The Isolate Pseudomonas multiresinivorans QL-9a Quenches the Quorum Sensing Signal and Suppresses Plant Soft Rot Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
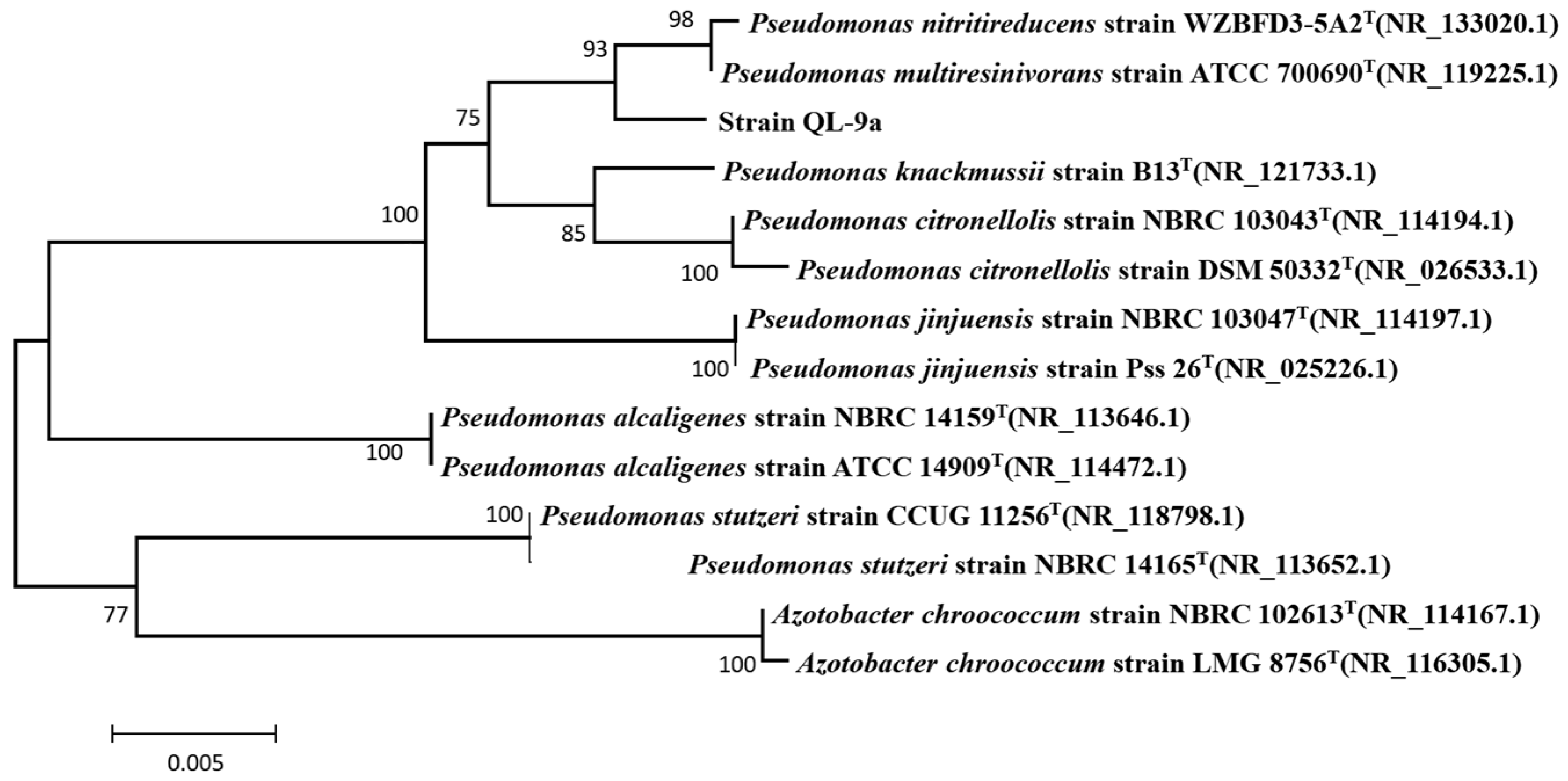
2.1. Identification and Characterization of the QL-9a Strain
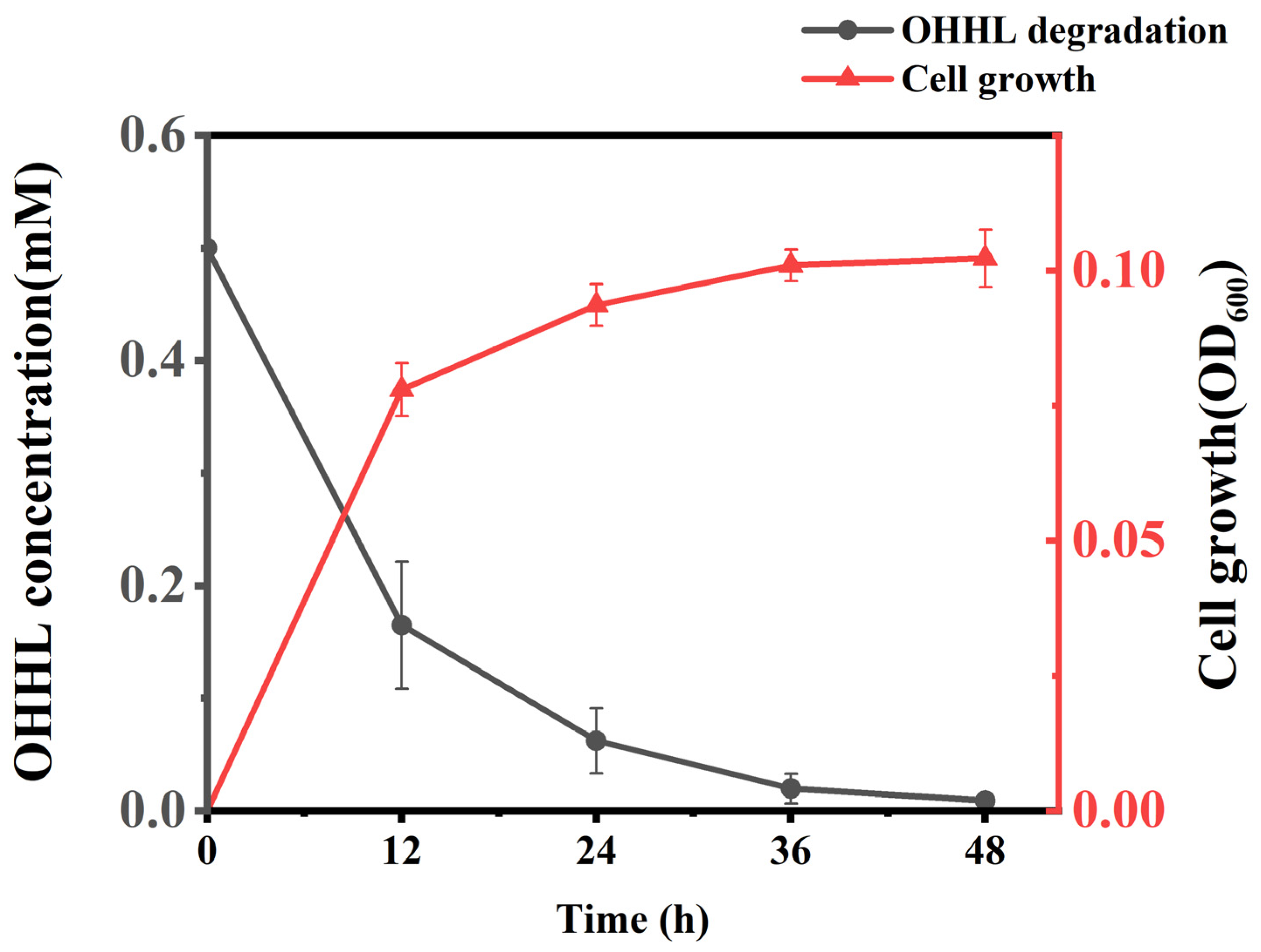
2.2. Growth and Degradability Test
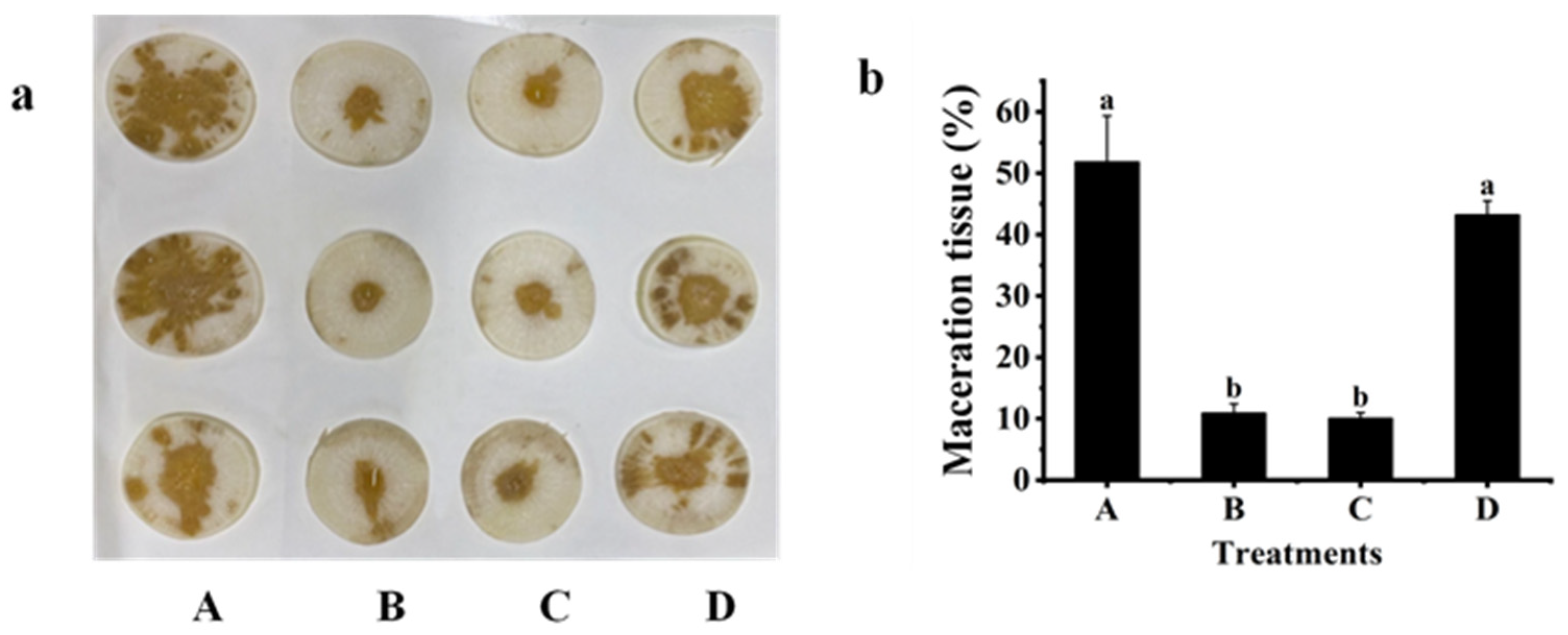
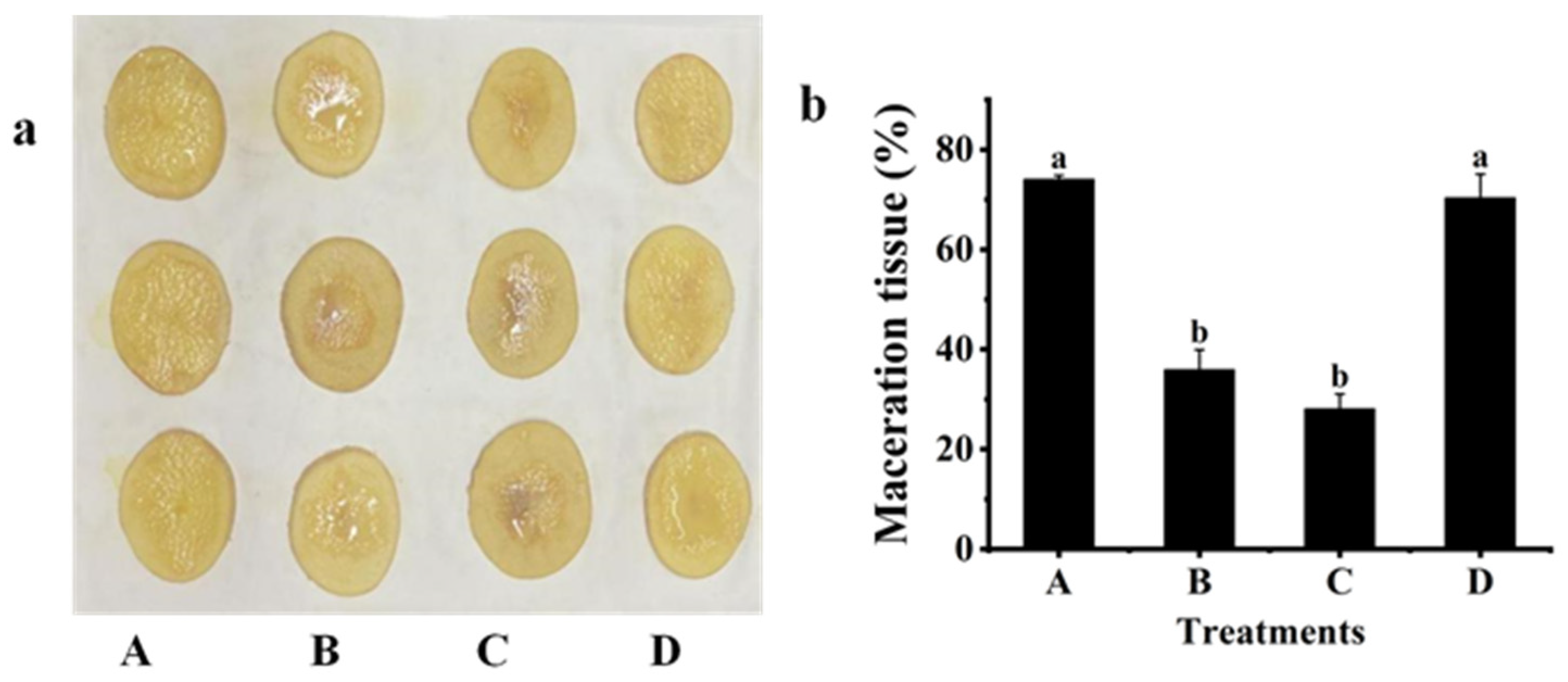
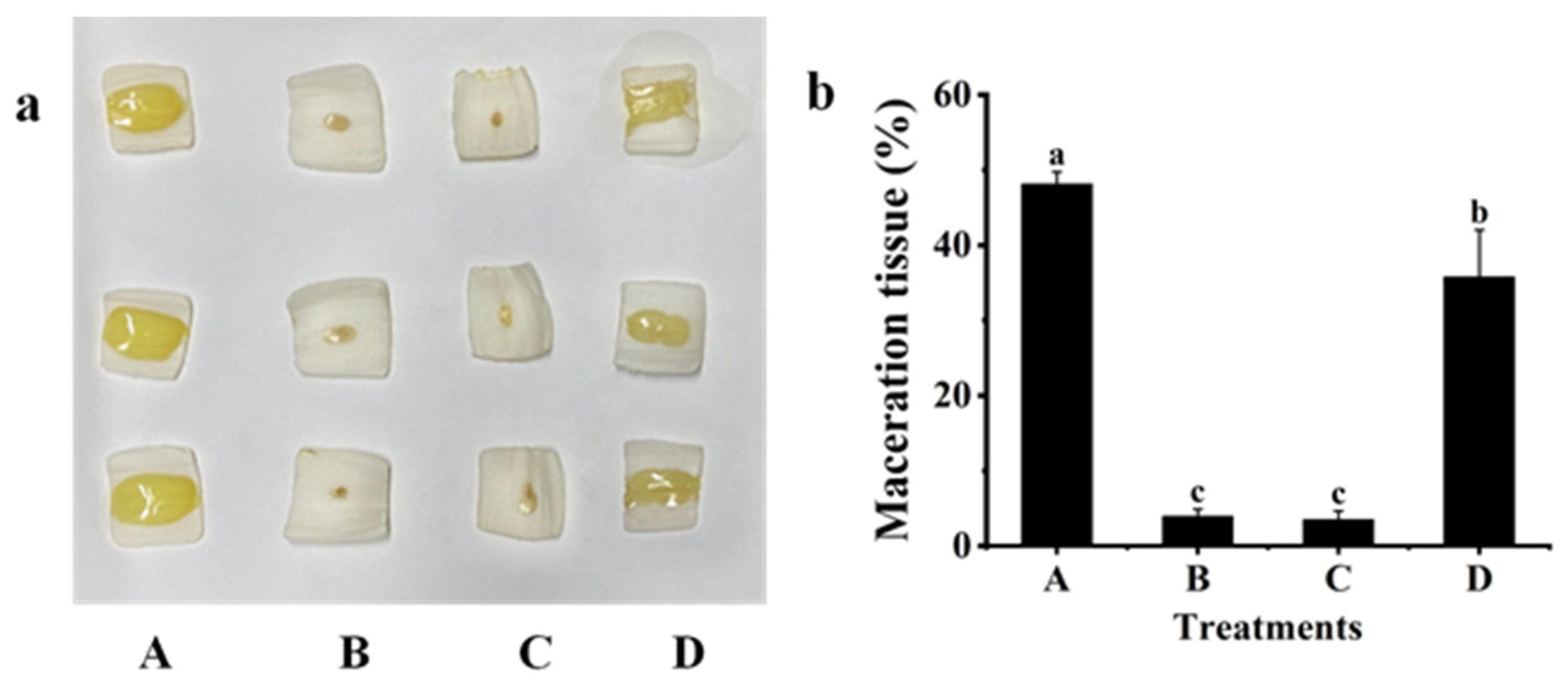
2.3. Biological Control Effect against Z3-3
2.4. Degradation Products and the Pathway of OHHL
2.5. Antagonism Test of the QL-9a Strain against Z3-3
2.6. Biocontrol Effect of Crude Enzymes
2.7. Acylase Activity Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plants and Chemicals
3.2. Strains and Media
3.3. Isolation of QL-9a
3.4. Identification of the QL-9a Strain
3.5. Determination of OHHL Degradation Activity by HPLC
3.6. Effect of the QL-9a Strain on Soft Rot Disease Caused by Z3-3
3.7. Identification of OHHL Degradation Products by GC-MS
3.8. Antagonism Test of the QL-9a Strain
3.9. Effect of the QL-9a Crude Enzyme on Z3-3
3.10. Acylase Activity Assay
3.11. Data Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuqua, W.C.; Winans, S.C.; Greenberg, E.P. Quorum sensing in bacteria: The LuxR-LuxI family of cell density-responsive transcriptional regulators. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watve, S.; Barrasso, K.; Jung, S.A.; Davis, K.J.; Hawver, L.A.; Khataokar, A.; Palaganas, R.G.; Neiditch, M.B.; Perez, L.J.; Ng, W.L. Parallel quorum-sensing system in Vibrio cholerae prevents signal interference inside the host. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, T.; Zhou, T.; Li, Q.; Xu, X.; Fan, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. Cupriavidus sp. HN-2, a novel quorum quenching bacterial isolate, is a potent biocontrol agent against Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zeng, C.; Wen, H.; Shi, Q.; Zhao, X.; Meng, Q.; Li, X.; Xiao, J. Discovery of AI-2 quorum sensing inhibitors targeting the LsrK/HPr protein–protein interaction site by molecular dynamics simulation, virtual screening, and bioassay evaluation. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, D.G.; Parsek, M.R.; Pearson, J.P.; Iglewski, B.H.; Costerton, J.W.; Greenberg, E.P. The involvement of cell-to-cell signals in the development of a bacterial biofilm. Science 1998, 280, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padder, S.A.; Prasad, R.; Shah, A.H. Quorum sensing: A less known mode of communication among fungi. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 210, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahreen, S.; Mukhtar, H.; Imre, K.; Morar, A.; Herman, V.; Sharif, S. Exploring the function of quorum sensing regulated biofilms in biological wastewater treatment: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, X.; Ye, T.; Mishra, S.; Bhatt, P.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. Quorum quenching in a novel Acinetobacter sp. XN-10 bacterial strain against Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høyland-Kroghsbo, N.M.; Bassler, B.L. Phage infection restores PQS signaling and enhances growth of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasI quorum-sensing mutant. J. Bacteriol. 2022, 204, e00557-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chen, W.; Bhatt, K.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, X.; Liu, S.; He, J.; Zhang, L.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wang, H.; et al. A novel bacterial strain Burkholderia sp. F25 capable of degrading diffusible signal factor signal shows strong biocontrol potential. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1071693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; He, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, M.; Mao, W.; Zhang, H.; Yao, B. Orally administered thermostable N-acyl homoserine lactonase from Bacillus sp. strain AI96 attenuates aeromonas hydrophila infection in zebrafish. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, R.J.; Labbate, M.; Kjelleberg, S. AHL-driven quorum-sensing circuits: Their frequency and function among the Proteobacteria. ISME J. 2008, 2, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H.; Purohit, A.A.; Leiros, H.K.S.; Johansen, J.A.; Kellermann, S.J.; Bjelland, A.M.; Willassen, N.P. The autoinducer synthases LuxI and AinS are responsible for temperature-dependent AHL production in the fish pathogen Aliivibrio salmonicida. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaplina, O.; Khmel, I.; Zaitseva, Y.; Khaitlina, S. The role of SprIR quorum sensing system in the regulation of Serratia proteamaculans 94 invasion. