Phytochemical Profile and Composition of Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): Varietal Differences and Effect of Germination under Elicited Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
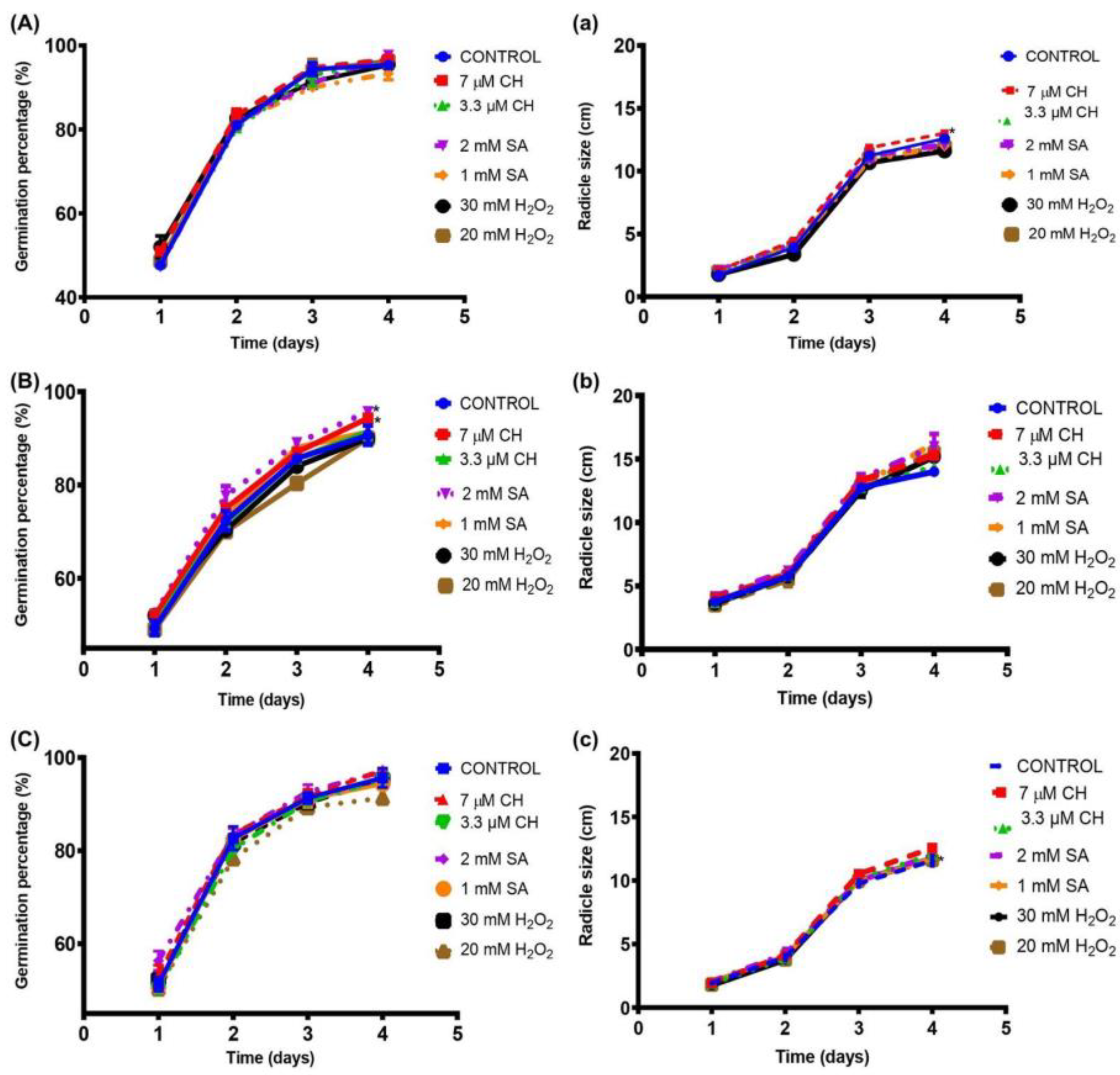
2.1. Increased Percentage of Germination and Radicle Size of Chickpea Seeds after Chemical Elicitation
2.2. Decreased Content of Antinutritional Compounds in Chickpea Sprouts after Chemical Elicitation
2.3. Increased Mono-, Di-, and Oligosaccharide Contents after Germination and Chemical Elicitation
2.4. Chemical Elicitation and Chickpea Varietal Effects on Phytochemical Profile of Chickpea Sprouts
3. Discussion
3.1. Increased Percentage of Germination and Radicle Size of Chickpea Seeds after Chemical Elicitation
3.2. Decreased Content of Antinutritional Compounds in Chickpea Sprouts after Chemical Elicitation
3.3. Increased Mono-, Di-, and Oligosaccharide Contents after Germination and Chemical Elicitation
3.4. Chemical Elicitation and Chickpea Varietal Effects on Phytochemical Profile of Chickpea Sprouts
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Germination Process and Chemical Elicitation Treatments
4.3. Quantitation of Antinutritional Compounds
4.4. Sample Preparation and Carbohydrate Profile and Mono-, Di-, and Oligosaccharide Contents
4.5. Sample Preparation and Analysis of Polyphenol Profile
4.6. Sample Preparation and Analysis of Phytosterol Profile
4.7. Sample Preparation and Analysis of Saponin Profile
4.8. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khalil, A.W.; Zeb, A.; Mahmood, F.; Tariq, S.; Khattak, B.A.; Shah, H. Comparison of sprout quality characteristics of desi and kabuli type chickpea cultivars (Cicer arietinum L.). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukanti, A.K.; Gaur, P.M.; Gowda, C.L.; Chibbar, R.N. Nutritional quality and health benefits of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): A review. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, S11–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SIAP. Servicio de Información Agroalimentaria y Pesquera. 2023. Secretaría de Agricultura y Desarrollo Rural. Gobierno de México. Available online: https://nube.siap.gob.mx/cierreagricola/ (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- Ortega Murrieta, P.F.; Fierros Leyva, G.A.; Padilla Valenzuela, I.; Valenzuela Herrera, V.; Acosta-Gallegos, J.A.; Gutiérres Perez, E.; Velarde Félix, S.; Rodríguez Cota, F.G. Blanoro, new white chickpea variety with extra-large grain for exportation. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Agríc. 2016, 7, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Arevalo, I.; Guzmán-Maldonado, S.H.; Sanchez, S.M.M.; Acosta-Gallegos, J.A. Steaming and Toasting Reduce the Nutrimental Quality, Total Phenols and Antioxidant Capacity of Fresh Kabuli Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2020, 75, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintero-Soto, M.F.; Saracho-Peña, A.G.; Chavez-Ontiveros, J.; Garzon-Tiznado, J.A.; Pineda-Hidalgo, K.V.; Delgado-Vargas, F.; Lopez-Valenzuela, J.A. Phenolic profiles and their contribution to the antioxidant activity of selected chickpea genotypes from Mexico and ICRISAT collections. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2018, 73, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltero-Díaz, L.; Andrade Arias, E.; Cabrera, G.; Arath, O.; Pérez Valdez, J. San Antonio 05, variedad de garbanzo forrajero para la región ciénega de Chapala, México. Agricul. Téc. Méx. 2008, 34, 263–265. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.K.; Gupta, K.; Sharma, A.; Das, M.; Ansari, I.A.; Dwivedi, P.D. Health risks and benefits of chickpea (Cicer arietinum) consumption. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldo, R.; Santos, C.S.; Pinto, E.; Vasconcelos, M.W. Widening the perspectives for legume consumption: The case of bioactive non-nutrients. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 772054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.-Y.; Lui, W.-Y.; Wu, K.; Chan, C.-L.; Dai, S.-H.; Sui, Z.-Q.; Corke, H. Bioactive compounds and bioactivities of germinated edible seeds and sprouts: An updated review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 59, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzo, A. The close linkage between nutrition and environment through biodiversity and sustainability: Local foods, traditional recipes, and sustainable diets. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Song, L.; Feng, S.; Liu, Y.; He, G.; Yioe, Y.; Liu, S.Q.; Huang, D. Germination dramatically increases isoflavonoid content and diversity in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) seeds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8606–8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Yang, X.; Xia, Z. Effects of sodium selenite and germination on the sprouting of chickpeas (Cicer arietinum L.) and its content of selenium, formononetin and biochanin A in the sprouts. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 146, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Arispuro, D.M.; Cuevas-Rodríguez, E.O.; Milán-Carrillo, J.; León-López, L.; Gutiérrez-Dorado, R.; Reyes-Moreno, C. Optimal germination condition impacts on the antioxidant activity and phenolic acids profile in pigmented desi chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) seeds. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Jin, Z.; Ohm, J.B.; Schwarz, P.