Genome-Wide Association Study of Xian Rice Grain Shape and Weight in Different Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Distribution and Correlation of Phenotype and Heritability of Grain Shape
2.2. Population Structure, Kinship, and LD Decay
2.3. Identification of Significant Loci for Related Traits through GWAS
2.4. Candidate Gene Identification and Haplotype Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials, Field Trials and Trait Measurements
4.2. Statistical Analysis
4.3. Genetic Fractal and Population Structure Analysis
4.4. Genome-Wide Association Mapping
4.5. Identification of Candidate Genes and Haplotype Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.X.; Yu, J.P.; Qian, Q.; Shang, L.G. Enhancement of Heat and Drought Stress Tolerance in Rice by Genetic Manipulation: A Systematic Review. Rice 2022, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.G.; Li, X.X.; He, H.Y.; Yuan, Q.L.; Song, Y.N.; Wei, Z.R.; Lin, H.; Hu, M.; Zhao, F.L.; Zhang, C.; et al. A super pan-genomic landscape of rice. Cell Res. 2022, 32, 878–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahra, N.; Hafeez, M.B.; Nawaz, A.; Farooq, M. Rice production systems and grain quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2022, 105, 103463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calingacion, M.; Laborte, A.; Nelson, A.; Resurreccion, A.; Concepcion, J.C.; Daygon, V.D.; Mumm, R.; Reinke, R.; Dipti, S.; Bassinello, P.Z.; et al. Diversity of Global Rice Markets and the Science Required for Consumer-Targeted Rice Breeding. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russinga, A.M. Correlation Studies on Yield and Yield Contributing Traits in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ind. J. Pure App. Biosci. 2020, 8, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khush, G.S. What it will take to Feed 5.0 Billion Rice consumers in 2030. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 59, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Xu, J.; Zeng, D.; Zhang, B.; Geng, M.; Zhang, G.; Huang, K.; Huang, L.; Xu, R.; Ge, S.; et al. Natural Variation in the Promoter of GSE5 Contributes to Grain Size Diversity in Rice. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Chen, H. Analysis of Status and Constraints of Rice Production in the World. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2010, 43, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H. Identification of Grain Size-Related QTLs in Korean japonica Rice Using Genome Resequencing and High-Throughput Image Analysis. Agriculture 2022, 12, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, T.; Matsuoka, M. Identifying and exploiting grain yield genes in rice. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.F.; Xing, Y.Z.; Li, J.X.; Yu, S.B.; Xu, C.G.; Zhang, Q.F. Genetic bases of appearance quality of rice grains in Shanyou 63, an elite rice hybrid. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2000, 101, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, D.A.; Lu, B.R.; Tomooka, N. Was Asian rice (Oryza sativa) domesticated more than once? Rice 2008, 1, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, D.Q. Pathways to Asian Civilizations: Tracing the Origins and Spread of Rice and Rice Cultures. Rice 2011, 4, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Y.; Jiang, L.R.; Zheng, J.S.; Wang, T.S.; Wang, H.C.; Huang, Y.M.; Hong, Z.L. Genetic bases of rice grain shape: So many genes, so little known. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.B.; Cheng, S.H.; Qian, Q. Progress and Prospects of Breeding by Gene Design in Rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2008, 22, 650–657. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, H.E.; Wenhua, L.; Jiang, H.U.; Chunfang, Z.; Shu, Y.; Tao, C.; Zhen, Z.; Qingyong, Z.; Kai, L.U.; Ling, Z. Additive Effects of QTLs/Genes on Rice Grain Size Traits Revealed by Genetic Comparisons. Rice Sci. 2023, 30, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, M.J.; Tai, T.H.; McClung, A.M.; Lai, X.H.; Hinga, M.E.; Lobos, K.B.; Xu, Y.; Martinez, C.P.; McCouch, S.R. Mapping quantitative trait loci for yield, yield components and morphological traits in an advanced backcross population between Oryza rufipogon and the Oryza sativa cultivar Jefferson. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluko, G.; Martinez, C.; Tohme, J.; Castano, C.; Bergman, C.; Oard, J.H. QTL mapping of grain quality traits from the interspecific cross Oryza sativa × O. glaberrima. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.; Wei, X.H.; Sang, T.; Zhao, Q.A.; Feng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Zhu, C.R.; Lu, T.T.; Zhang, Z.W.; et al. Genome-wide association studies of 14 agronomic traits in rice landraces. Nature Genet. 2010, 42, 961–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, X.; Li, C.; Wang, A.; Zhao, Q.; Li, W.; Guo, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhu, C. Genome-wide association study of flowering time and grain yield traits in a worldwide collection of rice germplasm. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Xu, R.; Li, Y.H. Molecular Networks of Seed Size Control in Plants. In Annual Review of Plant Biology; Merchant, S.S., Ed.; Annual Reviews: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2019; Volume 70, pp. 435–463. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.B.; Tao, Q.D.; Miao, J.; Yang, Z.F.; Gu, M.H.; Liang, G.H.; Zhou, Y. Evaluation of differential qPE9-1/DEP1 protein domains in rice grain length and weight variation. Rice 2019, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.B.; Xu, X.D.; Xu, C.G.; Li, X.H.; Xiao, J.H.; Zhang, Q.F. Differential expression of GS5 regulates grain size in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 2611–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.Z.; Ma, M.; Bai, C.; Huang, X.H.; Liu, J.L.; Fan, Y.Y.; Song, X.J. TGW3, a Major QTL that Negatively Modulates Grain Length and Weight in Rice. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.Y.; Bi, J.P.; Chen, Y.C.; Jiang, C.J.; Cui, M.M.; Chen, Y.D.; Hou, X.; Yuan, M.; et al. Fine-tuning OsCPK18/OsCPK4 activity via genome editing of phosphorylation motif improves rice yield and immunity. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 2258–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Gou, Y.J.; Heng, Y.Q.; Ding, W.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Zhou, D.G.; Li, X.Q.; Liang, C.R.; Wu, C.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; et al. Targeted manipulation of grain shape genes effectively improves outcrossing rate and hybrid seed production in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.K.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Wu, K.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, S.S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.B.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, C.X.; et al. The OsSPL16-GW7 regulatory module determines grain shape and simultaneously improves rice yield and grain quality. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Han, R.; Wu, K.; Zhang, J.; Fu, X. G-protein βγ subunits determine grain size through interaction with MADS-domain transcription factors in rice. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 852. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.J.; Huang, W.; Shi, M.; Zhu, M.Z.; Lin, H.X. A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Y.X.; Fang, Y.X.; Zeng, L.J.; Xu, J.; Yu, H.P.; Shi, Z.Y.; Pan, J.J.; Zhang, D.; Kang, S.J.; et al. A Rare Allele of GS2 Enhances Grain Size and Grain Yield in Rice. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, R.H.; Tong, H.N.; Shi, B.H.; Liu, Y.Q.; Fang, S.R.; Liu, D.P.; Xiao, Y.H.; Hu, B.; Liu, L.C.; Wang, H.R.; et al. Control of grain size and rice yield by GL2-mediated brassinosteroid responses. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 15195, Erratum in Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 16002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Achievements and Challenges in Understanding Plant Abiotic Stress Responses and Tolerance. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 1569–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennisi, E. Plant genetics: The blue revolution, drop by drop, gene by gene. Science 2008, 320, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, A.L.; Patterson, N.J.; Plenge, R.M.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Shadick, N.A.; Reich, D. Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nature Genet. 2006, 38, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenaillon, M.I.; Sawkins, M.C.; Long, A.D.; Gaut, R.L.; Doebley, J.F.; Gaut, B.S. Patterns of DNA sequence polymorphism along chromosome 1 of maize (Zea mays ssp. mays L.). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9161–9166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shugeairy, Z. Genome Wide Association Mapping for Drought Recovery Trait in Rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Int. J. Appl. Agric. Sci. 2015, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yang, W.; Chang, Y.; Ma, X.; Tu, H.; Xiong, F.; Jiang, N.; Feng, H.; Huang, C.; Yang, P. Genome-Wide Association Studies of Image Traits Reveal Genetic Architecture of Drought Resistance in Rice. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habier, D.; Fernando, R.L.; Garrick, D.J. Genomic BLUP Decoded: A Look into the Black Box of Genomic Prediction. Genetics 2013, 194, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yueying, W.; Jahan, N.; Haitao, H.; Ping, C.; Lianguang, S.; Haiyan, L.; Guojun, D.; Jiang, H.; Zhenyu, G.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Analysis and Allelic Mining of Grain Shape-Related Traits in Rice. Rice Sci. 2019, 26, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chen, H.; Qian, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zheng, G.; Xiang, J.; Feng, T.; Li, M.; Zeng, W.; Bao, Y.