Screening and Evaluation of Dermo-Cosmetic Activities of the Invasive Plant Species Polygonum cuspidatum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Screening and Evaluation of the Dermo-cosmetic Potential of Crude Ethanolic Extracts of Invasive P. cuspidatum
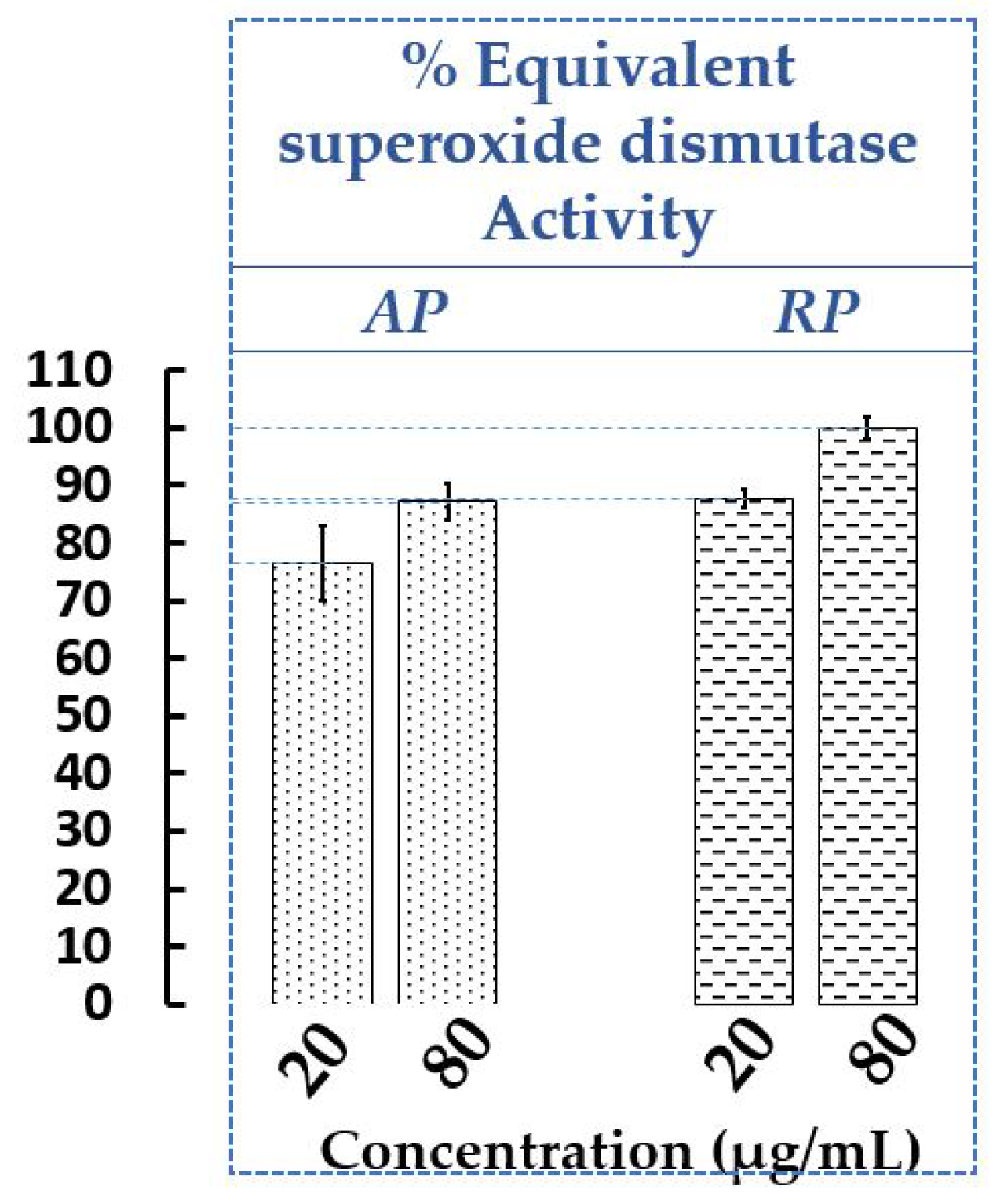
2.1.1. Determination of Antioxidant Activity of Extracts of AP and RP of P. cuspidatum
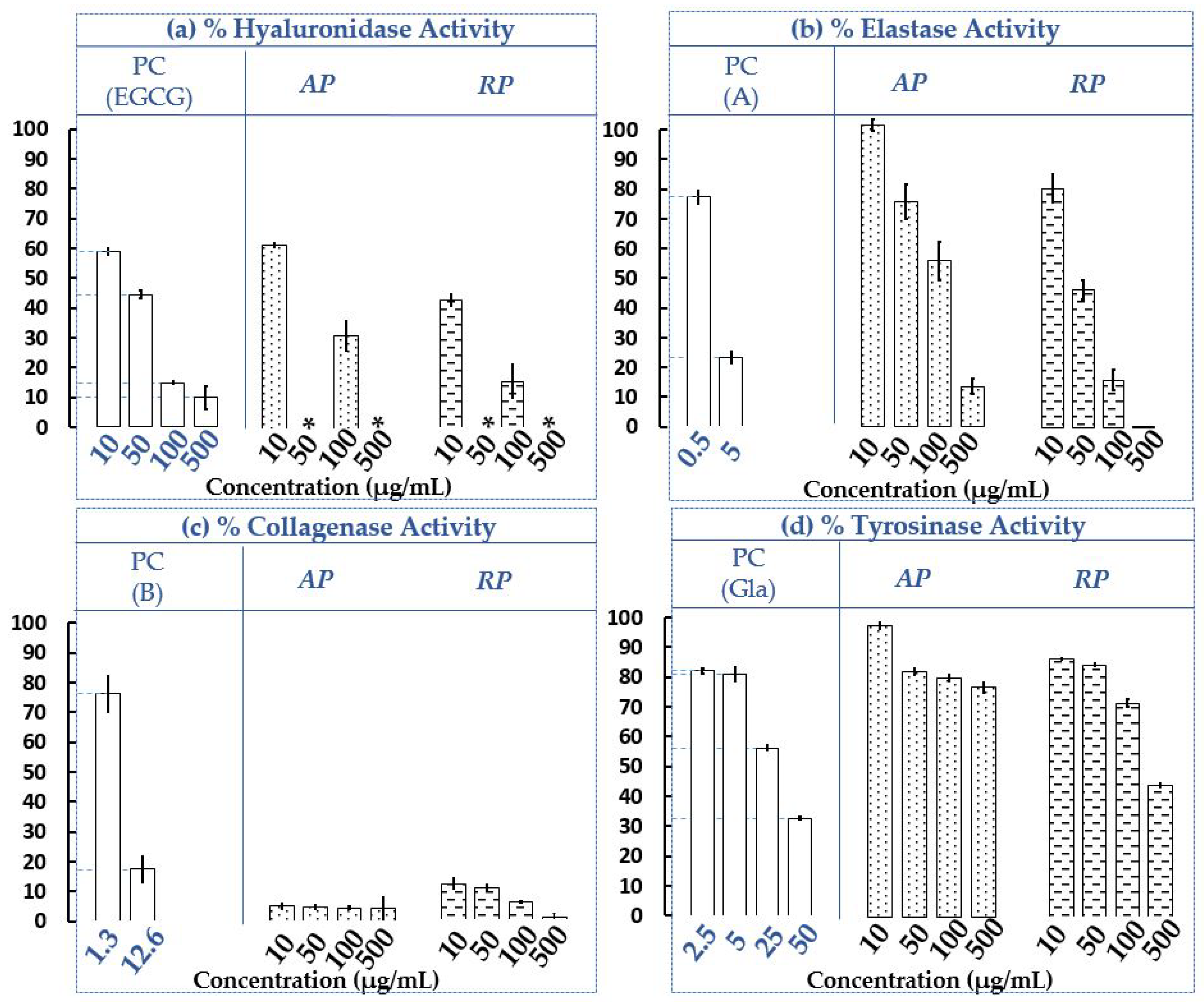
2.1.2. Determination of the Influence of AP and RP Extracts from Invasive P. cuspidatum on Hyaluronidase, Elastase, Collagenase and Tyrosinase Residual Activities
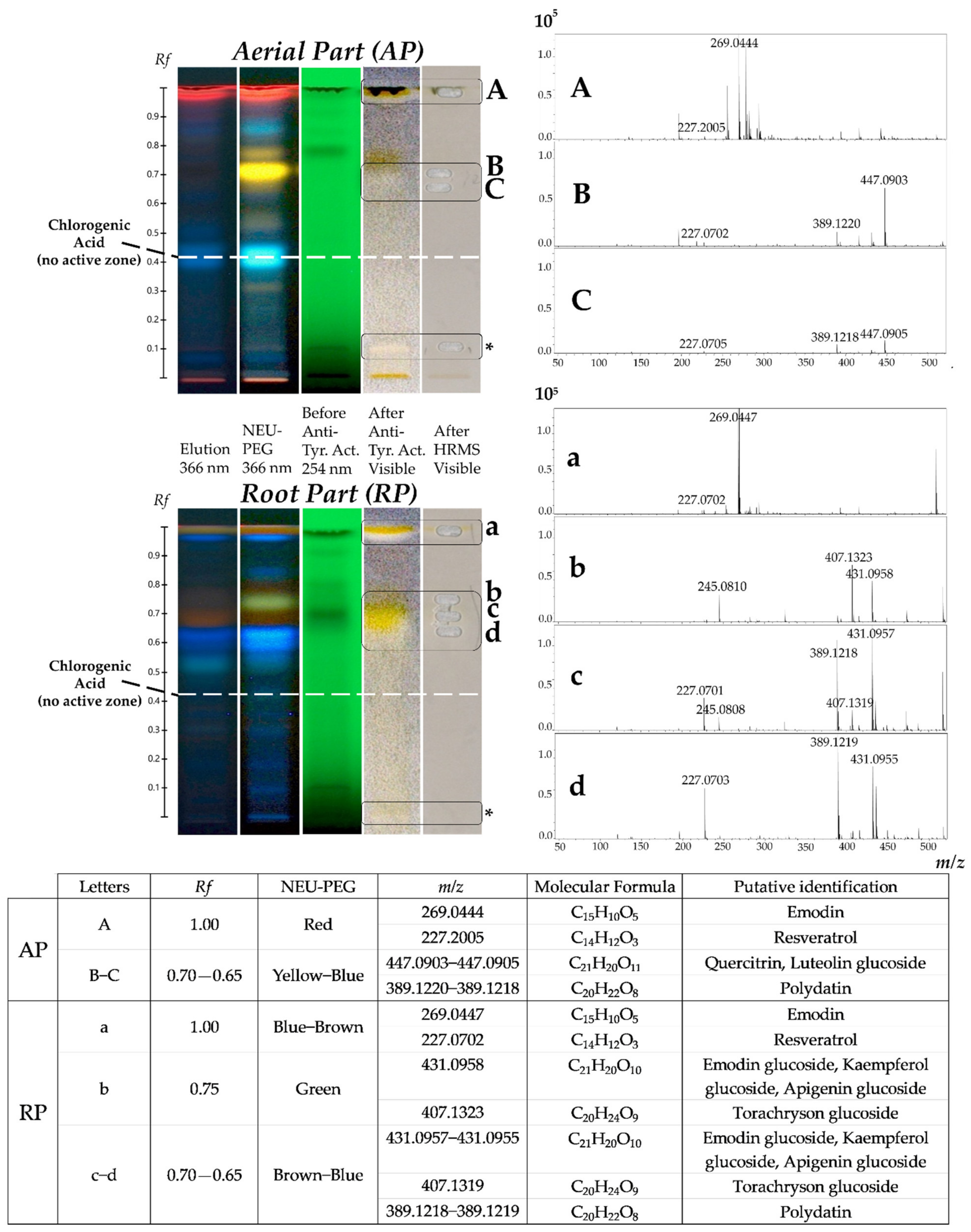
2.2. Use of the HPTLC-Bioautography/HRMS Approach for the Screening and Identification of Potential Tyrosinase Inhibitors in Ethanolic Extracts of AP and RP of Invasive P. cuspidatum
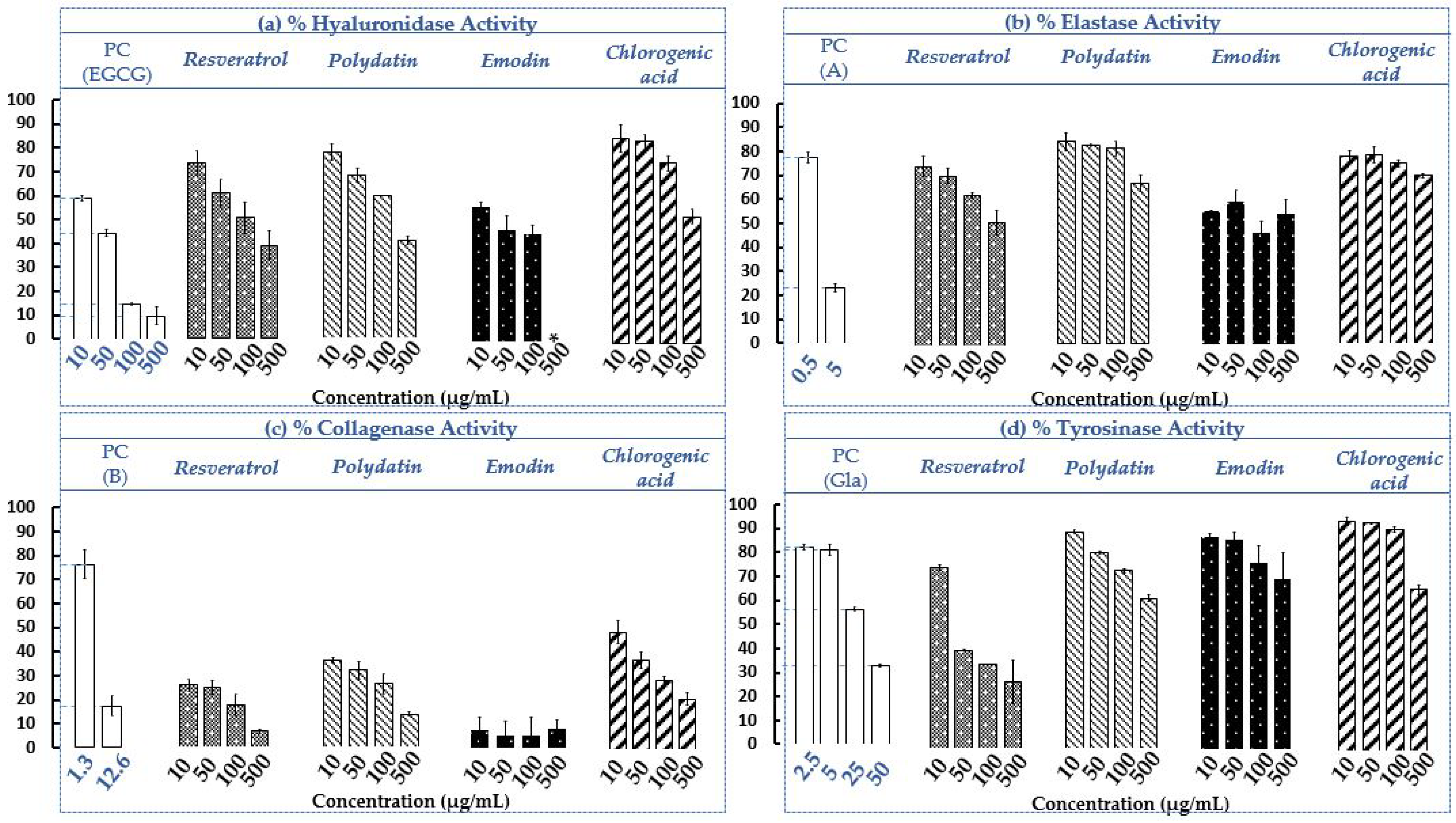
2.3. Determination of Hyaluronidase, Elastase, Collagenase and Tyrosinase Residual Activities in The Presence of the Four Selected Standards (Resveratrol, Polydatin, Emodin and Chlorogenic acid)
2.4. Evaluation of the Chemical Compositions of AP and RP of Invasive P. cuspidatum
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Ultrasound Assisted Plant Extraction
3.4. Assays of Enzymatic Activities
3.4.1. Equivalent Superoxide Dismutase Activity Assay
3.4.2. Hyaluronidase Activity Assay and Capillary Electrophoresis Conditions
3.4.3. Elastase Activity Assay
3.4.4. Collagenase Activity Assay
3.4.5. Tyrosinase Activity Assay
3.5. HPTLC-Bioautography/HRMS Analysis
3.5.1. High Performance Thin layer chromatography (HPTLC)
3.5.2. HPTLC-Bioautography
3.5.3. HPTLC-Bioautography/HRMS
3.6. UHPLC-UV/HRMS/MS Analysis
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richardson, D.M.; Pysek, P.; Rejmanek, M.; Barbour, M.G.; Panetta, F.D.; West, C.J. Naturalization and Invasion of Alien Plants: Concepts and Definitions. Divers. Distrib. 2000, 6, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyšek, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Simberloff, D.; Bacher, S.; Blackburn, T.M.; Carlton, J.T.; Dawson, W.; Essl, F.; Foxcroft, L.C.; Genovesi, P.; et al. Scientists’ Warning on Invasive Alien Species. Biol. Rev. 2020, 95, 1511–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conolly, A.P. The Distribution and History in the British Isles of Some Alien Species of Polygonum and Reynoutria. Watsonia 1977, 11, 291–311. [Google Scholar]
- Beerling, D.J.; Bailey, J.P.; Conolly, A.P. Fallopia japonica (Houtt.) Ronse Decraene. J. Ecol. 1994, 82, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J.N.; Tharayil, N.; DiTommaso, A.; Bhowmik, P.C. The Biology of Invasive Alien Plants in Canada. 5. Polygonum Cuspidatum Sieb. & Zucc. [= Fallopia Japonica (Houtt.) Ronse Decr.]. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2006, 86, 887–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguilera, A.G.; Alpert, P.; Dukes, J.S.; Harrington, R. Impacts of the Invasive Plant Fallopia japonica (Houtt.) on Plant Communities and Ecosystem Processes. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, G.M.; Bellard, C.; Bertelsmeier, C.; Bonnaud, E.; Genovesi, P.; Simberloff, D.; Courchamp, F. The 100th of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species. Biol. Invasions 2014, 16, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiébaut, M.; Nicolas, S.; Piola, F. “The Fad for Polygonum Will Fade Away!”: Historic Aspects of the Propagation and Success in France of the Reynoutria Complex Based on Archives. Bot. Lett. 2020, 167, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouvel-Oeil, F. Les Rivières. Available online: https://www.riviere-arly.com/les-rivieres/ (accessed on 2 March 2022).