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Improvement of the antioxidative activity of soluble phenolic compounds in chickpea by germination. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6179–6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, M.A.; Sharaf El-Din, M.G.; Selim, M.A.; Owis, A.I.; Abouzid, S.F.; Porzel, A.; Wessjohann, L.A.; Otify, A. Nuclear magnetic resonance metabolomics approach for the analysis of major legume sprouts coupled to chemometrics. Molecules 2021, 26, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjad, N.; Usman, M.; Ahsan, T.; Afzal, S. Effect of pretreatment of H2O2 on seed germination and vegetative growth of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Int. J. Water Resour. Environ. Sci. 2012, 1, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- León-López, L.; Escobar-Zúñiga, Y.; Salazar-Salas, N.Y.; Mora Rochín, S.; Cuevas-Rodríguez, E.O.; Reyes-Moreno, C.; Milán-Carrillo, J. Improving polyphenolic compounds: Antioxidant activity in chickpea sprouts through elicitation with hydrogen peroxide. Foods 2020, 9, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnle, G.G.; Dell’Aquila, C.; Aspinall, S.M.; Runswick, S.A.; Joosen, A.M.; Mulligan, A.A.; Bingham, S.A. Phytoestrogen content of fruits and vegetables commonly consumed in the UK based on LC–MS and 13C-labelled standards. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, M.; Jayaraman, S.; Eladl, M.A.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Abdelrahman, M.A.E.; Veeraraghavan, V.P.; Vengadassalapathy, S.; Umapathy, V.R.; Jaffer Hussain, S.F.; Krishnamoorthy, K.; et al. Comprehensive review on therapeutic perspectives of phytosterols in insulin resistance: A mechanistic approach. Molecules 2022, 27, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Singh, J.P.; Singh, N.; Kaur, A. Saponins in pulses and their health promoting activities: A review. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, M.; Heidari, M.A.; Kazemi, M.; Filinejad, A.R. Salicylic acid induced changes in some physiological parameters in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) under salt stress. Int. J. Agric. Technol. 2013, 9, 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza-Sánchez, M.; Guevara-González, R.G.; Castaño-Tostado, E.; Mercado-Silva, E.M.; Acosta-Gallegos, J.A.; Rocha-Guzmán, N.E.; Reynoso-Camacho, R. Effect of chemical stress on germination of cv Dalia bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as an alternative to increase antioxidant and nutraceutical compounds in sprouts. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohail, S.A.; Chaurasia, A.K.; Bara, B.M. Effect of different seed priming methods on germination and vigour of kabuli chickpea (Cicer kabulium L.) seeds. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2018, 7, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-San Vicente, M.; Plasencia, J. Salicylic acid beyond defence: Its role in plant growth and development. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3321–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, G. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) generation, scavenging and signaling in plants. In Oxidative Damage to Plants: Antioxidant Networks and Signaling, 1st ed.; Ahmad, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 557–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichyangkura, R.; Chadchawan, S. Biostimulant activity of chitosan in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, M.; Ruelland, E. Magical mystery tour: Salicylic acid signalling. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 114, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Grewal, S.K.; Gill, P.S.; Singh, S. Comparison of cultivated and wild chickpea genotypes for nutritional quality and antioxidant potential. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1864–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitra, U.; Singh, U.; Rao, P.V. Phytic acid, in vitro protein digestibility, dietary fiber, and minerals of pulses as influenced by processing methods. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1996, 49, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Adawy, T.A. Nutritional composition and antinutritional factors of chickpeas (Cicer arietinum L.) undergoing different cooking methods and germination. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2002, 57, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U. Antinutritional factors of chickpea and pigeon pea and their removal by processing. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1988, 38, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangola, M.P.; Jaiswal, S.; Kannan, U.; Gaur, P.M.; Båga, M.; Chibbar, R.N. Galactinol synthase enzyme activity influences raffinose family oligosaccharides (RFO) accumulation in developing chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) seeds. Phytochemistry 2016, 125, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elango, D.; Rajendran, K.; Van der Laan, L.; Sebastiar, S.; Raigne, J.; Thaiparambil, N.A.; El Haddad, N.; Raja, B.; Wang, W.; Ferela, A.; et al. Raffinose family oligosaccharides: Friend or foe for human and plant health? Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 829118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunraj, R.; Skori, L.; Kumar, A.; Hickerson, N.; Shoma, N.; Vairamani, M.; Samuel, M.A. Spatial regulation of alpha-galactosidase activity and its influence on raffinose family oligosaccharides during seed maturation and germination in Cicer arietinum. Plant Signal. Behav. 