The Role of Protein-Rich Extracts from Chondrus crispus as Biostimulant and in Enhancing Tolerance to Drought Stress in Tomato Plants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Proteins Contained in C. crispus Extracts Are Mainly Pigment-Protein Complexes
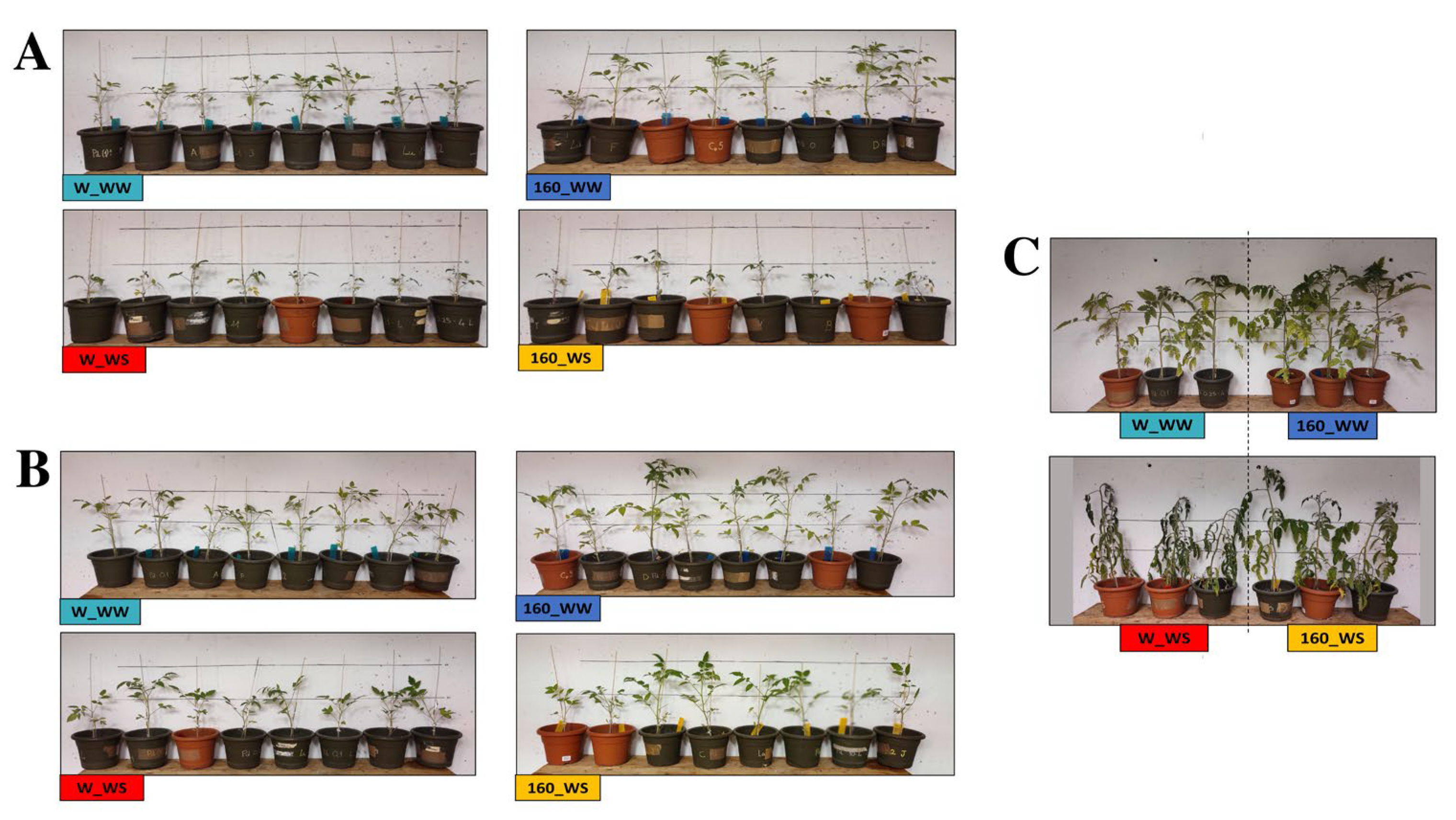
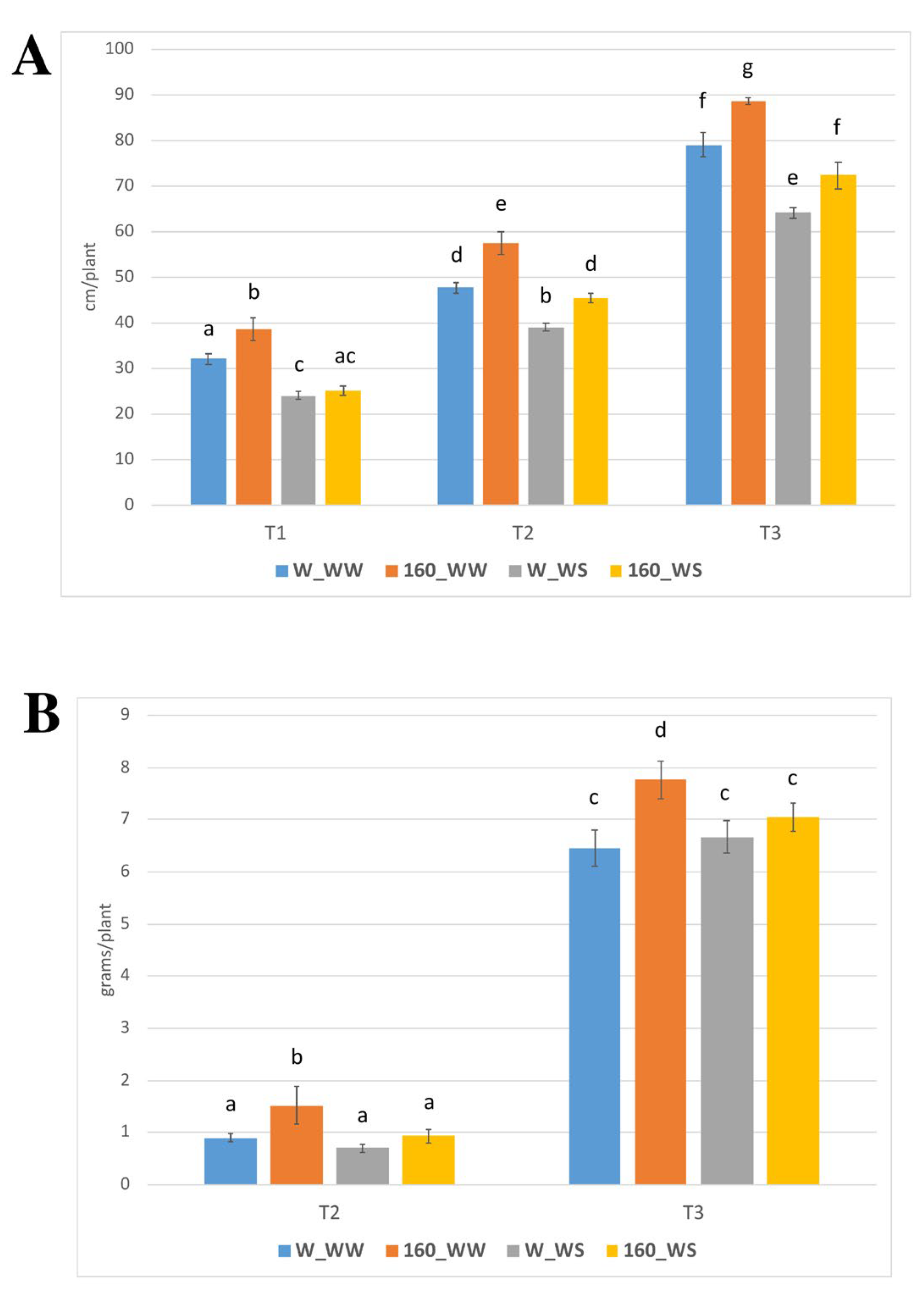
2.2. C. crispus Extract Treatment Stimulates Growth of Tomato Plants in Control Conditions and under Water Deficit
2.3. C. crispus Extract Increases Endogenous ABA Levels
2.4. C. crispus Extract Treatment Modulates Proline Levels in Tomato Plants
2.5. C. crispus Extract Treatment Modulates the Expression of a Stress Protective Gene under Drought
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Extract Preparation and Characterization
4.1.1. Hydrothermal Extraction with Subcritical Water
4.1.2. LC-MS/MS Analysis
4.1.3. Elaboration of Raw Data and Downstream Bioinformatic Analysis
4.2. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
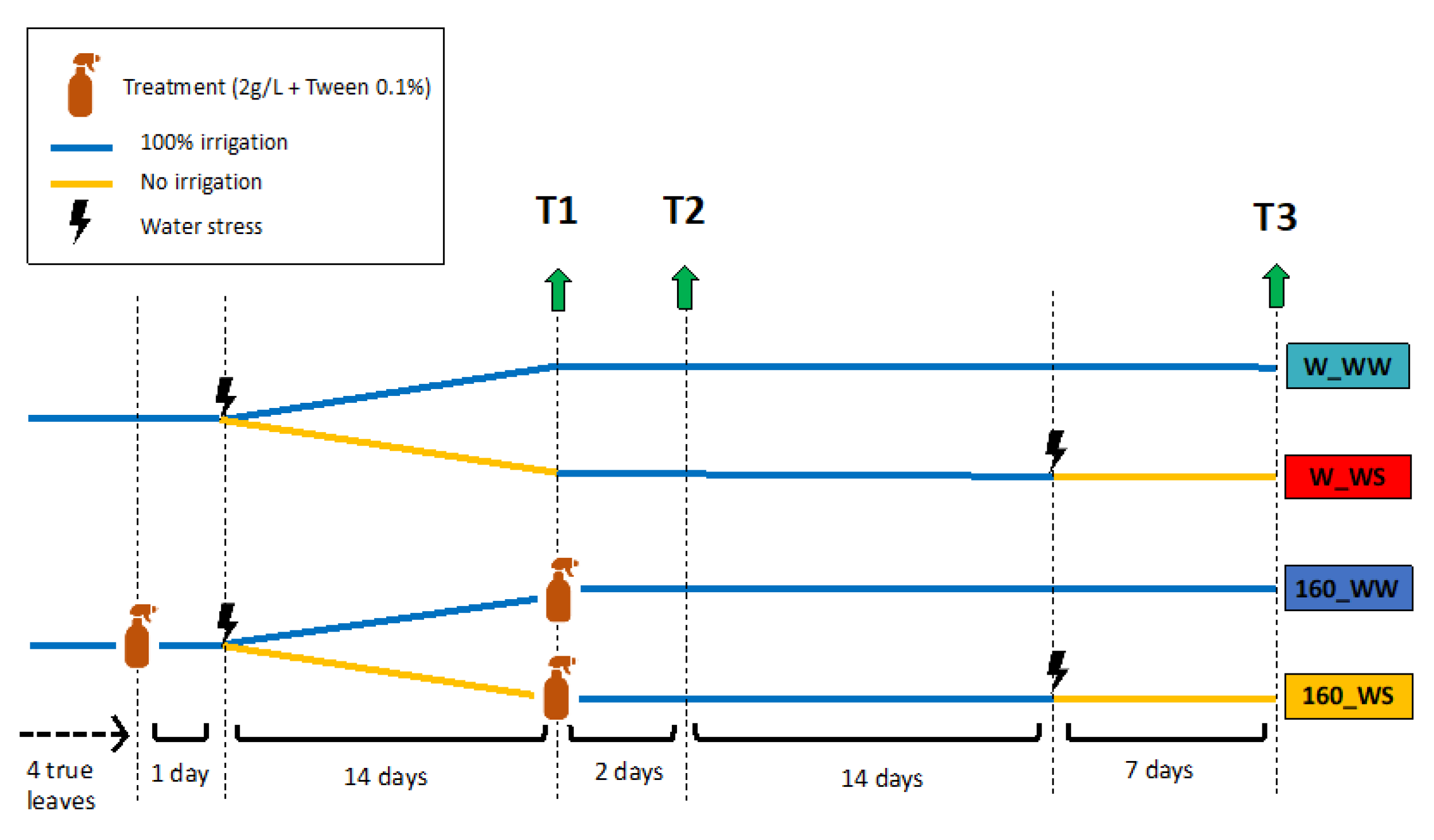
4.3. Biostimulant Application and Drought Stress Conditions
4.4. Shoot Length and Biomass Measurements
4.5. Determination of ABA Content
4.6. Determination of Proline Content
4.7. RNA Extraction and Relative Gene Expression by qRT-PCR of Drought Stress Marker Genes
4.8. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arora, N.K. Impact of climate change on agriculture production and its sustainable solutions. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 2, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placide, R.; Hirut, G.B.; Stephan, N.; Fekadu, B. Assessment of drought stress tolerance in root and tuber crops. Afr. J. Plant Sci. 2014, 8, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, L.S.; Pathma, J. Impact of agro-chemicals on environment: A global perspective. Plant Cell Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. 2021, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Caradonia, F.; Battaglia, V.; Righi, L.; Pascali, G.; La Torre, A. Plant Biostimulant Regulatory Framework: Prospects in Europe and Current Situation at International Level. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2018, 38, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Toward a sustainable agriculture through plant biostimulants: From experimental data to practical applications. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, D.; Cotas, J.; Rocha, C.P.; Araújo, G.S.; Figueirinha, A.; Gonçalves, A.M.; Bahcevandziev, K.; Pereira, L. Seaweeds’ carbohydrate polymers as plant growth promoters. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, O.; Ramsubhag, A.; Jayaraman, J. Biostimulant Properties of Seaweed Extracts in Plants: Implications towards Sustainable Crop Production. Plants 2021, 10, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.S.; Mantin, E.G.; Adil, M.; Bajpai, S.; Critchley, A.T.; Prithiviraj, B. Ascophyllum nodosum-Based Biostimulants: Sustainable Applications in Agriculture for the Stimulation of Plant Growth, Stress Tolerance, and Disease Management. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okolie, C.L.; Mason, B.; Critchley, A.T. Novel Proteins for Food, Pharmaceuticals and Agriculture; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 217–238. [Google Scholar]