- Dusz, M.-A.; Martin, F.-M.; Dommanget, F.; Petit, A.; Dechaume-Moncharmont, C.; Evette, A. Review of Existing Knowledge and Practices of Tarping for the Control of Invasive Knotweeds. Plants 2021, 10, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottet, M.; Piola, F.; Le Lay, Y.-F.; Rouifed, S.; Rivière-Honegger, A. How Environmental Managers Perceive and Approach the Issue of Invasive Species: The Case of Japanese Knotweed s.l. (Rhône River, France). Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 3433–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, P.; Marston, A. How Can Phytochemists Benefit from Invasive Plants? Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 1934578X0900401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiocchio, I.; Mandrone, M.; Tomasi, P.; Marincich, L.; Poli, F. Plant Secondary Metabolites: An Opportunity for Circular Economy. Molecules 2021, 26, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, P. Monographs for Quality Evaluation of Chinese Crude Drugs; World Scientific: Singapore, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.-Y.; Kuo, C.-H.; Liu, Y.-C.; Ye, L.-Y.; Chen, J.-H.; Shieh, C.-J. Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction of the Botanical Dietary Supplement Resveratrol and Other Constituents of Polygonum cuspidatum. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1810–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki El-Readi, M.; Yehia Eid, S.; Al-Amodi, H.S.; Wink, M. Fallopia japonica: Bioactive Secondary Metabolites and Molecular Mode of Anticancer. J. Tradit. Med. Clin. Nat. 2016, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Qin, R.; Li, X.; Zhou, H. Botany, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Potential Application of Polygonum Cuspidatum Sieb.et Zucc.: A Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 148, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucu, A.-A.; Baci, G.-M.; Dezsi, Ş.; Nap, M.-E.; Beteg, F.I.; Bonta, V.; Bobiş, O.; Caprio, E.; Dezmirean, D.S. New Approaches on Japanese Knotweed (Fallopia Japonica) Bioactive Compounds and Their Potential of Pharmacological and Beekeeping Activities: Challenges and Future Directions. Plants 2021, 10, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahimpašić, J.; Jogić, V.; Toromanović, M.; Džaferović, A.; Makić, H.; Dedić, S. Japanese Knotweed (Reynoutria Japonica) as a Phytoremediator of Heavy Metals. J. Agric. Food Environ. Sci. 2020, 74, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogačnik, L.; Rogelj, A.; Ulrih, N.P. Chemiluminescence Method for Evaluation of Antioxidant Capacities of Different Invasive Knotweed Species. Anal. Lett. 2016, 49, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogačnik, L.; Bergant, T.; Skrt, M.; Poklar Ulrih, N.; Viktorová, J.; Ruml, T. In Vitro Comparison of the Bioactivities of Japanese and Bohemian Knotweed Ethanol Extracts. Foods 2020, 9, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, S.; Kashiwagi, T.; Ebisu, T.; Shimamura, T.; Ukeda, H. Content of Resveratrol and Glycoside and Its Contribution to the Antioxidative Capacity of Polygonum Cuspidatum (Itadori) Harvested in Kochi. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dołowacka-Jóźwiak, A.; Matkowski, A.; Nawrot-Hadzik, I. Antiglycoxidative Properties of Extracts and Fractions from Reynoutria Rhizomes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leu, Y.