Magnolin Inhibits Paclitaxel-Induced Cold Allodynia and ERK1/2 Activation in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation of Magnolin
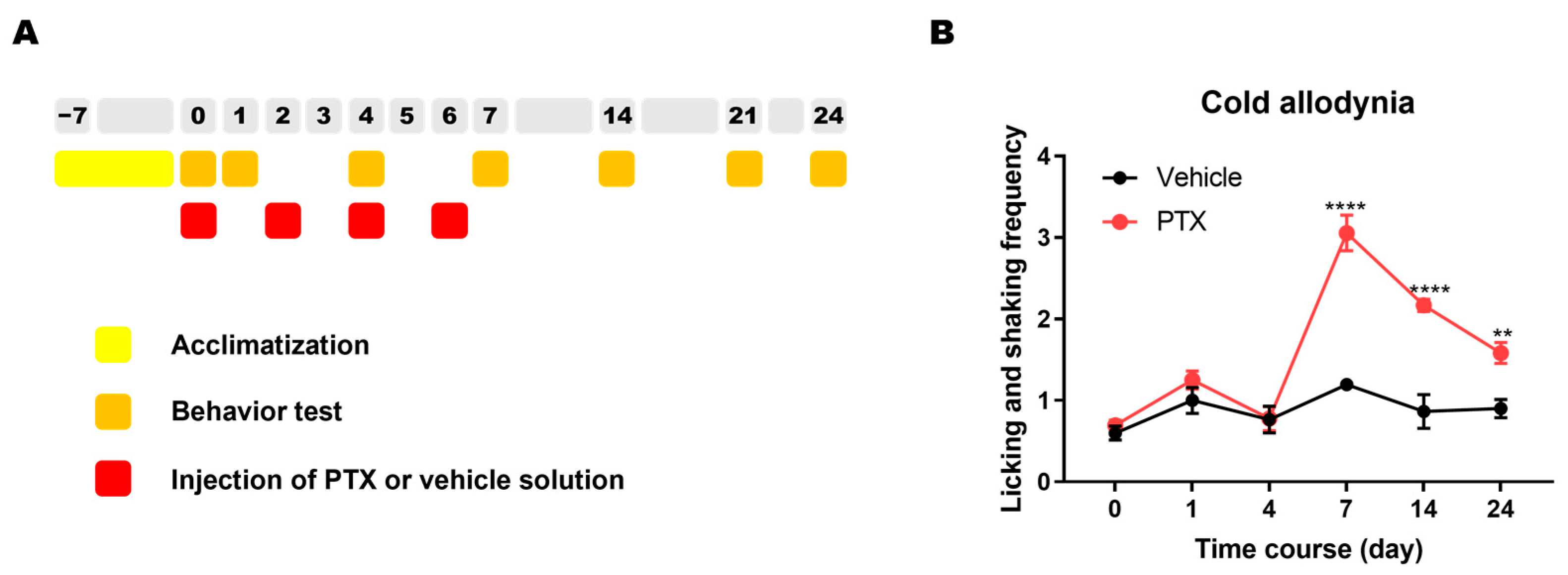
2.2. Cold Allodynia in Mice after Injection of PTX
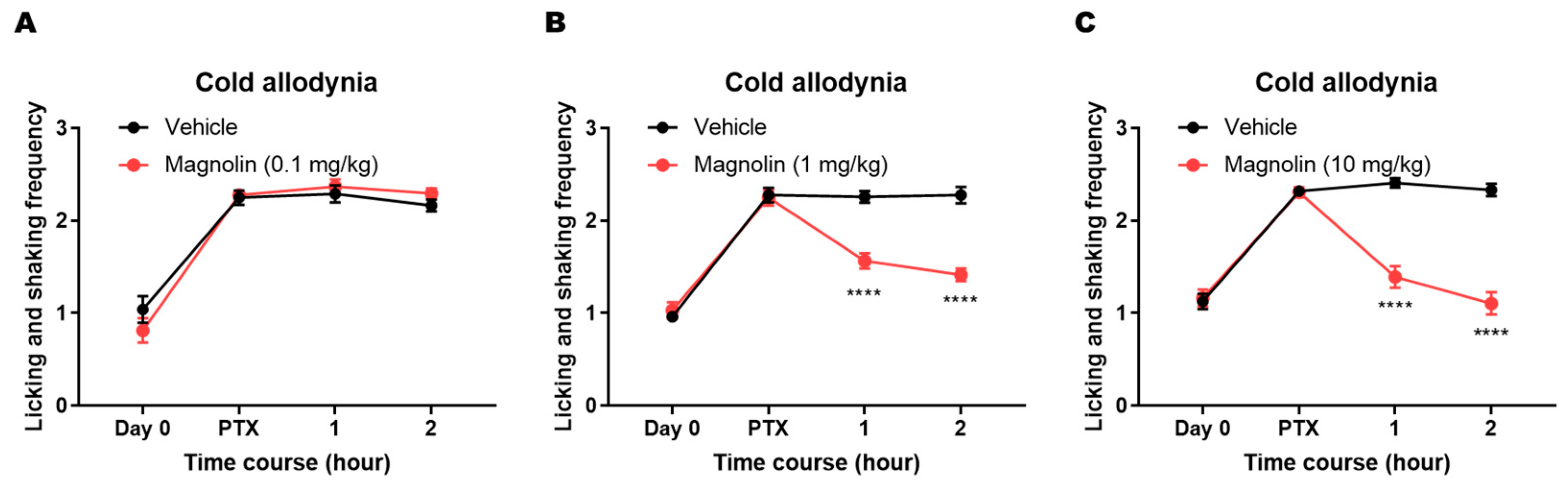
2.3. Analgesic Effect of Magnolin on PTX-Induced Cold Allodynia
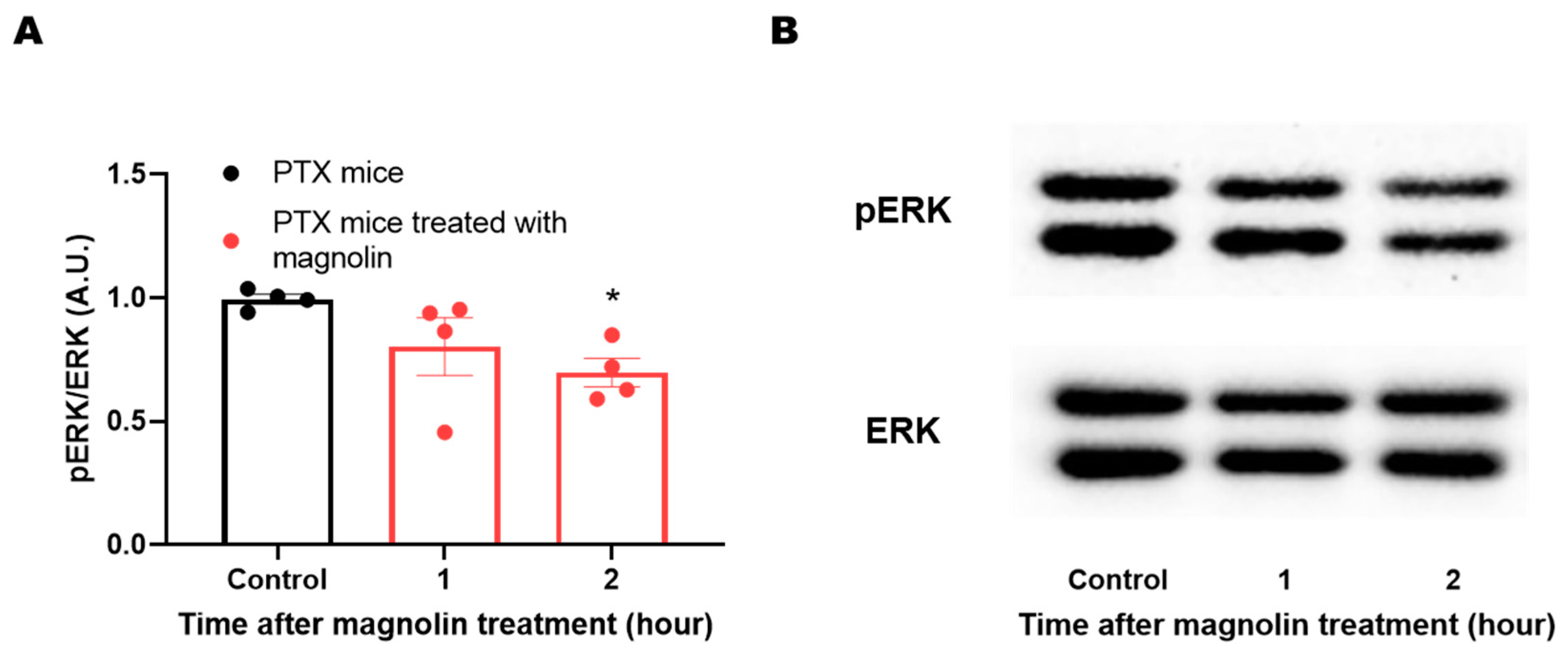
2.4. Effect of Magnolin Treatment on ERK Phosphorylation in the DRG of PTX-Treated Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. UHPLC-PDA-MS Analysis
4.3. Isolation of Major Lignans from M. denudata
4.3.1. (+)-Magnolin (1)
4.3.2. Kobusin (2)
4.3.3. Aschantin (3)
4.4. Experimental Animals
4.5. Paclitaxel Administration
4.6. Behavioral Assessment
4.7. Experimental Schedule
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alqahtani, F.Y.; Aleanizy, F.S.; El Tahir, E.; Alkahtani, H.M.; AlQuadeib, B.T. Chapter Three—Paclitaxel. In Profiles of Drug Substances, Excipients and Related Methodology; Brittain, H.G., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2019; Volume 44, pp. 205–238. [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty, P.M.; Cata, J.P.; Cordella, J.V.; Burton, A.; Weng, H.-R. Taxol-induced sensory disturbance is characterized by preferential impairment of myelinated fiber function in cancer patients. Pain 2004, 109, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.L.; Lopes, A.H.; Guimarães, R.M.; Cunha, T.M. CXCL1/CXCR2 signaling in pathological pain: Role in peripheral and central sensitization. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 105, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, H.S.; Bae, C.; Wang, J.; Lee, K.H.; Hankerd, K.M.; Kim, H.K.; Chung, J.M.; La, J.H. Peripheral and central oxidative stress in chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. Mol. Pain 2019, 15, 1744806919840098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Garraway, S.M.; Weyerbacher, A.R.; Shin, S.J.; Inturrisi, C.E. Activation of the neuronal extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 in the spinal cord dorsal horn is required for complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced pain hypersensitivity. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 14087–14096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-B.; Jing, P.-B.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Cao, D.-L.; Gao, M.-H.; Jiang, B.-C.; Gao, Y.-J. Chemokine receptor CCR2 contributes to neuropathic pain and the associated depression via increasing NR2B-mediated currents in both D1 and D2 dopamine receptor-containing medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens shell. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 2320–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Jin, F.H.; Zhang, M.Y.; Qi, F. Inhibition of Peripheral ERK Signaling Ameliorates Persistent Muscle Pain Around Trigger Points in Rats. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 963689720960190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.T.