- Deolu-Ajayi, A.O.; van der Meer, I.M.; van der Werf, A.; Karlova, R. The power of seaweeds as plant biostimulants to boost crop production under abiotic stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2022, 45, 2537–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmody, N.; Goñi, O.; Łangowski, Ł.; O’Connell, S. Extract Biostimulant Processing and Its Impact on Enhancing Heat Stress Tolerance During Tomato Fruit Set. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łangowski, Ł.; Goñi, O.; Marques, F.S.; Hamawaki, O.T.; da Silva, C.O.; Nogueira, A.P.O.; Teixeira, M.A.J.; Glasenapp, J.S.; Pereira, M.; O’Connell, S. Ascophyllum nodosum Extract (SealicitTM) Boosts Soybean Yield Through Reduction of Pod Shattering-Related Seed Loss and Enhanced Seed Production. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 631768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.S.; Borza, T.; Critchley, A.T.; Prithiviraj, B. Carrageenans from Red Seaweeds as Promoters of Growth and Elicitors of Defense Response in Plants. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, L.V.; Aurigue, F.B.; Relleve, L.S.; Montefalcon, D.R.V.; Lopez, G.E. P, Characterization of low molecular weight fragments from gamma irradiated κ-carrageenan used as plant growth promoter. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2016, 118, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, J.; Castro, J.; Contreras, R.A.; González, A.; Moenne, A. Oligo-carrageenans induce a long-term and broad-range pro-tection against pathogens in tobacco plants (var. Xanthi). Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 79, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, K.; Anand, K.G.V.; Kubavat, D.; Ghosh, A. Role of Kappaphycus alvarezii seaweed extract and its active constituents, glycine betaine, choline chloride, and zeatin in the alleviation of drought stress at critical growth stages of maize crop. J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 34, 1791–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, G.; Nardi, S.; Cardarelli, M.; Ertani, A.; Lucini, L.; Canaguier, R.; Rouphael, Y. Protein hydrolysates as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, G.; Hoagland, L.; Ruzzi, M.; Cardarelli, M.; Bonini, P.; Canaguier, R.; Rouphael, Y. Biostimulant Action of Protein Hydrolysates: Unraveling Their Effects on Plant Physiology and Microbiome. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Carillo, P.; Cristofano, F.; Cardarelli, M.; Colla, G. Effects of vegetal-versus animal-derived protein hydrolysate on sweet basil morpho-physiological and metabolic traits. