Genome-Wide Identification of the Trihelix Transcription Factor Family and Functional Analysis of the Drought Stress-Responsive Genes in Melilotus albus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
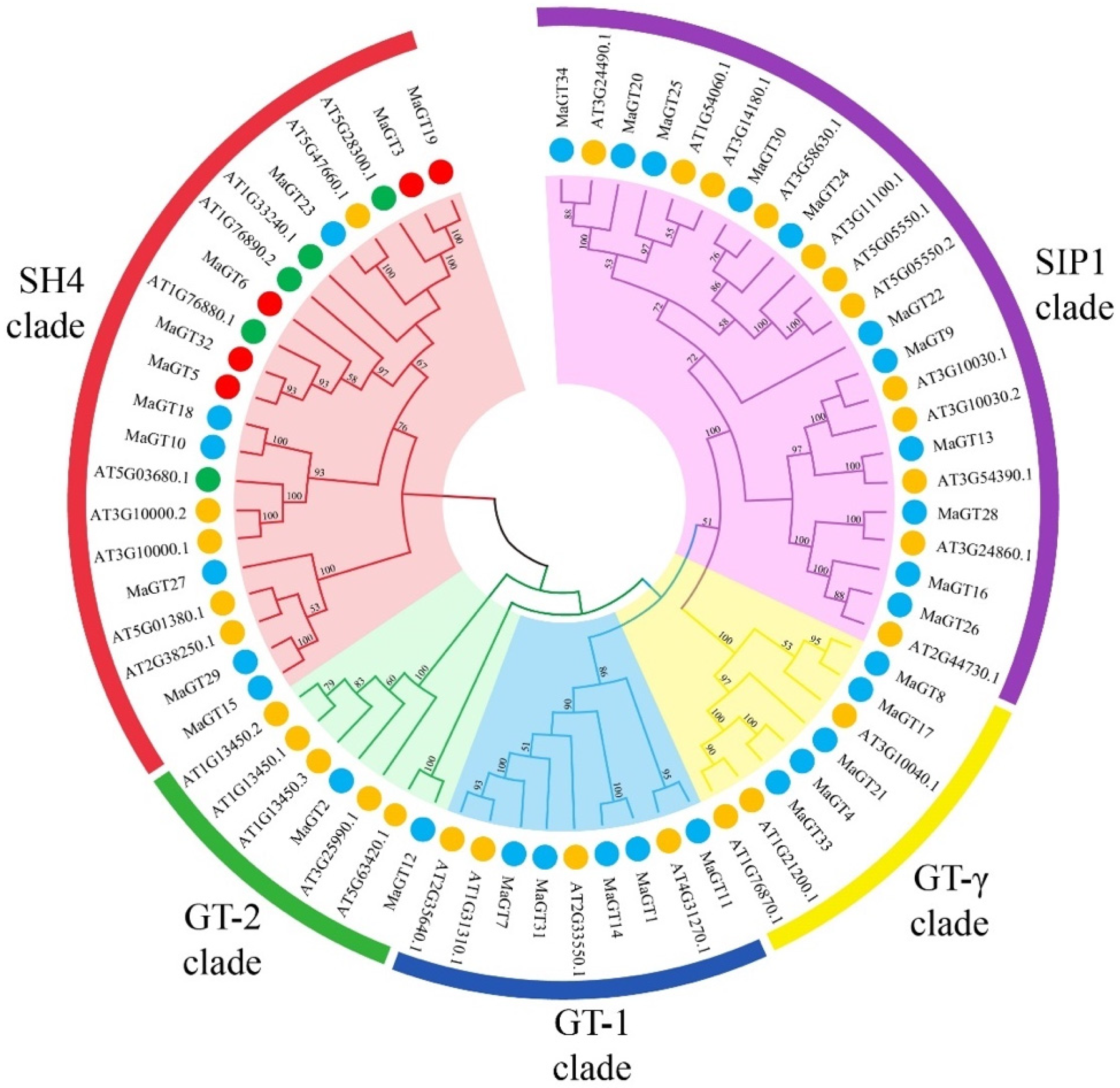
2.1. Phylogenetic Categories Analysis of MaGT Genes
2.2. Genomic Organization and In Silico Analysis of the Subcellular Localization of MaGTs
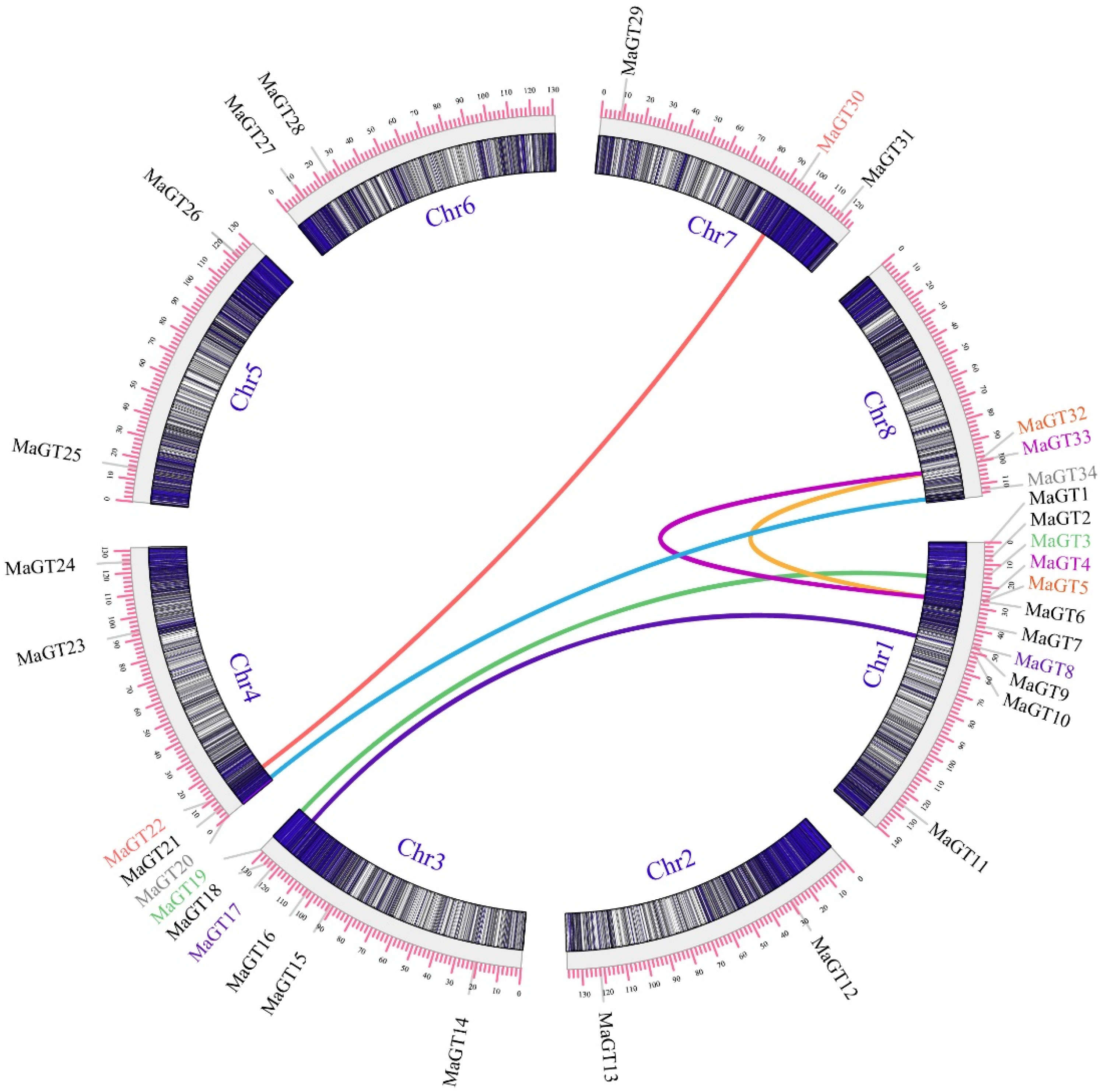
2.3. Chromosomal Location Analysis of the MaGT Genes
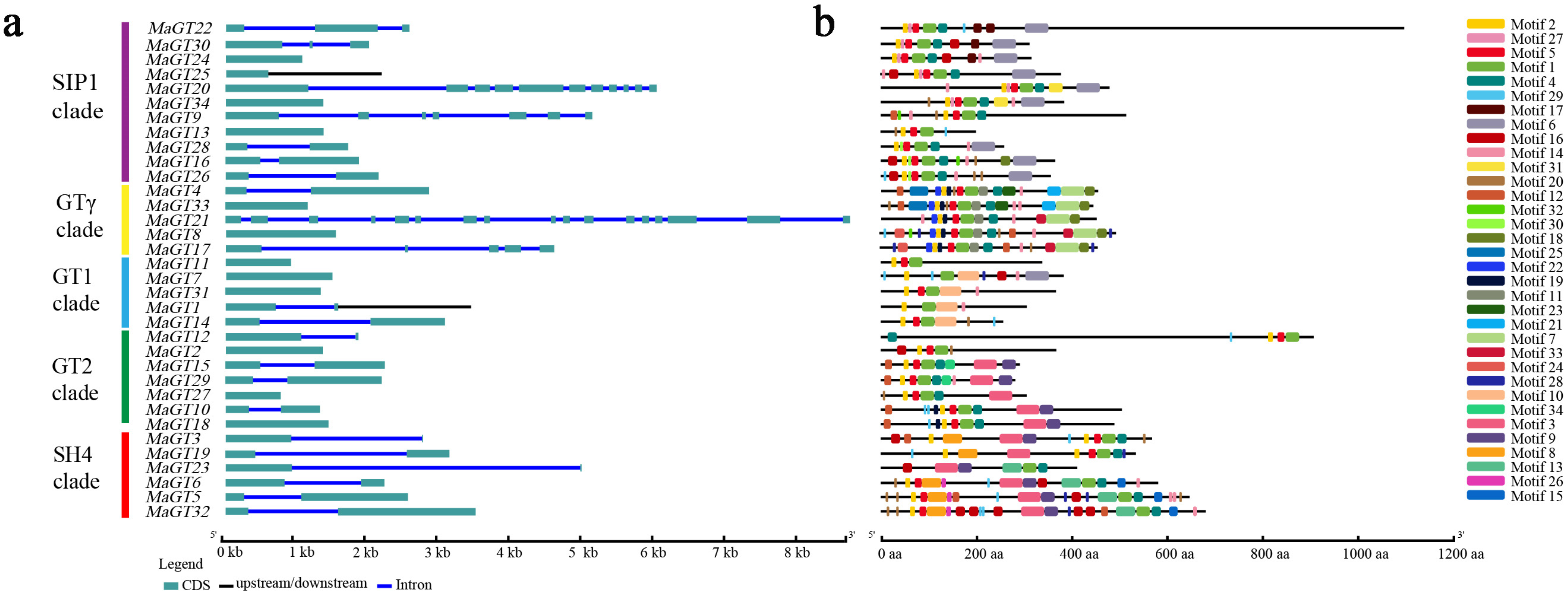
2.4. Structural Features and Conserved Motifs of the MaGT Genes
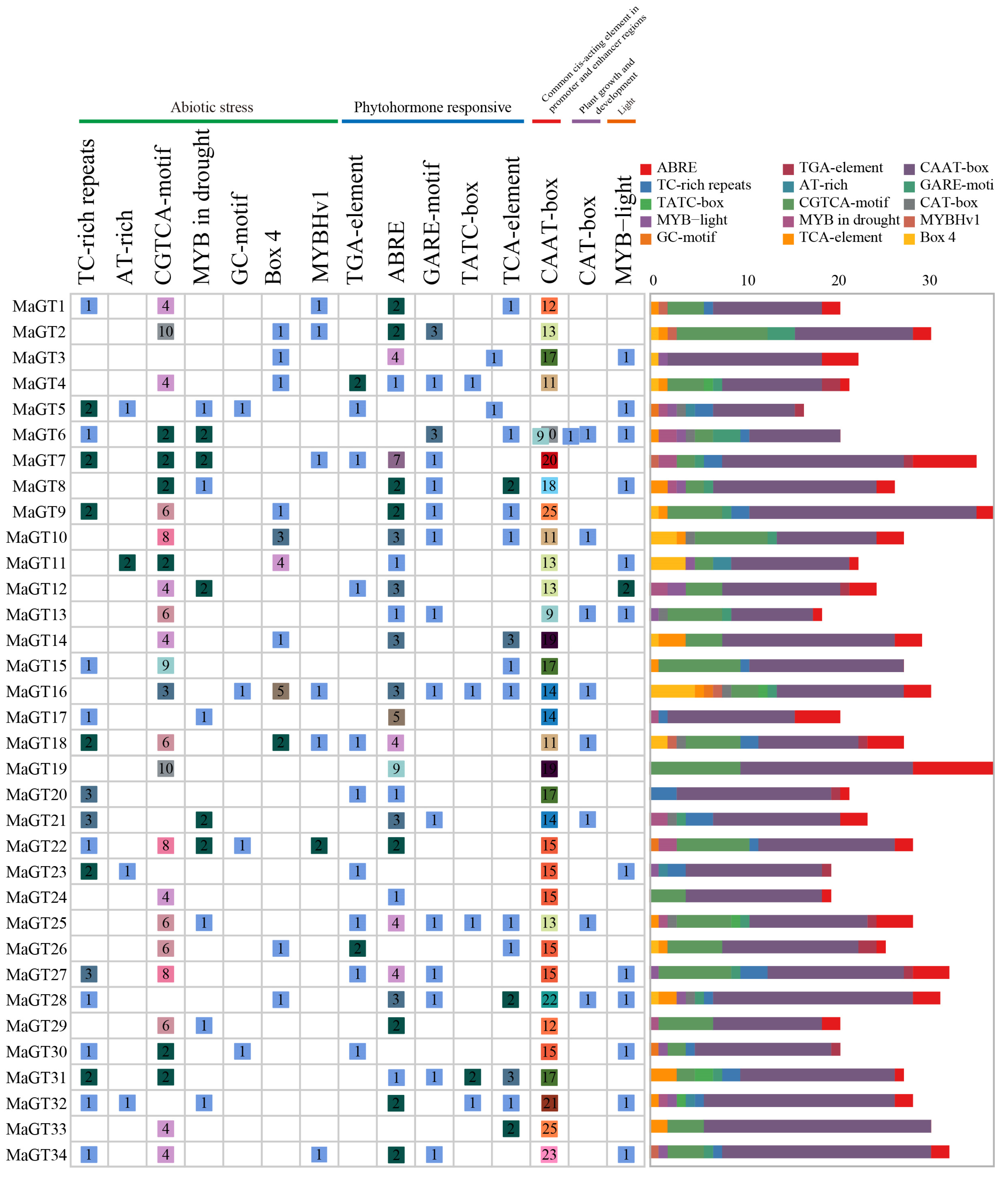
2.5. Identification of Cis-Acting Elements in the MaGT Gene Promoters
2.6. Collinearity Gene Analysis of MaGT
2.7. Expression Analysis of the MaGT Genes in M. albus
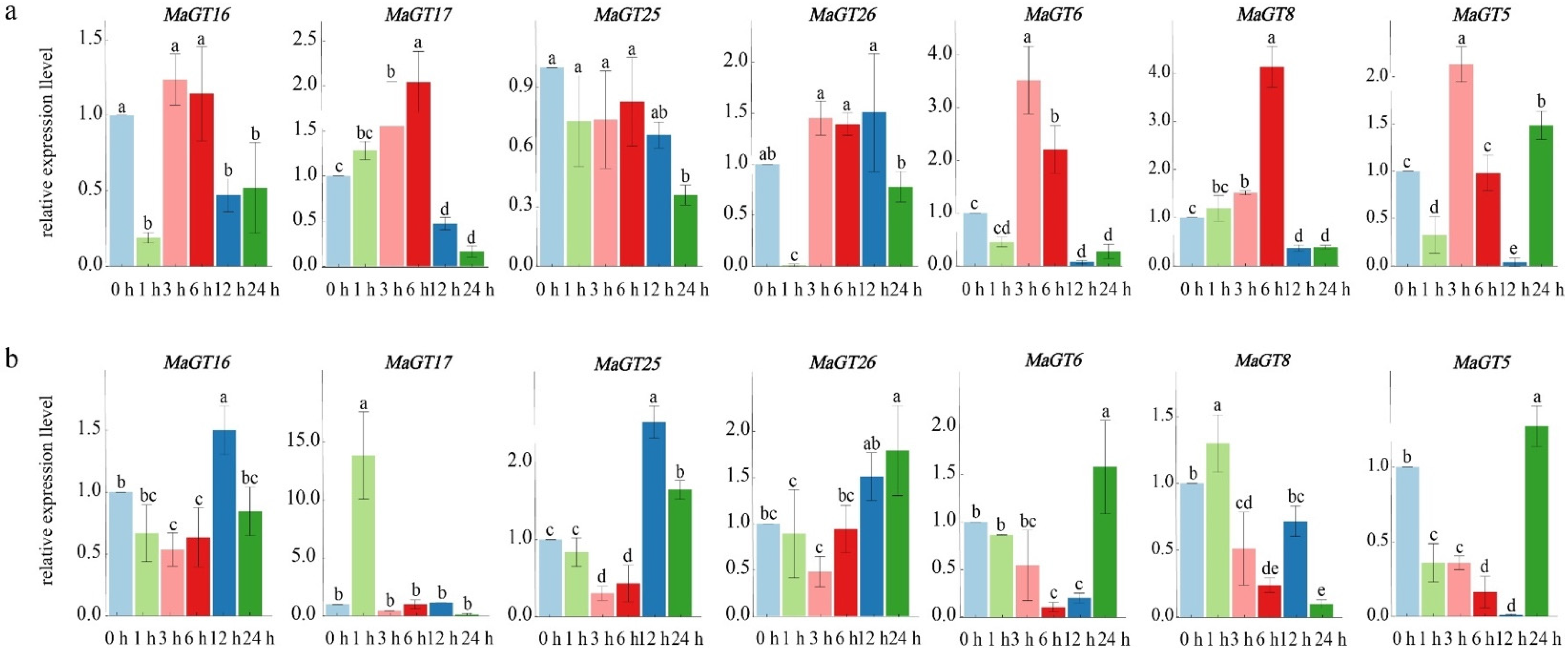
2.8. Expression Analysis of MaGT Genes in Response to Drought Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Treatments
4.2. Identification and Sequence Analysis of the Trihelix Genes in M. albus
4.3. Chromosomal Distribution and In Silico Gene Prediction
4.4. Gene Structure, Conserved Motif Identification and Cis-Acting Regulatory Element Analysis
4.5. Duplication Analysis
4.6. Transcriptome Analysis for Drought Stress Treatment
4.7. RNA Isolation and Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR (qRT–PCR) Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, J.-K. Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandalinas, S.I.; Fichman, Y.; Devireddy, A.R.; Sengupta, S.; Azad, R.K.; Mittler, R. Systemic signaling during abiotic stress combination in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 13810–13820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedoroff, N.V.; Battisti, D.S.; Beachy, R.N.; Cooper, P.J.; Fischhoff, D.A.; Hodges, C.; Knauf, V.C.; Lobell, D.; Mazur, B.J.; Molden, D. Radically rethinking agriculture for the 21st century. Science 2010, 327, 833–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Q.; Bai, L.; Zhang, T.; Huang, S.; Song, C. Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate regulates SCAB1-mediated F-actin reorganization during stomatal closure in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 477–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soma, F.; Takahashi, F.; Suzuki, T.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Plant Raf-like kinases regulate the mRNA population upstream of ABA-unresponsive SnRK2 kinases under drought stress. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, N.J.; Urwin, P.E. The interaction of plant biotic and abiotic stresses: From genes to the field. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 3523–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Q.; Asim, M.; Zhang, R.; Khan, R.; Farooq, S.; Wu, J. Transcription factors interact with ABA through gene expression and signaling pathways to mitigate drought and salinity stress. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, P.J.; Kay, S.A.; Chua, N.-H. Sequence-specific interactions of a pea nuclear factor with light-responsive elements upstream of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 2543–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagano, Y. Several features of the GT-factor trihelix domain resemble those of the MYB DNA-binding domain. Plant Physiol. 2000, 124, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perisic, O.; Lam, E. A tobacco DNA binding protein that interacts with a light-responsive box II element. Plant Cell 1992, 4, 831–838. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan-Levy, R.N.; Brewer, P.B.; Quon, T.; Smyth, D.R. The trihelix family of transcription factors–light, stress and development. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Sun, J.; Mao, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Zheng, H.; Zhen, Z.; Zhao, H. Genome-wide characterization and identification of trihelix transcription factor and expression profiling in response to abiotic stresses in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Ma, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling analysis of the Trihelix gene family under abiotic stresses in Medicago truncatula. Genes 2020, 11, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, P.B.; Howles, P.A.; Dorian, K.; Griffith, M.E.; Ishida, T.; Kaplan-Levy, R.N.; Kilinc, A.; Smyth, D.R. PETAL LOSS, a trihelix transcription factor gene, regulates perianth architecture in the Arabidopsis flower. Development 2004, 66, 2475–2485. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Xie, K.; Hou, X.; Hu, H.; Xiong, L. Systematic analysis of GT factor family of rice reveals a novel subfamily involved in stress responses. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2010, 283, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.-J.; Lydiate, D.J.; Li, X.; Lui, H.; Gjetvaj, B.; Hegedus, D.D.; Rozwadowski, K. Repression of seed maturation genes by a trihelix transcriptional repressor in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.-M.; Zou, H.-F.; Lei, G.; Wei, W.; Zhou, Q.-Y.; Niu, C.-F.; Liao, Y.; Tian, A.-G.; Ma, B.; Zhang, W.-K. Soybean Trihelix transcription factors GmGT-2A and GmGT-2B improve plant tolerance to abiotic stresses in transgenic Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Tang, S.; Mei, F.; Peng, X.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Yan, X.; Zeng, X.; Liu, F.; Wu, Y. BnSIP1-1, a trihelix family gene, mediates abiotic stress tolerance and ABA signaling in Brassica napus. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Duan, Z.; Xu, P.; Yan, Q.; Meng, M.; Cao, M.; Jones, C.S.; Zong, X.; Zhou, P.; Wang, Y. Genome and systems biology of Melilotus albus provides insights into coumarins biosynthesis. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 592–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Yan, Q.; Wu, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zong, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, J. Genome-Wide analysis of the UDP-glycosyltransferase family reveals its roles in coumarin biosynthesis and abiotic stress in Melilotus albus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sherif, E.A. Melilotus indicus (L.) All., a salt-tolerant wild leguminous herb with high potential for use as a forage crop in salt-affected soils. Flora-Morphol. Distrib. Funct. Ecol. Plants 2009, 204, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooker, R.W.; Bennett, A.E.; Cong, W.F.; Daniell, T.J.; George, T.S.; Hallett, P.D.; Hawes, C.; Iannetta, P.P.; Jones, H.G.; Karley, A.J. Improving intercropping: A synthesis of research in agronomy, plant physiology and ecology. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Hu, R.; Gu, T.; Han, J.; Qiu, D.; Su, P.; Feng, J.; Chang, J.; Yang, G.; He, G. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of trihelix gene family under abiotic stresses in wheat. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Organization of cis-acting regulatory elements in osmotic-and cold-stress-responsive promoters. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, M.B.; Bücker-Neto, L.; Castilhos, G.; Turchetto-Zolet, A.C.; Wiebke-Strohm, B.; Bodanese-Zanettini, M.H.; Margis-Pinheiro, M. Identification and in silico characterization of soybean trihelix-GT and bHLH transcription factors involved in stress responses. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2012, 35, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Shen, W.; Shaheen, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Pang, H.; Ahmed, Z. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the trihelix transcription factors in sunflower. Biol. Plant. 2021, 65, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, Y. GT-Factor Trihelix domain is structurally related to the MYB DNA-binding domain. Plant Cell Physiol. 2000, 41, s59. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, N.; Zhai, Q.; Li, H.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W. Genome-wide identification of ERF transcription factor family and functional analysis of the drought stress-responsive genes in Melilotus albus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, M.; Chen, S.; Yang, M.; Ding, Y.; Peng, Y.; Dong, Y.; Yang, H. Genome-wide identification and expression profile analysis of trihelix transcription factor family genes in response to abiotic stress in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Xu, X.; Li, J. Genome-wide identification and characterization of GRAS transcription factors in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). PeerJ 2017, 5, e3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, P.; Liu, T.; Ren, H.; Li, Y.; Hou, X. Genome-wide analysis and expression divergence of the trihelix family in Brassica rapa: Insight into the evolutionary patterns in plants. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, X.; Li, C.; Yang, C. Comprehensive analysis of trihelix genes and their expression under biotic and abiotic stresses in Populus trichocarpa. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Lin, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, R.; Zhang, L. Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of soybean trihelix gene family. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. The transcriptional regulatory network in the drought response and its crosstalk in abiotic stress responses including drought, cold, and heat. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santner, A.; Estelle, M. Recent advances and emerging trends in plant hormone signalling. Nature 2009, 459, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Savojardo, C.; Martelli, P.L.; Fariselli, P.; Profiti, G.; Casadio, R. BUSCA: An integrative web server to predict subcellular localization of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W459–W466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, P.; Park, K.-J.; Obayashi, T.; Fujita, N.; Harada, H.; Adams-Collier, C.; Nakai, K. WoLF PSORT: Protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W585–W587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wei, N.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the heavy metal ATPase (HMA) gene family in Medicago truncatula under copper stress. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Giles, K.E.; Felsenfeld, G. DNA· RNA triple helix formation can function as a cis-acting regulatory mechanism at the human β-globin locus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 6130–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, X.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, X.; Jin, X.; Ndayambaza, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the aquaporin gene family in Medicago truncatula. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene Name | Gene ID | Protein Length (aa) | Protein MW (kDa) | PI | Protein GRAVY | Predicted Subcellular Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MaGT1 | Malbus0100234.1 | 301 | 34.02 | 4.96 | −0.871 | nucl |
