Effects of Foliar-Applied Mixed Mineral Fertilizers and Organic Biostimulants on the Growth and Hybrid Seed Production of a Male-Sterile Inbred Maize Line
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
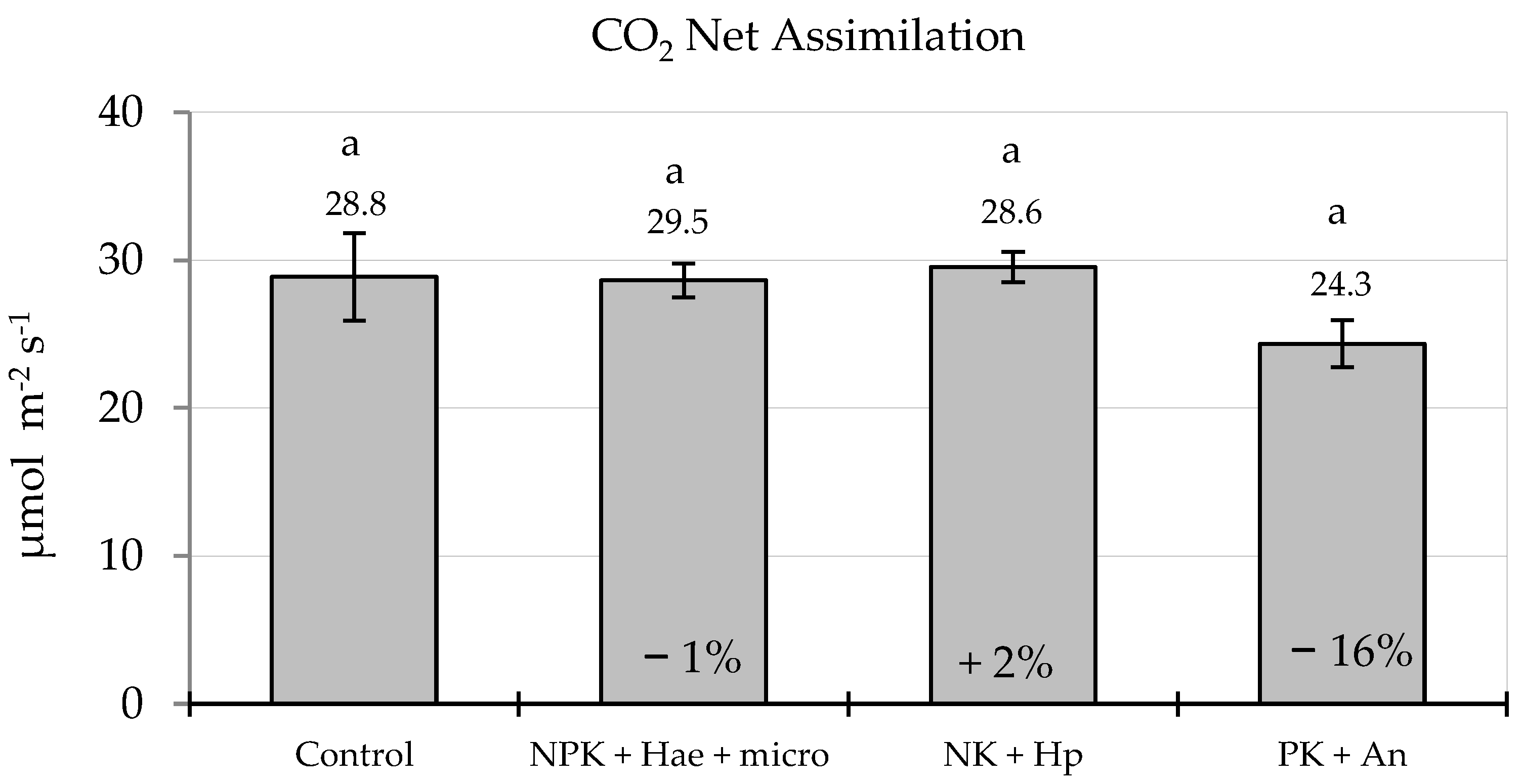
2.1. Shoot Parameters
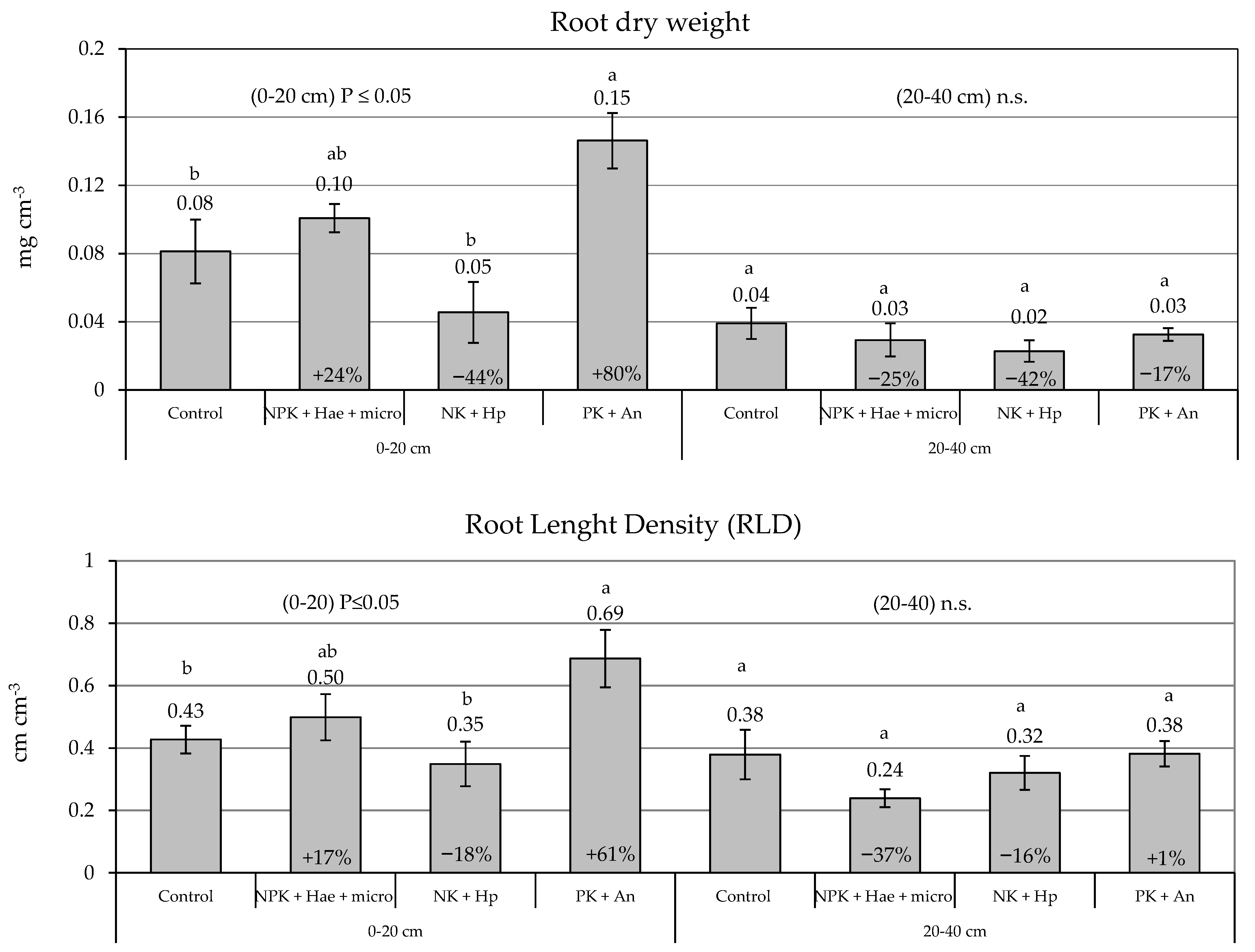
2.2. Root Parameters
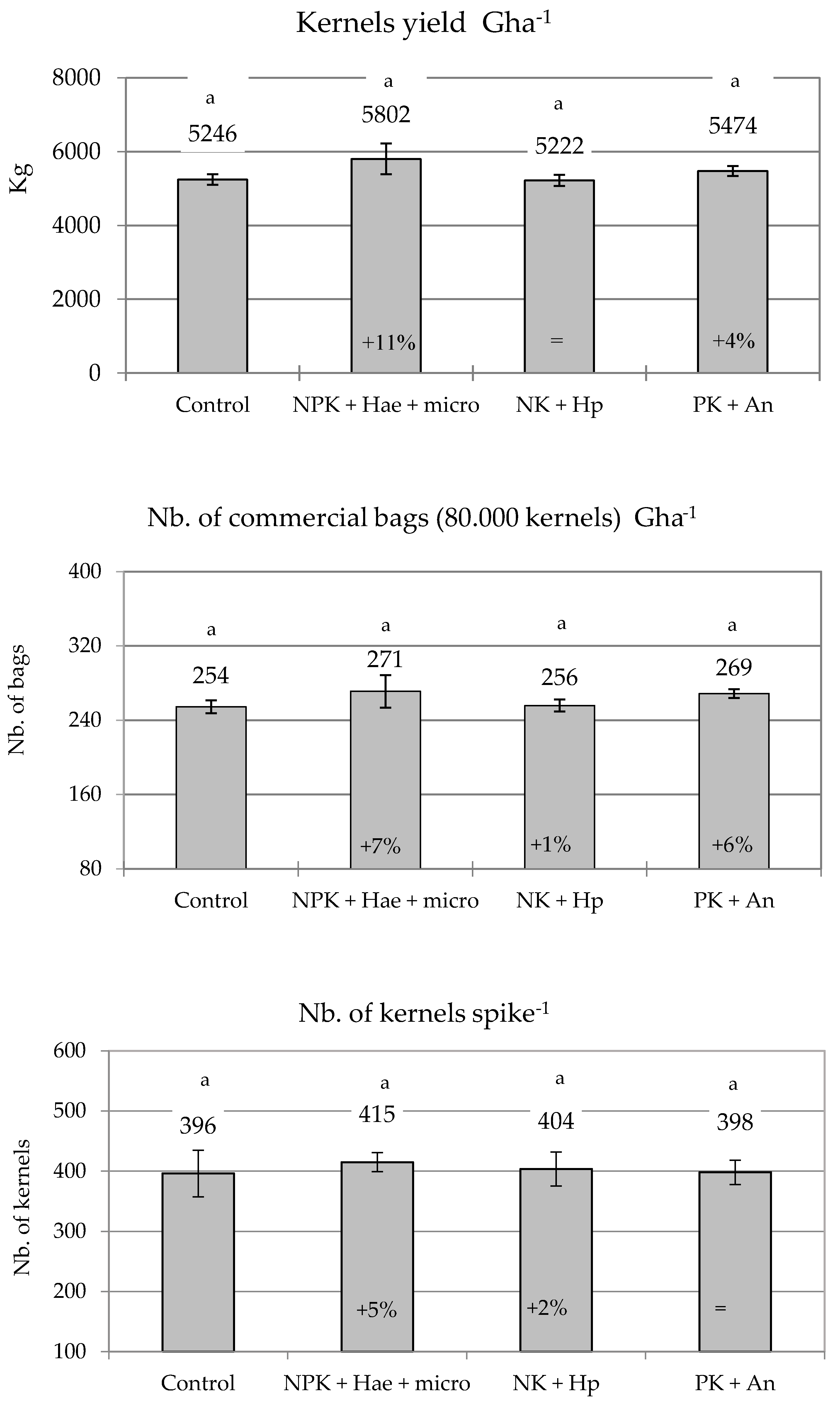
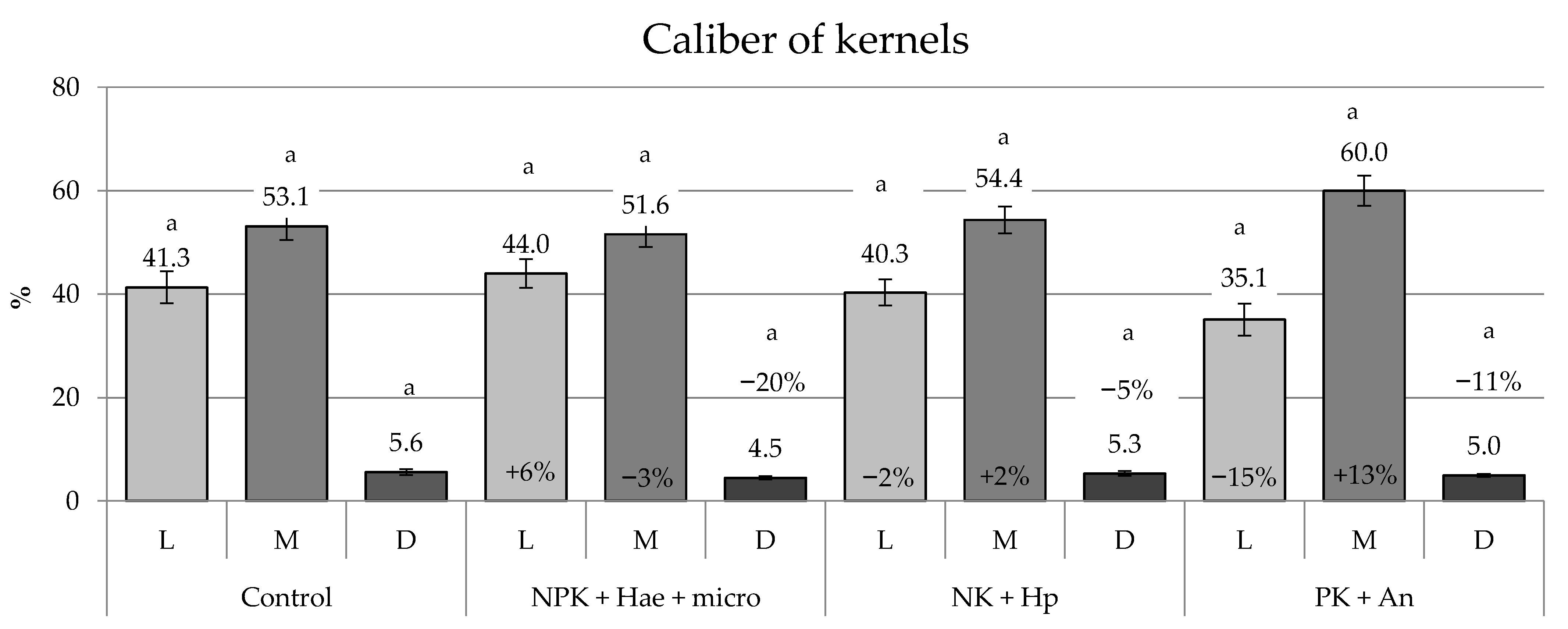
2.3. Yield, Caliber, and Germinability of Kernels
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Field Trial Set-Up
4.2. Plant Physiological Parameters
4.3. Plant Height and Biomass
4.4. Root Growth Analysis
4.5. Hybrid Seed Yield and Yield Components
4.6. Seed Germinability
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krishnasree, R.K.; Sheeja, K.R.; Chacko, S.R. Foliar nutrition in vegetables: A review. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2021, 10, 2393–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, V.; Brown, P.H. From plant surface to plant metabolism: The uncertain fate of foliar-applied nutrients. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visioli, G.; Bonas, U.; Dal Cortivo, C.; Pasini, G.; Marmiroli, N.; Mosca, G.; Vamerali, T. Variations in yield and gluten proteins in durum wheat varieties under late-season foliar versus soil application of nitrogen fertilizer in a northern Mediterranean environment. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 2360–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fageria, N.K.; Barbosa Filho, M.P.; Moreira, A.; Guimarães, C.M. Foliar fertilization of crop plants. J. Plant Nutr. 2009, 32, 1044–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Liu, C.; Huang, M.; Liu, K.; Yan, D. Effects of foliar fertilization: A review of current status and future perspectives. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matschi, S.; Vasquez, M.F.; Bourgault, R.; Steinbach, P.; Chamness, J.; Kaczmar, N.; Smith, L.G. Structure-function analysis of the maize bulliform cell cuticle and its potential role in dehydration and leaf rolling. Plant Direct 2020, 4, e00282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankee, W. Mechanism of foliar penetration of solutions. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 2013, 18, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, A. Biophysical and biochemical characteristics of cutin, a plant barrier biopolymer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1620, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Biostimulants in agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- du Jardin, P. Plant biostimulants: Definition, concept, main categories and regulation. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Pascale, S.; Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Plant biostimulants: Innovative tool for enhancing plant nutrition in organic farming. Eur. J. Hortic. Sci. 2017, 82, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Dal Cortivo, C.; Panozzo, A.; Barion, G.; Visioli, G.; Giannelli, G.; Vamerali, T. Comparing Soil vs. Foliar nitrogen supply of the whole fertilizer dose in common wheat. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, A.F.; Nakabonge, G.; Ssekandi, J.; Founoune-Mboup, H.; Badji, A.; Ndiaye, A.; Ekwangu, J. Combined effects of indigenous arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) and NPK fertilizer on growth and yields of maize and soil nutrient availability. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, M.; Seadh, S.; Abido, W.A.E.; El-Sadik, I.S. Effect of Spraying with Nano-Zinc and Mineral Npk Levels on Productivity and Grains Quality of Maize. J. Plant Prod. 2022, 13, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afe, A.I.; Atanda, S.; Aduloju, M.O.; Ogundare, S.K.; Talabi, A.A. Response of maize (Zea mays L.) to combined application of organic and inorganic (soil and foliar applied) fertilizers. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 3006–3010. [Google Scholar]
- Bukvić, G.; Antunović, M.; Popović, S.; Rastija, M. Effect of P and Zn fertilisation on biomass yield and its uptake by maize lines (Zea mays L.). Plant Soil Environ. 2003, 49, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leach, K.A.; Hameleers, A. The effects of a foliar spray containing phosphorus and zinc on the development, composition, and yield of forage maize. Grass Forage Sci. 2001, 56, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girma, K.; Martin, K.L.; Freeman, K.W.; Mosali, J.; Teal, R.K.; William, R.R.; Moges, S.M.; Arnall, D.B. Determination of optimum rate and growth stage for foliar-applied phosphorus in corn. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2010, 38, 1137–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández, V.; Bahamonde, H.A.; Peguero-Pina, J.J.; Gil-Pelegrín, E.; Sancho-Knapik, D.; Gil1, L.; Goldbach, H.E.; Eichert, T. Physico-chemical properties of plant cuticles and their functional and ecological significance. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 5293–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brankov, M.; Dragicevic, V.; Simi, M.; Filipovic, M.; Kresovic, M.; Mandic, V. Diminishing herbicide stress in maize inbred lines by application of foliar fertilizer. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2017, 18, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Klavins, M.; Grandovska, S.; Obuka, V.; Ievinsh, G. Comparative study of biostimulant properties of industrially and experimentally produced humic substances. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, B.; Seckler, M.M. Alkaline extraction of humic substances from peat applied to organic-mineral fertilizer production. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 31, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandiera, M.; Mosca, G.; Vamerali, T. Humic acids affect root characteristics of fodder radish (Raphanus sativus L. var. oleiformis Pers.) in metal-polluted wastes. Desalination 2009, 246, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, L.O.; Villordon, A. Root branching and nutrient efficiency: Status and way forward in root and tuber crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeannin, I.; Lescure, J.C.; Morot-Gaudry, J.F. The effects of aqueous seaweed sprays on the growth of maize. Bot. Mar. 1991, 34, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.S.; Mantin, E.G.; Adil, M.; Bajpai, S.; Critchley, A.T.; Prithiviraj, B. Ascophyllum nodosum-based biostimulants: Sustainable applications in agriculture for the stimulation of plant growth, stress tolerance, and disease management. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ertani, A.; Francioso, O.; Tinti, A.; Schiavon, M.; Pizzeghello, D.; Nardi, S. Evaluation of seaweed extracts from Laminaria and Ascophyllum nodosum spp. as biostimulants in Zea mays L. using a combination of chemical, biochemical and morphological approaches. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, H.D.; Fiorini, I.V.A.; Von Pinho, R.G.; Resende, F.R.; Resende, E.L.; Pereira, C.S. Ascophyllum nodosum seaweed extract effects in maize crop. Sci. Electron. Arch. 2018, 11, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Suganya, A.; Saravanan, A.; Manivannan, N. Role of zinc nutrition for increasing zinc availability, uptake, yield, and quality of maize (Zea mays L.) grains: An overview. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 51, 2001–2021. [Google Scholar]
- Stevanović, L.; Simić, M.; Dragičević, V. Studies on maize inbred lines susceptibility to herbicides. Genetika 2010, 42, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brankov, M.; Simić, M.; Dolijanović, Ž.; Rajković, M.; Mandić, V.; Dragičević, V. The Response of maize lines to foliar fertilizing. Agriculture 2020, 10, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecha, J.; Fürst, T.; Kolomazník, K.; Friebrová, V.; Svoboda, P. Protein biostimulant foliar uptake modeling: The impact of climatic conditions. AIChE J. 2012, 58, 2010–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, H.; Lauer, J. Critical Stages in the Life of a Corn Plant. 2000. Available online: http://corn.agronomy.wisc.edu/Management/pdfs/CriticalStages.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2023).