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 284, 110123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponthier, E.; Domínguez, H.; Torres, M.D. The microwave assisted extraction sway on the features of antioxidant compounds and gelling biopolymers from Mastocarpus stellatus. Algal Res. 2020, 51, 102081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Viñas, M.; González-Ballesteros, N.; Torres, M.D.; López-Hortas, L.; Vanini, C.; Domingo, G.; Rodríguez-Argüelles, M.C.; Domínguez, H. Efficient extraction of carrageenans from Chondrus crispus for the green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and formulation of printable hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solankey, S.S.; Singh, R.K.; Baranwal, D.K.; Singh, D.K. Genetic Expression of Tomato for Heat and Drought Stress Tolerance: An Overview. Int. J. Veg. Sci. 2015, 21, 496–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilinskas, B.A.; Greenwald, L.S. Phycobilisome structure and function. Photosynth. Res. 1986, 10, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, L.; Ferrante, A. Agronomic management for enhancing plant tolerance to abiotic stresses—Drought, salinity, hypoxia, and lodging. Horticulturae 2017, 34, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goñi, O.; Quille, P.; O’Connell, S. Ascophyllum nodosum extract biostimulants and their role in enhancing tolerance to drought stress in tomato plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 126, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacomassi, L.M.; Viveiros, J.D.O.; Oliveira, M.P.; Momesso, L.; de Siqueira, G.F.; Crusciol, C.A.C. A Seaweed Extract-Based Biostimulant Mitigates Drought Stress in Sugarcane. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 865291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Boukhari, M.E.M.; Barakate, M.; Bouhia, Y.; Lyamlouli, K. Trends in Seaweed Extract Based Biostimulants: Manufacturing Process and Beneficial Effect on Soil-Plant Systems. Plants 2020, 9, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rady, M.M.; Taha, R.S.; Mahdi, A.H. Proline enhances growth, productivity and anatomy of two varieties of Lupinus termis L. grown under salt stress. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2016, 102, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Basu, N.; Bhunia, A.; Banerjee, S.K. Counteraction of exogenous L-proline with NaCl in salt-sensitive cultivar of rice. Biol. Plant. 1993, 35, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, S.; Hayat, Q.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wani, A.S.; Pichtel, J.; Ahmad, A. Role of proline under changing environments: A review. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Qin, F. ABA regulation of plant responses to drought and salt stresses. In Abscisic Acid: Metabolism, Transport and Signaling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 315–336. [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Taji, T.; Naramoto, M.; Seki, M.; Kato, T.; Tabata, S.; Kakubari, Y.