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Hong, J.; Liu, J.; Wu, L.J.; Zhang, C.H.; Wu, H.G.; et al. Moxibustion eases chronic inflammatory visceral pain through regulating MEK, ERK and CREB in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6220–6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, R. Overexpression of miR-206 ameliorates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in rats via the MEK/ERK pathway by targeting brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 646, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Quirion, R. The ERK/MAPK pathway, as a target for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2005, 9, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xiao, Y.; Li, S.; Zhu, X.; Meng, L.; Song, C.; Yu, C.; Jiang, N.; Liu, Y. Synergistic activity of magnolin combined with B-RAF inhibitor SB590885 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via targeting PI3K-AKT/mTOR and ERK MAPK pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 3816–3824. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, D.K. Therapeutic Effectiveness of Magnolin on Cancers and Other Human complications. Pharmacol. Res. Mod. Chin. Med. 2022, 6, 100203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.J.; Lee, H.S.; Ryu, H.W.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, Z.; Lee, H.K.; Oh, S.R.; Cho, Y.Y. Targeting of magnolin on ERKs inhibits Ras/ERKs/RSK2-signaling-mediated neoplastic cell transformation. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Li, A.; Huang, Y.; Teng, R.H.; Yang, Y.; Yao, Y.X. CXCR3 contributes to neuropathic pain via ERK activation in the anterior cingulate cortex. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 531, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, S.B.; Gao, Y.J.; Xing, J.L.; Xian, H.; Li, Z.Z.; Shen, S.N.; Wu, S.X.; Luo, C.; Xie, R.G. Spinal CCL2 Promotes Pain Sensitization by Rapid Enhancement of NMDA-Induced Currents Through the ERK-GluN2B Pathway in Mouse Lamina II Neurons. Neurosci. Bull. 2020, 36, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z.J. Proteinase-activated receptor 2 sensitizes transient receptor potential vanilloid 1, transient receptor potential vanilloid 4, and transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 in paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 2011, 193, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.D.; Xiao, Y. Involvement of the Sodium Channel Nav1.7 in Paclitaxel-induced Peripheral Neuropathy through ERK1/2 Signaling in Rats. Curr. Neurovascular Res. 2020, 17, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.-H.; Kim, J.-A.; Park, S.-H.; Son, A.-R.; Chang, T.-S.; Chang, H.-W.; Chung, S.-R.; Lee, S.-H. Isolation of melanin biosynthesis inhibitory compounds from the flowers of Magnolia denudata. Korean J. Pharmacogn. 2004, 35, 152–156. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Jeon, C.