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Rice Grain Shape and Chalkiness in a Worldwide Collection of Xian Accessions. Plants 2023, 12, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomura, A.; Izawa, T.; Ebana, K.; Ebitani, T.; Kanegae, H.; Konishi, S.; Yano, M. Deletion in a gene associated with grain size increased yields during rice domestication. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Ding, C.; Qian, Q. Molecular bases of rice grain size and quality for optimized productivity. Sci. Bull. 2023, 38, 314–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.Y.S.; Barratt, B.J.; Clayton, D.G.; Todd, J.A. Genome-wide association studies: Theoretical and practical concerns. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.P.; Singh, A.; Mueller, D.S.; Singh, A.K. Genome-wide association and epistasis studies unravel the genetic architecture of sudden death syndrome resistance in soybean. Plant J. 2015, 84, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.X.; Tan, R.J.; Zhang, S.C.; Collins, P.J.; Yuan, J.Z.; Du, W.Y.; Gu, C.H.; Ou, S.J.; Song, Q.J.; An, Y.Q.C.; et al. Integrating GWAS and gene expression data for functional characterization of resistance to white mould in soya bean. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasawa, N.; Hibara, K.I.; Heppard, E.P.; Vander Velden, K.A.; Luck, S.; Beatty, M.; Nagato, Y.; Sakai, H. GIANT EMBRYO encodes CYP78A13, required for proper size balance between embryo and endosperm in rice. Plant J. 2013, 75, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.B.; Gao, M.J.; Yin, X.; Liu, J.Y.; Xu, Y.H.; Zeng, L.J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.B.; Wang, J.M.; Zhang, X.M.; et al. Control of Rice Embryo Development, Shoot Apical Meristem Maintenance, and Grain Yield by a Novel Cytochrome P450. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.J.; Wu, T.T.; Ye, J.; Sun, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, J.; Tang, J.P.; Chen, G.M.; Wang, C.M.; Wan, J.M. SNP-based analysis of genetic diversity reveals important alleles associated with seed size in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 93, Erratum in BMC Plant Biol.2016, 16, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.Y.; Liu, L.T.; Li, T.; Yan, S.; Kuang, B.J.; Huang, S.J.; Yan, C.J.; Wang, T. OsKinesin-13A Is an Active Microtubule Depolymerase Involved in Glume Length Regulation via Affecting Cell Elongation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, K.; Kurinami, S.; Oki, K.; Abe, Y.; Ando, T.; Kono, I.; Yano, M.; Kitano, H.; Iwasaki, Y. A Novel Kinesin 13 Protein Regulating Rice Seed Length. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 1315–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, H.; Zheng, X.M.; Jin, M.N.; Weng, J.F.; Ma, J.; Ren, Y.L.; Zhou, K.N.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. An evolutionarily conserved gene, FUWA, plays a role in determining panicle architecture, grain shape and grain weight in rice. Plant J. 2015, 83, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Chen, K.; Dong, N.Q.; Shi, C.L.; Ye, W.W.; Gao, J.P.; Shan, J.X.; Lin, H.X. GRAIN SIZE AND NUMBER1 Negatively Regulates the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4-OsMPK6 Cascade to Coordinate the Trade-off between Grain Number per Panicle and Grain Size in Rice. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 871–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Ito, M.; Sumikura, T.; Nakayama, A.; Nishimura, T.; Kitano, H.; Yamaguchi, I.; Koshiba, T.; Hibara, K.I.; Nagato, Y.; et al. The rice FISH BONE gene encodes a tryptophan aminotransferase, which affects pleiotropic auxin-related processes. Plant J. 2014, 78, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rellosa, M.C.; Reano, R.A.; Capilit, G.L.S.; de Guzman, F.C.; Ali, J.; Hamilton, N.R.S.; Mauleon, R.P.; Alexandrov, N.N.; Leung, H. The 3,000 rice genomes project. GigaScience 2014, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.J.; Liang, S.S.; Ponce, K.; Marundon, S.; Ye, G.Y.; Zhao, X.Q. Factors affecting head rice yield and chalkiness in indica rice. Field Crop. Res. 2015, 172, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClung, C.R. Making Hunger Yield. Science 2014, 344, 699–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.; Xiong, M.; Chang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, R.; Lin, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, M.; Liu, C.; Liu, E. Mining Candidate Genes and Favorable Haplotypes for Flag Leaf Shape in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Based on a Genome-Wide Association Study. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, P.J.; Zhang, Z.; Kroon, D.E.; Casstevens, T.M.; Ramdoss, Y.; Buckler, E.S. TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.A.; Lee, S.H.; Goddard, M.E.; Visscher, P.M. GCTA: A Tool for Genome-wide Complex Trait Analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, S.S.; Xu, J.Y.; He, W.M.; Yang, T.L. PopLDdecay: A fast and effective tool for linkage disequilibrium decay analysis based on variant call format files. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1786–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.X.; Yeung, J.M.Y.; Cherny, S.S.; Sham, P.C. Evaluating the effective numbers of independent tests and significant p-value thresholds in commercial genotyping arrays and public imputation reference datasets. Hum. Genet. 2012, 131, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



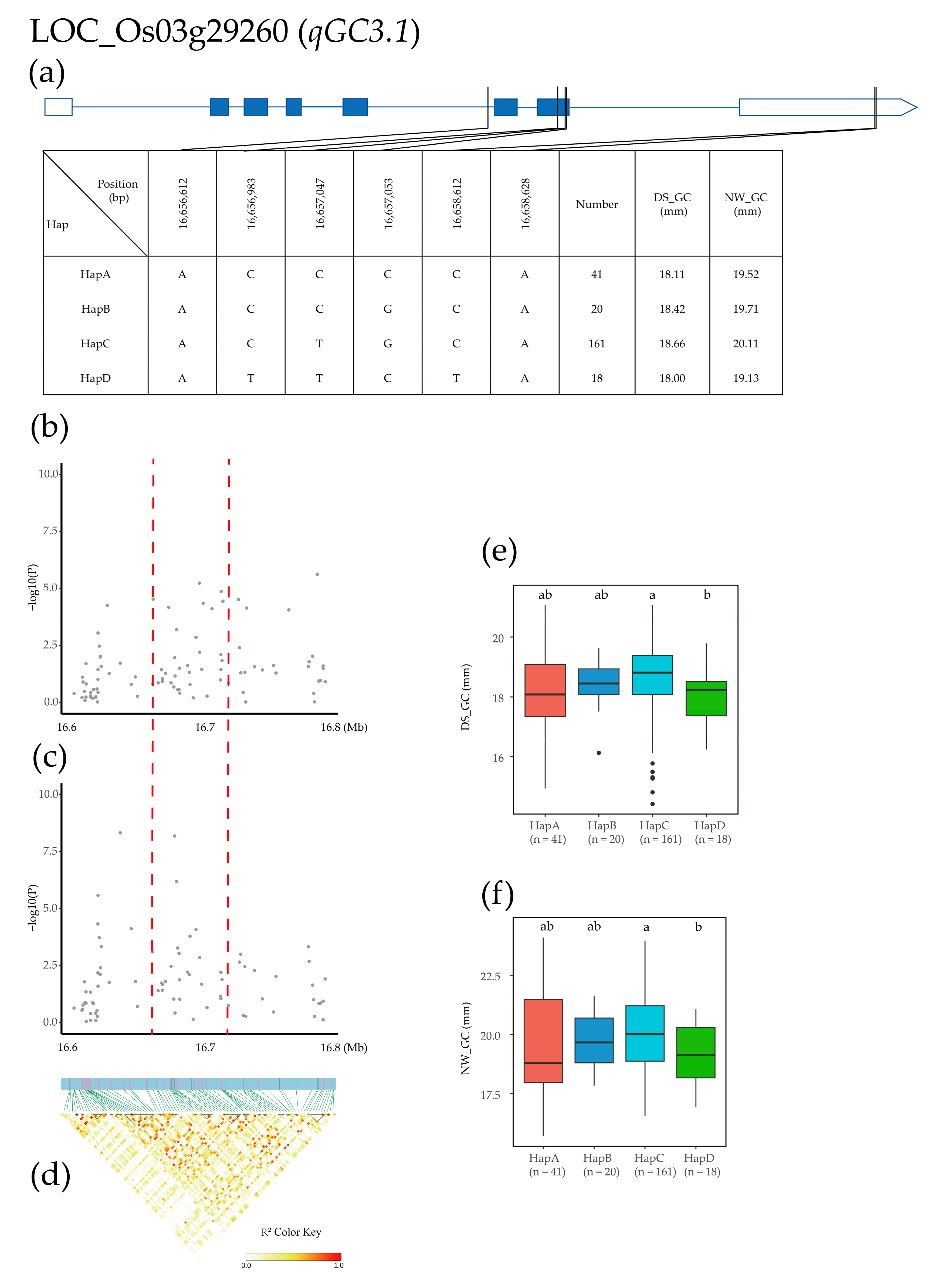


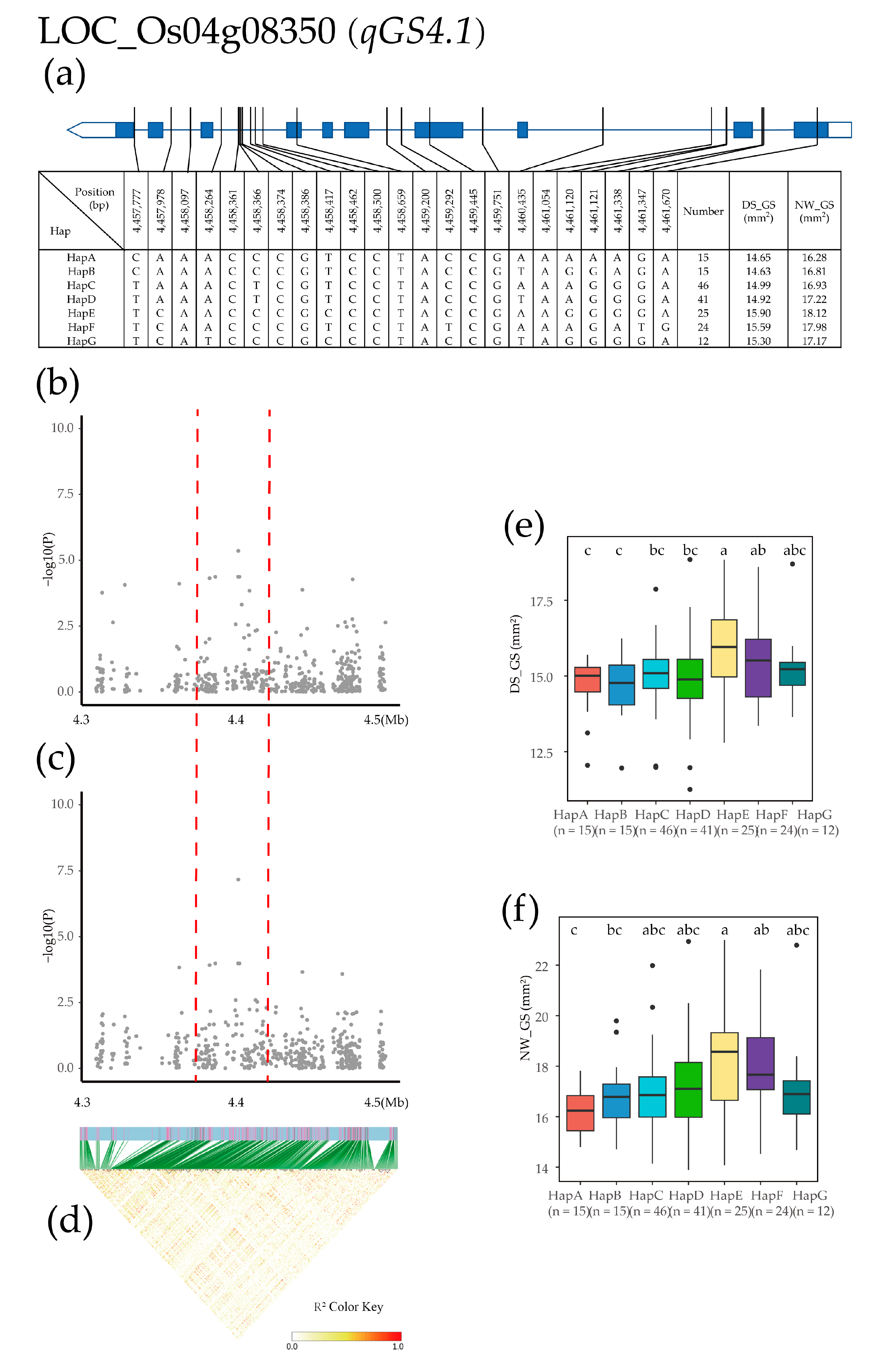

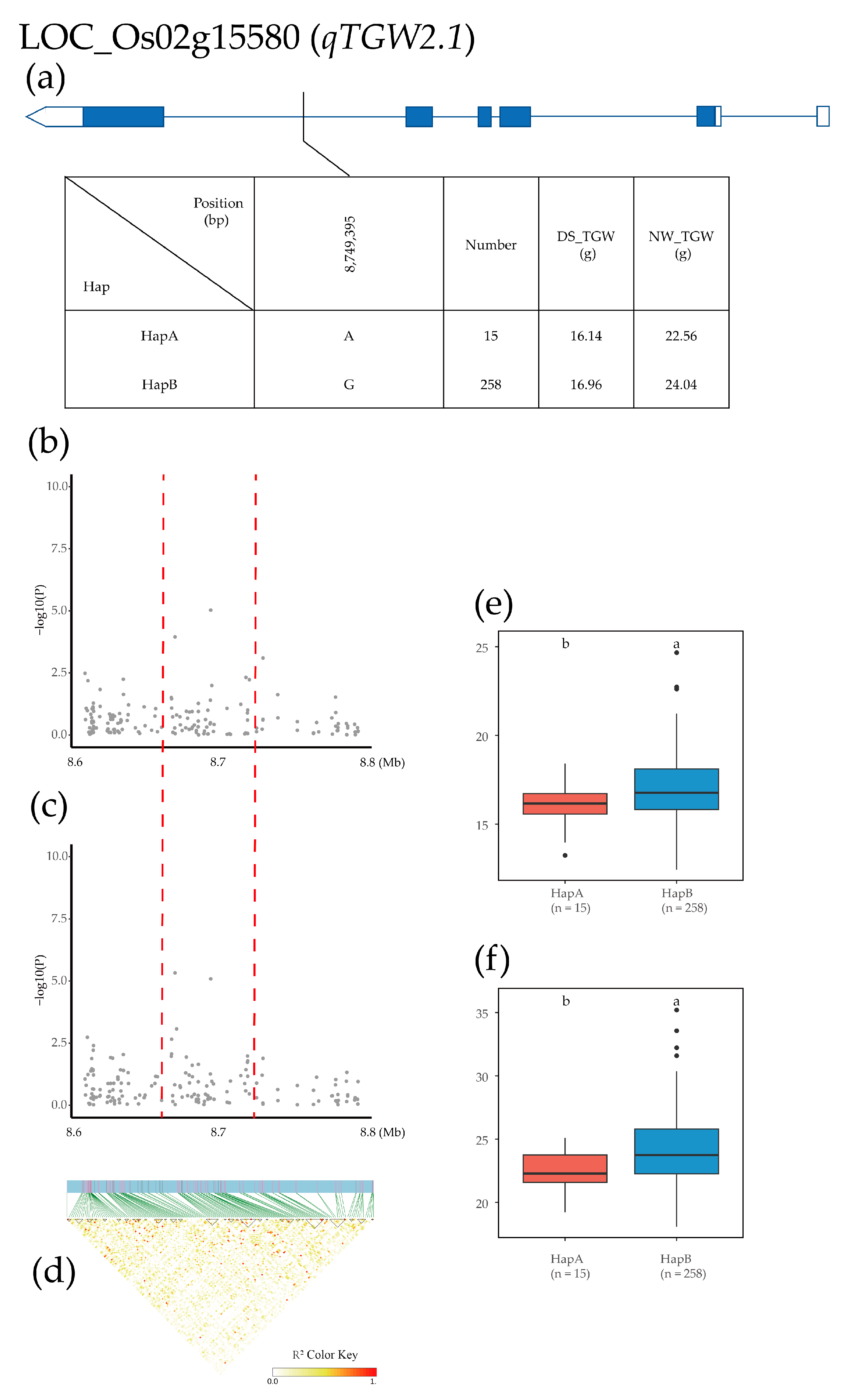
| Treatment | Year | Mean ± SD | Max | Min | CV (%) | H2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC (mm) | DS | 2017 | 18.53 ± 3.05 | 23.59 | 7.58 | 16.44% | 0.72 |
| 2018 | 18.38 ± 1.68 | 22.86 | 13.48 | 9.11% | |||
| NW | 2017 | 19.90 ± 1.67 | 24.60 | 15.74 | 8.39% | 0.97 | |
| 2018 | 19.78 ± 1.66 | 23.80 | 15.39 | 8.42% | |||
| GL (mm) | DS | 2017 | 8.09 ± 0.80 | 10.08 | 4.27 | 9.84% | 0.94 |
| 2018 | 7.78 ± 0.79 | 9.79 | 5.57 | 10.13% | |||
| NW | 2017 | 8.36 ± 0.83 | 10.53 | 6.32 | 9.91% | 0.98 | |
| 2018 | 8.31 ± 0.82 | 10.27 | 6.07 | 9.89% | |||
| GLWR | DS | 2017 | 3.21 ± 0.49 | 4.84 | 2.02 | 15.28% | 0.97 |
| 2018 | 3.14 ± 0.45 | 4.38 | 2.06 | 14.46% | |||
| NW | 2017 | 3.14 ± 0.52 | 4.51 | 1.99 | 16.69% | 0.98 | |
| 2018 | 3.11 ± 0.51 | 4.43 | 1.98 | 16.43% | |||
| GS (mm2) | DS | 2017 | 15.26 ± 2.76 | 22.16 | 5.46 | 18.08% | 0.68 |
| 2018 | 14.97 ± 1.92 | 20.91 | 9.70 | 12.81% | |||
| NW | 2017 | 17.34 ± 1.90 | 24.31 | 12.95 | 10.97% | 0.96 | |
| 2018 | 17.25 ± 1.91 | 24.15 | 12.6 | 11.06% | |||
| GW (mm) | DS | 2017 | 2.59 ± 0.25 | 3.48 | 1.33 | 9.71% | 0.95 |
| 2018 | 2.52 ± 0.23 | 3.31 | 1.96 | 8.95% | |||
| NW | 2017 | 2.72 ± 0.27 | 3.68 | 2.23 | 9.94% | 0.98 | |
| 2018 | 2.73 ± 0.26 | 3.56 | 2.18 | 9.66% | |||
| TGW(g) | DS | 2017 | 16.67 ± 3.04 | 28.88 | 9.79 | 18.26% | 0.71 |
| 2018 | 17.21 ± 3.16 | 28.10 | 8.75 | 18.38% | |||
| NW | 2017 | 23.99 ± 3.26 | 35.99 | 17.18 | 13.58% | 0.99 | |
| 2018 | 23.96 ± 3.32 | 38.33 | 17.17 | 13.87% |
| Trait | QTL | Chr | Lead SNP (bp) | DS R2 (%) | NW R2 (%) | DS p-Value | NW p-Value | Known Genes/QTLs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC | qGC3.1 | 3 | 16,743,121 | 15.62% | 28.75% | 6 × 10−6 | 6.15 × 10−11 | |