2020, 15, 1709707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaivani, V.; Nikarika, R.; Shoma, N.; Arunraj, R. Delayed hydrolysis of Raffinose Family Oligosaccharides (RFO) affects critical germination of chickpeas. 3 Biotech. 2021, 11, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisa, H.A.; Gao, Y.; Yili, A.; Ma, Q.; Cheng, Z. Beneficial role of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) functional factors in the intervention of Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes Mellitus. In Bioactive Food as Dietary Interventions for Diabetes, 2nd ed.; Watson, R.R., Preedy, V.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ren, G. Isoflavone content and composition in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) sprouts germinated under different conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 2701–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butkutė, B.; Taujenis, L.; Norkevičienė, E. Small-seeded legumes as a novel food source. Variation of nutritional, mineral and phytochemical profiles in the chain: Raw seeds-sprouted seeds-microgreens. Molecules 2019, 24, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirotén, Á.; Bravo, D.; Landete, J.M. Bacterial metabolism as responsible of beneficial effects of phytoestrogens on human health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1922–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikara, S.; Nagaprashantha, L.D.; Singhal, J.; Horne, D.; Awasthi, S.; Singhal, S.S. Oxidative stress and dietary phytochemicals: Role in cancer chemoprevention and treatment. Cancer Lett. 2018, 413, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, A.R.; Ema, T.I.; Siddiquee, M.F.; Shahriar, A.; Ahmed, H.; Mosfeq-Ul-Hasan, M.; Rahman, N.; Islam, R.; Uddin, M.R.; Mizan, M.F.R. Natural flavonols: Actions, mechanisms, and potential therapeutic utility for various diseases. Beni. Suef. Univ. J. Basic. Appl. Sci. 2023, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, R.; Khan, M.; Asaf, S.; Lubna; Asif, S.; Kim, K.M. Bioactivity and therapeutic potential of kaempferol and quercetin: New insights for plant and human health. Plants 2022, 11, 2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xue, R.; Lv, M.; Qi, Y.; Yu, W.; Xie, Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Tian, X.; Han, B. Stepwise tracking strategy to screen ingredient from Galla Chinensis based on the “mass spectrometry guided preparative chromatography coupled with systems pharmacology”. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 284, 114533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, D.; Kim, J.; Nam, G.; Zhao, X.; Kwon, J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Yoon, S.Y.; Chung, S.J. Ethyl gallate dual-targeting PTPN6 and PPARγ shows anti-diabetic and anti-obese effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xia, L. Molecular mechanism of β-sitosterol and its derivatives in tumor progression. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 926975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Dai, Z.; Liu, A.B.; Huang, J.; Narsipur, N.; Guo, G.; Kong, B.; Reuhl, K.; Lu, W.; Luo, Z.; et al. Intake of stigmasterol and β-sitosterol alters lipid metabolism and alleviates NAFLD in mice fed a high-fat western-style diet. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2018, 1863, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, R.G.; Price, K.; Rose, M.; Rhodes, M.; Fenwick, R. A preliminary study on the effect of germination on saponin content and composition of lentils and chickpeas. Z. Lebensm Unters Forsch. 1996, 203, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serventi, L.; Chitchumroonchokchai, C.; Riedl, K.M.; Kerem, Z.; Berhow, M.A.; Vodovotz, Y.; Schwartz, S.J.; Failla, M.L. Saponins from soy and chickpea: Stability during beadmaking and in vitro bioaccessibility. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6703–6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.R.; Kwak, S.M.; Bang, S.H.; Jeong, J.E.; Kim, D.J. Chronic saponin treatment attenuates damage to the pancreas in chronic alcohol-treated diabetic rats. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kakade, M.L.; Rackis, J.J.; McGhee, J.E.; Puski, G. Determination of trypsin inhibitor activity of soy products: A collaborative analysis of an improved procedure. Cereal Chem. 1974, 51, 376–382. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, G.; More, L.J.; McKenzie, N.H.; Stewart, J.C.; Pusztai, A. A survey of the nutritional and haemagglutination properties of legume seeds generally available in the UK. Br. J. Nutr. 1983, 50, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G.; Alonso, R.; Marzo, F.; Santidrián, S. A modified method for the indirect quantitative analysis of phytate in foodstuffs. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 225, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Hernández, M.G.; Ochoa-Martínez, L.A.; Rutiaga-Quiñones, J.G.; Rocha-Guzmán, N.E.; Lara-Ceniceros, T.E.; Contreras-Esquivel, J.C.; Prado-Barragán, L.A.; Rutiaga-Quiñones, O.M. Effect of ultrasound pre-treatment on the physicochemical composition of Agave durangensis leaves and potential enzyme production. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Sánchez, M.; Pérez-Ramírez, I.F.; Wall-Medrano, A.; Martinez-Gonzalez, A.I.; Gallegos-Corona, M.A.; Reynoso-Camacho, R. Chemically induced common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) sprouts ameliorate dyslipidemia by lipid intestinal absorption inhibition. J. Funct. Foods. 2019, 52, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Niu, X.; Yang, G.; Wang, L.; Duan, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, C. Quantitative determination of free phytosterols in tobacco leaves by UPLC-MS/MS. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2013, 36, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Blanoro | Patron | San Antonio | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Trypsin Inhibitory Activity 1 | Haemagglutinating Activity 2 | Phytic Acid Content 3 | Trypsin Inhibitory Activity 1 | Haemagglutinating Activity 2 | Phytic Acid Content 3 | Trypsin Inhibitory Activity 1 | Haemagglutinating Activity 2 | Phytic Acid Content 3 |