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, J.U.; Quan, F.S.; Lee, K.; Kim, W.; Kim, S.K. Suppressive Effects of Bee Venom Acupuncture on Paclitaxel-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats: Mediation by Spinal α2-Adrenergic Receptor. Toxins 2017, 9, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, J.U.; Quan, F.S.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, W. The efficacy of combination treatment of gabapentin and electro-acupuncture on paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 21, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yoo, J.H.; Kim, S.K. Long-Lasting and Additive Analgesic Effects of Combined Treatment of Bee Venom Acupuncture and Venlafaxine on Paclitaxel-Induced Allodynia in Mice. Toxins 2020, 12, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, G.; Kim, S.K. Therapeutics for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: Approaches with Natural Compounds from Traditional Eastern Medicine. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Z.Y.; Gerner, P.; Woolf, C.J.; Ji, R.R. ERK is sequentially activated in neurons, microglia, and astrocytes by spinal nerve ligation and contributes to mechanical allodynia in this neuropathic pain model. Pain 2005, 114, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Zhuo, M. Activation of Erk in the anterior cingulate cortex during the induction and expression of chronic pain. Mol. Pain. 2008, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, M.; Tian, Z.; Darvish-Ghane, S.; Zhuo, M. Pre-LTP requires extracellular signal-regulated kinase in the ACC. Mol. Pain. 2016, 12, 1744806916647373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, G.; Kim, S.J. Sustained Activity of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor: Homer, Arrestin, and Beyond. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 5125624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, S.M.; Liu, J.; Hsu, T.; Baguley, B.C.; McKeage, M.J. Paclitaxel induces nucleolar enlargement in dorsal root ganglion neurons in vivo reducing oxaliplatin toxicity. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 1942–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.S.; Akter, S.; Ramproshad, S.; Mondal, B.; Riaz, T.A.; Islam, M.T.; Khan, I.N.; Docea, A.O.; Calina, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; et al. Targeting Ras-ERK cascade by bioactive natural products for potential treatment of cancer: An updated overview. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.Y.; Shin, S.H.; Lee, M.H.; Malakhova, M.; Kurinov, I.; Wu, Q.; Xu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Liu, K.; et al. A natural small molecule, catechol, induces c-Myc degradation by directly targeting ERK2 in lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 35001–35014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi Jeong, S.; Davaatseren, M.; Kim, W.; Sung Kwang, P.; Kim, S.H.; Haeng Jeon, H.; Myung