Combination of Biochar and Trichoderma harzianum Can Improve the Phytoremediation Efficiency of Brassica juncea and the Rhizosphere Micro-Ecology in Cadmium and Arsenic Contaminated Soil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
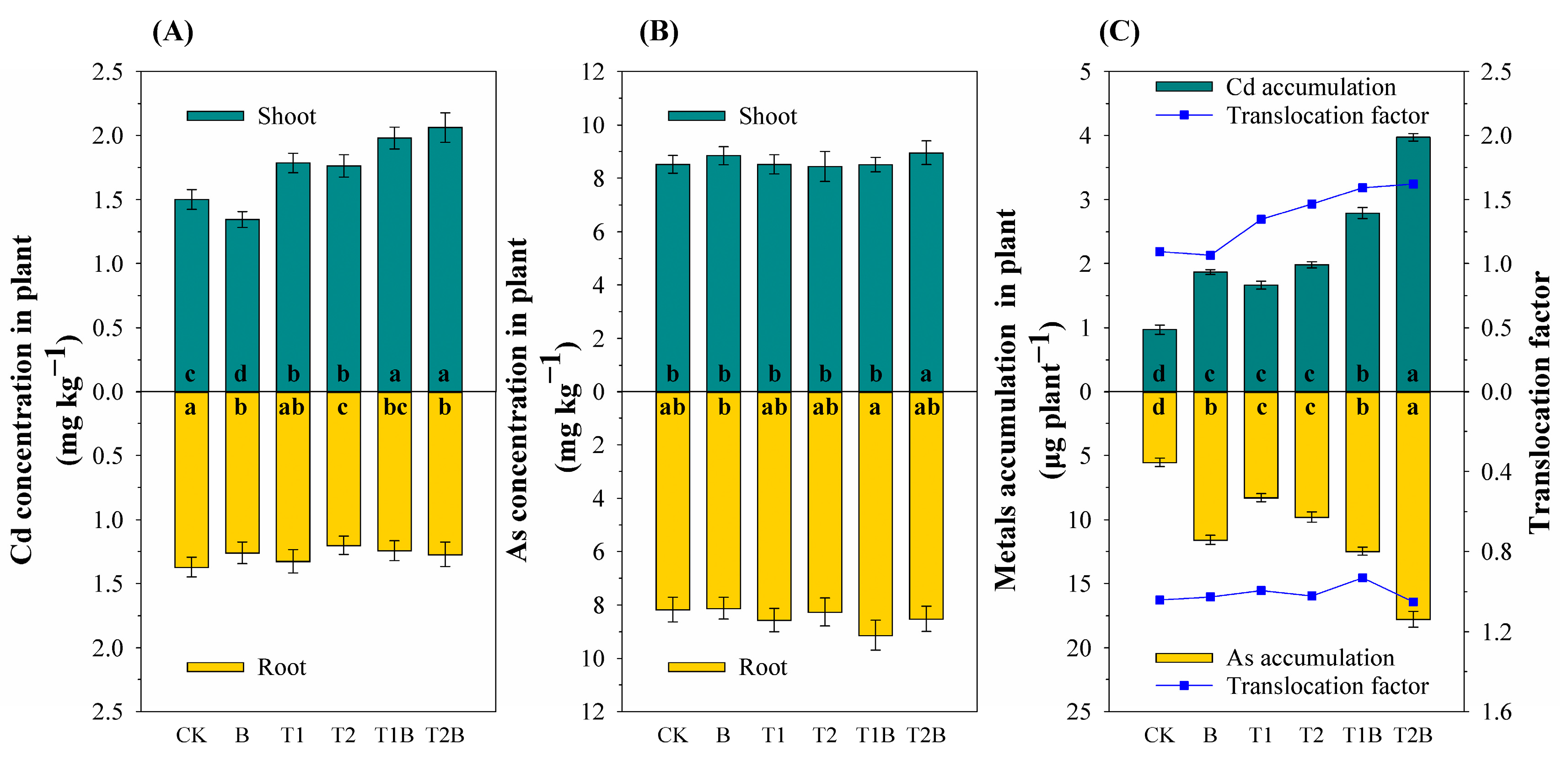
2.1. Plant Growth and PTEs Content
2.2. Soil PTEs Content and Availability
2.3. Enzyme Activity and Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.4. Diversity and Community Structure of Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Community
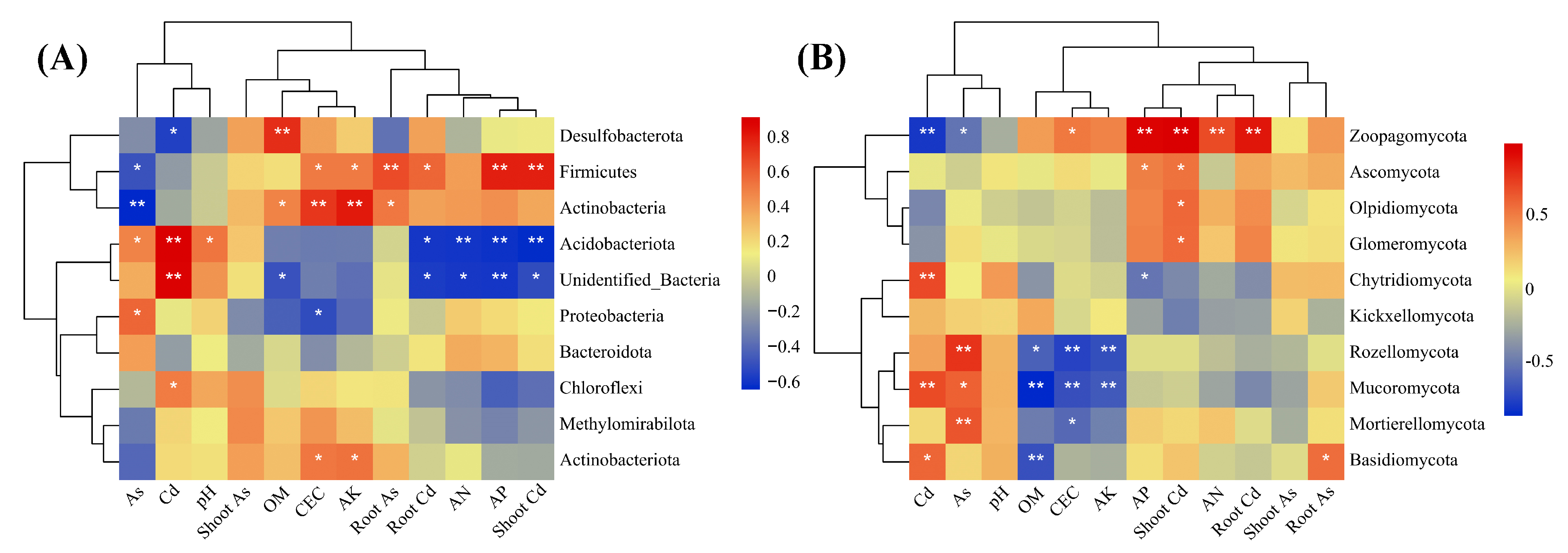
2.5. Responses of Phytoremediation to Microhabitat Properties of Rhizosphere Soil
3. Discussion
3.1. Soil PTEs Content and Plant PTEs Accumulation
3.2. Plant Stress Tolerance and Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.3. Microbial Community Diversity and Structure Differences
3.4. Modulation Mechanisms between Phytoremediation and Rhizosphere Microecology
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Experimental Design and Sample Collection
4.3. Soil and Plant Physicochemical Properties and Enzyme Activities
4.4. Potentially Toxic Elements Analysis
4.5. Potentially Toxic Elements Translocation and Accumulation
4.6. DNA Isolation, Sequencing, and Microbial Diversity Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Man, X.; Huang, H.; Chen, F.; Gu, Y.; Liang, R.; Wang, B.; Jordan, R.W.; Jiang, S. Anthropogenic impacts on the temporal variation of heavy metals in Daya Bay (South China). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Li, H.; Hu, F.; Jiao, J. Investigation and evaluation of soil heavy metals in a wheat-maize cropping system in upland China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Subrahmanyam, G.; Mondal, R.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Shabnam, A.A.; Jigyasu, D.K.; Malyan, S.K.; Fagodiya, R.K.; Khan, S.A.; Yu, Z.-G. Bio-remediation approaches for alleviation of cadmium contamination in natural resources. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Song, Y.; Chen, L.; Ji, J.; Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Yang, Z.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L.; Theiss, F. Human health risks of heavy metals in paddy rice based on transfer characteristics of heavy metals from soil to rice. Catena 2019, 175, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, G.; Purchase, D.; Mulla, S.I.; Saratale, G.D.; Bharagava, R.N. Phytoremediation of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Sites: Eco-environmental Concerns, Field Studies, Sustainability Issues, and Future Prospects. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 249, 71–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, B. Paper Increase of P and Cd bioavailability in the rhizosphere by endophytes promoted phytoremediation efficiency of Phytolacca acinosa. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Fang, A.; Li, A. Submerged macrophytes mediated remediation of molybdenum-contaminated sediments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 48962–48971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadel, U.; Nesme, J.; Michalke, B.; Vestergaard, G.; Plaza, G.A.; Schroder, P.; Radl, V.; Schloter, M. Changes induced by heavy metals in the plant-associated microbiome of Miscanthus × giganteus. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.; Zeng, C.; Wan, C.; Liu, Z.; Dong, X.; Peng, J.; Lin, H.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Yan, M. Metabolic Profiles of Brassica juncea Roots in Response to Cadmium Stress. Metabolites 2021, 11, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, S.S.; Sharma, V.; Shukla, A.K.; Taneja, P.K.; Kaur, L.; Verma, V.; Kaur, M.; Kaur, J. Exploration of Cd transformations in Cd spiked and EDTA-chelated soil for phytoextraction by Brassica species. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunaidi, A.A.; Lim, L.H.; Metali, F. Transfer of heavy metals from soils to curly mustard (Brassica juncea (L.) Czern.) grown in an agricultural farm in Brunei Darussalam. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, R.; Xia, B.; Zeng, X.; Qiu, R.; Tang, Y.; Hu, Z. Adsorption of Cadmium by Brassica juncea (L.) Czern. and Brassica pekinensis (Lour.) Rupr in Pot Experiment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Khan, M.J.; Shah, A.; Deeba, F.; Hussain, H.; Yazdan, F.; Khan, M.U.; Khan, M.D. Screening of various Brassica species for phytoremediation of heavy metals-contaminated soil of Lakki Marwat, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 37765–37776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, P.; Chaudhary, P.; Ahmad, S.; Bhatt, K.; Chandra, D.; Chen, S. Chapter 2—Recent advances in the application of microbial inoculants in the phytoremediation of xenobiotic compounds. In Unravelling Plant-Microbe Synergy; Chandra, D., Bhatt, P., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, S.; Anand, V.; Singh, P.; Roy, A.; Pallavi, S.; Bist, V.; Kaur, J.; Srivastava, S.; Katiyar, R.; Srivastava, S. Chapter 16—Microbial systems as a source of novel genes for enhanced phytoremediation of contaminated soils. In Microbe Mediated Remediation of Environmental Contaminants; Kumar, A., Singh, V.K., Singh, P., Mishra, V.K., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2021; pp. 177–198. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Sun, K.; Han, L. Effect of biochar on soil heavy metal speciation and bioavailability: A review. Environ. Chem. 2021, 40, 1643–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Shen, W.; Wu, X.; Hu, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, J. Remediation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soil by Passivation of Biochar Complex Minerals. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 51, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Gasco, G.; Alvarez, M.L.; Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Mendez, A. Combining phytoextraction by Brassica napus and biochar amendment for the remediation of a mining soil in Riotinto (Spain). Chemosphere 2019, 231, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, B.; Lehr, V.I. Biochar effects on phosphorus availability in agricultural soils: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Wang, D.; Riaz, M.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, C. Investigating the effect of biochar on the potential of increasing cotton yield, potassium efficiency and soil environment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, D.; Chen, H.; Qin, J.; Chen, G.; Qiu, R. Polyaspartic acid assisted-phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated farmland: Phytoextraction efficiency, soil quality, and rhizosphere microbial community. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 862, 160736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Long, M.; Tai, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Sun, X.; Tang, D.; Sun, L. Microbiological inoculation with and without biochar reduces the bioavailability of heavy metals by microbial correlation in pig manure composting. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 248, 114294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, N.; Sunilkumar, C.R.; Bhavya, G.; Nandini, B.; Abhijith, P.; Satapute, P.; Shetty, H.S.; Govarthanan, M.; Jogaiah, S. Warhorses in soil bioremediation: Seed biopriming with PGPF secretome to phytostimulate crop health under heavy metal stress. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsharkawy, M.M. Suppression of Potato virus Y Infection in Tobacco by Plant Growth Promoting Fungi. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2016, 26, 695–700. [Google Scholar]
