miR2118 Negatively Regulates Bacterial Blight Resistance through Targeting Several Disease Resistance Genes in Rice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
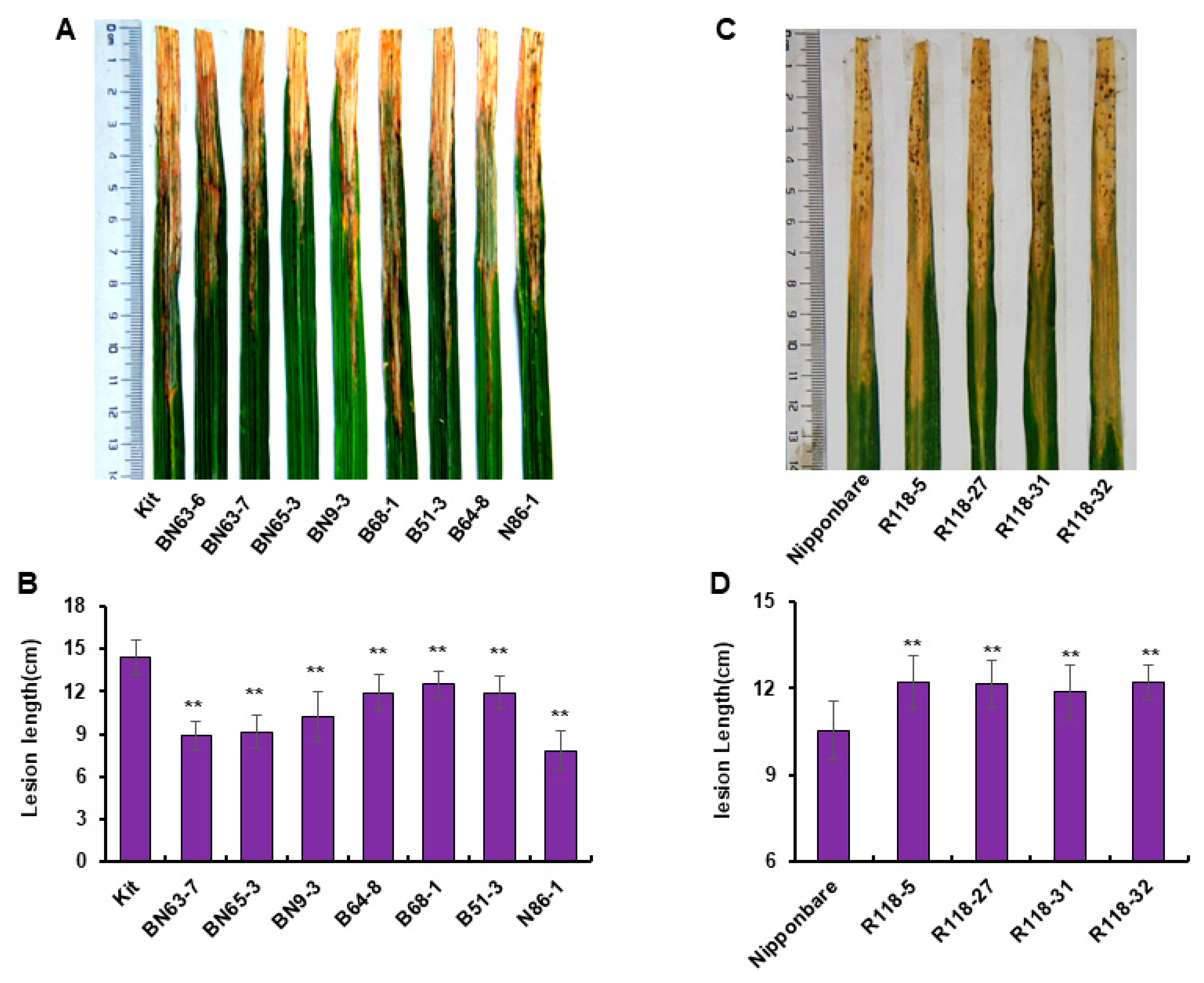
2.1. MIR2118 CRISPR Homozygous Line Screening
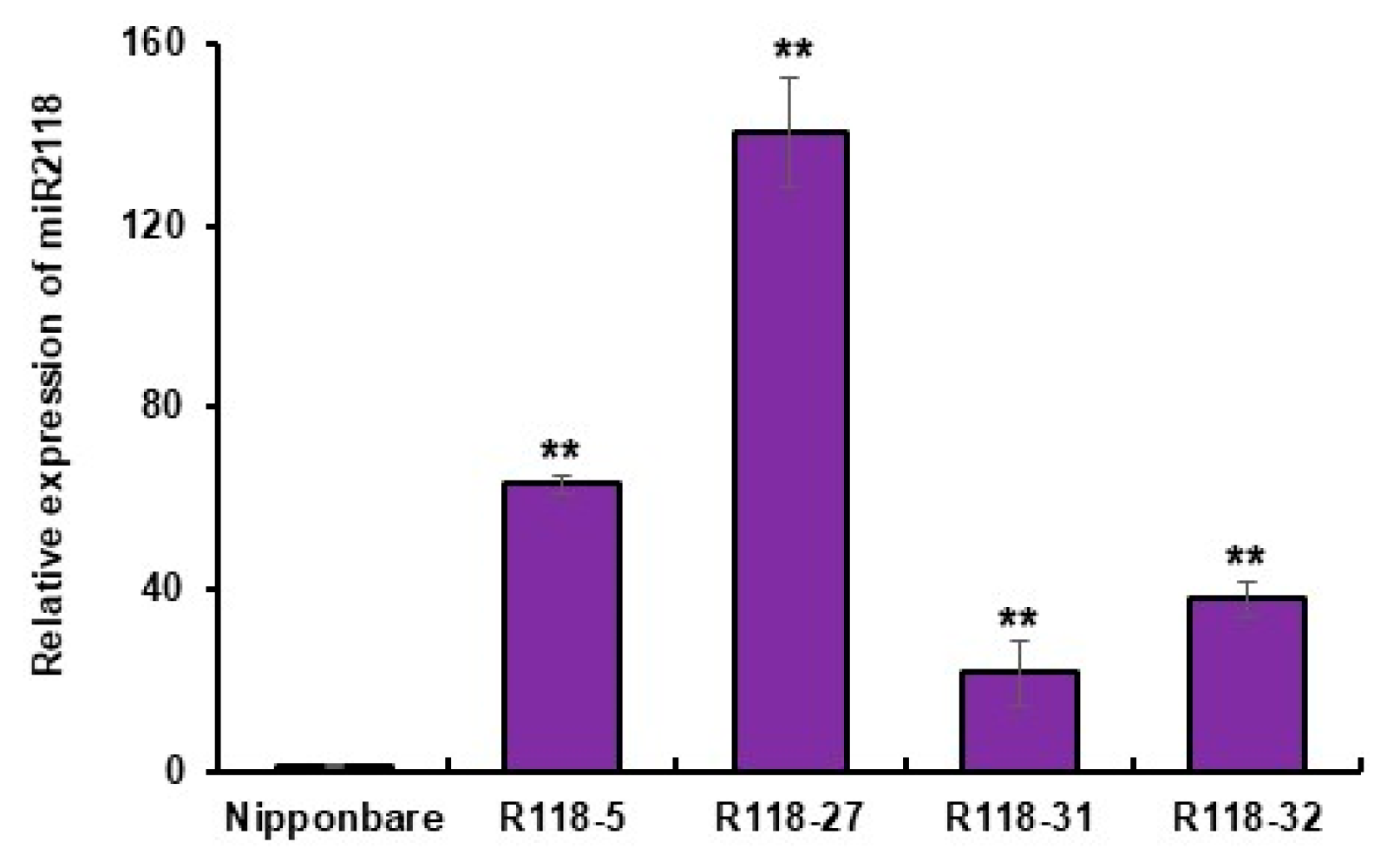
2.2. MIR2118b OE Material Identification
2.3. Disease Resistance Detection
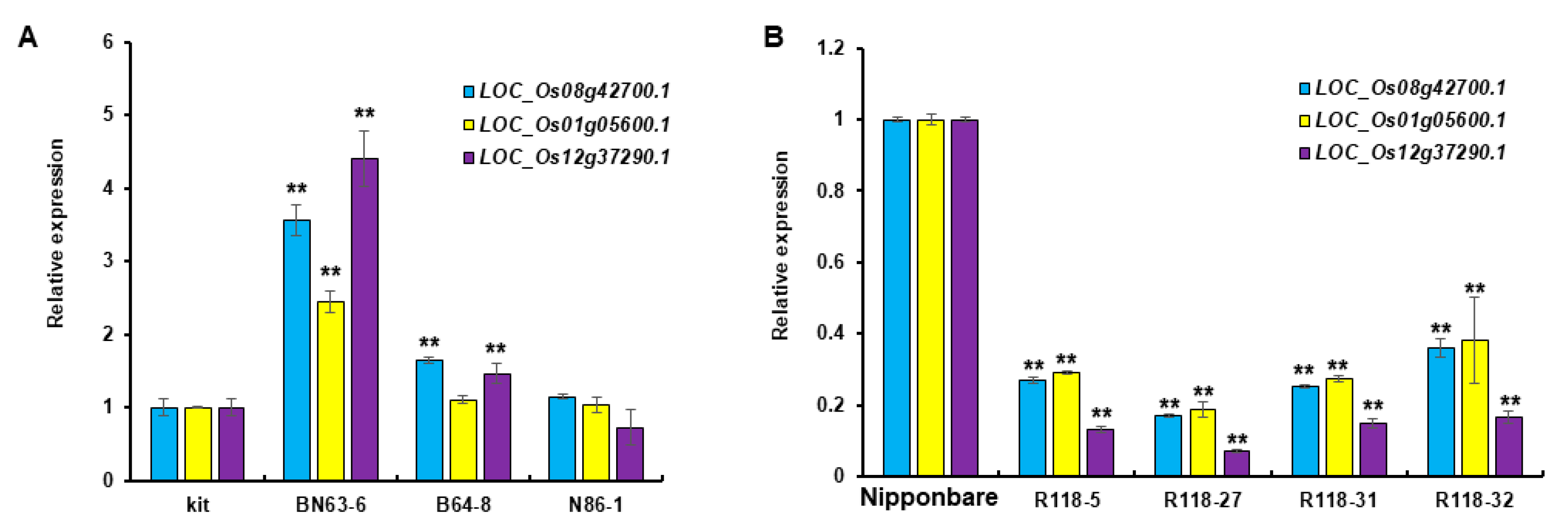
2.4. Validation of the Target Genes of miR2118
2.4.1. Construction of Related Vectors
2.4.2. Protoplast Transient Expression for Target Gene Validation
2.4.3. Target Gene Expression Level Analysis of Transgenic Materials
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Rice Materials
4.2. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription, and RT-qPCR Analysis
4.3. Disease Resistance Detection
4.4. Prediction of Target Genes
4.5. Construction of Vector
4.6. Rice Protoplast Transient Expression System
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhart, B.J.; Weinstein, E.G.; Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, B.; David, P.B. MicroRNAs in plants. Gene Dev. 2002, 16, 1616–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, F.; Martienssen, R.A. The expanding world of small RNAs in plants. Nat. Rev. Cell. Biol. 2015, 16, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuperus, J.T.; Fahlgren, N.; Carrington, J.C. Evolution and Functional Diversification of miRNA Genes. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, Y.; Agron, M.; Praher, D.; Technau, U. The evolutionary origin of plant and animal microRNAs. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khraiwesh, B.; Zhu, J.K.; Zhu, J.H. Role of miRNAs and siRNAs in biotic and abiotic stress responses of plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1819, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, L.I.; Chinnusamy, V.; Sunkar, R. The role of microRNAs and other endogenous small RNAs in plant stress responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1779, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; He, H.; Yu, D.Q. Identification of Nitrogen Starvation-Responsive MicroRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.X.; Allen, E.; Wilken, A.; Carrington, J.C. DICER-LIKE 4 functions in trans-acting small interfering RNA biogenesis and vegetative phase change in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12984–12989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo-Quaye, C.; Eshoo, T.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Axtell, M.J. Endogenous siRNA and miRNA targets identified by sequencing of the Arabidopsis degradome. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aukerman, M.J.; Sakai, H. Regulation of flowering time and floral organ identity by a microRNA and its APETALA2-like target genes. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2730–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.M. A microRNA as a translational repressor of APETALA2 in Arabidopsis flower development. Science 2004, 303, 2022–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandikota, M.; Birkenbihl, R.P.; Hohmann, S.; Cardon, G.H.; Saedler, H.; Huijser, P. The miRNA156/157 recognition element in the 3′ UTR of the Arabidopsis SBP box gene SPL3 prevents early flowering by translational inhibition in seedlings. Plant J. 2007, 49, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.B.; Liu, L.; Zhuang, X.H.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.G.; Cui, X.; Ji, L.J.; Pan, Z.Q.; Cao, X.F.; Mo, B.X. MicroRNAs inhibit the translation of target mRNAs on the endoplasmic reticulum in Arabidopsis. Cell 2013, 153, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, R.; Palatnik, J.F.; Riester, M.; Schommer, C.; Schmid, M.; Weigel, D. Specific effects of microRNAs on the plant transcriptome. Dev. Cell 2005, 8, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodersen, P.; Sakvarelidze-Achard, L.; Bruun-Rasmussen, M.; Dunoyer, P.; Yamamoto, Y.Y.; Sieburth, L.; Voinnet, O. Widespread translational inhibition by plant miRNAs and siRNAs. Science 2008, 320, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldrich, P.; Segundo, B.S. MicroRNAs in Rice Innate Immunity. Rice 2016, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Qi, Y.; Zhou, J.M. Identification of microRNAs involved in pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered plant innate immunity. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 2222–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, L.; Dunoyer, P.; Jay, F.; Arnold, B.; Dharmasiri, N.; Estelle, M.; Voinnet, O.; Jones, J.D.G. A plant miRNA contributes to antibacterial resistance by repressing auxin signaling. Science 2006, 312, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; Valli, A.; Todesco, M.; Todesco, M.; Mateos, I.; Puga, M.I.; Rubio-Somoza, I.; Leyva, A.; Weigel, D.; García, J.A.; et al. Target mimicry provides a new mechanism for regulation of microRNA activity. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahlgren, N.; Howell, M.D.; Kasschau, K.D.; Chapman, E.J.; Sullivan, C.M.; Cumbie, J.S.; Givan, S.A.; Law, T.F.; Grant, S.R.; Dangl, J.L.; et al. High throughput sequencing of Arabidopsis microRNAs: Evidence for frequent birth and death of MIRNA genes. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, S.; Cristina, P.P.; Christelle, S.; Moreno, A.B.; Donaire, L.; Zytnicki, M.; Notredame, C.; César, L.; Segundo, B.S. Identification of a novel microRNA (miRNA) from rice that targets an alternatively spliced transcript of the Nramp6 (Natural resistance-associated macrophage protein 6) gene involved in pathogen resistance. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanabhan, C.; Zhang, X.; Jin, H. Host small RNAs are big contributors to plant innate immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagadeeswaran, G.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.F.; Lata, I.; Fangshukla, L.I.; Matts, J.; Hoyt, P.; Macmil, S.L.; Wiley, G.B.; Roe, B.A.; et al. Cloning and characterization of small RNAs from Medicago truncatula reveals four novel legume-specific microRNA families. New Phytol. 2009, 184, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivaprasad, P.V.; Chen, H.M.; Patel, K.; Bond, D.M.; Santos, B.A.C.M.; Baulcombe, D.C. A MicroRNA superfamily regulates nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeats and other mRNAs. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccara, M.; Sarazin, A.; Thiébeauld, O.; Jay, F.; Voinnet, O. The Arabidopsis miR472-RDR6 silencing pathway modulates PAMP- and effector-triggered immunity through the post-transcriptional control of disease resistance genes. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.X.; Jeong, D.H.; De, P.E.; Park, S.; Rosen, B.D.; Li, Y.; Gonzalez, A.J.; Yan, Z.; Kitto, S.L.; Grusak, M.A. MicroRNAs as master regulators of the plant NB-LRR defense gene family via the production of phased, trans-acting siRNAs. Gene Dev. 2011, 25, 2540–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Pignatta, D.; Bendix, C.; Brunkard, J.O.; Cohn, M.M.; Tung, J.; Sun, H.Y.; Kumar, P.; Baker, B. MicroRNA regulation of plant innate immune receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1790–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vries, S.D.; Kloesges, T.; Rose, L.E. Evolutionarily Dynamic, but Robust, Targeting of Resistance Genes by the miR482/2118 Gene Family in the Solanaceae. Genome Bio. Evol. 2015, 7, 3307–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.J.; Li, Y.; Han, X.L.; Shen, F.F. Genome-wide profiling of miRNAs and other small non-coding RNAs in the verticillium dahliae-inoculated cotton roots. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vries, S.D.; Kukuk, A.; Von Dahlen, J.K.; Schnake, A.; Kloesges, T.; Rose, L.E. Expression profiling across wild and cultivated tomatoes supports the relevance of early miR482/2118 suppression for Phytophthora resistance. Proc. R. Soc. B 2018, 285, 20172560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.H.; Fan, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Llewellyn, D.; Wilson, I. miR482 regulation of NBS-LRR defense genes during fungal pathogen infection in Cotton. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Chen, Y.T.; Cao, Y.Q.; Chen, H.M.; Wang, J.C.; Bi, Y.-M.; Tian, F.; Yang, F.H.; Rothstein, S.J.; Zhou, X.P. Overexpression of miR169o, an overlapping microRNA in response to both nitrogen limitation and bacterial infection, promotes nitrogen use efficiency and susceptibility to bacterial blight in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018, 59, 1234–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhao, P.X. psRNATarget: A plant small RNA target analysis server (2017 release). Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W49–W54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiebaut, F.; Rojas, C.A.; Grativol, C.; Motta, M.R.; Vieira, T.; Regulski, M.; Martienssen, R.A.; Farinelli, L.; Hemerly, A.S.; Ferreira-Paulo, C.G. Genome-wide identification of microRNA and siRNA-responsive to endophytic beneficial diazotrophic bacteria in maize. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Tai, H.; Sun, S.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Y.; Li, W.X.; Sebastien, P. Cloning and characterization of maize miRNAs involved in responses to nitrogen deficiency. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liu, Q.; Chen, L.Y.; Kuang, J.B.; Walk, T.; Wang, J.X.; Liao, H. Genome-wide identification of soybean microRNAs and their targets reveals their organ-specificity and responses to phosphate starvation. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.X.; Wu, G.T.; Yan, F.; Lu, Y.W.; Zheng, H.Y.; Lin, L.; Chen, H.R. Identification of novel Oryza sativa miRNAs in deep sequencing-based small RNA libraries of rice infected with Rice stripe virus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Kasprzewska, A.; Tennessen, K.; Fernandes, J.; Nan, G.L.; Walbot, V.; Sundaresan, V.; Vance, V.; Bowman, L.H. Clusters and superclusters of phased small RNAs in the developing inflorescence of rice. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas-Huertero, C.; Perez, B.; Rabanal, F.; Blanco-Melo, D.; Rosa, C.D.L.; Estrada-Navarrete, G.; Sanchez, F.; Covarrubias, A.A.; Reyes, J.L. Conserved and novel mirnas in the legume Phaseolus vulgaris in response to stress. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 4, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.F.; Li, W.F.; Han, S.Y.; Xu, H.Y.; Qi, L.W. Role of cin-miR2118 in drought stress responses in Caragana intermedia and Tobacco. Gene 2015, 574, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.Z.; Huang, S.; Li, S.M.; Song, G.Q.; Li, G.Y. Evolution of phas loci in the young spike of allohexaploid wheat. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y. Characterize the function of candidate overlapping miRNAs response to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae infection and nitrogen starvation stress in Rice. Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences Dissertation. April, 2015 (In Chinese). CAAS. 2015. Available online: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/thesis/ChJUaGVzaXNOZXdTMjAyMzA5MDESCFkyNzg4MDIxGghmY29qcWxzNA%3D%3D (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- Chen, S.; Songkumarn, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, G.L. A versatile zero background T-vector system for gene cloning and functional genomics. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.B.; Liu, B.; Weeks, D.P.; Spalding, M.H.; Yang, B. Large chromosomal deletions and heritable small genetic changes induced by CRISPR/Cas9 in rice. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 10903–10914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tao, L.Z.; Zeng, L.R.; Vega-Sanchez, M.E.; Umemura, K.; Wang, G.L. A highly efficient transient protoplast system for analyzing defence gene expression and protein–protein interactions in rice. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2006, 7, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Chen, S.B.; Ning, Y.S.; Wang, G.L. Rice (Oryza sativa) protoplast isolation and its application for transient expression analysis: Rice protoplast isolation and transient expression analysis. Curr. Protoc. Plant Biol. 2016, 1, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.X.; Cao, Y.Q.; Zhu, X.M.; Yu, C.; Tian, F.; Yang, F.H.; Chen, H.M.; He, C.Y. Rapid validation of target rice miRNAs genes in transient expression system. Biotechnol. Bull. 2019, 35, 57–63. [Google Scholar]

| b Locus | n Locus | |
|---|---|---|
| BN63-6 a | Del 9 nt (21645316-5324)/Ins 1 nt (21645336-)/ del 4 nt (21645381-5384) | Del 45 nt (21661545-1589) |
| BN9-3 a | Del 5 nt (21645316-5320)/Ins 1 nt (21645336-)/ Ins 1 nt (21645381-) | Del 2 nt (21661543-1544) |
| BN65-3 a | Del 29 nt (21645294-5322)/Ins 1 nt(21645336-)/ Ins 1 nt (21645382-) | Ins 1 nt (21661545-) |
| B51-3 b | Ins 210 nt (21645321-)/del 1 nt (21645321-)/ del 38 nt (21645348-5385) | |
| B64-8 b | Del 23 nt (21645306-5328)/Ins 1 nt (21645381-) | |
| B68-1 b | Ins 1 nt (21645320-)/Ins 1 nt (21645382-) | |
| N86-1 c | Del 27 nt (21661533-1559)/Ins 7 nt (21661532-) |
| Target Gene | Sequence | Inhibition | Target Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os08g42700.1 | GGGGAAUGGGUG GCAUUGGGAA | Cleavage | cDNA|resistance protein, putative, expressed |