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Regulation of drought tolerance by gene manipulation of 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase, a key enzyme in abscisic acid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2001, 27, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Chen, C.; Khatri, K.; Rathore, M.S.; Pandey, S.P. Gracilaria dura extract confers drought tolerance in wheat by modulating abscisic acid homeostasis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 136, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharath, P.; Gahir, S.; Raghavendra, A.S. Abscisic Acid-Induced Stomatal Closure: An Important Component of Plant Defense Against Abiotic and Biotic Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 615114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavendra, A.S.; Gonugunta, V.K.; Christmann, A.; Grill, E. ABA perception and signalling. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaniello, A.; Scartazza, A.; Gresta, F.; Loreti, E.; Biasone, A.; Di Tommaso, D.; Piaggesi, A.; Perata, P. Ascophyllum nodosum Seaweed Extract Alleviates Drought Stress in Arabidopsis by Affecting Photosynthetic Performance and Related Gene Expression. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasul, F.; Gupta, S.; Olas, J.J.; Gechev, T.; Sujeeth, N.; Mueller-Roeber, B. Priming with a Seaweed Extract Strongly Improves Drought Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Yin, H.; Wang, W.-X.; Zhao, X.-M.; Du, Y.-G. Alginate oligosaccharides enhanced Triticum aestivum L. tolerance to drought stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 62, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wally, O.S.D.; Critchley, A.T.; Hiltz, D.; Craigie, J.S.; Han, X.; Zaharia, L.I.; Abrams, S.R.; Prithiviraj, B. Regulation of Phytohormone Biosynthesis and Accumulation in Arabidopsis Following Treatment with Commercial Extract from the Marine Macroalga Ascophyllum nodosum. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2012, 32, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrozza, A.; Santaniello, A.; Summerer, S.; Di Tommaso, G.; Di Tommaso, D.; Paparelli, E.; Piaggesi, A.; Perata, P.; Cellini, F. Physiological responses to Megafol® treatments in tomato plants under drought stress: A phenomic and molecular approach. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 174, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Wang, Z. Plant Dehydrins: Expression, Regulatory Networks, and Protective Roles in Plants Challenged by Abiotic Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhu, H.