- Wonglom, P.; Ito, S.-I.; Sunpapao, A. Volatile organic compounds emitted from endophytic fungus Trichoderma asperellum T1 mediate antifungal activity, defense response and promote plant growth in lettuce (Lactuca sativa). Fungal Ecol. 2020, 43, 100867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.G.; Shim, J.; Bang, K.-S.; Shea, P.J.; Oh, B.-T. Trichoderma virens PDR-28: A heavy metal-tolerant and plant growth-promoting fungus for remediation and bioenergy crop production on mine tailing soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 132, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, E.; Ahari, A.B.; Arzanlou, M.; Oustan, S.; Khazaei, S.H. Tolerance to heavy metals in filamentous fungi isolated from contaminated mining soils in the Zanjan Province, Iran. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Panja, A. 13—Signatures of signaling pathways underlying plant-growth promotion by fungi. In Biocontrol Agents and Secondary Metabolites; Jogaiah, S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2021; pp. 321–346. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, M.; Ur-Rahman, S.; Hassani, D.; Hayat, K.; Zhou, P.; Hui, N. Advances in fungal-assisted phytoremediation of heavy metals: A review. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 475–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harindintwali, J.D.; Zhou, J.; Yang, W.; Gu, Q.; Yu, X. Biochar-bacteria-plant partnerships: Eco-solutions for tackling heavy metal pollution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 204, 111020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Wei, J.; Guan, F.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Luo, Y. Biochar and bacteria inoculated biochar enhanced Cd and Cu immobilization and enzymatic activity in a polluted soil. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Tang, L.; Su, M.; Tian, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Hu, S. Enhanced Pb immobilization via the combination of biochar and phosphate solubilizing bacteria. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedjimi, B. Phytoremediation: A sustainable environmental technology for heavy metals decontamination. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.R.; Xu, J.Y.; He, D.Y.; Bu, D.R.; Lu, Y.Y.; Zhao, Y.X.; Chen, Y.R.; Tian, X.F. Combining paecilomyces variotii extracts and biochar for the remediation of alkaline Cd-contaminated soil. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Yue, X.; Wang, J.; Ren, B.; Qu, L.; Han, H. Effects of Bacillus thuringiensis HC-2 Combined with Biochar on the Growth and Cd and Pb Accumulation of Radish in a Heavy Metal-Contaminated Farmland under Field Conditions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Askar, A.A.; Ezzat, A.S.; Ghoneem, K.M.; Saber, W.I.A. Trichoderma harzianum WKY5 and its Gibberellic Acid Control of Rhizoctonia solani, Improve Sprouting, Growth and Productivity of Potato. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2016, 26, 787–796. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, J.B.S.; da Costa Neto, V.P.; de Sousa, C.D.A.; de Carvalho Filho, M.R.; Rodrigues, A.C.; Bonifacio, A. Trichoderma and bradyrhizobia act synergistically and enhance the growth rate, biomass and photosynthetic pigments of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) grown in controlled conditions. Symbiosis 2020, 80, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xie, X.