| Raw seed | 37.8 ± 1.0 a | 7.0 ± 0.2 a | 0.61 ± 0.04 a | 18.7 ± 0.6 a | 7.8 ± 0.3 a | 0.62 ± 0.03 a | 26.4 ± 1.7 a | 6.4 ± 0.5 a | 0.48 ± 0.05 a |
| Control 4 | 28.9 ± 0.9 b | 3.4 ± 0.4 b | 0.37 ± 0.03 b | 14.7 ± 1.2 b | 5.4 ± 0.5 b | 0.37 ± 0.02 b | 19.5 ± 1.6 b | 4.3 ± 0.2 b | 0.29 ± 0.03 b |
| 1 mM SA | 19.5 ± 0.8 e | 2.4 ± 0.3 d | 0.19 ± 0.01 d | 10.9 ± 0.8 cd | 4.1 ± 0.2 c | 0.34 ± 0.01 bc | 15.9 ± 0.8 de | 3.2 ± 0.3 cd | 0.22 ± 0.01 bc |
| 2 mM SA | 19.3 ± 1.5 e | 1.3 ± 0.1 e | 0.29 ± 0.02 c | 9.2 ± 0.8 e | 2.1 ± 0.1 e | 0.30 ± 0.02 cde | 13.1 ± 0.1 f | 2.5 ± 0.3 e | 0.17 ± 0.02 cd |
| 3.3 μM CH | 26.5 ± 2.3 bc | 2.8 ± 0.1 c | 0.22 ± 0.0 b c | 12.1 ± 0.2 c | 3.3 ± 0.3 d | 0.31 ± 0.02 cd | 18.9 ± 1.0 bc | 3.4 ± 0.2 c | 0.23 ± 0.03 bc |
| 7 μM CH | 23.9 ± 2.1 cd | 1.4 ± 0.1 e | 0.19 ± 0.01 d | 10.7 ± 0.3 d | 3.0 ± 0.1 d | 0.25 ± 0.02 e | 14.8 ± 1.0 ef | 3.0 ± 0 cde | 0.20 ± 0.01 cd |
| 20 mM H2O2 | 24.6 ± 0.7 cd | 3.0 ± 0.1 c | 0.29 ± 0.02 c | 14.7 ± 0.4 b | 3.9 ± 0.2 c | 0.30 ± 0.02 cde | 18.1 ± 0.5 bc | 3.4 ± 0.4 c | 0.20 ± 0.02 cd |
| 30 mM H2O2 | 22.5 ± 0.9 d | 2.1 ± 0.2 d | 0.34 ± 0.03 bc | 14.0 ± 0.6 b | 3.0 ± 0.1 d | 0.28 ± 0.02 de | 16.9 ± 0.8 cd | 2.8 ± 0.2 de | 0.13 ± 0.02 d |
| Monosaccharides | Disaccharides | Oligosaccharides | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fructose | Glucose | Mannose | Sucrose | Raffinose | Stachyose | |
| Retention time (min) | 4.39 | 4.92 | 4.77 | 5.69 | 6.84 | 7.68 |
| m/z | 179 | 179 | 179 | 341 | 503 | 665 |
| Fragments | 71, 89 | 89, 119 | 89, 119 | 89, 119, 179 | 89, 179, 323 | 89, 179, 323 |
| Treatment | Blanoro (g/100 g) | |||||
| Raw seed | 0.19 ± 0.01 e | 0.03 ± 0.00 d | LDL | 7.01 ± 0.02 d | 0.10 ± 0.10 d | 1.20 ± 0.01 d |
| Control | 0.70 ± 0.01 c | 0.45 ± 0.01 a | 0.53 ± 0.01 d | 12.50 ± 0.02 b | 0.72 ± 0.01 b | 1.46 ± 0.01 c |
| 2 mM SA | 0.82 ± 0.01 a | 0.40 ± 0.01 b | 0.77 ± 0.02 b | 13.88 ± 0.16 a | 0.76 ± 0.01 a | 1.59 ± 0.04 b |
| 7 μM CH | 0.62 ± 0.00 d | 0.32 ± 0.02 c | 0.96 ± 0.02 a | 11.92 ± 0.07 c | 0.66 ± 0.01 c | 1.63 ± 0.04 b |
| 30 mM H2O2 | 0.77 ± 0.01 b | 0.43 ± 0.01 ab | 0.72 ± 0.01 c | 13.96 ± 0.01 a | 0.68 ± 0.00 c | 1.75 ± 0.01 a |
| Treatment | Patron (g/100 g) | |||||
| Raw seed | 0.27 ± 0.00 e | 0.01 ± 0.00 e | 0.18 ± 0.02 e | 3.31 ± 0.02 d | 0.15 ± 0.00 d | 0.92 ± 0.02 b |
| Control | 0.76 ± 0.02 a | 0.47 ± 0.01 a | 0.31 ± 0.00 d | 12.43 ± 0.10 a | 0.38 ± 0.00 c | 0.46 ± 0.01 d |
| 2 mM SA | 0.47 ± 0.02 c | 0.40 ± 0.01 b | 0.97 ± 0.01 b | 11.54 ± 0.11 b | 0.37 ± 0.00 c | 0.44 ± 0.00 d |
| 7 μM CH | 0.55 ± 0.02 b | 0.28 ± 0.01 c | 0.93 ± 0.01 c | 11.37 ± 0.07 b | 0.49 ± 0.01 b | 0.78 ± 0.01 c |
| 30 mM H2O2 | 0.40 ± 0.01 d | 0.12 ± 0.01 d | 1.35 ± 0.03 a | 10.56 ± 0.01 c | 0.64 ± 0.00 a | 1.58 ± 0.01 a |
| Treatment | San Antonio (g/100 g) | |||||
| Raw seed | 0.11 ± 0.00 c | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.09 ± 0.01 d | 2.60 ± 0.01 c | 0.14 ± 0.01 d | 0.99 ± 0.02 b |
| Control | 0.48 ± 0.01 b | 0.28 ± 0.01 a | 0.73 ± 0.03 b | 11.48 ± 0.12 b | 0.30 ± 0.00 c | 0.32 ± 0.00 c |
| 2 mM SA | 0.65 ± 0.02 a | 0.29 ± 0.01 a | 0.72 ± 0.02 b | 12.14 ± 0.08 a | 0.78 ± 0.00 ab | 2.15 ± 0.01 a |
| 7 μM CH | 0.49 ± 0.02 b | 0.27 ± 0.02 a | 0.67 ± 0.02 c | 11.58 ± 0.08 b | 0.74 ± 0.03 b | 2.17 ± 0.03 a |
| 30 mM H2O2 | 0.65 ± 0.00 a | 0.30 ± 0.01 a | 0.92 ± 0.04 a | 12.63 ± 0.06 a | 0.80 ± 0.01 a | 2.17 ± 0.02 a |
| Phenolic Compounds | Retention Time | m/z | Control | 1 mM SA | 2 mM SA | 20 mM H2O2 | 30 mM H2O2 | 3.3 μM CH | 7 μM CH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blanoro | |||||||||
| Chlorogenic acid | 1.9 | 353.1, 191.1 179.0 | 0.26 ± 0.01 b | 0.26 ± 0.00 b | 0.32 ± 0.02 a | 0.20 ± 0.00 d | 0.23 ± 0.00 c | 0.25 ± 0.00 b | 0.23 ± 0.00 c |
| Epicatechin | 2.0 | 289.1, 203.1 109.1 | 0.32 ± 0.01 b | 0.30 ± 0.00 b | 0.43 ± 0.00 a | 0.24 ± 0.01 d | 0.28 ± 0.00 c | 0.30 ± 0.00 b | 0.27 ± 0.00 c |
| Catechin | 3.0 | 289.1, 203.1 109.1 | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | 0.06 ± 0.00 a | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | 0.06 ± 0.00 a | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | 0.06 ± 0.00 a |
| Gallic acid | 3.7 | 169.0, 125.0 | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 b |
| p-hydroxybenzoic acid | 4.2 | 137.0, 108.0 | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a |
| Genistein | 5.2 | 269.0, 133.0 | 1.60 ± 0.01 b | 1.47 ± 0.01 d | 1.83 ± 0.01 a | 1.28 ± 0.01 f | 1.28 ± 0.00 f | 1.56 ± 0.01 c | 1.33 ± 0.00 e |
| Daidzein | 5.6 | 255.1, 91.0 | 0.29 ± 0.01 bc | 0.31 ± 0.00 b | 0.34 ± 0.00 a | 0.23 ± 0.00 f | 0.24 ± 0.00 ef | 0.28 ± 0.00 c | 0.25 ± 0.00 de |
| Matairesinol | 6.2 | 357.1, 122.0 83.1 | 0.29 ± 0.00 b | 0.29 ± 0.00 b | 0.37 ± 0.00 a | 0.20 ± 0.00 e | 0.23 ± 0.00 d | 0.27 ± 0.00 c | 0.26 ± 0.00 c |