| MaGT2 | Malbus0100838.1 | 363 | 41.61 | 5.66 | −0.801 | nucl |
| MaGT3 | Malbus0101348.1 | 564 | 65.08 | 5.75 | −1.096 | nucl |
| MaGT4 | Malbus0102155.1 | 450 | 51.09 | 6.45 | −1.020 | nucl |
| MaGT5 | Malbus0102157.1 | 643 | 71.17 | 5.73 | −0.936 | nucl |
| MaGT6 | Malbus0102158.1 | 577 | 65.79 | 6.65 | −1.149 | nucl |
| MaGT7 | Malbus0102789.1 | 379 | 42.71 | 9.24 | −1.023 | nucl |
| MaGT8 | Malbus0103196.1 | 491 | 56.18 | 6.33 | −1.250 | nucl |
| MaGT9 | Malbus0103198.1 | 510 | 55.84 | 6.19 | −0.498 | nucl |
| MaGT10 | Malbus0103240.1 | 551 | 63.64 | 6.37 | −1.181 | nucl |
| MaGT11 | Malbus0105376.1 | 334 | 38.46 | 5.24 | −0.927 | nucl |
| MaGT12 | Malbus0202497.1 | 903 | 100.83 | 8.72 | −0.407 | nucl |
| MaGT13 | Malbus0205206.1 | 195 | 21.82 | 9.54 | −0.929 | nucl |
| MaGT14 | Malbus0300581.1 | 252 | 27.62 | 6.08 | −0.446 | nucl |
| MaGT15 | Malbus0302275.1 | 287 | 34.45 | 6.56 | −1.288 | nucl |
| MaGT16 | Malbus0302927.1 | 361 | 40.88 | 9.41 | −0.915 | nucl |
| MaGT17 | Malbus0304312.1 | 452 | 52.21 | 6.05 | −1.262 | nucl |
| MaGT18 | Malbus0304336.1 | 485 | 56.00 | 6.35 | −1.097 | nucl |
| MaGT19 | Malbus0305007.1 | 530 | 60.97 | 6.57 | −0.879 | nucl |
| MaGT20 | Malbus0400261.1 | 475 | 54.68 | 4.55 | −1.316 | nucl |
| MaGT21 | Malbus0400501.1 | 447 | 50.94 | 6.51 | −1.005 | nucl |
| MaGT22 | Malbus0400738.1 | 1093 | 125.16 | 8.87 | −0.729 | nucl |
| MaGT23 | Malbus0403089.1 | 407 | 45.71 | 5.92 | −0.930 | nucl |
| MaGT24 | Malbus0404505.1 | 311 | 35.13 | 5.12 | −0.842 | cyto |
| MaGT25 | Malbus0500809.1 | 374 | 40.91 | 9.66 | −0.869 | nucl |
| MaGT26 | Malbus0504730.1 | 352 | 38.57 | 8.90 | −0.825 | chlo |