Sunny, K.; Kim, Y.S.; Dae Young, K. Vitisin A suppresses LPS-induced NO production by inhibiting ERK, p38, and NF-kappaB activation in RAW 264.7 cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polier, G.; Neumann, J.; Thuaud, F.; Ribeiro, N.; Gelhaus, C.; Schmidt, H.; Giaisi, M.; Kohler, R.; Muller, W.W.; Proksch, P.; et al. The natural anticancer compounds rocaglamides inhibit the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway by targeting prohibitin 1 and 2. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilioti, E.; Holmbom, B.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Moutsatsou, P. Lignans 7-hydroxymatairesinol and 7-hydroxymatairesinol 2 exhibit anti-inflammatory activity in human aortic endothelial cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Bae, D.S.; Um, B.H.; Pan, C.H.; Kim, C.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.K. Anti-inflammatory effects of gomisin N, gomisin J, and schisandrin C isolated from the fruit of Schisandra chinensis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.S.; He, Y.H.; Zheng, X.K.; Dong, B.B.; Zhang, Y.L.; Cao, Y.G.; Yang, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.K. Lignans from flower buds of Magnolia biondii. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2018, 43, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lim, H.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.D.; Jeon, R.; Ryu, J.H. In vitro anti-inflammatory activity of lignans isolated from Magnolia fargesii. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 937–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.J.; Lee, M.H.; Yoo, S.M.; Choi, K.I.; Song, J.H.; Jang, J.H.; Oh, S.R.; Ryu, H.W.; Lee, H.S.; Surh, Y.J.; et al. Magnolin inhibits cell migration and invasion by targeting the ERKs/RSK2 signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, S.H.; Kim, P.S.; Cho, J.Y.; Park, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Yoo, E.S.; Baik, K.U.; Lee, J.S.; Park, M.H. Isolation and identification of inhibitory compounds on TNF-alpha production from Magnolia fargesii. Arch. Pharm. Res. 1998, 21, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.A.; Lee, Y.D.; Lee, C.B.; Go, H.K.; Kim, J.P.; Seo, J.J.; Rhee, Y.K.; Kim, A.M.; Na, D.J. Extracts of Magnoliae flos inhibit inducible nitric oxide synthase via ERK in human respiratory epithelial cells. Nitric Oxide 2009, 20, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, M.; Pouyssegur, J. Targeting the ERK signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Ann. Med. 2006, 38, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zou, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, J.; Chen, M. Magnolin inhibits prostate cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Huang, K.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Q. Magnolin Inhibits Proliferation and Invasion of Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells by Targeting the ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 68, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Lee, C.J.; An, H.J.; Yoo, S.M.; Kang, H.