Glandular and Non-Glandular Trichomes from Phlomis herba-venti subsp. pungens Leaves: Light, Confocal, and Scanning Electron Microscopy and Histochemistry of the Secretory Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Trichomes Distribution—Two Types of Trichomes were Observed on the Leaf Epidermis: Glandular (Capitates and Dendroids) and Non-Glandular (Figure 3)
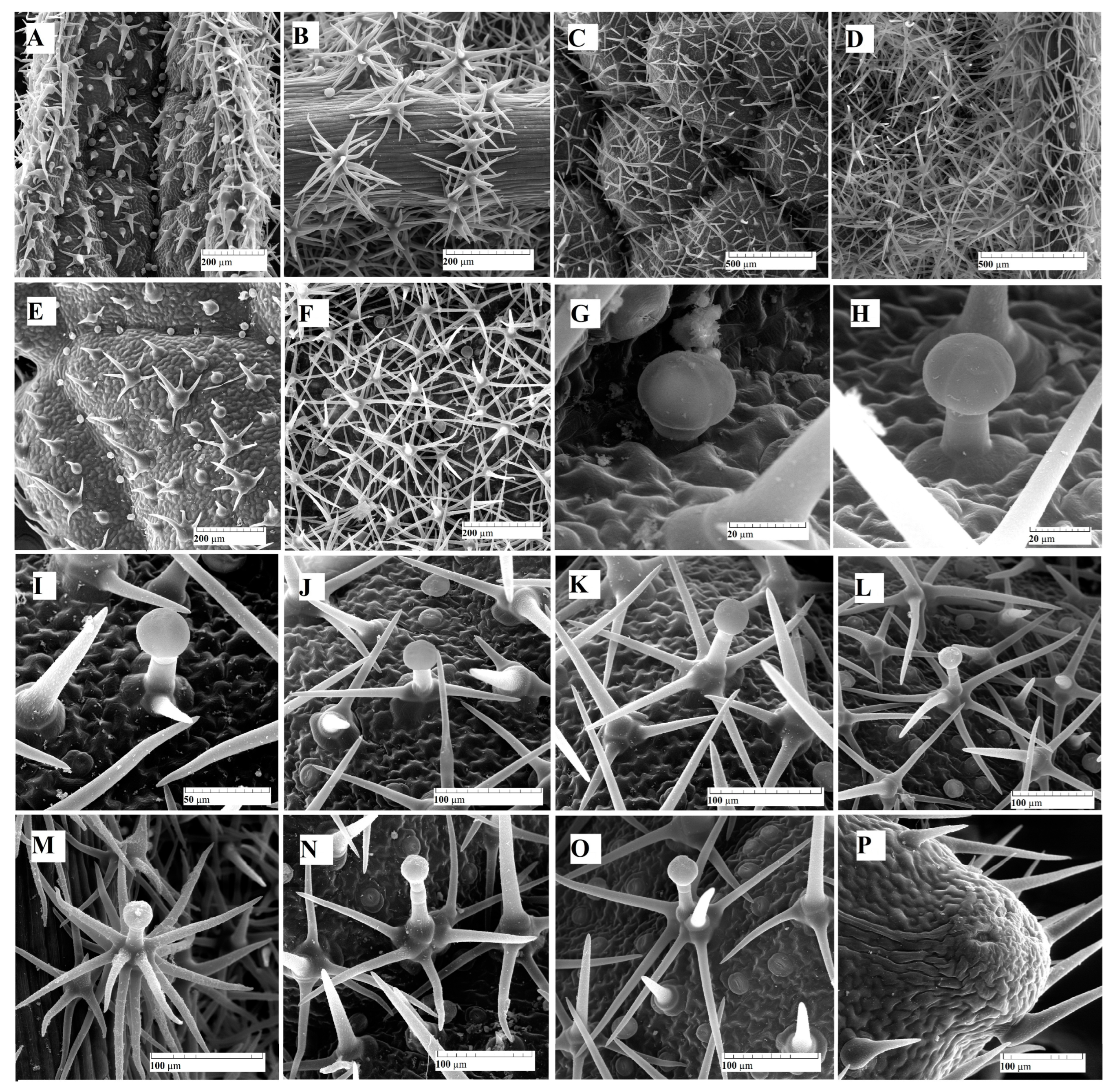
2.2. Microscopic Description of Trichomes
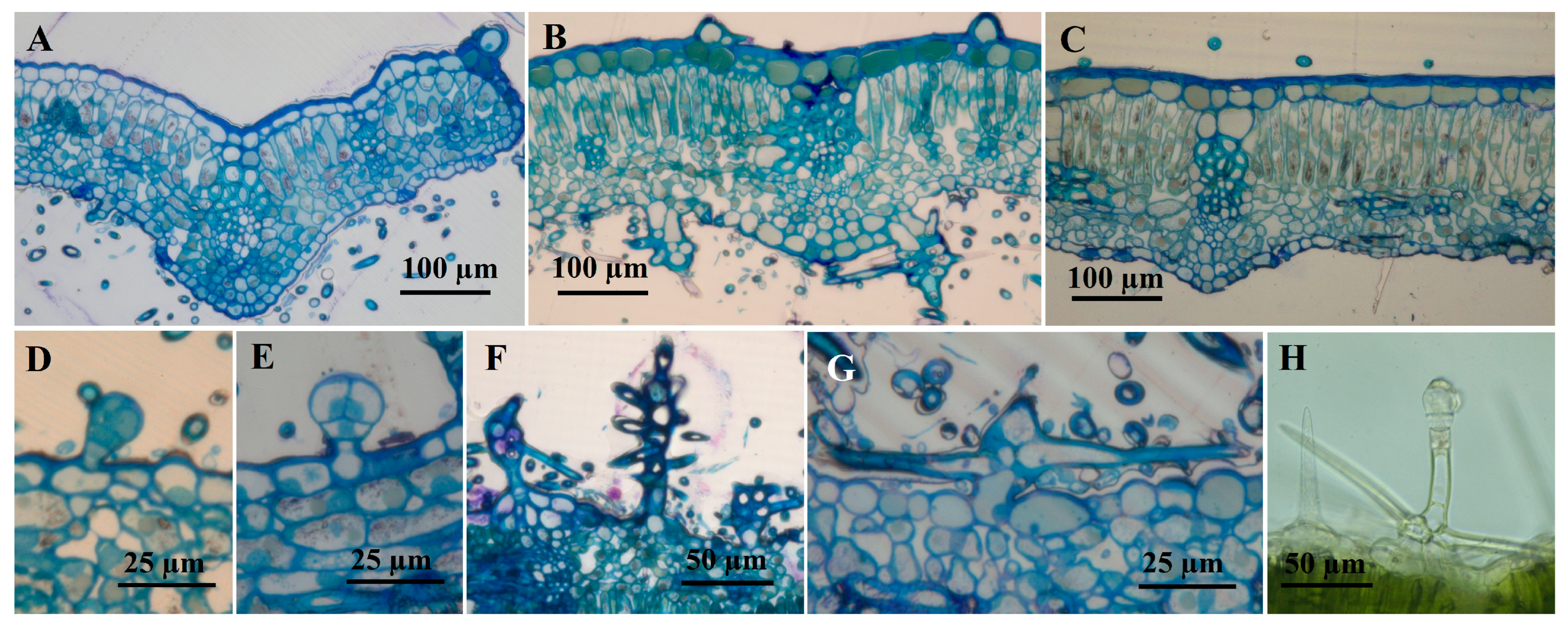
2.3. Histochemistry of Glandular Trichomes
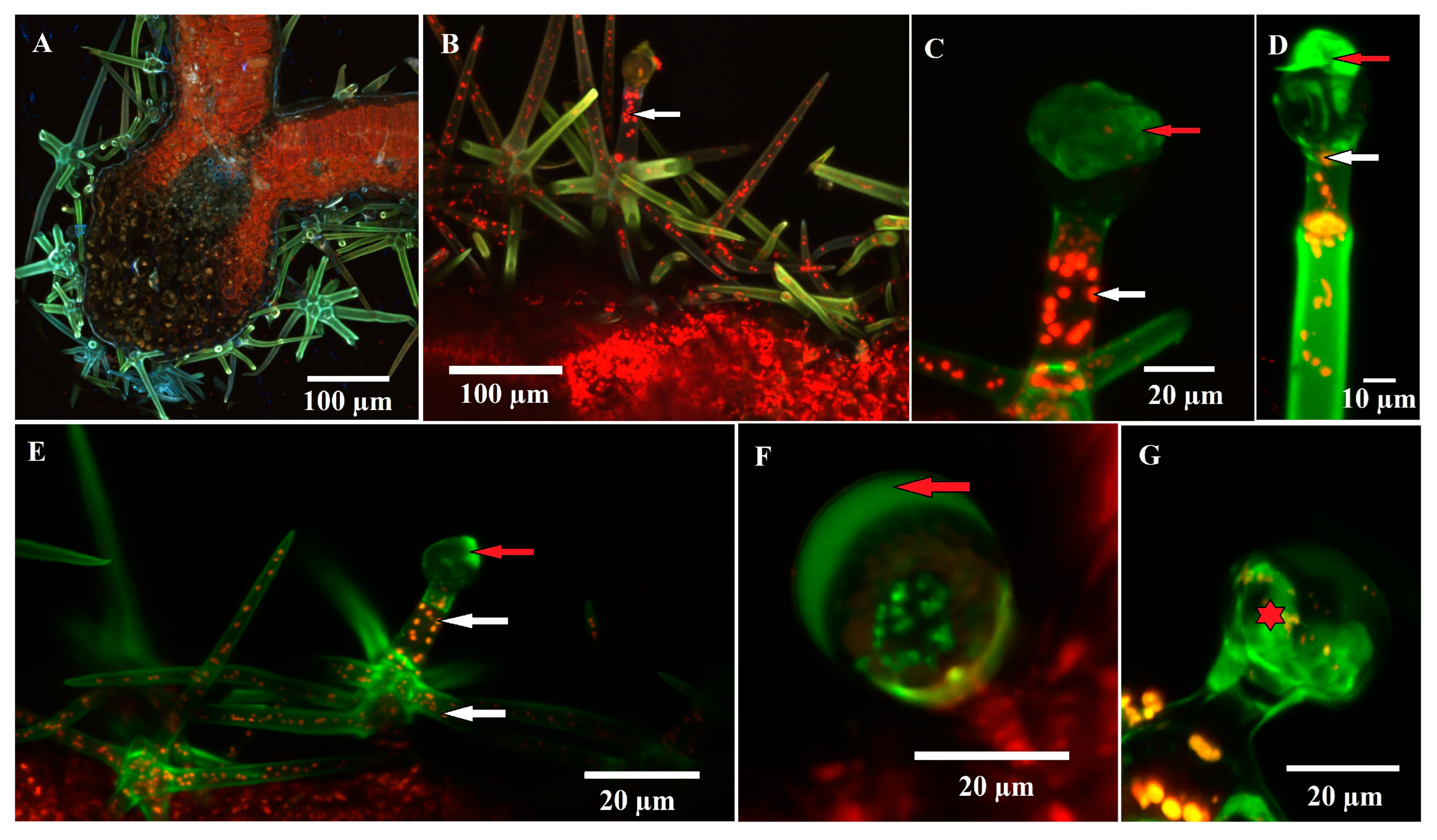
2.4. Confocal Microscopy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Light Microscopy
4.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.4. Histochemical Investigations
4.5. Confocal Microscopy
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Shen, C.; Meng, P.; Tan, G.; Lv, L. Analysis and Review of Trichomes in Plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, D.A. The Role of Trichomes in Plant Defense. Q. Rev. Biol. 1973, 48, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gairola, S.; Naidoo, Y.; Bhatt, A.; Nicholas, A. An Investigation of the Foliar Trichomes of Tetradenia riparia (Hochst.) Codd [Lamiaceae]: An Important Medicinal Plant of Southern Africa. Flora—Morphol. Distrib. Funct. Ecol. Plants 2009, 204, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstic, L.; Malencic, D.; Anackov, G. Structural Investigations of Trichomes and Essential Oil Composition of Salvia verticillata. Bot. Helv. 2006, 116, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi, G. Glandular Hairs of Salvia officinalis: New Data on Morphology, Localization and Histochemistry in Relation to Function. Ann. Bot. 1999, 84, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkama, E. Changes in Leaf Trichomes and Epicuticular Flavonoids during Leaf Development in Three Birch Taxa. Ann. Bot. 2004, 94, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.-K.; Hong, S.-P.; Smets, E.; Huysmans, S. Phylogenetic Significance of Leaf Micromorphology and Anatomy in the Tribe Mentheae (Nepetoideae: Lamiaceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2009, 160, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüzbaşıoğlu, E.; Dadandı, M.Y.; Özcan, S. Estimation of Phylogenetic Relationships of Phlomis Species Based on Seed Protein Polymorphism. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 12, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.-Z. Comparative Analysis of Essential Oil Components of Three Phlomis Species in Qinling Mountains of China. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywood, V.H. Flora Europaea: Notulae Systematicae ad Floram Europaeam Spectantes: No. 9. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1971, 64, 199–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morteza-Semnani, K.; Saeedi, M.; Mahdavi, M.R.; Rahimi, F. Antimicrobial Studies on Extracts of Three Species of Phlomis. Pharm. Biol. 2006, 44, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çam, M.E.; Bulut, G.; Hazar Yavuz, A.N.; Kabasakal, L.; Taşkın, T. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Phlomis pungens and Coridothymus capitatus. mpj 2018, 22, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, V.P.; Raman, V.; Raeski, P.A.; Urban, A.M.; Swiech, J.N.; Miguel, M.D.; Farago, P.V.; Khan, I.A.; Budel, J.M. Anatomy, Micromorphology, and Histochemistry of Leaves and Stems of Cantinoa althaeifolia (Lamiaceae). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2020, 83, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascensão, L. Glandular Trichomes on the Leaves and Flowers of Plectranthus ornatus: Morphology, Distribution and Histochemistry. Ann. Bot. 1999, 84, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coisin, M.; Gostin, I. Micromorphological Data Concerning Salvia glutinosa L. (Lamiaceae). An. Stiint. Univ. Al. I. Cuza Iasi Sect. II A Biol. Veg. 2011, 57, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Çalı, I.Ö. Anatomy and Trichome Characteristics of Endemic Taxon Phlomis russeliana (Sims.) Bentham and Their Systematic Implications. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2016, 45, 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Gostin, I.; Nistor, A. Histo-Anatomical Pecularities of Vegetative Aerial Organs of Phlomis tuberosa from David’s Valley Reservation Iasi. Lucr. Stiint. Ser. Hortic. (USAMV Iasi) 2007, 50, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Haratym, W.; Weryszko-Chmielewska, E. Ultrastructural and Histochemical Analysis of Glandular Trichomes of Marrubium vulgare L. (Lamiaceae). Flora 2017, 231, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Kirchoff, B.K.; Liao, J. The Capitate and Peltate Glandular Trichomes of Lavandula pinnata L. (Lamiaceae): Histochemistry, Ultrastructure, and Secretion. J. Torrey Bot. Soc. 2008, 135, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, A.; Demirci, B.; Baser, K.H.C. Micromorphology of Glandular Trichomes of Nepeta congesta Fisch. & Mey. Var. congesta (Lamiaceae) and Chemical Analysis of the Essential Oils. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2007, 73, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Srividya, N.; Parrish, A.N.; Yue, W.; Shan, M.; Wu, Q.; Lange, B.M. Morphology of Glandular Trichomes of Japanese Catnip (Schizonepeta tenuifolia Briquet) and Developmental Dynamics of Their Secretory Activity. Phytochemistry 2018, 150, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidoo, Y.; Kasim, N.; Heneidak, S.; Nicholas, A.; Naidoo, G. Foliar Secretory Trichomes of Ocimum obovatum (Lamiaceae): Micromorphological Structure and Histochemistry. Plant Syst. Evol. 2013, 299, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, Y.; Dladla, T.; Dewir, Y.H.; Gangaram, S.; Naidoo, C.M.; Rihan, H.Z. The Micromorphology and Histochemistry of Foliar Mixed Indumentum of Leucas lavandulaefolia (Lamiaceae). Plants 2021, 10, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedi, Z.; Salmaki, Y. Trichome Morphology and Its Significance in the Systematics of Phlomoides (Lamiaceae; Lamioideae; Phlomideae). Flora—Morphol. Distrib. Funct. Ecol. Plants 2015, 213, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolakaki, A.; Christodoulakis, N.S. Secretory Structures and Cytochemical Investigation of the Leaf of Phlomis fruticosa, a Seasonally Dimorphic Subshrub. Secreting Activity of the Leaf-Originating Calluses. Flora—Morphol. Distrib. Funct. Ecol. Plants 2007, 202, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, H.; Amirahmadi, A.; Atri, M.; Naderi, R. An Investigation of the Anatomy, Palynology and Trichome Types of Phlomis olivieri (Lamiaceae). Taxon. Biosyst. 