Microwave-Assisted Hydrodistillation of the Insecticidal Essential Oil from Carlina acaulis: A Fractional Factorial Design Optimization Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
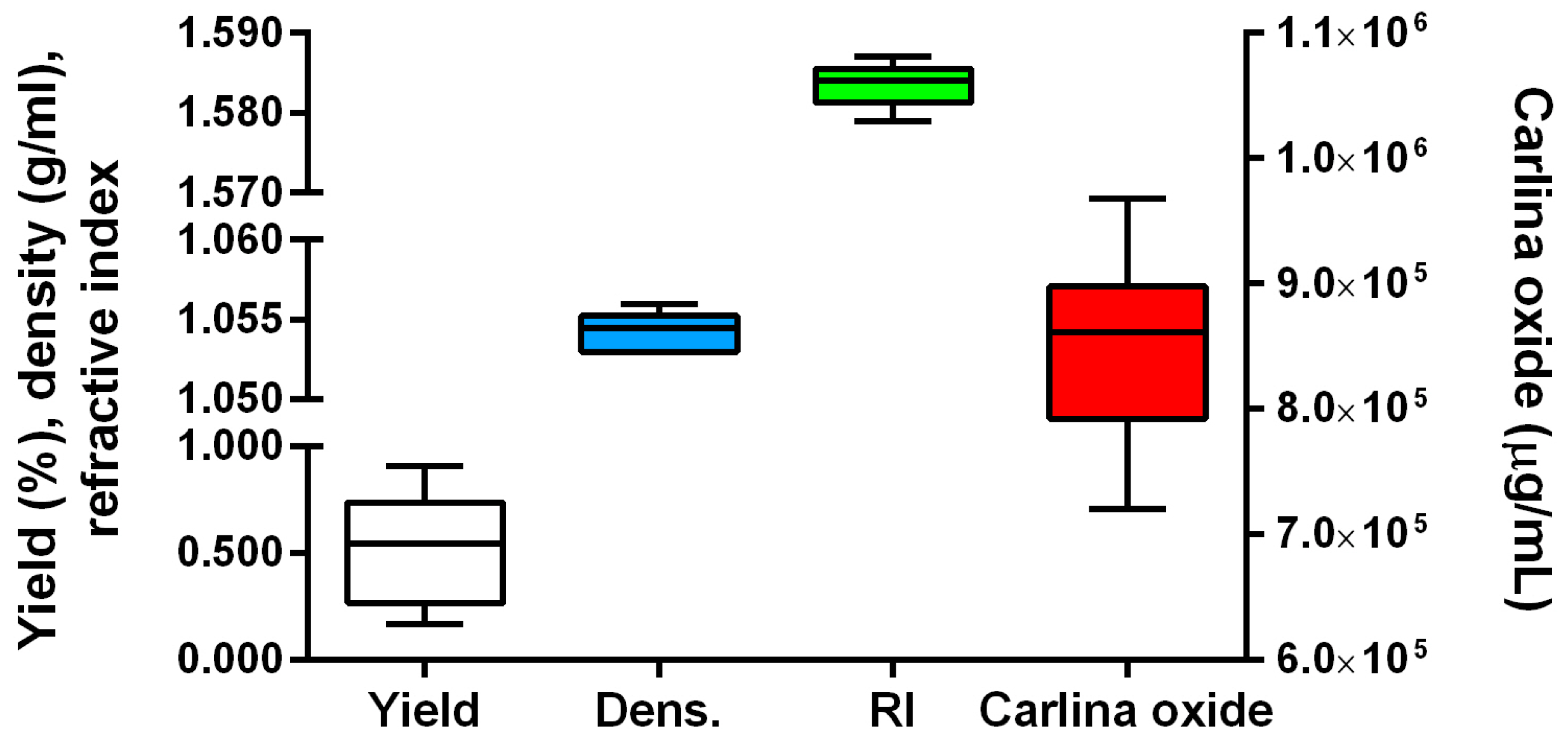
2.1. Preliminary Screening
2.2. The Effect of the Extraction Time
2.3. Comparison of MAH and HD
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Sample Preparation
4.3. Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAH)
4.4. Design of Experiment (DoE)
| Run | Uncoded Variables | Coded Variables a | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP (W/g) | ET (min) | W (%) | Mo | Mi | Cycles | MP | ET | W | Mo | Mi | Cycles | |
| 1 | 1 | 90 | 65 | N | N | N | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | 1.45 | 90 | 65 | N | Y | N | + | - | - | - | + | - |
| 3 | 1 | 210 | 65 | N | Y | Y | - | + | - | - | + | + |
| 4 | 1.45 | 210 | 65 | N | N | Y | + | + | - | - | - | + |
| 5 | 1 | 90 | 85 | N | Y | Y | - | - | + | - | + | + |
| 6 | 1.45 | 90 | 85 | N | N | Y | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| 7 | 1 | 210 | 85 | N | N | N | - | + | + | - | - | - |
| 8 | 1.45 | 210 | 85 | N | Y | N | + | + | + | - | + | - |
| 9 | 1 | 90 | 65 | Y | N | Y | - | - | - | + | - | + |
| 10 | 1.45 | 90 | 65 | Y | Y | Y | + | - | - | + | + | + |
| 11 | 1 | 210 | 65 | Y | Y | N | - | + | - | + | + | - |
| 12 | 1.45 | 210 | 65 | Y | N | N | + | + | - | + | - | - |
| 13 | 1 | 90 | 85 | Y | Y | N | - | - | + | + | + | - |
| 14 | 1.45 | 90 | 85 | Y | N | N | + | - | + | + | - | - |
| 15 | 1 | 210 | 85 | Y | N | Y | - | + | + | + | - | + |
| 16 | 1.45 | 210 | 85 | Y | Y | Y | + | + | + | + | + | + |
4.5. Hydrodistillation (HD)
4.6. Analysis of EOs Chemical-Physical Properties
4.6.1. Density Determination
4.6.2. Refractive Index (RI)
4.6.3. GC-MS Analysis
Chemicals and Reagents
Preparation of Standard Solutions
EO Characterization and Quantification of Carlina Oxide
Linearity of the Quantification Method
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- López, M.D.; Cantó-Tejero, M.; Pascual-Villalobos, M.J. New Insights into biopesticides: Solid and liquid formulations of essential oils and derivatives. Front. Agron. 2021, 3, 763530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnault-Roger, C.; Vincent, C.; Arnason, J.T. Essential oils in insect control: Low-risk products in a high-stakes world. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2012, 57, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavela, R.; Benelli, G. Essential oils as ecofriendly biopesticides? Challenges and constraints. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isman, M.B. Commercial development of plant essential oils and their constituents as active ingredients in bioinsecticides. Phytochem. Rev. 2020, 19, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menossi, M.; Ollier, R.P.; Casalongué, C.A.; Alvarez, V.A. Essential oil-loaded bio-nanomaterials for sustainable agricultural applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 2109–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, P.; Plainfossé, H.; Brochet, X.; Chemat, F.; Fernandez, X. Extraction of natural fragrance ingredients: History overview and future trends. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1900424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Destandau, E.; Michel, T.; Elfakir, C. Microwave-Assisted Extraction; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2013; Volume 4, pp. 113–156. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorini, D.; Scortichini, S.; Bonacucina, G.; Greco, N.G.; Mazzara, E.; Petrelli, R.; Torresi, J.; Maggi, F.; Cespi, M. Cannabidiol-enriched hemp essential oil obtained by an optimized microwave-assisted extraction using a central composite design. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 154, 112688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzara, E.; Carletti, R.; Petrelli, R.; Mustafa, A.M.; Caprioli, G.; Fiorini, D.; Scortichini, S.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Sut, S.; Nuñez, S.; et al. Green extraction of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) using microwave method for recovery of three valuable fractions (essential oil, phenolic compounds and cannabinoids): A central composite design optimization study. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 6220–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benelli, G.; Pavela, R.; Petrelli, R.; Nzekoue, F.K.; Cappellacci, L.; Lupidi, G.; Quassinti, L.; Bramucci, M.; Sut, S.; Dall’Acqua, S.; et al. Carlina oxide from Carlina acaulis root essential oil acts as a potent mosquito larvicide. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 137, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelli, G.; Pavoni, L.; Zeni, V.; Ricciardi, R.; Cosci, F.; Cacopardo, G.; Gendusa, S.; Spinozzi, E.; Petrelli, R.; Cappellacci, L.; et al. Developing a highly stable Carlina acaulis essential oil nanoemulsion for managing Lobesia Botrana. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavela, R.; Maggi, F.; Petrelli, R.; Cappellacci, L.; Buccioni, M.; Palmieri, A.; Canale, A.; Benelli, G. Outstanding insecticidal activity and sublethal effects of Carlina acaulis root essential oil on the housefly, Musca domestica, with insights on its toxicity on human cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 111037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, R.; Pistillo, M.; Germinara, G.S.; Lo Verde, G.; Sinacori, M.; Maggi, F.; Petrelli, R.; Spinozzi, E.; Cappellacci, L.; Zeni, V.; et al. Bioactivity of Carlina acaulis essential oil and its main component towards the olive fruit fly, Bactrocera oleae: Ingestion toxicity, electrophysiological and behavioral insights. Insects 2021, 12, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavallieratos, N.G.; Nika, E.P.; Skourti, A.; Spinozzi, E.; Ferrati, M.; Petrelli, R.; Maggi, F.; Benelli, G. Carlina acaulis essential oil: A candidate product for agrochemical industry due to its pesticidal capacity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 188, 115572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavela, R.; Pavoni, L.; Bonacucina, G.; Cespi, M.; Cappellacci, L.; Petrelli, R.; Spinozzi, E.; Aguzzi, C.; Zeppa, L.; Ubaldi, M.; et al. Encapsulation of Carlina acaulis essential oil and carlina oxide to develop long-lasting mosquito larvicides: Microemulsions versus nanoemulsions. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 94, 899–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinozzi, E.; Ferrati, M.; Cappellacci, L.; Caselli, A.; Perinelli, D.R.; Bonacucina, G.; Maggi, F.; Strzemski, M.; Petrelli, R.; Pavela, R.; et al. Carlina acaulis L. (Asteraceae): Biology, phytochemistry, and application as a promising source of effective green insecticides and acaricides. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 192, 116076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Ospina, J.; Tovar, C.D.G.; Flores, J.C.M.; Orozco, M.S.S. Relationship between refractive index and thymol concentration in essential oils of Lippia origanoides kunth. Chil. J. Agric. Anim. Sci. 2016, 32, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazzara, E.; Scortichini, S.; Fiorini, D.; Maggi, F.; Petrelli, R.; Cappellacci, L.; Morgese, G.; Morshedloo, M.R.; Palmieri, G.F.; Cespi, M. A design of experiment (DoE) approach to model the yield and chemical composition of ajowan (Trachyspermum ammi L.) essential oil obtained by microwave-assisted extraction. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemat, S.; Aït-Amar, H.; Lagha, A.; Esveld, D.C. Microwave-assisted extraction kinetics of terpenes from caraway seeds. Chem. Eng. Process. 2005, 44, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.A.; Mathie, D.; Phan-Tan-Luu, R. Overview. In Pharmaceutical Experimental Design; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- FFNSC. Flavors and Fragrances of Natural and Synthetic Compounds. Mass Spectral Database. 2; Shimadzu Corps.: Kyoto, Japan, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry, 4th ed.; Allured Publishing Corp.: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- NIST. Mass Spectral Library (NIST/EPA/NIH). 17; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spinozzi, E.; Ferrati, M.; Giudice, D.L.; Felicioni, E.; Petrelli, R.; Benelli, G.; Maggi, F.; Cespi, M. Microwave-Assisted Hydrodistillation of the Insecticidal Essential Oil from Carlina acaulis: A Fractional Factorial Design Optimization Study. Plants 2023, 12, 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12030622
Spinozzi E, Ferrati M, Giudice DL, Felicioni E, Petrelli R, Benelli G, Maggi F, Cespi M. Microwave-Assisted Hydrodistillation of the Insecticidal Essential Oil from Carlina acaulis: A Fractional Factorial Design Optimization Study. Plants. 2023; 12(3):622. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12030622
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpinozzi, Eleonora, Marta Ferrati, Desiree Lo Giudice, Eugenio Felicioni, Riccardo Petrelli, Giovanni Benelli, Filippo Maggi, and Marco Cespi. 2023. "Microwave-Assisted Hydrodistillation of the Insecticidal Essential Oil from Carlina acaulis: A Fractional Factorial Design Optimization Study" Plants 12, no. 3: 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12030622
APA StyleSpinozzi, E., Ferrati, M., Giudice, D. L., Felicioni, E., Petrelli, R., Benelli, G., Maggi, F., & Cespi, M. (2023). Microwave-Assisted Hydrodistillation of the Insecticidal Essential Oil from Carlina acaulis: A Fractional Factorial Design Optimization Study. Plants, 12(3), 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12030622