| Methyl gallate | 7.1 | 167.0, 140.0 124.0, 111.1 | 0.07 ± 0.00 bc | 0.08 ± 0.00 b | 0.11 ± 0.00 a | 0.06 ± 0.00 cd | 0.05 ± 0.00 d | 0.06 ± 0.00 cd | 0.08 ± 0.00 b |
| Secoisolariciresinol | 9.6 | 361.2, 346.1 165.0, 121.1 | 0.10 ± 0.00 b | 0.10 ± 0.00 b | 0.10 ± 0.00 b | 0.10 ± 0.00 b | 0.10 ± 0.00 b | 0.32 ± 0.00 a | 0.10 ± 0.00 b |
| Ethyl gallate | 12.1 | 197.0, 169.0 124.0 | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 b |
| Kaempferol | 14.1 | 285.1, 151.0 | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | 0.06 ± 0.00 a | 0.10 ± 0.00 c | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | 0.05 ± 0.00 b |
| Protocatechuic acid | 14.5 | 315.1, 123.0 108.0 | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a |
| Epicatechin gallate | 14.7 | 441.1, 331.1 289.1, 168.9 | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | 0.08 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 c | 0.04 ± 0.00 c | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | 0.05 ± 0.00 b |
| Epigallocatechin gallate | 16.0 | 457.1, 331.1 287.1, 169.1 | 0.20 ± 0.00 e | 0.28 ± 0.00 c | 0.33 ± 0.00 b | 0.19 ± 0.00 e | 0.19 ± 0.00 e | 0.37 ± 0.00 a | 0.25 ± 0.00 d |
| p-Coumaric acid | 16.2 | 163.0, 146.0 119.1 | 0.09 ± 0.00 cd | 0.11 ± 0.00 b | 0.15 ± 0.00 a | 0.08 ± 0.00 d | 0.08 ± 0.00 d | 0.10 ± 0.00 bc | 0.09 ± 0.00 cd |
| Rosmarinic acid | 16.7 | 359.1, 197.1 179.1 | LDL | LDL | 0.002 ± 0.000 | LDL | LDL | LDL | LDL |
| Quercetin | 17.2 | 301.1, 179.1 151.1 | 0.19 ± 0.00 ef | 0.27 ± 0.01 b | 0.55 ± 0.00 a | 0.18 ± 0.00 f | 0.20 ± 0.00 de | 0.24 ± 0.00 c | 0.24 ± 0.00 c |
| Formononetin | 17.4 | 267.1, 252.1 191.1 | 3.37 ± 0.03 e | 4.59 ± 0.06 b | 6.08 ± 0.06 a | 3.22 ± 0.01 f | 3.24 ± 0.01 f | 4.05 ± 0.01 c | 4.10 ± 0.02 d |
| Biochanin A | 18.9 | 283.1, 268.1 211.1, 109.1 | 4.46 ± 0.03 d | 5.44 ± 0.07 c | 6.37 ± 0.05 a | 4.37 ± 0.01 d | 4.45 ± 0.04 d | 5.66 ± 0.01 b | 5.33 ± 0.09 c |
| Sinapic acid | 21.3 | 223.1, 208.0 | 0.001 ± 0.000 c | 0.002 ± 0.000 b | 0.005 ± 0.000 a | LDL | LDL | LDL | LDL |
| Eriocitrin | 21.5 | 595.2, 287.1 151.0 | LDL | LDL | LDL | LDL | LDL | 0.003 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 a |
| Ellagic acid | 22.5 | 301.0, 229.0 185.0, 145.0 | 0.003 ± 0.000 b | 0.002 ± 0.000 c | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.003 ± 0.000 b | 0.002 ± 0.000 c | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a |
| Rutin | 27.0 | 609.1, 301.1 151.1 | 0.21 ± 0.00 b | 0.21 ± 0.00 b | 0.22 ± 0.00 b | 0.27 ± 0.00 a | 0.28 ± 0.00 a | 0.28 ± 0.00 a | 0.28 ± 0.00 a |
| Patron | |||||||||
| Chlorogenic acid | 1.9 | 353.1, 191.1 179.0 | 0.32 ± 0.00 d | 0.27 ± 0.00 e | 0.38 ± 0.01 b | 0.35 ± 0.00 c | 0.40 ± 0.00 a | 0.42 ± 0.00 a | 0.38 ± 0.00 b |
| Epicatechin | 2.0 | 289.1, 245.1 123.1 | 0.43 ± 0.00 f | 0.39 ± 0.00 g | 0.60 ± 0.00 c | 0.49 ± 0.00 e | 0.70 ± 0.01 a | 0.66 ± 0.00 b | 0.55 ± 0.00 d |
| Catechin | 3.0 | 289.1, 203.1 109.1 | 0.05 ± 0.00 a | 0.05 ± 0.00 a | 0.05 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 b | 0.05 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 b | 0.05 ± 0.00 a |
| Gallic acid | 3.7 | 169.0, 125.0 | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.03 ± 0.00 ab | 0.03 ± 0.00 ab | 0.03 ± 0.00 ab | 0.03 ± 0.00 ab | 0.03 ± 0.00 ab | 0.04 ± 0.00 a |
| p-hydroxybenzoic acid | 4.2 | 137.0, 108.0 | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.0 a |
| Genistein | 5.2 | 269.0, 133.0 | 1.43 ± 0.01 c | 1.20 ± 0.01 d | 1.63 ± 0.00 b | 1.37 ± 0.01 c | 1.68 ± 0.01 a | 1.42 ± 0.01 c | 1.64 ± 0.01 b |
| Daidzein | 5.6 | 255.1, 91.0 | 0.23 ± 0.00 cd | 0.21 ± 0.00 d | 0.31 ± 0.00 a | 0.24 ± 0.00 c | 0.30 ± 0.00 ab | 0.28 ± 0.00 b | 0.30 ± 0.00 ab |
| Matairesinol | 6.2 | 357.1, 122.0 83.1 | 0.27 ± 0.00 d | 0.23 ± 0.00 e | 0.37 ± 0.00 ab | 0.31 ± 0.00 c | 0.35 ± 0.00 b | 0.38 ± 0.00 a | 0.32 ± 0.00 c |
| Methyl gallate | 7.1 | 167.0, 140.0 124.0, 111.1 | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.05 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 a |
| Secoisolariciresinol | 9.6 | 361.2, 165.0 346.1, 121.1 | 0.10 ± 0.00 ab | 0.10 ± 0.00 ab | 0.10 ± 0.00 ab | 0.07 ± 0.00 c | 0.10 ± 0.00 ab | 0.11 ± 0.00 a | 0.11 ± 0.00 a |
| Ethyl gallate | 12.1 | 197.0, 124.0 169.0 | 0.02 ± 0.00 ab | 0.02 ± 0.00 ab | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 ab | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 ab | 0.02 ± 0.00 ab |
| Kaempferol | 14.1 | 285.1, 151.0 | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 ab |
| Protocatechuic acid | 14.5 | 315.1, 123.0 108.0 | 0.004 ± 0.000 b | 0.004 ± 0.000 b | 0.004 ± 0.00 b | 0.004 ± 0.000 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.001 ± 0.00 d | 0.002 ± 0.000 c |
| Epicatechin gallate | 14.7 | 441.1, 331.1 289.1, 168.9 | 0.04 ± 0.00 ab | 0.03 ± 0.00 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 ab | 0.03 ± 0.00 b | 0.05 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 ab |
| Epigallocatechin gallate | 16.0 | 457.1, 331.1 287.1, 169.1 | 0.12 ± 0.03 e | 0.11 ± 0.00 e | 0.17 ± 0.00 d | 0.18 ± 0.00 cd | 0.20 ± 0.00 b | 0.33 ± 0.00 a | 0.19 ± 0.00 bc |
| p-Coumaric acid | 16.2 | 163.0, 146.0 119.1 | 0.04 ± 0.00 b | 0.03 ± 0.00 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 b | 0.06 ± 0.00 a | 0.06 ± 0.00 a | 0.06 ± 0.00 a |
| Rosmarinic acid | 16.7 | 359.1, 197.1 179.1 | LDL | LDL | LDL | LDL | LDL | 0.002 ± 0.000 | LDL |
| Quercetin | 17.2 | 301.1, 179.1 151.1 | 0.06 ± 0.00 cd | 0.05 ± 0.00 d | 0.07 ± 0.00 c | 0.06 ± 0.00 cd | 0.09 ± 0.00 b | 0.26 ± 0.00 a | 0.10 ± 0.00 b |