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Huang, B. Regulation mechanism of plant response to heavy metal stress mediated by endophytic fungi. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2023, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Butt, T.A.; Naqvi, S.T.A.; Yousaf, S.; Qureshi, M.K.; Zafar, M.I.; Farooq, G.; Nawaz, I.; Iqbal, M. Lead tolerant endophyte Trametes hirsuta improved the growth and lead accumulation in the vegetative parts of Triticum aestivum L. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shahir, A.A.; El-Tayeh, N.A.; Ali, O.M.; Abdel Latef, A.A.H.; Loutfy, N. The Effect of Endophytic Talaromyces pinophilus on Growth, Absorption and Accumulation of Heavy Metals of Triticum aestivum Grown on Sandy Soil Amended by Sewage Sludge. Plants 2021, 10, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Ren, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, L.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, A. Physicochemical features, metal availability and enzyme activity in heavy metal-polluted soil remediated by biochar and compost. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Zhang, B.; Gao, X.; Cui, S.; Guan, C.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Peng, Y. Recent progresses, challenges, and opportunities of carbon-based materials applied in heavy metal polluted soil remediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 158810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Tan, W.; Wang, G.; Zhao, X.; Dang, Q.; Yu, H.; Xi, B. Nitrogen addition promotes the transformation of heavy metal speciation from bioavailable to organic bound by increasing the turnover time of organic matter: An analysis on soil aggregate level. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, M.A.; Gomis, M.P.; Perez-Murcia, M.D.; Gangi, D.; Ceglie, F.G.; Paredes, C.; Perez-Espinosa, A.; Bernal, M.P.; Moral, R. Use of livestock waste composts as nursery growing media: Effect of a washing pre-treatment. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 281, 109954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, B.; Dong, Y.; Lin, H. Endophyte colonization enhanced cadmium phytoremediation by improving endosphere and rhizosphere microecology characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 434, 128829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.K.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, S.P.; Yang, J.E.; Kim, S.C. Heavy metal remediation in soil with chemical amendments and its impact on activity of antioxidant enzymes in Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and soil enzymes. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2020, 63, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, F.; Samsampour, D.; Seyahooei, M.A.; Bagheri, A.; Soltani, J. Fungal endophytes alleviate drought-induced oxidative stress in mandarin (Citrus reticulata L.): Toward regulating the ascorbate-glutathione cycle. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 261, 108991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Janda, T.; Szalai, G. Interactions between plant hormones and thiol-related heavy metal chelators. Plant Growth Regul. 2018, 85, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, P.-Y.; Guo, W.; Chen, Z.-L.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.-Z. Soil Enzyme Stoichiometric Characteristics of Pinus massoniana Plantations at Different Stand Ages in Mid-subtropical Areas. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2022, 43, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, C.; Fernandez, C.; Escuer, M.; Campos-Herrera, R.; Beltran Rodriguez, M.E.; Carbonell, G.; Rodriguez Martin, J.A. Effect of soil properties, heavy metals and emerging contaminants in the soil nematodes diversity. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, T.; Covino, S.; Cvancarova, M.; Filipova, A.; Petruccioli, M.; D’Annibale, A.; Cajthaml, T. Bioremediation of long-term PCB-contaminated soil by white-rot fungi. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Hu, C.; Lin, J.; Wang, X.; Tang, C.; Dai, Z.; Xu, J. Contamination with multiple heavy metals decreases microbial diversity and favors generalists as the keystones in microbial occurrence networks. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ullah, S.; Niu, A.; Liao, Z.; Qin, Q.; Xu, S.; Lin, C. Heavy metal pollution increases CH4 and decreases CO2 emissions due to soil microbial changes in a mangrove wetland: Microcosm experiment and field examination. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, B.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qu, C.; Tang, J.; Wu, Y.; Tan, W.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, T. The relationships between heavy metals and bacterial communities in a coal gangue site. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 322, 121136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Qiao, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, Z.; Yu, C. Microbial community succession in soils under long-term heavy metal stress from community diversity-structure to KEGG function pathways. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Disi, Z.; Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Zouari, N. Investigating the simultaneous removal of hydrocarbons and heavy metals by highly adapted Bacillus and Pseudomonas strains. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 27, 102513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xiao, W.; Ye, Y.; Wu, C.; Hu, Y.; Shi, H. Adaptation of soil fungi to heavy metal contamination in paddy fields-a case study in eastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 27819–27830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Agostini, A.; Caltagirone, C.; Caredda, A.; Cicatelli, A.; Cogoni, A.; Farci, D.; Guarino, F.; Garau, A.; Labra, M.; Lussu, M.; et al. Heavy metal tolerance of orchid populations growing on abandoned mine tailings: A case study in Sardinia Island (Italy). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 110018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayawardene, N.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Dai, D.Q.; Tang, L.Z.; Aptroot, A.; Castaneda-Ruiz, R.F.; Druzhinina, I.S.; Cai, F.; Ekanayaka, A.H.; Erdogdu, M.; et al. A dynamic portal for a community-driven, continuously updated classification of Fungi and fungus-like organisms: Outlineoffungi.org. Mycosphere 2020, 11, 1514–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, R.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. Changes of heavy metal fractions during co-composting of agricultural waste and river sediment with inoculation of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 378, 120757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, B.; He, Y. Effects of endophytes inoculation on rhizosphere and endosphere microecology of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) grown in vanadium-contaminated soil and its enhancement on phytoremediation. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, X.; Ling, Q.; Li, S.; Wei, J.; Xin, M.; Xie, D.; Chen, X.; Liu, K.; Yu, F. Bacterial extracellular polymeric substances: Impact on soil microbial community composition and their potential role in heavy metal-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 240, 113701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, G.