Genetic Mapping of Seven Kinds of Locus for Resistance to Asian Soybean Rust
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Genetic Loci of Seven Rpps
2.2. Genetic Effect of Seven Rpps
3. Discussion
3.1. Position of Resistance Loci
3.2. The Effect of Introducing Resistance Genes
3.3. The Necessity of Marker-Assisted Selection for ASR Resistance and Utility of Markers
3.4. Second Resistance Gene Rpp3 in Rpp5-Carrying Varieties, Kinoshita and Shiranui
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Soybean Populations to Map ASR Resistance Loci
4.2. Resistant Phenotyping in the Mapping Populations
4.3. Genotyping of DNA Markers on the Mapping Populations
4.4. Linkage Analysis of SSR Markers and Deciding Rpp Loci
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akamatsu, H.; Yamanaka, N.; Soares, R.M.; Ivancovich, A.J.G.; Lavilla, M.A.; Bogado, A.N.; Morel, G.; Scholz, R.; Yamaoka, Y.; Kato, M. Pathogenic variation of South American Phakopsora pachyrhizi populations isolated from soybeans from 2010 to 2015. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2017, 51, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langenbach, C.; Campe, R.; Beyer, S.F.; Mueller, A.N.; Conrath, U. Fighting Asian soybean rust. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murithi, H.M.; Beed, F.; Tukamuhabwa, P.; Thomma, B.P.H.J.; Joosten, M.H.A.J. Soybean production in eastern and southern Africa and threat of yield loss due to soybean rust caused by Phakopsora pachyrhizi. Plant Pathol. 2016, 65, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rodríguez, J.C.; Vicente-Hernández, Z.; Grajales-Solís, M.; Yamanaka, N. Virulence diversity of Phakopsora pachyrhizi in Mexico. PhytoFrontiers 2022, 2, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Yasmin, L.; Rubayet, M.T.; Akamatsu, H.; Yamanaka, N. A major variation in the virulence of the Asian soybean rust pathogen (Phakopsora pachyrhizi) in Bangladesh. Plant Pathol. 2022, 71, 1355–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larzábal, J.; Rodríguez, M.; Yamanaka, N.; Stewart, S. Pathogenic variability of Asian soybean rust fungus within fields in Uruguay. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2022, 47, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, N.; Lemos, N.G.; Uno, M.; Akamatsu, H.; Yamaoka, Y.; Abdelnoor, R.V.; Braccini, A.L.; Suenaga, K. Resistance to Asian soybean rust in soybean lines with the pyramided three Rpp genes. Crop. Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2013, 13, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamanaka, N.; Morishita, M.; Mori, T.; Lemos, N.G.; Hossain, M.M.; Akamatsu, H.; Kato, M.; Yamaoka, Y. Multiple Rpp-gene pyramiding confers resistance to Asian soybean rust isolates that are virulent on each of the pyramided genes. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2015, 40, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, N.; Hossain, M.M. Pyramiding three rust-resistance genes confers a high level of resistance in soybean (Glycine max). Plant Breed. 2019, 138, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Morel, A.; Yamanaka, N. Resistance to Asian soybean rust and yield of new soybean cultivars, JFNC 1 and JFNC 2, harboring three resistance genes. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2022, 47, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, N.G.; Braccini, A.L.; Abdelnoor, R.V.; Oliveira, M.C.N.; Suenaga, K.; Yamanaka, N. Characterization of genes Rpp2, Rpp4, and Rpp5 for resistance to soybean rust. Euphytica 2011, 182, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwa, T.; Muraki, Y.; Yamanaka, N. Near-isogenic soybean lines carrying Asian soybean rust resistance genes for practical pathogenicity validation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeven, A.C.; Knott, D.R.; Johnson, R. Investigation of linkage drag in near isogenic lines of wheat by testing for seedling reaction to races of stem rust, leaf rust and yellow rust. Euphytica 1983, 32, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, L.N.; Muraki, Y.; Yamanaka, N. Characterization of three soybean landraces resistant to Asian soybean rust disease. Mol. Breed. 2020, 40, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, N.; Hossain, M.M.; Yamaoka, Y. Molecular mapping of Asian soybean rust resistance in Chinese and Japanese soybean lines, Xiao Jing Huang, Himeshirazu, and Iyodaizu B. Euphytica 2015, 205, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Akamatsu, H.; Morishita, M.; Mori, T.; Yamaoka, Y.; Suenaga, K.; Soares, R.M.; Bogado, A.N.; Ivancovich, A.J.G.; Yamanaka, N. Molecular mapping of Asian soybean rust resistance in soybean landraces PI 594767A, PI 587905 and PI 416764. Plant Pathol. 