The inhibition of the reaction by the plant extracts was quantified in terms of half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50), i.e., the concentration at which a substance exerts half of its maximal inhibitory effect. The IC50 was calculated using a four-parameter regression model: y = d + (a − d)/(1 + (x/IC50)b), where y is the response and x is the concentration, a and d are lower and upper asymptotes, respectively, and b is the steepness of the linear portion of the curve [50].
3.5. Data Analysis
All extractions and enzyme assays were performed with at least three replicates. The heat map analysis was conducted using a ClustVis web tool for visualizing the clustering of multivariate data that is based on the heatmap R package (version 0.7.7) [51]. The bean plots were generated using a BoxPlotR web tool for the generation of box plots [52]. Czekanowski similarity indices (sc) were calculated as the ratio of the double sum of the lesser scores of each glycoalkaloid to the sum of all glycoalkaloids in the specific sample and were used as a measure of similarity between two categorical distributions [53]. The correlation between specific glycoalkaloids and inhibition activities were calculated using Pearson’s correlation in JASP, an open-source graphical software package for basic statistical procedures [54].
4. Conclusions
The presented study provides a framework for creating data sets for further biologically active compound identification and analysis. Specifically, using this framework we were able to demonstrate that the composition of glycoalkaloids in plant extracts rather than the total concentration is a driver of inhibitory activity. The S. sisymbriifolium leaf extract with the highest AChE inhibition had a unique glycoalkaloid, tentatively identified as malonyl solanandaine, which was not identified in the other Solanum species used in this study. This chemometric study will help in the bioprospecting of underexploited Solanum species for exploring bioactive compounds with potential biological activities for the development of green bioformulation. This, as in the case of this study, can be a useful tool for screening for the potential pesticidal activities of plant tissues. Recently, the multivariant analysis was identified as a critical tool in the chemotaxonomy of eggplants (S. melongena) and their wild relatives [55]. However, this is, to the best of our knowledge, the first report of the analysis of glycoalkaloids across the seven studied Solanum species. In addition, the proposed workflow can be applied to other areas of study, such as chemophenetic analysis, which is an emerging concept relating to plant chemosystematics, and chemotaxonomy, which is based on the plant specialized metabolites profile [56].
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/plants11030269/s1, Table S1: Concentrations of individual glycoalkaloids in plant extracts analyzed. Figure S1: HPLC TOF MS chromatographic profiles of leaves, stems, and roots of studied Solanum plants. Figure S2. Reported structures of glycoalkaloids referenced in the manuscript and identified in Table 1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization—L.-M.D. and I.P.; Data curation—I.P.; Formal analysis—B.S.; Funding acquisition—L.-M.D.; Investigation—I.P.; Methodology—J.K. and S.S.P.; Resources—J.K.; Visualization—I.P.; Writing—original draft—I.P.; Writing—review and editing—S.S.P., B.S., L.-M.D., and J.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Institute of Food and Agriculture, 2017-51102-27271. Publication of this article was funded by the University of Idaho—Open Access Publishing Fund.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Hannah Gross, Ricardo Lopez, and Anne Pollard for help with the growing and sampling of plants and Jing Wang for help with enzyme analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Ginzberg, I.; Tokuhisa, J.G.; Veilleux, R.E. Potato steroidal glycoalkaloids: Biosynthesis and genetic manipulation. Potato Res. 2009, 52, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itkin, M.; Heinig, U.; Tzfadia, O.; Bhide, A.J.; Shinde, B.; Cardenas, P.D.; Bocobza, S.E.; Unger, T.; Malitsky, S.; Finkers, R.; et al. Biosynthesis of antinutritional alkaloids in solanaceous crops is mediated by clustered genes. Science 2013, 341, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M. Potato Glycoalkaloids and metabolites: Roles in the plant and in the diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8655–8681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, S.E.; Brunton, N.P.; Jones, P.W.; O’Brien, N.M.; Collins, S.G.; Maguire, A.R. Bioactivities of glycoalkaloids and their aglycones from Solanum species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3454–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingley, G.A. Physical conditions and their effects upon infection by some insect parasitic nematodes. In Parasitology; Cambridge Univ Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984; Volume 89, p. R79. [Google Scholar]