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Luo, N.; Meng, Q.; Wang, P. Dissecting the critical stage in the response of maize kernel set to individual and combined drought and heat stress around flowering. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 179, 104213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningning, Y.; Ren, B.; Zhao, B.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J. Leaf-nitrogen status affects grain yield formation through modification of spike differentiation in maize. Field Crops Res. 2021, 271, 108238. [Google Scholar]
- Lasekan, A.; Abu, B.F.; Hashim, D. Potential of chicken by-products as sources of useful biological resources. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klompong, V.; Benjakul, S.; Kantachote, D.; Shahidi, F. Antioxidative activity and functional properties of protein hydrolysate of yellow stripe trevally (Selaroides leptolepis) as influenced by the degree of hydrolysis and enzyme type. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Hernández, J.M.; Benítez-García, I.; Mazorra-Manzano, M.A.; Ramírez-Suárez, J.C.; Sánchez, E. Strategies for production, characterization and application of protein-based biostimulants in agriculture: A review. Chil. J. Agric. Ros. 2020, 80, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertani, A.; Pizzeghello, D.; Altissimo, A.; Nardi, S. Use of meat hydrolyzate derived from tanning residues as plant biostimulant for hydroponically grown maize. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2013, 176, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.C.; Lu, G.H.; Jao, C.L. Antioxidative properties of peptides prepared from tuna cooking juice hydrolysates with orientase (Bacillus subtilis). Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, M.; Ghimire, S.K.; Ojha, B.R.; Shrestha, J. Analysis of genetic diversity among the maize inbred lines (Zea mays L.) under heat stress condition. J. Maize Res. Develop. 2017, 3, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.X.; Robison, D.J. Nondestructive and rapid estimation of hardwood foliar nitrogen status using the SPAD-502 chlorophyll meter. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 181, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murchie, E.H.; Lawson, T. Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis: A guide to good practice and understanding some new applications. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 3983–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romdhane, L.; Ebinezer, L.B.; Panozzo, A.; Barion, G.; Dal Cortivo, C.; Radhouane, L.; Vamerali, T. Effects of soil amendment with wood ash on transpiration, growth, and metal uptake in two contrasting maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids to drought tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 661909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Středa, T.; Haberle, J.; Klimešov, J.; Klimek-Kopyra, A.; Středová, H.; Bodner, G.; Chloupek, O. Field phenotyping of plant roots by electrical capacitance—A standardized methodological protocol for application in plant breeding: A review. Int. Agrophys. 2020, 34, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Rosário, G.; Oliveira, M.; van Noordwijk, M.; Gaze, S.R.; Brouwer, G.; Bona, S.; Mosca, G.; Hairiah, K. Auger sampling, ingrowth cores and pinboard methods. In Root Methods; Smit, A.L., Bengough, A.G., Engels, C., van Noordwijk, M., Pellerin, S., van de Geijn, S.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 175–210. [Google Scholar]