2015, 64, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamanaka, N.; Morishita, M.; Mori, T.; Muraki, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Hossain, M.M.; Yamaoka, Y.; Kato, M. The locus for resistance to Asian soybean rust in PI 587855. Plant Breed. 2016, 135, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Calvo, E.S.; Kiihl, R.A.S.; Harada, A.; Hiromoto, D.M.; Vieira, L.G.E. Molecular mapping of soybean rust (Phakopsora pachyrhizi) resistance genes: Discovery of a novel locus and alleles. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 117, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyten, D.L.; Hartman, G.L.; Nelson, R.L.; Frederick, R.D.; Concibido, V.C.; Narvel, J.M.; Cregan, P.B. Map location of the Rpp1 locus that confers resistance to soybean rust in soybean. Crop. Sci. 2007, 47, 837–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, N.; Curley, J.; Frederick, R.D.; Hyten, D.L.; Nelson, R.L.; Hartman, G.L.; Diers, B.W. Mapping and confirmation of a new allele at Rpp1 from soybean PI 594538A conferring RB lesion-type resistance to soybean rust. Crop. Sci. 2009, 49, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Kim, M.; King, Z.R.; Harris, D.K.; Buck, J.W.; Li, Z.; Diers, B.W. Fine mapping of the Asian soybean rust resistance gene Rpp2 from soybean PI 230970. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteros, M.J.; Missaoui, A.M.; Phillips, D.V.; Walker, D.R.; Boerma, H.R. Mapping and confirmation of the ‘Hyuuga’ red-brown lesion resistance gene for Asian soybean rust. Crop. Sci. 2007, 47, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyten, D.L.; Smith, J.R.; Frederick, R.D.; Tucker, M.L.; Song, Q.; Cregan, P.B. Bulked segregant analysis using the GoldenGate assay to locate the Rpp3 locus that confers resistance to soybean rust in soybean. Crop. Sci. 2009, 49, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.D.F.; Silva, D.C.G.; Yang, C.; Pedley, K.F.; Zhang, C.; Van de Mortel, M.; Hill, J.H.; Shoemaker, R.C.; Abdelnoor, R.V.; Whitham, S.A.; et al. Identification and analyses of candidate genes for Rpp4-mediated resistance to Asian soybean rust in soybean. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kendrick, M.D.; Harris, D.K.; Ha, B.K.; Hyten, D.L.; Cregan, P.B.; Frederick, R.D.; Boerma, H.R.; Pedley, K.F. Identification of a second Asian soybean rust resistance gene in Hyuuga soybean. Phytopathology 2011, 101, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Smith, J.R.; Ray, J.D.; Frederick, R.D. Identification of a new soybean rust resistance gene in PI 567102B. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Yamanaka, N.; Akamatsu, H.; Suenaga, K. Pathogenic races of soybean rust Phakopsora pachyrhizi collected in Tsukuba and vicinity in Ibaraki, Japan. J. General Plant Pathol. 2014, 80, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.R.; McDonald, S.C.; Harris, D.K.; Boerma, H.R.; Buck, J.W.; Sikora, E.J.; Weaver, D.B.; Wright, D.L.; Marois, J.J.; Li, Z. Genomic regions associated with resistance to soybean rust (Phakopsora pachyrhizi) under field conditions in soybean germplasm accessions from Japan, Indonesia and Vietnam. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 3073–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, N.; Kato, M.; Akamatsu, H.; Yamaoka, Y. Laboratory Manual for Studies on Soybean Rust Resistance. Version 26. 2021. Available online: https://www.jircas.go.jp/en/publication/manual_guideline/30 (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- Silva, D.C.G.; Yamanaka, N.; Brogin, R.L.; Arias, C.A.A.; Nepomuceno, A.L.; Di Mauro, A.O.; Pereira, S.S.; Nogueira, L.M.; Passianotto, A.L.L.; Abdelnoor, R.V. Molecular mapping of two loci that confer resistance to Asian rust in soybean. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 117, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, E.; Green, P.; Abrahamson, J.; Barlow, A.; Daly, M.J.; Lincoln, S.E.; Newberg, L.A. Mapmaker: An interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1987, 11, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Basten, C.J.; Zeng, Z.B. Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5: Department of Statistics; North Carolina State University: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2012; Available online: http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm (accessed on 10 February 2023).