-L.; Hwang, T.-L.; Hu, J.-W.; Fang, J.-Y. Anthraquinones From Polygonum Cuspidatum as Tyrosinase Inhibitors for Dermal Use. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-T.; Chiu, C.-C.; Liao, W.-T.; Liu, Y.-C.; David Wang, H.-M. Polygonum cuspidatum Extracts as Bioactive Antioxidaion, Anti-Tyrosinase, Immune Stimulation and Anticancer Agents. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 119, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann Franco, D.C.; Gonçalves de Carvalho, G.S.; Rocha, P.R.; da Silva Teixeira, R.; da Silva, A.D.; Barbosa Raposo, N.R. Inhibitory Effects of Resveratrol Analogs on Mushroom Tyrosinase Activity. Molecules 2012, 17, 11816–11825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeong, E.T.; Jin, M.H.; Kim, M.-S.; Chang, Y.H.; Park, S.G. Inhibition of Melanogenesis by Piceid Isolated from Polygonum cuspidatum. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2010, 33, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón de la Lastra, C.; Villegas, I. Resveratrol as an Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Aging Agent: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2005, 49, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Terrier, L.; Hay, A.-E.; Marston, A.; Hostettmann, K. Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibition Activities and Chemical Profiles of Polygonum sachalinensis F.Schmidt Ex Maxim (Polygonaceae). Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Bansal, Y.; Bhandari, R.; Marwaha, L.; Singh, R.; Chopra, K.; Kuhad, A. Resveratrol Protects against ICV Collagenase-Induced Neurobehavioral and Biochemical Deficits. J. Inflamm. 2017, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Nam, Y.; Song, J.; Kim, H. Gastroprotective and Healing Effects of Polygonum cuspidatum Root on Experimentally Induced Gastric Ulcers in Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozin, B.; Gavrilovic, M.; Kladar, N.; Rat, M.; Anackov, G.; Gavaric, N. Highly Invasive Alien Plant Reynoutria japonica Houtt. Represents a Novel Source for Pharmaceutical Industry—Evidence from Phenolic Profile and Biological Activity. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2017, 82, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrot-Hadzik, I.; Matkowski, A.; Pitułaj, A.; Sterczała, B.; Olchowy, C.; Szewczyk, A.; Choromańska, A. In Vitro Gingival Wound Healing Activity of Extracts from Reynoutria Japonica Houtt Rhizomes. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Trill, J.; Tan, L.-L.; Chang, W.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Willcox, M.; Xia, R.-Y.; Jiang, Y.; Moore, M.; Liu, J.-P.; et al. Reynoutria Japonica Houtt for Acute Respiratory Tract Infections in Adults and Children: A Systematic Review. Front. Pharm. 2022, 13, 787032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrot-Hadzik, I.; Zmudzinski, M.; Matkowski, A.; Preissner, R.; Kęsik-Brodacka, M.; Hadzik, J.; Drag, M.; Abel, R. Reynoutria Rhizomes as a Natural Source of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Inhibitors–Molecular Docking and In Vitro Study. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hromádková, Z.; Hirsch, J.; Ebringerová, A. Chemical Evaluation of Fallopia Species Leaves and Antioxidant Properties of Their Non-Cellulosic Polysaccharides. Chem. Pap. 2010, 64, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato-Noguchi, H. Allelopathy of Knotweeds as Invasive Plants. Plants 2021, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Khalil, A.A.K.