| MaGT27 | Malbus0600554.1 | 301 | 35.30 | 8.67 | −1.139 | nucl |
| MaGT28 | Malbus0601283.1 | 254 | 29.85 | 9.20 | −0.980 | nucl |
| MaGT29 | Malbus0700349.1 | 277 | 33.56 | 6.44 | −1.156 | nucl |
| MaGT30 | Malbus0703059.1 | 307 | 34.57 | 9.82 | −0.896 | nucl |
| MaGT31 | Malbus0704843.1 | 362 | 40.55 | 5.57 | −0.843 | nucl |
| MaGT32 | Malbus0803535.1 | 677 | 75.10 | 5.81 | −1.002 | nucl |
| MaGT33 | Malbus0803540.1 | 441 | 50.31 | 5.98 | −1.093 | nucl |
| MaGT34 | Malbus0803943.1 | 380 | 43.62 | 4.55 | −1.083 | nucl |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, Q.; Li, H.; Wei, N.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W. Genome-Wide Identification of the Trihelix Transcription Factor Family and Functional Analysis of the Drought Stress-Responsive Genes in Melilotus albus. Plants 2023, 12, 3696. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12213696
Zhai Q, Li H, Wei N, Zhang J, Liu W. Genome-Wide Identification of the Trihelix Transcription Factor Family and Functional Analysis of the Drought Stress-Responsive Genes in Melilotus albus. Plants. 2023; 12(21):3696. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12213696
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Qingyan, Hang Li, Na Wei, Jiyu Zhang, and Wenxian Liu. 2023. "Genome-Wide Identification of the Trihelix Transcription Factor Family and Functional Analysis of the Drought Stress-Responsive Genes in Melilotus albus" Plants 12, no. 21: 3696. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12213696
APA StyleZhai, Q., Li, H., Wei, N., Zhang, J., & Liu, W. (2023). Genome-Wide Identification of the Trihelix Transcription Factor Family and Functional Analysis of the Drought Stress-Responsive Genes in Melilotus albus. Plants, 12(21), 3696. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12213696