| Pop. | Parental Cross | Target Gene | Chromo-some | Numbers of Markers | Numbers of Marker Loci | Total Length of Linkage Group | Position of Target Rpps 2 | One of the Nearest Markers 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Xiao Jin Huang × BRS184 | Rpp1 | Chr. 18 | 10 | 7 | 15.4 cM | 10.8 cM | SSR18_1854 |
| 2 | BRS184 × Himeshirazu | Rpp1 | Chr. 18 | 9 | 7 | 14.1 cM | 11.7 cM | Sct_187 |
| 3 | KS 1034 × BRS184 | Rpp1 | Chr. 18 | 6 | 5 | 10.6 cM | 6.3 cM | Sct_187 |
| 4 | BRS184 × PI 594767A | Rpp1-b | Chr. 18 | 7 | 5 | 17.0 cM | 16.4 cM | SSR18_1861 |
| 5 | BRS184 × PI 587905 | Rpp1-b | Chr. 18 | 6 | 4 | 5.6 cM | 5.4 cM | SSR18_1861 |
| 6 | BRS184 × PI 587855 | Rpp1-b | Chr. 18 | 11 | 8 | 15.9 cM | 13.3 cM | SSR18_1861 |
| 7 | PI 587880A × No12-1-A 1 | Rpp1-b | Chr. 18 | 17 | 8 | 11.1 cM | 7.4 cM | SSR18_1861 |
| 8 | Iyodaizu B × BRS184 | Rpp2 | Chr. 16 | 9 | 8 | 15.7 cM | 8.7–9.4 cM | SSR16_0908 |
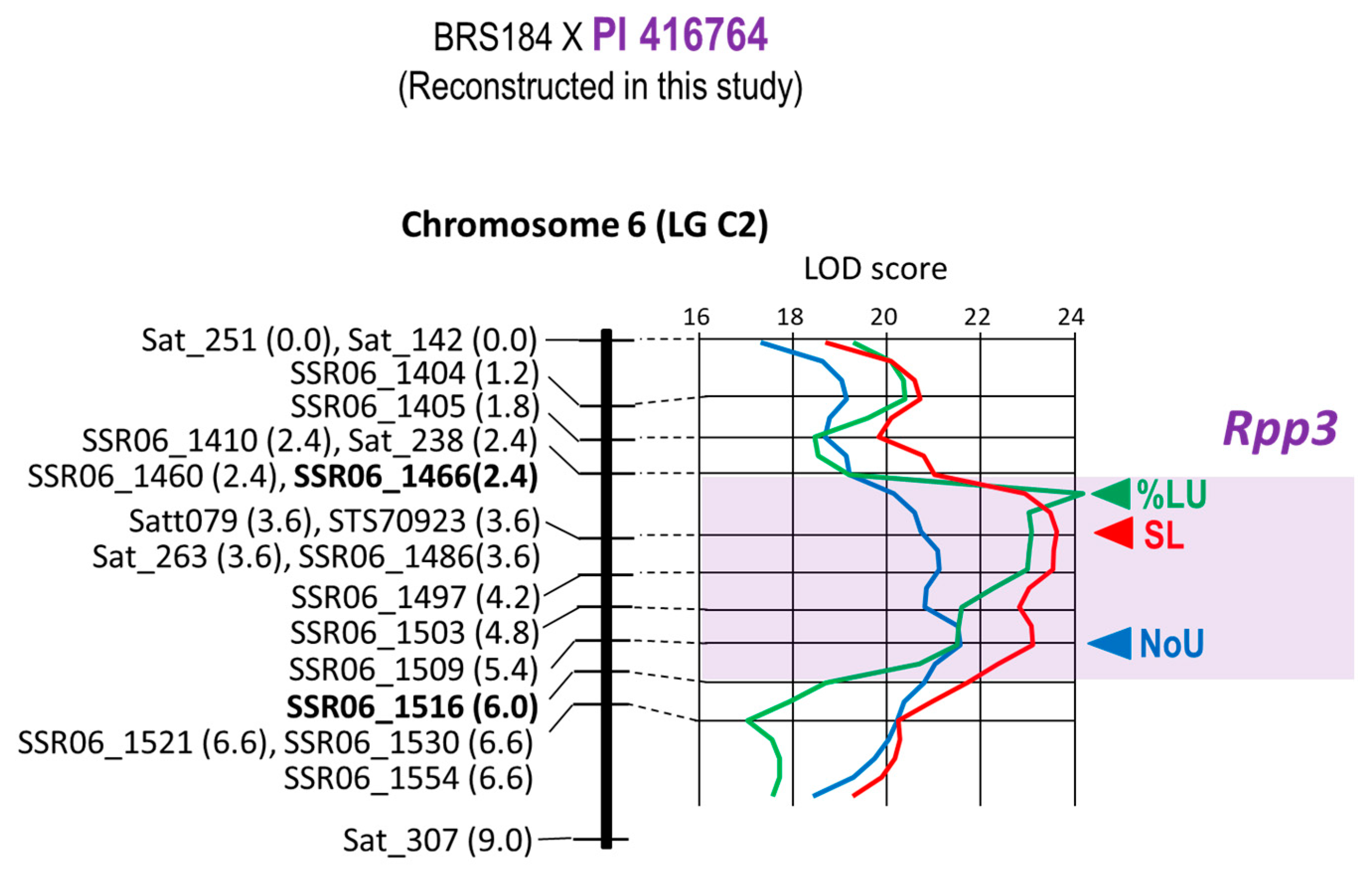
| 9 | BRS184 × PI 416764 | Rpp3 | Chr. 6 | 20 | 11 | 9.0 cM | 2.4–6.0 cM | Satt079 4 |
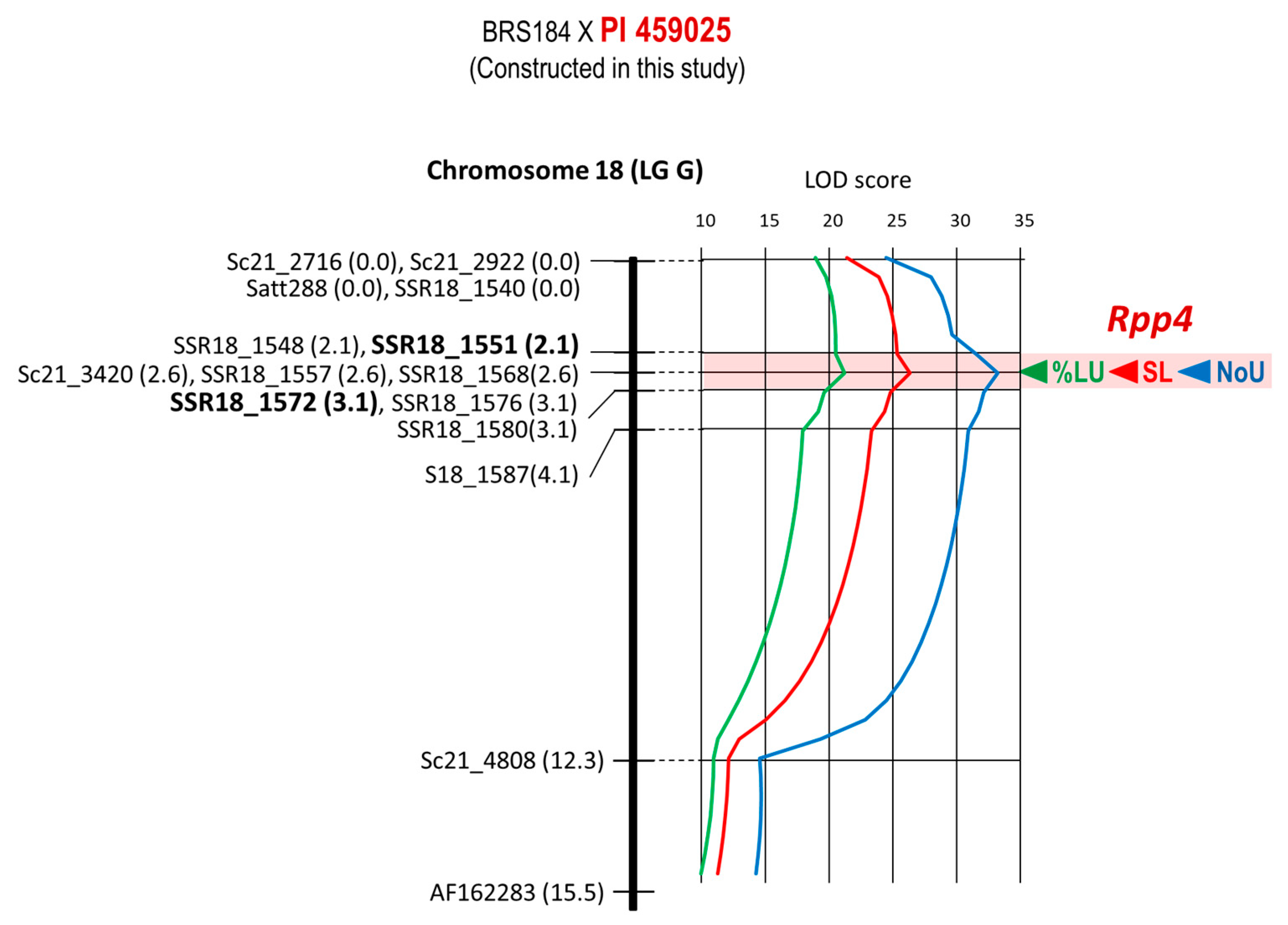
| 10 | BRS184 × PI 459025 | Rpp4 | Chr. 18 | 15 | 7 | 15.5 cM | 2.1–3.1 cM | SSR18_1568 |
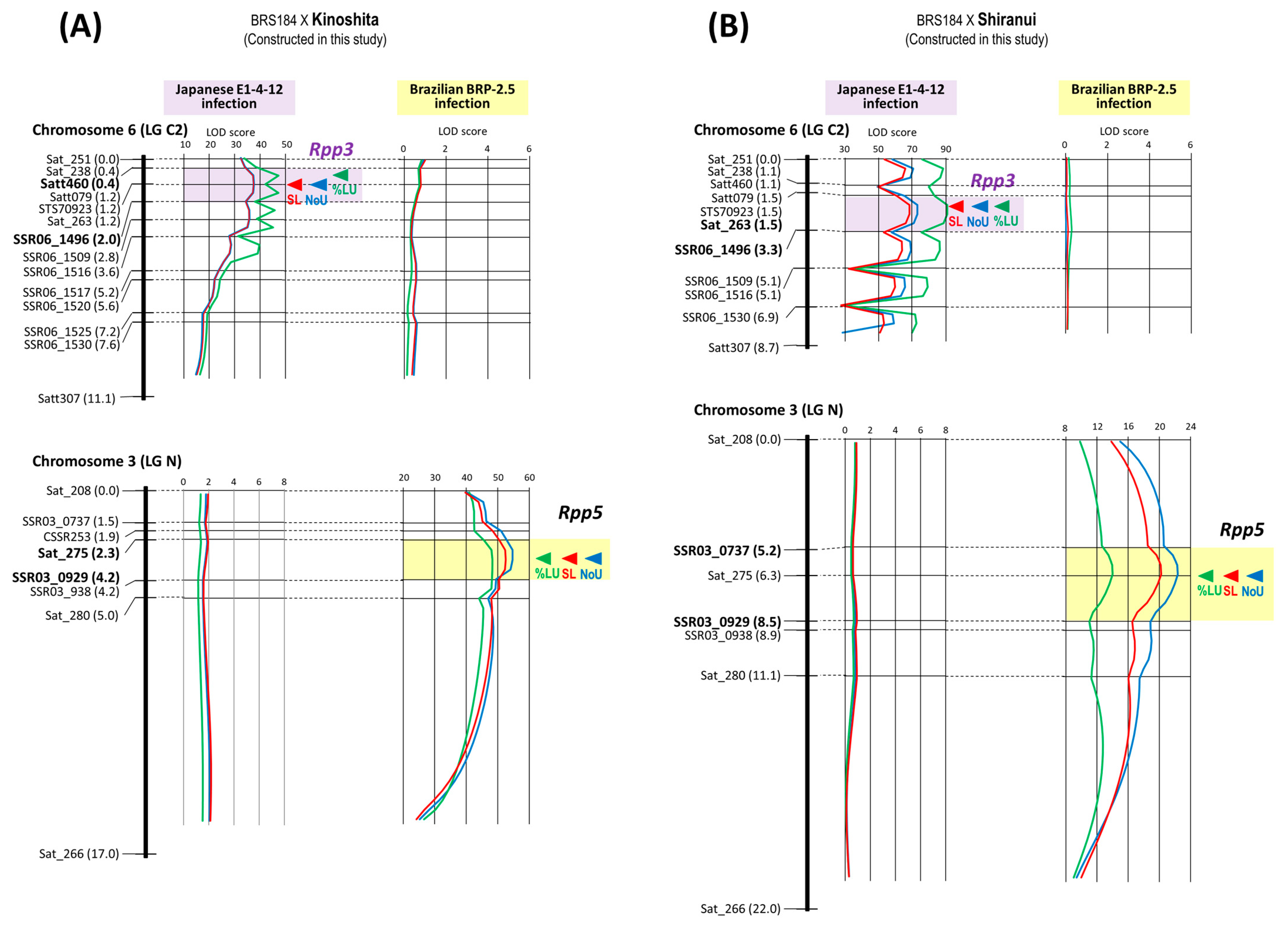
| 11 | BRS184 × Kinoshita | Rpp5 | Chr. 3 | 8 | 8 | 17.0 cM | 2.3–4.2 cM | SSR03_0929 |
| Rpp3 | Chr. 6 | 14 | 11 | 11.1 cM | 0.4–2.0 cM | Sat_263 | ||