| Formononetin | 17.4 | 267.1, 252.1 191.1 | 1.52 ± 0.00 c | 1.26 ± 0.01 d | 1.31 ± 0.01 d | 1.52 ± 0.01 c | 2.13 ± 0.01 b | 3.26 ± 0.01 a | 2.06 ± 0.01 b |
| Biochanin A | 18.9 | 283.1, 268.1 109.1 | 1.37 ± 0.01 d | 1.07 ± 0.01 e | 1.04 ± 0.00 e | 1.48 ± 0.01 c | 1.85 ± 0.01 b | 2.44 ± 0.03 a | 1.87 ± 0.02 b |
| Sinapic acid | 21.3 | 223.1, 208.0 | 0.005 ± 0.000 e | 0.005 ± 0.000 e | 0.005 ± 0.000 e | 0.04 ± 0.00 ab | 0.02 ± 0.00 cd | 0.03 ± 0.00 bc | 0.05 ± 0.00 a |
| Eriocitrin | 21.5 | 595.2, 287.1 151.0 | 0.005 ± 0.000 b | LDL | LDL | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a |
| Ellagic acid | 22.5 | 301.0, 229.0 185.0, 145.0 | 0.004 ± 0.000 b | 0.004 ± 0.000 b | 0.003 ± 0.000 c | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.002 ± 0.000 d | 0.003 ± 0.000 c | 0.003 ± 0.000 c |
| Rutin | 27.0 | 609.1, 301.1 151.1 | 0.20 ± 0.00 b | 0.26 ± 0.00 a | 0.27 ± 0.00 a | 0.21 ± 0.00 b | 0.27 ± 0.00 a | 0.21 ± 0.00 b | 0.27 ± 0.00 a |
| San Antonio | |||||||||
| Chlorogenic acid | 1.9 | 353.1, 191.1 179.0 | 0.33 ± 0.01 b | 0.33 ± 0.00 b | 0.33 ± 0.01 b | 0.38 ± 0.00 a | 0.25 ± 0.00 c | 0.34 ± 0.01 b | 0.40 ± 0.00 a |
| Epicatechin | 2.0 | 289.1, 245.1 123.1 | 0.40 ± 0.00 b | 0.40 ± 0.00 b | 0.37 ± 0.00 c | 0.40 ± 0.00 b | 0.18 ± 0.00 d | 0.41 ± 0.00 ab | 0.45 ± 0.02 a |
| Catechin | 3.0 | 289.1, 203.1 109.1 | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a |
| Gallic acid | 3.7 | 169.0, 125.0 | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a |
| p-hydroxybenzoic acid | 4.2 | 137.0, 108.0 | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a |
| Genistein | 5.2 | 269.1, 159.1 133.1 | 1.84 ± 0.01 d | 2.03 ± 0.01 c | 1.86 ± 0.00 d | 2.42 ± 0.01 b | 2.42 ± 0.01 b | 2.02 ± 0.01 c | 2.49 ± 0.02 a |
| Daidzein | 5.6 | 253.1, 137.1 | 0.35 ± 0.00 c | 0.37 ± 0.00 c | 0.35 ± 0.00 c | 0.46 ± 0.02 a | 0.42 ± 0.00 b | 0.40 ± 0.00 b | 0.47 ± 0.01 a |
| Matairesinol | 6.2 | 357.1, 122.0 83.1 | 0.27 ± 0.00 c | 0.27 ± 0.00 c | 0.27 ± 0.00 c | 0.32 ± 0.00 b | 0.38 ± 0.00 a | 0.25 ± 0.00 c | 0.39 ± 0.00 a |
| Methyl gallate | 7.1 | 167.0, 140.0 124.0, 111.1 | 0.05 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 ab | 0.03 ± 0.00 b | 0.03 ± 0.00 b | 0.05 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 ab | 0.04 ± 0.00 ab |
| Secoisolariciresinol | 9.6 | 361.2, 165.0 346.1, 121.1 | 0.11 ± 0.00 c | 0.19 ± 0.00 a | 0.14 ± 0.00 b | 0.13 ± 0.00 b | 0.13 ± 0.00 b | 0.13 ± 0.00 b | 0.11 ± 0.00 c |
| Ethyl gallate | 12.1 | 197.0, 124.0 169.0 | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 ab | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 a |
| Kaempferol | 14.1 | 285.1, 151.0 | 0.05 ± 0.00 bc | 0.05 ± 0.00 bc | 0.06 ± 0.00 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 c | 0.05 ± 0.00 bc | 0.05 ± 0.00 bc | 0.08 ± 0.00 a |
| Protocatechuic acid | 14.5 | 315.1, 123.0 108.0 | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a |
| Epicatechin gallate | 14.7 | 441.1, 331.1 289.1, 168.9 | 0.06 ± 0.00 b | 0.06 ± 0.00 b | 0.09 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 c | 0.05 ± 0.00 bc | 0.06 ± 0.00 b | 0.09 ± 0.00 a |
| Epigallocatechin gallate | 16.0 | 457.1, 331.1 287.1, 169.1 | 0.15 ± 0.00 c | 0.15 ± 0.00 c | 0.16 ± 0.00 c | 0.12 ± 0.00 d | 0.25 ± 0.00 a | 0.13 ± 0.00 d | 0.19 ± 0.00 b |
| p-Coumaric acid | 16.2 | 163.0, 146.0 119.1 | 0.06 ± 0.00 ab | 0.06 ± 0.00 ab | 0.06 ± 0.00 ab | 0.03 ± 0.03 c | 0.07 ± 0.00 a | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | 0.07 ± 0.00 a |
| Rosmarinic acid | 16.7 | 359.1, 197.1 179.1 | 0.002 ± 0.000 a | 0.002 ± 0.000 a | LDL | 0.002 ± 0.000 a | 0.002 ± 0.000 a | 0.002 ± 0.000 a | 0.001 ± 0.000 b |
| Quercetin | 17.2 | 301.1, 179.1 151.1 | 0.14 ± 0.00 d | 0.12 ± 0.00 e | 0.26 ± 0.00 b | 0.10 ± 0.00 f | 0.17 ± 0.00 c | 0.07 ± 0.00 g | 0.32 ± 0.00 a |
| Formononetin | 17.4 | 267.1, 252.1 191.1 | 2.53 ± 0.00 e | 2.57 ± 0.01 d | 3.00 ± 0.00 c | 2.07 ± 0.00 f | 3.39 ± 0.01 b | 1.84 ± 0.02 g | 3.66 ± 0.02 a |
| Biochanin A | 18.9 | 283.1, 268.1 211.1, 109.1 | 1.96 ± 0.01 c | 2.35 ± 0.01 b | 1.77 ± 0.01 d | 1.75 ± 0.02 d | 2.96 ± 0.01 a | 1.31 ± 0.02 e | 2.39 ± 0.02 b |
| Sinapic acid | 21.3 | 223.1, 208.0 | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 ab | 0.02 ± 0.00 ab | 0.01 ± 0.00 bc | 0.02 ± 0.00 ab | 0.01 ± 0.00 bc | 0.02 ± 0.00 ab |
| Eriocitrin | 21.5 | 595.2, 287.1 151.1 | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.005 ± 0.000 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.003 ± 0.000 c | LDL | 0.003 ± 0.000 c |
| Ellagic acid | 22.5 | 301.0, 229.0 185.0, 145.0 | 0.004 ± 0.000 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a |
| Rutin) | 27.0 | 609.1, 301.1 151.1 | 0.28 ± 0.00 a | 0.29 ± 0.00 a | 0.29 ± 0.00 a | 0.29 ± 0.00 a | 0.29 ± 0.00 a | 0.29 ± 0.00 a | 0.29 ± 0.00 a |
| Phytosterols | Retention Time | m/z | Control | 1 mM SA | 2 mM SA | 20 mM H2O2 | 30 mM H2O2 | 3.3 μM CH | 7 μM CH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blanoro | |||||||||
| Brassicasterol | 2.1 | 381.4, 297.3 147.3, 84.3 | 16.38 ± 0.45 d | 37.46 ± 0.39 a | 25.37 ± 0.14 c | 36.67 ± 0.69 ab | 36.05 ± 0.84 b | 36.87 ± 0.75 ab | 36.61 ± 0.79 ab |
| Ergosterol | 2.3 | 379.4, 295.3 184.3, 158.4 | 4.26 ± 0.16 e | 23.72 ± 0.15 a | 19.76 ± 0.42 c | 22.41 ± 0.32 b | 23.05 ± 0.70 ab | 20.59 ± 0.29 c | 17.90 ± 0.20 d |
| Fucosterol | 2.7 | 395.4, 355.3 303.3, 195.3 121.3 | 2.65 ± 0.06 c | 2.55 ± 0.03 c | 6.62 ± 0.15 b | 12.10 ± 0.10 a | 2.21 ± 0.07 d | 1.65 ± 0.07 e | 1.61 ± 0.07 e |
| Avenasterol | 3.8 | 395.4, 109.3 81.3 | 40.10 ± 0.93 c | 48.38 ± 0.27 b | 61.80 ± 0.46 a | 49.88 ± 1.73 b | 35.83 ± 0.24 d | 19.38 ± 0.55 e | 19.57 ± 0.29 e |