- Flanders, K.L.; Hawkes, J.G.; Radcliffe, E.B.; Lauer, F.I. Insect resistance in potatoes: Sources, evolutionary relationships, morphological and chemical defenses, and ecogeographical associations. Euphytica 1992, 61, 83–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierenga, J.M.; Hollingworth, R.M. Inhibition of insect acetylcholinesterase by the potato glycoalkaloid α-chaconine. Nat. Toxins 1992, 1, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissenberg, M.; Levy, A.; Svoboda, J.A.; Ishaaya, I. The effect of some Solanum steroidal alkaloids and glycoalkaloids on larvae of the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum, and the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Phytochemistry 1998, 47, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankara Pillai, S.; Dandurand, L.-M. Effect of steroidal glycoalkaloids on hatch and reproduction of the potato cyst nematode Globodera pallida. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 2975–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandurand, L.M.; Zasada, I.A.; LaMondia, J.A. Effect of the trap crop, Solanum sisymbriifolium, on Globodera pallida, Globodera tabacum, and Globodera ellingtonae. J. Nematol. 2019, 51, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, G.P.P.; Borges, C.V.; Vianello, F.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Minatel, I.O. Phytochemicals in organic and conventional fruits and vegetables. Fruit Veg. Phytochemistry 2017, 3, 1305–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, M.; Dao, L. Distribution of glycoalkaloids in potato plants and commercial potato products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejarano, L.; Mignolet, E.; Devaux, A.; Espinola, N.; Carrasco, E.; Larondelle, Y. Glycoalkaloids in potato tubers: The effect of variety and drought stress on the α-solanine and α-chaconine contents of potatoes. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 2096–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roddick, J.G.; Melchers, G. Steroidal glycoalkaloid content of potato, tomato and their somatic hybrids. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1985, 70, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-B.; Meyer, R.S.; Whitaker, B.D.; Litt, A.; Kennelly, E.J. A new liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry-based strategy to integrate chemistry, morphology, and evolution of eggplant (Solanum) species. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1314, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, I.E.; Morra, M.J. Optimization of hidden target screening for Solanum sisymbriifolium glycoalkaloids. Chromatographia 2021, 84, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, P.D.; Sonawane, P.D.; Heinig, U.; Jozwiak, A.; Panda, S.; Abebie, B.; Kazachkova, Y.; Pliner, M.; Unger, T.; Wolf, D.; et al. Pathways to defense metabolites and evading fruit bitterness in genus Solanum evolved through 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.-Y.; Shen, X.-F.; Wang, L.; Wu, Z.-W.; Li, F.; Chen, B.; Zhang, G.-L.; Wang, M.-K. Bioactive steroidal alkaloids from the fruits of Solanum nigrum. Phytochemistry 2018, 147, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.-K.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.-Y.; Kennelly, E.J. Solanum steroidal glycoalkaloids: Structural diversity, biological activities, and biosynthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 8, 1413–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelario, F.; De Maria, S.; Rivelli, A.R.; Russo, D.; Milella, L.; Bufo, S.A.; Scrano, L. A Complete survey of glycoalkaloids using LC-FTICR-MS and IRMPD in a commercial variety and a local landrace of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) and their anticholinesterase and antioxidant activities. Toxins 2019, 11, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usubillaga, A.; Aziz, I.; Tettamanzi, M.C.; Waibel, R.; Achenbach, H. Steroidal alkaloids from Solanum sycophanta. Phytochemistry 1997, 44, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, K.; Shimizu, K.; Kubo, I. Arudonine, an allelopathic steroidal glycoalkaloid from the root bark of Solanum arundo Mattei. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, M.; Kakiuchi, T.; Ebisawa, H.; Shiono, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Kai, T.; Ikeda, T.; Miyashita, H.; Yoshimitsu, H.; Nohara, T. Steroidal glycosides from the fruits of Solanum viarum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xiang, L.; Yi, X.; He, X. Potential Anti-inflammatory steroidal saponins from the berries of Solanum nigrum L. (European black nightshade). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4262–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahara, S.; Nakamura, T.; Someya, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Yamashita, T.; Nohara, T. Steroidal glycosides, indiosides A-E, from Solanum indicum. Phytochemistry 1996, 43, 1319–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, A.; Manika, N.; Verma, R.K.; Singh, S.C.; Srivastava, S.K. Simple and reliable methods for the determination of three steroidal glycosides in the eight species of Solanum by reversed-phase HPLC coupled with diode array detection. Phytochem. Anal. 2013, 24, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; He, X.; Wang, G.; Gao, H.; Zhou, G.; Ye, W.; Yao, X. Steroidal saponins from Solanum nigrum. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1158–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.C.; Chand, R.; Sati, O.P.; Sharma, A.K. Oligofurostanosides from Solanum nigrum. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 1241–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yi, X.; He, X. Anti-inflammatory steroidal glycosides from the berries of Solanum nigrum L. (European black nightshade). Phytochemistry 2018, 148, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Shimode, M.; Tsutsumi, S.; Yasuda, S.; Okawa, M.; Kinjo, J.; Miyashita, H.; Ikeda, T.; Yoshimitsu, H.; Nohara, T. A new steroidal glycoside from the fruits of Solanum myriacanthum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 26, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honbu, T.; Ikeda, T.; Zhu, X.-H.; Yoshihara, O.; Okawa, M.; Nafady, A.M.; Nohara, T. New steroidal glycosides from the fruits of Solanum anguivi. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1918–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Hongo, M.; Yoshikawa, M.; Nakamura, S.; Hongo, M.; Sugimoto, S.; Matsuda, H.; Yoshikawa, M. Steroidal saponins and pseudoalkaloid oligoglycoside from Brazilian natural medicine, “fruta do lobo” (fruit of Solanum lycocarpum). Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakya, R.; Navarre, D.A. LC-MS analysis of solanidane glycoalkaloid diversity among tubers of four wild potato species and three cultivars (Solanum tuberosum). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6949–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisalberti, E. Steroidal glycoalkaloids: Isolation, structure, analysis, and biosynthesis. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2006, 1, 859–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larcher, R.; Nardin, T. Suspect screening of glycoalkaloids in plant extracts using neutral loss—High resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1596, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, J.L.; Cleven, C.D.; Brown, S.D. Identification of “Known unknowns” utilizing accurate mass data and Chemical Abstracts Service databases. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 22, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, M.G.; Saldanha, A.A.; Costa Rodrigues, J.P.; Cotta Mendes, I.; Ferreira, L.M.; Amado, P.A.; de Souza Farias, K.; Santos Zanuncio, V.S.; da Silva, D.B.; Pinto, F.C.H.; et al. Chemical composition, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of the ethanol extract of ripe fruits of Solanum lycocarpum St. Hil. (Solanaceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 262, 113125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, T.; Ando, J.; Miyazono, A.; Zhu, X.-H.; Tsumagari, H.; Nohara, T.; Yokomizo, K.; Uyeda, M. Anti-herpes virus activity of solanum steroidal glycosides. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 23, 363–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Mata, M.-C.; Yokoyama, W.E.; Hong, Y.-J.; Prohens, J. α-Solasonine and α-solamargine contents of Gboma (Solanum macrocarpon L.) and scarlet (Solanum aethiopicum L.) eggplants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5502–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoko, M.L.K.; van den Berg, R.G.; Feron, R.M.C.; van der Weerden, G.M.; Mariani, C. Genetic diversity of the African hexaploid species Solanum scabrum Mill. and Solanum nigrum L. (Solanaceae). Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2008, 55, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Särkinen, T.; Poczai, P.; Barboza, G.E.; van der Weerden, G.M.; Baden, M.; Knapp, S. A revision of the Old World black nightshades (Morelloid clade of Solanum L., Solanaceae). PhytoKeys 2018, 106, 1–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, F.J.; Villaño, D.; Plazas, M.; Vilanova, S.; Ferreres, F.; Prohens, J.; Moreno, D.A. Phenolic profile and biological activities of the Pepino (Solanum muricatum) fruit and its wild relative S. caripense. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, R.A.; Myers, N.R.; Bohs, L. Phylogenetic relationships among the “Spiny solanum” (Solanum subgenus Leptostemonum, Solanaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2006, 93, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohs, L. A Chloroplast DNA Phylogeny of Solanum section Lasiocarpa. Syst. Bot. 2004, 29, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shaboury, G.A.; Haroun, S.A.; Shaker, K.; Badr, A. Systematics implications of GC-MS analysis of secondary metabolites in the ethanol extract of Solanum species from South West Saudi Arabia. Egypt. J. Bot. 2017, 57, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nasr, H. Toxicity and Biochemical Effect of organophosphates and bio-pesticides against Root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita. J. Pollut. Eff. Control 2015, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niño, J.; Hernández, J.A.; Correa, Y.M.; Mosquera, O.M. In vitro inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by crude plant extracts from Colombian flora. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2006, 101, 783–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roddick, J.G. The acetylcholinesterase-inhibitory activity of steroidal glycoalkaloids and their aglycones. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 2631–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebaugh, J.L. Guidelines for accurate EC50/IC50 estimation. Pharm. Stat. 2011, 10, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metsalu, T.; Vilo, J. ClustVis: A web tool for visualizing clustering of multivariate data using Principal Component Analysis and heatmap. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W566–W570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, M.; Wildenhain, J.; Rappsilber, J.; Tyers, M. BoxPlotR: A web tool for generation of box plots. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, A.; Telcs, A. A note on the Jaccardized Czekanowski similarity index. Scientometrics 2014, 98, 1397–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, J.; Selker, R.; Marsman, M.; Jamil, T.; Dropmann, D.; Verhagen, J.; Ly, A.; Gronau, Q.F.; Šmíra, M.; Epskamp, S.; et al. JASP: Graphical statistical software for common statistical designs. J. Stat. Softw. 2019, 88, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haliński, Ł.P.; Samuels, J.; Stepnowski, P. Multivariate analysis as a key tool in chemotaxonomy of brinjal eggplant, African eggplants and wild related species. Phytochemistry 2017, 144, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidorn, C. Plant chemophenetics—A new term for plant chemosystematics/plant chemotaxonomy in the macro-molecular era. Phytochemistry 2019, 163, 147–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).