| 12 | BRS184 × Shiranui | Rpp5 | Chr. 3 | 7 | 7 | 22.0 cM | 5.2–8.5 cM | Sat_275 |
| Rpp3 | Chr. 6 | 11 | 7 | 8.7 cM | 1.5–3.3 cM | Sat_263 | ||
| 13 | BRS184 × PI 567102B | Rpp6 | Chr. 18 | 13 | 10 | 13.1 cM | 1.5–3.5 cM | SSR18_0356 |
| Pop. | Parental Cross | Target Gene | The Nearest Markers | Pathogen | Additive Effect 1 | Dominance Effect 1 | Degree of Dominance | Variance Explained (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Xiao Jin Huang × BRS184 | Rpp1 | SSR18_1854 | T1-2 | −0.69 | −0.72 | 1.04 | 48.99% |
| 2 | BRS184 × Himeshirazu | Rpp1 | Sct_187 | E1-4-12 | −0.76 | −0.76 | 1.00 | 64.65% |
| 3 | KS 1034 × BRS184 | Rpp1 | Sct_187 | E1-4-12 | −0.93 | −0.80 | 0.86 | 60.54% |
| 4 | BRS184 × PI 594767A | Rpp1-b | SSR18_1861 | T1-2 | −1.40 | −1.40 | 1.00 | 55.93% |
| 5 | BRS184 × PI 587905 | Rpp1-b | SSR18_1861 | T1-2 | −1.68 | −1.55 | 0.92 | 64.18% |
| 6 | BRS184 × PI 587855 | Rpp1-b | SSR18_1861 | E1-4-12 | −0.85 | −0.85 | 1.00 | 65.41% |
| 7 | PI 587880A × No12-1-A | Rpp1-b | SSR18_1861 | BRP-2.1 | −0.86 | −0.87 | 1.01 | 48.94% |
| 8 | Iyodaizu B × BRS184 | Rpp2 | SSR16_0908 | E1-4-12 | −0.81 | −0.51 | 0.62 | 69.42% |
| 9 | BRS184 × PI 416764 | Rpp3 | Satt079 | T1-2 | −1.05 | −0.22 | 0.21 | 65.73% |
| 10 | BRS184 × PI 459025 | Rpp4 | SSR18_1568 | E1-4-12 | −0.90 | −0.41 | 0.46 | 70.59% |
| 11 | BRS184 × Kinoshita | Rpp5 | SSR03_0929 | BRP-2.5 | −1.15 | −0.03 | 0.02 | 82.60% |