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, S.-E.; Ahn, M.-J. 2-Methoxy-7-Acetonyljuglone Isolated from Reynoutria Japonica Increases the Activity of Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor-2 through Inhibition of Ubiquitin Degradation in HeLa Cells. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ardelean, F.; Moacă, E.A.; Păcurariu, C.; Antal, D.S.; Toma, C.-C.; Drăgan, S. Invasive Polygonum cuspidatum: Physico-chemical Analysis of Plant Extract with Pharmaceutical Potential. Ser. Stiintele Vietii 2016, 26, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Q. Antioxidant Potential of Ethanolic Extract of Polygonum Cuspidatum and Application in Peanut Oil. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, S.; Oszmiański, J. Profile of Bioactive Compounds in the Morphological Parts of Wild Fallopia Japonica (Houtt) and Fallopia Sachalinensis (F. Schmidt) and Their Antioxidative Activity. Molecules 2019, 24, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jug, U.; Naumoska, K.; Vovk, I. (−)-Epicatechin—An Important Contributor to the Antioxidant Activity of Japanese Knotweed Rhizome Bark Extract as Determined by Antioxidant Activity-Guided Fractionation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrot-Hadzik, I.; Ślusarczyk, S.; Granica, S.; Hadzik, J.; Matkowski, A. Phytochemical Diversity in Rhizomes of Three Reynoutria Species and Their Antioxidant Activity Correlations Elucidated by LC-ESI-MS/MS Analysis. Molecules 2019, 24, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Satooka, H.; Kubo, I. Resveratrol as a Kcat Type Inhibitor for Tyrosinase: Potentiated Melanogenesis Inhibitor. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, M.-M. The Effect of Emodin on Melanogenesis through the Modulation of ERK and MITF Signaling Pathway. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Liu, Z.; Hu, G.; Qu, L.; Yang, R. Investigation on the Binding of Aloe-Emodin with Tyrosinase by Spectral Analysis and Molecular Docking. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 211, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gębalski, J.; Graczyk, F.; Załuski, D. Paving the Way towards Effective Plant-Based Inhibitors of Hyaluronidase and Tyrosinase: A Critical Review on a Structure–Activity Relationship. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2022, 37, 1120–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, A.; West, L.E.; Guzzardi, L.; Bhatt, K.H.; Reid, E.E.; Scapagnini, G.; Micali, G. Cosmeceuticals in Dermatology. In Update in Cosmetic Dermatology; Tosti, A., Hexsel, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 87–113. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, J.V.; Praça, F.S.G.; Bentley, M.V.L.B.; Gaspar, L.R. Trans-Resveratrol and Beta-Carotene from Sunscreens Penetrate Viable Skin Layers and Reduce Cutaneous Penetration of UV-Filters. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 484, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lephart, E.D. Resveratrol, 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol, R-Equol, Racemic Equol or S-Equol as Cosmeceuticals to Improve Dermal Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ratz-Łyko, A.; Arct, J. Resveratrol as an Active Ingredient for Cosmetic and Dermatological Applications: A Review. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2019, 21, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, C.; Martí, M.; Martínez, V.; Rubio, L.; Parra, J.L.; Coderch, L. Antioxidant Cosmeto-Textiles: Skin Assessment. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 84, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igielska-Kalwat, J.; Firlej, M.; Lewandowska, A.; Biedziak, B. In Vivo Studies of Resveratrol Contained in Cosmetic Emulsions. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2019, 66, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Alarcón, C.; Denicola, A. Evaluating the Antioxidant Capacity of Natural Products: A Review on Chemical and Cellular-Based Assays. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 763, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apak, R.; Gorinstein, S.; Böhm, V.; Schaich, K.M.; Özyürek, M.; Güçlü, K. Methods of Measurement and Evaluation of Natural Antioxidant Capacity/Activity (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure App. Chem. 2013, 85, 957–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-Y.; Chan, Y.-P.; Chang, J. Antioxidant Activity of Extract from Polygonum cuspidatum. Biol. Res. 2007, 40, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.-L.; Gao, J.-P.; Han, Y.-L.; Xu, X.; Wu, R.; Gao, Y.; Cui, X.-H. Comparative Studies of Polydatin and Resveratrol on Mutual Transformation and Antioxidative Effect in Vivo. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashizume, H. Skin Aging and Dry Skin. J. Dermatol. 2004, 31, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayad, S.; Morin, P.; Nehmé, R. Use of Chromatographic and Electrophoretic Tools for Assaying Elastase, Collagenase, Hyaluronidase, and Tyrosinase Activity. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1529, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrchotová, N.; Sera, B.; Dadakova, E. HPLC and CE Analysis of Catechins, Stilbens and Quercetin in Flowers and Stems of Polygonum Cuspidatum, P. Sachalinense and P. x Bohemicum. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2010, 87, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Vaher, M.; Koel, M. Separation of Polyphenolic Compounds Extracted from Plant Matrices Using Capillary Electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 990, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayad, S.; Nehmé, R.; Langmajerová, M.; Ayela, B.; Colas, C.; Maunit, B.; Jacquinet, J.-C.; Vibert, A.; Lopin-Bon, C.; Zdeněk, G.; et al. Hyaluronidase Reaction Kinetics Evaluated by Capillary Electrophoresis with UV and High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HRMS) Detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 951, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandolini, V.; Maietti, A.; Tedeschi, P.; Durini, E.; Vertuani, S.; Manfredini, S. Capillary Electrophoresis Determination, Synthesis, and Stability of Resveratrol and Related 3-O-β-D-Glucopyranosides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehmé, R.; Nasreddine, R.; Orlic, L.; Lopin-Bon, C.; Hamacek, J.; Piazza, F. Kinetic Theory of Hyaluronan Cleavage by Bovine Testicular Hyaluronidase in Standard and Crowded Environments. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2021, 7, 129837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L. Rapid Quantitative HPTLC Analysis, on One Plate, of Emodin, Resveratrol, and Polydatin in the Chinese Herb Polygonum cuspidatum. Chromatographia 2005, 61, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawrył, M.A.; Waksmundzka-Hajnos, M. Two-Dimensional Thin-Layer Chromatography of Selected Polygonum Sp. Extracts on Polar-Bonded Stationary Phases. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 2812–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jug, U.; Vovk, I.; Glavnik, V.; Makuc, D.; Naumoska, K. Off-Line Multidimensional High Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography for Fractionation of Japanese Knotweed Rhizome Bark Extract and Isolation of Flavan-3-Ols, Proanthocyanidins and Anthraquinones. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1637, 461802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensa, M.; Glavnik, V.; Vovk, I. Flavan-3-ols and Proanthocyanidins in Japanese, Bohemian and Giant Knotweed. Plants 2021, 10, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavnik, V.; Vovk, I. High Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Methods on Diol Stationary Phase for the Analyses of Flavan-3-Ols and Proanthocyanidins in Invasive Japanese Knotweed. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1598, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metličar, V.; Vovk, I.; Albreht, A. Japanese and Bohemian Knotweeds as Sustainable Sources of Carotenoids. Plants 2019, 8, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dewanjee, S.; Gangopadhyay, M.; Bhattacharya, N.; Khanra, R.; Dua, T.K. Bioautography and Its Scope in the Field of Natural Product Chemistry. J. Pharm. Anal. 2015, 5, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jug, U.; Glavnik, V.; Kranjc, E.; Vovk, I. HPTLC–Densitometric and HPTLC–MS Methods for Analysis of Flavonoids. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2018, 41, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavnik, V.; Vovk, I. Extraction of Anthraquinones from Japanese Knotweed Rhizomes and Their Analyses by High Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry. Plants 2020, 9, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legerská, B.; Chmelová, D.; Ondrejovič, M.; Miertuš, S. The TLC-Bioautography as a Tool for Rapid Enzyme Inhibitors Detection—A Review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 52, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boo, Y.C. Human Skin Lightening Efficacy of Resveratrol and Its Analogs: From in Vitro Studies to Cosmetic Applications. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zou, K. Molecular Docking Study of Chlorogenic Acid as a Hyaluronidase Inhibitor. In Proceedings of the 2010 4th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Chengdu, China, 18–20 June 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Lee, J.-S.; Jang, H.-J.; Kim, S.-M.; Chang, M.S.; Park, S.H.; Kim, K.S.; Bae, J.; Park, J.-W.; Lee, B.; et al. Chlorogenic Acid Ameliorates Brain Damage and Edema by Inhibiting Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 and 9 in a Rat Model of Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Eur. J. Pharm. 2012, 689, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-R.; Habasi, M.; Xie, L.-Z.; Aisa, H. Effect of Chlorogenic Acid on Melanogenesis of B16 Melanoma Cells. Molecules 2014, 19, 12940–12948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, U.T.; Nguyen, L.T.H.; Kim, B.-A.; Choi, M.-J.; Yang, I.-J.; Shin, H.-M. Natural Compound Mixture, Containing Emodin, Genipin, Chlorogenic Acid, Cimigenoside, and Ginsenoside Rb1, Ameliorates Psoriasis-Like Skin Lesions by Suppressing Inflammation and Proliferation in Keratinocytes. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 9416962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pack, C.S.; Ryu, I.H.; Lee, K.S. Enzymological Evaluation of Oral Inflammation Inhibitory Activity by Aloe Vera Peel Extract. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2001, 33, 753–759. [Google Scholar]