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshafie, H.S.; Devescovi, G.; Venturi, V.; Camele, I.; Bufo, S.A. Study of the regulatory role of N-acyl homoserine lactones mediated quorum sensing in the biological activity of Burkholderia gladioli pv. agaricicola causing soft rot of Agaricus spp. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, M.C. Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii: Lessons learned from a xylem-dwelling pathogen of sweet corn. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2011, 12, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Hwang, B.J.; Shin, M.H.; Kim, J.A.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, J.K. N-acylhomoserine lactonase producing Rhodococcus spp. with different AHL-degrading activities. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 261, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Song, S.; Jia, Y. N-3-oxo-octanoyl homoserine lactone primes plant resistance against necrotrophic pathogen Pectobacterium carotovorum by coordinating jasmonic acid and auxin-signaling pathways. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 886268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, J.; Genin, S.; Magori, S.; Citovsky, V.; Sriariyanum, M.; Ronald, P.; Dow, M.; Verdier, V.; Beer, S.V.; Machado, M.A.; et al. Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology: Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Kang, J.; Chung, E.-H.; Lee, Y. Disruption of the metC gene affects methionine biosynthesis in Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum Pcc21 and reduces soft-rot disease. Plant Pathol. J. 2023, 39, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, S. A novel quorum quencher, Rhodococcus pyridinivorans XN-36, is a powerful agent for the biocontrol of soft rot disease in various host plants. Biol. Control. 2022, 169, 104889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garge, S.S.; Nerurkar, A.S. Attenuation of quorum sensing regulated virulence of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum through an AHL lactonase produced by Lysinibacillus sp. Gs50. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terta, M.; Kettani-Halabi, M.; Ibenyassine, K.; Tran, D.; Meimoun, P.; M’hand, R.A.; El-Maarouf-Bouteau, H.; Val, F.; Ennaji, M.M.; Bouteau, F. Arabidopsis thaliana cells: A model to evaluate the virulence of Pectobacterium carotovorum. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2010, 23, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Azaiez, S.; Ben Slimene, I.; Karkouch, I.; Essid, R.; Jallouli, S.; Djebali, N.; Elkahoui, S.; Limam, F.; Tabbene, O. Biological control of the soft rot bacterium Pectobacterium carotovorum by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain Ar10 producing glycolipid-like compounds. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 217, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, W.; Chen, S.F.; Lei, Q.; Li, J.; Bhatt, P.; Mishra, S.; Chen, S. Cellular response and molecular mechanism of glyphosate degradation by Chryseobacterium sp. Y16C. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 6650–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.J.; Zhang, W.; Lei, Q.; Chen, S.F.; Huang, Y.; Bhatt, K.; Liao, L.; Zhou, X. Pseudomonas aeruginosa based concurrent degradation of beta-cypermethrin and metabolite 3-phenoxybenzaldehyde, and its bioremediation efficacy in contaminated soils. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, S.A.; Collignon, P.J. Antimicrobial resistance: A one health perspective. In Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria from Livestock and Companion Animals; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 521–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Ye, T.; Li, Q.; Bhatt, P.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. Potential of a quorum quenching bacteria isolate Ochrobactrum intermedium D-2 against soft rot pathogen Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leguina, A.C.d.V.; Nieto, C.; Pajot, H.F.; Bertini, E.V.; Mac Cormack, W.; Castellanos de Figueroa, L.I.; Nieto-Peñalver, C.G. Inactivation of bacterial quorum sensing signals N-acyl homoserine lactones is widespread in yeasts. Fungal Biol. 2018, 122, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, V.C.; Wood, T.K.; Kumar, P. Evolution of resistance to quorum-sensing inhibitors. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 68, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ye, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, X.; Dai, W.; Chen, S. Identification of FadT as a novel quorum quenching enzyme for the degradation of diffusible signal factor in Cupriavidus pinatubonensis strain HN-2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 2, 9862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prazdnova, E.V.; Gorovtsov, A.V.; Vasilchenko, N.G.; Kulikov, M.P.; Statsenko, V.N.; Bogdanova, A.A.; Refeld, A.G.; Brislavskiy, Y.A.; Chistyakov, V.A.; Chikindas, M.L. Quorum-sensing inhibition by gram-positive bacteria. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.G.; Liu, Y.C.; Chang, C.Y. Inhibiting N-acyl-homoserine lactone synthesis and quenching Pseudomonas quinolone quorum sensing to attenuate virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluch, E.; Rewak-Soroczyńska, J.; Jędrusik, I.; Mazurkiewicz, E.; Jermakow, K. Prevention of biofilm formation by quorum quenching. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, W.J.; Bhatt, K.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.H.; Chen, S.; Wang, J. Innovative microbial disease biocontrol strategies mediated by quorum quenching and their multifaceted applications: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1063393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancu, M.M. Characterization of new diesel-degrading bacteria isolated from freshwater sediments. Int. Microbiol. 2023, 26, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, S.F.; Chen, W.J.; Zhu, X.; Mishra, S.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. Efficient biodegradation of multiple pyrethroid pesticides by Rhodococcus pyridinivorans strain Y6 and its degradation mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 469, 143863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, K.R.; Beck von Bodman, S.; Farrand, S.K. Conjugation factor of Agrobacterium tumefaciens regulates Ti plasmid transfer by autoinduction. Nature 1993, 362, 448–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, W.; Lin, Z.; Huang, Y.; El Sebai, T.N.; Alansary, N.; El-Hefny, D.E.; Mishra, S.; Bhatt, P.; Lü, H.; et al. Rapid biodegradation of the organophosphorus insecticide acephate by a novel strain Burkholderia sp. A11 and its impact on the structure of the indigenous microbial community. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 5261–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhan, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, F.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. Characterization of a pyrethroid-degrading Pseudomonas fulva strain P31 and biochemical degradation pathway of D-phenothrin. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, T.; Zhou, T.; Fan, X.; Bhatt, P.