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Lv, C.; Bai, L.; Zhang, K.; He, H.; Dai, J. Cultivar-specific response of rhizosphere bacterial community to uptake of cadmium and mineral elements in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 249, 114403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Wang, K.; He, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L. Characterization of physicochemical parameters and bioavailable heavy metals and their interactions with microbial community in arsenic-contaminated soils and sediments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 49672–49683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Effects of heavy metal pollution and soil physicochemical properties on the Sphagnum farmland soil microbial community structure in Southern Guizhou, China. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2023, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, H.; Mou, L.; Ru, J.; Zhao, J.; Xiao, S. Long-term and high-concentration heavy-metal contamination strongly influences the microbiome and functional genes in Yellow River sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.N.; Kour, D.; Kaur, T.; Devi, R.; Yadav, A. Endophytic fungal communities and their biotechnological implications for agro-environmental sustainability. Folia Microbiol. 2022, 67, 203–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Li, K.-Y.; Yang, H.; Deng, C.-J.; Liang, H.; Song, L.-H. Effects of Biochar Application on Yellow Soil Nutrients and Enzyme Activities. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2022, 43, 4655–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.B.; Piao, S.L.; Chen, A.P.; Liu, Y.W.; Liu, L.L.; Peng, S.S.; Sardans, J.; Sun, Y.; Penuelas, J.; Zeng, H. Afforestation neutralizes soil pH. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, B.; Luo, S.; Luo, H.; Huang, H.; Xu, F.; Feng, S.; Xu, H. Improved phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils by Miscanthus floridulus under a varied rhizosphere ecological characteristic. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 151995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.L.; Page, A.L. Methods of Soil Analysis: Chemical and Microbiological Proerpteis; Amen Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Xie, Y.; Luo, Y.; Sheng, M.; Xu, F.; Xu, H. Ecological responses of soil microbial abundance and diversity to cadmium and soil properties in farmland around an enterprise-intensive region. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, F.; Xie, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, A.; Li, L.; Xu, H. Effect of modified coconut shell biochar on availability of heavy metals and biochemical characteristics of soil in multiple heavy metals contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayawardena, M.A.A.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Chapter Three—Exposure, Toxicity, Health Impacts, and Bioavailability of Heavy Metal Mixtures. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 138, pp. 175–234. [Google Scholar]
- Bogati, K.A.; Golinska, P.; Sewerniak, P.; Burkowska-But, A.; Walczak, M. Deciphering the Impact of Induced Drought in Agriculture Soils: Changes in Microbial Community Structure, Enzymatic and Metabolic Diversity. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1969, 1, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H. Effect of Morchella Mycelium on Soil Enzymatic Activity. Biotechnol. Bull. 2020, 36, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Sedlak, J.; Lindsay, R.H. Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal. Biochem. 1968, 25, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wen, M.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Z.; Wang, C. Effect of phenanthrene on the biological characteristics of earthworm casts and their relationships with digestive and anti-oxidative systems. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 193, 110359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, T.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Qiu, G. Combined remediation effects of biochar, zeolite and humus on Cd-contaminated weakly alkaline soils in wheat farmland. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wu, S.; Wu, F.; Leung, H.M.; Lin, X.; Wong, M.H. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhance both absorption and stabilization of Cd by Alfred stonecrop (Sedum alfredii Hance) and perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) in a Cd-contaminated acidic soil. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigrist, M.; Albertengo, A.; Beldoménico, H.; Tudino, M. Determination of As(III) and total inorganic As in water samples using an on-line solid phase extraction and flow injection hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiowatana, J.; McLaren, R.G.; Chanmekha, N.; Samphao, A. Fractionation of Arsenic in Soil by a Continuous-Flow Sequential Extraction Method. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 1940–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tüzen, M. Determination of heavy metals in soil, mushroom and plant samples by atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2003, 74, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Huang, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Huang, J.; Zhuo, R.; Wu, Z.; Qin, X.; Gao, Y.; et al. Enhanced Cd phytostabilization and rhizosphere bacterial diversity of Robinia pseudoacacia L. by endophyte Enterobacter sp. YG-14 combined with sludge biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zuo, M.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Li, G.; Li, C.; Lis, X.; et al. Characteristics and diversity of microbial communities in lead-zinc tailings under heavy metal stress in north-west China. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 74, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, S.; Zhou, B.; Duan, M.; Cao, T.; Wen, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Cheng, W.; Zhu, H.; et al. Combination of Biochar and Trichoderma harzianum Can Improve the Phytoremediation Efficiency of Brassica juncea and the Rhizosphere Micro-Ecology in Cadmium and Arsenic Contaminated Soil. Plants 2023, 12, 2939. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12162939
Yao S, Zhou B, Duan M, Cao T, Wen Z, Chen X, Wang H, Wang M, Cheng W, Zhu H, et al. Combination of Biochar and Trichoderma harzianum Can Improve the Phytoremediation Efficiency of Brassica juncea and the Rhizosphere Micro-Ecology in Cadmium and Arsenic Contaminated Soil. Plants. 2023; 12(16):2939. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12162939
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Shaoxiong, Beibei Zhou, Manli Duan, Tao Cao, Zhaoquan Wen, Xiaopeng Chen, Hui Wang, Min Wang, Wen Cheng, Hongyan Zhu, and et al. 2023. "Combination of Biochar and Trichoderma harzianum Can Improve the Phytoremediation Efficiency of Brassica juncea and the Rhizosphere Micro-Ecology in Cadmium and Arsenic Contaminated Soil" Plants 12, no. 16: 2939. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12162939
APA StyleYao, S., Zhou, B., Duan, M., Cao, T., Wen, Z., Chen, X., Wang, H., Wang, M., Cheng, W., Zhu, H., Yang, Q., & Li, Y. (2023). Combination of Biochar and Trichoderma harzianum Can Improve the Phytoremediation Efficiency of Brassica juncea and the Rhizosphere Micro-Ecology in Cadmium and Arsenic Contaminated Soil. Plants, 12(16), 2939. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12162939