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, K.D.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, H.S.; Cho, Y.Y. Magnolin targeting of ERK1/2 inhibits cell proliferation and colony growth by induction of cellular senescence in ovarian cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Gui, D.; Li, J.; Xing, T.; Wang, N. Magnolin protects against contrast-induced nephropathy in rats via antioxidation and antiapoptosis. Oxidative Med. Cell Longev. 2014, 2014, 203458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.J.; Pan, W.W.; Liu, S.B.; Shen, Z.F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, M.; Belcher, E.K.; Mohile, N.A.; Kesler, S.R.; Janelsins, M.C.; Hohmann, A.G.; Kleckner, I.R. Review of the Role of the Brain in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 693133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, H.K.; Kim, W.; Kim, S.K. Phytochemicals of Cinnamomi Cortex: Cinnamic Acid, but not Cinnamaldehyde, Attenuates Oxaliplatin-Induced Cold and Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats. Nutrients 2019, 11, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, W.; Yoon, S.H.; Kim, S.K. Anti-allodynic effect of Buja in a rat model of oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy via spinal astrocytes and pro-inflammatory cytokines suppression. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, W.; Li, D.; Kim, Y.; Lee, K.; Kim, S.K. The Suppressive Effects of Cinnamomi Cortex and Its Phytocompound Coumarin on Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Cold Allodynia in Rats. Molecules 2016, 21, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, B.S.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, H.N.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, D.S.; Bae, H.; Min, B.I.; Kim, S.K. Gyejigachulbu-Tang Relieves Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Cold and Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats via the Suppression of Spinal Glial Activation. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2014, 2014, 436482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, D.I.; Wood, J.N.; Emery, E.C. Molecular mechanisms of cold pain. Neurobiol. Pain 2020, 7, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.I.; Luiz, A.P.; Iseppon, F.; Millet, Q.; Emery, E.C.; Wood, J.N. Silent cold-sensing neurons contribute to cold allodynia in neuropathic pain. Brain 2021, 144, 1711–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carozzi, V.A.; Canta, A.; Chiorazzi, A. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: What do we know about mechanisms? Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 596, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruta, T.; Nemoto, T.; Hidaka, K.; Koshida, T.; Shirasaka, T.; Yanagita, T.; Takeya, R.; Tsuneyoshi, I. Upregulation of ERK phosphorylation in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons contributes to oxaliplatin-induced chronic neuropathic pain. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, H.; Gagnon, J.; Therrien, M. ERK signalling: A master regulator of cell behaviour, life and fate. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 607–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, W.; Zhen, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Niu, X.; Zhang, B.; Yang, Z.; Peng, D. Mechanism of ERK/CREB pathway in pain and analgesia. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1156674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jia, Z.K.; Chen, F.J.; Sang, Z.Y.; Ma, L.Y. Comparative analysis of natural cold acclimation and deacclimation of two Magnolia species with different winter hardiness. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2015, 37, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Duan, X.; Zhu, Z.; Sang, Z.; Duan, J.; Jia, Z.; Ma, L. Physiological and transcriptome analysis of Magnolia denudata leaf buds during long-term cold acclimation. BMC Plant. Biol. 2021, 21, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polomano, R.C.; Mannes, A.J.; Clark, U.S.; Bennett, G.J. A painful peripheral neuropathy in the rat produced by the chemotherapeutic drug, paclitaxel. Pain 2001, 94, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatters, S.J.; Bennett, G.J. Ethosuximide reverses paclitaxel- and vincristine-induced painful peripheral neuropathy. Pain 2004, 109, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Chung, Y.; Choi, S.; Min, B.I.; Kim, S.K. Duloxetine Protects against Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain and Spinal Neuron Hyperexcitability in Rodents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, N.; Chung, G.; Son, S.-R.; Park, J.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Park, K.-T.; Cho, I.-H.; Jang, D.S.; Kim, S.K. Magnolin Inhibits Paclitaxel-Induced Cold Allodynia and ERK1/2 Activation in Mice. Plants 2023, 12, 2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122283
Kim N, Chung G, Son S-R, Park JH, Lee YH, Park K-T, Cho I-H, Jang DS, Kim SK. Magnolin Inhibits Paclitaxel-Induced Cold Allodynia and ERK1/2 Activation in Mice. Plants. 2023; 12(12):2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122283
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Nari, Geehoon Chung, So-Ri Son, Jae Hyun Park, Young Hyun Lee, Keon-Tae Park, Ik-Hyun Cho, Dae Sik Jang, and Sun Kwang Kim. 2023. "Magnolin Inhibits Paclitaxel-Induced Cold Allodynia and ERK1/2 Activation in Mice" Plants 12, no. 12: 2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122283
APA StyleKim, N., Chung, G., Son, S.-R., Park, J. H., Lee, Y. H., Park, K.-T., Cho, I.-H., Jang, D. S., & Kim, S. K. (2023). Magnolin Inhibits Paclitaxel-Induced Cold Allodynia and ERK1/2 Activation in Mice. Plants, 12(12), 2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122283