2014, 6, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Yetişen, K. Morphological and Anatomical Study of the Endemic Species Phlomis monocephala (Lamiaceae). Phytol. Balc. 2014, 20, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Delnavazi, M.R.; Baba-Ali, F.; Soufiabadi, S.; Sherafatmand, M.; Ghahremani, F.; Tavakoli, S.; Yassa, N. Essential Oil Composition, Antioxidant Activity and Total Phenolic Content of Some Lamiaceae Taxa Growing in Northwest of Iran. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 20, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sarikurkcu, C.; Uren, M.C.; Kocak, M.S.; Cengiz, M.; Tepe, B. Chemical Composition, Antioxidant, and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities of the Essential Oils of Three Phlomis Species as Well as Their Fatty Acid Compositions. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalilzadeh, M.A.; Tajbakhsh, M.; Rineh, A. Study of the Essential Oils Composition of Leaves and Flowers of Two Subspecies Phlomis herba-venti (Pungens and Lenkoranica) from Iran. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2008, 20, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi, S.; Rustaiyan, A.; Azar, P.A.; Larijani, K. Composition of the Essential Oils of Cyclotrichium straussii (Bornm.) Rech. f. and Phlomis pungens Willd. from Iran. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2006, 18, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morteza-Semnani, K.; Azadbakht, M.; Goodarzi, A. The Essential Oils Composition of Phlomis herba-venti L. Leaves and flowers of Iranian Origin. Flavour Fragr. J. 2004, 19, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, M. Improved Staining Procedures for Photographic Documentation of Phenolic Deposits in Semithin Sections of Plant Tissue. J. Microsc. 1995, 179, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabe, M. Techniques Histologiques; Masson e Cie: Paris, France, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Gahan, P.B. Plant Histochemistry and Cytochemistry; Academic Press: London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Cappelletti, E.M.; Caniato, R.; Appendino, G. Localization of the Cytotoxic Hydroperoxyeudesmanolides in Artemisia Umbelliformis. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1986, 14, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, R.; Carde, J.P. Histochimie—Coloration Differentielle des Inclusions Lipidiques et Terpeniques des Pseudophylles du Pin Maritime au Moyen du Reactif NADI. C. R. Hebd. Seances L’Acad. Sci. 1964, 258, 1338. [Google Scholar]
- High, O.B. Lipid Histochemistry; Royal Microscopical Society: Microscopy Handbooks 06; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- McManus, J.F.A. Histological and Histochemical Uses of Periodic Acid. Stain Technol. 1948, 23, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundrett, M.C.; Kendrick, B.; Peterson, C.A. Efficient Lipid Staining in Plant Material with Sudan Red 7B or Fluoral Yellow 088 in Polyethylene Glycol-Glycerol. Biotech. Histochem. 1991, 66, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, D.A. Plant Microtechnique; McGrawHill: New York, NY, USA, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Pearse, A.G.E. Histochemistry Theorical and Applied; Churchill Livingston: Edinburgh, UK, 1985; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Santos Tozin, L.R.D.; De Melo Silva, S.C.; Rodrigues, T.M. Non-Glandular Trichomes in Lamiaceae and Verbenaceae Species: Morphological and Histochemical Features Indicate More than Physical Protection. N. Z. J. Bot. 2016, 54, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, I.E. Unicitatea Patrimoniului Natural Din Rezervaţia de Fâneţe Seculare de La Valea Lui David Iaşi. Mnemosyne 2013, 4, 7–37. [Google Scholar]
- Fahn, A. Secretory Tissues in Vascular Plants. New Phytol. 1988, 108, 229–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabourniotis, G.; Liakopoulos, G.; Nikolopoulos, D.; Bresta, P. Protective and Defensive Roles of Non-Glandular Trichomes against Multiple Stresses: Structure–Function Coordination. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, Y.; Heneidak, S.; Bhatt, A.; Kasim, N.; Naidoo, G. Morphology, Histochemistry, and Ultrastructure of Foliar Mucilage-Producing Trichomes of Harpagophytum Procumbens (Pedaliaceae). Turk. J. Bot. 2014, 38, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werker, E. Trichome Diversity and Development. Adv. Bot. Res. 2000, 31, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.K. Trichome Micromorphology of Egyptian Ballota (Lamiaceae) with Emphasis on Its Systematic Implication. Pak. J. Bot. 2012, 44, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, C.-L.; Dong, Z.-H.; Peng, H.; Liu, Z.-W. Trichome Micromorphology of the East Asiatic Genus Chelonopsis (Lamiaceae) and Its Systematic Implications. Flora—Morphol. Distrib. Funct. Ecol. Plants 2010, 205, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleci Bini, L.; Giuliani, C. The glandular trichomes of the Labiatae. A Review. Acta Hortic. 2006, 723, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, I.L.-B.; Boubaker, J.; Sgaier, M.B.; Skandrani, I.; Bhouri, W.; Neffati, A.; Kilani, S.; Bouhlel, I.; Ghedira, K.; Chekir-Ghedira, L. Phytochemistry and Biological Activities of Phlomis Species. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 125, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasaian, J.; Alesheikh, P.; Mohammadi, A. Chemical Compositions and Biological Activities of Scutellaria Genus Essential Oils (Lamiaceae). Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2020, 15, e62279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, Ö. Essential Oil and Fatty Acid Composition of Leaves of Some Lamiaceae Taxa from Turkey. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2018, 21, 1706–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzelac, B.; Stojičić, D.; Budimir, S. Glandular Trichomes on the Leaves of Nicotiana Tabacum: Morphology, Developmental Ultrastructure, and Secondary Metabolites. In Plant Cell and Tissue Differentiation and Secondary Metabolites; Ramawat, K.G., Ekiert, H.M., Goyal, S., Eds.; Reference Series in Phytochemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, C. Morphological and Anatomical Studies on Two Varieties of Phlomis pungens Wild. (Lamiaceae). Sci. Res. Essays 2011, 6, 5168–5178. [Google Scholar]