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. Acinetobacter lactucae strain QL-1, a novel quorum quenching candidate against bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Xu, J.L.; Hu, J.; Wang, L.H.; Ong, S.L.; Leadbetter, J.R.; Zhang, L.H. Acyl-homoserine lactone acylase from Ralstonia strain XJ12B represents a novel and potent class of quorum-quenching enzymes. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Chen, W.J.; Huang, Y.; Wei, M.; Chang, C. Insights into the metabolic pathways and biodegradation mechanisms of chloroacetamide herbicides. Environ. Res. 2023, 229, 115918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, P.N.N.; Rovida, A.F.d.S.; Silva, C.R.; Pileggi, S.A.V.; Olchanheski, L.R.; Pileggi, M. Specific quorum sensing molecules are possibly associated with responses to herbicide toxicity in a Pseudomonas strain. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajiagha, M.N.; Kafil, H.S. Efflux pumps and microbial biofilm formation. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2023, 112, 105459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Zhou, T.; Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Fan, X.; Mishra, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Chen, S. Whole-genome sequencing analysis of quorum quenching bacterial strain Acinetobacter lactucae QL-1 identifies the FadY enzyme for degradation of the diffusible signal factor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyappan, S.V.; Bhaskaran, K. Extracellular lactonase-mediated quorum quenching by a novel Bacillus velezensis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2022, 369, fnac095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Kang, H.O.; Jang, H.S.; Lee, J.K.; Koo, B.T.; Yum, D.Y. Identification of extracellular N-acylhomoserine lactone acylase from a Streptomyces sp. and its application to quorum quenching. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2632–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, D.H.; Lee, S.W.; Mikolaityte, V.; Kim, Y.W.; Jeong, H.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, J.K. Identification of a second type of AHL-lactonase from Rhodococcus sp. BH4, belonging to the α/β hydrolase superfamily. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Lin, Q.; Dong, L.; Wu, W.; Liang, Z.; Dong, Z.; Ye, H.; Liao, L.; Zhang, L.H. A bacterial isolate capable of quenching both diffusible signal factor- and N-acylhomoserine lactone-family quorum sensing signals shows much enhanced biocontrol potencies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 7716–7726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualpa, J.; Lopez, G.; Nievas, S.; Coniglio, A.; Halliday, N.; Cámara, M.; Cassán, F. Azospirillum brasilense Az39, a model rhizobacterium with AHL quorum-quenching capacity. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 1850–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.; Bhatt, K.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, S.; Chen, S. Biofilm formation in xenobiotic-degrading microorganisms. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2022, 28, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.J.; Petersen, A.; Whiteley, M.; Leadbetter, J.R. Identification of QuiP, the product of gene PA1032, as the second acyl-homoserine lactone acylase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uroz, S.; Chhabra, S.R.; Cámara, M.; Williams, P.; Oger, P.; Dessaux, Y. N-acylhomoserine lactone quorum-sensing molecules are modified and degraded by Rhodococcus erythropolis W2 by both amidolytic and novel oxidoreductase activities. Microbiology 2005, 151, 3313–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Fan, X.; Li, J.; Ye, T.; Mishra, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. Exploration of the quorum-quenching mechanism in Pseudomonas nitroreducens W-7 and its potential to attenuate the virulence of Dickeya zeae EC1. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 694161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librizzi, V.; Malacrinò, A.; Li Destri Nicosia, M.G.; Barger, N.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; Pangallo, S.; Agosteo, G.E.; Schena, L. Extracts from environmental strains of Pseudomonas spp. effectively control fungal plant diseases. Plants 2022, 11, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lin, N.; Chen, Y.; Liang, Z.; Liao, L.; Lv, M.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; He, F.; Chen, S.H.; et al. Biocontrol of sugarcane smut disease by interference of fungal sexual mating and hyphal growth using a bacterial isolate. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, G.; Morrissey, J.P.; Higgins, P.; O’gara, F. Molecular-based strategies to exploit Pseudomonas biocontrol strains for environmental biotechnology applications. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 56, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.S.; Liao, L.S.; Chen, S.H.; Zhang, L.H. A quorum quenching bacterial isolate contains multiple substrate-inducible genes conferring degradation of diffusible signal factor. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02930-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazantseva, O.A.; Buzikov, R.M.; Pilipchuk, T.A.; Valentovich, L.N.; Kazantsev, A.N.; Kalamiyets, E.I.; Shadrin, A.M. The bacteriophage Pf-10-A component of the biopesticide “Multiphage” used to control agricultural crop diseases caused by Pseudomonas syringae. Viruses 2021, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; He, F.; Lin, N.; Chen, Y.; Liang, Z.; Liao, L.; Lv, M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.H.; Zhou, J.; et al. Pseudomonas sp. ST4 produces variety of active compounds to interfere fungal sexual mating and hyphal growth. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yang, S.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G. Characteristics of biological control and mechanisms of Pseudomonas chlororaphis zm-1 against peanut stem rot. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Zhu, X.; Yan, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Chen, S. The Isolate Pseudomonas multiresinivorans QL-9a Quenches the Quorum Sensing Signal and Suppresses Plant Soft Rot Disease. Plants 2023, 12, 3037. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173037
Liu S, Zhu X, Yan Z, Liu H, Zhang L, Chen W, Chen S. The Isolate Pseudomonas multiresinivorans QL-9a Quenches the Quorum Sensing Signal and Suppresses Plant Soft Rot Disease. Plants. 2023; 12(17):3037. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173037
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Siqi, Xixian Zhu, Zhenchen Yan, Hui Liu, Lianhui Zhang, Wenjuan Chen, and Shaohua Chen. 2023. "The Isolate Pseudomonas multiresinivorans QL-9a Quenches the Quorum Sensing Signal and Suppresses Plant Soft Rot Disease" Plants 12, no. 17: 3037. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173037
APA StyleLiu, S., Zhu, X., Yan, Z., Liu, H., Zhang, L., Chen, W., & Chen, S. (2023). The Isolate Pseudomonas multiresinivorans QL-9a Quenches the Quorum Sensing Signal and Suppresses Plant Soft Rot Disease. Plants, 12(17), 3037. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173037