| Rpp3 | Sat_263 | E1-4-12 | −0.81 | −0.74 | 0.91 | 51.50% | ||
| 12 | BRS184 × Shiranui | Rpp5 | Sat_275 | BRP-2.5 | −0.97 | −0.09 | 0.09 | 52.29% |
| Rpp3 | Sat_263 | E1-4-12 | −0.82 | −0.81 | 0.99 | 52.37% | ||
| 13 | BRS184 × PI 567102B | Rpp6 | SSR18_0356 | E1-4-12 | −0.64 | −0.61 | 0.96 | 59.07% |
| Pop. | Parental Cross | Target Gene | The Nearest Markers | Pathogen | Additive Effect 1 | Dominance Effect 1 | Degree of Dominance | Variance Explained (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Xiao Jin Huang × BRS184 | Rpp1 | SSR18_1854 | T1-2 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| 2 | BRS184 × Himeshirazu | Rpp1 | Sct_187 | E1-4-12 | −46.17% | −46.17% | 1.00 | 66.58% |
| 3 | KS 1034 × BRS184 | Rpp1 | Sct_187 | E1-4-12 | −49.57% | −40.84% | 0.82 | 59.62% |
| 4 | BRS184 × PI 594767A | Rpp1-b | SSR18_1861 | T1-2 | −23.21% | −23.06% | 0.99 | 57.61% |
| 5 | BRS184 × PI 587905 | Rpp1-b | SSR18_1861 | T1-2 | −49.47% | −37.37% | 0.76 | 69.03% |
| 6 | BRS184 × PI 587855 | Rpp1-b | SSR18_1861 | E1-4-12 | −47.62% | −47.42% | 1.00 | 67.78% |
| 7 | PI 587880A × No12-1-A | Rpp1-b | SSR18_1861 | BRP-2.1 | −44.71% | −45.24% | 1.01 | 62.11% |
| 8 | Iyodaizu B × BRS184 | Rpp2 | SSR16_0908 | E1-4-12 | −45.72% | −21.04% | 0.46 | 72.25% |
| 9 | BRS184 × PI 416764 | Rpp3 | Satt079 | T1-2 | −33.63% | 22.76% | −0.68 | 59.92% |