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Z. Classification and expression diversification of wheat dehydrin genes. Plant Sci. 2014, 214, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, T.S.; Uraji, M.; Tuya, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Murata, Y. Methylglyoxal inhibits seed germination and root elongation and up-regulates transcription of stress-responsive genes in ABA-dependent pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Biol. 2012, 14, 854–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graether, S.P.; Boddington, K.F. Disorder and function: A review of the dehydrin protein family. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, S.K.; Harryson, P. Plant Desiccation Tolerance; Lüttge, U., Beck, E., Bartels, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 289–305. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, T.; Fujita, Y.; Sayama, H.; Kidokoro, S.; Maruyama, K.; Mizoi, J.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. AREB1, AREB2, and ABF3 are master transcription factors that cooperatively regulate ABRE-dependent ABA signaling involved in drought stress tolerance and require ABA for full activation. Plant J. 2010, 61, 672–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.; Rayirath, U.P.; Subramanian, S.; Jithesh, M.N.; Rayorath, P.; Hodges, D.M.; Critchley, A.T.; Craigie, J.S.; Norrie, J.; Prithiviraj, B. Seaweed Extracts as Biostimulants of Plant Growth and Development. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2009, 28, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.S.S.; Fleming, C.; Selby, C.; Rao, J.R.; Martin, T. Plant biostimulants: A review on the processing of macroalgae and use of extracts for crop management to reduce abiotic and biotic stresses. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 465–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craigie, J.S. Seaweed extract stimuli in plant science and agriculture. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 371–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, I.; Chojnacka, K. Algal extracts: Technology and advances. Eng. Life Sci. 2014, 14, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Payan, J.P.; Stall, W. Papaya (Carica papaya) response to foliar treatments with organic complexes of peptides and amino acids. Proc. Fla. State Hortic. Soc. 2003, 116, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Parrado, J.; Escudero-Gilete, M.L.; Friaza, V.; García-Martínez, A.; González-Miret, M.L.; Bautista, J.D.; Heredia, F.J. Enzymatic vegetable extract with bio- active components: Influence of fertiliser on the colour and anthocyanins of red grapes. J. Sci. Food Agri. 2007, 87, 2310–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, K.; Zielony, T.; Marek, G. Effect of Aminoplant and Asahi on yield and quality of lettuce grown on rockwool. In Biostimulators in Modern Agriculture: Vegetable Crops; Monographs Series; Dąbrowski, Z.T., Ed.; Wieś Jutra: Warszawa, Poland, 2008; pp. 