| Stigmasterol | 6.3 | 395.3, 91.3 83.3 | 2.14 ± 0.15 e | 3.67 ± 0.05 b | 3.21 ± 0.09 c | 2.04 ± 0.04 e | 2.52 ± 0.09 d | 3.62 ± 0.03 b | 5.34 ± 0.22 a |
| β-Sitosterol | 7.3 | 397.3, 95.3 91.3 | 165.63 ± 0.08 c | 198.86 ± 0.58 a | 199.74 ± 0.98 a | 195.40 ± 0.65 b | 197.04 ± 0.99 ab | 197.95 ± 0.55 a | 199.74 ± 0.22 a |
| β-Campesterol | 87 | 383.3, 91.3 81.3 | 17.97 ± 0.07 e | 30.28 ± 0.40 b | 27.90 ± 0.27 c | 20.97 ± 0.62 d | 20.44 ± 0.06 d | 29.54 ± 0.65 bc | 35.95 ± 0.36 a |
| Avenasterol glucopyranoside | 16.9 | 395.4, 109.3 81.3 | 35.88 ± 0.14 a | 22.49 ± 0.45 d | 20.52 ± 0.29 e | 25.61 ± 0.36 c | 34.67 ± 0.28 b | 26.55 ± 0.91 c | 35.46 ± 0.22 a |
| Stigmastanol (sitostanol) | 17.1 | 399.4, 397.3 149.1, 95.3 91.3 | 4.93 ± 0.19 b | 3.65 ± 0.14 d | 4.53 ± 0.01 c | 4.91 ± 0.17 b | 6.65 ± 0.08 a | 5.11 ± 0.09 b | 5.09 ± 0.03 b |
| Sitosteryl glucopyranoside | 19.7 | 594.4, 397.3, 95.4 | 15.14 ± 0.20 a | 9.42 ± 0.21 d | 8.50 ± 0.12 e | 11.49 ± 0.26 b | 10.65 ± 0.19 c | 6.95 ± 0.17 f | 8.73 ± 0.08 e |
| Campesteryl glucopyranoside | 20.1 | 580.4, 383.3, 91.3 | 20.62 ± 0.62 e | 17.42 ± 0.17 f | 17.44 ± 0.17 f | 25.43 ± 0.31 d | 30.68 ± 0.64 c | 32.93 ± 0.32 b | 50.43 ± 1.77 a |
| Stigmasteryl glucopyranoside | 25.6 | 592.4, 395.3 83.3 | LDL | LDL | 3.35 ± 0.07 b | 0.79 ± 0.02 d | 3.37 ± 0.05 b | 1.04 ± 0.05 c | 4.71 ± 0.19 a |
| Patron | |||||||||
| Brassicasterol | 2.1 | 381.4, 297.3 147.3, 84.3 | 14.10 ± 0.20 e | 20.78 ± 1.11 d | 6.88 ± 0.32 g | 45.09 ± 0.17 b | 75.91 ± 1.09 a | 25.67 ± 0.34 c | 9.86 ± 0.15 f |
| Ergosterol | 2.3 | 379.4, 295.3 184.3, 158.4 | LDL | LDL | LDL | 12.79 ± 0.08 c | 34.04 ± 0.45 a | 19.33 ± 0.05 b | LDL |
| Fucosterol | 2.7 | 395.4, 355.3 303.3, 195.3 121.3 | 1.05 ± 0.04 g | 10.10 ± 0.20 f | 33.46 ± 0.38 b | 34.84 ± 0.54 a | 14.92 ± 0.03 d | 26.36 ± 1.33 c | 12.99 ± 0.04 e |
| Avenasterol | 3.8 | 395.4, 109.3 81.3 | 2.16 ± 0.01 d | LDL | 1.81 ± 0.11 f | 3.01 ± 0.14 b | 3.72 ± 0.12 a | 2.67 ± 0.03 c | 2.03 ± 0.02 e |
| Stigmasterol | 6.3 | 395.3, 91.3 83.3 | 2.04 ± 0.02 d | 29.14 ± 0.84 b | 31.00 ± 0.13 a | 25.57 ± 0.25 c | 29.71 ± 0.22 b | 24.43 ± 0.94 c | 24.73 ± 0.32 c |
| β-Sitosterol | 7.3 | 397.3, 95.3 91.3 | 198.34 ± 0.36 e | 231.89 ± 3.18 c | 227.17 ± 0.58 d | 226.44 ± 0.92 d | 246.79 ± 2.64 b | 293.15 ± 1.81 a | 296.48 ± 1.52 a |
| β-Campesterol | 87 | 383.3, 91.3 81.3 | 60.57 ± 0.41 b c | 56.90 ± 0.32 d | 59.04 ± 1.04 c | 61.92 ± 0.74 b | 56.33 ± 0.30 de | 55.97 ± 0.46 e | 65.62 ± 0.81 a |
| Avenasterol glucopyranoside | 16.9 | 395.4, 109.3 81.3 | 27.93 ± 0.16 e | 29.27 ± 0.11 d | 37.16 ± 0.24 a | 35.85 ± 0.37 b | 30.56 ± 0.20 c | 23.08 ± 0.21 f | 26.72 ± 0.40 e |
| Stigmastanol (sitostanol) | 17.1 | 399.4, 397.3 149.1, 95.3 91.3 | 3.00 ± 0.07 d | 2.18 ± 0.17 e | 4.09 ± 0.04 b | 4.10 ± 0.05 b | 3.47 ± 0.10 c | 4.86 ± 0.20 a | 3.91 ± 0.14 b |
| Sitosteryl glucopyranoside | 19.7 | 594.4, 397.3, 95.4 | 54.65 ± 0.16 a | 10.51 ± 0.17 f | 26.06 ± 0.94 c | 22.16 ± 0.44 d | 24.98 ± 0.35 c | 16.35 ± 0.06 e | 30.06 ± 0.23 b |
| Campesteryl glucopyranoside | 20.1 | 580.4, 383.3, 91.3 | 133.77 ± 2.45 a | 10.28 ± 0.19 e | 83.37 ± 0.76 c | 72.98 ± 0.52 d | 73.73 ± 0.93 d | 9.92 ± 0.24 e | 91.53 ± 0.88 b |
| Stigmasteryl glucopyranoside | 25.6 | 592.4, 395.3 83.3 | 3.24 ± 0.06 b | 11.71 ± 0.23 a | 11.80 ± 0.87 a | 3.49 ± 0.11 b | LDL | 2.91 ± 0.03 c | 2.87 ± 0.07 c |
| San Antonio | |||||||||
| Brassicasterol | 2.1 | 381.4, 297.3 147.3, 84.3 | 24.30 ± 0.21 a | 23.75 ± 0.03 a | 16.82 ± 0.53 c | 9.24 ± 0.16 d | 18.54 ± 0.35 b | 23.25 ± 0.79 a | 16.29 ± 0.49 c |
| Ergosterol | 2.3 | 379.4, 295.3 184.3, 158.4 | 8.35 ± 0.21 e | 4.92 ± 0.05 f | 33.16 ± 0.60 c | 46.33 ± 0.65 b | 34.28 ± 0.79 c | 51.69 ± 0.90 a | 29.95 ± 0.66 d |
| Fucosterol | 2.7 | 395.4, 355.3 303.3, 195.3 121.3 | 40.16 ± 0.57 e | 93.50 ± 1.21 a | 73.68 ± 0.5 c | 88.72 ± 1.01 b | 75.80 ± 1.07 c | 93.76 ± 1.01 a | 59.14 ± 0.29 d |
| Avenasterol | 3.8 | 395.4, 109.3 81.3 | 2.60 ± 0.02 e | 6.21 ± 0.10 b | 6.72 ± 0.17 a | 3.50 ± 0.15 d | 6.54 ± 0.09 a | 1.50 ± 0.13 f | 5.04 ± 0.06 c |
| Stigmasterol | 6.3 | 395.3, 91.3 83.3 | 7.00 ± 0.04 b | 3.99 ± 0.17 c | 3.76 ± 0.05 c | 3.71 ± 0.10 cd | 3.55 ± 0.09 de | 10.38 ± 0.15 a | 3.37 ± 0.16 e |
| β-Sitosterol | 7.3 | 397.3, 95.3 91.3 | 149.73 ± 1.87 d | 197.94 ± 3.74 b | 150.13 ± 2.51 d | 196.91 ± 3.74 b | 166.38 ± 2.31 c | 203.71 ± 2.03 b | 255.85 ± 1.80 a |
| β-Campesterol | 87 | 383.3, 91.3 81.3 | 25.72 ± 0.38 d | 30.21 ± 0.43 b | 26.10 ± 0.75 d | 31.35 ± 0.37 b | 27.36 ± 0.20 cd | 38.58 ± 0.10 a | 24.86 ± 0.70 d |
| Avenasterol glucopyranoside | 16.9 | 395.4, 109.3 81.3 | 36.04 ± 0.67 bc | 51.70 ± 1.18 a | 30.21 ± 0.27 d | 48.96 ± 2.10 a | 35.21 ± 0.34 c | 37.72 ± 0.39 b | 21.02 ± 0.86 e |
| Stigmastanol (sitostanol) | 17.1 | 399.4, 397.3 149.1, 95.3 91.3 | 6.20 ± 0.13 d | 8.27 ± 0.15 a | 6.44 ± 0.13 cd | 8.20 ± 0.15 a | 6.64 ± 0.09 bc | 6.92 ± 0.20 b | 3.52 ± 0.03 e |
| Sitosteryl glucopyranoside | 19.7 | 594.4, 397.3, 95.4 | 37.14 ± 0.40 c | 30.66 ± 0.24 d | 38.52 ± 0.49 b | 27.69 ± 0.51 e | 24.69 ± 0.29 f | 45.57 ± 0.36 a | 30.86 ± 0.85 d |
| Campesteryl glucopyranoside | 20.1 | 580.4, 383.3, 91.3 | 139.09 ± 1.39 c | 140.69 ± 1.26 c | 146.37 ± 1.50 b | 136.15 ± 0.72 d | 114.73 ± 2.01 e | 151.01 ± 1.55 a | 99.98 ± 4.30 f |
| Stigmasteryl glucopyranoside | 25.6 | 592.4, 395.3 83.3 | 4.33 ± 0.03 d | 1.97 ± 0.02 f | 4.33 ± 0.01 d | 6.79 ± 0.11 b | 5.74 ± 0.09 c | 8.64 ± 0.14 a | 2.39 ± 0.03 e |