- Ao, C.; Higa, T.; Ming, H.; Ding, Y.; Tawata, S. Isolation and Identification of Antioxidant and Hyaluronidase Inhibitory Compounds from Ficus Microcarpa L. Fil. Bark. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2010, 25, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zembower, D.E.; Kam, C.M.; Powers, J.C.; Zalkow, L.H. Novel Anthraquinone Inhibitors of Human Leukocyte Elastase and Cathepsin G. J. Med. Chem. 1992, 35, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, S.; Rajtar, G.; Manarini, S.; Celardo, A.; Rotilio, D.; De Gaetano, G.; Evangelista, V.; Cerletti, C. Effect of Trans -Resveratrol, a Natural Polyphenolic Compound, on Human Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte Function: Trans -Resveratrol and Human PMN Leukocyte Function. Br. J. Pharm. 1998, 123, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, Y.-F.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chang, W.-Y.; Syu, Y.-T.; Hwang, T.-L. Resveratrol Suppresses Neutrophil Activation via Inhibition of Src Family Kinases to Attenuate Lung Injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 145, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Metori, K.; Mineo, S.; Matsumoto, H.; Satoh, T. Studies on Collagenase Inhibitors. II. Inhibitory Effets of Anthraquinones on Bacterial Collagenase. Yakugaku Zasshi J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 1990, 110, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.; Hu, Y.; Guo, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; He, W.; Tan, H. Resveratrol as a Novel Agent for Treatment of Multiple Myeloma with Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitory Activity. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2006, 27, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelis, A.; Hubert, J.; Aligiannis, N.; Michalea, R.; Abedini, A.; Nuzillard, J.-M.; Gangloff, S.; Skaltsounis, A.-L.; Renault, J.-H. Bio-Guided Isolation of Methanol-Soluble Metabolites of Common Spruce (Picea abies) Bark by-Products and Investigation of Their Dermo-Cosmetic Properties. Molecules 2016, 21, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, K.-D.; Chan, Y.-H.; Chen, H.-J.; Lin, S.-P.; Cheng, K.-C. Tyrosinase-Based TLC Autography for Anti-Melanogenic Drug Screening. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bralley, E. Nutraceutical Properties of Muscadine Grape (Vitis rotundifolia), Sorghum bicolor, and Polygonum cuspidatum. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Georgia, Athens, GA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wittenauer, J.; Mäckle, S.; Sußmann, D.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Carle, R. Inhibitory Effects of Polyphenols from Grape Pomace Extract on Collagenase and Elastase Activity. Fitoterapia 2015, 101, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brás, N.F.; Gonçalves, R.; Mateus, N.; Fernandes, P.A.; Ramos, M.J.; de Freitas, V. Inhibition of Pancreatic Elastase by Polyphenolic Compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10668–10676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrot-Hadzik, I.; Granica, S.; Domaradzki, K.; Pecio, Ł.; Matkowski, A. Isolation and Determination of Phenolic Glycosides and Anthraquinones from Rhizomes of Various Reynoutria Species. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, P.; Hay, A.