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ertani, A.; Schiavon, M.; Muscolo, A.; Nardi, S. Alfalfa plant-derived biostimulant stimulate short-term growth of salt stressed Zea mays L. plants. Plant Soil 2013, 364, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, G.; Rouphael, Y.; Canaguier, R.; Svecova, E.; Cardarelli, M. Biostimulant action of a plant-derived protein hydrolysate produced through enzymatic hydrolysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G.; Giordano, M.; El-Nakhel, C.; Kyriacou, M.C.; De Pascale, S. Foliar applications of a legume-derived protein hydrolysate elicit dose-dependent increases of growth, leaf mineral composition, yield and fruit quality in two greenhouse tomato cultivars. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 226, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrada, A.; Delisle-Houde, M.; Nguyen, T.T.; Tweddell, R.J.; Dorais, M. Drench Application of Soy Protein Hydrolysates Increases Tomato Plant Fitness, Fruit Yield, and Resistance to a Hemibiotrophic Pathogen. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Nakanomyo, I.; Motose, H.; Iwamoto, K.; Sawa, S.; Dohmae, N.; Fukuda, H. Dodeca-CLE Peptides as Suppressors of Plant Stem Cell Differentiation. Science 2006, 313, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, T.; Sawa, S.; Kinoshita, A.; Mizuno, S.; Kakimoto, T.; Fukuda, H.; Sakagami, Y. A Plant Peptide Encoded by CLV3 Identified by in Situ MALDI-TOF MS Anal. Science 2006, 313, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vani, L.; Ciavatta, C. Attività Biostimolante degli Idrolizzati Proteici. L’informatore Agrar. 2007, 44, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumiya, Y.; Kubo, M. Soybean peptide: Novel plant growth promoting peptide from soybean. In Soybean and Nutrition; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; Chapter 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varia, J.; Kamaleson, C.; Lerer, L. Biostimulation with phycocyanin-rich Spirulina extract in hydroponic vertical farming. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 299, 111042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, A. Abiotic Stress Responses in Plants: Metabolism, Productivity and Sustainability; Ahmad, P., Prasad, M.N.V., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 215–234. [Google Scholar]
- Hotta, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Takaoka, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Konnai, M. Promotive effects of 5-aminolevulinic acid on the yield of several crops. Plant Growth Regul. 1997, 22, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Nishihara, E.; Watanabe, S.; Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, K.; Takeuchi, Y. Enhancement of Growth and Fruit Maturity in 2-year-old Grapevines cv. Delaware by 5-Aminolevulinic Acid. Plant Growth Regul. 