- Vamerali, T.; Guarise, M.; Ganis, A.; Bona, S.; Mosca, G. Analysis of root images from auger sampling with a fast procedure: A case of application to sugar beet. Plant Soil 2003, 255, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Root Dry Weight (g cm−3) | RLD (cm cm−3) | RAD (cm2 cm−3) | D (µm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | Mean | % var. vs. C | Mean | % var. vs. C | Mean | % var. vs. C | Mean | % var. vs. C |
| Control | 0.060 ab | 0.403 ab | 0.064 ab | 996 a | ||||
| NPK + Hae + micro | 0.061 ab | +2% | 0.368 ab | −9% | 0.058 ab | −9% | 948 a | −5% |
| NK + Hp | 0.037 b | −38% | 0.334 b | −17% | 0.045 b | −30% | 886 a | −11% |
| PK + An | 0.089 a | +48% | 0.534 a | +33% | 0.079 a | +23% | 910 a | −9% |
| Treatments (T) | - | ** | - | * | - | * | - | n.s. |
| Soil Layer (SL) | - | *** | - | ** | - | *** | - | *** |
| T × SL | - | ** | - | n.s. | - | * | - | n.s. |
| Germination Rate (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatments | Warm (25 °C) | Cold (12 °C) | ||
| Control | 98.9 ± 0.6 a | 94.6 ± 2.9 a | ||
| NPK + Hae + micro | 99.5 ± 0.2 a | +1% | 91.3 ± 2.5 a | −3% |
| NK + Hp | 99.2 ± 0.5 a | = | 94.0 ± 1.6 a | −1% |
| PK + An | 96.9 ± 2.2 a | −2% | 92.1 ± 2.7 a | −3% |
| Soil Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Clay | 27% |
| Silt | 57% |
| Sand | 16% |
| pH | 8.49 |
| Organic matter | 1.75% |
| Total N | 953 mg kg−1 |
| Assimilable P2O5 | 19.7 mg kg−1 |
| Exchangeable K2O | 152 mg kg−1 |
| Fertilizer/Biostimulant Code (Type of Formulation) | Composition | Value (%) |
|---|---|---|
| NPK + Hae + micro (powder) | Organic C (from hydrolyzed animal epithelium) | 7.5 |
| Total N: | 10.0 | |
| N-NH3 | 6.0 | |
| N-NO3 | 2.5 | |
| Organic N | 1.5 | |
| Total P2O5: | 5.0 | |
| P2O5 soluble in neutral ammonium citrate | 5.0 | |
| P2O5 soluble in water | 5.0 | |
| Water-soluble K2O | 17.0 | |
| Water-soluble SO3 | 23.0 | |
| Water-soluble MgO | 5.0 | |
| Fe-EDTA | 0.2 | |
| Mn-EDTA | 0.1 | |
| Mo | 0.001 | |
| Zn-EDTA | 0.1 | |
| NK + Hp (liquid suspension) | Organic C (from humified peat) | 8.7 |
| Total N | 13.0 | |
| Organic N | 0.5 | |
| Ureic N | 12.5 | |
| Water-soluble K2O | 5.0 | |
| PK + An (liquid) | Organic C (from Ascophyllum nodosum) | m.v. |
| Total P2O5 | 13.0 | |
| Water-soluble K2O | 5.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boscaro, R.; Panozzo, A.; Piotto, S.; Moore, S.S.; Barion, G.; Wang, Y.; Vamerali, T. Effects of Foliar-Applied Mixed Mineral Fertilizers and Organic Biostimulants on the Growth and Hybrid Seed Production of a Male-Sterile Inbred Maize Line. Plants 2023, 12, 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12152837
Boscaro R, Panozzo A, Piotto S, Moore SS, Barion G, Wang Y, Vamerali T. Effects of Foliar-Applied Mixed Mineral Fertilizers and Organic Biostimulants on the Growth and Hybrid Seed Production of a Male-Sterile Inbred Maize Line. Plants. 2023; 12(15):2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12152837
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoscaro, Riccardo, Anna Panozzo, Simone Piotto, Selina Sterup Moore, Giuseppe Barion, Yu Wang, and Teofilo Vamerali. 2023. "Effects of Foliar-Applied Mixed Mineral Fertilizers and Organic Biostimulants on the Growth and Hybrid Seed Production of a Male-Sterile Inbred Maize Line" Plants 12, no. 15: 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12152837
APA StyleBoscaro, R., Panozzo, A., Piotto, S., Moore, S. S., Barion, G., Wang, Y., & Vamerali, T. (2023). Effects of Foliar-Applied Mixed Mineral Fertilizers and Organic Biostimulants on the Growth and Hybrid Seed Production of a Male-Sterile Inbred Maize Line. Plants, 12(15), 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12152837