-E.; Marston, A.; Lou, H.; Hostettmann, K. Chemical Variability of the Invasive Neophytes Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. and Zucc. and Polygonum Sachalinensis F. Schmidt Ex Maxim. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2009, 37, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.; Cai, Y.-Z.; Brooks, J.D.; Corke, H. Antibacterial Properties of Polygonum Cuspidatum Roots and Their Major Bioactive Constituents. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, S. UPLC-PDA-Q/TOF-MS Identification of Bioactive Compounds and on-Line UPLC-ABTS Assay in Fallopia Japonica Houtt and Fallopia Sachalinensis (F. Schmidt) Leaves and Rhizomes Grown in Poland. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alperth, F.; Melinz, L.; Fladerer, J.-P.; Bucar, F. UHPLC Analysis of Reynoutria Japonica Houtt. Rhizome Preparations Regarding Stilbene and Anthranoid Composition and Their Antimycobacterial Activity Evaluation. Plants 2021, 10, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao-Ngoc, P.; Leclercq, L.; Rossi, J.-C.; Hertzog, J.; Tixier, A.-S.; Chemat, F.; Nasreddine, R.; Al Hamoui Dit Banni, G.; Nehmé, R.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; et al. Water-Based Extraction of Bioactive Principles from Blackcurrant Leaves and Chrysanthellum Americanum: A Comparative Study. Foods 2020, 9, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.-J.; Lee, E.H.; Kang, T.H.; Ha, S.K.; Oh, M.S.; Kim, S.M.; Yoon, T.-J.; Kang, C.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, S.Y. Inhibitory Effects of Arbutin on Melanin Biosynthesis of α-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone-Induced Hyperpigmentation in Cultured Brownish Guinea Pig Skin Tissues. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2009, 32, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Males, Z.; Medic-Saric, M.; Bucar, F. Flavonoids of Guiera Senegalensis J. F. GMEL. Thin-Layer Chromatography and Numerical Methods. Croat. Chem. Acta 1998, 11, 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Chandana, N.G.A.S.S.; Morlock, G.E. Comprehensive Bioanalytical Multi-Imaging by Planar Chromatography in Situ Combined with Biological and Biochemical Assays Highlights Bioactive Fatty Acids in Abelmosk. Talanta 2021, 223, 121701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quinty, V.; Colas, C.; Nasreddine, R.; Nehmé, R.; Piot, C.; Draye, M.; Destandau, E.; Da Silva, D.; Chatel, G. Screening and Evaluation of Dermo-Cosmetic Activities of the Invasive Plant Species Polygonum cuspidatum. Plants 2023, 12, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010083
Quinty V, Colas C, Nasreddine R, Nehmé R, Piot C, Draye M, Destandau E, Da Silva D, Chatel G. Screening and Evaluation of Dermo-Cosmetic Activities of the Invasive Plant Species Polygonum cuspidatum. Plants. 2023; 12(1):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010083
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuinty, Vanille, Cyril Colas, Rouba Nasreddine, Reine Nehmé, Christine Piot, Micheline Draye, Emilie Destandau, David Da Silva, and Gregory Chatel. 2023. "Screening and Evaluation of Dermo-Cosmetic Activities of the Invasive Plant Species Polygonum cuspidatum" Plants 12, no. 1: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010083
APA StyleQuinty, V., Colas, C., Nasreddine, R., Nehmé, R., Piot, C., Draye, M., Destandau, E., Da Silva, D., & Chatel, G. (2023). Screening and Evaluation of Dermo-Cosmetic Activities of the Invasive Plant Species Polygonum cuspidatum. Plants, 12(1), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010083