- Muravnik, L.E. The Structural Peculiarities of the Leaf Glandular Trichomes: A Review. In Plant Cell and Tissue Differentiation and Secondary Metabolites; Ramawat, K.G., Ekiert, H.M., Goyal, S., Eds.; Reference Series in Phytochemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, L. Autofluorescence in Plants. Molecules 2020, 25, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergau, N.; Bennewitz, S.; Syrowatka, F.; Hause, G.; Tissier, A. The Development of Type VI Glandular Trichomes in the Cultivated Tomato Solanum lycopersicum and a Related Wild Species S. habrochaites. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muravnik, L.E.; Kostina, O.V.; Mosina, A.A. Glandular Trichomes of the Leaves in Three Doronicum Species (Senecioneae, Asteraceae): Morphology, Histochemistry, and Ultrastructure. Protoplasma 2019, 256, 789–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergau, N.; Navarette Santos, A.; Henning, A.; Balcke, G.U.; Tissier, A. Autofluorescence as a Signal to Sort Developing Glandular Trichomes by Flow Cytometry. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 28, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
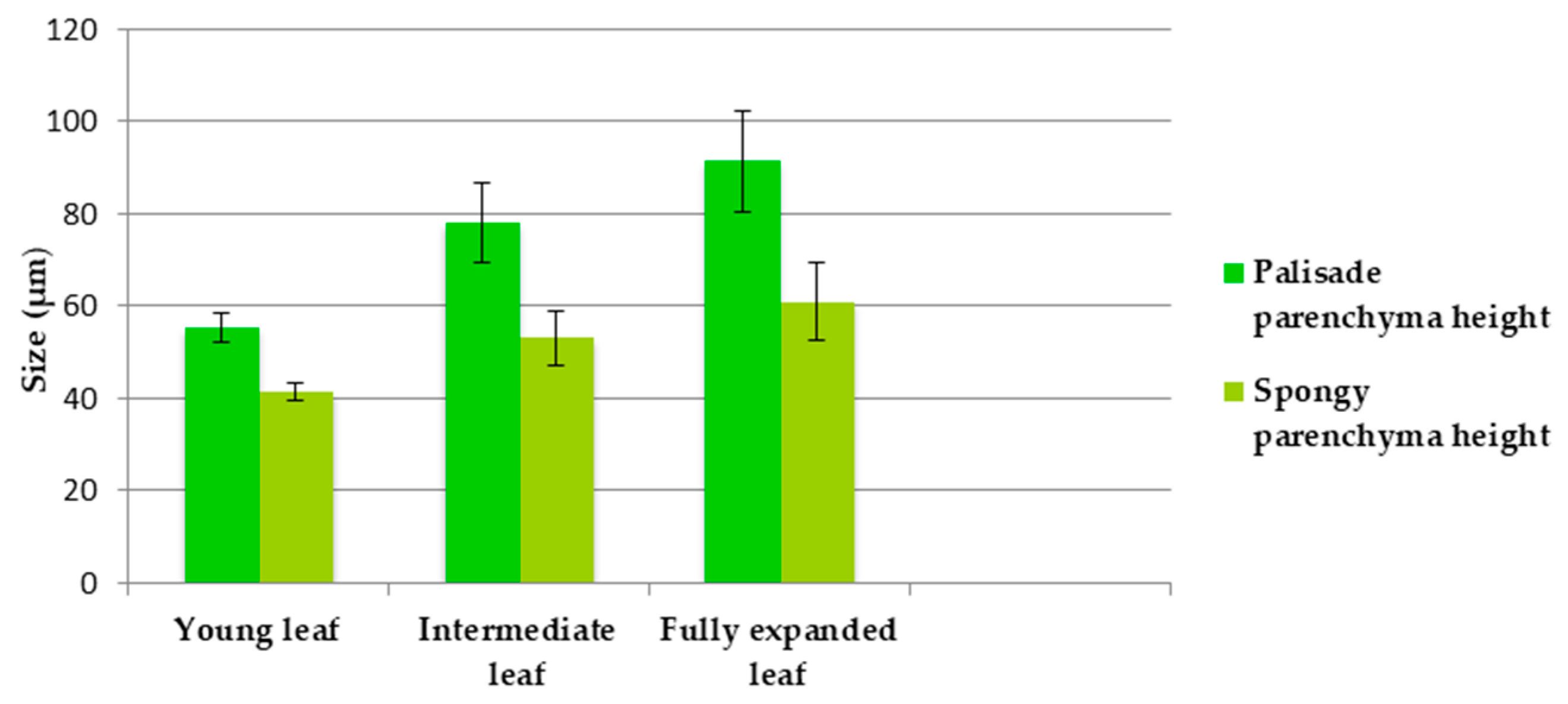


| Developmental Stage of the Leaf | Non-Glandular Trichomes/mm2 | Glandular Capitate Trichomes/mm2 | Glandular Dendroid Trichomes/mm2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper Epidermis | Lower Epidermis | Upper Epidermis | Lower Epidermis | Upper Epidermis | Lower Epidermis | |
| Very young leaf (S1) | 222.17 ± 44.71 | 225.70 ± 37.38 | 120.46 ± 31.57 | 56.12 ± 17.44 | 0 | 8.54 ± 8.23 |
| Intermediate leaf (S2) | 68.91 ± 9.15 | 95.82 ± 44.51 | 41.97 ± 15.34 | 25.39 ± 19.55 | 1.55 ± 2.5 | 14.36 ± 16.24 |
| Fully expanded leaf (S3) | 62.57 ± 9.28 | 86.94 ± 11.83 | 34.89 ± 15.84 | 17.38 ± 9.16 | 1.06 ± 3.35 | 2.89 ± 6.1 |
| Staining Technique | Target Product/Authors | Glandular Capitate Trichomes (C1) | Glandular Capitate Trichomes (C2) | Glandular Dendroid Trichomes (D) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | Figure | Color | Figure | Color | Figure | ||
| Toluidine Blue | Phenols (Gutmann 1995) [33] | Blue | 4C | Violet blue | 4D | Blue | 5A |