| GL | qGL3.1 | 3 | 16,725,044 | 19.34% | 18.56% | 1.36 × 10−7 | 1.57 × 10−7 | GS3 |
| qGL5.1 | 5 | 955,623 | 14.82% | 14.83% | 8.4 × 10−6 | 5.38 × 10−6 | OsMKP1; GSN1 | |
| qGL8.1 | 8 | 18,001,936 | 15.80% | 15.99% | 2.63 × 10−6 | 1.35 × 10−6 | ||
| GLWR | qGLWR3.1 | 3 | 16,725,044 | 16.32% | 16.63% | 4.1 × 10−7 | 2.19 × 10−7 | GS3 |
| qGLWR3.2 | 3 | 21,067,616 | 13.28% | 12.98% | 1.14 × 10−5 | 1.23 × 10−5 | ||
| GS | qGS2.1 | 2 | 7,792,944 | 17.72% | 24.46% | 1.09 × 10−5 | 4.70 × 10−8 | OsGSK3 |
| qGS3.1 | 3 | 13,224,102 | 18.82% | 23.45% | 5.04 × 10−6 | 8.07 × 10−8 | ||
| qGS4.1 | 4 | 4,445,624 | 18.81% | 23.37% | 4.40 × 10−6 | 6.75 × 10−8 | ||
| qGS4.2 | 4 | 21,851,870 | 18.77% | 23.04% | 6.06 × 10−6 | 1.55 × 10−7 | ||
| qGS12.1 | 12 | 18,698,797 | 25.40% | 23.37% | 7.17 × 10−8 | 7.01 × 10−8 | ||
| GW | qGW1.1 | 1 | 3,526,032 | 17.91% | 15.51% | 9.99 × 10−7 | 2.42 × 10−6 | OsRA2; OsCrll4 |
| qGW7.1 | 7 | 11,595,349 | 16.30% | 16.49% | 3.71 × 10−6 | 8.76 × 10−7 | ||
| qGW8.1 | 8 | 6,558,586 | 18.35% | 18.73% | 1.38 × 10−5 | 2.17 × 10−6 | ||
| qGW11.1 | 11 | 26,572,137 | 18.20% | 18.18% | 6.51 × 10−7 | 1.55 × 10−7 | ||
| TGW | qTGW2.1 | 2 | 8,783,659 | 20.04% | 18.13% | 9.35 × 10−6 | 8.08 × 10−6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, N.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Bai, D.; Li, K.; Zhao, X.; Xiang, J.; Liang, Z.; Qian, Y.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Xian Rice Grain Shape and Weight in Different Environments. Plants 2023, 12, 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12132549
Wang N, Zhang W, Wang X, Zheng Z, Bai D, Li K, Zhao X, Xiang J, Liang Z, Qian Y, et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Xian Rice Grain Shape and Weight in Different Environments. Plants. 2023; 12(13):2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12132549
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Nansheng, Wanyang Zhang, Xinchen Wang, Zhenzhen Zheng, Di Bai, Keyang Li, Xueyu Zhao, Jun Xiang, Zhaojie Liang, Yingzhi Qian, and et al. 2023. "Genome-Wide Association Study of Xian Rice Grain Shape and Weight in Different Environments" Plants 12, no. 13: 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12132549
APA StyleWang, N., Zhang, W., Wang, X., Zheng, Z., Bai, D., Li, K., Zhao, X., Xiang, J., Liang, Z., Qian, Y., Wang, W., & Shi, Y. (2023). Genome-Wide Association Study of Xian Rice Grain Shape and Weight in Different Environments. Plants, 12(13), 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12132549