2006, 49, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, N.J. The Bradford Method for Protein Quantitation. In The Protein Protocols Handbook; Springer Protocols Handbooks; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Vannini, C.; Marsoni, M.; Scoccianti, V.; Ceccarini, C.; Domingo, G.; Bracale, M.; Crinelli, R. Proteasome-mediated remodeling of the proteome and phospho-proteome during kiwifruit pollen germination. J. Proteom. 2019, 192, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, I.; Domingo, G.; Bracale, M.; Loreto, F.; Pollastri, S. Isoprene Emission Influences the Proteomic Profile of Arabidopsis Plants under Well-Watered and Drought-Stress Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, P.S.; LaJoie, D.M.; Jorcyk, C.L. Bleach gel: A simple agarose gel for analyzing RNA quality. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Fromm, M.; Avramova, Z. Multiple exposures to drought ‘train’ transcriptional responses in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Protein IDs | Description | Peptide Counts | LFQ Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|
| M5DDI2 | R-phycoerythrin class I beta subunit | 6 | 214,290,000 |
| M5DDJ6 | Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase large chain | 6 | 150,300,000 |
| M5DDK1 | Phycocyanin, alpha chain | 5 | 50,310,000 |
| M5DDI6 | Allophycocyanin, beta chain | 9 | 38,074,000 |
| M5DDI5 | Phycocyanin, beta chain | 5 | 28,995,000 |
| M5DDJ9 | R-phycoerythrin class I alpha subunit | 3 | 26,409,000 |
| M5DBY2 | ATP synthase subunit alpha | 6 | 17,255,000 |
| R7QSM0 | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase | 4 | 17,039,000 |
| R7QMR3 | ATP synthase subunit alpha | 7 | 11,272,000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Domingo, G.; Marsoni, M.; Álvarez-Viñas, M.; Torres, M.D.; Domínguez, H.; Vannini, C. The Role of Protein-Rich Extracts from Chondrus crispus as Biostimulant and in Enhancing Tolerance to Drought Stress in Tomato Plants. Plants 2023, 12, 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12040845
Domingo G, Marsoni M, Álvarez-Viñas M, Torres MD, Domínguez H, Vannini C. The Role of Protein-Rich Extracts from Chondrus crispus as Biostimulant and in Enhancing Tolerance to Drought Stress in Tomato Plants. Plants. 2023; 12(4):845. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12040845
Chicago/Turabian StyleDomingo, Guido, Milena Marsoni, Milena Álvarez-Viñas, M. Dolores Torres, Herminia Domínguez, and Candida Vannini. 2023. "The Role of Protein-Rich Extracts from Chondrus crispus as Biostimulant and in Enhancing Tolerance to Drought Stress in Tomato Plants" Plants 12, no. 4: 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12040845
APA StyleDomingo, G., Marsoni, M., Álvarez-Viñas, M., Torres, M. D., Domínguez, H., & Vannini, C. (2023). The Role of Protein-Rich Extracts from Chondrus crispus as Biostimulant and in Enhancing Tolerance to Drought Stress in Tomato Plants. Plants, 12(4), 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12040845