| Potassium dichromate | Phenolic compounds (Gabe, 1968) [34] | None | Not shown | Brown | 4E | Light brown | 5B |
| Ferric chloride | phenolic compounds (Gahan, 1984) [35] | Brown | Not shown | Brown | Not shown | Brown | 5C |
| Concentrated sulfuric acid | sesquiterpenes (Cappellatti et al., 1986) [36] | Yellow | 4F | No color | 4G | Dark yellow | 5D |
| NADI reagent | terpenes /essential oil (David and Carde, 1964) [37] | None | Not shown | Blue-violet | 4H, I | Blue | 5E, F |
| Nile Blue | Neutral lipids (pink) and acid lipids (blue) (High, 1984) [38] | Blue | 4K | Blue | 4J | Blue | 5G |
| PAS reagent | Polysaccharides (McManus, 1948) [39] | Red | 4L, M | None | 4N | Light red | 5H |
| Sudan Red | Total lipids (Brundett el al., 1991) [40] | Orange—red | 4O | Orange—red | 4P | Orange—red | 5I, J |
| Ruthenium Red | Acid polysaccharides (Johansen, 1940) [41] | Pink | 4R | No color | 4S | Pink | 5K |
| Sudan black | Total lipids (Pearse, 1985) [42] | Dark blue | 4T, U | Dark blue | Not shown | Dark blue | 5L |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gostin, I.N. Glandular and Non-Glandular Trichomes from Phlomis herba-venti subsp. pungens Leaves: Light, Confocal, and Scanning Electron Microscopy and Histochemistry of the Secretory Products. Plants 2023, 12, 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12132423
Gostin IN. Glandular and Non-Glandular Trichomes from Phlomis herba-venti subsp. pungens Leaves: Light, Confocal, and Scanning Electron Microscopy and Histochemistry of the Secretory Products. Plants. 2023; 12(13):2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12132423
Chicago/Turabian StyleGostin, Irina Neta. 2023. "Glandular and Non-Glandular Trichomes from Phlomis herba-venti subsp. pungens Leaves: Light, Confocal, and Scanning Electron Microscopy and Histochemistry of the Secretory Products" Plants 12, no. 13: 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12132423
APA StyleGostin, I. N. (2023). Glandular and Non-Glandular Trichomes from Phlomis herba-venti subsp. pungens Leaves: Light, Confocal, and Scanning Electron Microscopy and Histochemistry of the Secretory Products. Plants, 12(13), 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12132423