| Saponins | Retention Time | m/z | Control | 1 mM SA | 2 mM SA | 20 mM H2O2 | 30 mM H2O2 | 3.3 μM CH | 7 μM CH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blanoro | |||||||||
| Phaseoside I | 9.8 | 1252.5 1091.5, 959.5 | 134.42 ± 3.12 d | 177.14 ± 0.95 b | 217.70 ± 2.33 a | 158.87 ± 2.30 c | 120.67 ± 1.99 e | 131.73 ± 1.91 d | 124.93 ± 3.20 e |
| Soyasaponin Bb (I) | 11.7 | 941.5, 489.5 | 142.71 ± 0.70 a | 124.51 ± 2.38 b | 115.78 ± 0.78 c | 113.04 ± 0.78 cd | 124.14 ± 1.21 b | 107.57 ± 3.51 d | 93.06 ± 1.78 e |
| Soyasaponin Ba (V) | 13.1 | 957.5, 795.5 633.5 | 253.45 ± 1.65 c | 285.74 ± 13.27 a | 241.45 ± 5.37 d | 263.83 ± 3.68 b | 272.78 ± 7.80 ab | 233.52 ± 2.92 e | 237.45 ± 2.43 de |
| Soyasaponin Af | 13.7 | 1273.6, 943.5 811.5, 329.5 | 686.75 ± 7.89 d | 816.64 ± 11.57 b | 948.68 ± 7.12 a | 766.53 ± 11.45 c | 944.52 ± 11.68 a | 507.23 ± 2.84 e | 473.94 ± 4.21 f |
| Soyasaponin Bd | 14.9 | 955.5, 793.5 631.5 | 61.70 ± 0.21 d | 74.08 ± 0.98 b | 49.52 ± 1.03 f | 63.47 ± 0.41 c | 48.76 ± 1.47 f | 75.84 ± 0.26 a | 56.06 ± 0.93 e |
| Soyasaponin βg (VI) | 19.2 | 1067.5, 533.5 | 771.86 ± 4.91 c | 835.41 ± 6.75 c | 961.30 ± 7.25 a | 913.43 ± 20.92 b | 854.98 ± 18.14 c | 621.34 ± 8.72 d | 542.97 ± 4.85 e |
| Soyasaponin αg | 27.2 | 1083.5, 561.5 559.5, 541.5 | 58.40 ± 0.18 f | 80.90 ± 1.49 e | 87.18 ± 1.12 d | 99.28 ± 0.72 c | 48.72 ± 1.14 g | 121.05 ± 0.65 b | 147.00 ± 4.02 a |
| Patron | |||||||||
| Phaseoside I | 9.8 | 1252.5 1091.5, 959.5 | 22.37 ± 0.51 e | 45.20 ± 0.97 d | 52.95 ± 1.81 c | 42.46 ± 0.96 d | 131.97 ± 3.66 b | 168.89 ± 3.93 a | 45.30 ± 1.39 d |
| Soyasaponin Bb (I) | 11.7 | 941.5, 489.5 | 59.92 ± 1.66 cd | 88.31 ± 2.96 a | 62.29 ± 0.97 bc | 65.18 ± 1.36 b | 64.90 ± 1.18 b | 92.33 ± 1.98 a | 56.81 ± 2.00 d |
| Soyasaponin Ba (V) | 13.1 | 957.5, 795.5 633.5 | 178.81 ± 3.71 b | 139.55 ± 6.36 d | 147.19 ± 0.46 c | 144.88 ± 2.96 cd | 172.60 ± 3.27 b | 185.67 ± 3.00 a | 148.02 ± 1.19 c |
| Soyasaponin Af | 13.7 | 1273.6, 943.5 811.5, 329.5 | 269.79 ± 4.37 d | 277.66 ± 3.27 d | 298.36 ± 6.92 c | 298.80 ± 2.96 c | 354.00 ± 2.54 b | 411.43 ± 5.00 a | 347.52 ± 9.03 b |
| Soyasaponin Bd | 14.9 | 955.5, 793.5 631.5 | 102.48 ± 1.18 d | 117.30 ± 0.50 c | 119.53 ± 1.63 c | 120.36 ± 2.69 c | 102.26 ± 1.16 d | 260.03 ± 1.84 a | 249.29 ± 4.92 b |
| Soyasaponin βg (VI) | 19.2 | 1067.5, 533.5 | 306.43 ± 6.02 c | 326.42 ± 4.84 b | 302.33 ± 6.63 cd | 255.05 ± 4.69 e | 333.63 ± 5.36 b | 384.49 ± 4.39 a | 290.92 ± 5.64 d |
| Soyasaponin αg | 27.2 | 1083.5, 561.5 559.5, 541.5 | 249.20 ± 2.53 d | 261.45 ± 3.21 d | 230.39 ± 3.33 e | 318.39 ± 8.29 b | 383.43 ± 6.23 a | 295.63 ± 6.68 c | 310.84 ± 4.19 b |
| San Antonio | |||||||||
| Phaseoside I | 9.8 | 1252.5 1091.5, 959.5 | 65.78 ± 3.95 f | 93.03 ± 3.58 e | 109.19 ± 2.54 d | 122.39 ± 3.23 c | 114.12 ± 2.71 d | 147.15 ± 1.46 b | 170.99 ± 1.01 a |
| Soyasaponin Bb (I) | 11.7 | 941.5, 489.5 | 89.10 ± 3.65 c | 109.13 ± 2.36 b | 153.79 ± 5.69 a | 109.54 ± 3.35 b | 89.58 ± 3.61 c | 79.98 ± 0.63 d | 67.06 ± 1.18 e |
| Soyasaponin Ba (V) | 13.1 | 957.5, 795.5 633.5 | 231.78 ± 5.94 bc | 250.51 ± 3.33 a | 205.03 ± 4.02 e | 215.71 ± 5.33 d | 225.54 ± 4.30 cd | 237.32 ± 0.81 b | 234.94 ± 2.68 b |
| Soyasaponin Af | 13.7 | 1273.6, 943.5 811.5, 329.5 | 473.44 ± 7.25 g | 719.01 ± 5.82 b | 613.75 ± 9.27 d | 530.90 ± 2.19 f | 571.67 ± 9.85 e | 678.25 ± 11.80 c | 752.27 ± 8.29 a |
| Soyasaponin Bd | 14.9 | 955.5, 793.5 631.5 | 39.65 ± 0.90 b | 36.74 ± 0.49 c | LDL | 37.52 ± 1.01 bc | LDL | 47.82 ± 1.39 a | 47.36 ± 1.15 a |
| Soyasaponin βg (VI) | 19.2 | 1067.5, 533.5 | 506.50 ± 7.29 e | 638.01 ± 8.65 b | 520.03 ± 4.35 e | 602.69 ± 5.72 c | 606.66 ± 5.57 c | 566.98 ± 10.66 d | 685.96 ± 3.70 a |
| Soyasaponin αg | 27.2 | 1083.5, 561.5 559.5, 541.5 | 127.23 ± 3.76 cd | 138.39 ± 4.31 b | 176.72 ± 3.30 a | 132.01 ± 1.23 c | 86.96 ± 3.38 e | 91.62 ± 7.30 e | 125.29 ± 3.54 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Ramírez, I.F.; Escobedo-Alvarez, D.E.; Mendoza-Sánchez, M.; Rocha-Guzmán, N.E.; Reynoso-Camacho, R.; Acosta-Gallegos, J.A.; Ramos-Gómez, M. Phytochemical Profile and Composition of Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): Varietal Differences and Effect of Germination under Elicited Conditions. Plants 2023, 12, 3093. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173093
Pérez-Ramírez IF, Escobedo-Alvarez DE, Mendoza-Sánchez M, Rocha-Guzmán NE, Reynoso-Camacho R, Acosta-Gallegos JA, Ramos-Gómez M. Phytochemical Profile and Composition of Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): Varietal Differences and Effect of Germination under Elicited Conditions. Plants. 2023; 12(17):3093. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173093
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Ramírez, Iza Fernanda, Diana E. Escobedo-Alvarez, Magdalena Mendoza-Sánchez, Nuria E. Rocha-Guzmán, Rosalía Reynoso-Camacho, Jorge A. Acosta-Gallegos, and Minerva Ramos-Gómez. 2023. "Phytochemical Profile and Composition of Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): Varietal Differences and Effect of Germination under Elicited Conditions" Plants 12, no. 17: 3093. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173093
APA StylePérez-Ramírez, I. F., Escobedo-Alvarez, D. E., Mendoza-Sánchez, M., Rocha-Guzmán, N. E., Reynoso-Camacho, R., Acosta-Gallegos, J. A., & Ramos-Gómez, M. (2023). Phytochemical Profile and Composition of Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): Varietal Differences and Effect of Germination under Elicited Conditions. Plants, 12(17), 3093. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173093