| 10 | BRS184 × PI 459025 | Rpp4 | SSR18_1568 | E1-4-12 | −38.64% | −1.12% | 0.03 | 63.43% |
| 11 | BRS184 × Kinoshita | Rpp5 | SSR03_0929 | BRP-2.5 | −40.19% | 21.15% | −0.53 | 72.61% |
| Rpp3 | Sat_263 | E1-4-12 | −42.26% | −36.57% | 0.87 | 55.69% | ||
| 12 | BRS184 × Shiranui | Rpp5 | Sat_275 | BRP-2.5 | −29.98% | 5.70% | −0.19 | 36.61% |
| Rpp3 | Sat_263 | E1-4-12 | −42.50% | −41.42% | 0.97 | 55.93% | ||
| 13 | BRS184 × PI 567102B | Rpp6 | SSR18_0356 | E1-4-12 | −40.00% | −38.23% | 0.96 | 59.38% |
| Pop. | Parental Cross | Target Gene | The Nearest Markers | Pathogen | Additive Effect 1 | Dominance Effect 1 | Degree of Dominance | Variance Explained (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Xiao Jin Huang × BRS184 | Rpp1 | SSR18_1854 | T1-2 | −0.57 | −0.61 | 1.07 | 45.87% |
| 2 | BRS184 × Himeshirazu | Rpp1 | Sct_187 | E1-4-12 | −0.94 | −0.94 | 1.00 | 66.32% |
| 3 | KS 1034 × BRS184 | Rpp1 | Sct_187 | E1-4-12 | −1.42 | −1.23 | 0.87 | 60.54% |
| 4 | BRS184 × PI 594767A | Rpp1-b | SSR18_1861 | T1-2 | −1.46 | −1.45 | 1.00 | 57.38% |
| 5 | BRS184 × PI 587905 | Rpp1-b | SSR18_1861 | T1-2 | −1.48 | −1.33 | 0.90 | 66.92% |
| 6 | BRS184 × PI 587855 | Rpp1-b | SSR18_1861 | E1-4-12 | −1.00 | −1.00 | 1.00 | 66.84% |
| 7 | PI 587880A × No12-1-A | Rpp1-b | SSR18_1861 | BRP-2.1 | −0.88 | −0.90 | 1.01 | 59.73% |
| 8 | Iyodaizu B × BRS184 | Rpp2 | SSR16_0908 | E1-4-12 | −0.96 | −0.52 | 0.55 | 71.16% |