| LOC_Os01g05600.1 | AGGGGAUGGGAG GCAUCGGUAA | Cleavage | cDNA|NBS-LRR disease resistance protein, putative, expressed |
| LOC_Os12g37290.1 | GGGGAAUGGGU GGUAUUGGGAA | Cleavage | cDNA|resistance protein T10rga2-1A, putative, expressed |
| Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) | Restriction Enzyme | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIR2118-F | GGATCCTATACGC ATGGTGTTTCACTTAC | BamH I, Pst I | Amplified MIR2118 gene |
| MIR2118-R | CTGCAGTTTAGAGGG ACAGAAGAGTTTGA | ||
| 42700-F | tcgacGGGGAATGGGTG GCATTGGGAActgca | Pst I, Sal I | Construction of LUC-42700 fusion vector |
| 42700-R | gTTCCCAATGCCACCC ATTCCCCg | ||
| 42700m3-F | tcgacGGGGAATGGGTG ctaGCATTGGGAActgca | Pst I, Sal I | Construction of LUC-42700m3 fusion vector |
| 42700m3-R | gTTCCCAATGCtagCACCCATTCCCCg | ||
| 05600-F | tcgacAGGGGATGGGAGGCATCGGTAActgca | Pst I, Sal I | Construction of LUC-05600 fusion vector |
| 05600-R | gTTACCGATGCCTCCCA TCCCCTg | ||
| 05600m3-F | tcgacAGGGGATGGGAG ctaGCATCGGTAActgca | Pst I, Sal I | Construction of LUC-05600m3 fusion vector |
| 05600m3-R | gTTACCGATGC tagCTCCCATCCCCTg | ||
| 37290-F | tcgacGGGGAAUGGGU GGUAUUGGGAActgca | Pst I, Sal I | Construction of LUC-37290 fusion vector |
| 37290-R | gTTCCCAATACCACC CATTCCCCg | ||
| 37290m3-F | tcgacGGGGAAUGGGUG ctaGUAUUGGGAActgca | Pst I, Sal I | Construction of LUC-37290m3 fusion vector |
| 37290m3-R | gTTCCCAATA tagCCACCCATTCCCCg |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J.; Cao, Y.; Hu, J.; Yu, C.; Yang, F.; Tian, F.; Chen, H. miR2118 Negatively Regulates Bacterial Blight Resistance through Targeting Several Disease Resistance Genes in Rice. Plants 2023, 12, 3815. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12223815
Zhu X, Kuang Y, Chen Y, Shi J, Cao Y, Hu J, Yu C, Yang F, Tian F, Chen H. miR2118 Negatively Regulates Bacterial Blight Resistance through Targeting Several Disease Resistance Genes in Rice. Plants. 2023; 12(22):3815. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12223815
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xiumei, Yongjie Kuang, Yutong Chen, Jia Shi, Yaqian Cao, Jixiang Hu, Chao Yu, Fenghuan Yang, Fang Tian, and Huamin Chen. 2023. "miR2118 Negatively Regulates Bacterial Blight Resistance through Targeting Several Disease Resistance Genes in Rice" Plants 12, no. 22: 3815. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12223815
APA StyleZhu, X., Kuang, Y., Chen, Y., Shi, J., Cao, Y., Hu, J., Yu, C., Yang, F., Tian, F., & Chen, H. (2023). miR2118 Negatively Regulates Bacterial Blight Resistance through Targeting Several Disease Resistance Genes in Rice. Plants, 12(22), 3815. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12223815