| 9 | BRS184 × PI 416764 | Rpp3 | Satt079 | T1-2 | −1.03 | 0.04 | −0.04 | 71.63% |
| 10 | BRS184 × PI 459025 | Rpp4 | SSR18_1568 | E1-4-12 | −0.99 | −0.24 | 0.24 | 69.12% |
| 11 | BRS184 × Kinoshita | Rpp5 | SSR03_0929 | BRP-2.5 | −1.10 | 0.08 | −0.07 | 83.05% |
| Rpp3 | Sat_263 | E1-4-12 | −0.98 | −0.88 | 0.90 | 51.71% | ||
| 12 | BRS184 × Shiranui | Rpp5 | Sat_275 | BRP-2.5 | −1.04 | −0.07 | 0.06 | 48.93% |
| Rpp3 | Sat_263 | E1-4-12 | −1.09 | −1.07 | 0.99 | 52.55% | ||
| 13 | BRS184 × PI 567102B | Rpp6 | SSR18_0356 | E1-4-12 | −0.80 | −0.77 | 0.96 | 58.38% |
| Pop. | Target Gene | Parental Cross | Population Structure | Numbers of Genotypes | Inoculation Target 3 | Pathogenic Strain | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rpp1 | Xiao Jin Huang × BRS184 | F2 | 90 | Plant | T1-2 | [15] |
| 2 | Rpp1 | BRS184 × Himeshirazu | F2 | 120 | Plant | E1-4-12 | [15] |
| 3 | Rpp1 | KS 1034 × BRS184 | F2 | 163 | Leaf | E1-4-12 | [14] |
| 4 | Rpp1-b | BRS184 × PI 594767A | F2 | 82 | Plant | T1-2 | [16] |
| 5 | Rpp1-b | BRS184 × PI 587905 | F2 | 117 | Plant | T1-2 | [16] |
| 6 | Rpp1-b | BRS184 × PI 587855 | F2 | 106 | Plant | E1-4-12 | [17] |
| 7 | Rpp1-b1 | PI 587880A × No12-1-A | F2 | 96 | Plant | BRP-2.1 | - |
| 8 | Rpp2 | Iyodaizu B × BRS184 | F2 | 143 | Plant | E1-4-12 | [15] |
| 9 | Rpp3 | BRS184 × PI 416764 | F2 | 86 | Plant | T1-2 | [16] |
| 10 | Rpp4 | BRS184 × PI 459025 | BC3F2 | 97 | Plant | E1-4-12 | - |
| 11 | Rpp5, (Rpp3) | BRS184 × Kinoshita 2 | F2 | 130 | Leaf | BRP-2.5, E1-4-12 | - |
| 12 | Rpp5, (Rpp3) | BRS184 × Shiranui | F2 | 138 | Leaf | BRP-2.5, E1-4-12 | - |
| 13 | Rpp6 | BRS184 × PI 567102B | F2 | 100 | Plant | E1-4-12 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamanaka, N.; Aoyagi, L.N.; Hossain, M.M.; Aoyagi, M.B.F.; Muraki, Y. Genetic Mapping of Seven Kinds of Locus for Resistance to Asian Soybean Rust. Plants 2023, 12, 2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122263
Yamanaka N, Aoyagi LN, Hossain MM, Aoyagi MBF, Muraki Y. Genetic Mapping of Seven Kinds of Locus for Resistance to Asian Soybean Rust. Plants. 2023; 12(12):2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122263
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamanaka, Naoki, Luciano N. Aoyagi, Md. Motaher Hossain, Martina B. F. Aoyagi, and Yukie Muraki. 2023. "Genetic Mapping of Seven Kinds of Locus for Resistance to Asian Soybean Rust" Plants 12, no. 12: 2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122263
APA StyleYamanaka, N., Aoyagi, L. N., Hossain, M. M., Aoyagi, M. B. F., & Muraki, Y. (2023). Genetic Mapping of Seven Kinds of Locus for Resistance to Asian Soybean Rust. Plants, 12(12), 2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122263








